
Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science) ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 69-78.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2025.01.008
• Clinical research • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2024-08-26
Accepted:2024-09-27
Online:2025-01-28
Published:2025-01-28
Contact:
ZHAO Xinxin
E-mail:zhaoxinxin@renji.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
ZHAO Xinxin, PEI Mengchao. Study on multi-parametric texture analysis for quantifying brain magnetic susceptibility in patients with Parkinson′s disease[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(1): 69-78.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://xuebao.shsmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2025.01.008
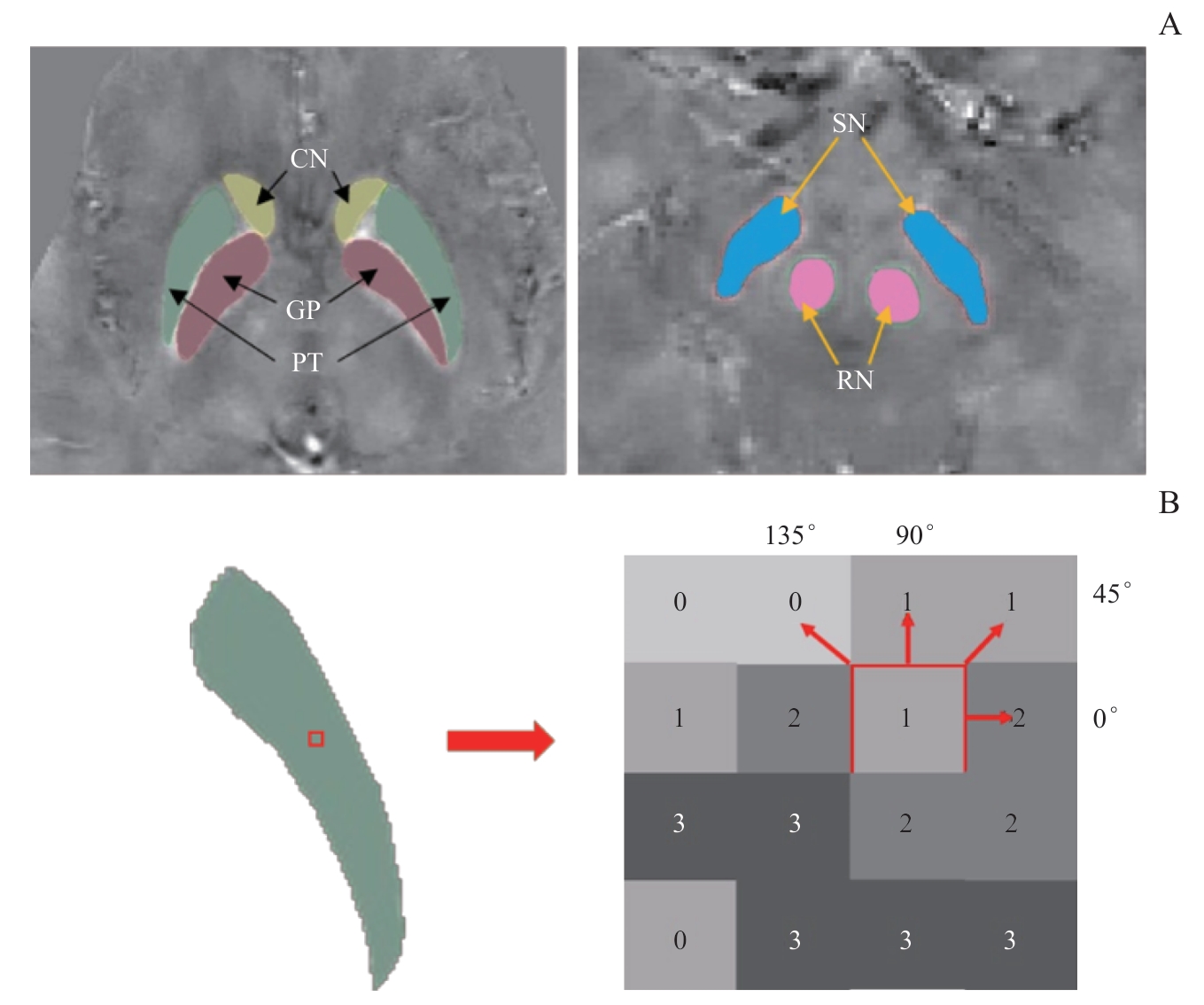
Fig 1 Schematic representation of the definition of regions of interest in gray matter nuclei and an illustration of the generation of gray-level run-length matrices
| Feature | Description | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| RLNonUni | run length non-uniformity | |
| GLevNonU | gray-level non-uniformity | |
| LngREmph | long-run emphasis | |
| ShrtREmp | short-run emphasis | |
| Fraction | fraction of image in runs |
Tab 1 Description and equation of texture parameters based on run-length matrix (GLRLM)
| Feature | Description | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| RLNonUni | run length non-uniformity | |
| GLevNonU | gray-level non-uniformity | |
| LngREmph | long-run emphasis | |
| ShrtREmp | short-run emphasis | |
| Fraction | fraction of image in runs |
| Item | PD ( n=20) | HC ( n=20) | χ2/F value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age/year | 62.15±10.15 | 61.58±9.24 | 0.941 | 0.534 |
| Gender/ n(%) | 0.100 | 0.752 | ||
| Male | 11 (55.0) | 10 (50.0) | ||
| Female | 9 (45.0) | 10 (50.0) | ||
| Height/cm | 164.68±8.76 | 162.72±7.77 | 1.858 | 0.494 |
| Weight/kg | 71.17±8.84 | 60.83±10.23 | 2.049 | 0.152 |
| BMI/(kg·m -2) | 21.48±1.83 | 22.73±1.65 | 1.414 | 0.427 |
Tab 2 Demographic information on subjects
| Item | PD ( n=20) | HC ( n=20) | χ2/F value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age/year | 62.15±10.15 | 61.58±9.24 | 0.941 | 0.534 |
| Gender/ n(%) | 0.100 | 0.752 | ||
| Male | 11 (55.0) | 10 (50.0) | ||
| Female | 9 (45.0) | 10 (50.0) | ||
| Height/cm | 164.68±8.76 | 162.72±7.77 | 1.858 | 0.494 |
| Weight/kg | 71.17±8.84 | 60.83±10.23 | 2.049 | 0.152 |
| BMI/(kg·m -2) | 21.48±1.83 | 22.73±1.65 | 1.414 | 0.427 |
| Patient | UPDRS-III/score |
|---|---|
| 1 | 8 |
| 2 | 9 |
| 3 | 7 |
| 4 | 33 |
| 5 | 36 |
| 6 | 12 |
| 7 | 21 |
| 8 | 24 |
| 9 | 19 |
| 10 | 23 |
| 11 | 36 |
| 12 | 7 |
| 13 | 40 |
| 14 | 5 |
| 15 | 34 |
| 16 | 44 |
| 17 | 37 |
| 18 | 50 |
| 19 | 41 |
| 20 | 55 |
