小鼠输卵管上皮类器官的构建及表型验证
Establishment and phenotype verification of mouse oviductal epithelial organoids
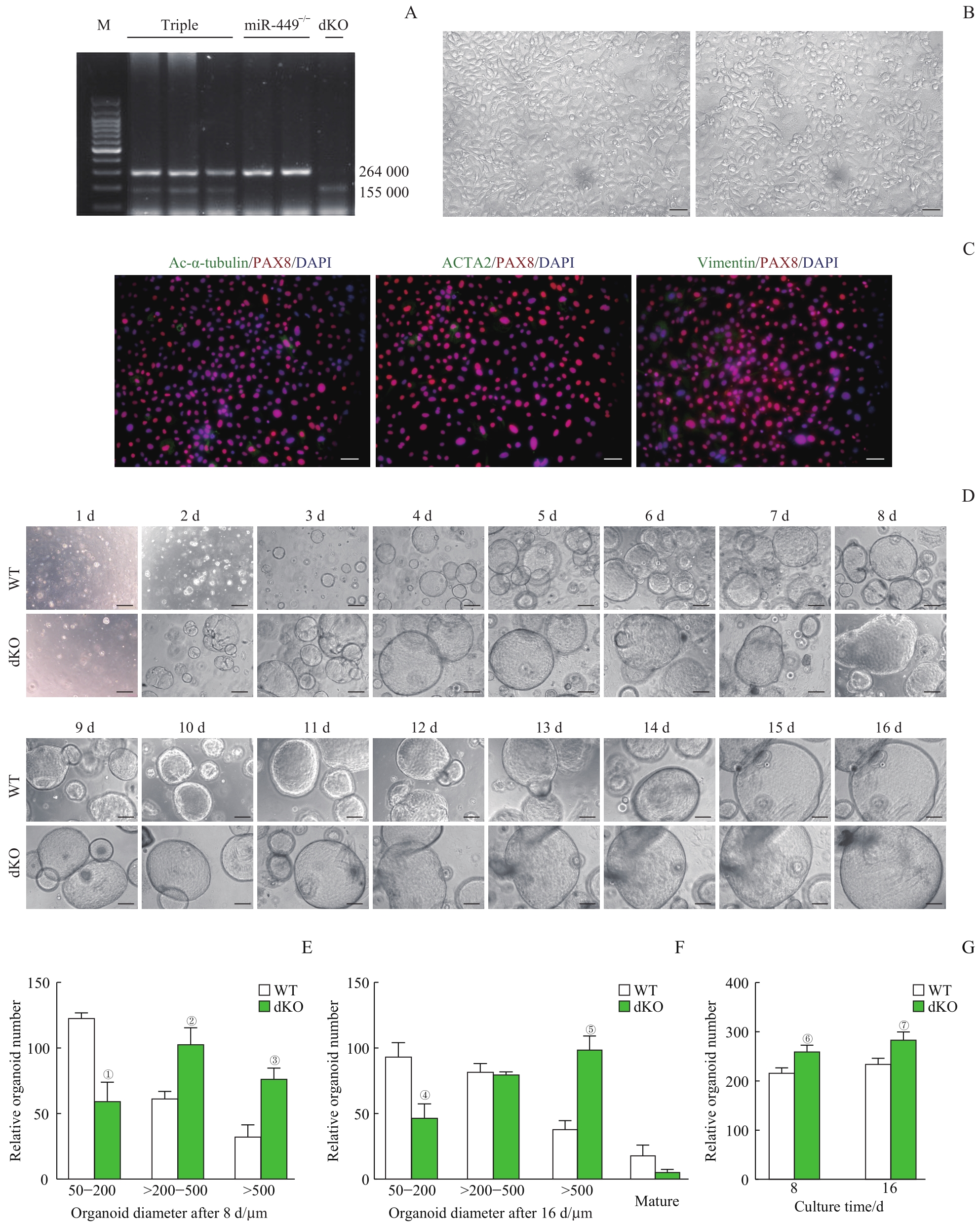
Note: A. Different genotypes of mice detected by PCR. Triple (miR-34b/c+/- and miR-449-/-), miR-449-/-, and dKO (miR-34b/c-/- and miR-449-/-). B. Primary culture of the oviductal epithelial cells (×400, scale bar=50 μm). C. Identification of the purity of the isolated oviductal epithelial cells using immunofluorescent staining. Ac-α-tubulin for showing ciliated cells, PAX8 for showing secretory cells, ACTA2 for showing smooth muscle cells, and vimentin for showing fibroblasts (×400, scale bar=50 μm). D. Phase contrast images of organoids formation and growth from WT mice and dKO mice (×100, scale bar=200 μm). E. The numbers of the organoids with different sizes were counted after 8 d. F. The numbers of the organoids with different sizes were counted after 16 d. G. The total numbers of organoids were counted after 8 d and 16 d. ①P=0.002, ②P=0.007, ③P=0.004, ④P=0.006, ⑤P=0.001, ⑥P=0.011, ⑦P=0.013, compared with the WT group.