骨肉瘤是儿童和青少年最常见的原发性骨源性恶性肿瘤,具有生长迅速和早期转移的特点[1-2]。目前,骨肉瘤的主要治疗策略是手术治疗和化学治疗(化疗)。然而,80%的骨肉瘤患者在诊断时已经转移到肺部,对其成功治疗提出了相当大的挑战[3]。此外,使用化疗的患者中,耐药性和不良反应也是主要面临的问题[4]。因此,有必要开发高效低毒性的辅助性抗骨肉瘤天然药物。芦丁是一种黄酮类糖苷,在西番莲、茶、苹果等植物尤其是在苦荞麦中含量丰富[5],并因其显著的抗氧化、抗肿瘤和抗炎症作用而日益受到人们的关注[6-7]。研究表明,芦丁在乳腺癌[8]、胰腺癌[9]和结肠癌[10]等多种癌症中具有抗肿瘤作用。然而,芦丁在骨肉瘤中的作用鲜有报道。因此,本文拟探究芦丁对体内外骨肉瘤进展的影响及其作用机制。
1 材料与方法
1.1 主要试剂和仪器
芦丁(纯度98.6%)(美国Selleck),DMEM培养基、胎牛血清(fetal bovine serum,FBS)(美国Invitrogen),青链霉素混合液(100×)、CCK-8试剂盒、RIPA裂解缓冲液、Annexin V-FITC细胞凋亡检测试剂盒、二辛宁可酸(bicinchoninic acid,BCA)蛋白质测定试剂盒和ECL发光溶液(上海碧云天生物技术公司),Transwell小室(美国Corning),Matrigel基质胶(美国BD Biosciences),兔源一抗B细胞淋巴瘤-2(B-cell lymphoma-2,Bcl-2)和Bcl-2相关X蛋白(Bcl-2 associated X protein,Bax)、甘油醛3-磷酸脱氢酶(glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase,GAPDH)抗体以及辣根过氧化物酶(horseradish peroxidase,HRP)标记的山羊抗兔IgG(英国Abcam)。
MQX-200型酶标仪(美国Bio-Tek),Calibur型流式细胞仪(美国BD),IX71型倒置荧光显微镜(日本Olympus),ChemiDoc MP型全能型成像系统(美国Bio-Rad)。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 细胞培养
人成骨细胞hFOB1.19和人骨肉瘤细胞系MG63、U2OS购自美国典型培养物收藏中心。将骨肉瘤细胞置于含有10% FBS、青霉素-链霉素溶液(1×)的DMEM培养基中,于37 ℃和5% CO2培养箱中培养。
1.2.2 CCK-8实验
将hFOB1.19、MG63和U2OS细胞以5×103个/mL的密度置于96孔板中,分别用0、5、10、20、40、80、160 μmol/L的芦丁(溶解于DMSO)在37 ℃、5% CO2条件下培养细胞24、48、72 h后,每孔加入10 μL CCK-8溶液,37 ℃培养箱中培养2 h,酶标仪读取各孔的吸光度值并计算细胞存活率。
1.2.3 克隆形成实验
将MG63和U2OS细胞接种在6孔板中,密度为800个/孔,在培养箱中培养,然后用0、10、20、40 μmol/L的芦丁培养14 d,用结晶紫染色10 min。倒置荧光显微镜下观察并计数细胞克隆数(含有50个及以上细胞为1个克隆),计算克隆形成率。
1.2.4 Western blotting实验
分别用0、10、20、40 μmol/L芦丁处理MG63和U2OS细胞24 h后,用RIPA裂解液裂解细胞并提取蛋白质。BCA试剂盒检测蛋白质浓度,并使用SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳分离蛋白质。将样品转移到PVDF膜上,用5%脱脂奶粉封闭膜1 h。加入抗Ki67、Bcl-2和Bax抗体在4 ℃培养过夜,次日加入HRP标记的山羊抗兔IgG在37 ℃培养1 h。使用ChemiDoc MP成像系统对蛋白质带进行拍照,并用Image J软件分析蛋白条带的灰度值。
1.2.5 流式细胞术
