
JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE) ›› 2021, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 173-179.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2021.02.008
• Clinical research • Previous Articles Next Articles
Pei-kun HU( ), Jie HE, Lian-ming WU, Heng GE, Jian-rong XU, Jun PU(
), Jie HE, Lian-ming WU, Heng GE, Jian-rong XU, Jun PU( )
)
Received:2020-06-01
Online:2021-02-28
Published:2021-02-28
Contact:
Jun PU
E-mail:hupei-kun@foxmail.com;pujun310@hotmail.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
Pei-kun HU, Jie HE, Lian-ming WU, Heng GE, Jian-rong XU, Jun PU. Effect of microvascular obstruction on left ventricle function and prognosis in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction[J]. JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE), 2021, 41(2): 173-179.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://xuebao.shsmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2021.02.008
| Characteristic | MVO (+) group (N=82) | MVO (-) group (N=42) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age/year | 58.6±7.9 | 58.7±8.4 | 0.958 |
| Gender/n (%) | 0.098 | ||
| Male | 76 (92.7) | 34 (81.0) | |
| Female | 6 (7.3) | 8 (19.0) | |
| Smoking history/n (%) | 65 (79.3) | 30 (71.4) | 0.329 |
| Drinking history/n (%) | 22 (26.8) | 13 (31.0) | 0.629 |
| Hypertension/n (%) | 48 (58.5) | 19 (45.2) | 0.160 |
| Diabetes mellitus/n (%) | 30 (36.6) | 12 (28.6) | 0.372 |
| Hypercholesterolemia/n (%) | 46 (56.1) | 19 (45.2) | 0.252 |
| Previous angina/n (%) | 42 (51.2) | 25 (59.5) | 0.380 |
| Renal dysfunction/n (%) | 3 (3.7) | 0 (0) | 0.524 |
| Previous stroke/n (%) | 0 (0) | 1 (2.4) | 0.732 |
| Pain-to-balloon time/h | 5.5±3.2 | 4.9±1.6 | 0.166 |
| Reperfusion therapy/n (%) | 1.000 | ||
| PPCI | 41 (50.0) | 21 (50.0) | |
| PCI after thrombolysis | 41 (50.0) | 21 (50.0) | |
| Culprit vessel/n (%) | 0.398 | ||
| LAD | 47 (57.3) | 25 (59.5) | |
| LCX | 10 (12.2) | 2 (4.8) | |
| RCA | 25 (30.5) | 15 (35.7) | |
| Killip class/n (%) | 1.000 | ||
| Ⅰ | 74 (90.2) | 38 (90.5) | |
| Ⅱ | 7 (8.5) | 3 (7.1) | |
| Ⅲ | 1 (1.2) | 1 (2.4) | |
| Time delay from the onset of chest pain to CMR/d | 5.2±2.2 | 5.3±1.8 | 0.863 |
Tab 1 Comparison of baseline characteristics between the two groups
| Characteristic | MVO (+) group (N=82) | MVO (-) group (N=42) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age/year | 58.6±7.9 | 58.7±8.4 | 0.958 |
| Gender/n (%) | 0.098 | ||
| Male | 76 (92.7) | 34 (81.0) | |
| Female | 6 (7.3) | 8 (19.0) | |
| Smoking history/n (%) | 65 (79.3) | 30 (71.4) | 0.329 |
| Drinking history/n (%) | 22 (26.8) | 13 (31.0) | 0.629 |
| Hypertension/n (%) | 48 (58.5) | 19 (45.2) | 0.160 |
| Diabetes mellitus/n (%) | 30 (36.6) | 12 (28.6) | 0.372 |
| Hypercholesterolemia/n (%) | 46 (56.1) | 19 (45.2) | 0.252 |
| Previous angina/n (%) | 42 (51.2) | 25 (59.5) | 0.380 |
| Renal dysfunction/n (%) | 3 (3.7) | 0 (0) | 0.524 |
| Previous stroke/n (%) | 0 (0) | 1 (2.4) | 0.732 |
| Pain-to-balloon time/h | 5.5±3.2 | 4.9±1.6 | 0.166 |
| Reperfusion therapy/n (%) | 1.000 | ||
