
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (10): 1482-1489.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2022.10.015
• 综述 • 上一篇
冯奕源1( ), 徐忠匀1, 丁琳1, 尹雅芙1, 王辉1, 程维维1,2(
), 徐忠匀1, 丁琳1, 尹雅芙1, 王辉1, 程维维1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-01-10
接受日期:2022-06-14
出版日期:2022-10-28
发布日期:2022-12-02
通讯作者:
程维维
E-mail:fengyy1019@sina.com;wcheng37@outlook.com
作者简介:冯奕源(1997—),女,硕士生;电子信箱:fengyy1019@sina.com。
基金资助:
FENG Yiyuan1( ), XU Zhongyun1, DING Lin1, YIN Yafu1, WANG Hui1, CHENG Weiwei1,2(
), XU Zhongyun1, DING Lin1, YIN Yafu1, WANG Hui1, CHENG Weiwei1,2( )
)
Received:2022-01-10
Accepted:2022-06-14
Online:2022-10-28
Published:2022-12-02
Contact:
CHENG Weiwei
E-mail:fengyy1019@sina.com;wcheng37@outlook.com
Supported by:摘要:
作为微卫星重复扩增疾病的主要致病机制之一,异常扩增的DNA重复序列通过重复序列介导的不依赖AUG (repeat associated non-AUG,RAN)翻译产生毒性蛋白,进而造成神经元死亡。肌萎缩侧索硬化(amyotrophic lateral sclerosis,ALS)是最常见的运动神经元退行性疾病,额颞叶痴呆(frontotemporal dementia,FTD)则是继阿尔茨海默病之后最常见的痴呆综合征。C9ORF72基因中GGGGCC重复序列[GGGGCC repeat,(G4C2)n]异常扩增突变是导致遗传性ALS/FTD发生的最常见的突变类型。C9ORF72 (G4C2)n异常扩增的致病机制通常被认为有3种:① C9ORF72 (G4C2)n异常扩增抑制C9ORF72基因转录,导致C9ORF72蛋白的功能缺失。② C9ORF72 (G4C2)n异常扩增形成的RNA聚集体,与多种RNA结合蛋白(RNA binding protein,RBP)发生不可逆结合,导致这些RBP的功能缺失。③由C9ORF72 (G4C2)n异常扩增形成的重复序列经RAN翻译产生多聚二肽重复蛋白(dipeptide repeat protein,DPR),导致其获得了细胞毒性。目前,越来越多的证据提示C9ORF72 (G4C2)n RAN翻译在ALS/FTD疾病的发生发展中扮演重要角色。然而,C9ORF72 (G4C2)n RAN翻译的起始及其调控机制仍不清楚。阐明C9ORF72 (G4C2)n RAN翻译的分子机制、探索以RAN翻译为靶点延缓疾病发生发展的可行性是目前该领域内的研究热点及难点。该文重点综述了C9ORF72 (G4C2)n RAN翻译的起始和调控机制相关研究的最新进展,并在此基础上探讨以C9ORF72 (G4C2)n RAN翻译为靶点降低细胞毒性、减缓神经元死亡的可行性。
中图分类号:
冯奕源, 徐忠匀, 丁琳, 尹雅芙, 王辉, 程维维. C9ORF72 (G4C2)n RAN翻译的起始及其调控机制[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(10): 1482-1489.
FENG Yiyuan, XU Zhongyun, DING Lin, YIN Yafu, WANG Hui, CHENG Weiwei. Initiation and regulatory mechanism of C9ORF72 (G4C2)n RAN translation[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2022, 42(10): 1482-1489.
