
Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science) ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (9): 1239-1248.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2025.09.016
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
YANG Quanjun( ), BAI Dingyuan, ZHOU Yuxuan, BAI Lu, GUO Cheng
), BAI Dingyuan, ZHOU Yuxuan, BAI Lu, GUO Cheng
Received:2025-04-24
Accepted:2025-07-03
Online:2025-09-28
Published:2025-09-30
Contact:
YANG Quanjun
E-mail:myotime@sjtu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
YANG Quanjun, BAI Dingyuan, ZHOU Yuxuan, BAI Lu, GUO Cheng. Role of isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 mutation-mediated D-2-hydroxyglutarate metabolic reprogramming in tumor immunoregulation and progress in related drug development[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(9): 1239-1248.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://xuebao.shsmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2025.09.016
| Cancer | Incidence | Key mechanism of action | Clinical feature | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glioma | 60%‒80% (low level); 5%‒10% (glioblastoma) | D-2HG inhibits α-KG-dependent dioxygenase, leading to a G-CIMP phenotype; causes epigenetic dysregulation and inhibition of cellular differentiation; reduces CD8+ T cell infiltration | Better prognosis (vs. IDH wild type) | [ |
| AML | 10%‒15% | D-2HG inhibits normal hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation; mutant IDH1/2 maintains NADPH homeostasis; upregulates PD-L1 expression and suppresses T-cell function | Longer median survival (vs. IDH wild type); susceptible to combined NPM1/FLT3 mutations | [ |
| Cholangiocarcinoma | 10%‒15% (intrahepatic) | D2HG accumulation leads to mitochondrial dysfunction; epigenetic silencing inhibits tumor suppressor gene expression; activation of HIF-1α pathway promotes tumor angiogenesis | Mutually exclusive with FGFR2 fusion; poorer prognosis | [ |
| Chondrosarcoma | 40%‒50% | Inhibits chondrocyte maturation; promotes abnormal cartilage matrix secretion; increases invasiveness | Low-grade tumors predominate; resistant to conventional chemotherapy | [ |
| MDS | <5% | D2HG inhibits hematopoietic stem cell differentiation; epigenetic abnormalities lead to genomic instability | IDH mutation with TP53 mutation, very poor prognosis | [ |
| Prostate cancer | <5% | Abnormal androgen signaling through epigenetic regulation of the AR pathway; metabolic synergy | Co-mutated with PTEN deletion; sensitive to PARP inhibitors | [ |
| Colorectal cancer | <5% | Rare mutations, often associated with microsatellite stabilization (MSS) or KRAS wild-type isoforms | Prognosis not significantly different from wild type; some patients stabilized, but limited efficacy | [ |
| Thyroid cancer | <5% | Metabolic reprogramming affects oxidative stress; synergistic progression with BRAF co-mutations | Poor prognosis; limited sample size; mechanism of resistance not defined | [ |
Tab 1 Roles of IDH1 mutations in different cancer types
| Cancer | Incidence | Key mechanism of action | Clinical feature | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glioma | 60%‒80% (low level); 5%‒10% (glioblastoma) | D-2HG inhibits α-KG-dependent dioxygenase, leading to a G-CIMP phenotype; causes epigenetic dysregulation and inhibition of cellular differentiation; reduces CD8+ T cell infiltration | Better prognosis (vs. IDH wild type) | [ |
