
JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE) ›› 2021, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (9): 1233-1239.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2021.09.015
• Clinical research • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jun-lin HE1,2( ), Qing LU3, Xin XU4, Shu-dong HU5(
), Qing LU3, Xin XU4, Shu-dong HU5( )
)
Received:2021-01-18
Online:2021-09-28
Published:2021-08-03
Contact:
Shu-dong HU
E-mail:912211529@qq.com;hsd2001054@163.com
CLC Number:
Jun-lin HE, Qing LU, Xin XU, Shu-dong HU. Value of CT radiomic features in preoperative prediction of cervical lymph node metastasis in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma[J]. JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE), 2021, 41(9): 1233-1239.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://xuebao.shsmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2021.09.015
| Item | CLNM group (n=55) | Non-CLNM group (n=69) | t value | P value | Item | CLNM group (n=55) | Non-CLNM group (n=69) | t value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age/year | 52.8±12.8 | 48.3±13.5 | 0.139 | 0.063 | Isthmus | 3 (5.5) | 0 (0) | ||
| Age group/n(%) | 4.051 | 0.044 | Right lobe | 22 (40.0) | 38 (55.1) | ||||
| ≥50 | 37 (67.3) | 34 (49.3) | Calcification/n(%) | 0.116 | 0.733 | ||||
| <50 | 18 (32.7) | 35 (50.7) | Negative | 28 (50.9) | 33 (47.8) | ||||
| Gender/n(%) | 0.304 | 0.581 | Positive | 27 (49.1) | 36 (52.2) | ||||
| Male | 12 (21.8) | 18 (26.1) | Boundary①/n(%) | 1.125 | 0.289 | ||||
| Female | 43 (78.2) | 51 (73.9) | Distinct | 12 (21.8) | 10 (14.5) | ||||
| Shape/n(%) | 1.360 | 0.713 | Indistinct | 43 (78.2) | 59 (85.5) | ||||
| Irregular | 43 (78.2) | 52 (75.4) | Capsule invasion/n(%) | 5.731 | 0.025 | ||||
| Regular | 12 (21.8) | 17 (24.6) | Negative | 4 (7.3) | 16 (23.2) | ||||
| Length to diameter/n(%) | 2.285 | 0.131 | Positive | 51 (92.7) | 53 (76.8) | ||||
| ≤1.0 | 26 (47.3) | 42 (60.9) | ETE/n(%) | 8.801 | 0.004 | ||||
| >1.0 | 29 (52.7) | 27 (39.1) | Negative | 27 (49.1) | 51 (73.9) | ||||
| Location/n(%) | 5.776 | 0.056 | Positive | 28 (50.9) | 18 (26.1) | ||||
| Left lobe | 30 (54.5) | 31 (44.9) |
Tab1 Baseline and clinical information of PTC patients(N=124)
| Item | CLNM group (n=55) | Non-CLNM group (n=69) | t value | P value | Item | CLNM group (n=55) | Non-CLNM group (n=69) | t value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age/year | 52.8±12.8 | 48.3±13.5 | 0.139 | 0.063 | Isthmus | 3 (5.5) | 0 (0) | ||
| Age group/n(%) | 4.051 | 0.044 | Right lobe | 22 (40.0) | 38 (55.1) | ||||
| ≥50 | 37 (67.3) | 34 (49.3) | Calcification/n(%) | 0.116 | 0.733 | ||||
| <50 | 18 (32.7) | 35 (50.7) | Negative | 28 (50.9) | 33 (47.8) | ||||
| Gender/n(%) | 0.304 | 0.581 | Positive | 27 (49.1) | 36 (52.2) | ||||