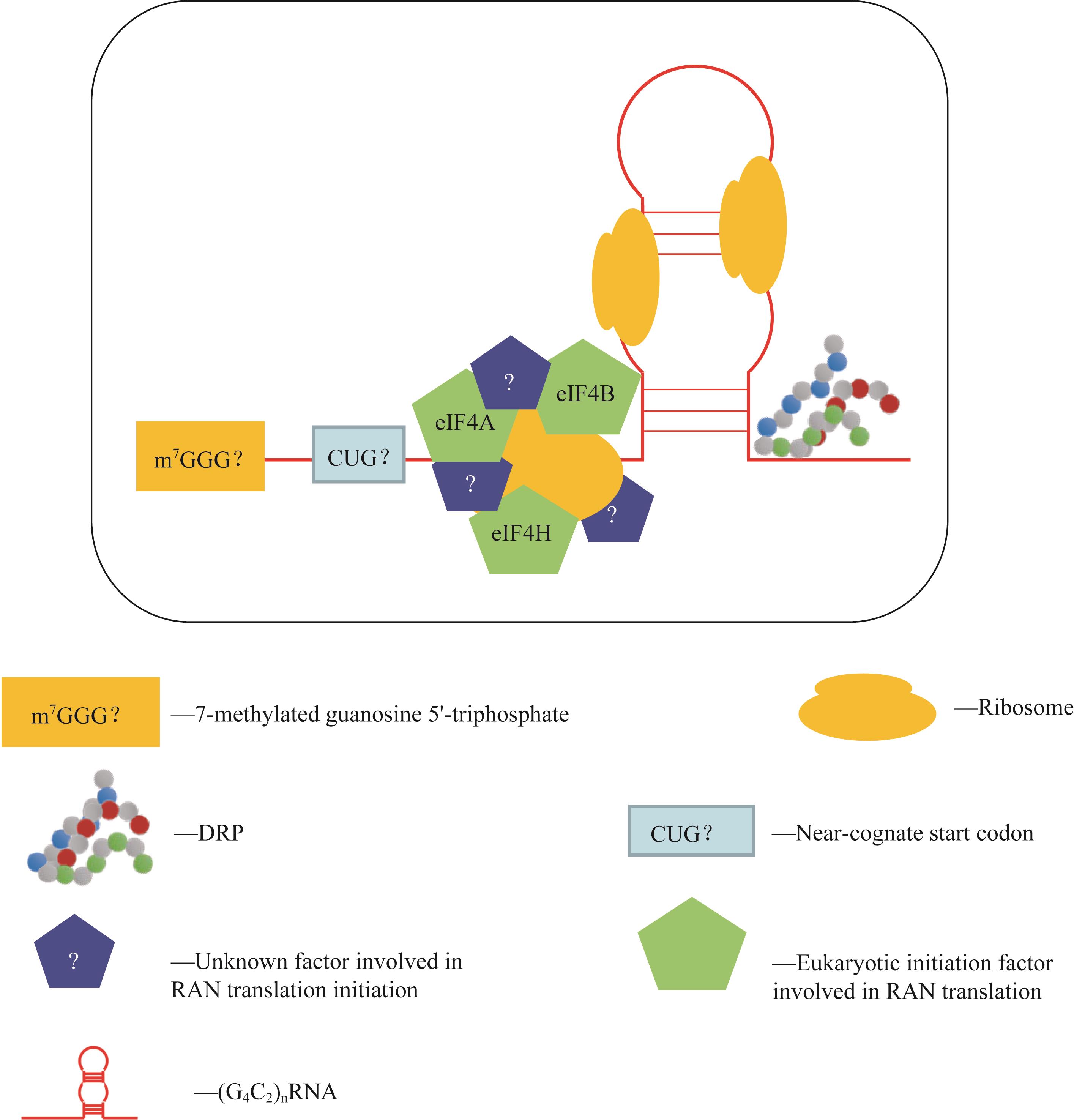
图1 RAN翻译起始示意图Note: eIF4A—eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A; eIF4B—eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4B; eIF4H—eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4H.