| AML | 10%‒15% | D-2HG inhibits normal hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation; mutant IDH1/2 maintains NADPH homeostasis; upregulates PD-L1 expression and suppresses T-cell function | Longer median survival (vs. IDH wild type); susceptible to combined NPM1/FLT3 mutations | [ |
| Cholangiocarcinoma | 10%‒15% (intrahepatic) | D2HG accumulation leads to mitochondrial dysfunction; epigenetic silencing inhibits tumor suppressor gene expression; activation of HIF-1α pathway promotes tumor angiogenesis | Mutually exclusive with FGFR2 fusion; poorer prognosis | [ |
| Chondrosarcoma | 40%‒50% | Inhibits chondrocyte maturation; promotes abnormal cartilage matrix secretion; increases invasiveness | Low-grade tumors predominate; resistant to conventional chemotherapy | [ |
| MDS | <5% | D2HG inhibits hematopoietic stem cell differentiation; epigenetic abnormalities lead to genomic instability | IDH mutation with TP53 mutation, very poor prognosis | [ |
| Prostate cancer | <5% | Abnormal androgen signaling through epigenetic regulation of the AR pathway; metabolic synergy | Co-mutated with PTEN deletion; sensitive to PARP inhibitors | [ |
| Colorectal cancer | <5% | Rare mutations, often associated with microsatellite stabilization (MSS) or KRAS wild-type isoforms | Prognosis not significantly different from wild type; some patients stabilized, but limited efficacy | [ |
| Thyroid cancer | <5% | Metabolic reprogramming affects oxidative stress; synergistic progression with BRAF co-mutations | Poor prognosis; limited sample size; mechanism of resistance not defined | [ |
| Inhibitor | Structure | Phase | Cancer type | Key result | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Ivosidenib (AG-120) | 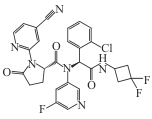 | Available | Relapsed/refractory AML; cholangiocarcinoma | In a Phase Ⅲ trial in cholangiocarcinoma: median OS = 10.3 months; 51% reduction in risk of death. In AML (Phase Ⅲ): median OS = 24 months in combination with azacitidine | [ |
Vorasidenib (AG-881) | 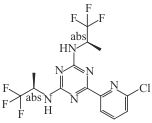 | Available | IDH1/2 mutant glioma | In double-blind Phase Ⅲ trial: median PFS 27.7 months vs 11.1 months (placebo) | [ |
Olutasidenib (FT-2102) | 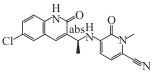 | Available | Relapsed/refractory AML | ORR 46%, median OS 10.5 months, CR/CRh 35%. Combination with azacitidine: CR/CRh 45% (treatment-naïve) vs 30% (previously treated) | [ |
DS-1001 (AB-218) | 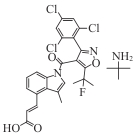 | Ⅰ | Glioma, AML, cholangiocarcinoma | Non-enhancing glioma ORR 33%, enhancing ORR 17.1% | [ |
| AGI-5198 | 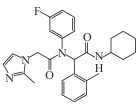 | Preclinical | Glioma | Inhibits mutant IDH1 enzyme; reduces D-2HG production; restores histone H3K9me3 demethylation and differentiation marker expression (GFAP) | [ |
| ML309 | 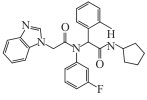 | Preclinical | IDH1 mutant glioma, colon cancer | Reduced D-2HG in glioma; reversed DNA hypermethylation and gene silencing in colon cancer (with vitamin C) | [ |
| Ranosidenib (HMPL-306) | 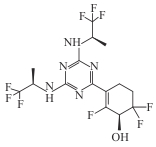 | Ⅰ/Ⅱ | AML, IDH1/2 mutant hematologic and solid tumors | Inhibition of mutant IDH1/2; reduced D-2HG; in AML Phase Ⅰ: CR/CRh 42%; remission in 67% (treatment-naïve) vs 29% (pretreated) | [ |
