二甲双胍改善由C9ORF72肌萎缩侧索硬化/额颞叶痴呆相关多聚甘氨酸-精氨酸诱导的线粒体损伤
Metformin ameliorates the mitochondrial damage induced by C9ORF72 amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/frontotemporal dementia-related poly-GR
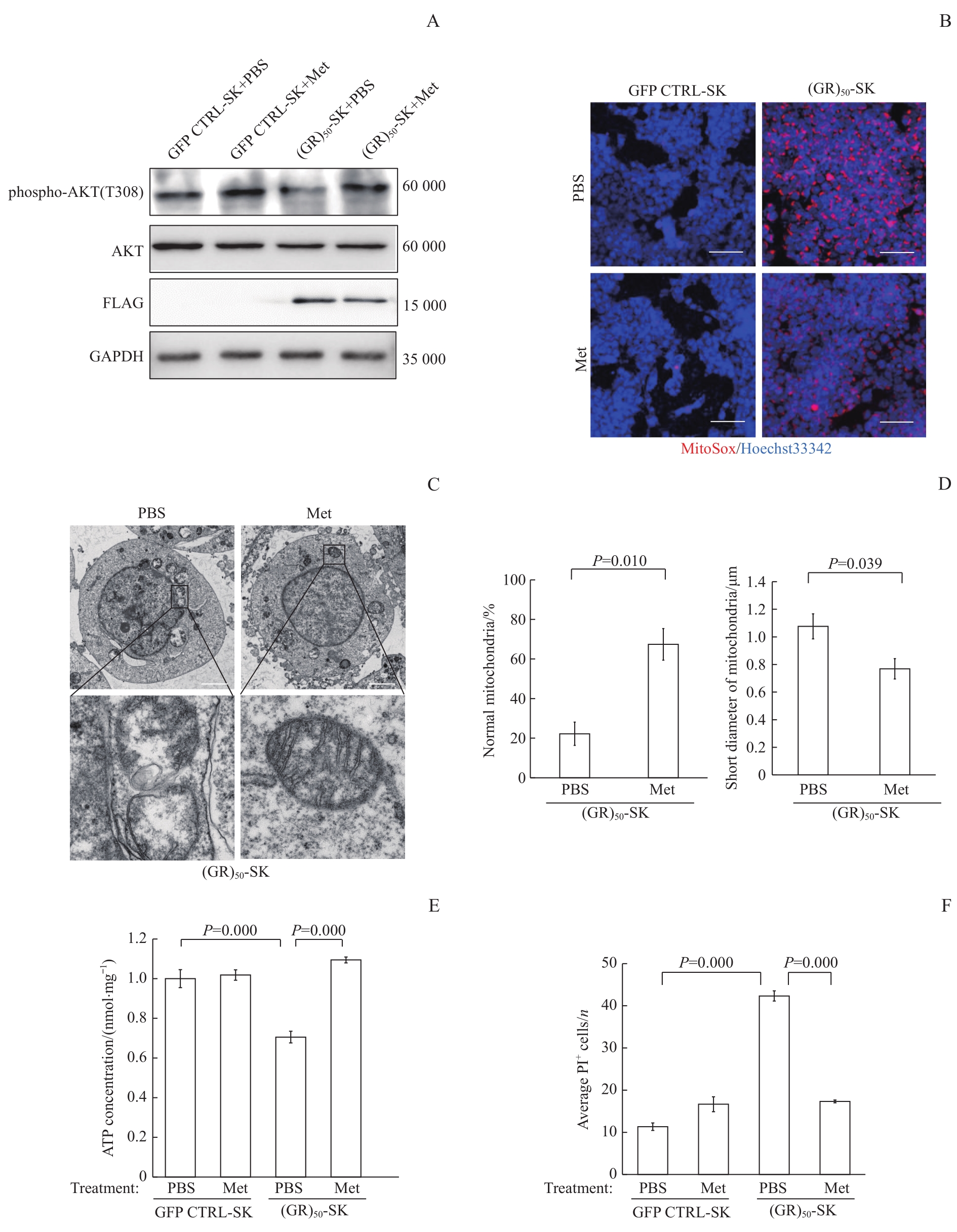
Note: A. Detection of the expression level of AKT and phosphorylated AKT in cells of different groups by Western blotting. B. Detection of the effect of metformin on mitochondrial ROS level of cells by MitoSOX Red superoxide indicator staining. Red fluorescence represents intracellular ROS, and blue fluorescence represents DAPI-stained nucleus. Scale bar=100 μm. C. Observation of mitochondrial morphology of (GR)50-SK cells treated with metformin by transmission electron microscope. Scale bar=100 μm. D. Quantification analysis of the proportion of normal mitochondria and length of mitochondrial short diameter of (GR)50-SK cells. E. Detection of the effect of metformin on ATP level in cells of different groups by ATP detection assay. F. Detection of the effect of metformin on apoptosis levels in cells of different groups by PI staining. Met—metformin.