将MG63和U2OS细胞密度调整为5×106个/mL并加至6孔板中,分别用0、10、20、40 μmol/L芦丁处理24 h后,用预冷PBS清洗细胞2次,再次悬浮并在12 000×g下离心5 min。加入5 μL Annexin V-FITC和10 μL碘化丙啶(propidium iodide,PI)溶液,在室温下避光培养细胞10 min。使用流式细胞仪分析细胞凋亡情况。
1.2.6 划痕闭合实验
将MG63和U2OS细胞接种到6孔板中(3×105个/孔)并培养24 h。当细胞贴壁后,用200 μL移液器枪头沿6孔板的直径垂直划伤细胞培养板。丢弃培养基,分别添加含有0、10、20、40 μmol/L芦丁的新鲜培养基。记录各组在不同时间点(0 h、24 h)的划痕面积,并用Image J软件计算划痕闭合率。
1.2.7 Transwell实验
用Matrigel涂覆在Transwell的上室,置于培养箱中放置30 min使其凝固。将MG63和U2OS细胞分别用0、10、20、40 μmol/L芦丁在无血清DMEM培养基中培养,并接种于Transwell上室(4×104个/孔)。Transwell下室培养基中添加10%的FBS,将培养板培养24 h后,用棉签将上室中的细胞完全清除,迁移到下室的细胞用PBS清洗,4%多聚甲醛固定,并用结晶紫染色。在显微镜下随机选择5个区域对细胞进行计数。
1.2.8 裸鼠移植瘤实验
12只18~20 g的SPF级4周龄BALB/c裸鼠购自并饲养于四川维通利华实验动物技术有限公司,生产许可证号为SCXK(川)2023-0040,使用许可证号为SYXK(川)2023-0263。将裸鼠饲养于无菌环境中,房间温度控制在26 ℃~28 ℃,湿度维持在50%~60%,光照时间10 h,自由进食高压灭菌水和无菌饲料,适应性喂养1周后进行实验。将MG63细胞(2×106个)皮下注射到裸鼠的右侧腹部,建立异种移植模型。在注射后第7日MG63细胞形成肿瘤后,将小鼠随机分为2组(每组6只):对照组和芦丁40 mg/kg组。芦丁40 mg/kg组腹腔注射芦丁(40 mg/kg),对照组腹腔注射等体积生理盐水,隔日1次,持续4周。所有小鼠每周测量1次肿瘤大小,计算体积。治疗后,在2%异氟醚麻醉下颈椎脱臼处死。取出异种移植肿瘤,用冰冷的PBS冲洗,称质量,4%多聚甲醛溶液固定,用于免疫组织化学分析和TUNEL测定。采集小鼠心、肝、脾、肺和肾组织,通过常规苏木精和伊红染色进行组织学检测。
1.2.9 免疫组织化学检测肿瘤组织中Ki67和VEGF的表达
小鼠腹部移植瘤组织在4%多聚甲醛溶液固定24 h,取出后进行石蜡包埋、切片、干燥、脱蜡,柠檬酸钠缓冲液修复,滴加抗Ki67(1∶100)和抗VEGF(1∶100)抗体并于4 ℃孵育过夜,生物素标记的山羊抗兔IgG 37 ℃孵育1 h,洗涤后避光显色并用苏木精复染细胞核,荧光显微镜下观察Ki67和VEGF的表达。Ki67阳性表达为细胞核中出现棕黄色颗粒物质,VEGF阳性表达为细胞质中出现棕黄色颗粒物质。
1.2.10 TUNEL检测组织凋亡水平
小鼠腹部移植瘤组织石蜡包埋、切片、脱蜡后,滴加蛋白酶K修复,放入内源性过氧化物酶封闭液封闭5 min,滴加TUNEL检测液37 ℃避光孵育1 h,洗涤后滴加DAB显色液进行显色并用苏木精复染细胞核,荧光显微镜下观察染色切片。凋亡细胞率=棕黄色细胞数/总细胞数×100%。
1.3 统计学分析
采用Graphpad Prism 9.0软件进行统计分析。所有数据以x±s表示。2组间比较采用t检验,多组间的差异比较采用单因素方差分析。P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
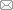
2.1 芦丁抑制骨肉瘤细胞活力
图1
图1
芦丁对骨肉瘤细胞活力的影响
Note: A. Viability of MG63 cells. B. Viability of U2OS cells. C. Viability of hFOB1.19 cells. ①P=0.002, ②P=0.001, ③P<0.001, ④P=0.003, compared with rutin 0 μmol/L group.
