
Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science) ›› 2026, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 1-14.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2026.01.001
• Innovative research team achievement column •
Zhu Ying, Sui Yi, Tang Yujie( )
)
Received:2025-07-02
Accepted:2025-11-25
Online:2026-01-28
Published:2026-01-30
Contact:
Tang Yujie
E-mail:yujietang@shsmu.edu.cn
About author:First author contact:Zhu Ying participated in experiment design, experiment implementation, data analysis, and paper writing and modification. Sui Yi participated in the preliminary experimental design and implementation, as well as paper writing and revision. Tang Yujie supervised the whole project development, and paper writing and revision. All authors have read the last version of paper and consented to submission.
Supported by:CLC Number:
Zhu Ying, Sui Yi, Tang Yujie. Molecular mechanisms of miRNA expression dysregulation in SHH-activated subtype medulloblastoma[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2026, 46(1): 1-14.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://xuebao.shsmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2026.01.001
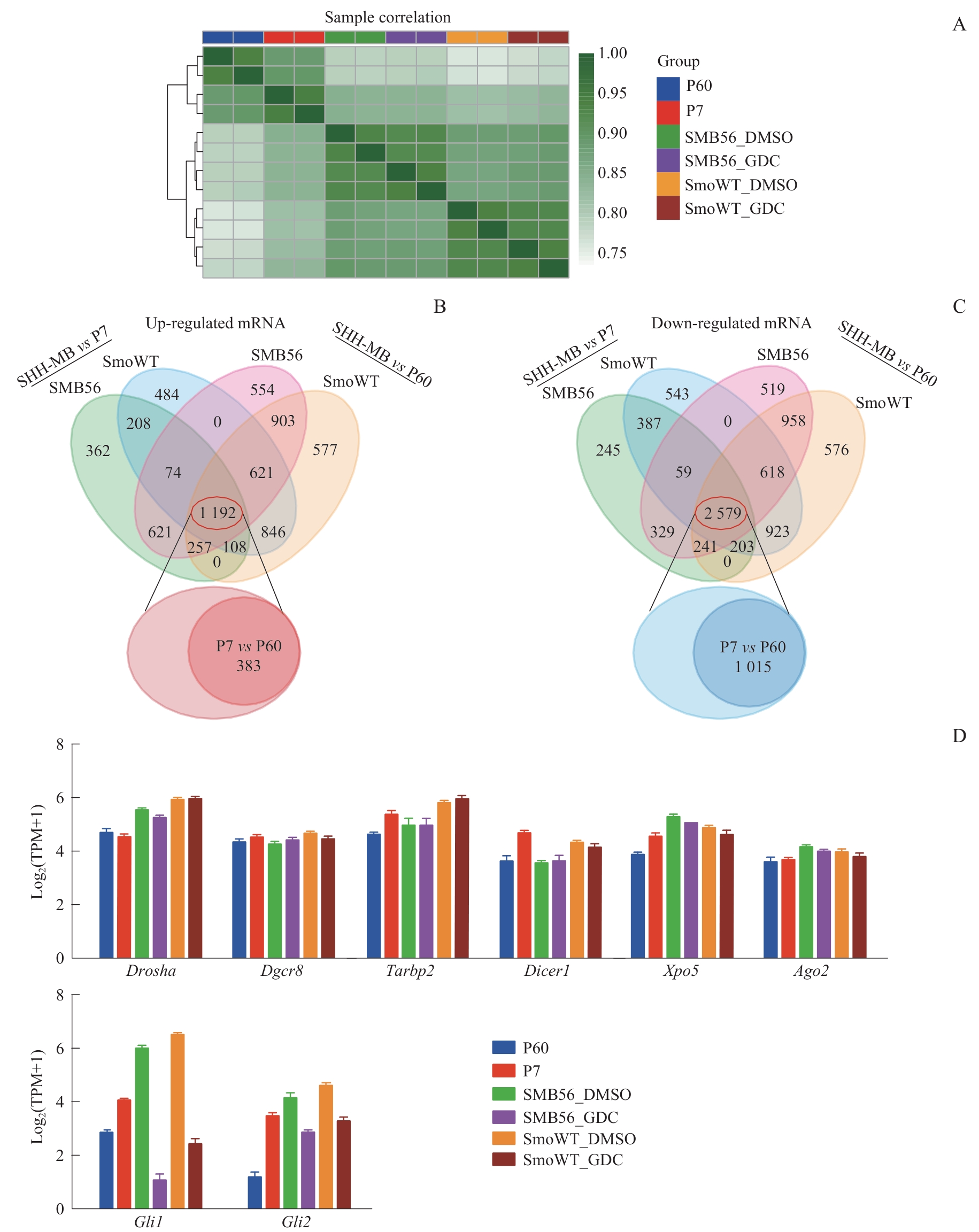
Fig 2 Comparison of mRNA transcriptomes between mouse SHH-MB models and normal nude mouse cerebellum, and mRNA expression levels of Hh pathway transcription factors and miRNA biogenesis genes
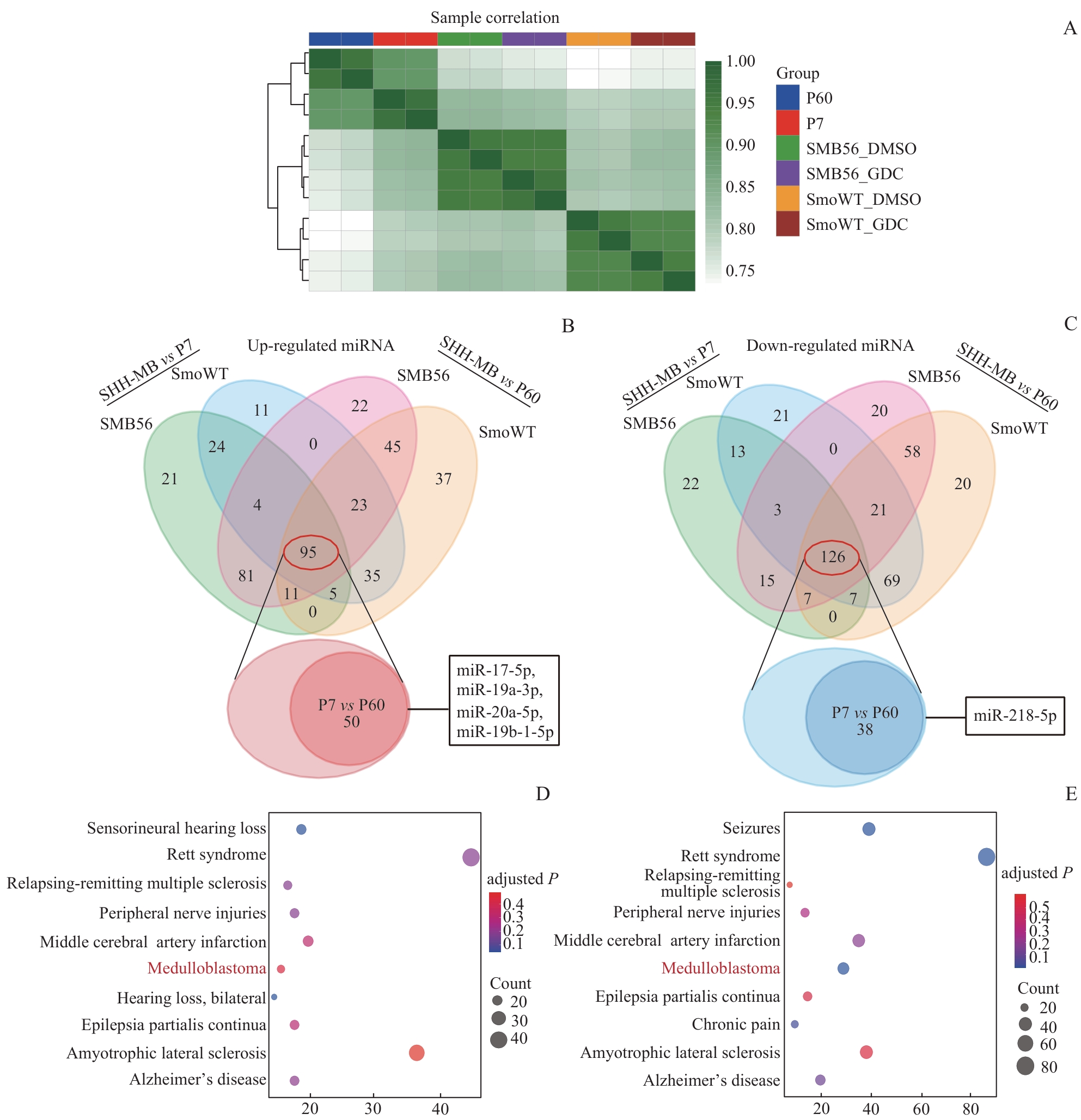
Fig 3 Comparison of miRNA transcriptomes between mouse SHH-MB models and normal nude mouse cerebellum, and DO enrichment analysis of differentially expressed miRNAs
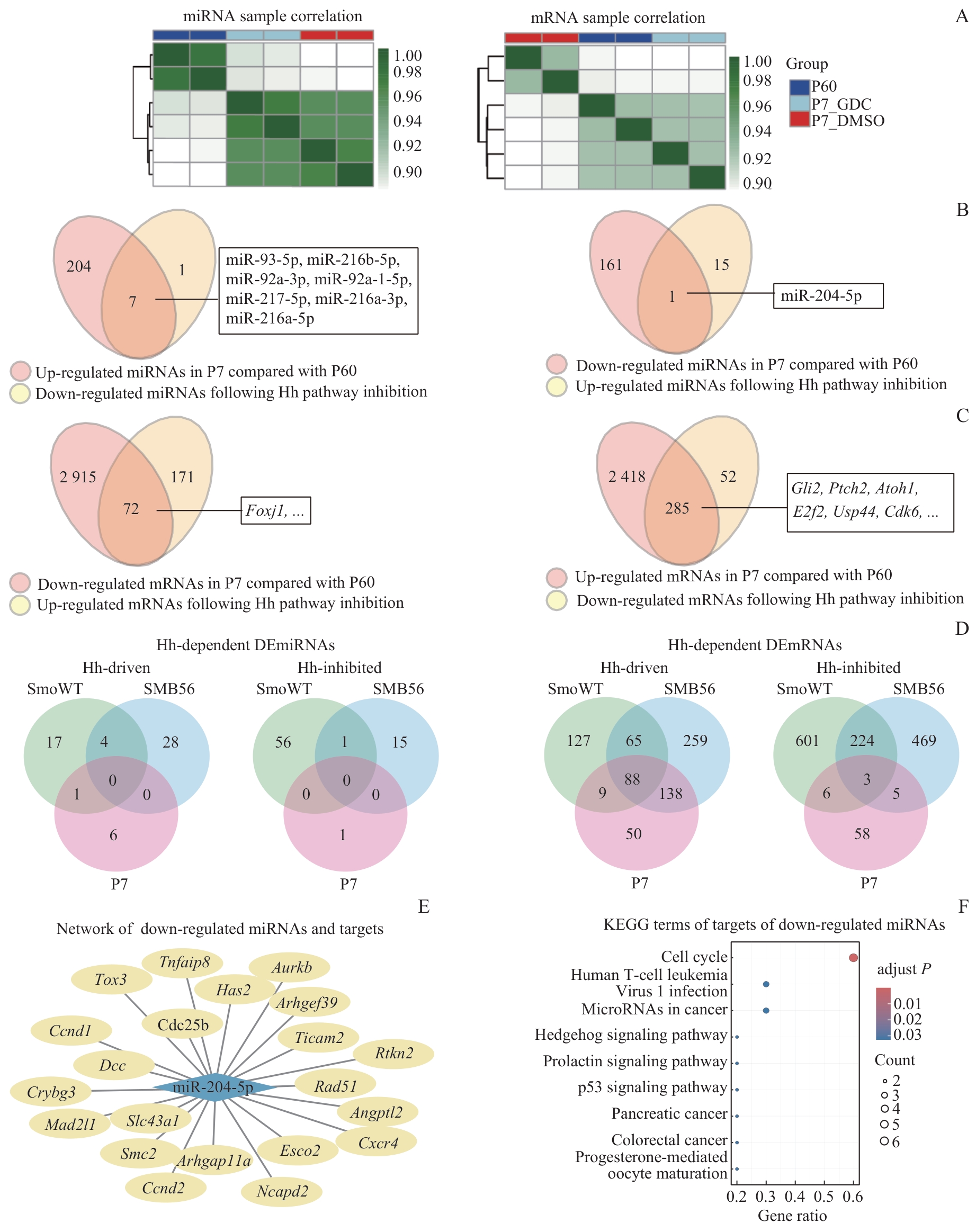
Fig 5 Hh pathway dependence of differentially expressed miRNAs/mRNAs in the developing cerebellum, comparison with SHH-MB models, and KEGG pathway enrichment of target genes
| [1] | Ostrom Q T, Price M, Neff C, et al. CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2016-2020[J]. Neuro Oncol, 2023, 25(12 Suppl 2): iv1-iv99. |
| [2] | Hovestadt V, Ayrault O, Swartling F J, et al. Medulloblastomics revisited: biological and clinical insights from thousands of patients[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2020, 20(1): 42-56. |
