[1]
ISLAMI F, WARD E M, SUNG H, et al. Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, part 1: national cancer statistics[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2021, 113(12): 1648-1669.
[本文引用: 1]
[2]
CHEVRIER S, LEVINE J H, ZANOTELLI V R T, et al. An immune atlas of clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Cell, 2017, 169(4): 736-749.e18.
[本文引用: 1]
[3]
KARAGIORGOU Z, FOUNTAS P N, MANOU D, et al. Proteoglycans determine the dynamic landscape of EMT and cancer cell stemness[J]. Cancers, 2022, 14(21): 5328.
[本文引用: 1]
[4]
KESH K, GUPTA V K, DURDEN B, et al. Therapy resistance, cancer stem cells and ECM in cancer: the matrix reloaded[J]. Cancers, 2020, 12(10): 3067.
[本文引用: 1]
[5]
HIRANI P, GAUTHIER V, ALLEN C E, et al. Targeting versican as a potential immunotherapeutic strategy in the treatment of cancer[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 712807.
[本文引用: 1]
[6]
MITSUI Y, SHIINA H, KATO T, et al. Versican promotes tumor progression, metastasis and predicts poor prognosis in renal carcinoma[J]. Mol Cancer Res, 2017, 15(7): 884-895.
[本文引用: 2]
[7]
吕磊, 郑福鑫, 周高峰, 等. 多功能蛋白聚糖基因对膀胱尿路上皮癌免疫浸润及预后的影响[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2023, 48(8): 921-928.
[本文引用: 1]
LÜ L, ZHENG F X, ZHOU G F, et al. Effect of VCAN on immune infiltration and prognosis of bladder urothelial carcinoma[J]. Medical Journal of Chinese People's Liberation Army, 2023, 48(8): 921-928.
[本文引用: 1]
[8]
SUN G S, ZHENG W B, TAN P Y, et al. Comprehensive analysis of VCAN expression profiles and prognostic values in HCC[J]. Front Genet, 2022, 13: 900306.
[本文引用: 3]
[9]
KATO K, FUKAI M, HATANAKA K C, et al. Versican secreted by cancer-associated fibroblasts is a poor prognostic factor in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2022, 29(11): 7135-7146.
[本文引用: 1]
[10]
WANG M Q, LI Y P, XU M, et al. VCAN, expressed highly in hepatitis B virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma, is a potential biomarker for immune checkpoint inhibitors[J]. World J Gastrointest Oncol, 2022, 14(10): 1933-1948.
[本文引用: 2]
[11]
DE WIT M, CARVALHO B, DELIS-VAN DIEMEN P M, et al. Lumican and versican protein expression are associated with colorectal adenoma-to-carcinoma progression[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(5): e0174768.
[本文引用: 2]
[12]
GUO J, LIU Y. INHBA promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of colon cancer cells through the upregulation of VCAN[J]. J Int Med Res, 2021, 49(6): 3000605211014998.
[本文引用: 2]
[13]
WANG L, FENG L, LIU L N, et al. Joint effect of THBS2 and VCAN accelerating the poor prognosis of gastric cancer[J]. Aging, 2023, 15(5): 1343-1357.
[本文引用: 1]
[14]
SONG J Q, WEI R Y, HUO S Y, et al. Versican enrichment predicts poor prognosis and response to adjuvant therapy and immunotherapy in gastric cancer[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 960570.
[15]
ZHAI L L, CHEN W J, CUI B S, et al. Overexpressed versican promoted cell multiplication, migration and invasion in gastric cancer[J]. Tissue Cell, 2021, 73: 101611.
[本文引用: 1]
[16]
CHENG Y, SUN H Z, WU L L, et al. V Up-regulation of VCAN promotes the proliferation, invasion and migration and serves as a biomarker in gastric cancer[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2020, 13: 8665-8675.
[本文引用: 1]
[17]
PAPADAS A, ARAUZ G, CICALA A, et al. Versican and versican-matrikines in cancer progression, inflammation, and immunity[J]. J Histochem Cytochem, 2020, 68(12): 871-885.
[本文引用: 3]
[18]
WU Y J, LA PIERRE D P, WU J, et al. The interaction of versican with its binding partners[J]. Cell Res, 2005, 15(7): 483-494.
[本文引用: 1]
[19]
PAPADAS A, ASIMAKOPOULOS F. Versican in the tumor microenvironment[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2020, 1272: 55-72.
[本文引用: 2]
[20]
KERN C B, NORRIS R A, THOMPSON R P, et al. Versican proteolysis mediates myocardial regression during outflow tract development[J]. Dev Dyn, 2007, 236(3): 671-683.
[本文引用: 2]
[21]
HAYES A, SUGAHARA K, FARRUGIA B, et al. Biodiversity of CS-proteoglycan sulphation motifs: chemical messenger recognition modules with roles in information transfer, control of cellular behaviour and tissue morphogenesis[J]. Biochem J, 2018, 475(3): 587-620.
[本文引用: 2]
[22]
KAMIYA N, WATANABE H, HABUCHI H, et al. Versican/PG-M regulates chondrogenesis as an extracellular matrix molecule crucial for mesenchymal condensation[J]. J Biol Chem, 2006, 281(4): 2390-2400.
[本文引用: 2]
[23]
FENG J, LI Y D, LI Y, et al. Versican promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation and cardiac repair[J]. Circulation, 2024, 149(13): 1004-1015.
[本文引用: 1]
[24]
WIGHT T N, KANG I, MERRILEES M J. Versican and the control of inflammation[J]. Matrix Biol, 2014, 35: 152-161.
[本文引用: 1]
[25]
MATSUMOTO K, SHIONYU M, GO M, et al. Distinct interaction of versican/PG-M with hyaluronan and link protein[J]. J Biol Chem, 2003, 278(42): 41205-41212.
[本文引用: 1]
[26]
DAY A J, MILNER C M. TSG-6: a multifunctional protein with anti-inflammatory and tissue-protective properties[J]. Matrix Biol, 2019, 78-79: 60-83.
[27]
WIGHT T N, KANG I, EVANKO S P, et al. Versican: a critical extracellular matrix regulator of immunity and inflammation[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 512.
[本文引用: 2]
[28]
TOCCHI A, PARKS W C. Functional interactions between matrix metalloproteinases and glycosaminoglycans[J]. FEBS J, 2013, 280(10): 2332-2341.
[本文引用: 1]
[29]
KANG I, HARTEN I A, CHANG M Y, et al. Versican deficiency significantly reduces lung inflammatory response induced by polyinosine-polycytidylic acid stimulation[J]. J Biol Chem, 2017, 292(1): 51-63.
[本文引用: 1]
[30]
DUTT S, KLÉBER M, MATASCI M, et al. Versican V0 and V1 guide migratory neural crest cells[J]. J Biol Chem, 2006, 281(17): 12123-12131.
[本文引用: 1]
[31]
WU Y J, SHENG W, CHEN L W, et al. Versican V1 isoform induces neuronal differentiation and promotes neurite outgrowth[J]. Mol Biol Cell, 2004, 15(5): 2093-2104.
[本文引用: 2]
[32]
MERRILEES M J, BEAUMONT B W, BRAUN K R, et al. Neointima formed by arterial smooth muscle cells expressing versican variant V3 is resistant to lipid and macrophage accumulation[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2011, 31(6): 1309-1316.
[本文引用: 1]
[33]
KANG I, YOON D W, BRAUN K R, et al. Expression of versican V3 by arterial smooth muscle cells alters tumor growth factor β (TGFβ)-, epidermal growth factor (EGF)-, and nuclear factor κB (NFκB)-dependent signaling pathways, creating a microenvironment that resists monocyte adhesion[J]. J Biol Chem, 2014, 289(22): 15393-15404.
[本文引用: 1]
[34]
KISCHEL P, WALTREGNY D, DUMONT B, et al. Versican overexpression in human breast cancer lesions: known and new isoforms for stromal tumor targeting[J]. Int J Cancer, 2010, 126(3): 640-650.
[本文引用: 1]
[35]
ZHANGYUAN G Y, WANG F, ZHANG H T, et al. VersicanV1 promotes proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma through the activation of EGFR-PI3K-AKT pathway[J]. Oncogene, 2020, 39(6): 1213-1230.
[本文引用: 3]
[36]
TAN R Y, ZHANG G H, LIU R C, et al. Identification of early diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers via WGCNA in stomach adenocarcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 636461.
[本文引用: 1]
[37]
陆思芬, 魏小珍, 牟必琴, 等. 基于生物信息数据探究VCAN在食管鳞状细胞癌预后中的作用[J]. 中国胸心血管外科临床杂志, 2022, 29(8): 1031-1041.
[本文引用: 1]
LU S F, WEI X Z, MOU B Q, et al. Exploring the role of VCAN in the prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma based on bioinformatics data[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, 2022, 29(8): 1031-1041.
[本文引用: 1]
[38]
YAMAUCHI N, KANKE Y, SAITO K, et al. Stromal expression of cancer-associated fibroblast-related molecules, versican and lumican, is strongly associated with worse relapse-free and overall survival times in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Oncol Lett, 2021, 21(6): 445.
[本文引用: 1]
[39]
DESJARDINS M, XIE J, GURLER H, et al. Versican regulates metastasis of epithelial ovarian carcinoma cells and spheroids[J]. J Ovarian Res, 2014, 7: 70.
[本文引用: 1]
[40]
DU W W, YANG W N, YEE A J. Roles of versican in cancer biology: tumorigenesis, progression and metastasis[J]. Histol Histopathol, 2013, 28(6): 701-713.
[本文引用: 1]
[41]
YANG B L, ZHANG Y, CAO L, et al. Cell adhesion and proliferation mediated through the G1 domain of versican[J]. J Cell Biochem, 1999, 72(2): 210-220.
[本文引用: 2]
[42]
XUE J P, CHEN J N, SHEN Q, et al. Addition of high molecular weight hyaluronic acid to fibroblast-like stromal cells modulates endogenous hyaluronic acid metabolism and enhances proteolytic processing and secretion of versican[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(7): 1681.
[本文引用: 1]
[43]
CATTARUZZA S, SCHIAPPACASSI M, KIMATA K, et al. The globular domains of PG-M/versican modulate the proliferation-apoptosis equilibrium and invasive capabilities of tumor cells[J]. FASEB J, 2004, 18(6): 779-781.
[本文引用: 1]
[44]
SHENG W, WANG G Z, WANG Y, et al. The roles of versican V1 and V2 isoforms in cell proliferation and apoptosis[J]. Mol Biol Cell, 2005, 16(3): 1330-1340.
[本文引用: 1]
[45]
CHEN H, ZHAO Y, ZHANG J J, et al. Promoting effects of miR-135b on human multiple myeloma cells via regulation of the Wnt/β-catenin/versican signaling pathway[J]. Cytokine, 2021, 142: 155495.
[本文引用: 1]
[46]
ANG L C, ZHANG Y, CAO L, et al. Versican enhances locomotion of astrocytoma cells and reduces cell adhesion through its G1 domain[J]. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol, 1999, 58(6): 597-605.
[本文引用: 1]
[47]
YEUNG T L, LEUNG C S, WONG K K, et al. TGF-β modulates ovarian cancer invasion by upregulating CAF-derived versican in the tumor microenvironment[J]. Cancer Res, 2013, 73(16): 5016-5028.
[本文引用: 1]
[48]
杨迷玲, 杨金花, 王娜, 等. Versican与胃癌上皮-间质转化相关蛋白的表达及意义[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2022, 51(12): 69-74.
[本文引用: 1]
YANG M L, YANG J H, WANG N, et al. Expression of versican and its relationship with epithelial-mesenchymal transition related proteins and clinical significance in gastric cancer[J]. Journal of Medical Research, 2022, 51(12): 69-74.
[本文引用: 1]
[49]
DU W W, FANG L, YANG W N, et al. The role of versican G3 domain in regulating breast cancer cell motility including effects on osteoblast cell growth and differentiation in vitro : evaluation towards understanding breast cancer cell bone metastasis[J]. BMC Cancer, 2012, 12: 341.
[本文引用: 1]
[50]
DOS REIS D C, DAMASCENO K A, DE CAMPOS C B, et al. Versican and tumor-associated macrophages promotes tumor progression and metastasis in canine and murine models of breast carcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2019, 9: 577.
[本文引用: 1]
[51]
ZHENG P S, WEN J P, ANG L C, et al. Versican/PG-M G3 domain promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis[J]. FASEB J, 2004, 18(6): 754-756.
[本文引用: 1]
[52]
LABROPOULOU V T, THEOCHARIS A D, RAVAZOULA P, et al. Versican but not decorin accumulation is related to metastatic potential and neovascularization in testicular germ cell tumours[J]. Histopathology, 2006, 49(6): 582-593.
[本文引用: 2]
[53]
EVANKO S P, POTTER-PERIGO S, BOLLYKY P L, et al. Hyaluronan and versican in the control of human T-lymphocyte adhesion and migration[J]. Matrix Biol, 2012, 31(2): 90-100.
[本文引用: 1]
[54]
POTTER-PERIGO S, JOHNSON P Y, EVANKO S P, et al. Polyinosine-polycytidylic acid stimulates versican accumulation in the extracellular matrix promoting monocyte adhesion[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2010, 43(1): 109-120.
[本文引用: 1]
[55]
KAUR A, ECKER B L, DOUGLASS S M, et al. Remodeling of the collagen matrix in aging skin promotes melanoma metastasis and affects immune cell motility[J]. Cancer Discov, 2019, 9(1): 64-81.
[本文引用: 1]
1
... 近年来,随着肿瘤的预防、诊断和治疗方法的不断进步,很多肿瘤患者的预后得到改善,但恶性肿瘤仍是全球人类死亡的主要原因之一[1 ] .因此,明确恶性肿瘤的发生发展机制,探索新的治疗靶点,对提高肿瘤治疗效果,改善患者预后尤为重要.肿瘤的发生发展不仅取决于肿瘤细胞自身,而且与肿瘤微环境(tumor microenvironment,TME)也密切相关[2 -3 ] .细胞外基质(extracellular matrix,ECM)是TME的重要组成部分,在肿瘤的发生发展中起着关键作用[4 ] .多能蛋白聚糖(versican)是一种大分子的硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖,属于外源凝集素蛋白聚糖家族,由染色体5q12~5q14位点上的VCAN 基因编码,是ECM的主要成分[5 ] .体内外研究显示,泌尿系统肿瘤[6 -7 ] 、肝细胞癌[8 -10 ] 、结直肠癌[11 -12 ] 、胃癌[13 -16 ] 等多种肿瘤组织中均存在versican的高表达,且与患者的不良预后密切相关,这为肿瘤的早期诊断和预后评估提供了新的生物标志物.然而,versican在恶性肿瘤中的作用机制尚未完全明确,现就目前versican在恶性肿瘤中的表达及生物学作用的相关研究进行综述. ...