Fig 1
Effect of rutin on the viability of osteosarcoma cells
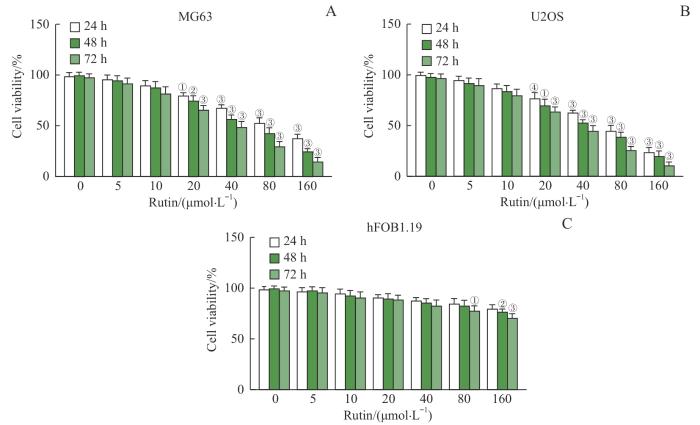
2.2 芦丁抑制骨肉瘤细胞的克隆形成
图2
图2
芦丁对骨肉瘤细胞克隆形成的影响
Note:A. Representative images of MG63 cell clones and statistics of colony formation rate. B. Representative images of U2OS cell clones and statistics of colony formation rate. C. Western blotting was used to detect the expression of Ki67 protein, and the relative expression of Ki67 in MG63 and U2OS cells was analyzed. ①P=0.005, ②P<0.001, ③P=0.019, compared with the rutin 0 μmol/L group.
Fig 2
Effect of rutin on the colony formation of osteosarcoma cells
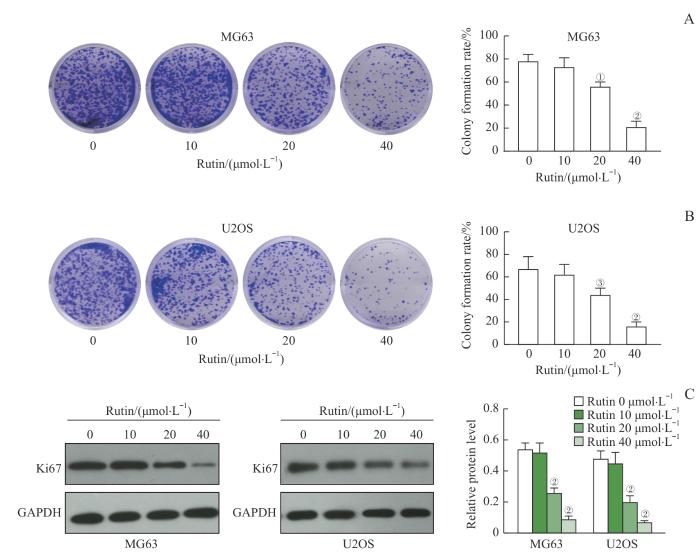
2.3 芦丁促进骨肉瘤细胞的凋亡
图3
图3
芦丁对骨肉瘤细胞凋亡的影响
Note: A. Apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry and the apoptosis rate of MG63 cells was analyzed. B. Apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry and the apoptosis rate of MG63 and U2OS cells was analyzed. C. The expression of Bax and Bcl-2 proteins was detected by Western blotting and the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio in MG63 and U2OS cells was calculated. ①P=0.001, ②P<0.001, compared with the rutin 0 μmol/L group.