| PPCI | 41 (50.0) | 21 (50.0) | |
| PCI after thrombolysis | 41 (50.0) | 21 (50.0) | |
| Culprit vessel/n (%) | 0.398 | ||
| LAD | 47 (57.3) | 25 (59.5) | |
| LCX | 10 (12.2) | 2 (4.8) | |
| RCA | 25 (30.5) | 15 (35.7) | |
| Killip class/n (%) | 1.000 | ||
| Ⅰ | 74 (90.2) | 38 (90.5) | |
| Ⅱ | 7 (8.5) | 3 (7.1) | |
| Ⅲ | 1 (1.2) | 1 (2.4) | |
| Time delay from the onset of chest pain to CMR/d | 5.2±2.2 | 5.3±1.8 | 0.863 |
| Index | MVO (+) group (N=82) | MVO (-) group (N=42) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blood biochemical index | |||
| CRP/(mg·L-1) | 5.92 (1.52, 22.03) | 3.95 (2.42, 12.53) | 0.720 |
| WBC/(×109·L-1) | 11.95 (10.01, 13.95) | 10.21 (7.92, 12.85) | 0.016 |
| Hb/(g·L-1) | 145.23±16.16 | 140.31±14.37 | 0.109 |
| PLT/(×109·L-1) | 195.85±48.77 | 211.36±49.15 | 0.097 |
| FBG/(g·L-1) | 2.81±0.71 | 2.88±0.58 | 0.588 |
| PT/s | 10.70 (10.00, 11.83) | 10.60 (10.10, 11.70) | 0.755 |
| APTT/s | 32.10 (28.70, 36.30) | 33.65 (29.15, 36.18) | 0.748 |
| INR | 0.94 (0.88, 0.99) | 0.93 (0.88, 1.01) | 0.919 |
| Scr/(μmol·L-1) | 71.70±19.35 | 70.11±14.27 | 0.640 |
| BUN/(mmol·L-1) | 5.60±1.65 | 5.32±1.76 | 0.375 |
| Glu/(mmol·L-1) | 5.72 (5.09, 6.61) | 5.29 (4.80, 6.16) | 0.093 |
| TAG/(mmol·L-1) | 1.37 (0.96, 2.51) | 1.31 (0.95, 1.63) | 0.240 |
| TC/(mmol·L-1) | 5.21±1.10 | 4.77±1.05 | 0.039 |
| HDL-Ch/(mmol·L-1) | 1.17±0.26 | 1.16±0.27 | 0.920 |
| LDL-Ch/(mmol·L-1) | 3.21±0.86 | 3.09±0.88 | 0.450 |
| CPK/(U·L-1) | 3 632.00 (2 547.00, 5 151.25) | 1 565.00 (1 074.50, 3 228.00) | 0.000 |
| CK-MB/(U·L-1) | 370.75 (241.43, 480.45) | 201.60 (120.95, 288.25) | 0.000 |
| cTnI/(ng·mL-1) | 26.34 (1.54, 80.85) | 10.33 (0.93, 28.40) | 0.022 |
| BNP/(pg·mL-1) | 101.50 (37.95, 275.00) | 93.80 (17.38, 203.00) | 0.202 |
| CMR index | |||
| LVEF/% | 47.07±8.94 | 53.95±5.79 | 0.000 |
| Percentage of myocardial infarction/% | 23.09 (17.41, 30.46) | 11.25 (6.40, 18.14) | 0.000 |
Tab 2 Comparison of blood biochemical indexes and CMR indexes between the two groups
| Index | MVO (+) group (N=82) | MVO (-) group (N=42) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blood biochemical index | |||
| CRP/(mg·L-1) | 5.92 (1.52, 22.03) | 3.95 (2.42, 12.53) | 0.720 |
| WBC/(×109·L-1) | 11.95 (10.01, 13.95) | 10.21 (7.92, 12.85) | 0.016 |
| Hb/(g·L-1) | 145.23±16.16 | 140.31±14.37 | 0.109 |
| PLT/(×109·L-1) | 195.85±48.77 | 211.36±49.15 | 0.097 |
| FBG/(g·L-1) | 2.81±0.71 | 2.88±0.58 | 0.588 |
| PT/s | 10.70 (10.00, 11.83) | 10.60 (10.10, 11.70) | 0.755 |
| APTT/s | 32.10 (28.70, 36.30) | 33.65 (29.15, 36.18) | 0.748 |
| INR | 0.94 (0.88, 0.99) | 0.93 (0.88, 1.01) | 0.919 |
| Scr/(μmol·L-1) | 71.70±19.35 | 70.11±14.27 | 0.640 |
| BUN/(mmol·L-1) | 5.60±1.65 | 5.32±1.76 | 0.375 |
| Glu/(mmol·L-1) | 5.72 (5.09, 6.61) | 5.29 (4.80, 6.16) | 0.093 |
| TAG/(mmol·L-1) | 1.37 (0.96, 2.51) | 1.31 (0.95, 1.63) | 0.240 |
| TC/(mmol·L-1) | 5.21±1.10 | 4.77±1.05 | 0.039 |
| HDL-Ch/(mmol·L-1) | 1.17±0.26 | 1.16±0.27 | 0.920 |
| LDL-Ch/(mmol·L-1) | 3.21±0.86 | 3.09±0.88 | 0.450 |
| CPK/(U·L-1) | 3 632.00 (2 547.00, 5 151.25) | 1 565.00 (1 074.50, 3 228.00) | 0.000 |