| [3] | Kool M, Korshunov A, Remke M, et al. Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: an international meta-analysis of transcriptome, genetic aberrations, and clinical data of WNT, SHH, Group 3, and Group 4 medulloblastomas[J]. Acta Neuropathol, 2012, 123(4): 473-484. |
| [4] | Northcott P A, Shih D J H, Peacock J, et al. Subgroup-specific structural variation across 1, 000 medulloblastoma genomes[J]. Nature, 2012, 488(7409): 49-56. |
| [5] | Northcott P A, Robinson G W, Kratz C P, et al. Medulloblastoma[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2019, 5(1): 11. |
| [6] | Thayer S P, Di Magliano M P, Heiser P W, et al. Hedgehog is an early and late mediator of pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis[J]. Nature, 2003, 425(6960): 851-856. |
| [7] | Mao J H, Ligon K L, Rakhlin E Y, et al. A novel somatic mouse model to survey tumorigenic potential applied to the Hedgehog pathway[J]. Cancer Res, 2006, 66(20): 10171-10178. |
| [8] | Pugh T J, Weeraratne S D, Archer T C, et al. Medulloblastoma exome sequencing uncovers subtype-specific somatic mutations[J]. Nature, 2012, 488(7409): 106-110. |
| [9] | Kieran M W, Chisholm J, Casanova M, et al. Phase I study of oral sonidegib (LDE225) in pediatric brain and solid tumors and a phase II study in children and adults with relapsed medulloblastoma[J]. Neuro Oncol, 2017, 19(11): 1542-1552. |
| [10] | Lorusso P M, Rudin C M, Reddy J C, et al. Phase I trial of hedgehog pathway inhibitor vismodegib (GDC-0449) in patients with refractory, locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2011, 17(8): 2502-2511. |
| [11] | Atwood S X, Li M, Lee A, et al. GLI activation by atypical protein kinase C ι/λ regulates the growth of basal cell carcinomas[J]. Nature, 2013, 494(7438): 484-488. |
| [12] | Buonamici S, Williams J, Morrissey M, et al. Interfering with resistance to smoothened antagonists by inhibition of the PI3K pathway in medulloblastoma[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2010, 2(51): 51ra70. |
| [13] | Kool M, Jones D T W, JäGer N, et al. Genome sequencing of SHH medulloblastoma predicts genotype-related response to smoothened inhibition[J]. Cancer Cell, 2014, 25(3): 393-405. |