Fig 1 Schematic of RAN translation initiation
| 1 | NELSON D L, ORR H T, WARREN S T. The unstable repeats: three evolving faces of neurological disease[J]. Neuron, 2013, 77(5): 825-843. |
| 2 | CASTELLI L M, HUANG W P, LIN Y H, et al. Mechanisms of repeat-associated non-AUG translation in neurological microsatellite expansion disorders[J]. Biochem Soc Trans, 2021, 49(2): 775-792. |
| 3 | MACDONALD M E, AMBROSE C M, DUYAO M P, et al. A novel gene containing a trinucleotide repeat that is expanded and unstable on Huntington's disease chromosomes. The Huntington's Disease Collaborative Research Group[J]. Cell, 1993, 72(6): 971-983. |
| 4 | VERKERK A J, PIERETTI M, SUTCLIFFE J S, et al. Identification of a gene (FMR-1) containing a CGG repeat coincident with a breakpoint cluster region exhibiting length variation in fragile X syndrome[J]. Cell, 1991, 65(5): 905-914. |
| 5 | BROOK J D, MCCURRACH M E, HARLEY H G, et al. Molecular basis of myotonic dystrophy: expansion of a trinucleotide (CTG) repeat at the 3' end of a transcript encoding a protein kinase family member[J]. Cell, 1992, 69(2): 385. |
| 6 | FU Y H, PIZZUTI A, FENWICK R G Jr, et al. An unstable triplet repeat in a gene related to myotonic muscular dystrophy[J]. Science, 1992, 255(5049): 1256-1258. |
| 7 | DEJESUS-HERNANDEZ M, MACKENZIE I R, BOEVE B F, et al. Expanded GGGGCC hexanucleotide repeat in noncoding region of C9ORF72 causes chromosome 9p-linked FTD and ALS[J]. Neuron, 2011, 72(2): 245-256. |
| 8 | BANEZ-CORONEL M, RANUM L P W. Repeat-associated non-AUG (RAN) translation: insights from pathology[J]. Lab Invest, 2019, 99(7): 929-942. |
| 9 | ZU T, GIBBENS B, DOTY N S, et al. Non-ATG-initiated translation directed by microsatellite expansions[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2011, 108(1): 260-265. |
| 10 | TODD P K, OH S Y, KRANS A, et al. CGG repeat-associated translation mediates neurodegeneration in fragile X tremor ataxia syndrome[J]. Neuron, 2013, 78(3): 440-455. |
| 11 | SELLIER C, BUIJSEN R A M, HE F, et al. Translation of expanded CGG repeats into FMRpolyG is pathogenic and may contribute to fragile X tremor ataxia syndrome[J]. Neuron, 2017, 93(2): 331-347. |
| 12 | MORI K, WENG S M, ARZBERGER T, et al. The C9orf72 GGGGCC repeat is translated into aggregating dipeptide-repeat proteins in FTLD/ALS[J]. Science, 2013, 339(6125): 1335-1338. |
| 13 | GENDRON T F, BIENIEK K F, ZHANG Y J, et al. Antisense transcripts of the expanded C9ORF72 hexanucleotide repeat form nuclear RNA foci and undergo repeat-associated non-ATG translation in c9FTD/ALS[J]. Acta Neuropathol, 2013, 126(6): 829-844. |
| 14 | ASH P E, BIENIEK K F, GENDRON T F, et al. Unconventional translation of C9ORF72 GGGGCC expansion generates insoluble polypeptides specific to c9FTD/ALS[J]. Neuron, 2013, 77(4): 639-646. |
| 15 | BAÑEZ-CORONEL M, AYHAN F, TARABOCHIA A D, et al. RAN translation in Huntington disease[J]. Neuron, 2015, 88(4): 667-677. |
| 16 | RENTON A E, MAJOUNIE E, WAITE A, et al. A hexanucleotide repeat expansion in C9ORF72 is the cause of chromosome 9p21-linked ALS-FTD[J]. Neuron, 2011, 72(2): 257-268. |
| 17 | SMITH B N, NEWHOUSE S, SHATUNOV A, et al. The C9ORF72 expansion mutation is a common cause of ALS+/-FTD in Europe and has a single founder[J]. Eur J Hum Genet, 2013, 21(1): 102-108. |
