
JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE) ›› 2021, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (5): 579-587.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2021.05.004
• Basic research • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ling-ling LI1,2( ), Qian LI2, Ming-yu LI2, Zheng LIU3, Qian-cheng SHEN2(
), Qian LI2, Ming-yu LI2, Zheng LIU3, Qian-cheng SHEN2( )
)
Online:2021-05-28
Published:2021-05-27
Contact:
Qian-cheng SHEN
E-mail:lingling117@sjtu.edu.cn;qcshen@shsmu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
Ling-ling LI, Qian LI, Ming-yu LI, Zheng LIU, Qian-cheng SHEN. Analysis of tumor immune-related differentially expressed genes in adults and children with acute myeloid leukemia[J]. JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE), 2021, 41(5): 579-587.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://xuebao.shsmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2021.05.004
| Disease status | Up-regulated DEG | Down-regulated DEG |
|---|---|---|
| Initial diagnosis/relapse① | CD63, CD53, CD44, CD58, CD74, CD99, CD97, CD244, CD27, CD22, CD3E, CD200, MAPK14, IL1RAP, CASP1, REL, C3AR1, FLT3, RUNX1, BCL2L1, TNFAIP3, TLR1, TNFSF13B, ITGA2B, CD275, PDGFC, TPSAB1, IL2RA, ABCB1, IL32, CCL25, CXCL16, CCL2, CCL23, CXCL2, CCL4, CCL1, CXCL12, KIT | CD55, MAPK11, CCL24, SPACA3, CD79A, CASP10, CD40LG, CD6, IL34, C3, IL1RAPL2, CD290, CD274, CD9, CD49b, CXCL13, LCN2, LTF |
| Complete remission② | IL8, CD83, CD87, REL, CDKN1A, CXCL2, CD141, CD54, CD354, CD53 | BLNK, IKBKB |
Tab 1 Comparison of tumor immune-related DEGs between the AML patients in initial diagnosis/relapse and in complete remission
| Disease status | Up-regulated DEG | Down-regulated DEG |
|---|---|---|
| Initial diagnosis/relapse① | CD63, CD53, CD44, CD58, CD74, CD99, CD97, CD244, CD27, CD22, CD3E, CD200, MAPK14, IL1RAP, CASP1, REL, C3AR1, FLT3, RUNX1, BCL2L1, TNFAIP3, TLR1, TNFSF13B, ITGA2B, CD275, PDGFC, TPSAB1, IL2RA, ABCB1, IL32, CCL25, CXCL16, CCL2, CCL23, CXCL2, CCL4, CCL1, CXCL12, KIT | CD55, MAPK11, CCL24, SPACA3, CD79A, CASP10, CD40LG, CD6, IL34, C3, IL1RAPL2, CD290, CD274, CD9, CD49b, CXCL13, LCN2, LTF |
| Complete remission② | IL8, CD83, CD87, REL, CDKN1A, CXCL2, CD141, CD54, CD354, CD53 | BLNK, IKBKB |
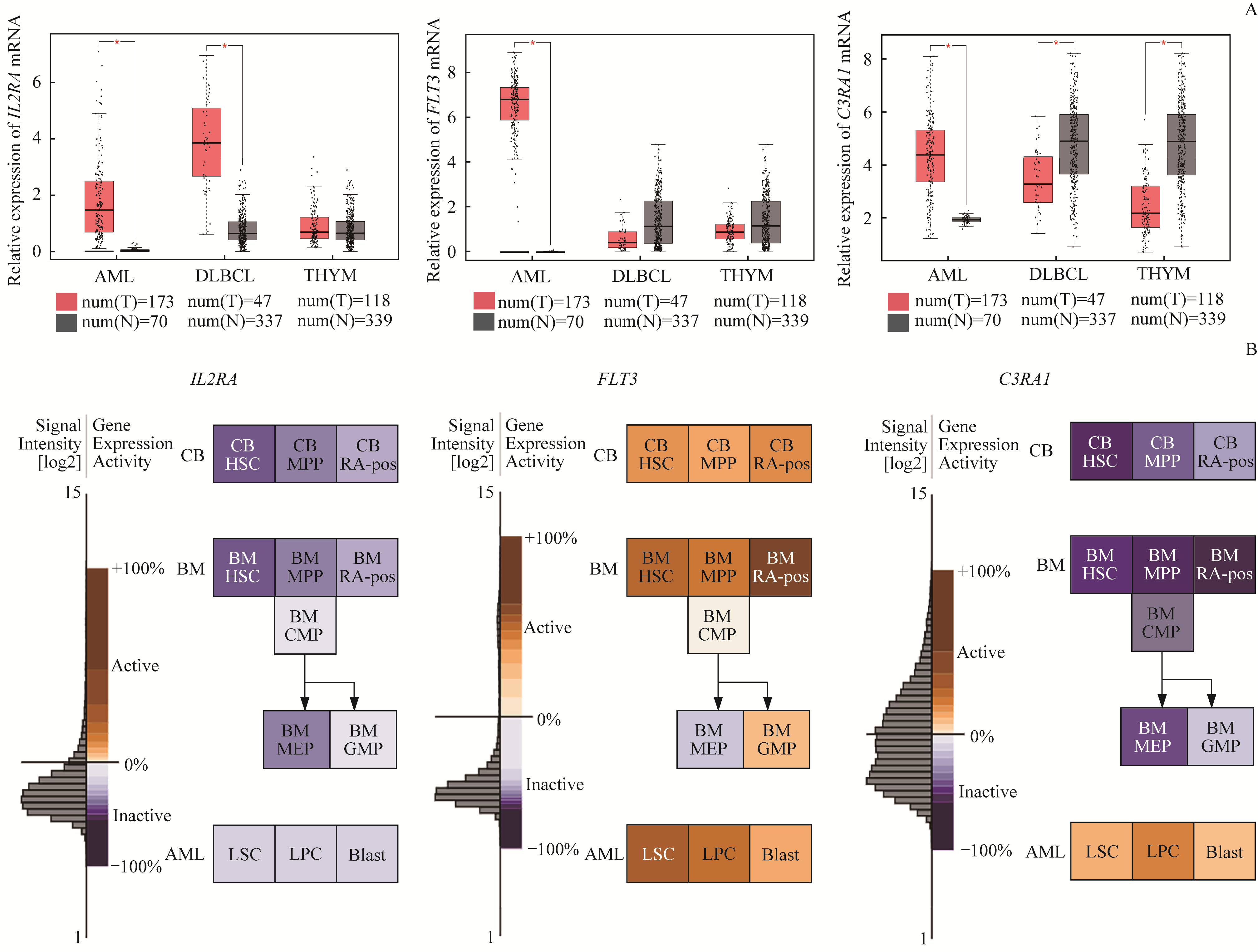
Fig 6 mRNA expression of key genes in the tumor tissues of the three diseases and in the tumor stem cells of the AML patients and the hematopoietic cells of normal people
| 1 | Vago L, Gojo I. Immune escape and immunotherapy of acute myeloid leukemia[J]. J Clin Invest, 2020, 130(4): 1552-1564. |
| 2 | Döhner H, Weisdorf DJ, Bloomfield CD. Acute myeloid leukemia[J]. N Engl J Med, 2015, 373(12): 1136-1152. |
| 3 | Swartz MA, Iida N, Roberts EW, et al. Tumor microenvironment complexity: emerging roles in cancer therapy[J]. Cancer Res, 2012, 72(10): 2473-2480. |
| 4 | Edgar R, Domrachev M, Lash AE. Gene Expression Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2002, 30(1): 207-210. |
