GPR87通过激活RHO/ROCK通路促进非小细胞肺癌的侵袭和迁移
GPR87 promotes invasion and migration through the RHO/ROCK pathway in non-small cell lung cancer
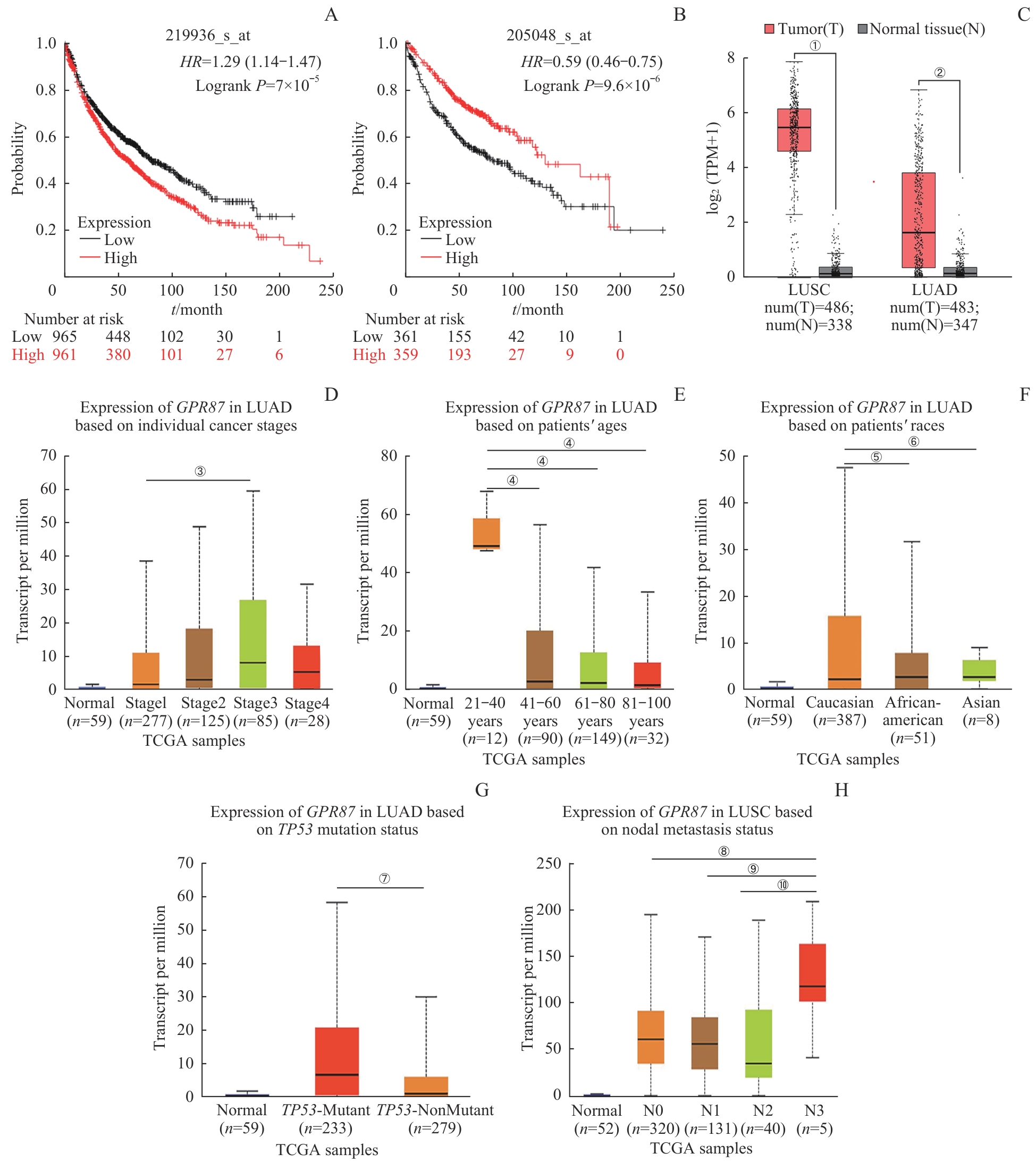
Note: GPR87 (A) and PSPH (B) were found to correlate with poor survival in NSCLC population with KM plotter. GPR87 mRNA levels in LUAD and LUSC (C) were both overexpressed, according to the GEPIA database. High expression of GPR87 was associated with poor clinical stage (D), age (E), race (F) and TP53 mutation status (G) in patients with LUAD, and with lymph node metastasis in patients with LUSC (H) in UALCAN database. Error bars represent the x±s. ①P=0.032, ②P=0.026, compared with the adjacent normal tissues. ③P=0.006, compared with stage1 LUAD patients. ④P<0.001, compared with the 21?40 year-old patients. ⑤P=0.005, ⑥P<0.001, compared with Caucasian patients. ⑦P<0.001, compared with the TP53-mutant group. ⑧P=0.007, ⑨P=0.005, ⑩P=0.004, compared with the N3-lymph node metastasis patients.