大黄素改善阿尔茨海默病认知障碍、内质网应激和神经炎症的研究
Research on the improvement of cognitive impairment, endoplasmic reticulum stress and neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease by emodin
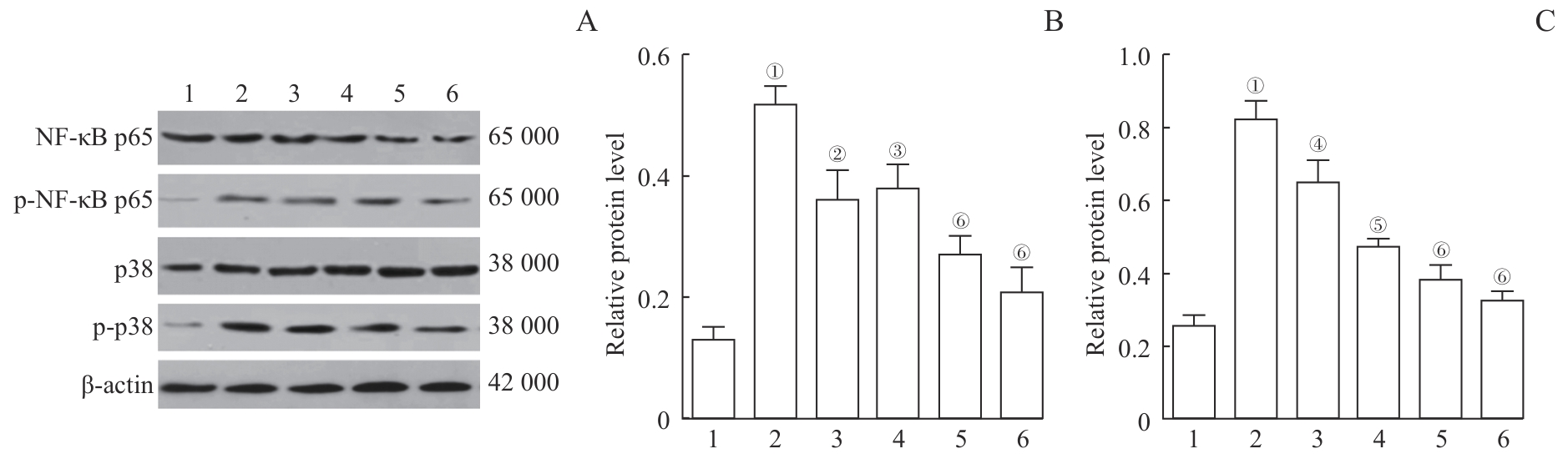
Note: A. Western blotting images of NF-κB p65, p-NF-κB p65, p38, and p-p38. B. Relative expression of p-NF-κB p65/NF-κB p65. C. Relative expression of p-p38/p38. 1—Control group, 2—AD group, 3—Emodin 25 mg/kg group, 4—Emodin 50 mg/kg group, 5—Emodin 100 mg/kg group, 6—Donepezil group. ①P<0.001, compared with the control group. ②P=0.035, ③P=0.042, ④P=0.028, ⑤P=0.007, ⑥P<0.001, compared with the AD group.