| CK-MB/(U·L-1) | 370.75 (241.43, 480.45) | 201.60 (120.95, 288.25) | 0.000 |
| cTnI/(ng·mL-1) | 26.34 (1.54, 80.85) | 10.33 (0.93, 28.40) | 0.022 |
| BNP/(pg·mL-1) | 101.50 (37.95, 275.00) | 93.80 (17.38, 203.00) | 0.202 |
| CMR index | |||
| LVEF/% | 47.07±8.94 | 53.95±5.79 | 0.000 |
| Percentage of myocardial infarction/% | 23.09 (17.41, 30.46) | 11.25 (6.40, 18.14) | 0.000 |
| Adverse event | MVO (+) group (N=82) | MVO (-) group (N=42) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| All-cause mortality/n (%) | 1 (1.2) | 0 (0) | 1.000 |
| Myocardial reinfarction/n (%) | 2 (2.4) | 0 (0) | 0.548 |
| Recurrent angina/n (%) | 8 (9.8) | 3 (7.1) | 0.880 |
| Heart failure/n (%) | 14 (17.1) | 1 (2.4) | 0.018 |
Tab 3 Comparison of adverse events within 30 days between the two groups
| Adverse event | MVO (+) group (N=82) | MVO (-) group (N=42) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| All-cause mortality/n (%) | 1 (1.2) | 0 (0) | 1.000 |
| Myocardial reinfarction/n (%) | 2 (2.4) | 0 (0) | 0.548 |
| Recurrent angina/n (%) | 8 (9.8) | 3 (7.1) | 0.880 |
| Heart failure/n (%) | 14 (17.1) | 1 (2.4) | 0.018 |
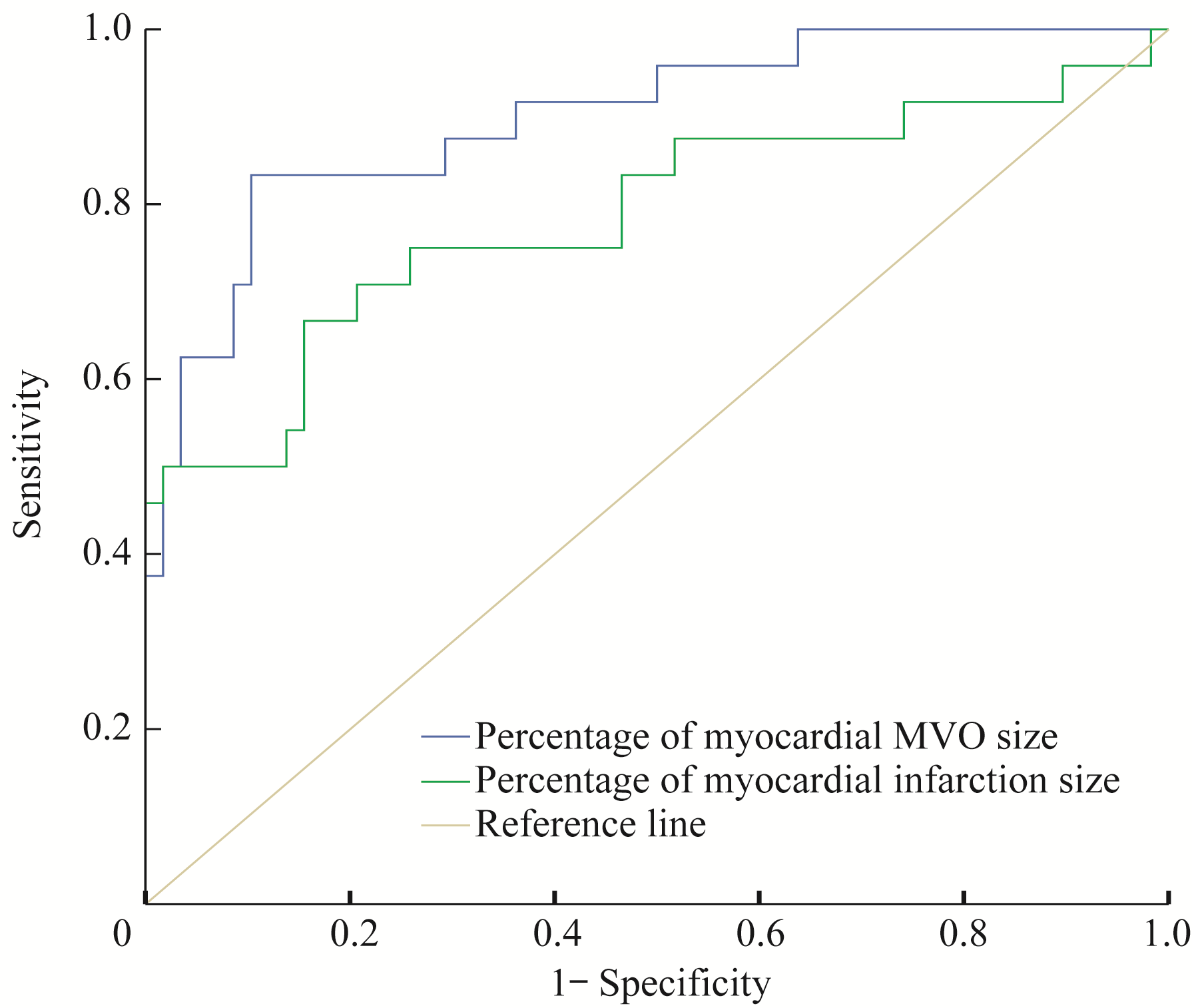
Fig 3 ROC curve of predictive value of the percentage of myocardial MVO size and myocardial infarction size for adverse events within 30 days in the MVO(+) patients
| Index | AUC | 95%CI | Youden index | Cut-off value | Sensitivity/% | Specificity/% | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage of myocardial MVO size | 0.899 | 0.823?0.975 | 0.730 | 2.99 | 83.3 | 89.7 | 0.000 |
| Percentage of myocardial infarction size | 0.785 | 0.660?0.911 | 0.512 | 29.70 | 66.7 | 84.5 | 0.000 |
Tab 4 Comparative analysis of predictive value of the percentage of myocardial MVO size and the percentage of myocardial infarction size
| Index | AUC | 95%CI | Youden index | Cut-off value | Sensitivity/% | Specificity/% | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage of myocardial MVO size | 0.899 | 0.823?0.975 | 0.730 | 2.99 | 83.3 | 89.7 | 0.000 |
| Percentage of myocardial infarction size | 0.785 | 0.660?0.911 | 0.512 | 29.70 | 66.7 | 84.5 | 0.000 |
| 1 | Nabel EG, Braunwald E. A tale of coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction[J]. N Engl J Med, 2012, 366(1): 54-63. |
| 2 | Çağdaş M, Karakoyun S, Rencüzoğulları İ, et al. Assessment of the relationship between reperfusion success and T-peak to T-end interval in patients with ST elevation myocardial infarction treated with percutaneous coronary intervention[J]. Anatol J Cardiol, 2018, 19(1): 50-57. |
| 3 | Fajar JK, Heriansyah T, Rohman MS. The predictors of no reflow phenomenon after percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with ST elevation myocardial infarction: a meta-analysis[J]. Indian Heart J, 2018, 70 (): S406-S418. |
| 4 | Niccoli G, Burzotta F, Galiuto L, et al. Myocardial no-reflow in humans[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2009, 54(4): 281-292. |
