基于Transformer和扩散模型的头颅侧位片颈椎分割方法在正畸临床中的初步应用
Preliminary application of a cervical vertebra segmentation method based on Transformer and diffusion model for lateral cephalometric radiographs in orthodontic clinical practice
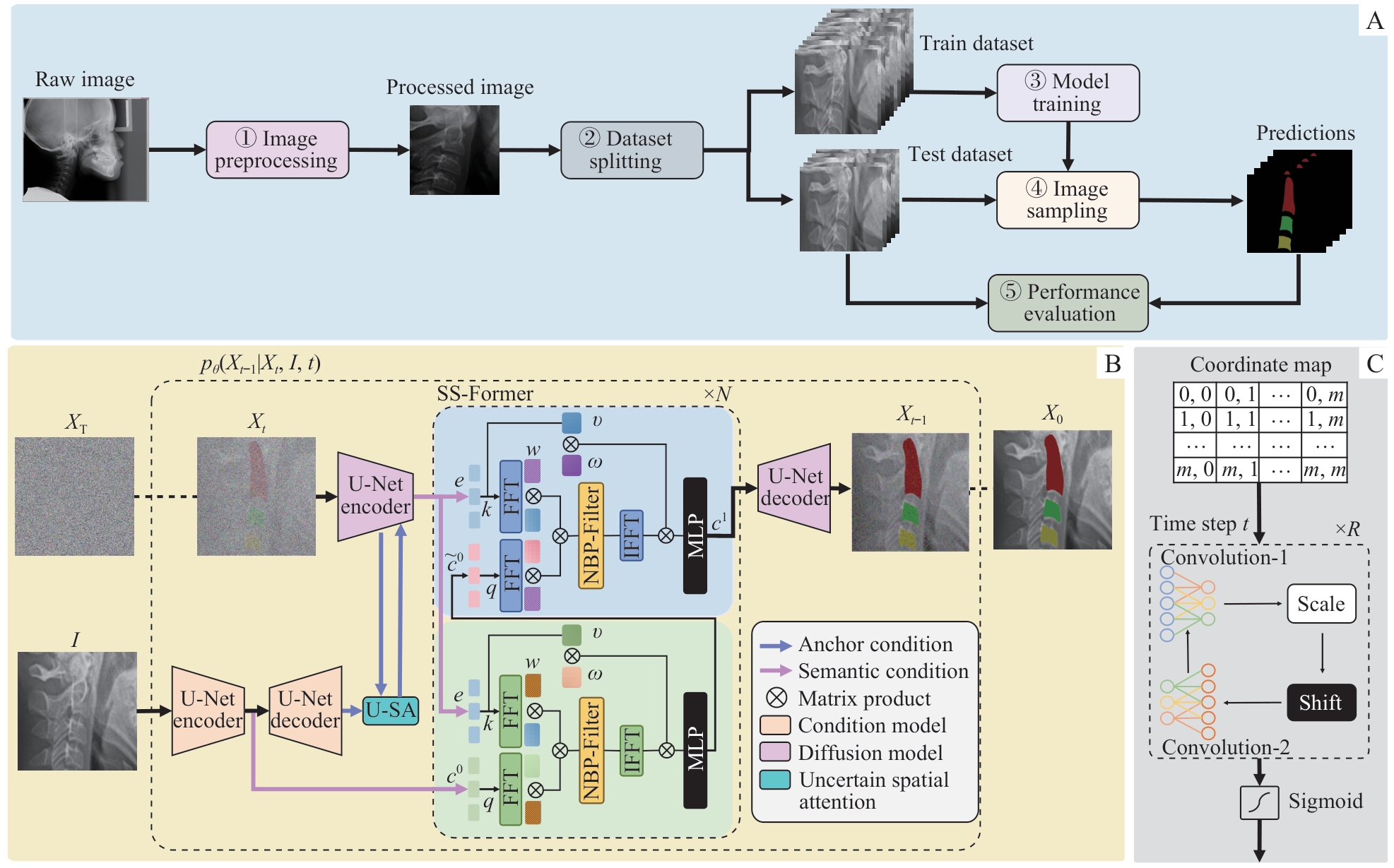
Note: A. Overall architecture of the MedSegDiff-V2 network. The network took raw cranial lateral slice data as input, and proceeded to obtain results pertaining to the segmentation of the cervical vertebrae. It was achieved through a five-step process. ①Image preprocessing. The region of interest (ROI) was cropped and resized to 256×256 pixels. ②Dataset splitting. The 191 images were divided into two sets: 152 for training and 39 for testing. ③Model training. The MedSegDiff-V2 model was trained using the training dataset. ④Image sampling. Images from the test dataset were sampled using the trained diffusion. ⑤Performance evaluation. The DSC and IoU formulas were used to calculate the corresponding metrics from the ground truth masks and model predictions of the test dataset. B. MedSegDiff-V2 architecture. A Transformer-based diffusion network for image segmentation. FFT—Fast Fourier Transform; IFFT—reverse operation of the FFT; MLP—multi-layer perceptron; U-SA—uncertain spatial attention; NBP-Filter—neural band-pass filter. C. Neural band-pass filter.