| 18 | MAJOUNIE E, RENTON A E, MOK K, et al. Frequency of the C9orf72 hexanucleotide repeat expansion in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia: a cross-sectional study[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2012, 11(4): 323-330. |
| 19 | MACKENZIE I R, ARZBERGER T, KREMMER E, et al. Dipeptide repeat protein pathology in C9ORF72 mutation cases: clinico-pathological correlations[J]. Acta Neuropathol, 2013, 126(6): 859-879. |
| 20 | ZU T, LIU Y J, BAÑEZ-CORONEL M, et al. RAN proteins and RNA foci from antisense transcripts in C9ORF72 ALS and frontotemporal dementia[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2013, 110(51): E4968-E4977. |
| 21 | LOPEZ-GONZALEZ R, LU Y B, GENDRON T F, et al. Poly(GR) in C9ORF72-related ALS/FTD compromises mitochondrial function and increases oxidative stress and DNA damage in iPSC-derived motor neurons[J]. Neuron, 2016, 92(2): 383-391. |
| 22 | ZHANG Y J, GENDRON T F, GRIMA J C, et al. C9ORF72 poly(GA) aggregates sequester and impair HR23 and nucleocytoplasmic transport proteins[J]. Nat Neurosci, 2016, 19(5): 668-677. |
| 23 | GENDRON T F, BELZIL V V, ZHANG Y J, et al. Mechanisms of toxicity in C9FTLD/ALS[J]. Acta Neuropathol, 2014, 127(3): 359-376. |
| 24 | ZHANG K J, WANG A L, ZHONG K K, et al. UBQLN2-HSP70 axis reduces poly-Gly-Ala aggregates and alleviates behavioral defects in the C9ORF72 animal model[J]. Neuron, 2021, 109(12): 1949-1962.e6. |
| 25 | TABET R, SCHAEFFER L, FREYERMUTH F, et al. CUG initiation and frameshifting enable production of dipeptide repeat proteins from ALS/FTD C9ORF72 transcripts[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1): 152. |
| 26 | GREEN K M, GLINEBURG M R, KEARSE M G, et al. RAN translation at C9orf72-associated repeat expansions is selectively enhanced by the integrated stress response[J]. Nat Commun, 2017, 8(1): 2005. |
| 27 | CHENG W W, WANG S P, MESTRE A A, et al. C9ORF72 GGGGCC repeat-associated non-AUG translation is upregulated by stress through eIF2α phosphorylation[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1): 51. |
| 28 | CLEARY J D, RANUM L P. New developments in RAN translation: insights from multiple diseases[J]. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 2017, 44: 125-134. |
| 29 | WOJCIECHOWSKA M, OLEJNICZAK M, GALKA-MARCINIAK P, et al. RAN translation and frameshifting as translational challenges at simple repeats of human neurodegenerative disorders[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2014, 42(19): 11849-11864. |
| 30 | GOODMAN L D, PRUDENCIO M, SRINIVASAN A R, et al. eIF4B and eIF4H mediate GR production from expanded G4C2 in a Drosophila model for C9orf72-associated ALS[J]. Acta Neuropathol Commun, 2019, 7(1): 62. |
| 31 | COOPER-KNOCK J, WALSH M J, HIGGINBOTTOM A, et al. Sequestration of multiple RNA recognition motif-containing proteins by C9orf72 repeat expansions[J]. Brain, 2014, 137(Pt 7): 2040-2051. |
| 32 | JODOIN R, CARRIER J C, RIVARD N, et al. G-quadruplex located in the 5' UTR of the BAG-1 mRNA affects both its cap-dependent and cap-independent translation through global secondary structure maintenance[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2019, 47(19): 10247-10266. |
| 33 | WOLFE A L, SINGH K, ZHONG Y, et al. RNA G-quadruplexes cause eIF4A-dependent oncogene translation in cancer[J]. Nature, 2014, 513(7516): 65-70. |