| 5 | Pu J, Ding S, Ge H, et al. Efficacy and safety of a pharmaco-invasive strategy with half-dose alteplase versus primary angioplasty in ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction: EARLY-MYO trial (early routine catheterization after alteplase fibrinolysis versus primary PCI in acute ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction)[J]. Circulation, 2017, 136(16): 1462-1473. |
| 6 | He J, Kong LC, Zeng JT, et al. Comparison of direct stenting with conventional strategy on myocardial impairments in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: a cardiac magnetic resonance imaging study[J]. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging, 2020, 36(6): 1167-1175. |
| 7 | de Waha S, Desch S, Eitel I, et al. Impact of early vs. late microvascular obstruction assessed by magnetic resonance imaging on long-term outcome after ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a comparison with traditional prognostic markers[J]. Eur Heart J, 2010, 31(21): 2660-2668. |
| 8 | Cochet AA, Lorgis L, Lalande A, et al. Major prognostic impact of persistent microvascular obstruction as assessed by contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance in reperfused acute myocardial infarction[J]. Eur Radiol, 2009, 19(9): 2117-2126. |
| 9 | Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, et al. Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction (2018)[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2018, 72(18): 2231-2264. |
| 10 | Ezekowitz JA, Kaul P, Bakal JA, et al. Declining in-hospital mortality and increasing heart failure incidence in elderly patients with first myocardial infarction[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2009, 53(1): 13-20. |
| 11 | Weir RA, Murphy CA, Petrie CJ, et al. Microvascular obstruction remains a portent of adverse remodeling in optimally treated patients with left ventricular systolic dysfunction after acute myocardial infarction[J]. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging, 2010, 3(4): 360-367. |
| 12 | Hammer-Hansen S, Leung SW, Hsu LY, et al. Early gadolinium enhancement for determination of area at risk: a preclinical validation study[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging, 2017, 10(2): 130-139. |
| 13 | Wu KC, Weiss RG, Thiemann DR, et al. Late gadolinium enhancement by cardiovascular magnetic resonance heralds an adverse prognosis in nonischemic cardiomyopathy[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2008, 51(25): 2414-2421. |
| 14 | Hamirani YS, Wong A, Kramer CM, et al. Effect of microvascular obstruction and intramyocardial hemorrhage by CMR on LV remodeling and outcomes after myocardial infarction: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging, 2014, 7(9): 940-952. |
| 15 | Abbas A, Matthews GH, Brown IW, et al. Cardiac MR assessment of microvascular obstruction[J]. Br J Radiol, 2015, 88(1047): 20140470. |
| 16 | Yellon DM, Hausenloy DJ. Myocardial reperfusion injury[J]. N Engl J Med, 2007, 357(11): 1121-1135. |
| 17 | Mangold A, Alias S, Scherz T, et al. Coronary neutrophil extracellular trap burden and deoxyribonuclease activity in ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome are predictors of ST-segment resolution and infarct size[J]. Circ Res, 2015, 116(7): 1182-1192. |
