
Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science) ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 653-660.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2025.05.015
• Brief original article • Previous Articles
HUANG Runyu1, ZHANG Chunye2, ZHANG Ying1, ZHAO Zhengyan1, YANG Yang3, WU Lan1( )
)
Received:2024-11-07
Accepted:2025-02-24
Online:2025-05-28
Published:2025-05-28
Contact:
WU Lan
E-mail:teana_wu@sina.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
HUANG Runyu, ZHANG Chunye, ZHANG Ying, ZHAO Zhengyan, YANG Yang, WU Lan. Features of oral peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(5): 653-660.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://xuebao.shsmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2025.05.015
| Year | Patient/ reference | Gender/ age | Location | B symptom | Radiographic feature | Ann Arbor staging | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | Case 1 | F/55 | Tongue | None | MRI showed a vaguely-bordered soft tissue thickening at the anterior tongue. In addition, MRI showed an intermediate T1 signal and slightly high T2 signal lesion at the right side of the tongue, which was about 3.6 cm×1.3 cm. The lesion demonstrated heterogeneous contrast enhancement | Ⅰ EA | / |
| 2024 | Case 2 | M/44 | Hard palate | None | MRI illustrated a vaguely-bordered soft tissue thickening, which measured approximately 3.4 cm×2.7 cm×1.2 cm and showed a slightly low T1 signal and slightly high T2 signal. The lesion demonstrated heterogeneous contrast enhancement. There were several enlarged lymph nodes in the level Ⅱ‒level Ⅳ cervical | Ⅳ A | GemOx-D |
| 2014 | 1/[2] | M/59 | The right side of the tongue base | None | CT scan presented an ill-defined, heterogeneous enhancing soft tissue mass lesion in the right tongue base and enlarged lymph nodes in the right level Ⅱ | Ⅱ A | CHOP+RT+VMAT |
| 2016 | 2/[3] | F/50 | The left side of the anterior tongue | None | MRI T2WI showed a bordered lesion at the anterior tongue | Ⅰ | None |
| 2017 | 3/[4] | F/42 | Near the median sulcus of the tongue | None | Enhanced MRI showed a bordered, bar-shaped, irregular lesion with intermediate T1 signal and slightly high T2 signal in the right portion of the tongue, and its size was about 8.5 mm×24.5 mm | / | Surgery, CHOP |
| 2018 | 4/[5] | F/25 | Upper lip, palate, and maxillary sinus | Fever, weight loss | CT scan with contrast showed an expansive and infiltrative formation with irregular contours and ulceration, extending from the upper lip to the nasolabial sulcus, with infiltration into the epidermis and nasal mucosa. The formation affected the right tear duct without bone involvement. In addition, CT showed a bilateral increase in the number and size of the cervical lymph nodes, mainly the submandibular chain | Ⅳ B | CHOEP |