| IHMT-IDH1-053 | 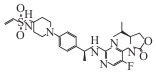 | Preclinical | IDH1 mutated solid tumors and hematological tumors | Covalently binds to Cys269; selectively inhibits mutant enzyme (IC50=4.7 nmol·L-1); reduces D-2HG (IC50=28 nmol·L-1 in transfected cells) | [ |
| BAY1436032 | 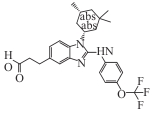 | Ⅰ | IDH1 mutant cholangiocarcinoma, AML | ORR 25%; PFS 5.6 months; median OS 12.8 months. In AML Phase Ⅰ: ORR 15%, 30% stable disease | [ |
| LY3410738 | 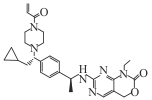 | Ⅰ | IDH1 mutant cholangiocarcinoma and other solid tumors, AML | Broad-spectrum inhibition of IDH1 R132H/C/G/S/L; manageable safety profile. In AML: in combination with cytarabine/doxorubicin, tumor inhibition 82%, median OS extended to 32 d | [ |
| IDH305 | 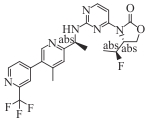 | Ⅰ | AML, MDS | CR/CRh/PR 35% (42% in AML, 28% in MDS); remission rate 57% in treatment-naïve vs 29% in pretreated | [ |
Tab 2 Summary of domestic and foreign IDH1 mutant inhibitors
| Inhibitor | Structure | Phase | Cancer type | Key result | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Ivosidenib (AG-120) |  | Available | Relapsed/refractory AML; cholangiocarcinoma | In a Phase Ⅲ trial in cholangiocarcinoma: median OS = 10.3 months; 51% reduction in risk of death. In AML (Phase Ⅲ): median OS = 24 months in combination with azacitidine | [ |
Vorasidenib (AG-881) |  | Available | IDH1/2 mutant glioma | In double-blind Phase Ⅲ trial: median PFS 27.7 months vs 11.1 months (placebo) | [ |
Olutasidenib (FT-2102) |  | Available | Relapsed/refractory AML | ORR 46%, median OS 10.5 months, CR/CRh 35%. Combination with azacitidine: CR/CRh 45% (treatment-naïve) vs 30% (previously treated) | [ |
DS-1001 (AB-218) |  | Ⅰ | Glioma, AML, cholangiocarcinoma | Non-enhancing glioma ORR 33%, enhancing ORR 17.1% | [ |
| AGI-5198 |  | Preclinical | Glioma | Inhibits mutant IDH1 enzyme; reduces D-2HG production; restores histone H3K9me3 demethylation and differentiation marker expression (GFAP) | [ |
| ML309 |  | Preclinical | IDH1 mutant glioma, colon cancer | Reduced D-2HG in glioma; reversed DNA hypermethylation and gene silencing in colon cancer (with vitamin C) | [ |
| Ranosidenib (HMPL-306) |  | Ⅰ/Ⅱ | AML, IDH1/2 mutant hematologic and solid tumors | Inhibition of mutant IDH1/2; reduced D-2HG; in AML Phase Ⅰ: CR/CRh 42%; remission in 67% (treatment-naïve) vs 29% (pretreated) | [ |
| IHMT-IDH1-053 |  | Preclinical | IDH1 mutated solid tumors and hematological tumors | Covalently binds to Cys269; selectively inhibits mutant enzyme (IC50=4.7 nmol·L-1); reduces D-2HG (IC50=28 nmol·L-1 in transfected cells) | [ |
| BAY1436032 |  | Ⅰ | IDH1 mutant cholangiocarcinoma, AML | ORR 25%; PFS 5.6 months; median OS 12.8 months. In AML Phase Ⅰ: ORR 15%, 30% stable disease | [ |
| LY3410738 |  | Ⅰ | IDH1 mutant cholangiocarcinoma and other solid tumors, AML | Broad-spectrum inhibition of IDH1 R132H/C/G/S/L; manageable safety profile. In AML: in combination with cytarabine/doxorubicin, tumor inhibition 82%, median OS extended to 32 d | [ |
| IDH305 |  | Ⅰ | AML, MDS | CR/CRh/PR 35% (42% in AML, 28% in MDS); remission rate 57% in treatment-naïve vs 29% in pretreated | [ |
| [1] | CLARK O, YEN K, MELLINGHOFF I K. Molecular pathways: isocitrate dehydrogenase mutations in cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2016, 22(8): 1837-1842. |
