


收稿日期: 2024-09-02
录用日期: 2024-11-28
网络出版日期: 2025-03-28
基金资助
科技基础资源调查专项(2018FY101000);国家自然科学基金(52103312)
Analysis of dentofacial characteristics in Han Chinese adults with facial harmony
Received date: 2024-09-02
Accepted date: 2024-11-28
Online published: 2025-03-28
Supported by
National Science and Technology Fundamental Resources Investigation Program of China(2018FY101000);National Natural Science Foundation of China(52103312)
目的·建立中国18~25岁颜面协调汉族人群Downs分析法头影测量正常值,并分析其性别特征及地域特征。方法·采用分层抽样,在中国7个自然地理区域分别进行受试者招募,筛选3万余人,最终共纳入883例符合要求的颜面协调者。收集受试者的基本资料,拍摄头颅定位侧位片,采用Downs分析法(使用解剖耳点)测量硬组织数据,并比较牙颌结构的性别差异及地区差异。结果·颌凸角、上下牙槽座角、下颌平面角以及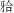 平面角,这4项硬组织指标的性别差异具有统计学意义(P<0.001)。其中女性颌凸角、下颌平面角、
平面角,这4项硬组织指标的性别差异具有统计学意义(P<0.001)。其中女性颌凸角、下颌平面角、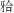 平面角皆大于男性,上下牙槽座角小于男性;上下中切牙角、下中切牙-
平面角皆大于男性,上下牙槽座角小于男性;上下中切牙角、下中切牙-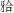 平面角、下中切牙-下颌平面角及上中切牙凸距这几项牙性指标的性别差异无统计学意义。Downs分析法10项指标的测量结果皆显示出地区差异,但部分地区之间也有共通特征。东北、华东、华南三个沿海地区的面角较小,下颌平面角、颌凸角、
平面角、下中切牙-下颌平面角及上中切牙凸距这几项牙性指标的性别差异无统计学意义。Downs分析法10项指标的测量结果皆显示出地区差异,但部分地区之间也有共通特征。东北、华东、华南三个沿海地区的面角较小,下颌平面角、颌凸角、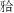 平面角及上中切牙凸距偏大,即相较于内陆地区,沿海地区的颜面协调者颏部靠后,下颌陡度更大,上前牙位置更靠前,硬组织轮廓有更凸的倾向。结论·中国颜面协调汉族成人牙颌结构存在性别差异,且该差异主要表现在骨组织指标上。各地区有独有的牙颌特征,也有部分共同特征。临床诊疗需考虑到这些特点以制定个性化治疗方案。
平面角及上中切牙凸距偏大,即相较于内陆地区,沿海地区的颜面协调者颏部靠后,下颌陡度更大,上前牙位置更靠前,硬组织轮廓有更凸的倾向。结论·中国颜面协调汉族成人牙颌结构存在性别差异,且该差异主要表现在骨组织指标上。各地区有独有的牙颌特征,也有部分共同特征。临床诊疗需考虑到这些特点以制定个性化治疗方案。
陈思悦 , 李思彤 , 顾恺隽 , 杜常欣 , 朱妍菲 , 郑朝 , 周璟 , 何颖 , 朱敏 . 颜面协调汉族成人的牙颌特征分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025 , 45(3) : 317 -323 . DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2025.03.008
Objective ·To establish Downs cephalometric norms for the Han Chinese aged 18‒25 with harmonious faces, and to analyze gender and regional characteristics. Methods ·A stratified sampling approach was used to recruit participants from seven geographic regions across China. Over 30 000 volunteers were screened, and 883 participants with harmonious faces were ultimately included. Basic demographic data were collected, and lateral cephalometric radiographs were taken. Hard tissue measurements were performed with Downs analysis (using anatomical porion). The data were then statistically analyzed to compare gender and regional differences in dentofacial structures. Results ·The gender differences in the four hard tissue measurements, the angle of convexity, A-B plane angle, mandibular plane angle, and occlusal plane angle, were statistically significant (P<0.001). Females showed larger values for the angle of convexity, mandibular plane angle, and occlusal plane angle, but smaller values for the A-B plane angle, compared to males. The gender differences in the interincisal angle, L1 to occlusal plane, L1 to mandibular plane, and U1 to AP plane were not statistically significant. There were regional differences in all 10 measurements of Downs analysis, though some regions shared common features. Specifically, the northeastern, eastern, and southern coastal regions exhibited a smaller facial angle, and larger mandibular plane angle, angle of convexity, occlusal plane angle, and U1 to AP plane. It suggested that, compared to inland regions, individuals from coastal regions tended to have more retrusive chins, steeper mandibular planes, more prominent upper incisors, and more convex hard tissue profiles. Conclusion ·Gender differences exist in the dentofacial hard tissue structures of Han Chinese adults with harmonious faces, primarily in skeletal measurements. Each region has its unique dentofacial characteristics, along with some common features. These differences should be taken into account in clinical diagnosis and treatment for the development of personalized and precise therapeutic strategies.
