
Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science) ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (9): 1138-1148.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2025.09.006
• Basic research • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Qianyu1,2, QIAN Yifei1,2, LI Songling3, ZHU Zijun1,2, QIN Wenli1,2, LIU Yanfeng1( ), QIU Bijun1(
), QIU Bijun1( )
)
Received:2025-04-27
Accepted:2025-07-06
Online:2025-09-28
Published:2025-09-30
Contact:
LIU Yanfeng, QIU Bijun
E-mail:lyf7858188@163.com;qiubijun2010@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
LI Qianyu, QIAN Yifei, LI Songling, ZHU Zijun, QIN Wenli, LIU Yanfeng, QIU Bijun. Function and mechanism of suppressor of zeste 12 in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(9): 1138-1148.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://xuebao.shsmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2025.09.006
| Gene | Forward (5′→3′) | Reverse (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| SUZ12 | AGGCTGACCACGAGCTTTTC | GGTGCTATGAGATTCCGAGTTC |
| CD13 | GACGCTGAGACCGTACCTC | TCAGTCTTGTCAATGTCGGGG |
| EpCAM | AATCGTCAATGCCAGTGTACTT | TCTCATCGCAGTCAGGATCATAA |
| CD24 | CTCCTACCCACGCAGATTTATTC | AGAGTGAGACCACGAAGAGAC |
| PKM2 | ATAACGCCTACATGGAAAAGTGT | TAAGCCCATCATCCACGTAGA |
| HK2 | TTGACCAGGAGATTGACATGGG | CAACCGCATCAGGACCTCA |
| PGK1 | TGGACGTTAAAGGGAAGCGG | GCTCATAAGGACTACCGACTTGG |
| ACTB | CATGTACGTTGCTATCCAGGC | CTCCTTAATGTCACGCACGAT |
| Cd13 | ATGGAAGGAGGCGTCAAGAAA | CGGATAGGGCTTGGACTCTTT |
| Epcam | GCGGCTCAGAGAGACTGTG | CCAAGCATTTAGACGCCAGTTT |
| Cd24 | GTTGCACCGTTTCCCGGTAA | CCCCTCTGGTGGTAGCGTTA |
| Cd34 | AAGGCTGGGTGAAGACCCTTA | TGAATGGCCGTTTCTGGAAGT |
| Cd44 | TCGATTTGAATGTAACCTGCCG | CAGTCCGGGAGATACTGTAGC |
| Pkm2 | GCCGCCTGGACATTGACTC | CCATGAGAGAAATTCAGCCGAG |
| Hk2 | TGATCGCCTGCTTATTCACGG | AACCGCCTAGAAATCTCCAGA |
| Pgk1 | ATGTCGCTTTCCAACAAGCTG | GCTCCATTGTCCAAGCAGAAT |
| Actb | GGCTGTATTCCCCTCCATCG | CCAGTTGGTAACAATGCCATGT |
Tab 1 Primer sequence
| Gene | Forward (5′→3′) | Reverse (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| SUZ12 | AGGCTGACCACGAGCTTTTC | GGTGCTATGAGATTCCGAGTTC |
| CD13 | GACGCTGAGACCGTACCTC | TCAGTCTTGTCAATGTCGGGG |
| EpCAM | AATCGTCAATGCCAGTGTACTT | TCTCATCGCAGTCAGGATCATAA |
| CD24 | CTCCTACCCACGCAGATTTATTC | AGAGTGAGACCACGAAGAGAC |
| PKM2 | ATAACGCCTACATGGAAAAGTGT | TAAGCCCATCATCCACGTAGA |
| HK2 | TTGACCAGGAGATTGACATGGG | CAACCGCATCAGGACCTCA |
| PGK1 | TGGACGTTAAAGGGAAGCGG | GCTCATAAGGACTACCGACTTGG |
| ACTB | CATGTACGTTGCTATCCAGGC | CTCCTTAATGTCACGCACGAT |
| Cd13 | ATGGAAGGAGGCGTCAAGAAA | CGGATAGGGCTTGGACTCTTT |
| Epcam | GCGGCTCAGAGAGACTGTG | CCAAGCATTTAGACGCCAGTTT |
| Cd24 | GTTGCACCGTTTCCCGGTAA | CCCCTCTGGTGGTAGCGTTA |
| Cd34 | AAGGCTGGGTGAAGACCCTTA | TGAATGGCCGTTTCTGGAAGT |
| Cd44 | TCGATTTGAATGTAACCTGCCG | CAGTCCGGGAGATACTGTAGC |
| Pkm2 | GCCGCCTGGACATTGACTC | CCATGAGAGAAATTCAGCCGAG |
| Hk2 | TGATCGCCTGCTTATTCACGG | AACCGCCTAGAAATCTCCAGA |
| Pgk1 | ATGTCGCTTTCCAACAAGCTG | GCTCCATTGTCCAAGCAGAAT |
| Actb | GGCTGTATTCCCCTCCATCG | CCAGTTGGTAACAATGCCATGT |