Fig 3
Effect of rutin on the apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells
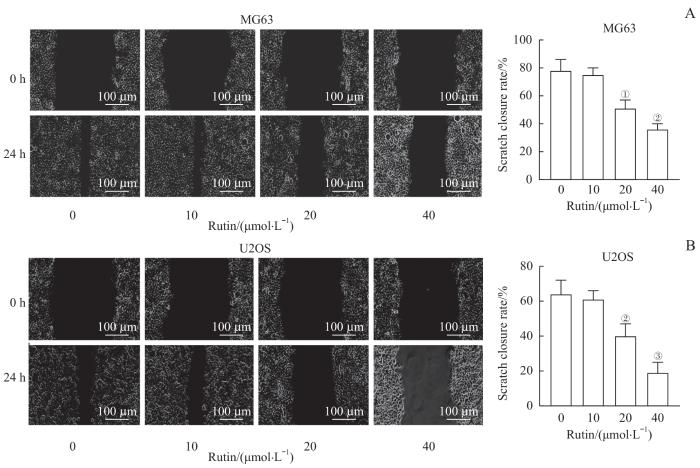
2.4 芦丁抑制骨肉瘤细胞的迁移
与芦丁0 μmol/L组比较,芦丁20 μmol/L组和40 μmol/L组处理后MG63和U2OS细胞划痕闭合率均降低,差异有统计学意义(均P<0.05,图4),而芦丁10 μmol/L组骨肉瘤细胞划痕闭合率变化差异无统计学意义。
图4
图4
芦丁对骨肉瘤细胞迁移的影响
Note: A. Migration ability was assessed by scratch closure assay and the scratch closure rate of MG63 cells was analyzed. B. Migration ability was assessed by scratch closure assay and the scratch closure rate of U2OS cells was analyzed. ①P=0.001, ②P<0.001, ③P=0.005, compared with the rutin 0 μmol/L group.
Fig 4
Effect of rutin on the migration of osteosarcoma cells
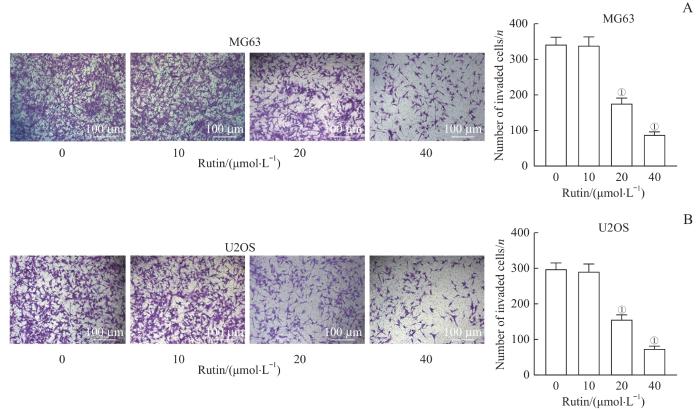
2.5 芦丁抑制骨肉瘤细胞的侵袭
Transwell分析结果显示,与芦丁0 μmol/L组比较,芦丁20 μmol/L组和40 μmol/L组MG63和U2OS细胞侵袭数目均显著减少(均P<0.001,图5),而芦丁10 μmol/L组骨肉瘤细胞侵袭数目变化无显著变化。
图5
图5
芦丁对骨肉瘤细胞侵袭的影响
Note: A. Transwell assay was used to assess the invasion ability and the number of invasive MG63 cells was analyzed. B. Transwell assay was used to assess the invasion ability and the number of invasive U2OS cells was analyzed. ①P<0.001, compared with the rutin 0 μmol/L group.
Fig 5
Effect of rutin on the invasion of osteosarcoma cells
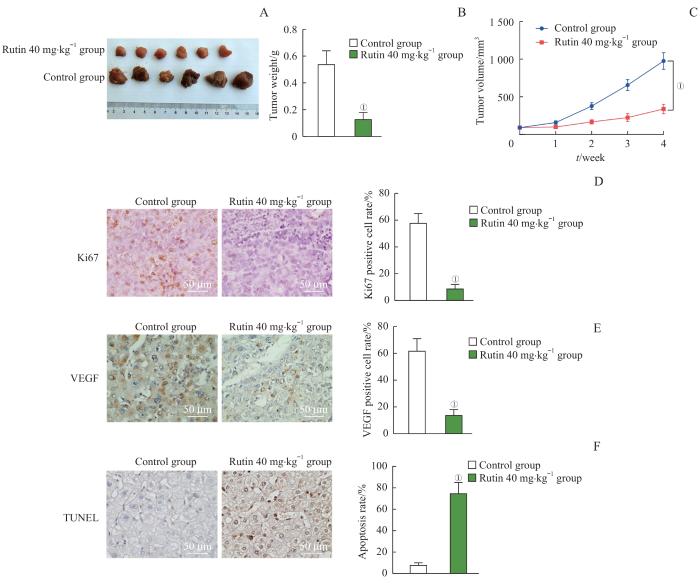
2.6 芦丁抑制体内骨肉瘤的生长
图6
图6
芦丁对骨肉瘤体内移植瘤生长的影响
Note: A. Tumor image. B. Tumor weight. C. Tumor volume. D. The expression of Ki67 detected by immunohistochemistry and statistical analysis of Ki67-positive cell rate. E. The expression of VEGF detected by immunohistochemistry and statistical analysis of VEGF-positive cell rate. F. The tumor cell apoptosis detected by TUNEL and analysis of apoptosis rate. ①P<0.001, compared with the control group.