| 5 | Vadakekolathu J, Minden MD, Hood T, et al. Immune landscapes predict chemotherapy resistance and immunotherapy response in acute myeloid leukemia[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2020, 12(546): eaaz0463. |
| 6 | Raney BJ, Dreszer TR, Barber GP, et al. Track data hubs enable visualization of user-defined genome-wide annotations on the UCSC Genome Browser[J]. Bioinformatics, 2014, 30(7): 1003-1005. |
| 7 | Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, et al. Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2015, 43(7): e47. |
| 8 | Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L, et al. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 1523. |
| 9 | Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, et al. GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2017, 45(W1): W98-W102. |
| 10 | Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S, et al. STRING v10: protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2015, 43(Database issue): D447-D452. |
| 11 | Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, et al. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks[J]. Genome Res, 2003, 13(11): 2498-2504. |
| 12 | Chin CH, Chen SH, Wu HH, et al. cytoHubba: identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome[J]. BMC Syst Biol, 2014, 8(): S11. |
| 13 | Bandettini WP, Kellman P, Mancini C, et al. MultiContrast Delayed Enhancement (MCODE) improves detection of subendocardial myocardial infarction by late gadolinium enhancement cardiovascular magnetic resonance: a clinical validation study[J]. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson, 2012, 14: 83. |
| 14 | Gentles AJ, Plevritis SK, Majeti R, et al. Association of a leukemic stem cell gene expression signature with clinical outcomes in acute myeloid leukemia[J]. JAMA, 2010, 304(24): 2706-2715. |
| 15 | Klemm F, Joyce JA. Microenvironmental regulation of therapeutic response in cancer[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2015, 25(4): 198-213. |
| 16 | Junttila MR, de Sauvage FJ. Influence of tumour micro-environment heterogeneity on therapeutic response[J]. Nature, 2013, 501(7467): 346-354. |
| 17 | Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, et al. Proposals for the classification of the acute leukaemias[J]. Br J Haematol, 1976, 33(4): 451-458. |
| 18 | Olkhanud PB, Damdinsuren B, Bodogai M, et al. Tumor-evoked regulatory B cells promote breast cancer metastasis by converting resting CD4⁺ T cells to T-regulatory cells[J]. Cancer Res, 2011, 71(10): 3505-3515. |
| 19 | Wejksza K, Lee-Chang C, Bodogai M, et al. Cancer-produced metabolites of 5-lipoxygenase induce tumor-evoked regulatory B cells via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α[J]. J Immunol, 2013, 190(6): 2575-2584. |
| 20 | Yamamoto Y, Kiyoi H, Nakano Y, et al. Activating mutation of D835 within the activation loop of FLT3 in human hematologic malignancies[J]. Blood, 2001, 97(8): 2434-2439. |