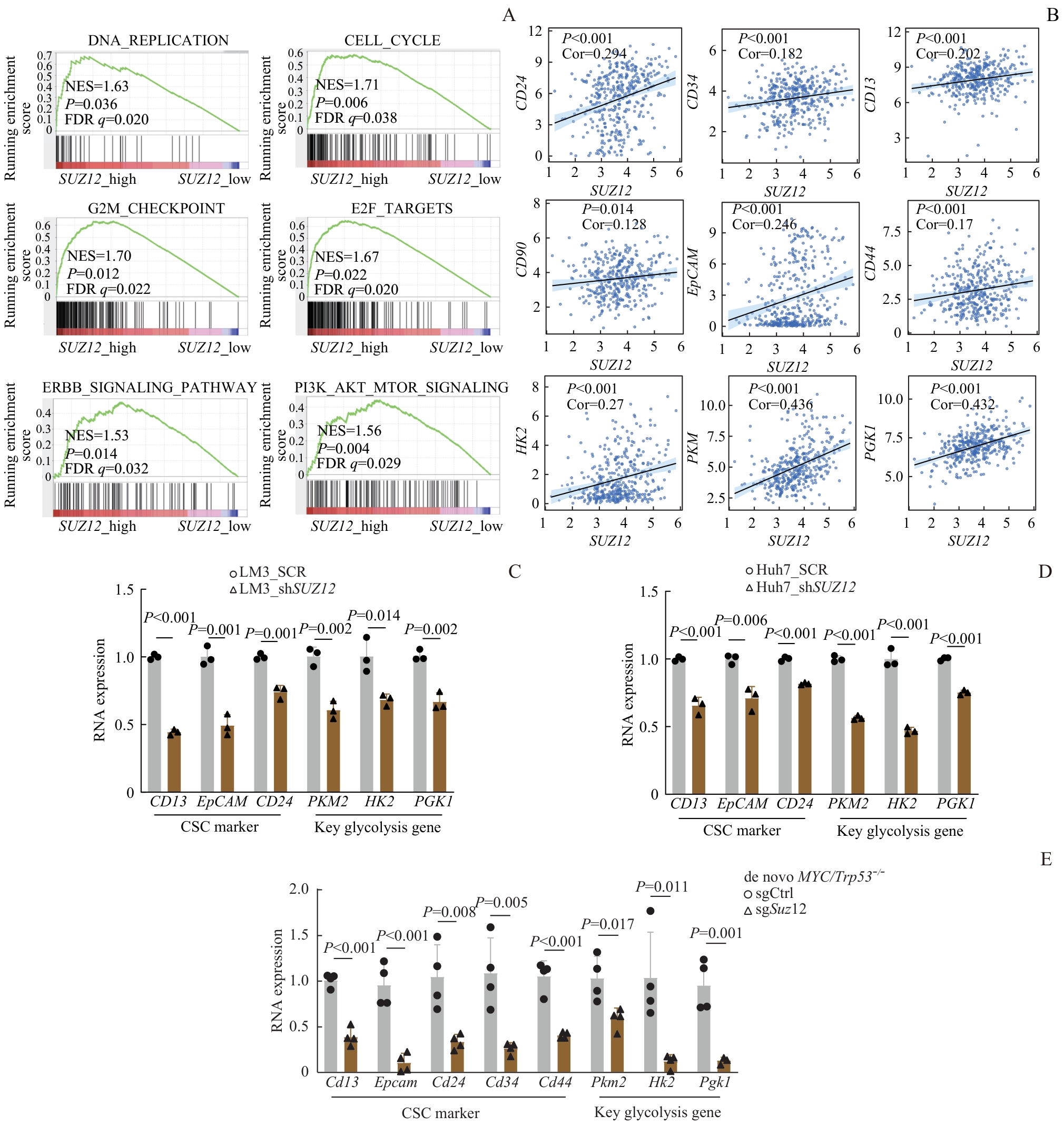
Fig 5 Bioinformatic analysis of SUZ12 expression in the TCGA liver cancer dataset and validation of mRNA expression levels in liver cancer cell lines and mouse liver cancer tissues
| [1] | SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. |
| [2] | LLOVET J M, KELLEY R K, VILLANUEVA A, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2021, 7(1): 6. |
| [3] | DONNE R, LUJAMBIO A. The liver cancer immune microenvironment: therapeutic implications for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2023, 77(5): 1773-1796. |
| [4] | ZHENG J J, WANG S Y, XIA L, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: signaling pathways and therapeutic advances[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2025, 10(1): 35. |
| [5] | JEPSEN P, OTT P, ANDERSEN P K, et al. Risk for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis: a Danish nationwide cohort study[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2012, 156(12): 841-847, W295. |
| [6] | SINGH M K, DAS B K, CHOUDHARY S, et al. Diabetes and hepatocellular carcinoma: a pathophysiological link and pharmacological management[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 106: 991-1002. |
| [7] | SINGAL A G, LAMPERTICO P, NAHON P. Epidemiology and surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma: new trends[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 72(2): 250-261. |
| [8] | MARRERO J A, KULIK L M, SIRLIN C B, et al. Diagnosis, staging, and management of hepatocellular carcinoma: 2018 practice guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 68(2): 723-750. |
| [9] | SCHULZE K, IMBEAUD S, LETOUZÉ E, et al. Exome sequencing of hepatocellular carcinomas identifies new mutational signatures and potential therapeutic targets[J]. Nat Genet, 2015, 47(5): 505-511. |
| [10] | CHAMMAS P, MOCAVINI I, DI CROCE L. Engaging chromatin: PRC2 structure meets function[J]. Br J Cancer, 2020, 122(3): 315-328. |
| [11] | KOUZNETSOVA V L, TCHEKANOV A, LI X M, et al. Polycomb repressive 2 complex: molecular mechanisms of function[J]. Protein Sci, 2019, 28(8): 1387-1399. |
| [12] | WU Y P, HU H J, ZHANG W, et al. SUZ12 is a novel putative oncogene promoting tumorigenesis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2018, 22(7): 3582-3594. |
| [13] | XIA R, JIN F Y, LU K, et al. SUZ12 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by regulating KLF2 and E-cadherin[J]. Tumour Biol, 2015, 36(7): 5341-5351. |
| [14] | RUIZ DE GALARRETA M, BRESNAHAN E, MOLINA-SÁNCHEZ P, et al. β-catenin activation promotes immune escape and resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Discov, 2019, 9(8): 1124-1141. |
| [15] | RAHIB L, SMITH B D, AIZENBERG R, et al. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States[J]. Cancer Res, 2014, 74(11): 2913-2921. |
| [16] | ZHOU J, SUN H C, WANG Z, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer (2022 edition)[J]. Liver Cancer, 2023, 12(5): 405-444. |
| [17] | ARECCO N, MOCAVINI I, BLANCO E, et al. Alternative splicing decouples local from global PRC2 activity[J]. Mol Cell, 2024, 84(6): 1049-1061. e1-e8. |