| 2020 | 5/[6] | M/ 75‒80 | The right side of the tongue base | None | CT scan showed a well-bordered cystic mass (2 cm in diameter) at the right base of the tongue extending into the pharynx | Ⅳ A | GDP+CHOP |
| 2021 | 6/[7] | F/63 | Submandibular region | / | / | / | / |
| 2021 | 7/[7] | M/67 | Buccal mucosa | / | / | / | / |
| 2021 | 8/[7] | M/57 | Hard palate | / | / | / | / |
| 2021 | 9/[7] | M/38 | Soft palate | / | / | / | / |
| 2021 | 10/[7] | M/59 | Buccal mucosa | / | / | / | / |
| 2021 | 11/[7] | F/56 | Tonsil | / | / | / | / |
| 2021 | 12/[7] | F/66 | Tonsil | / | / | / | / |
| 2023 | 13/[8] | M/34 | Right buccal mucosa | None | CT scan imaging showed destructive and expansive mass with central necrosis, extending to maxillary and ethmoid sinuses | Ⅱ EA | CHOEP+RT |
| 2024 | 14/[9] | F/37 | Maxillary gingiva | None | / | / | Anthracycline-based regimens |
| 2024 | 15/[9] | M/44 | Buccal mucosa | None | / | / | / |
| 2024 | 16/[9] | F/62 | Palate and gingiva | None | / | / | Anthracycline-based regimens |
| 2024 | 17/[9] | M/55 | Palate and maxillary sinus | None | CT scan illustrated the neoplasm invading the maxillary sinus and the orbital cavity, and extending toward the base of the skull | / | Anthracycline-based regimens |
| 2024 | 18/[9] | M/61 | Soft palate and tonsil | None | / | / | / |
Tab 1 Clinical features of oral PTCL-NOS
| Year | Patient/ reference | Gender/ age | Location | B symptom | Radiographic feature | Ann Arbor staging | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | Case 1 | F/55 | Tongue | None | MRI showed a vaguely-bordered soft tissue thickening at the anterior tongue. In addition, MRI showed an intermediate T1 signal and slightly high T2 signal lesion at the right side of the tongue, which was about 3.6 cm×1.3 cm. The lesion demonstrated heterogeneous contrast enhancement | Ⅰ EA | / |
| 2024 | Case 2 | M/44 | Hard palate | None | MRI illustrated a vaguely-bordered soft tissue thickening, which measured approximately 3.4 cm×2.7 cm×1.2 cm and showed a slightly low T1 signal and slightly high T2 signal. The lesion demonstrated heterogeneous contrast enhancement. There were several enlarged lymph nodes in the level Ⅱ‒level Ⅳ cervical | Ⅳ A | GemOx-D |
| 2014 | 1/[2] | M/59 | The right side of the tongue base | None | CT scan presented an ill-defined, heterogeneous enhancing soft tissue mass lesion in the right tongue base and enlarged lymph nodes in the right level Ⅱ | Ⅱ A | CHOP+RT+VMAT |