| Male | 12 (21.8) | 18 (26.1) | Boundary①/n(%) | 1.125 | 0.289 | ||||
| Female | 43 (78.2) | 51 (73.9) | Distinct | 12 (21.8) | 10 (14.5) | ||||
| Shape/n(%) | 1.360 | 0.713 | Indistinct | 43 (78.2) | 59 (85.5) | ||||
| Irregular | 43 (78.2) | 52 (75.4) | Capsule invasion/n(%) | 5.731 | 0.025 | ||||
| Regular | 12 (21.8) | 17 (24.6) | Negative | 4 (7.3) | 16 (23.2) | ||||
| Length to diameter/n(%) | 2.285 | 0.131 | Positive | 51 (92.7) | 53 (76.8) | ||||
| ≤1.0 | 26 (47.3) | 42 (60.9) | ETE/n(%) | 8.801 | 0.004 | ||||
| >1.0 | 29 (52.7) | 27 (39.1) | Negative | 27 (49.1) | 51 (73.9) | ||||
| Location/n(%) | 5.776 | 0.056 | Positive | 28 (50.9) | 18 (26.1) | ||||
| Left lobe | 30 (54.5) | 31 (44.9) |
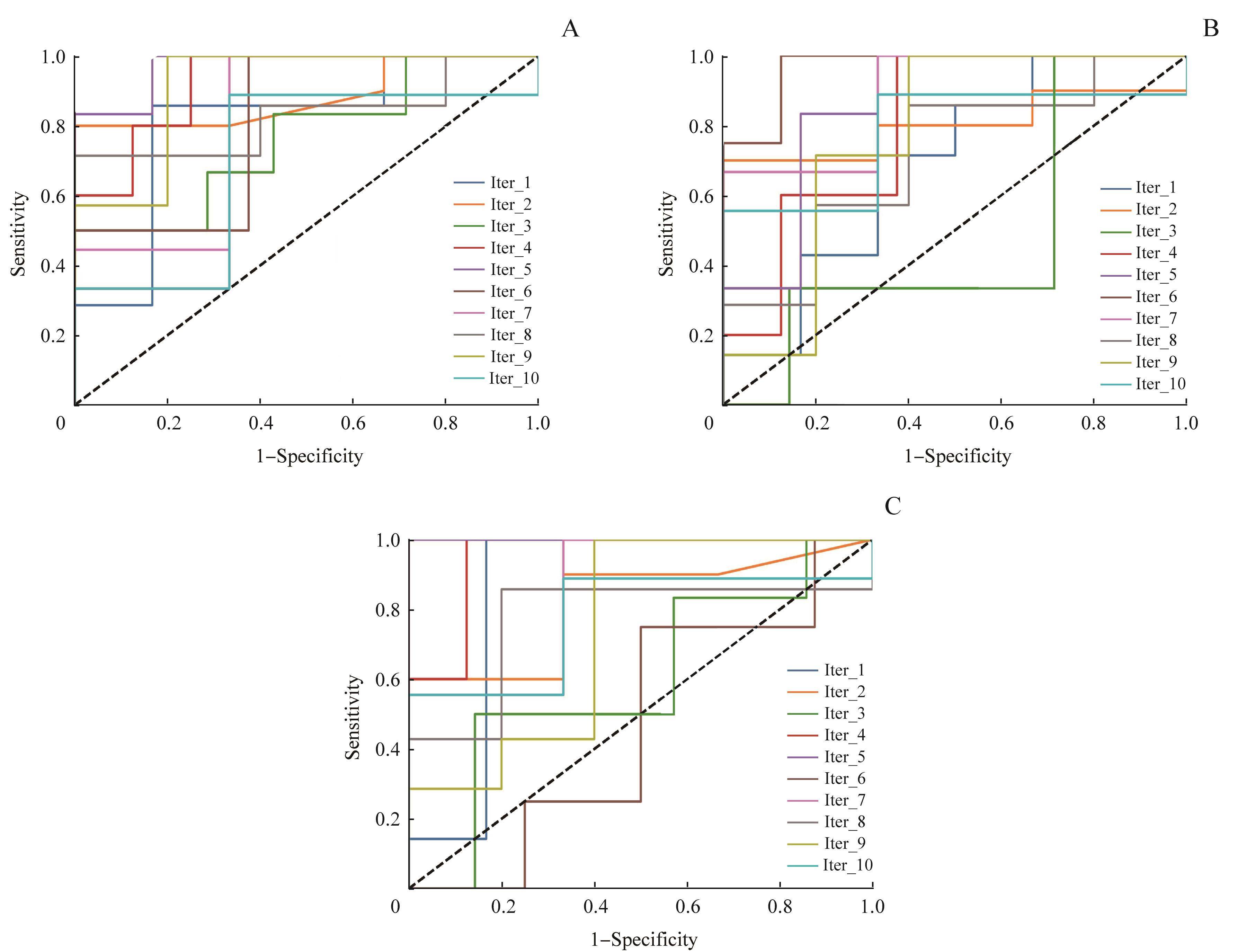
Fig 2 10-fold ROC curve of the maximum AUC in RF classification models of the pre-contrast phase (A), arterial phase (B) and venous phase (C) of patients with PTC
| Iteration | Training set | Validation set | Pre-contrast phase [top(k)=56] | Arterial phase [top(k)=94] | Venous phase [top(k)=47] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | AUC | Accuracy | AUC | Accuracy | AUC | |||
| 1 | 111 | 13 | 0.846 | 0.810 | 0.615 | 0.690 | 0.846 | 0.857 |
| 2 | 111 | 13 | 0.846 | 0.833 | 0.692 | 0.800 | 0.692 | 0.817 |
| 3 | 111 | 13 | 0.538 | 0.762 | 0.615 | 0.476 | 0.615 | 0.595 |
| 4 | 111 | 13 | 0.769 | 0.925 | 0.692 | 0.800 | 0.692 | 0.950 |
| 5 | 111 | 13 | 0.917 | 0.972 | 0.750 | 0.861 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| 6 | 111 | 13 | 0.583 | 0.812 | 0.583 | 0.969 | 0.500 | 0.469 |
| 7 | 111 | 13 | 0.833 | 0.815 | 0.833 | 0.889 | 0.750 | 0.852 |
| 8 | 111 | 13 | 0.750 | 0.829 | 0.667 | 0.714 | 0.750 | 0.771 |
| 9 | 111 | 13 | 0.833 | 0.914 | 0.750 | 0.771 | 0.667 | 0.743 |
| 10 | 111 | 13 | 0.750 | 0.704 | 0.750 | 0.778 | 0.750 | 0.778 |
| Average AUC | ‒ | ‒ | 0.767 | 0.843 | 0.695 | 0.775 | 0.726 | 0.783 |
Tab 2 Results of 10-fold cross-validation of RF classification model in pre-contrast phase,arterial phase and venous phase of patients with PTC
| Iteration | Training set | Validation set | Pre-contrast phase [top(k)=56] | Arterial phase [top(k)=94] | Venous phase [top(k)=47] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | AUC | Accuracy | AUC | Accuracy | AUC | |||
| 1 | 111 | 13 | 0.846 | 0.810 | 0.615 | 0.690 | 0.846 | 0.857 |
| 2 | 111 | 13 | 0.846 | 0.833 | 0.692 | 0.800 | 0.692 | 0.817 |
| 3 | 111 | 13 | 0.538 | 0.762 | 0.615 | 0.476 | 0.615 | 0.595 |
| 4 | 111 | 13 | 0.769 | 0.925 | 0.692 | 0.800 | 0.692 | 0.950 |
| 5 | 111 | 13 | 0.917 | 0.972 | 0.750 | 0.861 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| 6 | 111 | 13 | 0.583 | 0.812 | 0.583 | 0.969 | 0.500 | 0.469 |
| 7 | 111 | 13 | 0.833 | 0.815 | 0.833 | 0.889 | 0.750 | 0.852 |
| 8 | 111 | 13 | 0.750 | 0.829 | 0.667 | 0.714 | 0.750 | 0.771 |
