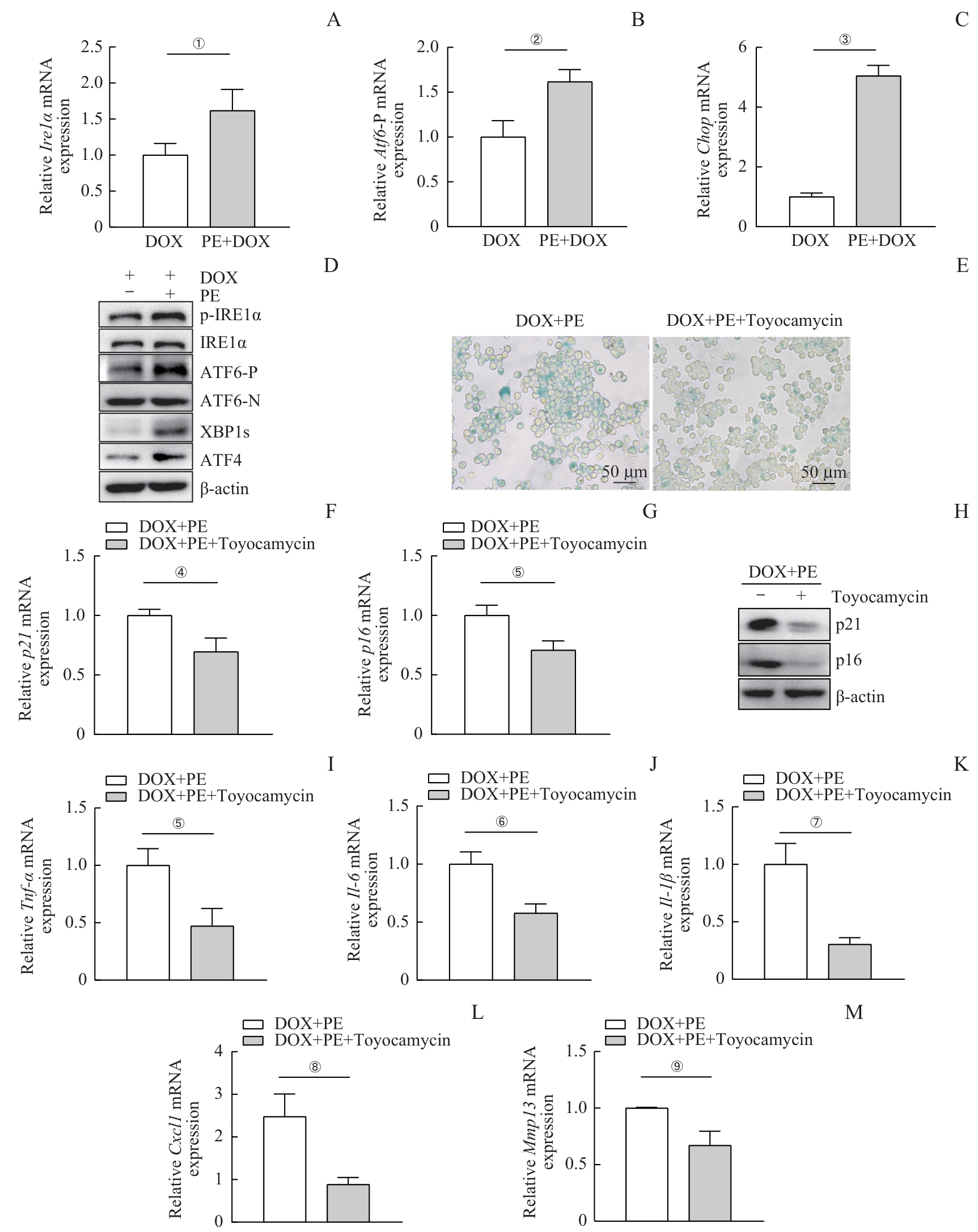
磷脂酰乙醇胺引起内质网应激促进巨噬细胞衰老及肝损伤
Phosphatidylethanolamine promotes macrophage senescence and liver injury by activating endoplasmic reticulum stress
Note:A‒C. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of Ire1α (A), Atf6 (B) and Chop (C) mRNA expression in RAW264.7 cells treated with DOX and PE (50 μmol·L-1). D. Western blotting analysis of endoplasmic reticulum stress-related proteins, including p-IRE1α, IRE1α, ATF6-P, ATF6-N, XBP1s and ATF4. E. SA-β-gal staining of RAW264.7 cells treated with Toyocamycin, DOX and PE. F/G. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of senescence marker mRNA expression, including p21 (F) and p16 (G). H. Western blotting analysis of proteins including p21 and p16. I‒M. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of SASP mRNA expression, including Tnf-α (I), Il-6 (J), Il-1β (K), Cxcl1 (L) and Mmp13 (M). ①P=0.033, ②P=0.009, ③P<0.001, ④P=0.014, ⑤P=0.012, ⑥P=0.005, ⑦P=0.003, ⑧P=0.008, ⑨P=0.010.