Fig 6
Effect of rutin on the growth of osteosarcoma xenograft tumors in vivo
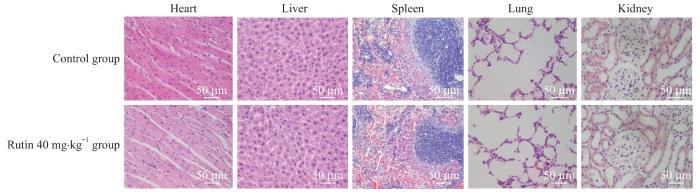
图7
图7
小鼠心、肝、脾、肺、肾组织学分析(H-E染色,×200)
Fig 7
Histological analysis of heart, liver, spleen, lung and kidney in mice (H-E staining, ×200)
3 讨论
抑制肿瘤细胞过度增殖是治疗恶性肿瘤需要解决的首要问题。我们通过CCK-8实验证实芦丁浓度在20 µmol/L以上时即对骨肉瘤细胞增殖有明显的抑制作用,克隆形成实验证实芦丁能明显抑制骨肉瘤细胞的克隆形成,流式细胞分析结果证实芦丁能够显著促进骨肉瘤细胞的凋亡。Ki67是反映细胞增殖活性的指标,其表达越高,提示肿瘤细胞生长越活跃。线粒体凋亡途径是一种经典的内源性凋亡途径,Bax和Bcl-2是该途径的重要调节蛋白。抗凋亡蛋白Bcl-2与线粒体结合,可阻止线粒体向细胞质释放细胞色素c;相反,促凋亡蛋白Bax转位到线粒体,增加线粒体膜通透性,促进细胞色素c释放,从而刺激caspase级联激活凋亡[14-15]。Western blotting结果表明芦丁能够显著下调Ki67的表达,并升高Bax/Bcl-2的比值,进一步提示芦丁能够抑制骨肉瘤细胞增殖,促进骨肉瘤细胞凋亡。这与之前报道的芦丁诱导其他肿瘤细胞凋亡的结果一致[9]。细胞迁移和侵袭是癌症转移的关键过程[16-17]。我们通过划痕闭合实验和Transwell实验观察芦丁对MG63和U2OS细胞迁移和侵袭的影响,结果表明,2种细胞系的迁移速率均受到抑制,并且芦丁显著减少了骨肉瘤侵袭细胞数量。这些结果表明芦丁可以抑制骨肉瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭能力。此外,裸鼠成瘤实验结果进一步验证了芦丁的肿瘤生长抑制作用。芦丁(40 mg/kg)可降低异种移植瘤的大小和质量,降低Ki67和促血管生长因子VEGF的表达。
值得注意的是,组织病理学数据表明芦丁没有明显的毒性作用。综上所述,本研究证实芦丁在体内外抑制骨肉瘤生长和转移的作用,为芦丁的有效开发和骨肉瘤的临床治疗提供了新的思路。
作者贡献声明
李想负责实验操作、数据采集和分析、论文撰写;魏鸣、吴文曦参与实验设计与实验操作;罗小琴、姚彪参与数据整理、论文的写作;伍思宇参与论文的修改。所有作者均阅读并同意了最终稿件的提交。
AUTHOR's CONTRIBUTIONS
LI Xiang was responsible for experimental operation, data collection and analysis, and thesis writing. WEI Ming and WU Wenxi participated in experimental design and experimental operation. LUO Xiaoqin and YAO Biao participated in data collation and thesis writing. WU Siyu participated in the revision of the thesis. All the authors have read the final version manuscript and agreed to its submission.
利益冲突声明
所有作者声明不存在利益冲突。
COMPETING INTERESTS
All authors disclare no relevant conflict of interests.
参考文献