| 9 | 111 | 13 | 0.833 | 0.914 | 0.750 | 0.771 | 0.667 | 0.743 |
| 10 | 111 | 13 | 0.750 | 0.704 | 0.750 | 0.778 | 0.750 | 0.778 |
| Average AUC | ‒ | ‒ | 0.767 | 0.843 | 0.695 | 0.775 | 0.726 | 0.783 |
| Order | Pre-contrast phase | Arterial phase | Venous phase |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Original_glcm_DifferenceAverage | Original_glcm_DifferenceVariance | Original_glcm_DifferenceVariance |
| 2 | Original_firstorder_Variance | Original_glcm_ClusterProminence | Original_glcm_Contrast |
| 3 | Original_glrlm_RunPercentage | Original_glcm_Contrast | Original_glrlm_ShortRunEmphasis |
| 4 | Original_glszm_GrayLevelNonUniformityNormalized | Original_firstorder_Kurtosis | Original_glszm_SmallAreaLowGrayLevelEmphasis |
| 5 | Original_glcm_SumSquares | Original_glcm_ClusterShade | Original_glcm_ClusterProminence |
| 6 | Original_glcm_JointEntropy | Original_shape_Maximum3DDiameter | Original_glrlm_RunVariance |
| 7 | Original_glcm_SumAverage | Original_glrlm_GrayLevelVariance | Original_firstorder_Skewness |
| 8 | Original_glcm_Contrast | Original_gldm_DependenceVariance | Original_glcm_MaximumProbability |
| 9 | Original_ngtdm_Strength | Original_glcm_SumSquares | Original_glcm_DifferenceAverage |
| 10 | Original_gldm_DependenceNonUniformityNormalized | Original_glcm_DifferenceEntropy | Original_glcm_ClusterShade |
Tab 3 Top 10 radiomic features in RF classification model of pre-contrast, arterial and venous phase of PTC patients(N=124)
| Order | Pre-contrast phase | Arterial phase | Venous phase |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Original_glcm_DifferenceAverage | Original_glcm_DifferenceVariance | Original_glcm_DifferenceVariance |
| 2 | Original_firstorder_Variance | Original_glcm_ClusterProminence | Original_glcm_Contrast |
| 3 | Original_glrlm_RunPercentage | Original_glcm_Contrast | Original_glrlm_ShortRunEmphasis |
| 4 | Original_glszm_GrayLevelNonUniformityNormalized | Original_firstorder_Kurtosis | Original_glszm_SmallAreaLowGrayLevelEmphasis |
| 5 | Original_glcm_SumSquares | Original_glcm_ClusterShade | Original_glcm_ClusterProminence |
| 6 | Original_glcm_JointEntropy | Original_shape_Maximum3DDiameter | Original_glrlm_RunVariance |
| 7 | Original_glcm_SumAverage | Original_glrlm_GrayLevelVariance | Original_firstorder_Skewness |
| 8 | Original_glcm_Contrast | Original_gldm_DependenceVariance | Original_glcm_MaximumProbability |
| 9 | Original_ngtdm_Strength | Original_glcm_SumSquares | Original_glcm_DifferenceAverage |
| 10 | Original_gldm_DependenceNonUniformityNormalized | Original_glcm_DifferenceEntropy | Original_glcm_ClusterShade |
| 1 | Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2019, 69(1): 7-34. |
| 2 | Vaccarella S, Franceschi S, Bray F, et al. Worldwide thyroid-cancer epidemic? The increasing impact of overdiagnosis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2016, 375(7): 614-617. |