Tab 3 UPDRS-III scores of the PD patients
| Patient | UPDRS-III/score |
|---|---|
| 1 | 8 |
| 2 | 9 |
| 3 | 7 |
| 4 | 33 |
| 5 | 36 |
| 6 | 12 |
| 7 | 21 |
| 8 | 24 |
| 9 | 19 |
| 10 | 23 |
| 11 | 36 |
| 12 | 7 |
| 13 | 40 |
| 14 | 5 |
| 15 | 34 |
| 16 | 44 |
| 17 | 37 |
| 18 | 50 |
| 19 | 41 |
| 20 | 55 |
| Item | Measurement | Inter-reader correlation coefficient (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| Mean | Magnetic susceptibility value | 0.91 (0.88—0.95) |
| GLRLM feature | RLNonUni | 0.92 (0.88—0.97) |
| GLevNonU | 0.90 (0.87—0.95) | |
| LngREmph | 0.91 (0.85—0.95) | |
| ShrtREmp | 0.93 (0.89—0.94) | |
| Fraction | 0.89 (0.86—0.92) |
Tab 4 Intra-observer and inter-observer correlation coefficients for the measurements
| Item | Measurement | Inter-reader correlation coefficient (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| Mean | Magnetic susceptibility value | 0.91 (0.88—0.95) |
| GLRLM feature | RLNonUni | 0.92 (0.88—0.97) |
| GLevNonU | 0.90 (0.87—0.95) | |
| LngREmph | 0.91 (0.85—0.95) | |
| ShrtREmp | 0.93 (0.89—0.94) | |
| Fraction | 0.89 (0.86—0.92) |
| Item | Measurement | AUC | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Magnetic susceptibility value | 0.678 | <0.001 |
| GLRLM feature | RLNonUni | 0.708 | <0.001 |
| GLevNonU | 0.646 | <0.001 | |
| LngREmph | 0.777 | <0.001 | |
| ShrtREmp | 0.714 | <0.001 | |
| Fraction | 0.716 | <0.001 |
Tab 6 Results of the ROC curve analyses of texture parameters and mean magnetic susceptibility values between the PD and HC groups
| Item | Measurement | AUC | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Magnetic susceptibility value | 0.678 | <0.001 |
| GLRLM feature | RLNonUni | 0.708 | <0.001 |
| GLevNonU | 0.646 | <0.001 | |
| LngREmph | 0.777 | <0.001 | |
| ShrtREmp | 0.714 | <0.001 | |
| Fraction | 0.716 | <0.001 |
| Gray Matter Nuclei | Measurement | r | radj2 | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN | Mean | Magnetic susceptibility | -0.305 | 0.043 | 0.191 |
| GLRLM feature | RLNonUni | 0.755 | 0.546 | <0.001 | |
| GLevNonU | 0.623 | 0.355 | 0.003 | ||
| LngREmph | -0.220 | -0.005 | 0.352 | ||
| ShrtREmp | 0.291 | 0.034 | 0.213 | ||
| Fraction | -0.201 | -0.013 | 0.395 | ||
| GP | Mean | Magnetic susceptibility | -0.038 | -0.054 | 0.874 |
| GLRLM feature | RLNonUni | 0.373 | 0.091 | 0.105 | |
| GLevNonU | 0.332 | 0.061 | 0.153 | ||
| LngREmph | 0.273 | 0.023 | 0.244 | ||
| ShrtREmp | 0.055 | -0.052 | 0.817 | ||
| Fraction | -0.152 | -0.031 | 0.521 | ||
| PT | Mean | Magnetic susceptibility | 0.038 | -0.054 | 0.874 |
| GLRLM feature | RLNonUni | 0.359 | 0.080 | 0.121 | |
| GLevNonU | 0.149 | -0.032 | 0.530 | ||
| LngREmph | -0.349 | 0.073 | 0.132 | ||
| ShrtREmp | 0.206 | -0.011 | 0.384 | ||
| Fraction | -0.262 | 0.017 | 0.264 | ||