| 34 | HAEUSLER A R, DONNELLY C J, PERIZ G, et al. C9orf72 nucleotide repeat structures initiate molecular cascades of disease[J]. Nature, 2014, 507(7491): 195-200. |
| 35 | ŠKET P, POHLEVEN J, KOVANDA A, et al. Characterization of DNA G-quadruplex species forming from C9ORF72 G4C2-expanded repeats associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal lobar degeneration[J]. Neurobiol Aging, 2015, 36(2): 1091-1096. |
| 36 | BRCIC J, PLAVEC J. NMR structure of a G-quadruplex formed by four d(G4C2) repeats: insights into structural polymorphism[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2018, 46(21): 11605-11617. |
| 37 | SUN Y J, ATAS E, LINDQVIST L, et al. The eukaryotic initiation factor eIF4H facilitates loop-binding, repetitive RNA unwinding by the eIF4A DEAD-box helicase[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2012, 40(13): 6199-6207. |
| 38 | HARMS U, ANDREOU A Z, GUBAEV A, et al. eIF4B, eIF4G and RNA regulate eIF4A activity in translation initiation by modulating the eIF4A conformational cycle[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2014, 42(12): 7911-7922. |
| 39 | WESTERGARD T, MCAVOY K, RUSSELL K, et al. Repeat-associated non-AUG translation in C9orf72-ALS/FTD is driven by neuronal excitation and stress[J]. EMBO Mol Med, 2019, 11(2): e9423. |
| 40 | ZU T, GUO S, BARDHI O, et al. Metformin inhibits RAN translation through PKR pathway and mitigates disease in C9orf72 ALS/FTD mice[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2020, 117(31): 18591-18599. |
| 41 | SONOBE Y, GHADGE G, MASAKI K, et al. Translation of dipeptide repeat proteins from the C9ORF72 expanded repeat is associated with cellular stress[J]. Neurobiol Dis, 2018, 116: 155-165. |
| 42 | HOLCIK M, SONENBERG N. Translational control in stress and apoptosis[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2005, 6(4): 318-327. |
| 43 | ORTEGA J A, DALEY E L, KOUR S, et al. Nucleocytoplasmic proteomic analysis uncovers eRF1 and nonsense-mediated decay as modifiers of ALS/FTD C9orf72 toxicity[J]. Neuron, 2020, 106(1): 90-107.e13. |
| 44 | JOVIČIĆ A, MERTENS J, BOEYNAEMS S, et al. Modifiers of C9orf72 dipeptide repeat toxicity connect nucleocytoplasmic transport defects to FTD/ALS[J]. Nat Neurosci, 2015, 18(9): 1226-1229. |
| 45 | KRAMER N J, HANEY M S, MORGENS D W, et al. CRISPR-Cas9 screens in human cells and primary neurons identify modifiers of C9ORF72 dipeptide-repeat-protein toxicity[J]. Nat Genet, 2018, 50(4): 603-612. |
| 46 | MAOR-NOF M, SHIPONY Z, LOPEZ-GONZALEZ R, et al. p53 is a central regulator driving neurodegeneration caused by C9orf72 poly(PR)[J]. Cell, 2021, 184(3): 689-708.e20. |
| 47 | BERSON A, GOODMAN L D, SARTORIS A N, et al. Drosophila Ref1/ALYREF regulates transcription and toxicity associated with ALS/FTD disease etiologies[J]. Acta Neuropathol Commun, 2019, 7(1): 65. |
| 48 | HAUTBERGUE G M, CASTELLI L M, FERRAIUOLO L, et al. SRSF1-dependent nuclear export inhibition of C9ORF72 repeat transcripts prevents neurodegeneration and associated motor deficits[J]. Nat Commun, 2017, 8: 16063. |
| 49 | WANG S P, LATALLO M J, ZHANG Z, et al. Nuclear export and translation of circular repeat-containing intronic RNA in C9ORF72-ALS/FTD[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 4908. |