| 2016 | 2/[3] | F/50 | The left side of the anterior tongue | None | MRI T2WI showed a bordered lesion at the anterior tongue | Ⅰ | None |
| 2017 | 3/[4] | F/42 | Near the median sulcus of the tongue | None | Enhanced MRI showed a bordered, bar-shaped, irregular lesion with intermediate T1 signal and slightly high T2 signal in the right portion of the tongue, and its size was about 8.5 mm×24.5 mm | / | Surgery, CHOP |
| 2018 | 4/[5] | F/25 | Upper lip, palate, and maxillary sinus | Fever, weight loss | CT scan with contrast showed an expansive and infiltrative formation with irregular contours and ulceration, extending from the upper lip to the nasolabial sulcus, with infiltration into the epidermis and nasal mucosa. The formation affected the right tear duct without bone involvement. In addition, CT showed a bilateral increase in the number and size of the cervical lymph nodes, mainly the submandibular chain | Ⅳ B | CHOEP |
| 2020 | 5/[6] | M/ 75‒80 | The right side of the tongue base | None | CT scan showed a well-bordered cystic mass (2 cm in diameter) at the right base of the tongue extending into the pharynx | Ⅳ A | GDP+CHOP |
| 2021 | 6/[7] | F/63 | Submandibular region | / | / | / | / |
| 2021 | 7/[7] | M/67 | Buccal mucosa | / | / | / | / |
| 2021 | 8/[7] | M/57 | Hard palate | / | / | / | / |
| 2021 | 9/[7] | M/38 | Soft palate | / | / | / | / |
| 2021 | 10/[7] | M/59 | Buccal mucosa | / | / | / | / |
| 2021 | 11/[7] | F/56 | Tonsil | / | / | / | / |
| 2021 | 12/[7] | F/66 | Tonsil | / | / | / | / |
| 2023 | 13/[8] | M/34 | Right buccal mucosa | None | CT scan imaging showed destructive and expansive mass with central necrosis, extending to maxillary and ethmoid sinuses | Ⅱ EA | CHOEP+RT |
| 2024 | 14/[9] | F/37 | Maxillary gingiva | None | / | / | Anthracycline-based regimens |
| 2024 | 15/[9] | M/44 | Buccal mucosa | None | / | / | / |
| 2024 | 16/[9] | F/62 | Palate and gingiva | None | / | / | Anthracycline-based regimens |
| 2024 | 17/[9] | M/55 | Palate and maxillary sinus | None | CT scan illustrated the neoplasm invading the maxillary sinus and the orbital cavity, and extending toward the base of the skull | / | Anthracycline-based regimens |
| 2024 | 18/[9] | M/61 | Soft palate and tonsil | None | / | / | / |
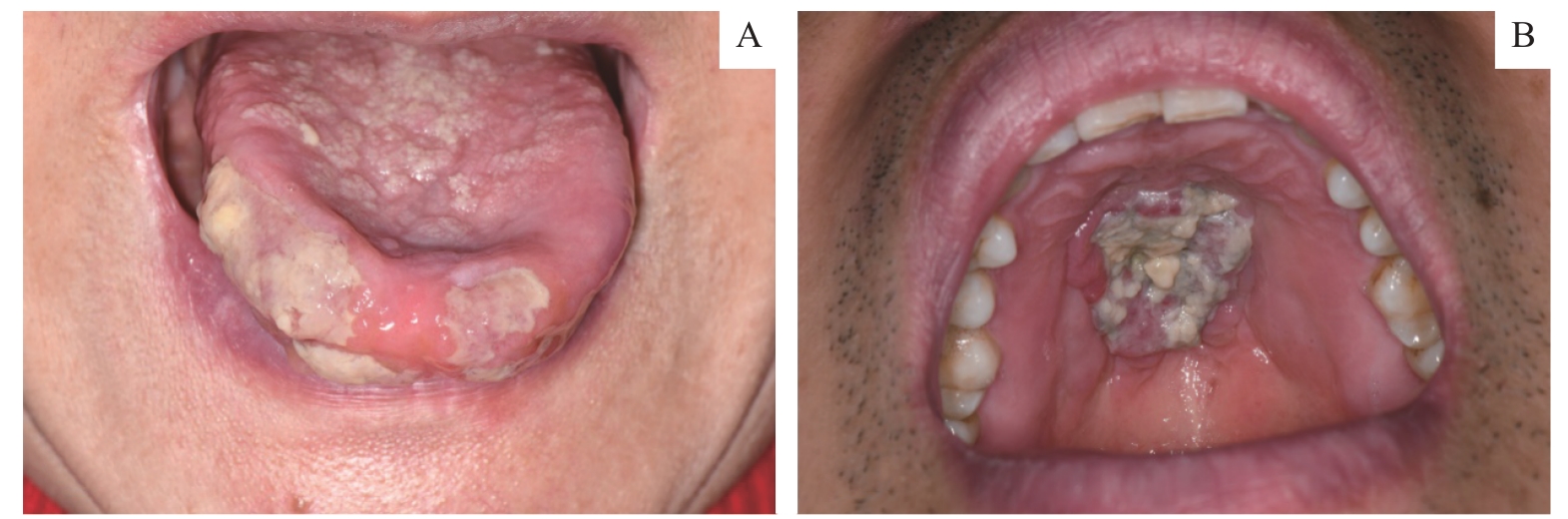
Fig 1 Clinical presentation of PTCL-NOSNote: A. A 55-year-old woman presenting a swollen tongue on her right side with several ulcers and an ulcerated nodular lesion. B. A 44-year-old man showing a destructive palatal ulcer with necrotic grey tissue surrounded by erythematous areas.