| 18 | Lombardo A, Niccoli G, Natale L, et al. Impact of microvascular obstruction and infarct size on left ventricular remodeling in reperfused myocardial infarction: a contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance imaging study[J]. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging, 2012, 28(4): 835-842. |
| 19 | Mori H, Isobe S, Sakai S, et al. Microvascular obstruction on delayed enhancement cardiac magnetic resonance imaging after acute myocardial infarction, compared with myocardial (201)Tl and (123)I-BMIPP dual SPECT findings[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2015, 84(8): 1516-1524. |
| 20 | Wong DT, Leung MC, Richardson JD, et al. Cardiac magnetic resonance derived late microvascular obstruction assessment post ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction is the best predictor of left ventricular function: a comparison of angiographic and cardiac magnetic resonance derived measurements[J]. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging, 2012, 28(8): 1971-1981. |
| 21 | Roger VL. Epidemiology of heart failure[J]. Circ Res, 2013, 113(6): 646-659. |
| 22 | Durante A, Laricchia A, Benedetti G, et al. Identification of high-risk patients after ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction: comparison between angiographic and magnetic resonance parameters[J]. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging, 2017, 10(6): e005841. |
| 23 | Zhang L, Mandry D, Chen B, et al. Impact of microvascular obstruction on left ventricular local remodeling after reperfused myocardial infarction[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2018, 47(2): 499-510. |
| 24 | Ørn S, Manhenke C, Greve OJ, et al. Microvascular obstruction is a major determinant of infarct healing and subsequent left ventricular remodelling following primary percutaneous coronary intervention[J]. Eur Heart J, 2009, 30(16): 1978-1985. |
| 25 | Borlaug BA, Lam CS, Roger VL, et al. Contractility and ventricular systolic stiffening in hypertensive heart disease insights into the pathogenesis of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2009, 54(5): 410-418. |
| [1] | CHEN Siyuan, SHI Qing, FU Di, WANG Li, CHENG Shu, XU Pengpeng, ZHAO Weili. Clinicopathologic characteristics, gene mutation profile, and prognostic analysis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with lung involvement [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(9): 1214-1220. |
| [2] | YAN Zhi, WU Xingyue, YAO Weiqin, YAN Lingzhi, JIN Song, SHANG Jingjing, SHI Xiaolan, WU Depei, FU Chengcheng. Dynamic changes and prognostic significance of immunoparesis in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(7): 807-814. |
| [3] | XU Tianyun, SHEN Yiming, JIANG Meng. Clinical management of heart failure with improved ejection fraction: treatment and maintenance [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(4): 493-499. |