| SN | Mean | Magnetic susceptibility | 0.627 | 0.359 | 0.003 |
| GLRLM feature | RLNonUni | -0.231 | 0.001 | 0.326 | |
| GLevNonU | 0.129 | -0.038 | 0.588 | ||
| LngREmph | 0.222 | -0.004 | 0.347 | ||
| ShrtREmp | -0.237 | 0.004 | 0.314 | ||
| Fraction | 0.281 | 0.028 | 0.230 | ||
| RN | Mean | Magnetic susceptibility | 0.667 | 0.413 | 0.001 |
| GLRLM feature | RLNonUni | 0.101 | -0.045 | 0.670 | |
| GLevNonU | 0.826 | 0.664 | <0.001 | ||
| LngREmph | -0.092 | -0.047 | 0.700 | ||
| ShrtREmp | 0.697 | 0.457 | 0.001 | ||
| Fraction | 0.434 | 0.143 | 0.056 | ||
Tab 7 Association between mean magnetic susceptibility values and texture features with UPDRS-III scores in the PD group
| Gray Matter Nuclei | Measurement | r | radj2 | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN | Mean | Magnetic susceptibility | -0.305 | 0.043 | 0.191 |
| GLRLM feature | RLNonUni | 0.755 | 0.546 | <0.001 | |
| GLevNonU | 0.623 | 0.355 | 0.003 | ||
| LngREmph | -0.220 | -0.005 | 0.352 | ||
| ShrtREmp | 0.291 | 0.034 | 0.213 | ||
| Fraction | -0.201 | -0.013 | 0.395 | ||
| GP | Mean | Magnetic susceptibility | -0.038 | -0.054 | 0.874 |
| GLRLM feature | RLNonUni | 0.373 | 0.091 | 0.105 | |
| GLevNonU | 0.332 | 0.061 | 0.153 | ||
| LngREmph | 0.273 | 0.023 | 0.244 | ||
| ShrtREmp | 0.055 | -0.052 | 0.817 | ||
| Fraction | -0.152 | -0.031 | 0.521 | ||
| PT | Mean | Magnetic susceptibility | 0.038 | -0.054 | 0.874 |
| GLRLM feature | RLNonUni | 0.359 | 0.080 | 0.121 | |
| GLevNonU | 0.149 | -0.032 | 0.530 | ||
| LngREmph | -0.349 | 0.073 | 0.132 | ||
| ShrtREmp | 0.206 | -0.011 | 0.384 | ||
| Fraction | -0.262 | 0.017 | 0.264 | ||
| SN | Mean | Magnetic susceptibility | 0.627 | 0.359 | 0.003 |
| GLRLM feature | RLNonUni | -0.231 | 0.001 | 0.326 | |
| GLevNonU | 0.129 | -0.038 | 0.588 | ||
| LngREmph | 0.222 | -0.004 | 0.347 | ||
| ShrtREmp | -0.237 | 0.004 | 0.314 | ||
| Fraction | 0.281 | 0.028 | 0.230 | ||
| RN | Mean | Magnetic susceptibility | 0.667 | 0.413 | 0.001 |
| GLRLM feature | RLNonUni | 0.101 | -0.045 | 0.670 | |
| GLevNonU | 0.826 | 0.664 | <0.001 | ||
| LngREmph | -0.092 | -0.047 | 0.700 | ||
| ShrtREmp | 0.697 | 0.457 | 0.001 | ||
| Fraction | 0.434 | 0.143 | 0.056 | ||
| 1 | DICKSON D W. Parkinson′s disease and Parkinsonism: neuropathology[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med, 2012, 2(8): a009258. |
| 2 | IRIZARRY M C, GROWDON W, GOMEZ-ISLA T, et al. Nigral and cortical Lewy bodies and dystrophic nigral neurites in Parkinson′s disease and cortical Lewy body disease contain alpha-synuclein immunoreactivity[J]. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol, 1998, 57(4): 334-337. |
| 3 | SPILLANTINI M G, SCHMIDT M L, LEE V M, et al. Alpha-synuclein in lewy bodies[J]. Nature, 1997, 388(6645): 839-840. |