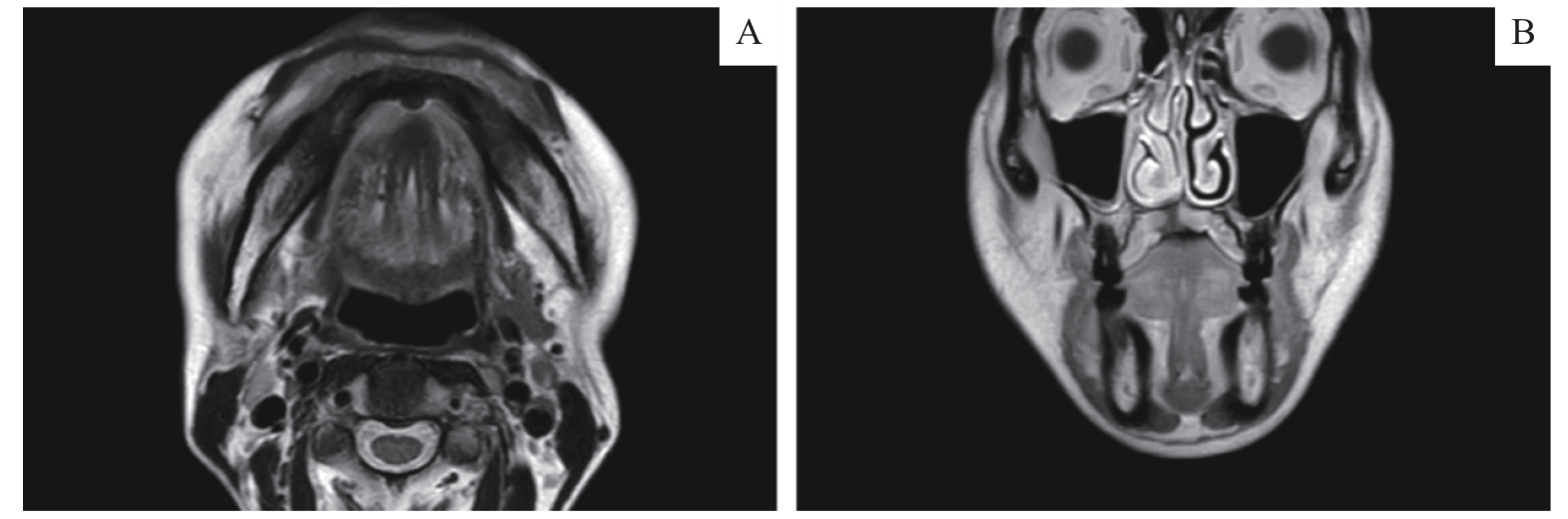
Fig 2 MR imaging findingsNote: A. An axial MRI scan presented local destruction of the tongue tip mucosa with unclear boundaries and high T2 signals at the periphery. B. In a coronal MRI, diffuse soft tissue thickening was shown with an unclear boundary on the right side of the palate, and the T1 signal was slightly low.
| Item | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | Major recurrent aphthous ulcer | Traumatic ulceration | Tuberculous ulcer | PTCL-NOS | ENKTL-NT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population | Middle-aged and elderly people | Adult | Teenagers and elderly people | / | Middle-aged people | Middle-aged people |
| Oral clinical manifestations | Persistent ulceration with raised margins and necrotic base; indurated on palpation | Oval or round ulcers with a white or yellow pseudomembrane and a surrounding erythematous halo; 1 cm or more in diameter | Frank ulceration is surrounded by a white hyperkeratotic lesion. The location and the shape of the ulcer correspond to the stimulating factor | Deep ulcer with undermined edges and red granular base covered by septic secretion | Ulceration, mass, or necrosis | Necrotic ulceration |
| Location of lesions | The margin of the tongue, and the belly of the tongue | The non-keratinized and keratinized oral mucosa | In a trauma-prone site | Labial mucosa, vestibule, and tongue | Tongue, palate, and buccal mucosa | Median mucosa of the palate |
| Systemic signs | Lymph node swelling, pain, or weight loss | / | / | Cough, anorexia, fatigue, low-grade fever and weight loss | Lymph node swelling, extra-nodal involvement of the gastrointestinal tract and skin, anemia, eosinophilia, or hypergammaglobulinaemia | Nasal mucosal symptoms or B symptoms |
| Clinical course | Persistent | Self-limiting, recurrent, and periodic | Self-limiting | Infection | Aggressive | Aggressive |
Complementary examinations | Biopsy | / | / | Chest X-ray, tuberculin skin test, bacterial culturing | Biopsy, blood test, bone marrow biopsy | Biopsy, blood test, bone marrow biopsy, EBER-ISH |
Tab 2 Differential diagnosis of oral mucosal ulcerative diseases
| Item | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | Major recurrent aphthous ulcer | Traumatic ulceration | Tuberculous ulcer | PTCL-NOS | ENKTL-NT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population | Middle-aged and elderly people | Adult | Teenagers and elderly people | / | Middle-aged people | Middle-aged people |