| [4] | WANG Boen, CHEN Siyuan, SHI Qing, ZHANG Muchen, YI Hongmei, DONG Lei, WANG Li, CHENG Shu, XU Pengpeng, ZHAO Weili. Clinicopathologic characteristics of patients with kidney-involved diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(9): 1162-1168. |
| [5] | SONG Chenlu, XIANG Jun, YANG Huizhong. Early alarming effect of serum heparin-binding protein on prognosis and occurrence of sepsis in severely burned patients [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(4): 474-481. |
| [6] | WANG Guijie, DU Chuanchong, LU Ye, ZHAO Jian, SHEN Xie, JIN Donglin, GENG Jiacai. Changes of serum high mobility group box 1 and soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 in patients with multiple injuries and their prognostic significance [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(3): 350-357. |
| [7] | LIU Qiming, LU Qifan, CHAI Yezi, JIANG Meng, PU Jun. Short-axis cine cardiac magnetic resonance images-derived radiomics for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and healthy control classification [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(1): 79-86. |
| [8] | LIU Qiming, LU Qifan, CHAI Yezi, JIANG Meng, PU Jun. Radiomics-based left ventricular ejection fraction prediction: a feasibility study [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(9): 1162-1168. |
| [9] | LUO Mengxing, ZOU Xin, GAO Yaxian, WU Xiaocui, YU Fangyou, HU Yang, ZENG Qibing, LIU Zhonghua. Analysis of the effect of anti-tuberculosis treatment and lung injury in patients with tuberculosis combined with underlying disease [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(8): 1017-1023. |
| [10] | LI Ying, TAN Yangxia, YIN Hongxin, JIANG Yanling, CHEN Li, MENG Guoyu. Research progress in the pathogenesis and prognosis of ZNF384 fusion subtype acute leukemia [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(5): 631-640. |
| [11] | MEN Ru, ZHU Minxia, ZHANG Weiming. Serum potassium level in maintenance hemodialysis patients and its effect on outcome [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(4): 507-513. |
| [12] | WANG Anjun, LIU Ningning. Efficacy of radiotherapy in patients with rectal cancer undergoing chemotherapy and surgery: a retrospective study based on the SEER database [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(3): 320-332. |
| [13] | LI Fang, LI Kaiyang, WANG Jue, YAN Ruiyang, SHEN Hui, LIU Min. Expression and clinical significance of PLA2G2A in kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(2): 152-161. |
| [14] | HOU Shumin, SHAO Jingbo. Research progress in clinical characteristics, diagnosis and prognosis of TdT-negative lymphoblastic lymphoma/acute lymphoblastic leukemia [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(1): 120-124. |
| [15] | QIU Jiahui, CAI Qianqian, YANG Yan, CHENG Feichi, QIU Zhengjun, HUANG Chen. Value of combined perineural lymphovascular invasion and tumor-stroma ratio in guiding the prognosis of colorecatal cancer [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2022, 42(8): 1070-1080. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||