| 3 | Londero SC, Krogdahl A, Bastholt L, et al. Papillary thyroid carcinoma in Denmark, 1996‒2008: outcome and evaluation of established prognostic scoring systems in a prospective national cohort[J]. Thyroid, 2015, 25(1): 78-84. |
| 4 | Lee YK, Kim D, Shin DY, et al. The prognosis of papillary thyroid cancer with initial distant metastasis is strongly associated with extensive extrathyroidal extension: a retrospective cohort study[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2019, 26(7): 2200-2209. |
| 5 | Mulla M, Schulte KM. Central cervical lymph node metastases in papillary thyroid cancer: a systematic review of imaging-guided and prophylactic removal of the central compartment[J]. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf), 2012, 76(1): 131-136. |
| 6 | Hall CM, Snyder SK, Lairmore TC. Central lymph node dissection improves lymph node clearance in papillary thyroid cancer patients with lateral neck metastases, even after prior total thyroidectomy[J]. Am Surg, 2018, 84(4): 531-536. |
| 7 | Mulla M, Schulte KM. The accuracy of ultrasonography in the preoperative diagnosis of cervical lymph node (LN) metastasis in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma: a meta-analysis[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2012, 81(8): 1965. |
| 8 | Suh CH, Baek JH, Choi YJ, et al. Performance of CT in the preoperative diagnosis of cervical lymph node metastasis in patients with papillary thyroid cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 2017, 38(1): 154-161. |
| 9 | Gross ND, Weissman JL, Talbot JM, et al. MRI detection of cervical metastasis from differentiated thyroid carcinoma[J]. Laryngoscope, 2001, 111(11Pt 1): 1905-1909. |
| 10 | Chen QH, Raghavan P, Mukherjee S, et al. Accuracy of MRI for the diagnosis of metastatic cervical lymphadenopathy in patients with thyroid cancer[J]. La Radiol Med, 2015, 120(10): 959-966. |
| 11 | Paek SH, Yi KH, Kim SJ, et al. Feasibility of sentinel lymph node dissection using Tc-99m phytate in papillary thyroid carcinoma[J]. Ann Surg Treat Res, 2017, 93(5): 240-245. |
| 12 | Suh CH, Choi YJ, Lee JJ, et al. Comparison of core-needle biopsy and fine-needle aspiration for evaluating thyroid incidentalomas detected by 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography: a propensity score analysis[J]. Thyroid, 2017, 27(10): 1258-1266. |
| 13 | Lambin P, Rios-Velazquez E, Leijenaar R, et al. Radiomics: extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2012, 48(4): 441-446. |
| 14 | van Griethuysen JJM, Fedorov A, Parmar C, et al. Computational radiomics system to decode the radiographic phenotype[J]. Cancer Res, 2017, 77(21): e104-e107. |
