靶向抑制CDK12/13在高级别胶质瘤中的体外治疗效果和作用分子机制探究
In vitro therapeutic effects and molecular mechanisms of targeted inhibition of CDK12/13 in high-grade gliomas
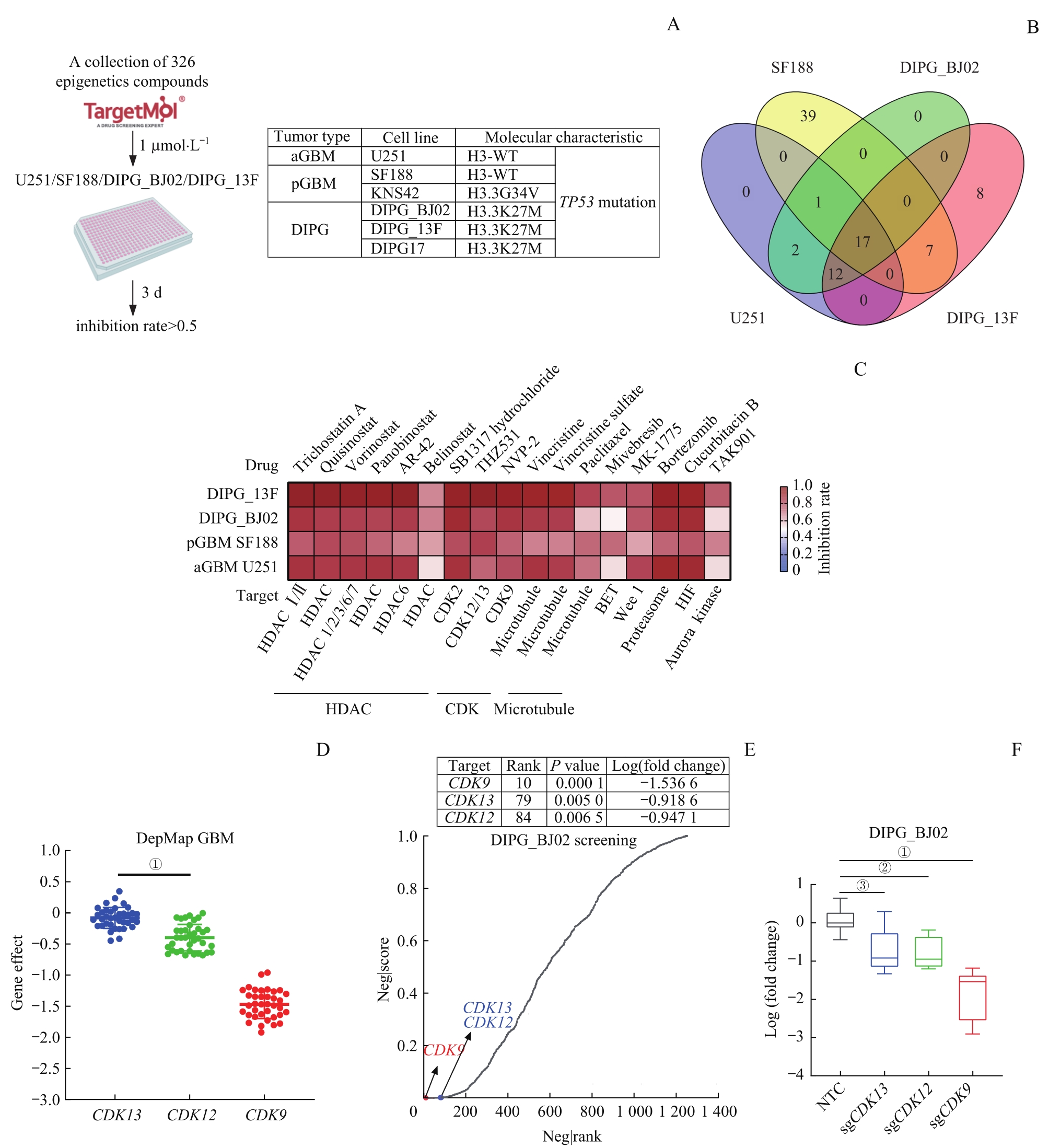
Note: A. Workflow of epigenetic transcription-related targeted small molecule drug library screening in aGBM (U251), pGBM (SF188) and DIPG (DIPG_13F, DIPG_BJ02) cell lines. B. Venn diagram of the epigenetic transcription-related targeted small molecule drug library screening in U251, SF188, DIPG_13F, and DIPG_BJ02 cell lines. C. Heatmap was used to display the screening effects of 17 small molecule classifications. D. Scatter plots showing the dependence of GBM cells on CDK12, CDK13 and CDK9 in DepMap database. E. Epigenetic transcription-related functional genome screening based on CRISPR-Cas9 in vitro for four weeks in DIPG_BJ02 cell line, with the sequencing results analyzed by MAGeCK algorithm. The top 200 genes are thought to be growth-dependent genes in DIPG_BJ02 cell line. F. Box plot of log (fold change) in sgCDK12, sgCDK13 and sgCDK9. NTC—negative control. ①P<0.000 1, ②P=0.001 8, ③P=0.002 9.