| 4 | ZECCA L, STROPPOLO A, GATTI A, et al. The role of iron and copper molecules in the neuronal vulnerability of locus coeruleus and substantia nigra during aging[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2004, 101(26): 9843-9848. |
| 5 | PÉRAN P, CHERUBINI A, ASSOGNA F, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging markers of Parkinson′s disease nigrostriatal signature[J]. Brain, 2010, 133(11): 3423-3433. |
| 6 | SIAN-HÜLSMANN J, MANDEL S, YOUDIM M B, et al. The relevance of iron in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease[J]. J Neurochem, 2011, 118(6): 939-957. |
| 7 | LEE D W, ANDERSEN J K, KAUR D. Iron dysregulation and neurodegeneration: the molecular connection[J]. Mol Interv, 2006, 6(2): 89-97. |
| 8 | LI W, WU B, LIU C L. Quantitative susceptibility mapping of human brain reflects spatial variation in tissue composition[J]. Neuroimage, 2011, 55(4): 1645-1656. |
| 9 | OSHIRO S, MORIOKA M S, KIKUCHI M. Dysregulation of iron metabolism in Alzheimer′s disease, Parkinson′s disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis[J]. Adv Pharmacol Sci, 2011, 2011: 378278. |
| 10 | LV Z Y, JIANG H, XU H M, et al. Increased iron levels correlate with the selective nigral dopaminergic neuron degeneration in Parkinson′s disease[J]. J Neural Transm, 2011, 118(3): 361-369. |
| 11 | FASANO M, BERGAMASCO B, LOPIANO L. Modifications of the iron-neuromelanin system in Parkinson′s disease[J]. J Neurochem, 2006, 96(4): 909-916. |
| 12 | WANG Y, LIU T. Quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM): decoding MRI data for a tissue magnetic biomarker[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2015, 73(1): 82-101. |
| 13 | HAACKE E M, LIU S F, BUCH S, et al. Quantitative susceptibility mapping: current status and future directions[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2015, 33(1): 1-25. |
| 14 | LIU C L, LI W, TONG K A, et al. Susceptibility-weighted imaging and quantitative susceptibility mapping in the brain[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2015, 42(1): 23-41. |
| 15 | DU G W, LIU T, LEWIS M M, et al. Quantitative susceptibility mapping of the midbrain in Parkinson′s disease[J]. Mov Disord, 2016, 31(3): 317-324. |
| 16 | MURAKAMI Y, KAKEDA S, WATANABE K, et al. Usefulness of quantitative susceptibility mapping for the diagnosis of Parkinson disease[J]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 2015, 36(6): 1102-1108. |
| 17 | LANGKAMMER C, SCHWESER F, KREBS N, et al. Quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) as a means to measure brain iron? A post mortem validation study[J]. Neuroimage, 2012, 62(3): 1593-1599. |
| 18 | ZHANG J, YU C S, JIANG G L, et al. 3D texture analysis on MRI images of Alzheimer′s disease[J]. Brain Imaging Behav, 2012, 6(1): 61-69. |