| [14] | Rack P G, Ni J, Payumo A Y, et al. Arhgap36-dependent activation of Gli transcription factors[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2014, 111(30): 11061-11066. |
| [15] | Zhao X S, Ponomaryov T, Ornell K J, et al. RAS/MAPK activation drives resistance to SMO inhibition, metastasis, and tumor evolution in SHH pathway-dependent tumors[J]. Cancer Res, 2015, 75(17): 3623-3635. |
| [16] | Hogg S J, Beavis P A, Dawson M A, et al. Targeting the epigenetic regulation of antitumour immunity[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2020, 19(11): 776-800. |
| [17] | Zhang B H, Pan X P, Cobb G P, et al. microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors[J]. Dev Biol, 2007, 302(1): 1-12. |
| [18] | Liu F, Jiang W Y, Sui Y, et al. CDK7 inhibition suppresses aberrant hedgehog pathway and overcomes resistance to smoothened antagonists[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2019, 116(26): 12986-12995. |
| [19] | Pak E, Mackenzie E L, Zhao X S, et al. A large-scale drug screen identifies selective inhibitors of class I HDACs as a potential therapeutic option for SHH medulloblastoma[J]. Neuro Oncol, 2019, 21(9): 1150-1163. |
| [20] | Mo J L, Liu F, Sun X, et al. Inhibition of the FACT complex targets aberrant hedgehog signaling and overcomes resistance to smoothened antagonists[J]. Cancer Res, 2021, 81(11): 3105-3120. |
| [21] | Tang Y J, Gholamin S, Schubert S, et al. Epigenetic targeting of Hedgehog pathway transcriptional output through BET bromodomain inhibition[J]. Nat Med, 2014, 20(7): 732-740. |
| [22] | Murchison E P, Hannon G J. miRNAs on the move: miRNA biogenesis and the RNAi machinery[J]. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2004, 16(3): 223-229. |
| [23] | Siomi H, Siomi M C. Posttranscriptional regulation of microRNA biogenesis in animals[J]. Mol Cell, 2010, 38(3): 323-332. |
| [24] | Lin S B, Gregory R I. MicroRNA biogenesis pathways in cancer[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2015, 15(6): 321-333. |
| [25] | Pereira D M, Rodrigues P M, Borralho P M, et al. Delivering the promise of miRNA cancer therapeutics[J]. Drug Discov Today, 2013, 18(5/6): 282-289. |