Key words: cephalometry; harmonious face; Han Chinese people; adult; normal occlusion
| 1 | ELKASEH A, SHAYEB M A, KUDURUTHULLAH S, et al. Cephalometrics of Libyan adults[J]. Asian J Surg, 2022, 45(5): 1089-1094. |
| 2 | 伊帕热·克力木江, 祖丽胡马尔·努尔艾合买提, 迪丽菲热·吐尔洪, 等. 新疆地区与广东地区正常 人群X线头影测量Arnett分析比较[J]. 中国美容医学, 2020, 29(8): 112-119. 人群X线头影测量Arnett分析比较[J]. 中国美容医学, 2020, 29(8): 112-119. |
| YIPARE K, ZULIHUMAER N, DILIFEIRE T, et al. Arnett cephalometry analysis and comparison of normal occlusion in Xinjiang and Guangdong[J]. Chinese Journal of Aesthetic Medicine, 2020, 29(8): 112-119. | |
| 3 | LE L N, DO T T, LE P K V, et al. Norms of soft tissue cephalometric in the 18?25 age demography in Vietnam[J]. J Orthod Sci, 2023, 12: 35. |
| 4 | 宇克莉, 张兴华, 程智, 等. 中国不同人群的头面部特征及其差异[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(4): 574-585. |
| YU K L, ZHANG X H, CHENG Z, et al. Head and facial characteristics and their differences among different peoples in China[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2024, 43(4): 574-585. | |
| 5 | 宋晴阳, 宇克莉, 郑连斌, 等. 藏缅语族彝语支7个族群成人的头面部特征[J]. 天津师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 41(6): 73-80. |
| SONG Q Y, YU K L, ZHENG L F, et al. Head and facial characteristics of seven ethnic groups in Yi language branch of Tibeto-Burman languages[J]. Journal of Tianjin Normal University(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 41(6): 73-80. | |
| 6 | 郭杰, 王春玲, 陈扬熙. 山东地区成人正常 颅颌面X线头影测量[J]. 山东大学学报(医学版), 2004, 42(4): 466-468. 颅颌面X线头影测量[J]. 山东大学学报(医学版), 2004, 42(4): 466-468. |
| GUO J, WANG C L, CHEN Y X. Cephalometric study of normal occlusion for adults of Shandong Province[J]. Journal of Shandong University (Health Science), 2004, 42(4): 466-468. | |
| 7 | 徐频频, 林燕, 刘小敏. 浙江丽水畲族、汉族青少年Downs头影测量分析[J]. 上海口腔医学, 2019, 28(5): 509-512. |
| XU P P, LI Y, LIU X M. Downs cephalometric analysis between juveniles of She and Han nationality in Lishui area of Zhejiang province[J]. Shanghai Journal of Stomatology, 2019, 28(5): 509-512. | |
| 8 | 李远远, 赵丙姣, 兰庭超, 等. 中国年轻成人正常 X线头影测量研究[J]. 临床口腔医学杂志, 2016, 32(4): 211-213, 214. X线头影测量研究[J]. 临床口腔医学杂志, 2016, 32(4): 211-213, 214. |
| LI Y Y, ZHAO B J, LAN T C, et al. Cephalometic analysis of Chinese young adults with normal occlusions[J]. Journal of Clinical Stomatology, 2016, 32(4): 211-213, 214. | |
| 9 | 吴雁格, 刘家琦, 张真真, 等. 恒牙列X线头影测量127项指标正常值研究[J]. 口腔医学, 2021, 41(9): 797-804. |
| WU Y G, LIU J Q, ZHANG Z Z, et al. Establishment of 127 indexes of permanent dentition cephalometric norm[J]. Stomatology, 2021, 41(9): 797-804. | |
| 10 | 戴宁, 孙蕙, 李蓉, 等. 西安地区正常 成人颅颌面结构头影测量分析[J]. 中国美容医学, 2010, 19(10): 1522-1524. 成人颅颌面结构头影测量分析[J]. 中国美容医学, 2010, 19(10): 1522-1524. |
| DAI N, SUN H, LI R, et al. Cephalometric study of adults with normal occlusion in Xi′an using Steiner method[J]. Chinese Journal of Aesthetic Medicine, 2010, 19(10): 1522-1524. | |
| 11 | 郑艳, 车锋哲. 中国延边地区朝鲜族正常 成人Downs分析法正常值的建立[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2010, 26(1): 90-93. 成人Downs分析法正常值的建立[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2010, 26(1): 90-93. |
| ZHENG Y, CHE F Z. Cephalometric study with Downs analysis on normal occlusion of Korean adults in China[J]. Journal of Practical Stomatology, 2010, 26(1): 90-93. | |