| 19 | HWANG E J, KIM H G, KIM D, et al. Texture analyses of quantitative susceptibility maps to differentiate Alzheimer′s disease from cognitive normal and mild cognitive impairment[J]. Med Phys, 2016, 43(8): 4718. |
| 20 | CHENG Z H, ZHANG J P, HE N Y, et al. Radiomic features of the nigrosome-1 region of the substantia nigra: using quantitative susceptibility mapping to assist the diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson′s disease[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2019, 11: 167. |
| 21 | LI G Y, ZHAI G Q, ZHAO X X, et al. 3D texture analyses within the substantia nigra of Parkinson′s disease patients on quantitative susceptibility maps and R2 maps[J]. Neuroimage, 2019, 188: 465-472. |
| 22 | MACKAY J W, KAPOOR G, DRIBAN J B, et al. Association of subchondral bone texture on magnetic resonance imaging with radiographic knee osteoarthritis progression: data from the osteoarthritis initiative bone ancillary study[J]. Eur Radiol, 2018, 28(11): 4687-4695. |
| 23 | TRAVERSO A, WEE L, DEKKER A, et al. Repeatability and reproducibility of radiomic features: a systematic review[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2018, 102(4): 1143-1158. |
| 24 | YAN S, LU J, LI Y H, et al. Spatiotemporal patterns of brain iron-oxygen metabolism in patients with Parkinson′s disease[J]. Eur Radiol, 2024, 34(5): 3074-3083. |
| 25 | GUAN X J, LANCIONE M, AYTON S, et al. Neuroimaging of Parkinson′s disease by quantitative susceptibility mapping[J]. Neuroimage, 2024, 289: 120547. |
| 26 | WANG Y, SPINCEMAILLE P, LIU Z, et al. Clinical quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM): biometal imaging and its emerging roles in patient care[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2017, 46(4): 951-971. |
| 27 | ESKREIS-WINKLER S, ZHANG Y, ZHANG J W, et al. The clinical utility of QSM: disease diagnosis, medical management, and surgical planning[J]. NMR Biomed, 2017, 30(4): e3668. |
| 28 | MAZZUCCHI S, FROSINI D, COSTAGLI M, et al. Quantitative susceptibility mapping in atypical Parkinsonisms[J]. Neuroimage Clin, 2019, 24: 101999. |
| 29 | LI K R, AVECILLAS-CHASIN J, NGUYEN T D, et al. Quantitative evaluation of brain iron accumulation in different stages of Parkinson′s disease[J]. J Neuroimaging, 2022, 32(2): 363-371. |
| [1] | CAO Mingming, WANG Hui, YIN Yafu. Current research status of imaging markers for cognitive impairment in Parkinson′s disease [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(5): 646-652. |
| [2] | Xiao-xiao ZHANG, Chen-cheng ZHANG, Yi-jie LAI, Bo-min SUN. Recent progresses in deep brain stimulation of subthalamic nucleus on Parkinson′s disease and its related depression [J]. JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE), 2021, 41(6): 815-820. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