| Oral clinical manifestations | Persistent ulceration with raised margins and necrotic base; indurated on palpation | Oval or round ulcers with a white or yellow pseudomembrane and a surrounding erythematous halo; 1 cm or more in diameter | Frank ulceration is surrounded by a white hyperkeratotic lesion. The location and the shape of the ulcer correspond to the stimulating factor | Deep ulcer with undermined edges and red granular base covered by septic secretion | Ulceration, mass, or necrosis | Necrotic ulceration |
| Location of lesions | The margin of the tongue, and the belly of the tongue | The non-keratinized and keratinized oral mucosa | In a trauma-prone site | Labial mucosa, vestibule, and tongue | Tongue, palate, and buccal mucosa | Median mucosa of the palate |
| Systemic signs | Lymph node swelling, pain, or weight loss | / | / | Cough, anorexia, fatigue, low-grade fever and weight loss | Lymph node swelling, extra-nodal involvement of the gastrointestinal tract and skin, anemia, eosinophilia, or hypergammaglobulinaemia | Nasal mucosal symptoms or B symptoms |
| Clinical course | Persistent | Self-limiting, recurrent, and periodic | Self-limiting | Infection | Aggressive | Aggressive |
Complementary examinations | Biopsy | / | / | Chest X-ray, tuberculin skin test, bacterial culturing | Biopsy, blood test, bone marrow biopsy | Biopsy, blood test, bone marrow biopsy, EBER-ISH |
| Year | Patient/ reference | EBER | CD3 | CD4 | CD8 | CD2 | CD7 | CD20 | Ki-67 | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | Case 1 | ‒ | + | + | + | + | + | ‒ | 60%‒70% | TIA-1 (partial+), GB (partial+), perforin (few cells+) |
| 2024 | Case 2 | / | + | / | / | + | + | ‒ | >90% | TIA-1(+), GB(+), perforin(+) |
| 2014 | 1/[2] | ‒ | + | + | + | / | / | ‒ | 80% | TIA-1(+), GB(+) |
| 2016 | 2/[3] | / | + | + | + | Few cells+ | Few cells+ | ‒ | 30%‒40% | / |
| 2017 | 3/[4] | ‒ | + | ‒ | + | / | / | ‒ | 30% | TIA-1(+) |
| 2018 | 4/[5] | ‒ | + | + | ‒ | + | / | ‒ | 60% | / |
| 2020 | 5/[6] | ‒ | + | + | ‒ | / | / | ‒ | 60% | TIA-1(‒), GB(‒) |
| 2020 | 6/[7] | ‒ | + | + | ‒ | / | / | ‒ | 60%‒95% | LCA(+) |
| 2020 | 7/[7] | ‒ | + | / | / | / | / | ‒ | 20% | LCA(+), GB(‒), CD30(‒) |
| 2020 | 8/[7] | ‒ | + | + | / | / | / | ‒ | 60%‒95% | |
| 2020 | 9/[7] | / | + | / | / | / | / | ‒ | 60%‒95% | GB(+) |
| 2020 | 10/[7] | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 60%‒95% | CD30(+) |
| 2020 | 11/[7] | / | + | + | + | ‒ | / | ‒ | 60%‒95% | TIA-1(+), GB(+), perforin(+) |