| [18] | LIU C H, SHI X F, WANG L, et al. SUZ12 is involved in progression of non-small cell lung cancer by promoting cell proliferation and metastasis[J]. Tumor Biol, 2014, 35(6): 6073-6082. |
| [19] | LIU Y L, GAO X, JIANG Y, et al. Expression and clinicopathological significance of EED, SUZ12 and EZH2 mRNA in colorectal cancer[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2015, 141(4): 661-669. |
| [20] | XUE C L, WANG K Y, JIANG X F, et al. The down-regulation of SUZ12 accelerates the migration and invasion of liver cancer cells via activating ERK1/2 pathway[J]. J Cancer, 2019, 10(6): 1375-1384. |
| [21] | WANG W H, STUDACH L L, ANDRISANI O M. Proteins ZNF198 and SUZ12 are down-regulated in hepatitis B virus (HBV) X protein-mediated hepatocyte transformation and in HBV replication[J]. Hepatology, 2011, 53(4): 1137-1147. |
| [22] | STUDACH L L, MENNE S, CAIRO S, et al. Subset of Suz12/PRC2 target genes is activated during hepatitis B virus replication and liver carcinogenesis associated with HBV X protein[J]. Hepatology, 2012, 56(4): 1240-1251. |
| [23] | NASSAR D, BLANPAIN C. Cancer stem cells: basic concepts and therapeutic implications[J]. Annu Rev Pathol, 2016, 11: 47-76. |
| [24] | LOH J J, MA S. Hallmarks of cancer stemness[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2024, 31(5): 617-639. |
| [25] | NGUYEN L V, VANNER R, DIRKS P, et al. Cancer stem cells: an evolving concept[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2012, 12(2): 133-143. |
| [26] | BATLLE E, CLEVERS H. Cancer stem cells revisited[J]. Nat Med, 2017, 23(10): 1124-1134. |
| [27] | HÖNIGOVA K, NAVRATIL J, PELTANOVA B, et al. Metabolic tricks of cancer cells[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2022, 1877(3): 188705. |
| [28] | ARTEAGA C L, ENGELMAN J A. ERBB receptors: from oncogene discovery to basic science to mechanism-based cancer therapeutics[J]. Cancer Cell, 2014, 25(3): 282-303. |
| [29] | TIAN L Y, SMIT D J, JÜCKER M. The role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma metabolism[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(3): 2652. |
| [30] | YEH Y C, HO H L, WU Y C, et al. AKT1 internal tandem duplications and point mutations are the genetic hallmarks of sclerosing pneumocytoma[J]. Mod Pathol, 2020, 33(3): 391-403. |
| [31] | LIN J, RAO D N, ZHANG M, et al. Metabolic reprogramming in the tumor microenvironment of liver cancer[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2024, 17(1): 6. |
| [32] | BLACKLEDGE N P, ROSE N R, KLOSE R J. Targeting Polycomb systems to regulate gene expression: modifications to a complex story[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2015, 16(11): 643-649. |
| [33] | WU G H, WANG Q, WANG D, et al. Targeting polycomb repressor complex 2-mediated bivalent promoter epigenetic silencing of secreted frizzled-related protein 1 inhibits cholangiocarcinoma progression[J]. Clin Transl Med, 2023, 13(12): e1502. |