| 21 | Reca R, Mastellos D, Majka M, et al. Functional receptor for C3a anaphylatoxin is expressed by normal hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells, and C3a enhances their homing-related responses to SDF-1[J]. Blood, 2003, 101(10): 3784-3793. |
| 22 | Möhle R, Bautz F, Rafii S, et al. The chemokine receptor CXCR-4 is expressed on CD34+ hematopoietic progenitors and leukemic cells and mediates transendothelial migration induced by stromal cell-derived factor-1[J]. Blood, 1998, 91(12): 4523-4530. |
| 23 | Lin Y, Ma Q, Li L, et al. The CXCL12-CXCR4 axis promotes migration, invasiveness, and EMT in human papillary thyroid carcinoma B-CPAP cells via NF-κB signaling[J]. Biochem Cell Biol, 2018, 96(5): 619-626. |
| 24 | Martin GH, Roy N, Chakraborty S, et al. CD97 is a critical regulator of acute myeloid leukemia stem cell function[J]. J Exp Med, 2019, 216(10): 2362-2377. |
| 25 | Zhao K, Yin LL, Zhao DM, et al. IL1RAP as a surface marker for leukemia stem cells is related to clinical phase of chronic myeloid leukemia patients[J]. Int J Clin Exp Med, 2014, 7(12): 4787-4798. |
| 26 | Warren CFA, Wong-Brown MW, Bowden NA. BCL-2 family isoforms in apoptosis and cancer[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2019, 10(3): 177. |
| 27 | Ferlin M, Noraz N, Hertogh C, et al. Insulin-like growth factor induces the survival and proliferation of myeloma cells through an interleukin-6-independent transduction pathway[J]. Br J Haematol, 2000, 111(2): 626-634. |
| 28 | Di Pietro A, Conseil G, Pérez-Victoria JM, et al. Modulation by flavonoids of cell multidrug resistance mediated by P-glycoprotein and related ABC transporters[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2002, 59(2): 307-322. |
| 29 | Chiu HY, Sun KH, Chen SY, et al. Autocrine CCL2 promotes cell migration and invasion via PKC activation and tyrosine phosphorylation of paxillin in bladder cancer cells[J]. Cytokine, 2012, 59(2): 423-432. |
| [1] | YU Zhiyuan, DONG Haiping, GAO Nan, MA Ke. Identification and mechanistic analysis of core genes associated with morphine tolerance in dorsal root ganglion: an integrative transcriptomics approach using WGCNA and machine learning algorithms [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(10): 1308-1319. |
| [2] | ZHOU Haixia, ZHANG Jing. Research progress of m6A methylation modification in regulating tumor immunity [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(1): 137-144. |
| [3] | ZHOU Xiaowen, LI Qian, ZHANG Zhe, SHEN Jianfeng, FAN Xianqun. RBX1 regulates uveal melanoma immune-related genes via STAT1 [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(6): 709-717. |
| [4] | ZHAO Zhuoming, LIU Zhenhao, LU Manman, ZHANG Yu, XU Linfeng, XIE Lu. Analysis of tumor-related features of non-small cell lung cancer based on TCR repertoire workflow [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(12): 1520-1528. |