| [26] | Mitchell P S, Parkin R K, Kroh E M, et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2008, 105(30): 10513-10518. |
| [27] | Abu-Halima M, Keller A, Becker L S, et al. Dynamic and static circulating cancer microRNA biomarkers: a validation study[J]. RNA Biol, 2023, 20(1): 1-9. |
| [28] | Kalhori M R, Soleimani M, Arefian E, et al. The potential role of miR-1290 in cancer progression, diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment: an oncomiR or onco-suppressor microRNA?[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2022, 123(3): 506-531. |
| [29] | Tanigawa K, Misono S, Mizuno K, et al. MicroRNA signature of small-cell lung cancer after treatment failure: impact on oncogenic targets by miR-30a-3p control[J]. Mol Oncol, 2023, 17(2): 328-343. |
| [30] | Hong D, Zang A M, Wang Z Y, et al. Elevation of microRNA-365 impedes malignant behaviors of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting PAX6[J]. Funct Integr Genomics, 2022, 22(5): 825-834. |
| [31] | Salm F, Dimitrova V, Von Bueren A O, et al. The phosphoinositide 3-Kinase p110α isoform regulates leukemia inhibitory factor receptor expression via c-Myc and miR-125b to promote cell proliferation in medulloblastoma[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(4): e0123958. |
| [32] | Lv S Q, Kim Y H, Giulio F, et al. Genetic alterations in microRNAs in medulloblastomas[J]. Brain Pathol, 2012, 22(2): 230-239. |
| [33] | Jiang Z H, Cushing L, Ai X B, et al. miR-326 is downstream of Sonic hedgehog signaling and regulates the expression of Gli2 and smoothened[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2014, 51(2): 273-283. |
| [34] | Northcott P A, Fernandez-L A, Hagan J P, et al. The miR-17/92 polycistron is up-regulated in sonic hedgehog-driven medulloblastomas and induced by N-myc in sonic hedgehog-treated cerebellar neural precursors[J]. Cancer Res, 2009, 69(8): 3249-3255. |
| [35] | Murphy B L, Obad S, Bihannic L, et al. Silencing of the miR-17~92 cluster family inhibits medulloblastoma progression[J]. Cancer Res, 2013, 73(23): 7068-7078. |
| [36] | Sui Y, Wang T, Mei Y Q, et al. Targeting super-enhancer-driven transcriptional dependencies suppresses aberrant hedgehog pathway activation and overcomes smoothened inhibitor resistance[J]. Cancer Res, 2024, 84(16): 2690-2706. |