| 2020 | 12/[7] | / | + | + | + | + | + | ‒ | 60%‒95% | TIA-1(+), GB(+), perforin(+), CD30(‒), PD-1(+) |
| 2023 | 13/[8] | / | + | / | / | / | + | ‒ | 70%‒80% | CD30(‒) |
| 2024 | 14/[9] | / | + | / | / | / | / | / | 70% | Perforin(‒), GB(‒) |
| 2024 | 15/[9] | / | + | / | / | / | / | / | 80% | GB(‒) |
| 2024 | 16/[9] | / | + | ‒ | + | / | / | / | 95% | Perforin(‒), GB(+), CD30(‒) |
| 2024 | 17/[9] | / | + | + | ‒ | / | / | / | 95% | GB(+), CD30(‒) |
| 2024 | 18/[9] | / | + | + | ‒ | / | / | / | 90% | GB(+), CD30(+) |
Tab 3 Immunohistochemical findings of oral PTCL-NOS
| Year | Patient/ reference | EBER | CD3 | CD4 | CD8 | CD2 | CD7 | CD20 | Ki-67 | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | Case 1 | ‒ | + | + | + | + | + | ‒ | 60%‒70% | TIA-1 (partial+), GB (partial+), perforin (few cells+) |
| 2024 | Case 2 | / | + | / | / | + | + | ‒ | >90% | TIA-1(+), GB(+), perforin(+) |
| 2014 | 1/[2] | ‒ | + | + | + | / | / | ‒ | 80% | TIA-1(+), GB(+) |
| 2016 | 2/[3] | / | + | + | + | Few cells+ | Few cells+ | ‒ | 30%‒40% | / |
| 2017 | 3/[4] | ‒ | + | ‒ | + | / | / | ‒ | 30% | TIA-1(+) |
| 2018 | 4/[5] | ‒ | + | + | ‒ | + | / | ‒ | 60% | / |
| 2020 | 5/[6] | ‒ | + | + | ‒ | / | / | ‒ | 60% | TIA-1(‒), GB(‒) |
| 2020 | 6/[7] | ‒ | + | + | ‒ | / | / | ‒ | 60%‒95% | LCA(+) |
| 2020 | 7/[7] | ‒ | + | / | / | / | / | ‒ | 20% | LCA(+), GB(‒), CD30(‒) |
| 2020 | 8/[7] | ‒ | + | + | / | / | / | ‒ | 60%‒95% | |
| 2020 | 9/[7] | / | + | / | / | / | / | ‒ | 60%‒95% | GB(+) |
| 2020 | 10/[7] | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 60%‒95% | CD30(+) |
| 2020 | 11/[7] | / | + | + | + | ‒ | / | ‒ | 60%‒95% | TIA-1(+), GB(+), perforin(+) |
| 2020 | 12/[7] | / | + | + | + | + | + | ‒ | 60%‒95% | TIA-1(+), GB(+), perforin(+), CD30(‒), PD-1(+) |
| 2023 | 13/[8] | / | + | / | / | / | + | ‒ | 70%‒80% | CD30(‒) |
| 2024 | 14/[9] | / | + | / | / | / | / | / | 70% | Perforin(‒), GB(‒) |
| 2024 | 15/[9] | / | + | / | / | / | / | / | 80% | GB(‒) |
| 2024 | 16/[9] | / | + | ‒ | + | / | / | / | 95% | Perforin(‒), GB(+), CD30(‒) |
| 2024 | 17/[9] | / | + | + | ‒ | / | / | / | 95% | GB(+), CD30(‒) |
| 2024 | 18/[9] | / | + | + | ‒ | / | / | / | 90% | GB(+), CD30(+) |
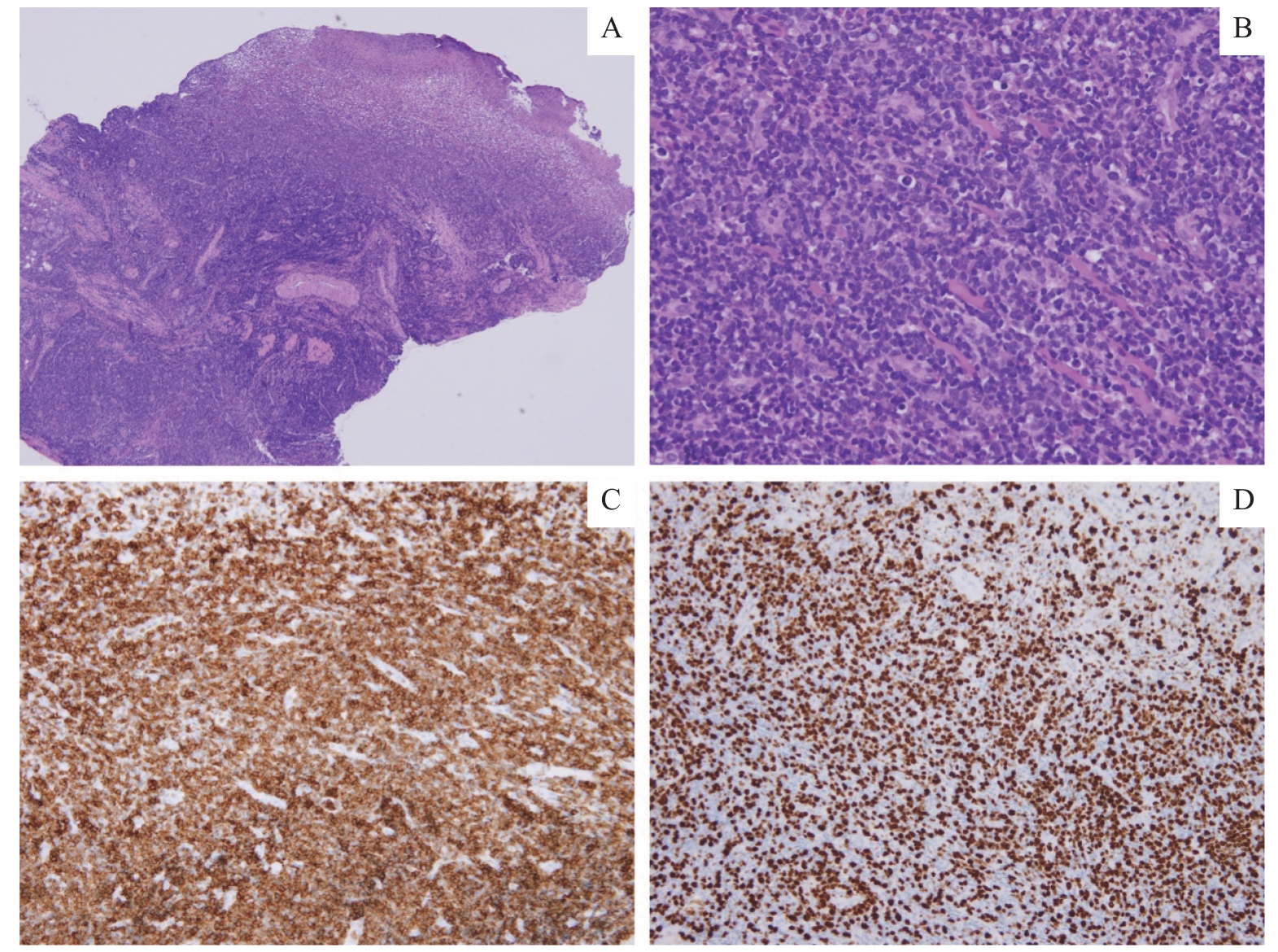
Fig 3 Histopathological examinationNote: A. Ulceration of the right tongue mucosa with diffuse infiltration of lymphoid cells (H-E staining, ×40). B. Atypical lymphoid cells exhibit hyperchromatic nuclei and a high nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio (H-E staining, ×200). C. CD3 positive (+) staining (×200). D. Ki-67 positivity in 60%‒70% of cells (×200).