| [5] | HU Jiacheng, ZHU Qian, WANG Jiaqi, WU Yingli, LEI Hu. Function of UCHL3 in maintaining the survival of FLT3-ITD positive acute myeloid leukemia cells [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2022, 42(10): 1383-1393. |
| [6] | Jianru WANG, Guangcao PENG, Mingjun ZHU. Screening potential hub genes associated with myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice based on GEO database and bioinformatics analysis [J]. JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE), 2022, 42(1): 51-62. |
| [7] | Ying XU, Yi-min CHU, Da-ming YANG, Ji LI, Hai-qin ZHANG, Hai-xia PENG. Construction of a metastasis prediction model of microsatellite instability-high colorectal cancer based on differentially expressed gene assembly [J]. JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE), 2021, 41(9): 1197-1206. |
| [8] | Rui-jie GENG, Lin YAO, Xin-xin HUANG, Shun-ying YU, Cheng-mei YUAN, Wu HONG, Qin-yu LÜ, Qing-zhong WANG, Zheng-hui YI, Yi-ru FANG. Identification of differentially expressed gene modules in major depressive disorder based on weighted gene co-expression network analysis [J]. JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE), 2021, 41(6): 724-731. |
| [9] | Ting QIU, Jing JIN, Yuan-yue CUI, Lei SONG, Xie LI, Ji-fang QU. A case report of fundus hemorrhage in recurrent acute myeloid leukemia [J]. JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE), 2021, 41(1): 123-125. |
| [10] | ZHAO Wei-guang, LIU Zhi-hong. Advances in study of regulation of tumor immune inflammatory microenvironment by cancer-associated fibroblasts [J]. JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE), 2020, 40(9): 1288-1293. |
| [11] | CHEN Ning-xin, HAN Ting-ting, ZHENG Shuang, LIU Wei, HU Yao-min. Identification of differentially expressed genes and pathways in lipoprotein lipase gene heterozygous knockout mice through gene microarray analysis [J]. JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE), 2020, 40(6): 736-743. |
| [12] | LI Qian, GAO Jing-ze, LI Yun, SONG Kun, SHEN Qian-cheng. Bioinformatics analysis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma genomic chip and prediction of targeted drug [J]. , 2020, 40(2): 194-. |
| [13] | DONG Xin-yi1, FAN Qiu-yue1, QIU Shu-han1, ZHOU Jia-yao1, LU Ying2. Clinical application of receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors to acute myeloid leukemia [J]. JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE), 2020, 40(12): 1665-1671. |
| [14] | ZHOU Han, YANG Xiao-sheng, LIAO Chen-long, ZHANG Wen-chuan. Analysis on characteristics of diabetic foot ulceration-related genes and immune cells [J]. JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE), 2020, 40(10): 1354-1359. |
| [15] | LI Qing-li, WEN Jun, MIN Xue-jie, ZHAO Li, ZHAO Xiao-ping. Effect of IDHgene mutation on acute myeloid leukemia [J]. , 2018, 38(8): 960-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||