| [34] | PIUNTI A, SHILATIFARD A. The roles of Polycomb repressive complexes in mammalian development and cancer[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2021, 22(5): 326-345. |
| [35] | YANG Q Q, ZHOU Z H, LI L, et al. The NEXT complex regulates H3K27me3 levels to affect cancer progression by degrading G4/U-rich lncRNAs[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2025, 53(4): gkaf107. |
| [36] | BHARTI R, DEY G, KHAN D, et al. Cell surface CD55 traffics to the nucleus leading to cisplatin resistance and stemness by inducing PRC2 and H3K27 trimethylation on chromatin in ovarian cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2024, 23(1): 121. |
| [37] | JIANG M, QI F, ZHANG K, et al. MARCKSL1-2 reverses docetaxel-resistance of lung adenocarcinoma cells by recruiting SUZ12 to suppress HDAC1 and elevate miR-200b[J]. Mol Cancer, 2022, 21(1): 150. |
| [1] | ZHU Zijun, QIAN Yife, LI Qianyu, LI Songling, QIN Wenli, LIU Yanfeng. Anaphase-promoting complex subunit 10 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through regulation of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(9): 1171-1182. |
| [2] | PANDIT Roshan, LU Junyao, HE Liheng, BAO Yujie, JI Ping, CHEN Yingying, XU Jie, WANG Ying. Role of tumor necrosis factor-α in coronavirus disease 2019-associated kidney injury [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(1): 1-10. |
| [3] | FAN Qiang, WU Guangbo, ZHAO Jinbo, ZHENG Lei, LUO Meng. Research progress in pathophysiological and molecular mechanism changes during decompensated phase of portal hypertension in liver cirrhosis [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(3): 379-384. |
| [4] | LI Qianyu, GUO Wenyun, QIAN Yifei, LI Songling, ZHU Zijun, LIU Yanfeng. Study on the significance and mechanism of ASGR1 in hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(9): 1107-1114. |
| [5] | YU Li, SU Xiandu, ZHANG Min, LI Yahui, WANG Le. Construction and validation of prognostic risk model for hepatocellular carcinoma based on biological analysis of palmitoyl-associated enzyme long-chain non-coding RNA [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(6): 747-754. |
| [6] | HU Chanchan, FAN Yi, XU Yuan, HU Zhijian, ZENG Yiming. Lipid metabolism and lung cancer: emerging roles in occurrence, progression, diagnosis and treatment [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2022, 42(12): 1766-1771. |
| [7] | Yihuan WANG, Ruokun LI, Huanhuan CHONG, Fuhua YAN. Research progress of Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of biological behavior of hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE), 2022, 42(1): 130-134. |
| [8] | Lei XIONG, Qian YI, Ming-fang XU, Jian CHEN. Expression and prognosis analysis of MRPL12 in lung adenocarcinoma [J]. JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE), 2021, 41(8): 1033-1040. |
| [9] | WANG Jun-ying1, LI Xin1, YIN Ting-yu2, LIU Jia2, WANG Xiao-dong3, ZHONG Hua1. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal cells immune thrombocytopenia patients on the biological behaviors of megakaryocytes [J]. , 2018, 38(6): 616-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||