| [2] | HAN S E, LIU Y, CAI S J, et al. IDH mutation in glioma: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets[J]. Br J Cancer, 2020, 122(11): 1580-1589. |
| [3] | MEDEIROS B C, FATHI A T, DINARDO C D, et al. Isocitrate dehydrogenase mutations in myeloid malignancies[J]. Leukemia, 2017, 31(2): 272-281. |
| [4] | SAHA S K, PARACHONIAK C A, GHANTA K S, et al. Mutant IDH inhibits HNF-4α to block hepatocyte differentiation and promote biliary cancer[J]. Nature, 2014, 513(7516): 110-114. |
| [5] | GROSS S, CAIRNS R A, MINDEN M D, et al. Cancer-associated metabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate accumulates in acute myelogenous leukemia with isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 and 2 mutations[J]. J Exp Med, 2010, 207(2): 339-344. |
| [6] | YANG H, YE D, GUAN K L, et al. IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in tumorigenesis: mechanistic insights and clinical perspectives[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2012, 18(20): 5562-5571. |
| [7] | RÖVER L K, GEVENSLEBEN H, DIETRICH J, et al. PD-1 (PDCD1) promoter methylation is a prognostic factor in patients with diffuse lower-grade gliomas harboring isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutations[J]. EBioMedicine, 2018, 28: 97-104. |
| [8] | DEJAEGHER J, SOLIE L, HUNIN Z, et al. DNA methylation based glioblastoma subclassification is related to tumoral T-cell infiltration and patient survival[J]. Neuro Oncol, 2021, 23(2): 240-250. |
| [9] | XU X, ZHAO J Y, XU Z, et al. Structures of human cytosolic NADP-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase reveal a novel self-regulatory mechanism of activity[J]. J Biol Chem, 2004, 279(32): 33946-33957. |
| [10] | DANG L, WHITE D W, GROSS S, et al. Cancer-associated IDH1 mutations produce 2-hydroxyglutarate[J]. Nature, 2009, 462: 739-744. |
| [11] | COHEN A L, HOLMEN S L, COLMAN H. IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in gliomas[J]. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep, 2013, 13(5): 345. |
| [12] | MARCUCCI G, MAHARRY K, WU Y Z, et al. IDH1 and IDH2 gene mutations identify novel molecular subsets within de novo cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia: a Cancer and Leukemia Group B study[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2010, 28(14): 2348-2355. |
| [13] | MARTÍNEZ-JIMÉNEZ F, MUIÑOS F, SENTÍS I, et al. A compendium of mutational cancer driver genes[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2020, 20(10): 555-572. |
| [14] | FLAVAHAN W A, DRIER Y, LIAU B B, et al. Insulator dysfunction and oncogene activation in IDH mutant gliomas[J]. Nature, 2016, 529(7584): 110-114. |
| [15] | TURCAN S, ROHLE D, GOENKA A, et al. IDH1 mutation is sufficient to establish the glioma hypermethylator phenotype[J]. Nature, 2012, 483(7390): 479-483. |
| [16] | SULKOWSKI P L, CORSO C D, ROBINSON N D, et al. 2-Hydroxyglutarate produced by neomorphic IDH mutations suppresses homologous recombination and induces PARP inhibitor sensitivity[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2017, 9(375): eaal2463. |
| [17] | GELMAN S J, NASER F, MAHIEU N G, et al. Consumption of NADPH for 2-HG synthesis increases pentose phosphate pathway flux and sensitizes cells to oxidative stress[J]. Cell Rep, 2018, 22(2): 512-522. |
| [18] | METALLO C M, GAMEIRO P A, BELL E L, et al. Reductive glutamine metabolism by IDH1 mediates lipogenesis under hypoxia[J]. Nature, 2011, 481(7381): 380-384. |