| 1 | SWERDLOW S H, CAMPO E, HARRIS N L, et al. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues[M]. Revised 4th ed. Lyon: IARC Press, 2017. |
| 2 | LEE J H, LEE S H. A poor prognostic case of peripheral T-cell lymphoma in the base of tongue with chemotherapy followed by radiation therapy[J]. Springerplus, 2014, 3: 731. |
| 3 | NARLA S, ANNAPURNESWARI S, PARAMESWARAN A, et al. Peripheral T-cell lymphoma of tongue: report of a rare case and review of literature[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol, 2016, 20(2): 332. |
| 4 | 薛敏, 高冶, 段介君. 以舌部肿物为表现的外周型T细胞淋巴瘤1例[J]. 宁夏医科大学学报, 2017, 39(1): 115-116. |
| XUE M, GAO Y, DUAN J J. A case of peripheral T-cell lymphoma presenting as a tongue mass[J]. Journal of Ningxia Medical University, 2017, 39(1): 115-116. | |
| 5 | DOS SANTOS H L R, ALVES C G B, ALMENDRA MATTOS R M, et al. Peripheral T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma manifesting as a primary lesion on the lip: a rare case report[J]. Spec Care Dentist, 2018, 38(6): 438-444. |
| 6 | REN X Y, CHENG Y, WU S F, et al. Primary non-Hodgkin lymphoma of the tongue base: the clinicopathology of seven cases and evaluation of HPV and EBV status[J]. Diagn Pathol, 2020, 15(1): 30. |
| 7 | ALMEIDA DE ARRUDA J A, DE CASTRO ABRANTES T, CUNHA J L S, et al. Mature T/NK-cell lymphomas of the oral and maxillofacial region: a multi-institutional collaborative study[J]. J Oral Pathol Med, 2021, 50(6): 548-557. |
| 8 | ASADI A A, MAHMOUDI H, MOFIDI A, et al. Peripheral T-cell lymphoma of the oral cavity: a case report[J]. Cancer Rep (Hoboken), 2023, 6(1): e1751. |
| 9 | DE OLIVEIRA E M, DE CÁCERES C V B L, FERNANDES-RODRIGUES C I, et al. Oral manifestations of peripheral T cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified: case series and review of the current literature[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2025, 139(2): e37-e45. |
| 10 | PILERI S A, TABANELLI V, FIORI S, et al. Peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified: clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and future treatment[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2021, 13(18): 4535. |
| 11 | COSTELLO R, SANCHEZ C, LE TREUT T, et al. Peripheral T-cell lymphoma gene expression profiling and potential therapeutic exploitations[J]. Br J Haematol, 2010, 150(1): 21-27. |
| 12 | LUO J J, CRAVER A, BAHL K, et al. Etiology of non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a review from epidemiologic studies[J]. J Natl Cancer Cent, 2022, 2(4): 226-234. |