| 12 | 沈云娟, 陈慧霞, 许晓聪. 常州地区正常 青少年X线头影测量研究(一)[J]. 口腔医学, 2009, 29(1): 41-42. 青少年X线头影测量研究(一)[J]. 口腔医学, 2009, 29(1): 41-42. |
| SHEN Y J, CHEN H X, XU X C. Cephlalometric study of adolescents with normal occlusion in Changzhou city (one)[J]. Stomatology, 2009, 29(1): 41-42. | |
| 13 | 阎秀林, 丁伟忠, 张扬. 不同耳点对头影测量值的影响及其相关因素分析[J]. 中国实用口腔科杂志, 2008, 1(12): 730-731. |
| YAN X L, DING W Z, ZHANG Y. The effects of anatomical porion and mechanical porion on cephalometric measurements and influencing factors in the location relationships of different porions[J].Chinese Journal of Practical Stomatology, 2008, 1(12): 730-731. | |
| 14 | 田乃学, 卢海平, 刘怡. 临床X线头影测量学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2021: 159-160 |
| TIAN N X, LU H P, LIU Y. Clinical X-ray cephalometry[M]. Beijing: People′s Medical Publishing House, 2021: 159-160. | |
| 15 | 傅民魁. 口腔正畸专科教程[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2007: 69-83. |
| FU M K. Textbook of orthodontics[M]. Beijing: People′s Medical Publishing House, 2007: 69-83. | |
| 16 | 赵志河. 口腔正畸学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2020: 62-72. |
| ZHAO Z H. Orthodontics[M]. Beijing: People′s Medical Publishing House, 2020: 62-72. | |
| 17 | 陈扬熙. 口腔正畸学: 基础、技术与临床[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2012: 217-224. |
| CHEN Y X. Orthodontics foudation, technology and clinical[M]. Beijing: People′s Medical Publishing House, 2012: 217-224. | |
| 18 | 朱梦婷, 马艳, 庞光明. 颏部审美评价方式的研究进展[J]. 中国美容医学, 2023, 32(3): 197-202. |
| ZHU M T, MA Y, PANG G M. Research Progress of Chin Aesthetic Evaluation Method[J]. Chinese Journal of Aesthetic Medicine, 2023, 32(3):197-202. | |
| 19 | 张若芳, 厉松, 张丁. 机械耳点与解剖耳点的二维差异及其对头影测量的影响[J]. 北京口腔医学, 2010, 18(3): 155-157. |
| ZHANG R F, LI S, ZHANG D. Two dimensional position difference between meachanial porion and anatomical porion and its effect on cephalometry[J]. Beijing Journal of Stomatology, 2010, 18(3): 155-157. | |
| 20 | SHRINIVAS K A, SUDHAKAR S S, KANNAN G, et al. Predictive equation for construction of anatomic porion with machine porion as reference point[J]. J Contemp Dent Pract, 2023, 24(4): 257-260. |
| 21 | 陈扬熙, 张德福. 哈尔滨市100名正常 儿童侧貌的X线头影测量研究[J]. 中华口腔科杂志, 1985, 20(1): 45-48. 儿童侧貌的X线头影测量研究[J]. 中华口腔科杂志, 1985, 20(1): 45-48. |
| CHEN Y X, ZHANG D F. Cephalometric study on the profiles of 100 normal occlusion children in harbin city[J]. Chinese Journal of Stomatology, 1985, 20(1): 45-48. | |
| 22 | 关慧娟, 卢青波, 庞梓萌, 等. 青少年安氏Ⅱ类2分类错 畸形非拔牙矫治前后面下部软硬组织的变化[J]. 中国医科大学学报, 2020, 49(7): 610-614. 畸形非拔牙矫治前后面下部软硬组织的变化[J]. 中国医科大学学报, 2020, 49(7): 610-614. |
| GUAN H J, LU Q B, PANG Z M, et al. Changes in soft and hard tissues in the lower face of adolescents with class Ⅱ division 2 malocclusion treated using a non-extraction protocol[J]. Journal of China Medical University, 2020, 49(7): 610-614. | |
| 23 | 关玲, 王培军, 张晔, 等. 哈尔滨地区成人个体化头影测量浮动正常值[J]. 口腔医学研究, 2009, 25(3): 358-360. |
| GUAN L, WANG P J, ZHANG Y, et al. Individual cephalometric floating norms for Harbin adult[J]. Journal of Oral Science Research, 2009, 25(3): 358-360. | |
| 24 | 李浙杭, 张芳, 段余峰, 等. 长沙地区汉族正常 颅颌面硬组织的三维测量[J]. 中南大学学报(医学版), 2018, 43(1): 58-67. 颅颌面硬组织的三维测量[J]. 中南大学学报(医学版), 2018, 43(1): 58-67. |
| LI Z H, ZHANG F, DUAN Y F. et al. Three dimensional measurement of craniofacial hard tissues for the Han nationality with normal occlusion in Changsha area[J]. Journal of Central South University (Medical Science), 2018, 43(1): 58-67. | |