| [37] | Kozomara A, Birgaoanu M, Griffiths-Jones S. miRBase: from microRNA sequences to function[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2019, 47(D1): D155-D162. |
| [38] | Jones T A, Jeyapalan J N, Forshew T, et al. Molecular analysis of pediatric brain tumors identifies microRNAs in pilocytic astrocytomas that target the MAPK and NF-κB pathways[J]. Acta Neuropathol Commun, 2015, 3: 86. |
| [39] | Laresgoiti U, Apraiz A, Olea M, et al. E2F2 and CREB cooperatively regulate transcriptional activity of cell cycle genes[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2013, 41(22): 10185-10198. |
| [40] | Xia Y H, Zhen L, Li H X, et al. MIRLET7BHG promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by activating hepatic stellate cells through exosomal SMO to trigger Hedgehog pathway[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(4): 326. |
| [41] | Zhang P X, Gao H, Yan R P, et al. has_circ_0070512 promotes prostate cancer progression by regulating the miR-338-3p/hedgehog signaling pathway[J]. Cancer Sci, 2023, 114(4): 1491-1506. |
| [42] | Tschaikner P, Enzler F, Torres-Quesada O, et al. Hedgehog and Gpr161: regulating cAMP signaling in the primary Cilium[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(1): 118. |
| [43] | Venkataraman S, Birks D K, Balakrishnan I, et al. microRNA 218 acts as a tumor suppressor by targeting multiple cancer phenotype-associated genes in medulloblastoma[J]. J Biol Chem, 2013, 288(3): 1918-1928. |
| [44] | Zhu K G, Ding H Y, Wang W G, et al. Tumor-suppressive miR-218-5p inhibits cancer cell proliferation and migration via EGFR in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(19): 28075-28085. |
| [45] | Mollashahi B, Aghamaleki F S, Movafagh A. The roles of miRNAs in medulloblastoma: a systematic review[J]. J Cancer Prev, 2019, 24(2): 79-90. |
| [1] | CAI Liu-yun, LUO Xiao-dong, LIANG Hao, HU Jian-guo. Inhibition of C2CD3 regulates the proliferation, invasion and migration of epithelial ovarian cancer through inhibiting Hedgehog pathway [J]. , 2018, 38(12): 1414-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||