| [19] | THOMAS D, WU M H, NAKAUCHI Y, et al. Dysregulated lipid synthesis by oncogenic IDH1 mutation is a targetable synthetic lethal vulnerability[J]. Cancer Discov, 2023, 13(2): 496-515. |
| [20] | SASAKI M, KNOBBE C B, ITSUMI M, et al. D-2-hydroxyglutarate produced by mutant IDH1 perturbs collagen maturation and basement membrane function[J]. Genes Dev, 2012, 26(18): 2038-2049. |
| [21] | DA SILVA R, UNO M, MARIE S K, et al. LOX expression and functional analysis in astrocytomas and impact of IDH1 mutation[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(3): e0119781. |
| [22] | ALDAPE K, ZADEH G, MANSOURI S, et al. Glioblastoma: pathology, molecular mechanisms and markers[J]. Acta Neuropathol, 2015, 129(6): 829-848. |
| [23] | MELLINGHOFF I K, VAN DEN BENT M J, BLUMENTHAL D T, et al. Vorasidenib in IDH1- or IDH2-mutant low-grade glioma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2023, 389(7): 589-601. |
| [24] | GREEN C L, EVANS C M, HILLS R K, et al. The prognostic significance of IDH1 mutations in younger adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia is dependent on FLT3/ITD status[J]. Blood, 2010, 116(15): 2779-2782. |
| [25] | DINARDO C D, STEIN A S, STEIN E M, et al. Mutant isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 inhibitor ivosidenib in combination with azacitidine for newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2021, 39(1): 57-65. |
| [26] | DINARDO C D, STEIN E M, DE BOTTON S, et al. Durable remissions with ivosidenib in IDH1-mutated relapsed or refractory AML[J]. N Engl J Med, 2018, 378(25): 2386-2398. |
| [27] | KELLEY R K, BRIDGEWATER J, GORES G J, et al. Systemic therapies for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 72(2): 353-363. |
| [28] | LAVACCHI D, CALIMAN E, ROSSI G, et al. Ivosidenib in IDH1-mutated cholangiocarcinoma: clinical evaluation and future directions[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2022, 237: 108170. |
| [29] | MÜLLER C, FRANKE S, REISLÄNDER T, et al. Sustained clinical response to ivosidenib in previously treated patients with advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma harboring an IDH1 R132 mutation: two case reports[J]. Case Rep Oncol, 2024, 17(1): 753-762. |
| [30] | LUK I S, BRIDGWATER C M, YU A, et al. SRC inhibition enables formation of a growth suppressive MAGI1-PP2A complex in isocitrate dehydrogenase-mutant cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2024, 16(747): eadj7685. |
| [31] | CHEN C B, ZHAO M, TIAN A X, et al. Aberrant activation of Wnt/β‑catenin signaling drives proliferation of bone sarcoma cells[J]. Oncotarget, 2015, 6(19): 17570-17583. |
| [32] | TARPEY P S, BEHJATI S, COOKE S L, et al. Frequent mutation of the major cartilage collagen gene COL2A1 in chondrosarcoma[J]. Nat Genet, 2013, 45(8): 923-926. |
| [33] | TAP W D, VILLALOBOS V M, COTE G M, et al. Phase I study of the mutant IDH1 inhibitor ivosidenib: safety and clinical activity in patients with advanced chondrosarcoma[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2020, 38(15): 1693-1701. |
| [34] | GU Y, YANG R S, YANG Y, et al. IDH1 mutation contributes to myeloid dysplasia in mice by disturbing heme biosynthesis and erythropoiesis[J]. Blood, 2021, 137(7): 945-958. |
