脑卒中后脑血管内皮细胞内质网应激抑制Wnt7/β-catenin通路导致血脑屏障损伤的机制研究
Mechanism of blood-brain barrier damage caused by the inhibition of Wnt7/β-catenin pathway induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress in cerebrovascular endothelial cells after stroke
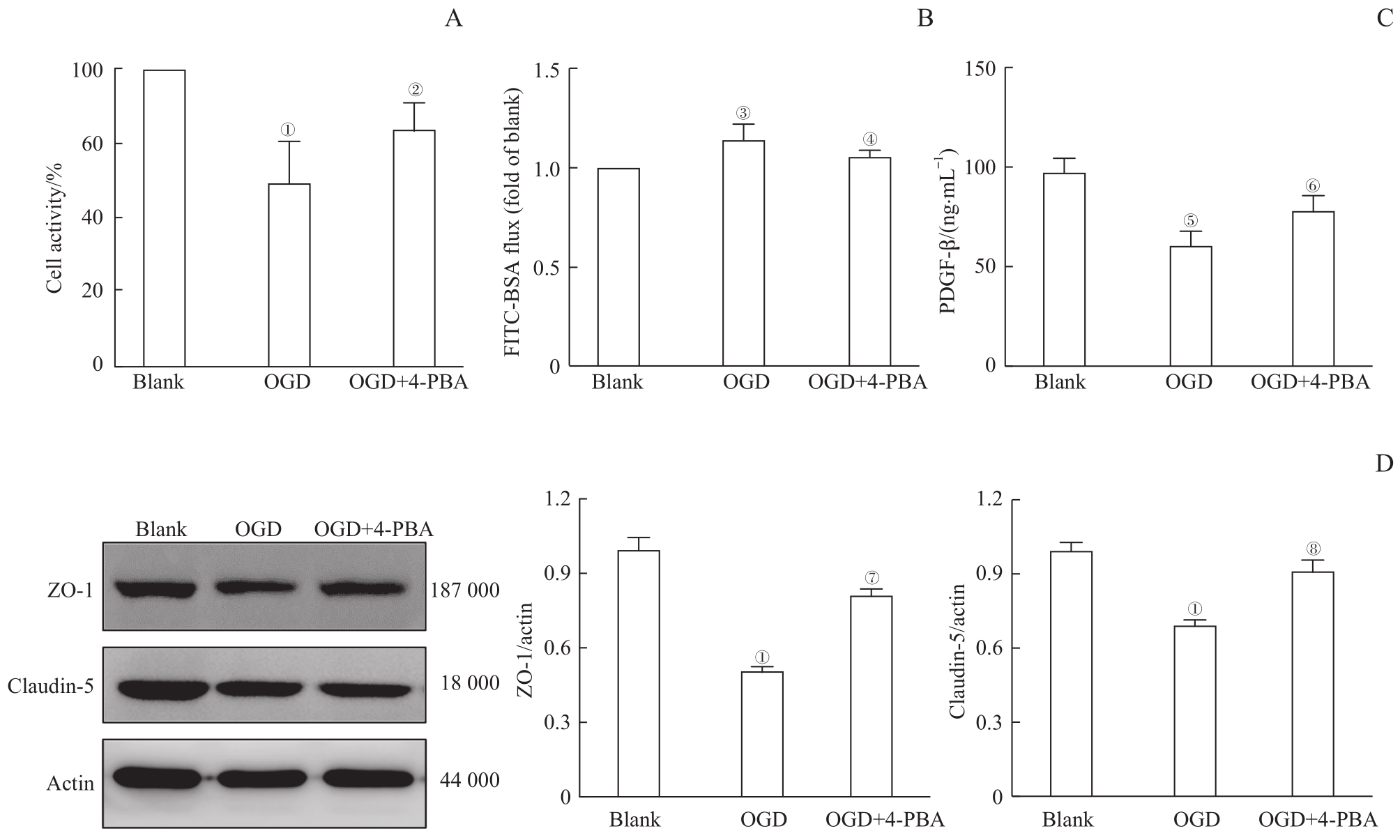
Note: A. Determination of activity of HBMECs by CCK-8 assay. B. The cell permeability of HBMECs analyzed with FITC-BSA leakage. C. Determination of the PDGF-β secretion of HBMECs by ELISA. D. Determination of the expression of ZO-1 and claudin-5 in HBMECs by Western blotting. ①P=0.000, ③P=0.002, ⑤P=0.001, compared with the Blank group; ②P=0.026, ④P=0.005, ⑥P=0.042, ⑦P=0.000, ⑧P=0.001, compared with the OGD group.