成人脑型肾上腺脑白质营养不良的临床及遗传学特征
Clinical and genetic characteristics of adult cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy
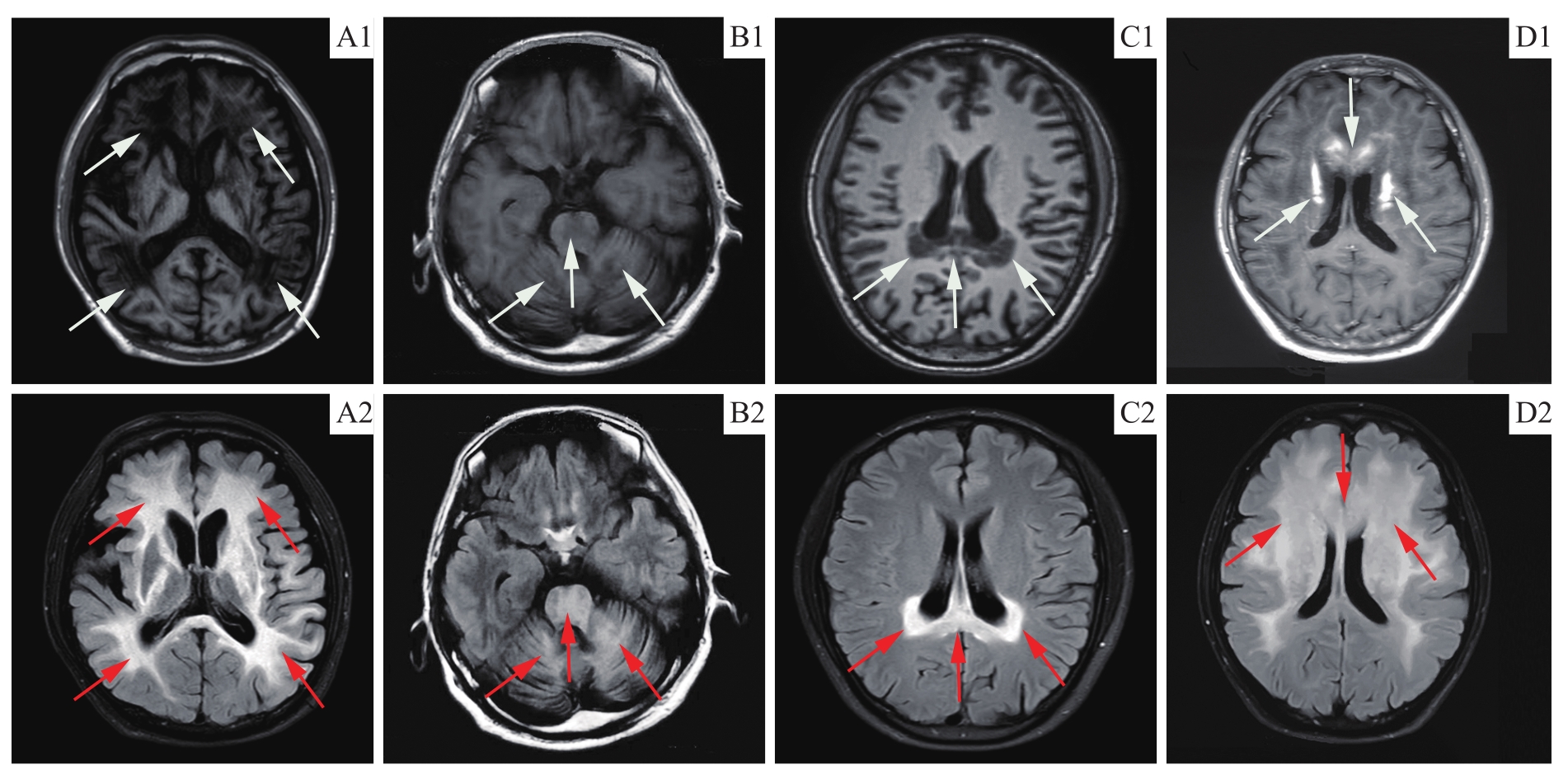
Note: A. Advanced ACALD patient (P3), extensive and diffuse distribution of white matter lesions with typical butterfly wing-like changes. B. Olivopontocerebellar ACALD patient (P4), white matter demyelinating lesions involving the bilateral cerebellar hemispheres and brainstem. C. Early stage ACALD patient (P5), white matter demyelinating lesions involving the posterior horn of the lateral ventricle and the corpus callosum. D. Rapidly progressive ACALD patient (P8), white matter demyelination lesions involving the anterior horn of the lateral ventricle and the anterior part of the white matter in the frontotemporal lobe. Some lesions showed patchy enhancement on the T1 enhanced sequence (D1, white arrow). Patients with ACALD had bilateral symmetrical cerebral white matter demyelinating lesions with low signal in T1 sequences (white arrows in A1-C1) and high signal in FLAIR sequences (red arrows in A2-D2).