| [35] | BONAVITACOLA J, CAFFREY M, JEREMIAS S, et al. FDA Approves Ivosidenib in IDH1-Mutated MDS [J]. American Journal of Managed Care, 2023, 29(9): SP854-SP855. |
| [36] | SAMUELI B, AL-AHMADIE H, CHEN Y B, et al. Histopathologic and molecular characterization of IDH-mutant prostatic adenocarcinoma[J]. Mod Pathol, 2025, 38(1): 100616. |
| [37] | HUANG J L, TSENG L H, PARINI V, et al. IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in colorectal cancers[J]. Am J Clin Pathol, 2021, 156(5): 777-786. |
| [38] | MURUGAN A K, QASEM E, AL-HINDI H, et al. Analysis of ALK, IDH1, IDH2 and MMP8 somatic mutations in differentiated thyroid cancers[J]. Mol Clin Oncol, 2021, 15(4): 210. |
| [39] | KADIYALA P, CARNEY S V, GAUSS J C, et al. Inhibition of 2-hydroxyglutarate elicits metabolic reprogramming and mutant IDH1 glioma immunity in mice[J]. J Clin Invest, 2021, 131(4): e139542. |
| [40] | MELLINGHOFF I K, LU M, WEN P Y, et al. Vorasidenib and ivosidenib in IDH1-mutant low-grade glioma: a randomized, perioperative phase 1 trial[J]. Nat Med, 2023, 29(3): 615-622. |
| [41] | NOTARANGELO G, SPINELLI J B, PEREZ E M, et al. Oncometabolite d-2HG alters T cell metabolism to impair CD8+ T cell function[J]. Science, 2022, 377(6614): 1519-1529. |
| [42] | MONTESINOS P, RECHER C, VIVES S, et al. Ivosidenib and azacitidine in IDH1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia[J]. N Engl J Med, 2022, 386(16): 1519-1531. |
| [43] | BHANSALI R S, PRATZ K W, LAI C. Recent advances in targeted therapies in acute myeloid leukemia[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2023, 16(1): 29. |
| [44] | BOTTOMLY D, LONG N, SCHULTZ A R, et al. Integrative analysis of drug response and clinical outcome in acute myeloid leukemia[J]. Cancer Cell, 2022, 40(8): 850-864.e9. |
| [45] | GRETEN T F, SCHWABE R, BARDEESY N, et al. Immunology and immunotherapy of cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 20(6): 349-365. |
| [46] | RAGGI C, TADDEI M L, RAE C, et al. Metabolic reprogramming in cholangiocarcinoma[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 77(3): 849-864. |
| [47] | VARACHEV V, SHEKHTMAN A, GUSKOV D, et al. Diagnostics of IDH1/2 mutations in intracranial chondroid tumors: comparison of molecular genetic methods and immunohistochemistry[J]. Diagnostics (Basel), 2024, 14(2): 200. |
| [48] | ROCK A, ALI S N, CHOW W A. Systemic therapy for chondrosarcoma[J]. Curr Treat Options Oncol, 2022, 23(2): 199-209. |
| [49] | GREENBERG P L, STONE R M, AL-KALI A, et al. Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Version 3.2022 Featured Updates to the NCCN Guidelines [J]. Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, 2022, 20(2): 107-117. |
| [50] | DINARDO C D, ROBOZ G J, WATTS J M, et al. Final phase 1 substudy results of ivosidenib for patients with mutant IDH1 relapsed/refractory myelodysplastic syndrome[J]. Blood Adv, 2024, 8(15): 4209-4220. |
| [51] | CSIZMAR C M, SALIBA A N, SWISHER E M, et al. PARP inhibitors and myeloid neoplasms: a double-edged sword[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2021, 13(24): 6385. |
| [52] | GONTHIER K, WEIDMANN C, BERTHIAUME L, et al. Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 sustains a hybrid cytoplasmic-mitochondrial tricarboxylic acid cycle that can be targeted for therapeutic purposes in prostate cancer[J]. Mol Oncol, 2023, 17(10): 2109-2125. |