| 13 | COCCO P, VERMEULEN R, FLORE V, et al. Occupational exposure to trichloroethylene and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma and its major subtypes: a pooled InterLymph analysis[J]. Occup Environ Med, 2013, 70(11): 795-802. |
| 14 | BASSIG B A, SHU X O, FRIESEN M C, et al. Occupational exposure to benzene and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in an extended follow-up of two population-based prospective cohorts of Chinese men and women[J]. Int J Cancer, 2024, 155(12): 2159-2168. |
| 15 | BRYER E, HENRY D. Isolated hypoglossal nerve palsy as a presenting symptom of metastatic peripheral T-cell lymphoma - not otherwise specified (PTCL-NOS): a unique case & a review of the literature[J]. Int J Hematol Oncol, 2018, 7(1): IJH03. |
| 16 | SCHMITZ N, DE LEVAL L. How I manage peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified and angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma: current practice and a glimpse into the future[J]. Br J Haematol, 2017, 176(6): 851-866. |
| 17 | WENT P, AGOSTINELLI C, GALLAMINI A, et al. Marker expression in peripheral T-cell lymphoma: a proposed clinical-pathologic prognostic score[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2006, 24(16): 2472-2479. |
| 18 | LIM S T, HEE S W, QUEK R, et al. Comparative analysis of extra-nodal NK/T-cell lymphoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma: significant differences in clinical characteristics and prognosis[J]. Eur J Haematol, 2008, 80(1): 55-60. |
| 19 | D′AMORE F, GAULARD P, TRÜMPER L, et al. Peripheral T-cell lymphomas: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up[J]. Ann Oncol, 2015, 26(Suppl 5): v108-v115. |
| 20 | SHEN Q D, WANG L, ZHU H Y, et al. Gemcitabine, oxaliplatin and dexamethasone (GemDOx) as salvage therapy for relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma[J]. J Cancer, 2021, 12(1): 163-169. |
| 21 | MINA A, PRO B. T time: emerging and new therapies for peripheral T-cell lymphoma[J]. Blood Rev, 2022, 52: 100889. |
| 22 | 李静, 李志铭. 外周T细胞淋巴瘤和结外NK/T细胞淋巴瘤研究进展[J]. 肿瘤药学, 2024, 14(1): 16-21. |
| LI J, LI Z M. Research progress of peripheral T-cell lymphoma and extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma [J]. Anti-tumor Pharmacy, 2024, 14(1): 16-21. |
| [1] | ZHAO Ling, GAO Run-lin, LIU Qiang, SHEN Yan-ying. Clinicopathological analysis of five cases of intrathyroid thymic carcinoma [J]. , 2018, 38(10): 1272-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||