1
... 近年来,随着肿瘤的预防、诊断和治疗方法的不断进步,很多肿瘤患者的预后得到改善,但恶性肿瘤仍是全球人类死亡的主要原因之一[1 ] .因此,明确恶性肿瘤的发生发展机制,探索新的治疗靶点,对提高肿瘤治疗效果,改善患者预后尤为重要.肿瘤的发生发展不仅取决于肿瘤细胞自身,而且与肿瘤微环境(tumor microenvironment,TME)也密切相关[2 -3 ] .细胞外基质(extracellular matrix,ECM)是TME的重要组成部分,在肿瘤的发生发展中起着关键作用[4 ] .多能蛋白聚糖(versican)是一种大分子的硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖,属于外源凝集素蛋白聚糖家族,由染色体5q12~5q14位点上的VCAN 基因编码,是ECM的主要成分[5 ] .体内外研究显示,泌尿系统肿瘤[6 -7 ] 、肝细胞癌[8 -10 ] 、结直肠癌[11 -12 ] 、胃癌[13 -16 ] 等多种肿瘤组织中均存在versican的高表达,且与患者的不良预后密切相关,这为肿瘤的早期诊断和预后评估提供了新的生物标志物.然而,versican在恶性肿瘤中的作用机制尚未完全明确,现就目前versican在恶性肿瘤中的表达及生物学作用的相关研究进行综述. ...
1
... 近年来,随着肿瘤的预防、诊断和治疗方法的不断进步,很多肿瘤患者的预后得到改善,但恶性肿瘤仍是全球人类死亡的主要原因之一[1 ] .因此,明确恶性肿瘤的发生发展机制,探索新的治疗靶点,对提高肿瘤治疗效果,改善患者预后尤为重要.肿瘤的发生发展不仅取决于肿瘤细胞自身,而且与肿瘤微环境(tumor microenvironment,TME)也密切相关[2 -3 ] .细胞外基质(extracellular matrix,ECM)是TME的重要组成部分,在肿瘤的发生发展中起着关键作用[4 ] .多能蛋白聚糖(versican)是一种大分子的硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖,属于外源凝集素蛋白聚糖家族,由染色体5q12~5q14位点上的VCAN 基因编码,是ECM的主要成分[5 ] .体内外研究显示,泌尿系统肿瘤[6 -7 ] 、肝细胞癌[8 -10 ] 、结直肠癌[11 -12 ] 、胃癌[13 -16 ] 等多种肿瘤组织中均存在versican的高表达,且与患者的不良预后密切相关,这为肿瘤的早期诊断和预后评估提供了新的生物标志物.然而,versican在恶性肿瘤中的作用机制尚未完全明确,现就目前versican在恶性肿瘤中的表达及生物学作用的相关研究进行综述. ...
1
... 近年来,随着肿瘤的预防、诊断和治疗方法的不断进步,很多肿瘤患者的预后得到改善,但恶性肿瘤仍是全球人类死亡的主要原因之一[1 ] .因此,明确恶性肿瘤的发生发展机制,探索新的治疗靶点,对提高肿瘤治疗效果,改善患者预后尤为重要.肿瘤的发生发展不仅取决于肿瘤细胞自身,而且与肿瘤微环境(tumor microenvironment,TME)也密切相关[2 -3 ] .细胞外基质(extracellular matrix,ECM)是TME的重要组成部分,在肿瘤的发生发展中起着关键作用[4 ] .多能蛋白聚糖(versican)是一种大分子的硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖,属于外源凝集素蛋白聚糖家族,由染色体5q12~5q14位点上的VCAN 基因编码,是ECM的主要成分[5 ] .体内外研究显示,泌尿系统肿瘤[6 -7 ] 、肝细胞癌[8 -10 ] 、结直肠癌[11 -12 ] 、胃癌[13 -16 ] 等多种肿瘤组织中均存在versican的高表达,且与患者的不良预后密切相关,这为肿瘤的早期诊断和预后评估提供了新的生物标志物.然而,versican在恶性肿瘤中的作用机制尚未完全明确,现就目前versican在恶性肿瘤中的表达及生物学作用的相关研究进行综述. ...
1
... 近年来,随着肿瘤的预防、诊断和治疗方法的不断进步,很多肿瘤患者的预后得到改善,但恶性肿瘤仍是全球人类死亡的主要原因之一[1 ] .因此,明确恶性肿瘤的发生发展机制,探索新的治疗靶点,对提高肿瘤治疗效果,改善患者预后尤为重要.肿瘤的发生发展不仅取决于肿瘤细胞自身,而且与肿瘤微环境(tumor microenvironment,TME)也密切相关[2 -3 ] .细胞外基质(extracellular matrix,ECM)是TME的重要组成部分,在肿瘤的发生发展中起着关键作用[4 ] .多能蛋白聚糖(versican)是一种大分子的硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖,属于外源凝集素蛋白聚糖家族,由染色体5q12~5q14位点上的VCAN 基因编码,是ECM的主要成分[5 ] .体内外研究显示,泌尿系统肿瘤[6 -7 ] 、肝细胞癌[8 -10 ] 、结直肠癌[11 -12 ] 、胃癌[13 -16 ] 等多种肿瘤组织中均存在versican的高表达,且与患者的不良预后密切相关,这为肿瘤的早期诊断和预后评估提供了新的生物标志物.然而,versican在恶性肿瘤中的作用机制尚未完全明确,现就目前versican在恶性肿瘤中的表达及生物学作用的相关研究进行综述. ...
2
... 近年来,随着肿瘤的预防、诊断和治疗方法的不断进步,很多肿瘤患者的预后得到改善,但恶性肿瘤仍是全球人类死亡的主要原因之一[1 ] .因此,明确恶性肿瘤的发生发展机制,探索新的治疗靶点,对提高肿瘤治疗效果,改善患者预后尤为重要.肿瘤的发生发展不仅取决于肿瘤细胞自身,而且与肿瘤微环境(tumor microenvironment,TME)也密切相关[2 -3 ] .细胞外基质(extracellular matrix,ECM)是TME的重要组成部分,在肿瘤的发生发展中起着关键作用[4 ] .多能蛋白聚糖(versican)是一种大分子的硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖,属于外源凝集素蛋白聚糖家族,由染色体5q12~5q14位点上的VCAN 基因编码,是ECM的主要成分[5 ] .体内外研究显示,泌尿系统肿瘤[6 -7 ] 、肝细胞癌[8 -10 ] 、结直肠癌[11 -12 ] 、胃癌[13 -16 ] 等多种肿瘤组织中均存在versican的高表达,且与患者的不良预后密切相关,这为肿瘤的早期诊断和预后评估提供了新的生物标志物.然而,versican在恶性肿瘤中的作用机制尚未完全明确,现就目前versican在恶性肿瘤中的表达及生物学作用的相关研究进行综述. ...
... Versican在多种肿瘤组织中异常表达,且与患者的临床病理特征及预后密切相关.一项研究[6 ] 表明,versican在肾细胞癌组织中高表达,并且其高表达与根治性肾切除术后的肿瘤复发转移率升高及患者5年生存率下降密切相关.Versican的V1亚型在肝细胞癌组织中高表达,并与不良预后相关[8 ,35 ] ;与正常肝脏组织相比,肝细胞癌组织中versican表达上调,并且恶性程度越高的亚型中versican的表达水平越高[8 ] .与腺瘤相比,结直肠癌组织中versican的表达显著增高,并且versican的表达促进了腺瘤向结直肠癌发展[11 ] .胃癌组织中versican的表达水平明显高于正常胃黏膜组织,并且versican的高表达与较高的TNM分期及患者的不良预后密切相关[15 ] ,是胃癌患者预后不良的独立预测因子[36 ] .在食管鳞状细胞癌组织中,versican较癌旁组织显著增高,且versican高表达患者的无病生存期明显缩短[37 ] .进一步的研究[38 ] 表明,食管癌组织中versican高表达与肿瘤血管和淋巴管浸润增加、淋巴结转移及患者预后不佳显著相关.在卵巢癌组织中,同样存在versican的高表达,且versican的高表达与卵巢癌腹膜转移率增加密切相关[39 ] . ...
1
... 近年来,随着肿瘤的预防、诊断和治疗方法的不断进步,很多肿瘤患者的预后得到改善,但恶性肿瘤仍是全球人类死亡的主要原因之一[1 ] .因此,明确恶性肿瘤的发生发展机制,探索新的治疗靶点,对提高肿瘤治疗效果,改善患者预后尤为重要.肿瘤的发生发展不仅取决于肿瘤细胞自身,而且与肿瘤微环境(tumor microenvironment,TME)也密切相关[2 -3 ] .细胞外基质(extracellular matrix,ECM)是TME的重要组成部分,在肿瘤的发生发展中起着关键作用[4 ] .多能蛋白聚糖(versican)是一种大分子的硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖,属于外源凝集素蛋白聚糖家族,由染色体5q12~5q14位点上的VCAN 基因编码,是ECM的主要成分[5 ] .体内外研究显示,泌尿系统肿瘤[6 -7 ] 、肝细胞癌[8 -10 ] 、结直肠癌[11 -12 ] 、胃癌[13 -16 ] 等多种肿瘤组织中均存在versican的高表达,且与患者的不良预后密切相关,这为肿瘤的早期诊断和预后评估提供了新的生物标志物.然而,versican在恶性肿瘤中的作用机制尚未完全明确,现就目前versican在恶性肿瘤中的表达及生物学作用的相关研究进行综述. ...
1
... 近年来,随着肿瘤的预防、诊断和治疗方法的不断进步,很多肿瘤患者的预后得到改善,但恶性肿瘤仍是全球人类死亡的主要原因之一[1 ] .因此,明确恶性肿瘤的发生发展机制,探索新的治疗靶点,对提高肿瘤治疗效果,改善患者预后尤为重要.肿瘤的发生发展不仅取决于肿瘤细胞自身,而且与肿瘤微环境(tumor microenvironment,TME)也密切相关[2 -3 ] .细胞外基质(extracellular matrix,ECM)是TME的重要组成部分,在肿瘤的发生发展中起着关键作用[4 ] .多能蛋白聚糖(versican)是一种大分子的硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖,属于外源凝集素蛋白聚糖家族,由染色体5q12~5q14位点上的VCAN 基因编码,是ECM的主要成分[5 ] .体内外研究显示,泌尿系统肿瘤[6 -7 ] 、肝细胞癌[8 -10 ] 、结直肠癌[11 -12 ] 、胃癌[13 -16 ] 等多种肿瘤组织中均存在versican的高表达,且与患者的不良预后密切相关,这为肿瘤的早期诊断和预后评估提供了新的生物标志物.然而,versican在恶性肿瘤中的作用机制尚未完全明确,现就目前versican在恶性肿瘤中的表达及生物学作用的相关研究进行综述. ...
3
... 近年来,随着肿瘤的预防、诊断和治疗方法的不断进步,很多肿瘤患者的预后得到改善,但恶性肿瘤仍是全球人类死亡的主要原因之一[1 ] .因此,明确恶性肿瘤的发生发展机制,探索新的治疗靶点,对提高肿瘤治疗效果,改善患者预后尤为重要.肿瘤的发生发展不仅取决于肿瘤细胞自身,而且与肿瘤微环境(tumor microenvironment,TME)也密切相关[2 -3 ] .细胞外基质(extracellular matrix,ECM)是TME的重要组成部分,在肿瘤的发生发展中起着关键作用[4 ] .多能蛋白聚糖(versican)是一种大分子的硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖,属于外源凝集素蛋白聚糖家族,由染色体5q12~5q14位点上的VCAN 基因编码,是ECM的主要成分[5 ] .体内外研究显示,泌尿系统肿瘤[6 -7 ] 、肝细胞癌[8 -10 ] 、结直肠癌[11 -12 ] 、胃癌[13 -16 ] 等多种肿瘤组织中均存在versican的高表达,且与患者的不良预后密切相关,这为肿瘤的早期诊断和预后评估提供了新的生物标志物.然而,versican在恶性肿瘤中的作用机制尚未完全明确,现就目前versican在恶性肿瘤中的表达及生物学作用的相关研究进行综述. ...
... Versican在多种肿瘤组织中异常表达,且与患者的临床病理特征及预后密切相关.一项研究[6 ] 表明,versican在肾细胞癌组织中高表达,并且其高表达与根治性肾切除术后的肿瘤复发转移率升高及患者5年生存率下降密切相关.Versican的V1亚型在肝细胞癌组织中高表达,并与不良预后相关[8 ,35 ] ;与正常肝脏组织相比,肝细胞癌组织中versican表达上调,并且恶性程度越高的亚型中versican的表达水平越高[8 ] .与腺瘤相比,结直肠癌组织中versican的表达显著增高,并且versican的表达促进了腺瘤向结直肠癌发展[11 ] .胃癌组织中versican的表达水平明显高于正常胃黏膜组织,并且versican的高表达与较高的TNM分期及患者的不良预后密切相关[15 ] ,是胃癌患者预后不良的独立预测因子[36 ] .在食管鳞状细胞癌组织中,versican较癌旁组织显著增高,且versican高表达患者的无病生存期明显缩短[37 ] .进一步的研究[38 ] 表明,食管癌组织中versican高表达与肿瘤血管和淋巴管浸润增加、淋巴结转移及患者预后不佳显著相关.在卵巢癌组织中,同样存在versican的高表达,且versican的高表达与卵巢癌腹膜转移率增加密切相关[39 ] . ...
... [8 ].与腺瘤相比,结直肠癌组织中versican的表达显著增高,并且versican的表达促进了腺瘤向结直肠癌发展[11 ] .胃癌组织中versican的表达水平明显高于正常胃黏膜组织,并且versican的高表达与较高的TNM分期及患者的不良预后密切相关[15 ] ,是胃癌患者预后不良的独立预测因子[36 ] .在食管鳞状细胞癌组织中,versican较癌旁组织显著增高,且versican高表达患者的无病生存期明显缩短[37 ] .进一步的研究[38 ] 表明,食管癌组织中versican高表达与肿瘤血管和淋巴管浸润增加、淋巴结转移及患者预后不佳显著相关.在卵巢癌组织中,同样存在versican的高表达,且versican的高表达与卵巢癌腹膜转移率增加密切相关[39 ] . ...
1
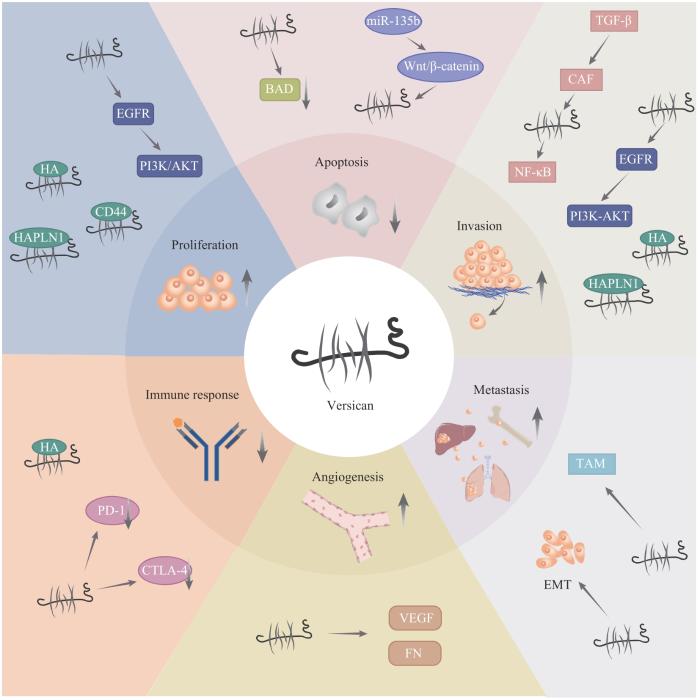
... 关于恶性星形细胞瘤的研究[41 ,46 ] 显示,versican的G1结构域通过与透明质酸、HAPLN1结合来减少肿瘤细胞的黏附,增强肿瘤细胞的迁移能力.而G3结构域的类EGF重复序列通过激活EGFR/PI3K/AKT信号通路,促进肝癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[35 ] .抑制素βA亚基可以通过上调versican的表达来促进结肠癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[12 ] .在卵巢癌中,转化生长因子-β(transforming growth factor-β,TGF-β)可以上调癌症相关成纤维细胞(cancer-associated fibroblast,CAF)来源的versican的表达,高表达的versican通过激活NF-κB信号通路促进肿瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭[47 ] .一项关于肝细胞癌的研究[9 ] 也显示,CAF来源的versican可显著促进肿瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭.胃癌组织中versican的表达与上皮-间质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition,EMT)相关蛋白的表达密切相关,且高表达versican的患者更容易发生淋巴结转移,提示versican可以通过调节EMT促进胃癌细胞的远处转移[48 ] .一项关于乳腺癌的研究[49 ] 发现,versican不仅可以增强肿瘤细胞在骨组织中的迁移、侵袭及生存能力,而且还能够抑制前成骨细胞的生长和分化,进而促进乳腺癌的骨转移.另一项乳腺癌的研究[50 ] 显示,ECM中versican的高表达与肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(tumor-associated macrophage,TAM)的大量浸润相关,而后者又与小鼠乳腺癌的肺转移结节数量的增加有关.Versican或将成为治疗恶性肿瘤转移的新靶点.(图1 ) ...
2
... 近年来,随着肿瘤的预防、诊断和治疗方法的不断进步,很多肿瘤患者的预后得到改善,但恶性肿瘤仍是全球人类死亡的主要原因之一[1 ] .因此,明确恶性肿瘤的发生发展机制,探索新的治疗靶点,对提高肿瘤治疗效果,改善患者预后尤为重要.肿瘤的发生发展不仅取决于肿瘤细胞自身,而且与肿瘤微环境(tumor microenvironment,TME)也密切相关[2 -3 ] .细胞外基质(extracellular matrix,ECM)是TME的重要组成部分,在肿瘤的发生发展中起着关键作用[4 ] .多能蛋白聚糖(versican)是一种大分子的硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖,属于外源凝集素蛋白聚糖家族,由染色体5q12~5q14位点上的VCAN 基因编码,是ECM的主要成分[5 ] .体内外研究显示,泌尿系统肿瘤[6 -7 ] 、肝细胞癌[8 -10 ] 、结直肠癌[11 -12 ] 、胃癌[13 -16 ] 等多种肿瘤组织中均存在versican的高表达,且与患者的不良预后密切相关,这为肿瘤的早期诊断和预后评估提供了新的生物标志物.然而,versican在恶性肿瘤中的作用机制尚未完全明确,现就目前versican在恶性肿瘤中的表达及生物学作用的相关研究进行综述. ...
... Versican与透明质酸相互作用可以吸引免疫细胞的黏附,从而减缓免疫细胞在组织中的迁移速度[53 -54 ] .此外,versican与其他ECM蛋白相互结合形成纤维结构来增加组织硬度,以形成天然的“物理屏障”,阻碍T细胞浸润,抑制肿瘤的免疫应答[55 ] .肝细胞癌组织中versican的表达与程序性死亡受体-1(programmed death-1,PD-1)、细胞毒性T淋巴细胞相关抗原-4(cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4,CTLA-4)的表达均呈明显的正相关,而与肿瘤突变负荷(tumor mutational burden,TMB)呈明显的负相关,这表明versican可能是恶性肿瘤免疫治疗耐药的潜在生物标志物之一[10 ] .(图1 ) ...
2
... 近年来,随着肿瘤的预防、诊断和治疗方法的不断进步,很多肿瘤患者的预后得到改善,但恶性肿瘤仍是全球人类死亡的主要原因之一[1 ] .因此,明确恶性肿瘤的发生发展机制,探索新的治疗靶点,对提高肿瘤治疗效果,改善患者预后尤为重要.肿瘤的发生发展不仅取决于肿瘤细胞自身,而且与肿瘤微环境(tumor microenvironment,TME)也密切相关[2 -3 ] .细胞外基质(extracellular matrix,ECM)是TME的重要组成部分,在肿瘤的发生发展中起着关键作用[4 ] .多能蛋白聚糖(versican)是一种大分子的硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖,属于外源凝集素蛋白聚糖家族,由染色体5q12~5q14位点上的VCAN 基因编码,是ECM的主要成分[5 ] .体内外研究显示,泌尿系统肿瘤[6 -7 ] 、肝细胞癌[8 -10 ] 、结直肠癌[11 -12 ] 、胃癌[13 -16 ] 等多种肿瘤组织中均存在versican的高表达,且与患者的不良预后密切相关,这为肿瘤的早期诊断和预后评估提供了新的生物标志物.然而,versican在恶性肿瘤中的作用机制尚未完全明确,现就目前versican在恶性肿瘤中的表达及生物学作用的相关研究进行综述. ...
... Versican在多种肿瘤组织中异常表达,且与患者的临床病理特征及预后密切相关.一项研究[6 ] 表明,versican在肾细胞癌组织中高表达,并且其高表达与根治性肾切除术后的肿瘤复发转移率升高及患者5年生存率下降密切相关.Versican的V1亚型在肝细胞癌组织中高表达,并与不良预后相关[8 ,35 ] ;与正常肝脏组织相比,肝细胞癌组织中versican表达上调,并且恶性程度越高的亚型中versican的表达水平越高[8 ] .与腺瘤相比,结直肠癌组织中versican的表达显著增高,并且versican的表达促进了腺瘤向结直肠癌发展[11 ] .胃癌组织中versican的表达水平明显高于正常胃黏膜组织,并且versican的高表达与较高的TNM分期及患者的不良预后密切相关[15 ] ,是胃癌患者预后不良的独立预测因子[36 ] .在食管鳞状细胞癌组织中,versican较癌旁组织显著增高,且versican高表达患者的无病生存期明显缩短[37 ] .进一步的研究[38 ] 表明,食管癌组织中versican高表达与肿瘤血管和淋巴管浸润增加、淋巴结转移及患者预后不佳显著相关.在卵巢癌组织中,同样存在versican的高表达,且versican的高表达与卵巢癌腹膜转移率增加密切相关[39 ] . ...
2
... 近年来,随着肿瘤的预防、诊断和治疗方法的不断进步,很多肿瘤患者的预后得到改善,但恶性肿瘤仍是全球人类死亡的主要原因之一[1 ] .因此,明确恶性肿瘤的发生发展机制,探索新的治疗靶点,对提高肿瘤治疗效果,改善患者预后尤为重要.肿瘤的发生发展不仅取决于肿瘤细胞自身,而且与肿瘤微环境(tumor microenvironment,TME)也密切相关[2 -3 ] .细胞外基质(extracellular matrix,ECM)是TME的重要组成部分,在肿瘤的发生发展中起着关键作用[4 ] .多能蛋白聚糖(versican)是一种大分子的硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖,属于外源凝集素蛋白聚糖家族,由染色体5q12~5q14位点上的VCAN 基因编码,是ECM的主要成分[5 ] .体内外研究显示,泌尿系统肿瘤[6 -7 ] 、肝细胞癌[8 -10 ] 、结直肠癌[11 -12 ] 、胃癌[13 -16 ] 等多种肿瘤组织中均存在versican的高表达,且与患者的不良预后密切相关,这为肿瘤的早期诊断和预后评估提供了新的生物标志物.然而,versican在恶性肿瘤中的作用机制尚未完全明确,现就目前versican在恶性肿瘤中的表达及生物学作用的相关研究进行综述. ...
... 关于恶性星形细胞瘤的研究[41 ,46 ] 显示,versican的G1结构域通过与透明质酸、HAPLN1结合来减少肿瘤细胞的黏附,增强肿瘤细胞的迁移能力.而G3结构域的类EGF重复序列通过激活EGFR/PI3K/AKT信号通路,促进肝癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[35 ] .抑制素βA亚基可以通过上调versican的表达来促进结肠癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[12 ] .在卵巢癌中,转化生长因子-β(transforming growth factor-β,TGF-β)可以上调癌症相关成纤维细胞(cancer-associated fibroblast,CAF)来源的versican的表达,高表达的versican通过激活NF-κB信号通路促进肿瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭[47 ] .一项关于肝细胞癌的研究[9 ] 也显示,CAF来源的versican可显著促进肿瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭.胃癌组织中versican的表达与上皮-间质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition,EMT)相关蛋白的表达密切相关,且高表达versican的患者更容易发生淋巴结转移,提示versican可以通过调节EMT促进胃癌细胞的远处转移[48 ] .一项关于乳腺癌的研究[49 ] 发现,versican不仅可以增强肿瘤细胞在骨组织中的迁移、侵袭及生存能力,而且还能够抑制前成骨细胞的生长和分化,进而促进乳腺癌的骨转移.另一项乳腺癌的研究[50 ] 显示,ECM中versican的高表达与肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(tumor-associated macrophage,TAM)的大量浸润相关,而后者又与小鼠乳腺癌的肺转移结节数量的增加有关.Versican或将成为治疗恶性肿瘤转移的新靶点.(图1 ) ...
1
... 近年来,随着肿瘤的预防、诊断和治疗方法的不断进步,很多肿瘤患者的预后得到改善,但恶性肿瘤仍是全球人类死亡的主要原因之一[1 ] .因此,明确恶性肿瘤的发生发展机制,探索新的治疗靶点,对提高肿瘤治疗效果,改善患者预后尤为重要.肿瘤的发生发展不仅取决于肿瘤细胞自身,而且与肿瘤微环境(tumor microenvironment,TME)也密切相关[2 -3 ] .细胞外基质(extracellular matrix,ECM)是TME的重要组成部分,在肿瘤的发生发展中起着关键作用[4 ] .多能蛋白聚糖(versican)是一种大分子的硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖,属于外源凝集素蛋白聚糖家族,由染色体5q12~5q14位点上的VCAN 基因编码,是ECM的主要成分[5 ] .体内外研究显示,泌尿系统肿瘤[6 -7 ] 、肝细胞癌[8 -10 ] 、结直肠癌[11 -12 ] 、胃癌[13 -16 ] 等多种肿瘤组织中均存在versican的高表达,且与患者的不良预后密切相关,这为肿瘤的早期诊断和预后评估提供了新的生物标志物.然而,versican在恶性肿瘤中的作用机制尚未完全明确,现就目前versican在恶性肿瘤中的表达及生物学作用的相关研究进行综述. ...
1
... Versican在多种肿瘤组织中异常表达,且与患者的临床病理特征及预后密切相关.一项研究[6 ] 表明,versican在肾细胞癌组织中高表达,并且其高表达与根治性肾切除术后的肿瘤复发转移率升高及患者5年生存率下降密切相关.Versican的V1亚型在肝细胞癌组织中高表达,并与不良预后相关[8 ,35 ] ;与正常肝脏组织相比,肝细胞癌组织中versican表达上调,并且恶性程度越高的亚型中versican的表达水平越高[8 ] .与腺瘤相比,结直肠癌组织中versican的表达显著增高,并且versican的表达促进了腺瘤向结直肠癌发展[11 ] .胃癌组织中versican的表达水平明显高于正常胃黏膜组织,并且versican的高表达与较高的TNM分期及患者的不良预后密切相关[15 ] ,是胃癌患者预后不良的独立预测因子[36 ] .在食管鳞状细胞癌组织中,versican较癌旁组织显著增高,且versican高表达患者的无病生存期明显缩短[37 ] .进一步的研究[38 ] 表明,食管癌组织中versican高表达与肿瘤血管和淋巴管浸润增加、淋巴结转移及患者预后不佳显著相关.在卵巢癌组织中,同样存在versican的高表达,且versican的高表达与卵巢癌腹膜转移率增加密切相关[39 ] . ...
1
... 近年来,随着肿瘤的预防、诊断和治疗方法的不断进步,很多肿瘤患者的预后得到改善,但恶性肿瘤仍是全球人类死亡的主要原因之一[1 ] .因此,明确恶性肿瘤的发生发展机制,探索新的治疗靶点,对提高肿瘤治疗效果,改善患者预后尤为重要.肿瘤的发生发展不仅取决于肿瘤细胞自身,而且与肿瘤微环境(tumor microenvironment,TME)也密切相关[2 -3 ] .细胞外基质(extracellular matrix,ECM)是TME的重要组成部分,在肿瘤的发生发展中起着关键作用[4 ] .多能蛋白聚糖(versican)是一种大分子的硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖,属于外源凝集素蛋白聚糖家族,由染色体5q12~5q14位点上的VCAN 基因编码,是ECM的主要成分[5 ] .体内外研究显示,泌尿系统肿瘤[6 -7 ] 、肝细胞癌[8 -10 ] 、结直肠癌[11 -12 ] 、胃癌[13 -16 ] 等多种肿瘤组织中均存在versican的高表达,且与患者的不良预后密切相关,这为肿瘤的早期诊断和预后评估提供了新的生物标志物.然而,versican在恶性肿瘤中的作用机制尚未完全明确,现就目前versican在恶性肿瘤中的表达及生物学作用的相关研究进行综述. ...
3
... Versican由3个不同的区域组成,分别为N端的G1结构域、C端的G3结构域及连接G1和G3的糖胺聚糖(glycosaminoglycan,GAG)[17 ] .其中G1结构域由1个免疫球蛋白(immunoglobulin,Ig)样模块和2个透明质酸结合区(即链接模块)构成[17 ] ;而G3结构域则由2个类表皮生长因子(epidermal growth factor,EGF)重复序列、1个碳水化合物识别区域(carbohydrate recognition domain,CRD;又称类凝集素序列)和1个补体结合蛋白(complement binding protein,CBP)调控序列组成[18 ] .GAG位于versican的中心,是硫酸软骨素(chondroitinsulfate,CS)链的附着区[19 ] .由于mRNA的选择性剪切,versican至少存在5种亚型,即V0~V4,每一种亚型具有不同长度的GAG,相对地可以结合不同数量的CS链[19 ] .其中V0亚型包含α-GAG和β-GAG,V1和V4亚型仅包含β-GAG,V2亚型仅包含α-GAG,而V3亚型则没有GAG[17 ] . ...
... [17 ];而G3结构域则由2个类表皮生长因子(epidermal growth factor,EGF)重复序列、1个碳水化合物识别区域(carbohydrate recognition domain,CRD;又称类凝集素序列)和1个补体结合蛋白(complement binding protein,CBP)调控序列组成[18 ] .GAG位于versican的中心,是硫酸软骨素(chondroitinsulfate,CS)链的附着区[19 ] .由于mRNA的选择性剪切,versican至少存在5种亚型,即V0~V4,每一种亚型具有不同长度的GAG,相对地可以结合不同数量的CS链[19 ] .其中V0亚型包含α-GAG和β-GAG,V1和V4亚型仅包含β-GAG,V2亚型仅包含α-GAG,而V3亚型则没有GAG[17 ] . ...
... [17 ]. ...
1
... Versican由3个不同的区域组成,分别为N端的G1结构域、C端的G3结构域及连接G1和G3的糖胺聚糖(glycosaminoglycan,GAG)[17 ] .其中G1结构域由1个免疫球蛋白(immunoglobulin,Ig)样模块和2个透明质酸结合区(即链接模块)构成[17 ] ;而G3结构域则由2个类表皮生长因子(epidermal growth factor,EGF)重复序列、1个碳水化合物识别区域(carbohydrate recognition domain,CRD;又称类凝集素序列)和1个补体结合蛋白(complement binding protein,CBP)调控序列组成[18 ] .GAG位于versican的中心,是硫酸软骨素(chondroitinsulfate,CS)链的附着区[19 ] .由于mRNA的选择性剪切,versican至少存在5种亚型,即V0~V4,每一种亚型具有不同长度的GAG,相对地可以结合不同数量的CS链[19 ] .其中V0亚型包含α-GAG和β-GAG,V1和V4亚型仅包含β-GAG,V2亚型仅包含α-GAG,而V3亚型则没有GAG[17 ] . ...
2
... Versican由3个不同的区域组成,分别为N端的G1结构域、C端的G3结构域及连接G1和G3的糖胺聚糖(glycosaminoglycan,GAG)[17 ] .其中G1结构域由1个免疫球蛋白(immunoglobulin,Ig)样模块和2个透明质酸结合区(即链接模块)构成[17 ] ;而G3结构域则由2个类表皮生长因子(epidermal growth factor,EGF)重复序列、1个碳水化合物识别区域(carbohydrate recognition domain,CRD;又称类凝集素序列)和1个补体结合蛋白(complement binding protein,CBP)调控序列组成[18 ] .GAG位于versican的中心,是硫酸软骨素(chondroitinsulfate,CS)链的附着区[19 ] .由于mRNA的选择性剪切,versican至少存在5种亚型,即V0~V4,每一种亚型具有不同长度的GAG,相对地可以结合不同数量的CS链[19 ] .其中V0亚型包含α-GAG和β-GAG,V1和V4亚型仅包含β-GAG,V2亚型仅包含α-GAG,而V3亚型则没有GAG[17 ] . ...
... [19 ].其中V0亚型包含α-GAG和β-GAG,V1和V4亚型仅包含β-GAG,V2亚型仅包含α-GAG,而V3亚型则没有GAG[17 ] . ...
2
... Versican在胚胎发育和炎症反应过程中均发挥重要作用.首先,在胚胎发育过程中,versican对于心血管形态的发生、神经及骨骼的发育至关重要[20 -22 ] .研究[20 ] 发现,在心脏的发育过程中,水解versican可以使心脏共同出口远端区域的心肌退化,逐渐被平滑肌取代并发育成动脉组织,促进心脏流出道(outflow tract,OFT)的形成.最近研究[23 ] 发现,versican在心肌细胞增殖和心肌修复过程中发挥重要作用.同时,versican还可以影响神经轴突的生长,从而调节神经组织的发育过程[21 ] .间充质细胞的凝聚是软骨发育的重要步骤,versican的CS链可以促进间充质基质的形成和软骨细胞的分化[22 ] .其次,在由感染和组织损伤引起的炎症反应过程中,versican也发挥着关键作用[24 ] .Versican作为ECM的重要组分之一,可以与透明质酸、肿瘤坏死因子刺激基因-6(tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene-6,TSG-6)蛋白、间α胰蛋白酶抑制剂(inter-α-trypsin inhibitor,ITI)等多种分子相互作用,形成稳定的支架,为侵入组织的炎症细胞充当“着陆带”[25 -27 ] .Versican可以直接通过CD44、P-选择素糖蛋白配体-1(P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1,PSGL-1)、Toll样受体(toll-like receptor,TLR)等细胞表面分子,或间接通过透明质酸与炎症细胞相互作用,从而促进肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)、白细胞介素-6(interleukin-6,IL-6)和核因子κB(nuclear factor κB,NF-κB)等炎症细胞因子的合成和分泌[27 ] .Versican还可以通过与多种调节炎症的细胞因子相互作用,影响它们的生物利用度和生物活性[28 ] .在小鼠肺炎模型中,敲除Vcan 基因,可降低蛋白versican表达,显著减少白细胞对肺的侵袭,并减少炎症细胞因子的表达[29 ] .不同的versican亚型的功能各不相同.如在神经系统发育过程中,versican V0和V1亚型可以抑制神经嵴细胞的迁移[30 ] .V1亚型可以促进神经轴突的生长[31 ] ,而V2亚型则表现为抑制[21 ] .此外V1亚型可以通过增强表皮生长因子受体(epithelial growth factor receptor,EGFR)和整合素的表达来诱导神经元的分化,而V2亚型则无此功能[31 ] .V3亚型的表达可以减少脂质的沉积和单核巨噬细胞的积累,从而降低动脉粥样硬化的发生[32 -33 ] .近年来,研究人员在乳腺癌组织中发现了V4亚型的存在,但其功能仍待进一步明确[34 ] . ...
... [20 ]发现,在心脏的发育过程中,水解versican可以使心脏共同出口远端区域的心肌退化,逐渐被平滑肌取代并发育成动脉组织,促进心脏流出道(outflow tract,OFT)的形成.最近研究[23 ] 发现,versican在心肌细胞增殖和心肌修复过程中发挥重要作用.同时,versican还可以影响神经轴突的生长,从而调节神经组织的发育过程[21 ] .间充质细胞的凝聚是软骨发育的重要步骤,versican的CS链可以促进间充质基质的形成和软骨细胞的分化[22 ] .其次,在由感染和组织损伤引起的炎症反应过程中,versican也发挥着关键作用[24 ] .Versican作为ECM的重要组分之一,可以与透明质酸、肿瘤坏死因子刺激基因-6(tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene-6,TSG-6)蛋白、间α胰蛋白酶抑制剂(inter-α-trypsin inhibitor,ITI)等多种分子相互作用,形成稳定的支架,为侵入组织的炎症细胞充当“着陆带”[25 -27 ] .Versican可以直接通过CD44、P-选择素糖蛋白配体-1(P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1,PSGL-1)、Toll样受体(toll-like receptor,TLR)等细胞表面分子,或间接通过透明质酸与炎症细胞相互作用,从而促进肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)、白细胞介素-6(interleukin-6,IL-6)和核因子κB(nuclear factor κB,NF-κB)等炎症细胞因子的合成和分泌[27 ] .Versican还可以通过与多种调节炎症的细胞因子相互作用,影响它们的生物利用度和生物活性[28 ] .在小鼠肺炎模型中,敲除Vcan 基因,可降低蛋白versican表达,显著减少白细胞对肺的侵袭,并减少炎症细胞因子的表达[29 ] .不同的versican亚型的功能各不相同.如在神经系统发育过程中,versican V0和V1亚型可以抑制神经嵴细胞的迁移[30 ] .V1亚型可以促进神经轴突的生长[31 ] ,而V2亚型则表现为抑制[21 ] .此外V1亚型可以通过增强表皮生长因子受体(epithelial growth factor receptor,EGFR)和整合素的表达来诱导神经元的分化,而V2亚型则无此功能[31 ] .V3亚型的表达可以减少脂质的沉积和单核巨噬细胞的积累,从而降低动脉粥样硬化的发生[32 -33 ] .近年来,研究人员在乳腺癌组织中发现了V4亚型的存在,但其功能仍待进一步明确[34 ] . ...
2
... Versican在胚胎发育和炎症反应过程中均发挥重要作用.首先,在胚胎发育过程中,versican对于心血管形态的发生、神经及骨骼的发育至关重要[20 -22 ] .研究[20 ] 发现,在心脏的发育过程中,水解versican可以使心脏共同出口远端区域的心肌退化,逐渐被平滑肌取代并发育成动脉组织,促进心脏流出道(outflow tract,OFT)的形成.最近研究[23 ] 发现,versican在心肌细胞增殖和心肌修复过程中发挥重要作用.同时,versican还可以影响神经轴突的生长,从而调节神经组织的发育过程[21 ] .间充质细胞的凝聚是软骨发育的重要步骤,versican的CS链可以促进间充质基质的形成和软骨细胞的分化[22 ] .其次,在由感染和组织损伤引起的炎症反应过程中,versican也发挥着关键作用[24 ] .Versican作为ECM的重要组分之一,可以与透明质酸、肿瘤坏死因子刺激基因-6(tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene-6,TSG-6)蛋白、间α胰蛋白酶抑制剂(inter-α-trypsin inhibitor,ITI)等多种分子相互作用,形成稳定的支架,为侵入组织的炎症细胞充当“着陆带”[25 -27 ] .Versican可以直接通过CD44、P-选择素糖蛋白配体-1(P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1,PSGL-1)、Toll样受体(toll-like receptor,TLR)等细胞表面分子,或间接通过透明质酸与炎症细胞相互作用,从而促进肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)、白细胞介素-6(interleukin-6,IL-6)和核因子κB(nuclear factor κB,NF-κB)等炎症细胞因子的合成和分泌[27 ] .Versican还可以通过与多种调节炎症的细胞因子相互作用,影响它们的生物利用度和生物活性[28 ] .在小鼠肺炎模型中,敲除Vcan 基因,可降低蛋白versican表达,显著减少白细胞对肺的侵袭,并减少炎症细胞因子的表达[29 ] .不同的versican亚型的功能各不相同.如在神经系统发育过程中,versican V0和V1亚型可以抑制神经嵴细胞的迁移[30 ] .V1亚型可以促进神经轴突的生长[31 ] ,而V2亚型则表现为抑制[21 ] .此外V1亚型可以通过增强表皮生长因子受体(epithelial growth factor receptor,EGFR)和整合素的表达来诱导神经元的分化,而V2亚型则无此功能[31 ] .V3亚型的表达可以减少脂质的沉积和单核巨噬细胞的积累,从而降低动脉粥样硬化的发生[32 -33 ] .近年来,研究人员在乳腺癌组织中发现了V4亚型的存在,但其功能仍待进一步明确[34 ] . ...
... [21 ].此外V1亚型可以通过增强表皮生长因子受体(epithelial growth factor receptor,EGFR)和整合素的表达来诱导神经元的分化,而V2亚型则无此功能[31 ] .V3亚型的表达可以减少脂质的沉积和单核巨噬细胞的积累,从而降低动脉粥样硬化的发生[32 -33 ] .近年来,研究人员在乳腺癌组织中发现了V4亚型的存在,但其功能仍待进一步明确[34 ] . ...
2
... Versican在胚胎发育和炎症反应过程中均发挥重要作用.首先,在胚胎发育过程中,versican对于心血管形态的发生、神经及骨骼的发育至关重要[20 -22 ] .研究[20 ] 发现,在心脏的发育过程中,水解versican可以使心脏共同出口远端区域的心肌退化,逐渐被平滑肌取代并发育成动脉组织,促进心脏流出道(outflow tract,OFT)的形成.最近研究[23 ] 发现,versican在心肌细胞增殖和心肌修复过程中发挥重要作用.同时,versican还可以影响神经轴突的生长,从而调节神经组织的发育过程[21 ] .间充质细胞的凝聚是软骨发育的重要步骤,versican的CS链可以促进间充质基质的形成和软骨细胞的分化[22 ] .其次,在由感染和组织损伤引起的炎症反应过程中,versican也发挥着关键作用[24 ] .Versican作为ECM的重要组分之一,可以与透明质酸、肿瘤坏死因子刺激基因-6(tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene-6,TSG-6)蛋白、间α胰蛋白酶抑制剂(inter-α-trypsin inhibitor,ITI)等多种分子相互作用,形成稳定的支架,为侵入组织的炎症细胞充当“着陆带”[25 -27 ] .Versican可以直接通过CD44、P-选择素糖蛋白配体-1(P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1,PSGL-1)、Toll样受体(toll-like receptor,TLR)等细胞表面分子,或间接通过透明质酸与炎症细胞相互作用,从而促进肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)、白细胞介素-6(interleukin-6,IL-6)和核因子κB(nuclear factor κB,NF-κB)等炎症细胞因子的合成和分泌[27 ] .Versican还可以通过与多种调节炎症的细胞因子相互作用,影响它们的生物利用度和生物活性[28 ] .在小鼠肺炎模型中,敲除Vcan 基因,可降低蛋白versican表达,显著减少白细胞对肺的侵袭,并减少炎症细胞因子的表达[29 ] .不同的versican亚型的功能各不相同.如在神经系统发育过程中,versican V0和V1亚型可以抑制神经嵴细胞的迁移[30 ] .V1亚型可以促进神经轴突的生长[31 ] ,而V2亚型则表现为抑制[21 ] .此外V1亚型可以通过增强表皮生长因子受体(epithelial growth factor receptor,EGFR)和整合素的表达来诱导神经元的分化,而V2亚型则无此功能[31 ] .V3亚型的表达可以减少脂质的沉积和单核巨噬细胞的积累,从而降低动脉粥样硬化的发生[32 -33 ] .近年来,研究人员在乳腺癌组织中发现了V4亚型的存在,但其功能仍待进一步明确[34 ] . ...
... [22 ].其次,在由感染和组织损伤引起的炎症反应过程中,versican也发挥着关键作用[24 ] .Versican作为ECM的重要组分之一,可以与透明质酸、肿瘤坏死因子刺激基因-6(tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene-6,TSG-6)蛋白、间α胰蛋白酶抑制剂(inter-α-trypsin inhibitor,ITI)等多种分子相互作用,形成稳定的支架,为侵入组织的炎症细胞充当“着陆带”[25 -27 ] .Versican可以直接通过CD44、P-选择素糖蛋白配体-1(P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1,PSGL-1)、Toll样受体(toll-like receptor,TLR)等细胞表面分子,或间接通过透明质酸与炎症细胞相互作用,从而促进肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)、白细胞介素-6(interleukin-6,IL-6)和核因子κB(nuclear factor κB,NF-κB)等炎症细胞因子的合成和分泌[27 ] .Versican还可以通过与多种调节炎症的细胞因子相互作用,影响它们的生物利用度和生物活性[28 ] .在小鼠肺炎模型中,敲除Vcan 基因,可降低蛋白versican表达,显著减少白细胞对肺的侵袭,并减少炎症细胞因子的表达[29 ] .不同的versican亚型的功能各不相同.如在神经系统发育过程中,versican V0和V1亚型可以抑制神经嵴细胞的迁移[30 ] .V1亚型可以促进神经轴突的生长[31 ] ,而V2亚型则表现为抑制[21 ] .此外V1亚型可以通过增强表皮生长因子受体(epithelial growth factor receptor,EGFR)和整合素的表达来诱导神经元的分化,而V2亚型则无此功能[31 ] .V3亚型的表达可以减少脂质的沉积和单核巨噬细胞的积累,从而降低动脉粥样硬化的发生[32 -33 ] .近年来,研究人员在乳腺癌组织中发现了V4亚型的存在,但其功能仍待进一步明确[34 ] . ...
1
... Versican在胚胎发育和炎症反应过程中均发挥重要作用.首先,在胚胎发育过程中,versican对于心血管形态的发生、神经及骨骼的发育至关重要[20 -22 ] .研究[20 ] 发现,在心脏的发育过程中,水解versican可以使心脏共同出口远端区域的心肌退化,逐渐被平滑肌取代并发育成动脉组织,促进心脏流出道(outflow tract,OFT)的形成.最近研究[23 ] 发现,versican在心肌细胞增殖和心肌修复过程中发挥重要作用.同时,versican还可以影响神经轴突的生长,从而调节神经组织的发育过程[21 ] .间充质细胞的凝聚是软骨发育的重要步骤,versican的CS链可以促进间充质基质的形成和软骨细胞的分化[22 ] .其次,在由感染和组织损伤引起的炎症反应过程中,versican也发挥着关键作用[24 ] .Versican作为ECM的重要组分之一,可以与透明质酸、肿瘤坏死因子刺激基因-6(tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene-6,TSG-6)蛋白、间α胰蛋白酶抑制剂(inter-α-trypsin inhibitor,ITI)等多种分子相互作用,形成稳定的支架,为侵入组织的炎症细胞充当“着陆带”[25 -27 ] .Versican可以直接通过CD44、P-选择素糖蛋白配体-1(P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1,PSGL-1)、Toll样受体(toll-like receptor,TLR)等细胞表面分子,或间接通过透明质酸与炎症细胞相互作用,从而促进肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)、白细胞介素-6(interleukin-6,IL-6)和核因子κB(nuclear factor κB,NF-κB)等炎症细胞因子的合成和分泌[27 ] .Versican还可以通过与多种调节炎症的细胞因子相互作用,影响它们的生物利用度和生物活性[28 ] .在小鼠肺炎模型中,敲除Vcan 基因,可降低蛋白versican表达,显著减少白细胞对肺的侵袭,并减少炎症细胞因子的表达[29 ] .不同的versican亚型的功能各不相同.如在神经系统发育过程中,versican V0和V1亚型可以抑制神经嵴细胞的迁移[30 ] .V1亚型可以促进神经轴突的生长[31 ] ,而V2亚型则表现为抑制[21 ] .此外V1亚型可以通过增强表皮生长因子受体(epithelial growth factor receptor,EGFR)和整合素的表达来诱导神经元的分化,而V2亚型则无此功能[31 ] .V3亚型的表达可以减少脂质的沉积和单核巨噬细胞的积累,从而降低动脉粥样硬化的发生[32 -33 ] .近年来,研究人员在乳腺癌组织中发现了V4亚型的存在,但其功能仍待进一步明确[34 ] . ...
1
... Versican在胚胎发育和炎症反应过程中均发挥重要作用.首先,在胚胎发育过程中,versican对于心血管形态的发生、神经及骨骼的发育至关重要[20 -22 ] .研究[20 ] 发现,在心脏的发育过程中,水解versican可以使心脏共同出口远端区域的心肌退化,逐渐被平滑肌取代并发育成动脉组织,促进心脏流出道(outflow tract,OFT)的形成.最近研究[23 ] 发现,versican在心肌细胞增殖和心肌修复过程中发挥重要作用.同时,versican还可以影响神经轴突的生长,从而调节神经组织的发育过程[21 ] .间充质细胞的凝聚是软骨发育的重要步骤,versican的CS链可以促进间充质基质的形成和软骨细胞的分化[22 ] .其次,在由感染和组织损伤引起的炎症反应过程中,versican也发挥着关键作用[24 ] .Versican作为ECM的重要组分之一,可以与透明质酸、肿瘤坏死因子刺激基因-6(tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene-6,TSG-6)蛋白、间α胰蛋白酶抑制剂(inter-α-trypsin inhibitor,ITI)等多种分子相互作用,形成稳定的支架,为侵入组织的炎症细胞充当“着陆带”[25 -27 ] .Versican可以直接通过CD44、P-选择素糖蛋白配体-1(P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1,PSGL-1)、Toll样受体(toll-like receptor,TLR)等细胞表面分子,或间接通过透明质酸与炎症细胞相互作用,从而促进肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)、白细胞介素-6(interleukin-6,IL-6)和核因子κB(nuclear factor κB,NF-κB)等炎症细胞因子的合成和分泌[27 ] .Versican还可以通过与多种调节炎症的细胞因子相互作用,影响它们的生物利用度和生物活性[28 ] .在小鼠肺炎模型中,敲除Vcan 基因,可降低蛋白versican表达,显著减少白细胞对肺的侵袭,并减少炎症细胞因子的表达[29 ] .不同的versican亚型的功能各不相同.如在神经系统发育过程中,versican V0和V1亚型可以抑制神经嵴细胞的迁移[30 ] .V1亚型可以促进神经轴突的生长[31 ] ,而V2亚型则表现为抑制[21 ] .此外V1亚型可以通过增强表皮生长因子受体(epithelial growth factor receptor,EGFR)和整合素的表达来诱导神经元的分化,而V2亚型则无此功能[31 ] .V3亚型的表达可以减少脂质的沉积和单核巨噬细胞的积累,从而降低动脉粥样硬化的发生[32 -33 ] .近年来,研究人员在乳腺癌组织中发现了V4亚型的存在,但其功能仍待进一步明确[34 ] . ...
1
... Versican在胚胎发育和炎症反应过程中均发挥重要作用.首先,在胚胎发育过程中,versican对于心血管形态的发生、神经及骨骼的发育至关重要[20 -22 ] .研究[20 ] 发现,在心脏的发育过程中,水解versican可以使心脏共同出口远端区域的心肌退化,逐渐被平滑肌取代并发育成动脉组织,促进心脏流出道(outflow tract,OFT)的形成.最近研究[23 ] 发现,versican在心肌细胞增殖和心肌修复过程中发挥重要作用.同时,versican还可以影响神经轴突的生长,从而调节神经组织的发育过程[21 ] .间充质细胞的凝聚是软骨发育的重要步骤,versican的CS链可以促进间充质基质的形成和软骨细胞的分化[22 ] .其次,在由感染和组织损伤引起的炎症反应过程中,versican也发挥着关键作用[24 ] .Versican作为ECM的重要组分之一,可以与透明质酸、肿瘤坏死因子刺激基因-6(tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene-6,TSG-6)蛋白、间α胰蛋白酶抑制剂(inter-α-trypsin inhibitor,ITI)等多种分子相互作用,形成稳定的支架,为侵入组织的炎症细胞充当“着陆带”[25 -27 ] .Versican可以直接通过CD44、P-选择素糖蛋白配体-1(P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1,PSGL-1)、Toll样受体(toll-like receptor,TLR)等细胞表面分子,或间接通过透明质酸与炎症细胞相互作用,从而促进肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)、白细胞介素-6(interleukin-6,IL-6)和核因子κB(nuclear factor κB,NF-κB)等炎症细胞因子的合成和分泌[27 ] .Versican还可以通过与多种调节炎症的细胞因子相互作用,影响它们的生物利用度和生物活性[28 ] .在小鼠肺炎模型中,敲除Vcan 基因,可降低蛋白versican表达,显著减少白细胞对肺的侵袭,并减少炎症细胞因子的表达[29 ] .不同的versican亚型的功能各不相同.如在神经系统发育过程中,versican V0和V1亚型可以抑制神经嵴细胞的迁移[30 ] .V1亚型可以促进神经轴突的生长[31 ] ,而V2亚型则表现为抑制[21 ] .此外V1亚型可以通过增强表皮生长因子受体(epithelial growth factor receptor,EGFR)和整合素的表达来诱导神经元的分化,而V2亚型则无此功能[31 ] .V3亚型的表达可以减少脂质的沉积和单核巨噬细胞的积累,从而降低动脉粥样硬化的发生[32 -33 ] .近年来,研究人员在乳腺癌组织中发现了V4亚型的存在,但其功能仍待进一步明确[34 ] . ...
2
... Versican在胚胎发育和炎症反应过程中均发挥重要作用.首先,在胚胎发育过程中,versican对于心血管形态的发生、神经及骨骼的发育至关重要[20 -22 ] .研究[20 ] 发现,在心脏的发育过程中,水解versican可以使心脏共同出口远端区域的心肌退化,逐渐被平滑肌取代并发育成动脉组织,促进心脏流出道(outflow tract,OFT)的形成.最近研究[23 ] 发现,versican在心肌细胞增殖和心肌修复过程中发挥重要作用.同时,versican还可以影响神经轴突的生长,从而调节神经组织的发育过程[21 ] .间充质细胞的凝聚是软骨发育的重要步骤,versican的CS链可以促进间充质基质的形成和软骨细胞的分化[22 ] .其次,在由感染和组织损伤引起的炎症反应过程中,versican也发挥着关键作用[24 ] .Versican作为ECM的重要组分之一,可以与透明质酸、肿瘤坏死因子刺激基因-6(tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene-6,TSG-6)蛋白、间α胰蛋白酶抑制剂(inter-α-trypsin inhibitor,ITI)等多种分子相互作用,形成稳定的支架,为侵入组织的炎症细胞充当“着陆带”[25 -27 ] .Versican可以直接通过CD44、P-选择素糖蛋白配体-1(P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1,PSGL-1)、Toll样受体(toll-like receptor,TLR)等细胞表面分子,或间接通过透明质酸与炎症细胞相互作用,从而促进肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)、白细胞介素-6(interleukin-6,IL-6)和核因子κB(nuclear factor κB,NF-κB)等炎症细胞因子的合成和分泌[27 ] .Versican还可以通过与多种调节炎症的细胞因子相互作用,影响它们的生物利用度和生物活性[28 ] .在小鼠肺炎模型中,敲除Vcan 基因,可降低蛋白versican表达,显著减少白细胞对肺的侵袭,并减少炎症细胞因子的表达[29 ] .不同的versican亚型的功能各不相同.如在神经系统发育过程中,versican V0和V1亚型可以抑制神经嵴细胞的迁移[30 ] .V1亚型可以促进神经轴突的生长[31 ] ,而V2亚型则表现为抑制[21 ] .此外V1亚型可以通过增强表皮生长因子受体(epithelial growth factor receptor,EGFR)和整合素的表达来诱导神经元的分化,而V2亚型则无此功能[31 ] .V3亚型的表达可以减少脂质的沉积和单核巨噬细胞的积累,从而降低动脉粥样硬化的发生[32 -33 ] .近年来,研究人员在乳腺癌组织中发现了V4亚型的存在,但其功能仍待进一步明确[34 ] . ...
... [27 ].Versican还可以通过与多种调节炎症的细胞因子相互作用,影响它们的生物利用度和生物活性[28 ] .在小鼠肺炎模型中,敲除Vcan 基因,可降低蛋白versican表达,显著减少白细胞对肺的侵袭,并减少炎症细胞因子的表达[29 ] .不同的versican亚型的功能各不相同.如在神经系统发育过程中,versican V0和V1亚型可以抑制神经嵴细胞的迁移[30 ] .V1亚型可以促进神经轴突的生长[31 ] ,而V2亚型则表现为抑制[21 ] .此外V1亚型可以通过增强表皮生长因子受体(epithelial growth factor receptor,EGFR)和整合素的表达来诱导神经元的分化,而V2亚型则无此功能[31 ] .V3亚型的表达可以减少脂质的沉积和单核巨噬细胞的积累,从而降低动脉粥样硬化的发生[32 -33 ] .近年来,研究人员在乳腺癌组织中发现了V4亚型的存在,但其功能仍待进一步明确[34 ] . ...
1
... Versican在胚胎发育和炎症反应过程中均发挥重要作用.首先,在胚胎发育过程中,versican对于心血管形态的发生、神经及骨骼的发育至关重要[20 -22 ] .研究[20 ] 发现,在心脏的发育过程中,水解versican可以使心脏共同出口远端区域的心肌退化,逐渐被平滑肌取代并发育成动脉组织,促进心脏流出道(outflow tract,OFT)的形成.最近研究[23 ] 发现,versican在心肌细胞增殖和心肌修复过程中发挥重要作用.同时,versican还可以影响神经轴突的生长,从而调节神经组织的发育过程[21 ] .间充质细胞的凝聚是软骨发育的重要步骤,versican的CS链可以促进间充质基质的形成和软骨细胞的分化[22 ] .其次,在由感染和组织损伤引起的炎症反应过程中,versican也发挥着关键作用[24 ] .Versican作为ECM的重要组分之一,可以与透明质酸、肿瘤坏死因子刺激基因-6(tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene-6,TSG-6)蛋白、间α胰蛋白酶抑制剂(inter-α-trypsin inhibitor,ITI)等多种分子相互作用,形成稳定的支架,为侵入组织的炎症细胞充当“着陆带”[25 -27 ] .Versican可以直接通过CD44、P-选择素糖蛋白配体-1(P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1,PSGL-1)、Toll样受体(toll-like receptor,TLR)等细胞表面分子,或间接通过透明质酸与炎症细胞相互作用,从而促进肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)、白细胞介素-6(interleukin-6,IL-6)和核因子κB(nuclear factor κB,NF-κB)等炎症细胞因子的合成和分泌[27 ] .Versican还可以通过与多种调节炎症的细胞因子相互作用,影响它们的生物利用度和生物活性[28 ] .在小鼠肺炎模型中,敲除Vcan 基因,可降低蛋白versican表达,显著减少白细胞对肺的侵袭,并减少炎症细胞因子的表达[29 ] .不同的versican亚型的功能各不相同.如在神经系统发育过程中,versican V0和V1亚型可以抑制神经嵴细胞的迁移[30 ] .V1亚型可以促进神经轴突的生长[31 ] ,而V2亚型则表现为抑制[21 ] .此外V1亚型可以通过增强表皮生长因子受体(epithelial growth factor receptor,EGFR)和整合素的表达来诱导神经元的分化,而V2亚型则无此功能[31 ] .V3亚型的表达可以减少脂质的沉积和单核巨噬细胞的积累,从而降低动脉粥样硬化的发生[32 -33 ] .近年来,研究人员在乳腺癌组织中发现了V4亚型的存在,但其功能仍待进一步明确[34 ] . ...
1
... Versican在胚胎发育和炎症反应过程中均发挥重要作用.首先,在胚胎发育过程中,versican对于心血管形态的发生、神经及骨骼的发育至关重要[20 -22 ] .研究[20 ] 发现,在心脏的发育过程中,水解versican可以使心脏共同出口远端区域的心肌退化,逐渐被平滑肌取代并发育成动脉组织,促进心脏流出道(outflow tract,OFT)的形成.最近研究[23 ] 发现,versican在心肌细胞增殖和心肌修复过程中发挥重要作用.同时,versican还可以影响神经轴突的生长,从而调节神经组织的发育过程[21 ] .间充质细胞的凝聚是软骨发育的重要步骤,versican的CS链可以促进间充质基质的形成和软骨细胞的分化[22 ] .其次,在由感染和组织损伤引起的炎症反应过程中,versican也发挥着关键作用[24 ] .Versican作为ECM的重要组分之一,可以与透明质酸、肿瘤坏死因子刺激基因-6(tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene-6,TSG-6)蛋白、间α胰蛋白酶抑制剂(inter-α-trypsin inhibitor,ITI)等多种分子相互作用,形成稳定的支架,为侵入组织的炎症细胞充当“着陆带”[25 -27 ] .Versican可以直接通过CD44、P-选择素糖蛋白配体-1(P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1,PSGL-1)、Toll样受体(toll-like receptor,TLR)等细胞表面分子,或间接通过透明质酸与炎症细胞相互作用,从而促进肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)、白细胞介素-6(interleukin-6,IL-6)和核因子κB(nuclear factor κB,NF-κB)等炎症细胞因子的合成和分泌[27 ] .Versican还可以通过与多种调节炎症的细胞因子相互作用,影响它们的生物利用度和生物活性[28 ] .在小鼠肺炎模型中,敲除Vcan 基因,可降低蛋白versican表达,显著减少白细胞对肺的侵袭,并减少炎症细胞因子的表达[29 ] .不同的versican亚型的功能各不相同.如在神经系统发育过程中,versican V0和V1亚型可以抑制神经嵴细胞的迁移[30 ] .V1亚型可以促进神经轴突的生长[31 ] ,而V2亚型则表现为抑制[21 ] .此外V1亚型可以通过增强表皮生长因子受体(epithelial growth factor receptor,EGFR)和整合素的表达来诱导神经元的分化,而V2亚型则无此功能[31 ] .V3亚型的表达可以减少脂质的沉积和单核巨噬细胞的积累,从而降低动脉粥样硬化的发生[32 -33 ] .近年来,研究人员在乳腺癌组织中发现了V4亚型的存在,但其功能仍待进一步明确[34 ] . ...
1
... Versican在胚胎发育和炎症反应过程中均发挥重要作用.首先,在胚胎发育过程中,versican对于心血管形态的发生、神经及骨骼的发育至关重要[20 -22 ] .研究[20 ] 发现,在心脏的发育过程中,水解versican可以使心脏共同出口远端区域的心肌退化,逐渐被平滑肌取代并发育成动脉组织,促进心脏流出道(outflow tract,OFT)的形成.最近研究[23 ] 发现,versican在心肌细胞增殖和心肌修复过程中发挥重要作用.同时,versican还可以影响神经轴突的生长,从而调节神经组织的发育过程[21 ] .间充质细胞的凝聚是软骨发育的重要步骤,versican的CS链可以促进间充质基质的形成和软骨细胞的分化[22 ] .其次,在由感染和组织损伤引起的炎症反应过程中,versican也发挥着关键作用[24 ] .Versican作为ECM的重要组分之一,可以与透明质酸、肿瘤坏死因子刺激基因-6(tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene-6,TSG-6)蛋白、间α胰蛋白酶抑制剂(inter-α-trypsin inhibitor,ITI)等多种分子相互作用,形成稳定的支架,为侵入组织的炎症细胞充当“着陆带”[25 -27 ] .Versican可以直接通过CD44、P-选择素糖蛋白配体-1(P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1,PSGL-1)、Toll样受体(toll-like receptor,TLR)等细胞表面分子,或间接通过透明质酸与炎症细胞相互作用,从而促进肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)、白细胞介素-6(interleukin-6,IL-6)和核因子κB(nuclear factor κB,NF-κB)等炎症细胞因子的合成和分泌[27 ] .Versican还可以通过与多种调节炎症的细胞因子相互作用,影响它们的生物利用度和生物活性[28 ] .在小鼠肺炎模型中,敲除Vcan 基因,可降低蛋白versican表达,显著减少白细胞对肺的侵袭,并减少炎症细胞因子的表达[29 ] .不同的versican亚型的功能各不相同.如在神经系统发育过程中,versican V0和V1亚型可以抑制神经嵴细胞的迁移[30 ] .V1亚型可以促进神经轴突的生长[31 ] ,而V2亚型则表现为抑制[21 ] .此外V1亚型可以通过增强表皮生长因子受体(epithelial growth factor receptor,EGFR)和整合素的表达来诱导神经元的分化,而V2亚型则无此功能[31 ] .V3亚型的表达可以减少脂质的沉积和单核巨噬细胞的积累,从而降低动脉粥样硬化的发生[32 -33 ] .近年来,研究人员在乳腺癌组织中发现了V4亚型的存在,但其功能仍待进一步明确[34 ] . ...
2
... Versican在胚胎发育和炎症反应过程中均发挥重要作用.首先,在胚胎发育过程中,versican对于心血管形态的发生、神经及骨骼的发育至关重要[20 -22 ] .研究[20 ] 发现,在心脏的发育过程中,水解versican可以使心脏共同出口远端区域的心肌退化,逐渐被平滑肌取代并发育成动脉组织,促进心脏流出道(outflow tract,OFT)的形成.最近研究[23 ] 发现,versican在心肌细胞增殖和心肌修复过程中发挥重要作用.同时,versican还可以影响神经轴突的生长,从而调节神经组织的发育过程[21 ] .间充质细胞的凝聚是软骨发育的重要步骤,versican的CS链可以促进间充质基质的形成和软骨细胞的分化[22 ] .其次,在由感染和组织损伤引起的炎症反应过程中,versican也发挥着关键作用[24 ] .Versican作为ECM的重要组分之一,可以与透明质酸、肿瘤坏死因子刺激基因-6(tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene-6,TSG-6)蛋白、间α胰蛋白酶抑制剂(inter-α-trypsin inhibitor,ITI)等多种分子相互作用,形成稳定的支架,为侵入组织的炎症细胞充当“着陆带”[25 -27 ] .Versican可以直接通过CD44、P-选择素糖蛋白配体-1(P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1,PSGL-1)、Toll样受体(toll-like receptor,TLR)等细胞表面分子,或间接通过透明质酸与炎症细胞相互作用,从而促进肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)、白细胞介素-6(interleukin-6,IL-6)和核因子κB(nuclear factor κB,NF-κB)等炎症细胞因子的合成和分泌[27 ] .Versican还可以通过与多种调节炎症的细胞因子相互作用,影响它们的生物利用度和生物活性[28 ] .在小鼠肺炎模型中,敲除Vcan 基因,可降低蛋白versican表达,显著减少白细胞对肺的侵袭,并减少炎症细胞因子的表达[29 ] .不同的versican亚型的功能各不相同.如在神经系统发育过程中,versican V0和V1亚型可以抑制神经嵴细胞的迁移[30 ] .V1亚型可以促进神经轴突的生长[31 ] ,而V2亚型则表现为抑制[21 ] .此外V1亚型可以通过增强表皮生长因子受体(epithelial growth factor receptor,EGFR)和整合素的表达来诱导神经元的分化,而V2亚型则无此功能[31 ] .V3亚型的表达可以减少脂质的沉积和单核巨噬细胞的积累,从而降低动脉粥样硬化的发生[32 -33 ] .近年来,研究人员在乳腺癌组织中发现了V4亚型的存在,但其功能仍待进一步明确[34 ] . ...
... [31 ].V3亚型的表达可以减少脂质的沉积和单核巨噬细胞的积累,从而降低动脉粥样硬化的发生[32 -33 ] .近年来,研究人员在乳腺癌组织中发现了V4亚型的存在,但其功能仍待进一步明确[34 ] . ...
1
... Versican在胚胎发育和炎症反应过程中均发挥重要作用.首先,在胚胎发育过程中,versican对于心血管形态的发生、神经及骨骼的发育至关重要[20 -22 ] .研究[20 ] 发现,在心脏的发育过程中,水解versican可以使心脏共同出口远端区域的心肌退化,逐渐被平滑肌取代并发育成动脉组织,促进心脏流出道(outflow tract,OFT)的形成.最近研究[23 ] 发现,versican在心肌细胞增殖和心肌修复过程中发挥重要作用.同时,versican还可以影响神经轴突的生长,从而调节神经组织的发育过程[21 ] .间充质细胞的凝聚是软骨发育的重要步骤,versican的CS链可以促进间充质基质的形成和软骨细胞的分化[22 ] .其次,在由感染和组织损伤引起的炎症反应过程中,versican也发挥着关键作用[24 ] .Versican作为ECM的重要组分之一,可以与透明质酸、肿瘤坏死因子刺激基因-6(tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene-6,TSG-6)蛋白、间α胰蛋白酶抑制剂(inter-α-trypsin inhibitor,ITI)等多种分子相互作用,形成稳定的支架,为侵入组织的炎症细胞充当“着陆带”[25 -27 ] .Versican可以直接通过CD44、P-选择素糖蛋白配体-1(P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1,PSGL-1)、Toll样受体(toll-like receptor,TLR)等细胞表面分子,或间接通过透明质酸与炎症细胞相互作用,从而促进肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)、白细胞介素-6(interleukin-6,IL-6)和核因子κB(nuclear factor κB,NF-κB)等炎症细胞因子的合成和分泌[27 ] .Versican还可以通过与多种调节炎症的细胞因子相互作用,影响它们的生物利用度和生物活性[28 ] .在小鼠肺炎模型中,敲除Vcan 基因,可降低蛋白versican表达,显著减少白细胞对肺的侵袭,并减少炎症细胞因子的表达[29 ] .不同的versican亚型的功能各不相同.如在神经系统发育过程中,versican V0和V1亚型可以抑制神经嵴细胞的迁移[30 ] .V1亚型可以促进神经轴突的生长[31 ] ,而V2亚型则表现为抑制[21 ] .此外V1亚型可以通过增强表皮生长因子受体(epithelial growth factor receptor,EGFR)和整合素的表达来诱导神经元的分化,而V2亚型则无此功能[31 ] .V3亚型的表达可以减少脂质的沉积和单核巨噬细胞的积累,从而降低动脉粥样硬化的发生[32 -33 ] .近年来,研究人员在乳腺癌组织中发现了V4亚型的存在,但其功能仍待进一步明确[34 ] . ...
1
... Versican在胚胎发育和炎症反应过程中均发挥重要作用.首先,在胚胎发育过程中,versican对于心血管形态的发生、神经及骨骼的发育至关重要[20 -22 ] .研究[20 ] 发现,在心脏的发育过程中,水解versican可以使心脏共同出口远端区域的心肌退化,逐渐被平滑肌取代并发育成动脉组织,促进心脏流出道(outflow tract,OFT)的形成.最近研究[23 ] 发现,versican在心肌细胞增殖和心肌修复过程中发挥重要作用.同时,versican还可以影响神经轴突的生长,从而调节神经组织的发育过程[21 ] .间充质细胞的凝聚是软骨发育的重要步骤,versican的CS链可以促进间充质基质的形成和软骨细胞的分化[22 ] .其次,在由感染和组织损伤引起的炎症反应过程中,versican也发挥着关键作用[24 ] .Versican作为ECM的重要组分之一,可以与透明质酸、肿瘤坏死因子刺激基因-6(tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene-6,TSG-6)蛋白、间α胰蛋白酶抑制剂(inter-α-trypsin inhibitor,ITI)等多种分子相互作用,形成稳定的支架,为侵入组织的炎症细胞充当“着陆带”[25 -27 ] .Versican可以直接通过CD44、P-选择素糖蛋白配体-1(P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1,PSGL-1)、Toll样受体(toll-like receptor,TLR)等细胞表面分子,或间接通过透明质酸与炎症细胞相互作用,从而促进肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)、白细胞介素-6(interleukin-6,IL-6)和核因子κB(nuclear factor κB,NF-κB)等炎症细胞因子的合成和分泌[27 ] .Versican还可以通过与多种调节炎症的细胞因子相互作用,影响它们的生物利用度和生物活性[28 ] .在小鼠肺炎模型中,敲除Vcan 基因,可降低蛋白versican表达,显著减少白细胞对肺的侵袭,并减少炎症细胞因子的表达[29 ] .不同的versican亚型的功能各不相同.如在神经系统发育过程中,versican V0和V1亚型可以抑制神经嵴细胞的迁移[30 ] .V1亚型可以促进神经轴突的生长[31 ] ,而V2亚型则表现为抑制[21 ] .此外V1亚型可以通过增强表皮生长因子受体(epithelial growth factor receptor,EGFR)和整合素的表达来诱导神经元的分化,而V2亚型则无此功能[31 ] .V3亚型的表达可以减少脂质的沉积和单核巨噬细胞的积累,从而降低动脉粥样硬化的发生[32 -33 ] .近年来,研究人员在乳腺癌组织中发现了V4亚型的存在,但其功能仍待进一步明确[34 ] . ...
1
... Versican在胚胎发育和炎症反应过程中均发挥重要作用.首先,在胚胎发育过程中,versican对于心血管形态的发生、神经及骨骼的发育至关重要[20 -22 ] .研究[20 ] 发现,在心脏的发育过程中,水解versican可以使心脏共同出口远端区域的心肌退化,逐渐被平滑肌取代并发育成动脉组织,促进心脏流出道(outflow tract,OFT)的形成.最近研究[23 ] 发现,versican在心肌细胞增殖和心肌修复过程中发挥重要作用.同时,versican还可以影响神经轴突的生长,从而调节神经组织的发育过程[21 ] .间充质细胞的凝聚是软骨发育的重要步骤,versican的CS链可以促进间充质基质的形成和软骨细胞的分化[22 ] .其次,在由感染和组织损伤引起的炎症反应过程中,versican也发挥着关键作用[24 ] .Versican作为ECM的重要组分之一,可以与透明质酸、肿瘤坏死因子刺激基因-6(tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene-6,TSG-6)蛋白、间α胰蛋白酶抑制剂(inter-α-trypsin inhibitor,ITI)等多种分子相互作用,形成稳定的支架,为侵入组织的炎症细胞充当“着陆带”[25 -27 ] .Versican可以直接通过CD44、P-选择素糖蛋白配体-1(P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1,PSGL-1)、Toll样受体(toll-like receptor,TLR)等细胞表面分子,或间接通过透明质酸与炎症细胞相互作用,从而促进肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)、白细胞介素-6(interleukin-6,IL-6)和核因子κB(nuclear factor κB,NF-κB)等炎症细胞因子的合成和分泌[27 ] .Versican还可以通过与多种调节炎症的细胞因子相互作用,影响它们的生物利用度和生物活性[28 ] .在小鼠肺炎模型中,敲除Vcan 基因,可降低蛋白versican表达,显著减少白细胞对肺的侵袭,并减少炎症细胞因子的表达[29 ] .不同的versican亚型的功能各不相同.如在神经系统发育过程中,versican V0和V1亚型可以抑制神经嵴细胞的迁移[30 ] .V1亚型可以促进神经轴突的生长[31 ] ,而V2亚型则表现为抑制[21 ] .此外V1亚型可以通过增强表皮生长因子受体(epithelial growth factor receptor,EGFR)和整合素的表达来诱导神经元的分化,而V2亚型则无此功能[31 ] .V3亚型的表达可以减少脂质的沉积和单核巨噬细胞的积累,从而降低动脉粥样硬化的发生[32 -33 ] .近年来,研究人员在乳腺癌组织中发现了V4亚型的存在,但其功能仍待进一步明确[34 ] . ...
3
... Versican在多种肿瘤组织中异常表达,且与患者的临床病理特征及预后密切相关.一项研究[6 ] 表明,versican在肾细胞癌组织中高表达,并且其高表达与根治性肾切除术后的肿瘤复发转移率升高及患者5年生存率下降密切相关.Versican的V1亚型在肝细胞癌组织中高表达,并与不良预后相关[8 ,35 ] ;与正常肝脏组织相比,肝细胞癌组织中versican表达上调,并且恶性程度越高的亚型中versican的表达水平越高[8 ] .与腺瘤相比,结直肠癌组织中versican的表达显著增高,并且versican的表达促进了腺瘤向结直肠癌发展[11 ] .胃癌组织中versican的表达水平明显高于正常胃黏膜组织,并且versican的高表达与较高的TNM分期及患者的不良预后密切相关[15 ] ,是胃癌患者预后不良的独立预测因子[36 ] .在食管鳞状细胞癌组织中,versican较癌旁组织显著增高,且versican高表达患者的无病生存期明显缩短[37 ] .进一步的研究[38 ] 表明,食管癌组织中versican高表达与肿瘤血管和淋巴管浸润增加、淋巴结转移及患者预后不佳显著相关.在卵巢癌组织中,同样存在versican的高表达,且versican的高表达与卵巢癌腹膜转移率增加密切相关[39 ] . ...
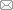
... 目前研究认为versican主要通过2种机制促进肿瘤细胞的增殖(图1 ):一是通过G3结构域中的2个类EGF重复序列促进肿瘤细胞增殖[40 ] ;二是通过G1结构域破坏细胞间黏附,从而促进细胞增殖[41 ] .Versican的V1亚型通过G3结构域中的类EGF重复序列激活表皮生长因子受体/磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B(epithelial growth factor receptor/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B,EGFR/PI3K/AKT)信号通路,促进肝癌细胞的增殖[35 ] .此外,versican还可以通过G1结构域与透明质酸、CD44、透明质酸和蛋白多糖连接蛋白1(hyaluronan and proteoglycan link protein 1,HAPLN1)等分子相互作用来促进细胞的增殖[42 ] . ...
... 关于恶性星形细胞瘤的研究[41 ,46 ] 显示,versican的G1结构域通过与透明质酸、HAPLN1结合来减少肿瘤细胞的黏附,增强肿瘤细胞的迁移能力.而G3结构域的类EGF重复序列通过激活EGFR/PI3K/AKT信号通路,促进肝癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[35 ] .抑制素βA亚基可以通过上调versican的表达来促进结肠癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[12 ] .在卵巢癌中,转化生长因子-β(transforming growth factor-β,TGF-β)可以上调癌症相关成纤维细胞(cancer-associated fibroblast,CAF)来源的versican的表达,高表达的versican通过激活NF-κB信号通路促进肿瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭[47 ] .一项关于肝细胞癌的研究[9 ] 也显示,CAF来源的versican可显著促进肿瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭.胃癌组织中versican的表达与上皮-间质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition,EMT)相关蛋白的表达密切相关,且高表达versican的患者更容易发生淋巴结转移,提示versican可以通过调节EMT促进胃癌细胞的远处转移[48 ] .一项关于乳腺癌的研究[49 ] 发现,versican不仅可以增强肿瘤细胞在骨组织中的迁移、侵袭及生存能力,而且还能够抑制前成骨细胞的生长和分化,进而促进乳腺癌的骨转移.另一项乳腺癌的研究[50 ] 显示,ECM中versican的高表达与肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(tumor-associated macrophage,TAM)的大量浸润相关,而后者又与小鼠乳腺癌的肺转移结节数量的增加有关.Versican或将成为治疗恶性肿瘤转移的新靶点.(图1 ) ...
1
... Versican在多种肿瘤组织中异常表达,且与患者的临床病理特征及预后密切相关.一项研究[6 ] 表明,versican在肾细胞癌组织中高表达,并且其高表达与根治性肾切除术后的肿瘤复发转移率升高及患者5年生存率下降密切相关.Versican的V1亚型在肝细胞癌组织中高表达,并与不良预后相关[8 ,35 ] ;与正常肝脏组织相比,肝细胞癌组织中versican表达上调,并且恶性程度越高的亚型中versican的表达水平越高[8 ] .与腺瘤相比,结直肠癌组织中versican的表达显著增高,并且versican的表达促进了腺瘤向结直肠癌发展[11 ] .胃癌组织中versican的表达水平明显高于正常胃黏膜组织,并且versican的高表达与较高的TNM分期及患者的不良预后密切相关[15 ] ,是胃癌患者预后不良的独立预测因子[36 ] .在食管鳞状细胞癌组织中,versican较癌旁组织显著增高,且versican高表达患者的无病生存期明显缩短[37 ] .进一步的研究[38 ] 表明,食管癌组织中versican高表达与肿瘤血管和淋巴管浸润增加、淋巴结转移及患者预后不佳显著相关.在卵巢癌组织中,同样存在versican的高表达,且versican的高表达与卵巢癌腹膜转移率增加密切相关[39 ] . ...
1
... Versican在多种肿瘤组织中异常表达,且与患者的临床病理特征及预后密切相关.一项研究[6 ] 表明,versican在肾细胞癌组织中高表达,并且其高表达与根治性肾切除术后的肿瘤复发转移率升高及患者5年生存率下降密切相关.Versican的V1亚型在肝细胞癌组织中高表达,并与不良预后相关[8 ,35 ] ;与正常肝脏组织相比,肝细胞癌组织中versican表达上调,并且恶性程度越高的亚型中versican的表达水平越高[8 ] .与腺瘤相比,结直肠癌组织中versican的表达显著增高,并且versican的表达促进了腺瘤向结直肠癌发展[11 ] .胃癌组织中versican的表达水平明显高于正常胃黏膜组织,并且versican的高表达与较高的TNM分期及患者的不良预后密切相关[15 ] ,是胃癌患者预后不良的独立预测因子[36 ] .在食管鳞状细胞癌组织中,versican较癌旁组织显著增高,且versican高表达患者的无病生存期明显缩短[37 ] .进一步的研究[38 ] 表明,食管癌组织中versican高表达与肿瘤血管和淋巴管浸润增加、淋巴结转移及患者预后不佳显著相关.在卵巢癌组织中,同样存在versican的高表达,且versican的高表达与卵巢癌腹膜转移率增加密切相关[39 ] . ...
1
... Versican在多种肿瘤组织中异常表达,且与患者的临床病理特征及预后密切相关.一项研究[6 ] 表明,versican在肾细胞癌组织中高表达,并且其高表达与根治性肾切除术后的肿瘤复发转移率升高及患者5年生存率下降密切相关.Versican的V1亚型在肝细胞癌组织中高表达,并与不良预后相关[8 ,35 ] ;与正常肝脏组织相比,肝细胞癌组织中versican表达上调,并且恶性程度越高的亚型中versican的表达水平越高[8 ] .与腺瘤相比,结直肠癌组织中versican的表达显著增高,并且versican的表达促进了腺瘤向结直肠癌发展[11 ] .胃癌组织中versican的表达水平明显高于正常胃黏膜组织,并且versican的高表达与较高的TNM分期及患者的不良预后密切相关[15 ] ,是胃癌患者预后不良的独立预测因子[36 ] .在食管鳞状细胞癌组织中,versican较癌旁组织显著增高,且versican高表达患者的无病生存期明显缩短[37 ] .进一步的研究[38 ] 表明,食管癌组织中versican高表达与肿瘤血管和淋巴管浸润增加、淋巴结转移及患者预后不佳显著相关.在卵巢癌组织中,同样存在versican的高表达,且versican的高表达与卵巢癌腹膜转移率增加密切相关[39 ] . ...
1
... Versican在多种肿瘤组织中异常表达,且与患者的临床病理特征及预后密切相关.一项研究[6 ] 表明,versican在肾细胞癌组织中高表达,并且其高表达与根治性肾切除术后的肿瘤复发转移率升高及患者5年生存率下降密切相关.Versican的V1亚型在肝细胞癌组织中高表达,并与不良预后相关[8 ,35 ] ;与正常肝脏组织相比,肝细胞癌组织中versican表达上调,并且恶性程度越高的亚型中versican的表达水平越高[8 ] .与腺瘤相比,结直肠癌组织中versican的表达显著增高,并且versican的表达促进了腺瘤向结直肠癌发展[11 ] .胃癌组织中versican的表达水平明显高于正常胃黏膜组织,并且versican的高表达与较高的TNM分期及患者的不良预后密切相关[15 ] ,是胃癌患者预后不良的独立预测因子[36 ] .在食管鳞状细胞癌组织中,versican较癌旁组织显著增高,且versican高表达患者的无病生存期明显缩短[37 ] .进一步的研究[38 ] 表明,食管癌组织中versican高表达与肿瘤血管和淋巴管浸润增加、淋巴结转移及患者预后不佳显著相关.在卵巢癌组织中,同样存在versican的高表达,且versican的高表达与卵巢癌腹膜转移率增加密切相关[39 ] . ...
1
... Versican在多种肿瘤组织中异常表达,且与患者的临床病理特征及预后密切相关.一项研究[6 ] 表明,versican在肾细胞癌组织中高表达,并且其高表达与根治性肾切除术后的肿瘤复发转移率升高及患者5年生存率下降密切相关.Versican的V1亚型在肝细胞癌组织中高表达,并与不良预后相关[8 ,35 ] ;与正常肝脏组织相比,肝细胞癌组织中versican表达上调,并且恶性程度越高的亚型中versican的表达水平越高[8 ] .与腺瘤相比,结直肠癌组织中versican的表达显著增高,并且versican的表达促进了腺瘤向结直肠癌发展[11 ] .胃癌组织中versican的表达水平明显高于正常胃黏膜组织,并且versican的高表达与较高的TNM分期及患者的不良预后密切相关[15 ] ,是胃癌患者预后不良的独立预测因子[36 ] .在食管鳞状细胞癌组织中,versican较癌旁组织显著增高,且versican高表达患者的无病生存期明显缩短[37 ] .进一步的研究[38 ] 表明,食管癌组织中versican高表达与肿瘤血管和淋巴管浸润增加、淋巴结转移及患者预后不佳显著相关.在卵巢癌组织中,同样存在versican的高表达,且versican的高表达与卵巢癌腹膜转移率增加密切相关[39 ] . ...
1
... 目前研究认为versican主要通过2种机制促进肿瘤细胞的增殖(图1 ):一是通过G3结构域中的2个类EGF重复序列促进肿瘤细胞增殖[40 ] ;二是通过G1结构域破坏细胞间黏附,从而促进细胞增殖[41 ] .Versican的V1亚型通过G3结构域中的类EGF重复序列激活表皮生长因子受体/磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B(epithelial growth factor receptor/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B,EGFR/PI3K/AKT)信号通路,促进肝癌细胞的增殖[35 ] .此外,versican还可以通过G1结构域与透明质酸、CD44、透明质酸和蛋白多糖连接蛋白1(hyaluronan and proteoglycan link protein 1,HAPLN1)等分子相互作用来促进细胞的增殖[42 ] . ...
2
... 目前研究认为versican主要通过2种机制促进肿瘤细胞的增殖(图1 ):一是通过G3结构域中的2个类EGF重复序列促进肿瘤细胞增殖[40 ] ;二是通过G1结构域破坏细胞间黏附,从而促进细胞增殖[41 ] .Versican的V1亚型通过G3结构域中的类EGF重复序列激活表皮生长因子受体/磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B(epithelial growth factor receptor/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B,EGFR/PI3K/AKT)信号通路,促进肝癌细胞的增殖[35 ] .此外,versican还可以通过G1结构域与透明质酸、CD44、透明质酸和蛋白多糖连接蛋白1(hyaluronan and proteoglycan link protein 1,HAPLN1)等分子相互作用来促进细胞的增殖[42 ] . ...
... 关于恶性星形细胞瘤的研究[41 ,46 ] 显示,versican的G1结构域通过与透明质酸、HAPLN1结合来减少肿瘤细胞的黏附,增强肿瘤细胞的迁移能力.而G3结构域的类EGF重复序列通过激活EGFR/PI3K/AKT信号通路,促进肝癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[35 ] .抑制素βA亚基可以通过上调versican的表达来促进结肠癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[12 ] .在卵巢癌中,转化生长因子-β(transforming growth factor-β,TGF-β)可以上调癌症相关成纤维细胞(cancer-associated fibroblast,CAF)来源的versican的表达,高表达的versican通过激活NF-κB信号通路促进肿瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭[47 ] .一项关于肝细胞癌的研究[9 ] 也显示,CAF来源的versican可显著促进肿瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭.胃癌组织中versican的表达与上皮-间质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition,EMT)相关蛋白的表达密切相关,且高表达versican的患者更容易发生淋巴结转移,提示versican可以通过调节EMT促进胃癌细胞的远处转移[48 ] .一项关于乳腺癌的研究[49 ] 发现,versican不仅可以增强肿瘤细胞在骨组织中的迁移、侵袭及生存能力,而且还能够抑制前成骨细胞的生长和分化,进而促进乳腺癌的骨转移.另一项乳腺癌的研究[50 ] 显示,ECM中versican的高表达与肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(tumor-associated macrophage,TAM)的大量浸润相关,而后者又与小鼠乳腺癌的肺转移结节数量的增加有关.Versican或将成为治疗恶性肿瘤转移的新靶点.(图1 ) ...
1
... 目前研究认为versican主要通过2种机制促进肿瘤细胞的增殖(图1 ):一是通过G3结构域中的2个类EGF重复序列促进肿瘤细胞增殖[40 ] ;二是通过G1结构域破坏细胞间黏附,从而促进细胞增殖[41 ] .Versican的V1亚型通过G3结构域中的类EGF重复序列激活表皮生长因子受体/磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B(epithelial growth factor receptor/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B,EGFR/PI3K/AKT)信号通路,促进肝癌细胞的增殖[35 ] .此外,versican还可以通过G1结构域与透明质酸、CD44、透明质酸和蛋白多糖连接蛋白1(hyaluronan and proteoglycan link protein 1,HAPLN1)等分子相互作用来促进细胞的增殖[42 ] . ...
1
... 研究[43 ] 显示,versican G1结构域高表达的肉瘤细胞可以抵抗细胞毒性药物所诱导的以及Fas介导的细胞凋亡.Versican V1亚型的表达与BCL-2相关细胞死亡激动剂(BCL-2 associated agonist of cell death,BAD)的表达呈负相关,当应用小干扰RNA减少versican V1亚型的表达时,促凋亡蛋白BAD的表达增加,versican V1亚型抑制肿瘤细胞凋亡的能力减弱[44 ] .一项关于多发性骨髓瘤(multiple myeloma)的研究[45 ] 显示,肿瘤组织中高表达的miR-135b可以通过激活Wnt/β连环蛋白(Wnt/β-catenin)信号通路来抑制肿瘤细胞的凋亡;versican在多发性骨髓瘤组织中高表达,是Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的关键分子,沉默VCAN 基因逆转了miR-135b抑制肿瘤细胞凋亡的作用;这表明miR-135b及其介导的Wnt/β-catenin信号通路可以通过调控versican来抑制肿瘤细胞的凋亡.(图1 ) ...
1
... 研究[43 ] 显示,versican G1结构域高表达的肉瘤细胞可以抵抗细胞毒性药物所诱导的以及Fas介导的细胞凋亡.Versican V1亚型的表达与BCL-2相关细胞死亡激动剂(BCL-2 associated agonist of cell death,BAD)的表达呈负相关,当应用小干扰RNA减少versican V1亚型的表达时,促凋亡蛋白BAD的表达增加,versican V1亚型抑制肿瘤细胞凋亡的能力减弱[44 ] .一项关于多发性骨髓瘤(multiple myeloma)的研究[45 ] 显示,肿瘤组织中高表达的miR-135b可以通过激活Wnt/β连环蛋白(Wnt/β-catenin)信号通路来抑制肿瘤细胞的凋亡;versican在多发性骨髓瘤组织中高表达,是Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的关键分子,沉默VCAN 基因逆转了miR-135b抑制肿瘤细胞凋亡的作用;这表明miR-135b及其介导的Wnt/β-catenin信号通路可以通过调控versican来抑制肿瘤细胞的凋亡.(图1 ) ...
1
... 研究[43 ] 显示,versican G1结构域高表达的肉瘤细胞可以抵抗细胞毒性药物所诱导的以及Fas介导的细胞凋亡.Versican V1亚型的表达与BCL-2相关细胞死亡激动剂(BCL-2 associated agonist of cell death,BAD)的表达呈负相关,当应用小干扰RNA减少versican V1亚型的表达时,促凋亡蛋白BAD的表达增加,versican V1亚型抑制肿瘤细胞凋亡的能力减弱[44 ] .一项关于多发性骨髓瘤(multiple myeloma)的研究[45 ] 显示,肿瘤组织中高表达的miR-135b可以通过激活Wnt/β连环蛋白(Wnt/β-catenin)信号通路来抑制肿瘤细胞的凋亡;versican在多发性骨髓瘤组织中高表达,是Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的关键分子,沉默VCAN 基因逆转了miR-135b抑制肿瘤细胞凋亡的作用;这表明miR-135b及其介导的Wnt/β-catenin信号通路可以通过调控versican来抑制肿瘤细胞的凋亡.(图1 ) ...
1
... 关于恶性星形细胞瘤的研究[41 ,46 ] 显示,versican的G1结构域通过与透明质酸、HAPLN1结合来减少肿瘤细胞的黏附,增强肿瘤细胞的迁移能力.而G3结构域的类EGF重复序列通过激活EGFR/PI3K/AKT信号通路,促进肝癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[35 ] .抑制素βA亚基可以通过上调versican的表达来促进结肠癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[12 ] .在卵巢癌中,转化生长因子-β(transforming growth factor-β,TGF-β)可以上调癌症相关成纤维细胞(cancer-associated fibroblast,CAF)来源的versican的表达,高表达的versican通过激活NF-κB信号通路促进肿瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭[47 ] .一项关于肝细胞癌的研究[9 ] 也显示,CAF来源的versican可显著促进肿瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭.胃癌组织中versican的表达与上皮-间质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition,EMT)相关蛋白的表达密切相关,且高表达versican的患者更容易发生淋巴结转移,提示versican可以通过调节EMT促进胃癌细胞的远处转移[48 ] .一项关于乳腺癌的研究[49 ] 发现,versican不仅可以增强肿瘤细胞在骨组织中的迁移、侵袭及生存能力,而且还能够抑制前成骨细胞的生长和分化,进而促进乳腺癌的骨转移.另一项乳腺癌的研究[50 ] 显示,ECM中versican的高表达与肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(tumor-associated macrophage,TAM)的大量浸润相关,而后者又与小鼠乳腺癌的肺转移结节数量的增加有关.Versican或将成为治疗恶性肿瘤转移的新靶点.(图1 ) ...
1
... 关于恶性星形细胞瘤的研究[41 ,46 ] 显示,versican的G1结构域通过与透明质酸、HAPLN1结合来减少肿瘤细胞的黏附,增强肿瘤细胞的迁移能力.而G3结构域的类EGF重复序列通过激活EGFR/PI3K/AKT信号通路,促进肝癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[35 ] .抑制素βA亚基可以通过上调versican的表达来促进结肠癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[12 ] .在卵巢癌中,转化生长因子-β(transforming growth factor-β,TGF-β)可以上调癌症相关成纤维细胞(cancer-associated fibroblast,CAF)来源的versican的表达,高表达的versican通过激活NF-κB信号通路促进肿瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭[47 ] .一项关于肝细胞癌的研究[9 ] 也显示,CAF来源的versican可显著促进肿瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭.胃癌组织中versican的表达与上皮-间质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition,EMT)相关蛋白的表达密切相关,且高表达versican的患者更容易发生淋巴结转移,提示versican可以通过调节EMT促进胃癌细胞的远处转移[48 ] .一项关于乳腺癌的研究[49 ] 发现,versican不仅可以增强肿瘤细胞在骨组织中的迁移、侵袭及生存能力,而且还能够抑制前成骨细胞的生长和分化,进而促进乳腺癌的骨转移.另一项乳腺癌的研究[50 ] 显示,ECM中versican的高表达与肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(tumor-associated macrophage,TAM)的大量浸润相关,而后者又与小鼠乳腺癌的肺转移结节数量的增加有关.Versican或将成为治疗恶性肿瘤转移的新靶点.(图1 ) ...
1
... 关于恶性星形细胞瘤的研究[41 ,46 ] 显示,versican的G1结构域通过与透明质酸、HAPLN1结合来减少肿瘤细胞的黏附,增强肿瘤细胞的迁移能力.而G3结构域的类EGF重复序列通过激活EGFR/PI3K/AKT信号通路,促进肝癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[35 ] .抑制素βA亚基可以通过上调versican的表达来促进结肠癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[12 ] .在卵巢癌中,转化生长因子-β(transforming growth factor-β,TGF-β)可以上调癌症相关成纤维细胞(cancer-associated fibroblast,CAF)来源的versican的表达,高表达的versican通过激活NF-κB信号通路促进肿瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭[47 ] .一项关于肝细胞癌的研究[9 ] 也显示,CAF来源的versican可显著促进肿瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭.胃癌组织中versican的表达与上皮-间质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition,EMT)相关蛋白的表达密切相关,且高表达versican的患者更容易发生淋巴结转移,提示versican可以通过调节EMT促进胃癌细胞的远处转移[48 ] .一项关于乳腺癌的研究[49 ] 发现,versican不仅可以增强肿瘤细胞在骨组织中的迁移、侵袭及生存能力,而且还能够抑制前成骨细胞的生长和分化,进而促进乳腺癌的骨转移.另一项乳腺癌的研究[50 ] 显示,ECM中versican的高表达与肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(tumor-associated macrophage,TAM)的大量浸润相关,而后者又与小鼠乳腺癌的肺转移结节数量的增加有关.Versican或将成为治疗恶性肿瘤转移的新靶点.(图1 ) ...
1
... 关于恶性星形细胞瘤的研究[41 ,46 ] 显示,versican的G1结构域通过与透明质酸、HAPLN1结合来减少肿瘤细胞的黏附,增强肿瘤细胞的迁移能力.而G3结构域的类EGF重复序列通过激活EGFR/PI3K/AKT信号通路,促进肝癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[35 ] .抑制素βA亚基可以通过上调versican的表达来促进结肠癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[12 ] .在卵巢癌中,转化生长因子-β(transforming growth factor-β,TGF-β)可以上调癌症相关成纤维细胞(cancer-associated fibroblast,CAF)来源的versican的表达,高表达的versican通过激活NF-κB信号通路促进肿瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭[47 ] .一项关于肝细胞癌的研究[9 ] 也显示,CAF来源的versican可显著促进肿瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭.胃癌组织中versican的表达与上皮-间质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition,EMT)相关蛋白的表达密切相关,且高表达versican的患者更容易发生淋巴结转移,提示versican可以通过调节EMT促进胃癌细胞的远处转移[48 ] .一项关于乳腺癌的研究[49 ] 发现,versican不仅可以增强肿瘤细胞在骨组织中的迁移、侵袭及生存能力,而且还能够抑制前成骨细胞的生长和分化,进而促进乳腺癌的骨转移.另一项乳腺癌的研究[50 ] 显示,ECM中versican的高表达与肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(tumor-associated macrophage,TAM)的大量浸润相关,而后者又与小鼠乳腺癌的肺转移结节数量的增加有关.Versican或将成为治疗恶性肿瘤转移的新靶点.(图1 ) ...
1
... 关于恶性星形细胞瘤的研究[41 ,46 ] 显示,versican的G1结构域通过与透明质酸、HAPLN1结合来减少肿瘤细胞的黏附,增强肿瘤细胞的迁移能力.而G3结构域的类EGF重复序列通过激活EGFR/PI3K/AKT信号通路,促进肝癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[35 ] .抑制素βA亚基可以通过上调versican的表达来促进结肠癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[12 ] .在卵巢癌中,转化生长因子-β(transforming growth factor-β,TGF-β)可以上调癌症相关成纤维细胞(cancer-associated fibroblast,CAF)来源的versican的表达,高表达的versican通过激活NF-κB信号通路促进肿瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭[47 ] .一项关于肝细胞癌的研究[9 ] 也显示,CAF来源的versican可显著促进肿瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭.胃癌组织中versican的表达与上皮-间质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition,EMT)相关蛋白的表达密切相关,且高表达versican的患者更容易发生淋巴结转移,提示versican可以通过调节EMT促进胃癌细胞的远处转移[48 ] .一项关于乳腺癌的研究[49 ] 发现,versican不仅可以增强肿瘤细胞在骨组织中的迁移、侵袭及生存能力,而且还能够抑制前成骨细胞的生长和分化,进而促进乳腺癌的骨转移.另一项乳腺癌的研究[50 ] 显示,ECM中versican的高表达与肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(tumor-associated macrophage,TAM)的大量浸润相关,而后者又与小鼠乳腺癌的肺转移结节数量的增加有关.Versican或将成为治疗恶性肿瘤转移的新靶点.(图1 ) ...
1
... 关于恶性星形细胞瘤的研究[41 ,46 ] 显示,versican的G1结构域通过与透明质酸、HAPLN1结合来减少肿瘤细胞的黏附,增强肿瘤细胞的迁移能力.而G3结构域的类EGF重复序列通过激活EGFR/PI3K/AKT信号通路,促进肝癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[35 ] .抑制素βA亚基可以通过上调versican的表达来促进结肠癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[12 ] .在卵巢癌中,转化生长因子-β(transforming growth factor-β,TGF-β)可以上调癌症相关成纤维细胞(cancer-associated fibroblast,CAF)来源的versican的表达,高表达的versican通过激活NF-κB信号通路促进肿瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭[47 ] .一项关于肝细胞癌的研究[9 ] 也显示,CAF来源的versican可显著促进肿瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭.胃癌组织中versican的表达与上皮-间质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition,EMT)相关蛋白的表达密切相关,且高表达versican的患者更容易发生淋巴结转移,提示versican可以通过调节EMT促进胃癌细胞的远处转移[48 ] .一项关于乳腺癌的研究[49 ] 发现,versican不仅可以增强肿瘤细胞在骨组织中的迁移、侵袭及生存能力,而且还能够抑制前成骨细胞的生长和分化,进而促进乳腺癌的骨转移.另一项乳腺癌的研究[50 ] 显示,ECM中versican的高表达与肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(tumor-associated macrophage,TAM)的大量浸润相关,而后者又与小鼠乳腺癌的肺转移结节数量的增加有关.Versican或将成为治疗恶性肿瘤转移的新靶点.(图1 ) ...
1
... 血管生成是恶性肿瘤进展的先决条件之一.Versican的G3结构域可以促进血管内皮生长因子(vascular endothelial growth factor,VEGF)和纤维连接蛋白(fibronectin,FN)的表达,三者互相协同可促进肿瘤血管的生成[51 ] ;同时新生血管内皮的形成又反过来促进versican的表达[52 ] .一项关于睾丸生殖细胞瘤的研究[52 ] 发现,versican高表达的肿瘤间质中微血管数量增加,这与其促进内皮细胞的迁移密切相关.(图1 ) ...
2
... 血管生成是恶性肿瘤进展的先决条件之一.Versican的G3结构域可以促进血管内皮生长因子(vascular endothelial growth factor,VEGF)和纤维连接蛋白(fibronectin,FN)的表达,三者互相协同可促进肿瘤血管的生成[51 ] ;同时新生血管内皮的形成又反过来促进versican的表达[52 ] .一项关于睾丸生殖细胞瘤的研究[52 ] 发现,versican高表达的肿瘤间质中微血管数量增加,这与其促进内皮细胞的迁移密切相关.(图1 ) ...
... [52 ]发现,versican高表达的肿瘤间质中微血管数量增加,这与其促进内皮细胞的迁移密切相关.(图1 ) ...
1
... Versican与透明质酸相互作用可以吸引免疫细胞的黏附,从而减缓免疫细胞在组织中的迁移速度[53 -54 ] .此外,versican与其他ECM蛋白相互结合形成纤维结构来增加组织硬度,以形成天然的“物理屏障”,阻碍T细胞浸润,抑制肿瘤的免疫应答[55 ] .肝细胞癌组织中versican的表达与程序性死亡受体-1(programmed death-1,PD-1)、细胞毒性T淋巴细胞相关抗原-4(cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4,CTLA-4)的表达均呈明显的正相关,而与肿瘤突变负荷(tumor mutational burden,TMB)呈明显的负相关,这表明versican可能是恶性肿瘤免疫治疗耐药的潜在生物标志物之一[10 ] .(图1 ) ...
1
... Versican与透明质酸相互作用可以吸引免疫细胞的黏附,从而减缓免疫细胞在组织中的迁移速度[53 -54 ] .此外,versican与其他ECM蛋白相互结合形成纤维结构来增加组织硬度,以形成天然的“物理屏障”,阻碍T细胞浸润,抑制肿瘤的免疫应答[55 ] .肝细胞癌组织中versican的表达与程序性死亡受体-1(programmed death-1,PD-1)、细胞毒性T淋巴细胞相关抗原-4(cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4,CTLA-4)的表达均呈明显的正相关,而与肿瘤突变负荷(tumor mutational burden,TMB)呈明显的负相关,这表明versican可能是恶性肿瘤免疫治疗耐药的潜在生物标志物之一[10 ] .(图1 ) ...
1
... Versican与透明质酸相互作用可以吸引免疫细胞的黏附,从而减缓免疫细胞在组织中的迁移速度[53 -54 ] .此外,versican与其他ECM蛋白相互结合形成纤维结构来增加组织硬度,以形成天然的“物理屏障”,阻碍T细胞浸润,抑制肿瘤的免疫应答[55 ] .肝细胞癌组织中versican的表达与程序性死亡受体-1(programmed death-1,PD-1)、细胞毒性T淋巴细胞相关抗原-4(cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4,CTLA-4)的表达均呈明显的正相关,而与肿瘤突变负荷(tumor mutational burden,TMB)呈明显的负相关,这表明versican可能是恶性肿瘤免疫治疗耐药的潜在生物标志物之一[10 ] .(图1 ) ...