| 15 | Barry WT, Kernagis DN, Dressman HK, et al. Intratumor heterogeneity and precision of microarray-based predictors of breast cancer biology and clinical outcome[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2010, 28(13): 2198-2206. |
| 16 | Gambardella C, Patrone R, di Capua F, et al. The role of prophylactic central compartment lymph node dissection in elderly patients with differentiated thyroid cancer: a multicentric study[J]. BMC Surg, 2019, 18(): 110. |
| 17 | Lu W, Zhong LZ, Dong D, et al. Radiomic analysis for preoperative prediction of cervical lymph node metastasis in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2019, 118: 231-238. |
| 18 | Liu TT, Zhou SC, Yu JH, et al. Prediction of lymph node metastasis in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma: a radiomics method based on preoperative ultrasound images[J]. Technol Cancer Res Treat, 2019, 18: 1533033819831713. |
| 19 | O′Connor JP, Rose CJ, Waterton JC, et al. Imaging intratumor heterogeneity: role in therapy response, resistance, and clinical outcome[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2015, 21(2): 249-257. |
| 20 | 徐天伟. 基于灰度共生矩阵的医学PET图像纹理分析研究[J]. 电脑知识与技术, 2017, 13(5): 219-220. |
| 21 | 颜智敏, 冯智超, 曹鹏, 等. 多层螺旋CT图像纹理分析对直肠癌转移性淋巴结的诊断价值[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2017, 51(6): 432-436. |
| 22 | El Naqa I, Grigsby P, Apte A, et al. Exploring feature-based approaches in PET images for predicting cancer treatment outcomes[J]. Pattern Recognit, 2009, 42(6): 1162-1171. |
| 23 | 梁子超, 李智炜, 赖铿, 等. 10折交叉验证用于预测模型泛化能力评价及其R软件实现[J]. 中国医院统计, 2020, 27(4): 289-292. |
| 24 | Rodríguez JD, Pérez A, Lozano JA. Sensitivity analysis of kappa-fold cross validation in prediction error estimation[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2010, 32(3): 569-575. |
| 25 | Johnstone IM, Titterington DM. Statistical challenges of high-dimensional data[J]. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci, 2009, 367(1906): 4237-4253. |
| 26 | Clarke R, Ressom HW, Wang A, et al. The properties of high-dimensional data spaces: implications for exploring gene and protein expression data[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2008, 8(1): 37-49. |
| [1] | LI Siyu, CHEN Ya, HU Wentao, DAI Yongming, WU Yingwei. Using diffusion-relaxation correlation spectroscopic imaging to assess the heterogeneity of head and neck tumors and identify occult lymph node metastasis [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(9): 1202-1213. |
| [2] | WU Lei, DU Fenglin, ZHAO Mingna, REN Yizhe, ZHANG Xianzhou, LOU Jiatao. Expression of PTPRN in lung adenocarcinoma and its mechanism of promoting tumor metastasis [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(7): 846-857. |
| [3] | WANG Rui, YUAN Ying, TAO Xiaofeng. Application value of synthetic magnetic resonance imaging in predicting cervical lymph node metastasis of oral cancer [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(7): 900-909. |