| 25 | ABUTAYYEM H, ALSHAMSI A, QUADRI M F A. Soft tissue cephalometric norms in emirati population: a cross-sectional study[J]. J Multidiscip Healthc, 2021, 14: 2863-2869. |
| 26 | OUéDRAOGO Y, BENYAHIA H, DIOUF J S, et al. Cephalometric norms of a Burkina Faso population[J]. Int Orthod, 2019, 17(1): 136-142. |
| 27 | HO T T T, LUONG Q T. Dental-craniofacial characteristics of southern Vietnamese people with well-balanced face on cephalometric films and its comparison with caucasians and northern Vietnamese population[J]. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent, 2021, 11(3): 316-323. |
| 28 | 张琳, 于舒婷, 张苗苗. 应用Ricketts分析法研究哈尔滨地区正常 锥形束CT[J]. 中国美容医学, 2019, 28(1): 115-118. 锥形束CT[J]. 中国美容医学, 2019, 28(1): 115-118. |
| ZHANG L, YU S T, ZHANG M M. Study on CBCT of normal occlusion in Harbin area by ricketts method[J]. Chinese Journal of Aesthetic Medicine, 2019, 28(1): 115-118. | |
| 29 | 祖丽胡马尔·努尔艾合买提, 迪丽菲热·吐尔洪, 巴哈尔尼萨·热扎克, 等. 乌鲁木齐地区成人正常 人群X线头影测量Arnett分析研究[J]. 中国美容医学, 2019, 28(9): 110-115. 人群X线头影测量Arnett分析研究[J]. 中国美容医学, 2019, 28(9): 110-115. |
| ZULIHUMAER N, DILIFEIRE T, BAHAERNISA R, et al. Arnett cephalometric analysis of adults with normal occlusion in Urumqi[J]. Chinese Journal of Aesthetic Medicine, 2019, 28(9): 110-115. | |
| 30 | RAKHSHAN V, GHORBANYJAVADPOUR F. Anteroposterior and vertical soft tissue cephalometric norms of Iranians, interethnic comparisons, sex dimorphism, and the effect of age on cephalometric variables[J]. Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2019, 23(2): 167-178. |
| 31 | 王新昱, 徐建光. 安徽地区正常 人群颅颌面部的三维头影测量[J]. 安徽医科大学学报, 2023, 58(1): 145-150. 人群颅颌面部的三维头影测量[J]. 安徽医科大学学报, 2023, 58(1): 145-150. |
| WANG X Y, XU J G. Three-dimensional cephalometric measurement of craniofacial hard tissues with normal occlusion in Anhui area[J]. Acta Universitatis Medicinalis Anhui, 2023, 58(1): 145-150. | |
| 32 | PIOMBINO P, ESPOSITO E, COMMITTERI U, et al. Facial soft tissue thickness measurement method and relationship with BMI, age and sex[J]. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2023, 124(4): 101420. |
| 33 | AL-TAEE R, AL-SAEDI A I L, NAHIDH M. Does body mass index affect soft tissue facial anthropometric measurements?[J]. Int J Morphol, 2021, 39(2): 520-526. |
| 34 | KARSLI N, TUHAN KUTLU E. Effect of body mass index on soft tissues in adolescents with skeletal class Ⅰ and normal facial height[J]. PeerJ, 2023, 11: e16196. |
| 35 | CHAIMONGKHOL T, MAHAKKANUKRAUH P. The facial soft tissue thickness related facial reconstruction by ultrasonographic imaging: a review[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2022, 337: 111365. |
| 36 | 中国营养学会肥胖防控分会, 中国营养学会临床营养分会, 中华预防医学会行为健康分会, 等. 中国居民肥胖防治专家共识[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2022, 43(5): 609-626. |
| Chinese Nutrition Society Obesity Prevention and Control Section, Chinese Nutrition Society Clinical Nutrition Section, Chinese Preventive Medicine Association Behavioral Health Section, et al. Expert consensus on obesity prevention and treatment in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Epidemiology, 2022, 43(5): 609-626. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |