
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (12): 1490-1503.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2024.12.002
• 论著 · 基础研究 • 上一篇
袁灏琳( ), 李念念, 胡珺晖, 沈锦虹, 高振飞, 关建, 刘峰, 殷善开(
), 李念念, 胡珺晖, 沈锦虹, 高振飞, 关建, 刘峰, 殷善开( )
)
收稿日期:2024-04-12
接受日期:2024-05-21
出版日期:2024-12-25
发布日期:2024-12-25
通讯作者:
殷善开
E-mail:hlyuan78@126.com;skyin@sjtu.edu.cn
作者简介:袁灏琳(1995—),女,硕士生;电子信箱:hlyuan78@126.com。
基金资助:
YUAN Haolin( ), LI Niannian, HU Junhui, SHEN Jinhong, GAO Zhenfei, GUAN Jian, LIU Feng, YIN Shankai(
), LI Niannian, HU Junhui, SHEN Jinhong, GAO Zhenfei, GUAN Jian, LIU Feng, YIN Shankai( )
)
Received:2024-04-12
Accepted:2024-05-21
Online:2024-12-25
Published:2024-12-25
Contact:
YIN Shankai
E-mail:hlyuan78@126.com;skyin@sjtu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的·探索神经型一氧化氮合酶(nitric oxide synthase 1,NOS1)遗传变异rs7305526和rs11615756与失眠、睡眠时长和阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停(obstructive sleep apnea,OSA)临床数量性状的相关性。方法·利用Allen Human Brain Atlas数据集分析NOS1基因在人类全脑水平的表达模式,通过表达数量性状位点分析rs7305526和rs11615756对NOS1基因表达的影响。利用英国生物银行(United Kingdom Biobank,UKB)的全基因组关联研究(Genome Wide Association Study,GWAS)数据集,采用回归分析探讨rs7305526和rs11615756与失眠及睡眠时长2种睡眠性状的相关性。利用上海睡眠健康队列研究(Shanghai Sleep Health Study Cohort,SSHS)基于标准多导睡眠监测(polysomnography,PSG)的临床监测数据,分析rs7305526和rs11615756与OSA临床数量性状(包括呼吸、血氧和睡眠结构性状)的相关性。结果·NOS1基因在睡眠调节脑区(杏仁核、基底前脑、纹状体和丘脑)和呼吸中枢(间脑和脑桥被盖部)的部分核团呈较高的表达水平,而在大脑和小脑皮层、脑桥等区域呈低水平的表达或不表达。rs7305526和rs11615756与NOS1在大脑皮层的表达水平均呈显著负相关,此外rs11615756同样与杏仁核中NOS1的表达水平呈显著负相关。UKB GWAS数据显示rs7305526与失眠、睡眠时长无显著相关,而rs11615756仅与睡眠时长呈显著负相关。SSHS临床监测数据显示,rs7305526与最低血氧饱和度(lowest pulse blood oxygen saturation,LSpO2)、呼吸暂停低通气指数和非快速眼动睡眠(non-rapid eye movement,NREM)2期时间占比等OSA临床数量性状的变化显著相关。虽然rs11615756仅与NREM 2和3期次数呈显著负相关,但在根据OSA严重程度分层后,rs11615756和rs7305526与部分呼吸血氧性状存在显著相关性。结论·NOS1基因变异与人类睡眠时长性状和OSA呼吸、血氧、睡眠结构性状存在显著关联,rs7305526(C>A)对睡眠性状的调节独立于对呼吸、血氧的调节。
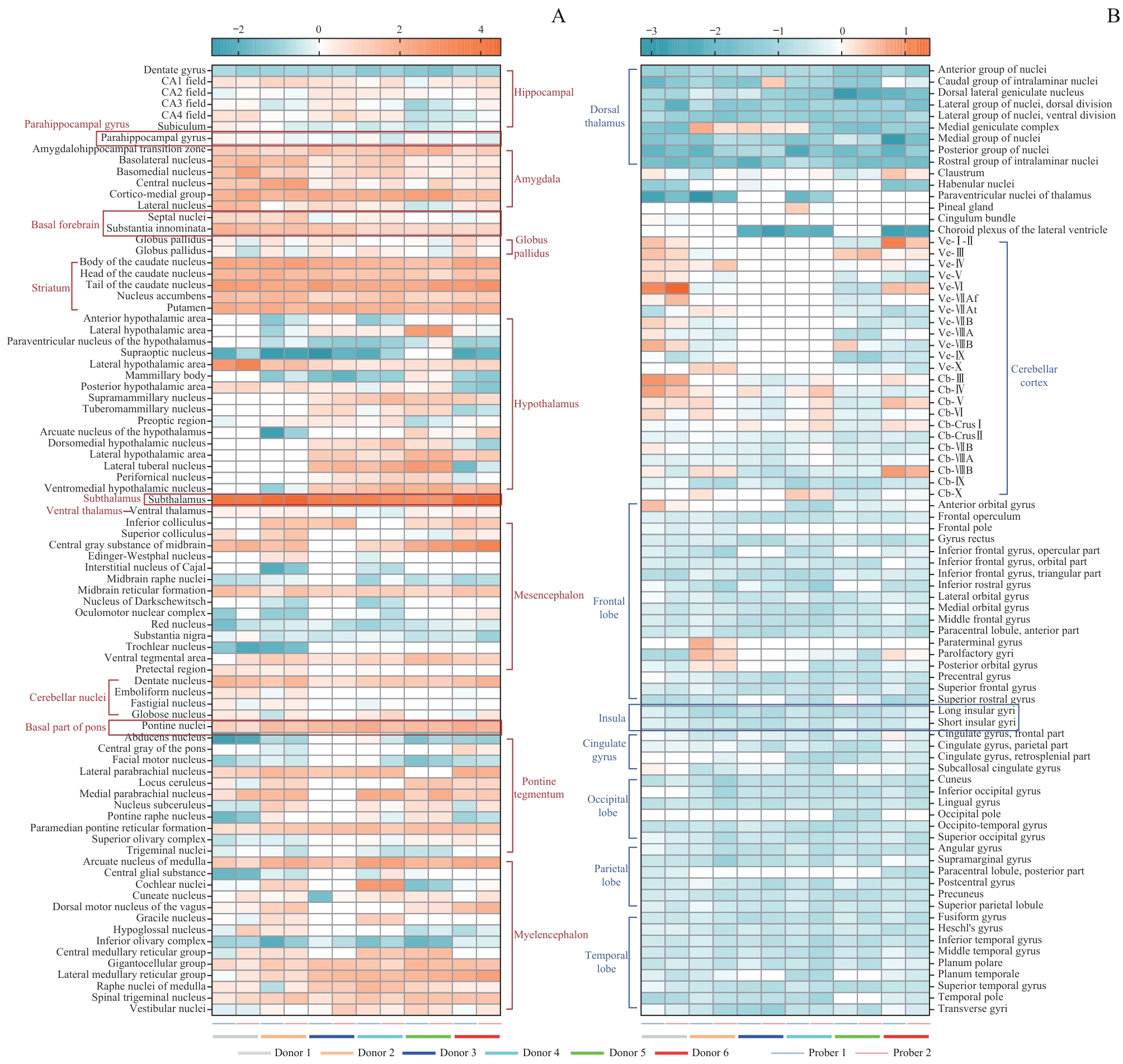
图1 AHBA数据库6位捐赠者169个核团中 NOS1 基因表达情况热图Note: A. Brain regions with relatively high levels of NOS1 gene expression. B. Brain regions with relatively low or no NOS1 expression.
Fig 1 Heatmap of the expression levels of the NOS1 gene in 169 nuclei from 6 donors in the AHBA database
| SNP | Tissue | Effect size | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| rs7305526 | Brain cortex | -0.127 | 0.044 |
| Lung | -0.136 | <0.001 | |
| Tibial nerve | 0.178 | <0.001 | |
| Colon sigmoid | -0.061 | 0.039 | |
| Heart atrial appendage | -0.155 | 0.014 | |
| Minor salivary gland | 0.141 | 0.033 | |
| Thyroid | 0.099 | 0.049 | |
| rs11615756 | Brain amygdala | -0.224 | 0.008 |
| Brain cortex | -0.151 | 0.028 | |
| Esophagus mucosa | -0.084 | 0.031 | |
| Thyroid | 0.104 | 0.049 | |
| Skeletal muscle | 0.061 | 0.017 | |
| Pancreas | 0.114 | 0.020 |
表1 rs7305526和rs11615756的eQTL分析
Tab 1 eQTL analysis of rs7305526 and rs11615756
| SNP | Tissue | Effect size | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| rs7305526 | Brain cortex | -0.127 | 0.044 |
| Lung | -0.136 | <0.001 | |
| Tibial nerve | 0.178 | <0.001 | |
| Colon sigmoid | -0.061 | 0.039 | |
| Heart atrial appendage | -0.155 | 0.014 | |
| Minor salivary gland | 0.141 | 0.033 | |
| Thyroid | 0.099 | 0.049 | |
| rs11615756 | Brain amygdala | -0.224 | 0.008 |
| Brain cortex | -0.151 | 0.028 | |
| Esophagus mucosa | -0.084 | 0.031 | |
| Thyroid | 0.104 | 0.049 | |
| Skeletal muscle | 0.061 | 0.017 | |
| Pancreas | 0.114 | 0.020 |
| Sleep trait | GWAS catalog accession | PMID | Author and year | Population | Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insomnia | GCST004695 | 28604731 | HAMMERSCHLAG 2017 | European (UK) | 113 006 |
| GCST90267286 | 37106081 | SCHOELER 2023 | European (UK) | 283 595 | |
| Sleep duration | GCST003839 | 27494321 | JONES 2016 | European (UK) | 127 573 |
| GCST006914 | 30531941 | DOHERTY 2018 | European (UK) | 91 105 | |
| GCST007561 | 30846698 | DASHTI 2019 | European (UK) | 446 118 |
表2 本研究使用的UKB睡眠性状相关GWAS数据集
Tab 2 GWAS datasets of sleep traits from UKB used in data mining
| Sleep trait | GWAS catalog accession | PMID | Author and year | Population | Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insomnia | GCST004695 | 28604731 | HAMMERSCHLAG 2017 | European (UK) | 113 006 |
| GCST90267286 | 37106081 | SCHOELER 2023 | European (UK) | 283 595 | |
| Sleep duration | GCST003839 | 27494321 | JONES 2016 | European (UK) | 127 573 |
| GCST006914 | 30531941 | DOHERTY 2018 | European (UK) | 91 105 | |
| GCST007561 | 30846698 | DASHTI 2019 | European (UK) | 446 118 |
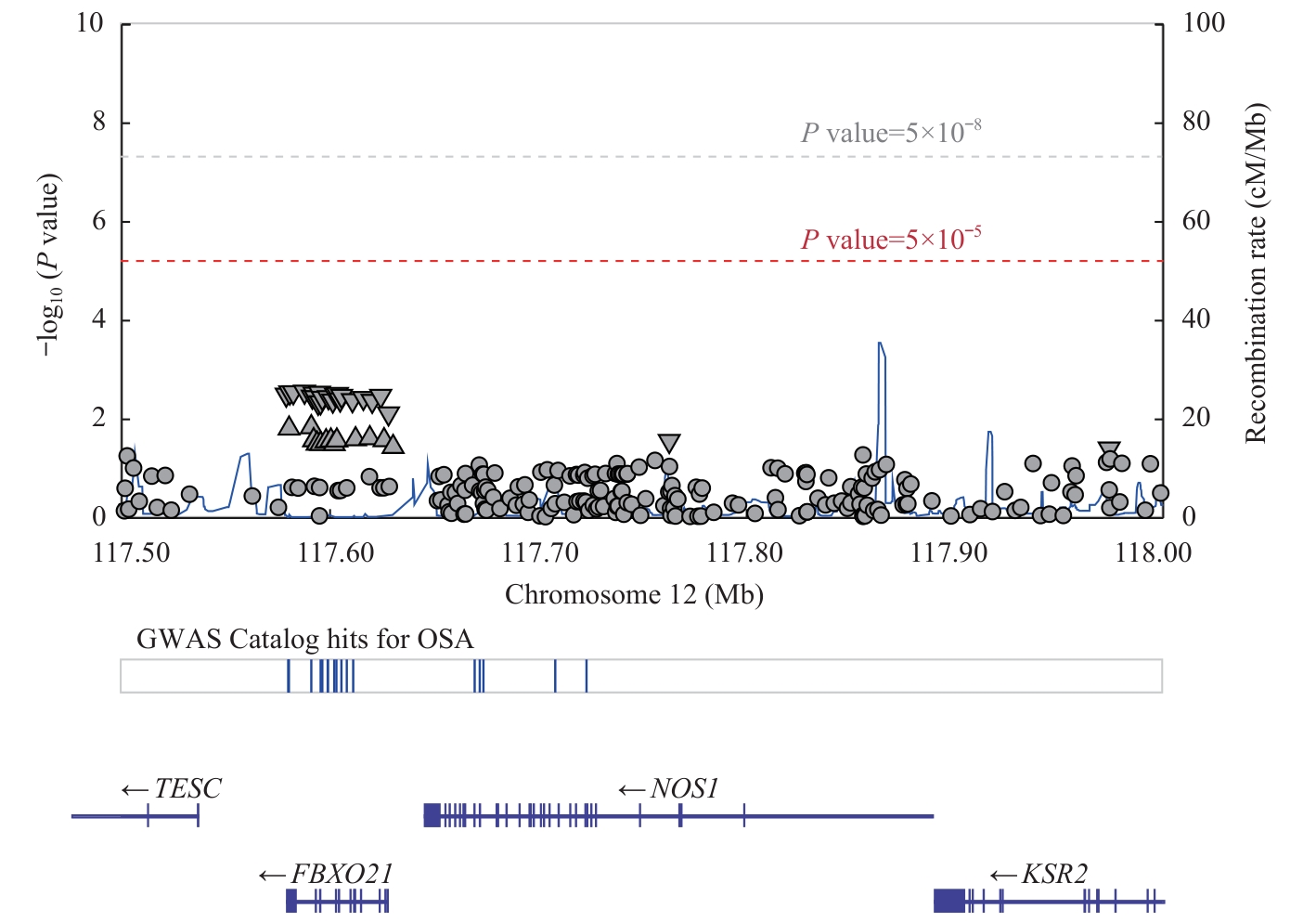
图3 LocusZoom分析 NOS1 SNP与OSA发病风险的关联Note: TESC—tescalcin; FBXO21—F-box protein 21; KSR2—kinase suppressor of RAS 2; Mb—megabase; cM—centimorgan.
Fig 3 LocusZoom analysis of the associations between NOS1 SNPs with OSA occurrence
| Variable | Overall (n=6 026) | AA (n=1 941) | CA (n=2 867) | CC (n=1 077) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype/n(%) | <0.001 | ||||
| AA | 1 941 (32.2) | 1 941 (100.0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| CA | 2 867 (47.6) | 0 (0) | 2 867 (100.0) | 0 (0) | |
| CC | 1 077 (17.9) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 077 (100.0) | |
| NA | 141 (2.3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| Gender/n(%) | 0.175 | ||||
| Male | 5 325 (88.4) | 1 699 (87.5) | 2 538 (88.5) | 967 (89.8) | |
| Female | 701 (11.6) | 242 (12.5) | 329 (11.5) | 110 (10.2) | |
| Smoking status/n(%) | 0.924 | ||||
| Never | 3 926 (65.2) | 1 262 (65.0) | 1 872 (65.3) | 708 (65.7) | |
| Ever | 2 100 (34.8) | 679 (35.0) | 995 (34.7) | 369 (34.3) | |
| Drinking status/n(%) | 0.862 | ||||
| Never | 3 637 (60.4) | 1 181 (60.8) | 1 722 (60.1) | 650 (60.4) | |
| Ever | 2 389 (39.6) | 760 (39.2) | 1 145 (39.9) | 427 (39.6) | |
| AHI (events/h)①/n(%) | <0.001 | ||||
| AHI< 5 (Non-OSA) | 764 (12.7) | 212 (10.9) | 360 (12.6) | 173 (16.1) | |
| 5 ≤AHI < 15 (Mild-OSA) | 318 (5.3) | 90 (4.6) | 161 (5.6) | 63 (5.9) | |
| 15 ≤AHI < 30 (Moderate-OSA) | 1 245 (20.7) | 407 (21.0) | 577 (20.1) | 235 (21.9) | |
| ≥30 (Severe-OSA) | 3 692 (61.3) | 1 231 (63.4) | 1 766 (61.6) | 603 (56.1) | |
| T2DM status/n(%) | 0.787 | ||||
| No | 5 580 (92.6) | 1 790 (92.2) | 2 658 (92.7) | 999 (92.8) | |
| Yes | 446 (7.4) | 151 (7.8) | 209 (7.3) | 78 (7.2) | |
| Hypertension status/n(%) | 0.761 | ||||
| No | 5 141 (85.3) | 1 649 (85.0) | 2 452 (85.5) | 925 (85.9) | |
| Yes | 885 (14.7) | 292 (15.0) | 415 (14.5) | 152 (14.1) |
表3 rs7305526各基因型特征
Tab 3 Characteristics of each genotype of rs7305526
| Variable | Overall (n=6 026) | AA (n=1 941) | CA (n=2 867) | CC (n=1 077) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype/n(%) | <0.001 | ||||
| AA | 1 941 (32.2) | 1 941 (100.0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| CA | 2 867 (47.6) | 0 (0) | 2 867 (100.0) | 0 (0) | |
| CC | 1 077 (17.9) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 077 (100.0) | |
| NA | 141 (2.3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| Gender/n(%) | 0.175 | ||||
| Male | 5 325 (88.4) | 1 699 (87.5) | 2 538 (88.5) | 967 (89.8) | |
| Female | 701 (11.6) | 242 (12.5) | 329 (11.5) | 110 (10.2) | |
| Smoking status/n(%) | 0.924 | ||||
| Never | 3 926 (65.2) | 1 262 (65.0) | 1 872 (65.3) | 708 (65.7) | |
| Ever | 2 100 (34.8) | 679 (35.0) | 995 (34.7) | 369 (34.3) | |
| Drinking status/n(%) | 0.862 | ||||
| Never | 3 637 (60.4) | 1 181 (60.8) | 1 722 (60.1) | 650 (60.4) | |
| Ever | 2 389 (39.6) | 760 (39.2) | 1 145 (39.9) | 427 (39.6) | |
| AHI (events/h)①/n(%) | <0.001 | ||||
| AHI< 5 (Non-OSA) | 764 (12.7) | 212 (10.9) | 360 (12.6) | 173 (16.1) | |
| 5 ≤AHI < 15 (Mild-OSA) | 318 (5.3) | 90 (4.6) | 161 (5.6) | 63 (5.9) | |
| 15 ≤AHI < 30 (Moderate-OSA) | 1 245 (20.7) | 407 (21.0) | 577 (20.1) | 235 (21.9) | |
| ≥30 (Severe-OSA) | 3 692 (61.3) | 1 231 (63.4) | 1 766 (61.6) | 603 (56.1) | |
| T2DM status/n(%) | 0.787 | ||||
| No | 5 580 (92.6) | 1 790 (92.2) | 2 658 (92.7) | 999 (92.8) | |
| Yes | 446 (7.4) | 151 (7.8) | 209 (7.3) | 78 (7.2) | |
| Hypertension status/n(%) | 0.761 | ||||
| No | 5 141 (85.3) | 1 649 (85.0) | 2 452 (85.5) | 925 (85.9) | |
| Yes | 885 (14.7) | 292 (15.0) | 415 (14.5) | 152 (14.1) |
| Variable | Overall (n=6 026) | CC (n=3 352) | TC (n=2 236) | TT (n=385) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype/n(%) | <0.001 | ||||
| CC | 3 352 (55.6) | 3 352 (100.0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| TC | 2 236 (37.1) | 0 (0) | 2 236 (100.0) | 0 (0) | |
| TT | 3 85 (6.4) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 385 (100.0) | |
| NA | 53 (0.9) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| Gender/n(%) | 0.027 | ||||
| Male | 5 325 (88.4) | 2 965 (88.5) | 1 956 (87.5) | 355 (92.2) | |
| Female | 701 (11.6) | 387 (11.5) | 280 (12.5) | 30 (7.8) | |
| Smoking status/n(%) | 0.599 | ||||
| Never | 3 926 (65.2) | 2 183 (65.1) | 1 465 (65.5) | 242 (62.9) | |
| Ever | 2 100 (34.8) | 1 169 (34.9) | 771 (34.5) | 143 (37.1) | |
| Drinking status/n(%) | 0.513 | ||||
| Never | 3 637 (60.4) | 2 004 (59.8) | 1 371 (61.3) | 231 (60.0) | |
| Ever | 2 389 (39.6) | 1 348 (40.2) | 865 (38.7) | 154 (40.0) | |
| AHI (events/h)①/n(%) | 0.685 | ||||
| AHI< 5 (Non-OSA) | 764 (12.7) | 421 (12.6) | 293 (13.1) | 44 (11.4) | |
| 5 ≤AHI < 15 (Mild-OSA) | 318 (5.3) | 184 (5.5) | 109 (4.9) | 22 (5.7) | |
| 15 ≤AHI < 30 (Moderate-OSA) | 1 245 (20.7) | 700 (20.9) | 459 (20.6) | 70 (18.2) | |
| ≥30 (Severe-OSA) | 3 692 (61.3) | 2 044 (61.0) | 1 371 (61.4) | 249 (64.7) | |
| T2DM status/n(%) | 0.989 | ||||
| No | 5 580 (92.6) | 3 104 (92.6) | 2 072 (92.7) | 356 (92.5) | |
| Yes | 446 (7.4) | 248 (7.4) | 164 (7.3) | 29 (7.5) | |
| Hypertension status/n(%) | 0.568 | ||||
| No | 5 141 (85.3) | 2 863 (85.4) | 1 896 (84.8) | 334 (86.8) | |
| Yes | 885 (14.7) | 489 (14.6) | 340 (15.2) | 51 (13.2) |
表4 rs11615756各基因型特征
Tab 4 Characteristics of each genotype of rs11615756
| Variable | Overall (n=6 026) | CC (n=3 352) | TC (n=2 236) | TT (n=385) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype/n(%) | <0.001 | ||||
| CC | 3 352 (55.6) | 3 352 (100.0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| TC | 2 236 (37.1) | 0 (0) | 2 236 (100.0) | 0 (0) | |
| TT | 3 85 (6.4) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 385 (100.0) | |
| NA | 53 (0.9) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| Gender/n(%) | 0.027 | ||||
| Male | 5 325 (88.4) | 2 965 (88.5) | 1 956 (87.5) | 355 (92.2) | |
| Female | 701 (11.6) | 387 (11.5) | 280 (12.5) | 30 (7.8) | |
| Smoking status/n(%) | 0.599 | ||||
| Never | 3 926 (65.2) | 2 183 (65.1) | 1 465 (65.5) | 242 (62.9) | |
| Ever | 2 100 (34.8) | 1 169 (34.9) | 771 (34.5) | 143 (37.1) | |
| Drinking status/n(%) | 0.513 | ||||
| Never | 3 637 (60.4) | 2 004 (59.8) | 1 371 (61.3) | 231 (60.0) | |
| Ever | 2 389 (39.6) | 1 348 (40.2) | 865 (38.7) | 154 (40.0) | |
| AHI (events/h)①/n(%) | 0.685 | ||||
| AHI< 5 (Non-OSA) | 764 (12.7) | 421 (12.6) | 293 (13.1) | 44 (11.4) | |
| 5 ≤AHI < 15 (Mild-OSA) | 318 (5.3) | 184 (5.5) | 109 (4.9) | 22 (5.7) | |
| 15 ≤AHI < 30 (Moderate-OSA) | 1 245 (20.7) | 700 (20.9) | 459 (20.6) | 70 (18.2) | |
| ≥30 (Severe-OSA) | 3 692 (61.3) | 2 044 (61.0) | 1 371 (61.4) | 249 (64.7) | |
| T2DM status/n(%) | 0.989 | ||||
| No | 5 580 (92.6) | 3 104 (92.6) | 2 072 (92.7) | 356 (92.5) | |
| Yes | 446 (7.4) | 248 (7.4) | 164 (7.3) | 29 (7.5) | |
| Hypertension status/n(%) | 0.568 | ||||
| No | 5 141 (85.3) | 2 863 (85.4) | 1 896 (84.8) | 334 (86.8) | |
| Yes | 885 (14.7) | 489 (14.6) | 340 (15.2) | 51 (13.2) |
| SNP | Genotype | Ratio of individuals of each genotype/% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-OSA | OSA | ||
| rs7305526 | AA | 28.46 | 33.66 |
| CA | 48.32 | 48.78 | |
| CC | 23.22 | 17.55 | |
| rs11615756 | CC | 55.54 | 56.22 |
| TC | 38.65 | 37.23 | |
| TT | 5.80 | 6.55 | |
表5 rs7305526和rs11615756在非OSA和OSA人群中的各基因型比率
Tab 5 Individual genotype ratios of rs7305526 and rs11615756 in non-OSA and OSA populations
| SNP | Genotype | Ratio of individuals of each genotype/% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-OSA | OSA | ||
| rs7305526 | AA | 28.46 | 33.66 |
| CA | 48.32 | 48.78 | |
| CC | 23.22 | 17.55 | |
| rs11615756 | CC | 55.54 | 56.22 |
| TC | 38.65 | 37.23 | |
| TT | 5.80 | 6.55 | |
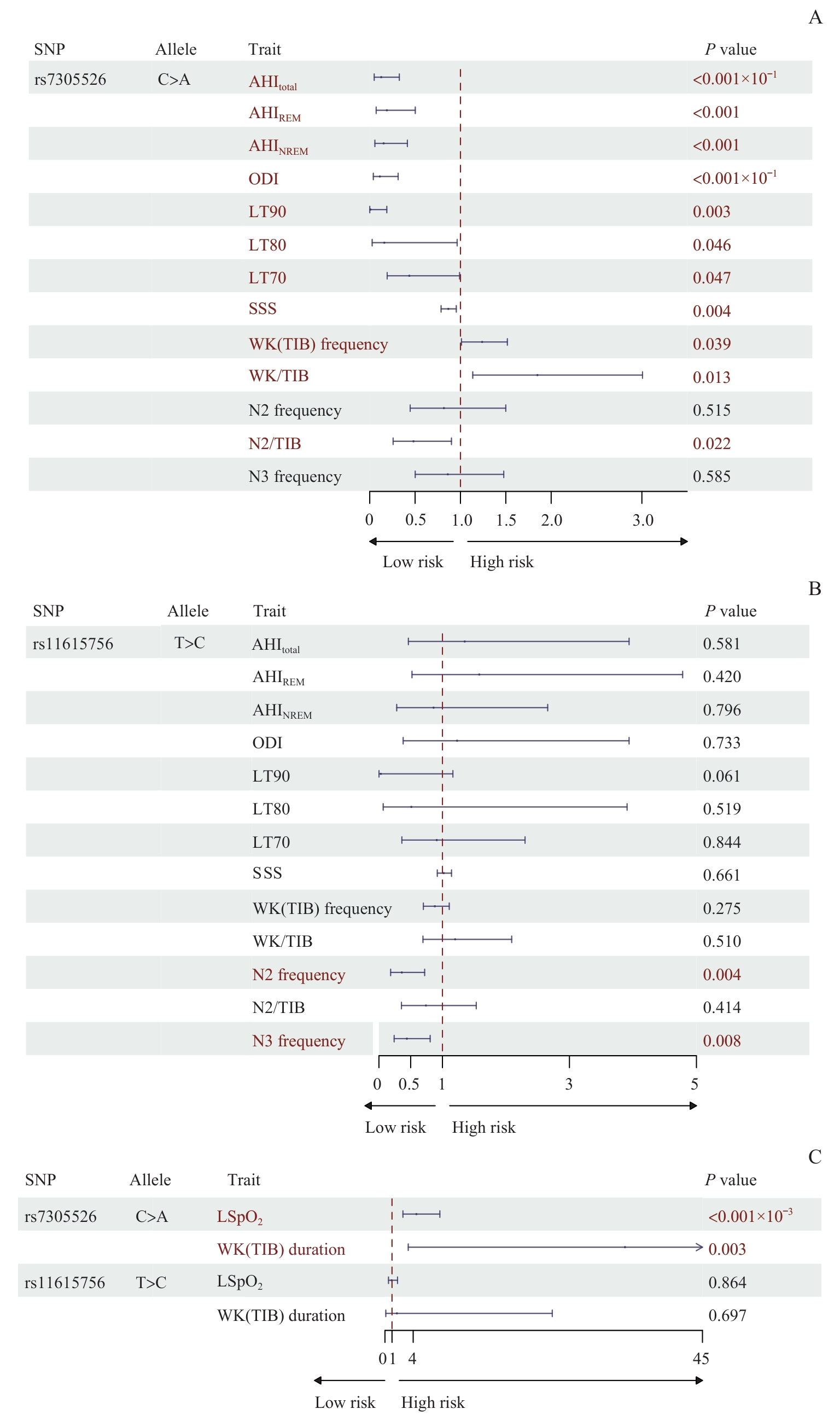
图4 rs7305526和rs11615756与OSA临床数量性状的关联Note: A. Forest plot illustrating the association of genetic variant rs7305526 with clinical quantitative traits of OSA. B. Forest plot illustrating the associations of genetic variant rs11615756 with clinical quantitative traits of OSA. C. Forest plot illustrating the associations of rs7305526 and rs11615756 with additional clinical quantitative traits of OSA.
Fig 4 Associations of genetic variants rs7305526 and rs11615756 with clinical quantitative traits of OSA
| SNP | Allele | Trait | OR | 95%CI | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| rs7305526 | C>A | AHItotal | 0.126 | 0.049 | 0.326 | <0.001 |
| AHIREM | 0.189 | 0.071 | 0.502 | <0.001 | ||
| AHINREM | 0.153 | 0.057 | 0.415 | <0.001 | ||
| ODI | 0.111 | 0.040 | 0.313 | <0.001 | ||
| LT90 | 0.008 | 0.001 | 0.188 | 0.003 | ||
| LT80 | 0.160 | 0.027 | 0.964 | 0.046 | ||
| LT70 | 0.436 | 0.192 | 0.990 | 0.047 | ||
| LSpO2 | 4.455 | 2.548 | 7.784 | <0.001 | ||
| SSS | 0.866 | 0.787 | 0.954 | 0.004 | ||
| WK(TIB) frequency | 1.239 | 1.011 | 1.517 | 0.039 | ||
| WK(TIB) duration | 34.022 | 3.300 | 350.724 | 0.003 | ||
| WK/TIB | 1.848 | 1.136 | 3.007 | 0.013 | ||
| N2 frequency | 0.818 | 0.446 | 1.500 | 0.515 | ||
| N2/TIB | 0.482 | 0.258 | 0.901 | 0.022 | ||
| N3 frequency | 0.861 | 0.501 | 1.477 | 0.586 | ||
| rs11615756 | T>C | AHItotal | 1.352 | 0.464 | 3.939 | 0.581 |
| AHIREM | 1.578 | 0.521 | 4.783 | 0.420 | ||
| AHINREM | 0.862 | 0.280 | 2.658 | 0.796 | ||
| ODI | 1.225 | 0.381 | 3.939 | 0.733 | ||
| LT90 | 0.032 | 0.001 | 1.165 | 0.061 | ||
| LT80 | 0.512 | 0.067 | 3.908 | 0.519 | ||
| LT70 | 0.911 | 0.361 | 2.301 | 0.844 | ||
| LSpO2 | 0.946 | 0.501 | 1.785 | 0.864 | ||
| SSS | 1.025 | 0.919 | 1.143 | 0.661 | ||
| WK(TIB) frequency | 0.880 | 0.700 | 1.107 | 0.275 | ||
| WK(TIB) duration | 1.690 | 0.120 | 23.712 | 0.697 | ||
| WK/TIB | 1.204 | 0.693 | 2.091 | 0.510 | ||
| N2 frequency | 0.364 | 0.184 | 0.720 | 0.004 | ||
| N2/TIB | 0.737 | 0.355 | 1.533 | 0.414 | ||
| N3 frequency | 0.440 | 0.240 | 0.807 | 0.008 | ||
表6 rs7305526和rs11615756与OSA临床数量性状的关联
Tab 6 Associations of genetic variants rs7305526 and rs11615756 with clinical quantitative traits of OSA
| SNP | Allele | Trait | OR | 95%CI | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| rs7305526 | C>A | AHItotal | 0.126 | 0.049 | 0.326 | <0.001 |
| AHIREM | 0.189 | 0.071 | 0.502 | <0.001 | ||
| AHINREM | 0.153 | 0.057 | 0.415 | <0.001 | ||
| ODI | 0.111 | 0.040 | 0.313 | <0.001 | ||
| LT90 | 0.008 | 0.001 | 0.188 | 0.003 | ||
| LT80 | 0.160 | 0.027 | 0.964 | 0.046 | ||
| LT70 | 0.436 | 0.192 | 0.990 | 0.047 | ||
| LSpO2 | 4.455 | 2.548 | 7.784 | <0.001 | ||
| SSS | 0.866 | 0.787 | 0.954 | 0.004 | ||
| WK(TIB) frequency | 1.239 | 1.011 | 1.517 | 0.039 | ||
| WK(TIB) duration | 34.022 | 3.300 | 350.724 | 0.003 | ||
| WK/TIB | 1.848 | 1.136 | 3.007 | 0.013 | ||
| N2 frequency | 0.818 | 0.446 | 1.500 | 0.515 | ||
| N2/TIB | 0.482 | 0.258 | 0.901 | 0.022 | ||
| N3 frequency | 0.861 | 0.501 | 1.477 | 0.586 | ||
| rs11615756 | T>C | AHItotal | 1.352 | 0.464 | 3.939 | 0.581 |
| AHIREM | 1.578 | 0.521 | 4.783 | 0.420 | ||
| AHINREM | 0.862 | 0.280 | 2.658 | 0.796 | ||
| ODI | 1.225 | 0.381 | 3.939 | 0.733 | ||
| LT90 | 0.032 | 0.001 | 1.165 | 0.061 | ||
| LT80 | 0.512 | 0.067 | 3.908 | 0.519 | ||
| LT70 | 0.911 | 0.361 | 2.301 | 0.844 | ||
| LSpO2 | 0.946 | 0.501 | 1.785 | 0.864 | ||
| SSS | 1.025 | 0.919 | 1.143 | 0.661 | ||
| WK(TIB) frequency | 0.880 | 0.700 | 1.107 | 0.275 | ||
| WK(TIB) duration | 1.690 | 0.120 | 23.712 | 0.697 | ||
| WK/TIB | 1.204 | 0.693 | 2.091 | 0.510 | ||
| N2 frequency | 0.364 | 0.184 | 0.720 | 0.004 | ||
| N2/TIB | 0.737 | 0.355 | 1.533 | 0.414 | ||
| N3 frequency | 0.440 | 0.240 | 0.807 | 0.008 | ||
| Gender | SNP | Allele | Trait | OR | 95%CI | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||
| Male | rs7305526 | C>A | AHItotal | 0.103 | 0.037 | 0.285 | <0.001 |
| AHIREM | 0.189 | 0.066 | 0.535 | 0.002 | |||
| AHINREM | 0.111 | 0.038 | 0.322 | <0.001 | |||
| ODI | 0.093 | 0.031 | 0.281 | <0.001 | |||
| LT90 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.116 | 0.001 | |||
| LT80 | 0.177 | 0.029 | 1.087 | 0.061 | |||
| LT70 | 0.540 | 0.252 | 1.154 | 0.112 | |||
| LSpO2 | 4.782 | 2.821 | 8.108 | <0.001 | |||
| SSS | 0.865 | 0.781 | 0.958 | 0.006 | |||
| WK (TIB) frequency | 1.215 | 0.979 | 1.508 | 0.078 | |||
| WK (TIB) duration | 36.696 | 3.154 | 426.991 | 0.004 | |||
| WK/TIB | 2.002 | 1.208 | 3.318 | 0.007 | |||
| N2 frequency | 0.781 | 0.412 | 1.482 | 0.450 | |||
| N2/TIB | 0.129 | 0.006 | 2.867 | 0.195 | |||
| N3 frequency | 2.881 | 0.268 | 30.958 | 0.382 | |||
| rs11615756 | T>C | AHItotal | 1.251 | 0.398 | 3.929 | <0.001 | |
| AHIREM | 1.246 | 0.385 | 4.039 | 0.002 | |||
| AHINREM | 0.890 | 0.268 | 2.962 | <0.001 | |||
| ODI | 1.049 | 0.303 | 3.638 | <0.001 | |||
| LT90 | 0.049 | 0.001 | 2.051 | 0.001 | |||
| LT80 | 0.369 | 0.047 | 2.868 | 0.061 | |||
| LT70 | 0.748 | 0.317 | 1.764 | 0.112 | |||
| LSpO2 | 1.159 | 0.638 | 2.105 | <0.001 | |||
| SSS | 1.020 | 0.909 | 1.144 | 0.006 | |||
| WK (TIB) frequency | 0.862 | 0.676 | 1.100 | 0.078 | |||
| WK (TIB) duration | 4.212 | 0.264 | 67.122 | 0.004 | |||
| WK/TIB | 1.430 | 0.808 | 2.531 | 0.007 | |||
| N2 frequency | 0.356 | 0.174 | 0.726 | 0.450 | |||
| N2/TIB | 0.823 | 0.025 | 27.424 | 0.195 | |||
| N3 frequency | 0.197 | 0.014 | 2.876 | 0.382 | |||
| Female | rs7305526 | C>A | AHItotal | 0.726 | 0.060 | 8.786 | 0.801 |
| AHIREM | 0.371 | 0.025 | 5.499 | 0.471 | |||
| AHINREM | 1.586 | 0.106 | 23.735 | 0.738 | |||
| ODI | 0.761 | 0.045 | 12.926 | 0.850 | |||
| LT90 | 0.238 | 0.002 | 5 373.921 | 0.779 | |||
| LT80 | 0.128 | 0.001 | 195.286 | 0.581 | |||
| LT70 | 0.163 | 0.006 | 4.516 | 0.283 | |||
| LSpO2 | 1.137 | 0.266 | 4.854 | 0.862 | |||
| SSS | 0.846 | 0.635 | 1.127 | 0.253 | |||
| WK (TIB) frequency | 1.352 | 0.766 | 2.384 | 0.298 | |||
| WK (TIB) duration | 26.286 | 0.017 | 41 622.230 | 0.384 | |||
| WK/TIB | 1.857 | 0.394 | 8.760 | 0.434 | |||
| N2 frequency | 1.020 | 0.152 | 6.841 | 0.984 | |||
| N2/TIB | 0.002 | 0.001 | 2.374 | 0.078 | |||
| N3 frequency | 11.913 | 0.017 | 8 142.930 | 0.456 | |||
| rs11615756 | T>C | AHItotal | 3.274 | 0.174 | 61.738 | 0.428 | |
| AHIREM | 19.344 | 0.799 | 468.319 | 0.068 | |||
| AHINREM | 0.808 | 0.034 | 19.383 | 0.895 | |||
| ODI | 5.700 | 0.202 | 161.096 | 0.307 | |||
| LT90 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 716.665 | 0.375 | |||
| LT80 | 14.017 | 0.003 | 65 377.371 | 0.539 | |||
| LT70 | 20.663 | 0.444 | 960.811 | 0.122 | |||
| LSpO2 | 0.397 | 0.073 | 2.162 | 0.285 | |||
| SSS | 1.092 | 0.781 | 1.529 | 0.606 | |||
| WK (TIB) frequency | 1.047 | 0.537 | 2.040 | 0.893 | |||
| WK (TIB) duration | 0.002 | 0.001 | 3.107 | 0.088 | |||
| WK/TIB | 0.303 | 0.049 | 1.871 | 0.198 | |||
| N2 frequency | 0.546 | 0.057 | 5.229 | 0.599 | |||
| N2/TIB | 0.093 | 0.001 | 2 235.485 | 0.644 | |||
| N3 frequency | 0.096 | 0.001 | 201.306 | 0.547 | |||
表7 男性与女性rs7305526和rs11615756与OSA临床数量性状的关联
Tab 7 Associations of genetic variants rs7305526 and rs11615756 with clinical quantitative traits of OSA in male and female groups
| Gender | SNP | Allele | Trait | OR | 95%CI | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||
| Male | rs7305526 | C>A | AHItotal | 0.103 | 0.037 | 0.285 | <0.001 |
| AHIREM | 0.189 | 0.066 | 0.535 | 0.002 | |||
| AHINREM | 0.111 | 0.038 | 0.322 | <0.001 | |||
| ODI | 0.093 | 0.031 | 0.281 | <0.001 | |||
| LT90 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.116 | 0.001 | |||
| LT80 | 0.177 | 0.029 | 1.087 | 0.061 | |||
| LT70 | 0.540 | 0.252 | 1.154 | 0.112 | |||
| LSpO2 | 4.782 | 2.821 | 8.108 | <0.001 | |||
| SSS | 0.865 | 0.781 | 0.958 | 0.006 | |||
| WK (TIB) frequency | 1.215 | 0.979 | 1.508 | 0.078 | |||
| WK (TIB) duration | 36.696 | 3.154 | 426.991 | 0.004 | |||
| WK/TIB | 2.002 | 1.208 | 3.318 | 0.007 | |||
| N2 frequency | 0.781 | 0.412 | 1.482 | 0.450 | |||
| N2/TIB | 0.129 | 0.006 | 2.867 | 0.195 | |||
| N3 frequency | 2.881 | 0.268 | 30.958 | 0.382 | |||
| rs11615756 | T>C | AHItotal | 1.251 | 0.398 | 3.929 | <0.001 | |
| AHIREM | 1.246 | 0.385 | 4.039 | 0.002 | |||
| AHINREM | 0.890 | 0.268 | 2.962 | <0.001 | |||
| ODI | 1.049 | 0.303 | 3.638 | <0.001 | |||
| LT90 | 0.049 | 0.001 | 2.051 | 0.001 | |||
| LT80 | 0.369 | 0.047 | 2.868 | 0.061 | |||
| LT70 | 0.748 | 0.317 | 1.764 | 0.112 | |||
| LSpO2 | 1.159 | 0.638 | 2.105 | <0.001 | |||
| SSS | 1.020 | 0.909 | 1.144 | 0.006 | |||
| WK (TIB) frequency | 0.862 | 0.676 | 1.100 | 0.078 | |||
| WK (TIB) duration | 4.212 | 0.264 | 67.122 | 0.004 | |||
| WK/TIB | 1.430 | 0.808 | 2.531 | 0.007 | |||
| N2 frequency | 0.356 | 0.174 | 0.726 | 0.450 | |||
| N2/TIB | 0.823 | 0.025 | 27.424 | 0.195 | |||
| N3 frequency | 0.197 | 0.014 | 2.876 | 0.382 | |||
| Female | rs7305526 | C>A | AHItotal | 0.726 | 0.060 | 8.786 | 0.801 |
| AHIREM | 0.371 | 0.025 | 5.499 | 0.471 | |||
| AHINREM | 1.586 | 0.106 | 23.735 | 0.738 | |||
| ODI | 0.761 | 0.045 | 12.926 | 0.850 | |||
| LT90 | 0.238 | 0.002 | 5 373.921 | 0.779 | |||
| LT80 | 0.128 | 0.001 | 195.286 | 0.581 | |||
| LT70 | 0.163 | 0.006 | 4.516 | 0.283 | |||
| LSpO2 | 1.137 | 0.266 | 4.854 | 0.862 | |||
| SSS | 0.846 | 0.635 | 1.127 | 0.253 | |||
| WK (TIB) frequency | 1.352 | 0.766 | 2.384 | 0.298 | |||
| WK (TIB) duration | 26.286 | 0.017 | 41 622.230 | 0.384 | |||
| WK/TIB | 1.857 | 0.394 | 8.760 | 0.434 | |||
| N2 frequency | 1.020 | 0.152 | 6.841 | 0.984 | |||
| N2/TIB | 0.002 | 0.001 | 2.374 | 0.078 | |||
| N3 frequency | 11.913 | 0.017 | 8 142.930 | 0.456 | |||
| rs11615756 | T>C | AHItotal | 3.274 | 0.174 | 61.738 | 0.428 | |
| AHIREM | 19.344 | 0.799 | 468.319 | 0.068 | |||
| AHINREM | 0.808 | 0.034 | 19.383 | 0.895 | |||
| ODI | 5.700 | 0.202 | 161.096 | 0.307 | |||
| LT90 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 716.665 | 0.375 | |||
| LT80 | 14.017 | 0.003 | 65 377.371 | 0.539 | |||
| LT70 | 20.663 | 0.444 | 960.811 | 0.122 | |||
| LSpO2 | 0.397 | 0.073 | 2.162 | 0.285 | |||
| SSS | 1.092 | 0.781 | 1.529 | 0.606 | |||
| WK (TIB) frequency | 1.047 | 0.537 | 2.040 | 0.893 | |||
| WK (TIB) duration | 0.002 | 0.001 | 3.107 | 0.088 | |||
| WK/TIB | 0.303 | 0.049 | 1.871 | 0.198 | |||
| N2 frequency | 0.546 | 0.057 | 5.229 | 0.599 | |||
| N2/TIB | 0.093 | 0.001 | 2 235.485 | 0.644 | |||
| N3 frequency | 0.096 | 0.001 | 201.306 | 0.547 | |||
| SNP | Trait | Non-OSA (n=764) | Mild-OSA (n=318) | Moderate-OSA (n=1 245) | Severe-OSA (n=3 692) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
P value | OR (95%CI) | P value | OR (95%CI) | P value | OR (95%CI) | P value | OR (95%CI) | ||
| rs7305526 | AHItotal | 0.530 | 0.955 (0.826‒1.104) | 0.290 | 0.818 (0.563‒1.188) | 0.619 | 1.090 (0.777‒1.528) | 0.206 | 0.593 (0.264‒1.334) |
| AHIREM | 0.763 | 1.176 (0.410‒3.380) | 0.965 | 1.070 (0.054‒21.232) | 0.890 | 0.894 (0.182‒4.383) | 0.577 | 0.749 (0.271‒2.070) | |
| AHINREM | 0.464 | 1.461 (0.529‒4.0332) | 0.143 | 4.276 (0.611‒29.910) | 0.846 | 1.076 (0.517‒2.239) | 0.206 | 0.538 (0.205‒1.408) | |
| ODI | 0.821 | 0.847 (0.199‒3.602) | 0.562 | 1.330 (0.505‒3.501) | 0.124 | 0.516 (0.222‒1.200) | 0.464 | 0.684 (0.247‒1.892) | |
| LT90 | 0.633 | 0.536 (0.041‒6.958) | 0.036 | 23.117 (1.232‒433.679) | 0.632 | 1.864 (0.146‒23.881) | 0.122 | 0.032 (0.001‒2.517) | |
| LT80 | 0.982 | 0.999 (0.907‒1.100) | 0.097 | 1.397 (0.941‒2.074) | 0.678 | 0.878 (0.475‒1.624) | 0.392 | 0.290 (0.017‒4.948) | |
| LT70 | 0.278 | 0.998 (0.993‒1.002) | 0.613 | 0.990 (0.951‒1.030) | 0.331 | 1.064 (0.939‒1.205) | 0.179 | 0.424 (0.121‒1.481) | |
| LSpO2 | 0.019 | 2.039 (1.124‒3.699) | 0.958 | 1.028 (0.372‒2.841) | 0.022 | 2.280 (1.129‒4.605) | 0.008 | 2.217 (1.226‒4.011) | |
| SSS | 0.421 | 0.888 (0.666‒1.186) | 0.333 | 1.193 (0.834‒1.706) | 0.995 | 1.001 (0.817‒1.226) | 0.153 | 0.923 (0.826‒1.030) | |
| WK (TIB) frequency | 0.215 | 1.498 (0.791‒2.838) | 0.016 | 0.369 (0.163‒0.832) | 0.130 | 1.432 (0.900‒2.281) | 0.244 | 1.158 (0.905‒1.4811) | |
| WK (TIB) duration | 0.119 | 406.376 (0.213‒775 370.391) | 0.606 | 0.060 (0.001‒2674.448) | 0.046 | 269.283 (1.095‒66 255.145) | 0.230 | 5.352 (0.345‒83.043) | |
| WK/TIB | 0.097 | 3.846 (0.784‒18.871) | 0.714 | 0.661 (0.072‒6.081) | 0.142 | 2.251 (0.763‒6.641) | 0.240 | 1.411 (0.794‒2.508) | |
| N2 frequency | 0.788 | 0.857 (0.277‒2.650 6) | 0.432 | 0.454 (0.063‒3.278) | 0.921 | 0.942 (0.289‒3.071) | 0.892 | 0.942 (0.398‒2.230) | |
| N2/TIB | 0.214 | 0.009 (0.001‒15.720) | 0.035 | 0.002 (0.001‒0.405) | 0.678 | 0.272 (0.001‒128.335) | 0.695 | 0.462 (0.010‒21.825) | |
| N3 frequency | 0.295 | 0.045 (0.001‒14.873) | 0.021 | 10 267.538 (3.963‒26 600 123.192) | 0.528 | 4.297 (0.046‒400.757) | 0.648 | 2.015 (0.099‒40.930) | |
| rs11615756 | AHItotal | 0.777 | 0.976 (0.823‒1.157) | 0.875 | 0.968 (0.639‒1.464) | 0.626 | 1.104 (0.742‒1.642) | 0.626 | 0.801 (0.328‒1.957) |
| AHIREM | 0.027 | 0.251 (0.074‒0.856) | 0.791 | 1.551 (0.060‒40.217) | 0.085 | 5.121 (0.800‒32.802) | 0.750 | 1.202 (0.389‒3.711) | |
| AHINREM | 0.029 | 0.270 (0.083‒0.875) | 0.504 | 0.500 (0.065‒3.838) | 0.392 | 1.457 (0.616‒3.448) | 0.377 | 0.620 (0.214‒1.793) | |
| ODI | 0.123 | 0.266 (0.050‒1.429) | 0.846 | 1.112 (0.381‒3.249) | 0.840 | 1.108 (0.411‒2.98) | 0.994 | 1.004 (0.327‒3.080) | |
| LT90 | 0.511 | 2.705 (0.139‒52.722) | 0.076 | 0.053 (0.002‒1.364) | 0.324 | 4.571 (0.222‒93.989) | 0.006 | 0.002 (0.001‒0.148) | |
| LT80 | 0.407 | 0.952 (0.848‒1.069) | 0.757 | 1.074 (0.682‒1.690) | 0.077 | 1.885 (0.933‒3.807) | 0.290 | 0.184 (0.008‒4.251) | |
| LT70 | 0.314 | 0.997 (0.992‒1.003) | 0.565 | 0.987 (0.943‒1.033) | 0.035 | 1.166 (1.011‒1.344) | 0.857 | 0.881 (0.221‒3.504) | |
| LSpO2 | 0.951 | 1.022 (0.511‒2.046) | 0.314 | 1.780 (0.577‒5.489) | 0.480 | 0.743 (0.326‒1.696) | 0.357 | 1.362 (0.706‒2.627) | |
| SSS | 0.697 | 1.070 (0.762‒1.501) | 0.019 | 0.626 (0.423‒0.926) | 0.949 | 0.992 (0.782‒1.259) | 0.435 | 1.050 (0.929‒1.186) | |
| WK (TIB) frequency | 0.238 | 0.636 (0.300‒1.349) | 0.835 | 1.101 (0.444‒2.731) | 0.917 | 0.971 (0.561‒1.682) | 0.470 | 0.905 (0.689‒1.188) | |
| WK (TIB) duration | 0.397 | 46.583 (0.006‒338 729.248) | 0.531 | 43.721 (0.001‒6 081 353.502) | 0.772 | 0.381 (0.001‒256.719) | 0.879 | 1.266 (0.061‒26.225) | |
| WK/TIB | 0.456 | 2.041 (0.313‒13.327) | 0.661 | 1.729 (0.148‒20.150) | 0.845 | 0.881 (0.245‒3.167) | 0.517 | 1.234 (0.653‒2.331) | |
| N2 frequency | 0.135 | 0.366 (0.098‒1.370) | 0.934 | 0.911 (0.099‒8.373) | 0.918 | 0.930 (0.234‒3.703) | 0.005 | 0.261 (0.101‒0.671) | |
| N2/TIB | 0.091 | 2 007.782 (0.296‒13 627 828.272) | 0.832 | 3.998 (0.001‒1 516 906.783) | 0.407 | 0.046 (0.001‒66.068) | 0.498 | 0.228 (0.003‒16.421) | |
| N3 frequency | 0.979 | 1.094 (0.001‒976.421) | 0.665 | 0.145 (0.001‒929.697) | 0.778 | 0.464 (0.002‒96.210) | 0.173 | 0.098 (0.004‒2.775) | |
表8 非OSA组,以及轻度、中度和重度OSA组rs7305526和rs11615756与OSA临床数量性状的关联
Tab 8 Associations between genetic variants rs7305526 and rs11615756 with clinical quantitative traits of OSA in non-OSA, mild-OSA, moderate-OSA and severe-OSA groups
| SNP | Trait | Non-OSA (n=764) | Mild-OSA (n=318) | Moderate-OSA (n=1 245) | Severe-OSA (n=3 692) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
P value | OR (95%CI) | P value | OR (95%CI) | P value | OR (95%CI) | P value | OR (95%CI) | ||
| rs7305526 | AHItotal | 0.530 | 0.955 (0.826‒1.104) | 0.290 | 0.818 (0.563‒1.188) | 0.619 | 1.090 (0.777‒1.528) | 0.206 | 0.593 (0.264‒1.334) |
| AHIREM | 0.763 | 1.176 (0.410‒3.380) | 0.965 | 1.070 (0.054‒21.232) | 0.890 | 0.894 (0.182‒4.383) | 0.577 | 0.749 (0.271‒2.070) | |
| AHINREM | 0.464 | 1.461 (0.529‒4.0332) | 0.143 | 4.276 (0.611‒29.910) | 0.846 | 1.076 (0.517‒2.239) | 0.206 | 0.538 (0.205‒1.408) | |
| ODI | 0.821 | 0.847 (0.199‒3.602) | 0.562 | 1.330 (0.505‒3.501) | 0.124 | 0.516 (0.222‒1.200) | 0.464 | 0.684 (0.247‒1.892) | |
| LT90 | 0.633 | 0.536 (0.041‒6.958) | 0.036 | 23.117 (1.232‒433.679) | 0.632 | 1.864 (0.146‒23.881) | 0.122 | 0.032 (0.001‒2.517) | |
| LT80 | 0.982 | 0.999 (0.907‒1.100) | 0.097 | 1.397 (0.941‒2.074) | 0.678 | 0.878 (0.475‒1.624) | 0.392 | 0.290 (0.017‒4.948) | |
| LT70 | 0.278 | 0.998 (0.993‒1.002) | 0.613 | 0.990 (0.951‒1.030) | 0.331 | 1.064 (0.939‒1.205) | 0.179 | 0.424 (0.121‒1.481) | |
| LSpO2 | 0.019 | 2.039 (1.124‒3.699) | 0.958 | 1.028 (0.372‒2.841) | 0.022 | 2.280 (1.129‒4.605) | 0.008 | 2.217 (1.226‒4.011) | |
| SSS | 0.421 | 0.888 (0.666‒1.186) | 0.333 | 1.193 (0.834‒1.706) | 0.995 | 1.001 (0.817‒1.226) | 0.153 | 0.923 (0.826‒1.030) | |
| WK (TIB) frequency | 0.215 | 1.498 (0.791‒2.838) | 0.016 | 0.369 (0.163‒0.832) | 0.130 | 1.432 (0.900‒2.281) | 0.244 | 1.158 (0.905‒1.4811) | |
| WK (TIB) duration | 0.119 | 406.376 (0.213‒775 370.391) | 0.606 | 0.060 (0.001‒2674.448) | 0.046 | 269.283 (1.095‒66 255.145) | 0.230 | 5.352 (0.345‒83.043) | |
| WK/TIB | 0.097 | 3.846 (0.784‒18.871) | 0.714 | 0.661 (0.072‒6.081) | 0.142 | 2.251 (0.763‒6.641) | 0.240 | 1.411 (0.794‒2.508) | |
| N2 frequency | 0.788 | 0.857 (0.277‒2.650 6) | 0.432 | 0.454 (0.063‒3.278) | 0.921 | 0.942 (0.289‒3.071) | 0.892 | 0.942 (0.398‒2.230) | |
| N2/TIB | 0.214 | 0.009 (0.001‒15.720) | 0.035 | 0.002 (0.001‒0.405) | 0.678 | 0.272 (0.001‒128.335) | 0.695 | 0.462 (0.010‒21.825) | |
| N3 frequency | 0.295 | 0.045 (0.001‒14.873) | 0.021 | 10 267.538 (3.963‒26 600 123.192) | 0.528 | 4.297 (0.046‒400.757) | 0.648 | 2.015 (0.099‒40.930) | |
| rs11615756 | AHItotal | 0.777 | 0.976 (0.823‒1.157) | 0.875 | 0.968 (0.639‒1.464) | 0.626 | 1.104 (0.742‒1.642) | 0.626 | 0.801 (0.328‒1.957) |
| AHIREM | 0.027 | 0.251 (0.074‒0.856) | 0.791 | 1.551 (0.060‒40.217) | 0.085 | 5.121 (0.800‒32.802) | 0.750 | 1.202 (0.389‒3.711) | |
| AHINREM | 0.029 | 0.270 (0.083‒0.875) | 0.504 | 0.500 (0.065‒3.838) | 0.392 | 1.457 (0.616‒3.448) | 0.377 | 0.620 (0.214‒1.793) | |
| ODI | 0.123 | 0.266 (0.050‒1.429) | 0.846 | 1.112 (0.381‒3.249) | 0.840 | 1.108 (0.411‒2.98) | 0.994 | 1.004 (0.327‒3.080) | |
| LT90 | 0.511 | 2.705 (0.139‒52.722) | 0.076 | 0.053 (0.002‒1.364) | 0.324 | 4.571 (0.222‒93.989) | 0.006 | 0.002 (0.001‒0.148) | |
| LT80 | 0.407 | 0.952 (0.848‒1.069) | 0.757 | 1.074 (0.682‒1.690) | 0.077 | 1.885 (0.933‒3.807) | 0.290 | 0.184 (0.008‒4.251) | |
| LT70 | 0.314 | 0.997 (0.992‒1.003) | 0.565 | 0.987 (0.943‒1.033) | 0.035 | 1.166 (1.011‒1.344) | 0.857 | 0.881 (0.221‒3.504) | |
| LSpO2 | 0.951 | 1.022 (0.511‒2.046) | 0.314 | 1.780 (0.577‒5.489) | 0.480 | 0.743 (0.326‒1.696) | 0.357 | 1.362 (0.706‒2.627) | |
| SSS | 0.697 | 1.070 (0.762‒1.501) | 0.019 | 0.626 (0.423‒0.926) | 0.949 | 0.992 (0.782‒1.259) | 0.435 | 1.050 (0.929‒1.186) | |
| WK (TIB) frequency | 0.238 | 0.636 (0.300‒1.349) | 0.835 | 1.101 (0.444‒2.731) | 0.917 | 0.971 (0.561‒1.682) | 0.470 | 0.905 (0.689‒1.188) | |
| WK (TIB) duration | 0.397 | 46.583 (0.006‒338 729.248) | 0.531 | 43.721 (0.001‒6 081 353.502) | 0.772 | 0.381 (0.001‒256.719) | 0.879 | 1.266 (0.061‒26.225) | |
| WK/TIB | 0.456 | 2.041 (0.313‒13.327) | 0.661 | 1.729 (0.148‒20.150) | 0.845 | 0.881 (0.245‒3.167) | 0.517 | 1.234 (0.653‒2.331) | |
| N2 frequency | 0.135 | 0.366 (0.098‒1.370) | 0.934 | 0.911 (0.099‒8.373) | 0.918 | 0.930 (0.234‒3.703) | 0.005 | 0.261 (0.101‒0.671) | |
| N2/TIB | 0.091 | 2 007.782 (0.296‒13 627 828.272) | 0.832 | 3.998 (0.001‒1 516 906.783) | 0.407 | 0.046 (0.001‒66.068) | 0.498 | 0.228 (0.003‒16.421) | |
| N3 frequency | 0.979 | 1.094 (0.001‒976.421) | 0.665 | 0.145 (0.001‒929.697) | 0.778 | 0.464 (0.002‒96.210) | 0.173 | 0.098 (0.004‒2.775) | |
| 1 | JORDAN A S, MCSHARRY D G, MALHOTRA A. Adult obstructive sleep apnoea[J]. Lancet, 2014, 383(9918): 736-747. |
| 2 | GOTTLIEB D J, PUNJABI N M. Diagnosis and management of obstructive sleep apnea: a review[J]. JAMA, 2020, 323(14): 1389-1400. |
| 3 | MARLETTA M A. Nitric oxide synthase: aspects concerning structure and catalysis[J]. Cell, 1994, 78(6): 927-930. |
| 4 | ABU-SOUD H M, STUEHR D J. Nitric oxide synthases reveal a role for calmodulin in controlling electron transfer[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1993, 90(22): 10769-10772. |
| 5 | MONCADA S, BOLAÑOS J P. Nitric oxide, cell bioenergetics and neurodegeneration[J]. J Neurochem, 2006, 97(6): 1676-1689. |
| 6 | ZHOU L, ZHU D Y. Neuronal nitric oxide synthase: structure, subcellular localization, regulation, and clinical implications[J]. Nitric Oxide, 2009, 20(4): 223-230. |
| 7 | ZHU L J, LI F, ZHU D Y. nNOS and neurological, neuropsychiatric disorders: a 20-year story[J]. Neurosci Bull, 2023, 39(9): 1439-1453. |
| 8 | CHANRION B, MANNOURY LA COUR C, BERTASO F, et al. Physical interaction between the serotonin transporter and neuronal nitric oxide synthase underlies reciprocal modulation of their activity[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2007, 104(19): 8119-8124. |
| 9 | DASHTI H S, DAGHLAS I, LANE J M, et al. Genetic determinants of daytime napping and effects on cardiometabolic health[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 900. |
| 10 | XU H J, LIU F, LI Z Q, et al. Genome-wide association study of obstructive sleep apnea and objective sleep-related traits identifies novel risk loci in Han Chinese individuals[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2022, 206(12): 1534-1545. |
| 11 | HAMMERSCHLAG A R, STRINGER S, DE LEEUW C A, et al. Genome-wide association analysis of insomnia complaints identifies risk genes and genetic overlap with psychiatric and metabolic traits[J]. Nat Genet, 2017, 49(11): 1584-1592. |
| 12 | SCHOELER T, SPEED D, PORCU E, et al. Participation bias in the UK Biobank distorts genetic associations and downstream analyses[J]. Nat Hum Behav, 2023, 7(7): 1216-1227. |
| 13 | JONES S E, TYRRELL J, WOOD A R, et al. Genome-wide association analyses in 128,266 individuals identifies new morningness and sleep duration loci[J]. PLoS Genet, 2016, 12(8): e1006125. |
| 14 | DOHERTY A, SMITH-BYRNE K, FERREIRA T, et al. GWAS identifies 14 loci for device-measured physical activity and sleep duration[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1): 5257. |
| 15 | DASHTI H S, JONES S E, WOOD A R, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies genetic loci for self-reported habitual sleep duration supported by accelerometer-derived estimates[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 1100. |
| 16 | DAMIANI M F, QUARANTA V N, FALCONE V A, et al. The Epworth Sleepiness Scale: conventional self vs physician administration[J]. Chest, 2013, 143(6): 1569-1575. |
| 17 | 岳丽萍, 金泽奇. Epworth嗜睡量表联合鼾声量表在阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征筛查中的应用[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2011, 18(10): 566, 568. |
| YUE L P, JIN Z Q. Application of Scale Epworth Sleepiness Score combined with Snore Scale in screening obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome[J]. Chinese Archives of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, 2011, 18(10): 566, 568. | |
| 18 | HASEGAWA E, MIYASAKA A, SAKURAI K, et al. Rapid eye movement sleep is initiated by basolateral amygdala dopamine signaling in mice[J]. Science, 2022, 375(6584): 994-1000. |
| 19 | KLINE D D, YANG T, PREMKUMAR D R, et al. Blunted respiratory responses to hypoxia in mutant mice deficient in nitric oxide synthase-3[J]. J Appl Physiol, 2000, 88(4): 1496-1508. |
| 20 | LIPTON A J, JOHNSON M A, MACDONALD T, et al. S-nitrosothiols signal the ventilatory response to hypoxia[J]. Nature, 2001, 413(6852): 171-174. |
| 21 | GAUTIER-SAUVIGNÉ S, COLAS D, PARMANTIER P, et al. Nitric oxide and sleep[J]. Sleep Med Rev, 2005, 9(2): 101-113. |
| 22 | TRAN T T, SPECK C L, PISUPATI A, et al. Increased hippocampal activation in ApoE-4 carriers and non-carriers with amnestic mild cognitive impairment[J]. Neuroimage Clin, 2016, 13: 237-245. |
| 23 | NAKAMURA T, OH C K, LIAO L J, et al. Noncanonical transnitrosylation network contributes to synapse loss in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Science, 2021, 371(6526): eaaw0843. |
| 24 | HE H S, BOEHRINGER R, HUANG A J Y, et al. CA2 inhibition reduces the precision of hippocampal assembly reactivation[J]. Neuron, 2021, 109(22): 3674-3687.e7. |
| 25 | KUMAR D, KOYANAGI I, CARRIER-RUIZ A, et al. Sparse activity of hippocampal adult-born neurons during REM sleep is necessary for memory consolidation[J]. Neuron, 2020, 107(3): 552-565.e10. |
| 26 | YU B, ICHINOSE F, BLOCH D B. Inhaled nitric oxide[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2019, 176(2): 246-255. |
| [1] | 沈煜斌, 欧茜文, 刘松. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停的动物模型研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(4): 501-508. |
| [2] | 高怡青, 彭裕, 许华俊, 易红良, 关建, 殷善开. 全球阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停指南质量评价[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(2): 237-249. |
| [3] | 陈淑梅,吴佳欐,李晓艳. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征患儿血压与儿茶酚胺水平的关系研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2019, 39(12): 1437-. |
| [4] | 应晨 1,刘彩虹 2,胡家安 2,江石湖 3,徐志红 2,孙璟 2. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征合并非酒精性脂肪性肝病患者血清脂肪代谢相关激素水平的研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2018, 38(10): 1203-. |
| [5] | 孙雯雯,阮玉凤,连鹏,应晨,胡家安,徐志红,孙璟. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征对非酒精性脂肪性肝病的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2016, 36(5): 707-. |
| [6] | 张豫文,石娟,张翼飞,顾卫琼,王卫庆,洪洁. 青少年肥胖人群发生阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征的代谢相关高危因素[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2016, 36(12): 1726-. |
| [7] | 唐志君,韦宗辉,吴勇德,文飞,田川. 重度阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征患者的肺功能分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2016, 36(12): 1817-. |
| [8] | 王 彦, 李庆云, 林莹妮, 等. 成年男性睡眠呼吸暂停综合征患者血清内脏脂肪素的变化[J]. , 2012, 32(4): 503-. |
| [9] | 施 俊, 吕静荣, 吴 皓. OSAHS患儿血清Th1/Th2细胞因子检测及临床意义[J]. , 2010, 30(10): 1243-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||