| [53] | WHITEHALL V J, DUMENIL T D, MCKEONE D M, et al. Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 R132C mutation occurs exclusively in microsatellite stable colorectal cancers with the CpG island methylator phenotype[J]. Epigenetics, 2014, 9(11): 1454-1460. |
| [54] | SEOK J Y, ASTVATSATURYAN K, PERALTA-VENTURINA M, et al. TROP-2, 5hmC, and IDH1 expression in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma[J]. Int J Surg Pathol, 2021, 29(4): 368-377. |
| [55] | ZHANG L J, SORENSEN M D, KRISTENSEN B W, et al. D-2-hydroxyglutarate is an intercellular mediator in IDH-mutant gliomas inhibiting complement and T cells[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 24(21): 5381-5391. |
| [56] | BÖTTCHER M, RENNER K, BERGER R, et al. D-2-hydroxyglutarate interferes with HIF-1α stability skewing T-cell metabolism towards oxidative phosphorylation and impairing Th17 polarization[J]. Oncoimmunology, 2018, 7(7): e1445454. |
| [57] | WU M J, KONDO H, KAMMULA A V, et al. Mutant IDH1 inhibition induces dsDNA sensing to activate tumor immunity[J]. Science, 2024, 385(6705): eadl6173. |
| [58] | YANG Q J, HAO J, CHI M Y, et al. D2HGDH-mediated D2HG catabolism enhances the anti-tumor activities of CAR-T cells in an immunosuppressive microenvironment[J]. Mol Ther, 2022, 30(3): 1188-1200. |
| [59] | JIANG T, ZHANG H W, WEN Y P, et al. 5-Aza-2-deoxycytidine alleviates the progression of primary biliary cholangitis by suppressing the FoxP3 methylation and promoting the Treg/Th17 balance[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2021, 96: 107820. |
| [60] | DE GOEDE K E, HARBER K J, GORKI F S, et al. D-2-Hydroxyglutarate is an anti-inflammatory immunometabolite that accumulates in macrophages after TLR4 activation[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2022, 1868(9): 166427. |
| [61] | POPOVICI-MULLER J, LEMIEUX R M, ARTIN E, et al. Discovery of AG-120 (ivosidenib): a first-in-class mutant IDH1 inhibitor for the treatment of IDH1 mutant cancers[J]. ACS Med Chem Lett, 2018, 9(4): 300-305. |
| [62] | LIANG Q M, WANG B L, ZOU F M, et al. Structure-based discovery of IHMT-IDH1-053 as a potent irreversible IDH1 mutant selective inhibitor[J]. Eur J Med Chem, 2023, 256: 115411. |
| [63] | XIAO K, ZHANG Z, WU Y, et al. Discovery of HMPL-306 (ranosidenib), a new potent and selective dual inhibitor of mutant IDH1 and 2 in clinical development for cancer treatment[J]. ACS Med Chem Lett, 2025, 16(3): 454-463. |
| [64] | ZHU A X, MACARULLA T, JAVLE M M, et al. Final overall survival efficacy results of ivosidenib for patients with advanced cholangiocarcinoma with IDH1 mutation: the phase 3 randomized clinical ClarIDHy trial[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2021, 7(11): 1669-1677. |
| [65] | WATTS J M, BAER M R, YANG J, et al. Olutasidenib alone or with azacitidine in IDH1-mutated acute myeloid leukaemia and myelodysplastic syndrome: phase 1 results of a phase 1/2 trial[J]. Lancet Haematol, 2023, 10(1): e46-e58. |
| [66] | DE BOTTON S, FENAUX P, YEE K R, et al. Olutasidenib (FT-2102) induces durable complete remissions in patients with relapsed or refractory IDH1-mutated AML[J]. Blood Adv, 2023, 7(13): 3117-3127. |
| [67] | CORTES J E, ROBOZ G J, BAER M R, et al. Olutasidenib in combination with azacitidine induces durable complete remissions in patients with relapsed or refractory mIDH1 acute myeloid leukemia: a multicohort open-label phase 1/2 trial[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2025, 18(1): 7. |