| [4] | QIAN Liheng, WEN Kailing, LIAO Yingna, LI Shuxin, NIE Huizhen. Study on the effect and mechanism of sorting nexin 1 on inhibiting the proliferation and migration of colorectal cancer cells [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(9): 1124-1135. |
| [5] | GENG Yao, ZHANG Yang, ZHAO Jie, LI Wei, CAI Guoqing. Expression of MTA1 in preeclamptic placental tissue and its effects on trophoblast function [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(11): 1383-1390. |
| [6] | LIU Qiming, LU Qifan, CHAI Yezi, JIANG Meng, PU Jun. Short-axis cine cardiac magnetic resonance images-derived radiomics for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and healthy control classification [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(1): 79-86. |
| [7] | LIU Qiming, LU Qifan, CHAI Yezi, JIANG Meng, PU Jun. Radiomics-based left ventricular ejection fraction prediction: a feasibility study [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(9): 1162-1168. |
| [8] | MA Ben, ZHAO Cheng, SHU Yijun, DONG Ping. Application progress of CT radiomics in gastrointestinal stromal tumor [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(7): 923-930. |
| [9] | CHENG Ran, HU Jiajia, LI Biao. Advances in the application of 18F-FDG PET/CT radiomics for diagnosis, treatment and prognosis prediction of lymphoma [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(6): 781-787. |
| [10] | XIAO Rong, TAO Shuangfen, CHEN Siyu, ZHENG Leizhen, ZHU Meiling. Advances in Helicobacter pylori infection involved in gastric cancer metastasis [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(4): 495-499. |
| [11] | BAI Long, XIA Xiang, CAO Hui, ZHANG Zizhen. Progress in application of peritoneal lavage fluid circulating tumor DNA to predicting peritoneal metastasis of gastrointestinal cancer [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(12): 1554-1561. |
| [12] | TANG Lei, XU Yingchun, ZHANG Fengchun. Review of the role of collagen in tumorigenesis and development [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(12): 1577-1584. |
| [13] | CUI Xiwei, CHUNG Manhon, AIMAIER Rehanguli, WANG Zhichao, LI Qingfeng. Role of human pleiotrophin in the metastasis of malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2022, 42(9): 1225-1238. |
| [14] | ZHANG Xiuqi, SHEN Baiyong. Advances in cytological mechanism of neural invasion in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2022, 42(6): 833-838. |
| [15] | WANG Hui, ZHAO Ying, WEN Lirong, CAO Jun, YANG Jiping, YUAN Yongming. Diagnostic value of PSA, TAP and MACC1 expression in blood of patients with prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2022, 42(4): 496-501. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||