| [68] | NATSUME A, ARAKAWA Y, NARITA Y, et al. The first-in-human phase I study of a brain-penetrant mutant IDH1 inhibitor DS-1001 in patients with recurrent or progressive IDH1-mutant gliomas[J]. Neuro Oncol, 2023, 25(2): 326-336. |
| [69] | ROHLE D, POPOVICI-MULLER J, PALASKAS N, et al. An inhibitor of mutant IDH1 delays growth and promotes differentiation of glioma cells[J]. Science, 2013, 340(6132): 626-630. |
| [70] | DAVIS M I, GROSS S, SHEN M, et al. Biochemical, cellular, and biophysical characterization of a potent inhibitor of mutant isocitrate dehydrogenase IDH1[J]. J Biol Chem, 2014, 289(20): 13717-13725. |
| [71] | GERECKE C, SCHUMACHER F, BERNDZEN A, et al. Vitamin C in combination with inhibition of mutant IDH1 synergistically activates TET enzymes and epigenetically modulates gene silencing in colon cancer cells[J]. Epigenetics, 2020, 15(3): 307-322. |
| [72] | HU L J, WEI X D, ZHAO W L, et al. HMPL-306 in relapsed or refractory IDH1- and/or IDH2-mutated acute myeloid leukemia: a phase 1 study[J]. Med, 2025, 6(6): 100575. |
| [73] | WICK A, BÄHR O, SCHULER M, et al. Phase I assessment of safety and therapeutic activity of BAY1436032 in patients with IDH1-mutant solid tumors[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2021, 27(10): 2723-2733. |
| [74] | HEUSER M, PALMISIANO N, MANTZARIS I, et al. Safety and efficacy of BAY1436032 in IDH1-mutant AML: phase I study results[J]. Leukemia, 2020, 34(11): 2903-2913. |
| [75] | PAUFF J M, PAPADOPOULOS K P, JANKU F, et al. A phase I study of LY3410738, a first-in-class covalent inhibitor of mutant IDH1 in cholangiocarcinoma and other advanced solid tumors[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2021, 39(3_suppl): TPS350. |
| [76] | SALAMA V, BROOKS N, SKWARSKA A, et al. Abstract 6417: ly3410738, a novel inhibitor of mutant IDH1 is more effective than Ivosidenib and potentiates antileukemic activity of standard chemotherapy in preclinical models of acute myeloid leukemia (AML)[J]. Cancer Res, 2020, 80(16_Supplement): 6417. |
| [77] | DINARDO C D, HOCHHAUS A, FRATTINI M G, et al. A phase 1 study of IDH305 in patients with IDH1R132-mutant acute myeloid leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2023, 149(3): 1145-1158. |
| [1] | WANG Xinyu, CHEN Qianye, SUN Jiping, LU Tingwei, HUANG Xiangru, SUN Siyuan, LIU Yuanqi, PAN Houwen, DAI Qinggang, SHEN Lei, JIANG Lingyong. Effect of jaw osteoblasts on B cell development via cytokine secretion [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(9): 1106-1115. |
| [2] | CHEN Zixuan, LIU Min. Progress in mechanisms and treatment of sunitinib resistance in renal cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(10): 1307-1315. |
| [3] | ZHANG Yirong, WEI Weiqing, MA Jiao, ZHANG Xue. Research on the role of SOX9 in regulating metabolic reprogramming in diffuse large B cell lymphoma [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(10): 1236-1244. |
| [4] | LIAO Jiong-bo, SHAO Kun, WANG Xiao, et al. Effects of myeloid-derived suppressor cells induced by dexamethasone on rejection of skin transplantation of mice [J]. , 2014, 34(6): 804-. |
| [5] | ZHAN Jia-ming, WANG Xiang-hui. Research progress of intravenous immunoglobulin application in renal transplantation [J]. , 2012, 32(8): 1092-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||