| 50 | ZHANG K, DONNELLY C J, HAEUSLER A R, et al. The C9orf72 repeat expansion disrupts nucleocytoplasmic transport[J]. Nature, 2015, 525(7567): 56-61. |
| 51 | FREIBAUM B D, LU Y B, LOPEZ-GONZALEZ R, et al. GGGGCC repeat expansion in C9orf72 compromises nucleocytoplasmic transport[J]. Nature, 2015, 525(7567): 129-133. |
| 52 | YAMADA S B, GENDRON T F, NICCOLI T, et al. RPS25 is required for efficient RAN translation of C9orf72 and other neurodegenerative disease-associated nucleotide repeats[J]. Nat Neurosci, 2019, 22(9): 1383-1388. |
| 53 | MAO Y H, DONG L M, LIU X M, et al. m6A in mRNA coding regions promotes translation via the RNA helicase-containing YTHDC2[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 5332. |
| 54 | SHEN L, PELLETIER J. General and target-specific DExD/H RNA helicases in eukaryotic translation initiation[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(12): E4402. |
| 55 | CHENG W W, WANG S P, ZHANG Z, et al. CRISPR-Cas9 screens identify the RNA helicase DDX3X as a repressor of C9ORF72 (GGGGCC)n repeat-associated non-AUG translation[J]. Neuron, 2019, 104(5): 885-898.e8. |
| 56 | LIU H H, LU Y N, PAUL T, et al. A helicase unwinds hexanucleotide repeat RNA G-quadruplexes and facilitates repeat-associated non-AUG translation[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2021, 143(19): 7368-7379. |
| 57 | TSENG Y J, SANDWITH S N, GREEN K M, et al. The RNA helicase DHX36-G4R1 modulates C9orf72 GGGGCC hexanucleotide repeat-associated translation[J]. J Biol Chem, 2021, 297(2): 100914. |
| 58 | FRATTA P, MIZIELINSKA S, NICOLL A J, et al. C9orf72 hexanucleotide repeat associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia forms RNA G-quadruplexes[J]. Sci Rep, 2012, 2: 1016. |
| 59 | REDDY K, ZAMIRI B, STANLEY S Y R, et al. The disease-associated r(GGGGCC)n repeat from the C9orf72 gene forms tract length-dependent uni- and multimolecular RNA G-quadruplex structures[J]. J Biol Chem, 2013, 288(14): 9860-9866. |
| 60 | CONLON E G, LU L, SHARMA A, et al. The C9ORF72 GGGGCC expansion forms RNA G-quadruplex inclusions and sequesters hnRNP H to disrupt splicing in ALS brains[J]. Elife, 2016, 5: e17820. |
| 61 | SU Z M, ZHANG Y J, GENDRON T F, et al. Discovery of a biomarker and lead small molecules to target r(GGGGCC)-associated defects in c9FTD/ALS[J]. Neuron, 2014, 83(5): 1043-1050. |
| 62 | SIMONE R, BALENDRA R, MOENS T G, et al. G-quadruplex-binding small molecules ameliorate C9orf72 FTD/ALS pathology in vitro and in vivo[J]. EMBO Mol Med, 2018, 10(1): 22-31. |
| 63 | WANG Z F, URSU A, CHILDS-DISNEY J L, et al. The hairpin form of r(G4C2)exp in c9ALS/FTD is repeat-associated non-ATG translated and a target for bioactive small molecules[J]. Cell Chem Biol, 2019, 26(2): 179-190.e12. |
| [1] | 汤开然, 吴琼, 黄思佳, 邱旭东, 李文彦, 邓华云, 黄雷. 与MUC1共同调控肿瘤化疗耐药的MUCIN家族成员的筛选[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(9): 1288-1295. |
| [2] | 褚云开, 廖春华, 邓华云, 黄雷. 黏蛋白1与肿瘤相关蛋白的调控网络研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(8): 1024-1033. |
| [3] | 刘宏强, 陆艳青, 高宇轩, 王一云, 王传东, 张晓玲. 构建高效载体OPEI沉默TRAF6促进骨关节炎软骨再生的研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(7): 846-857. |
| [4] | 赵久红, 童佳婷, 沈郅珺, 吕叶辉. 环状RNA与氧化应激互作机制的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(3): 393-399. |
| [5] | 陈仪婷, 赵安达, 李荣, 康文慧, 李生慧. 循环外泌体微RNA在支气管哮喘中的作用综述[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(3): 375-380. |
| [6] | 孙天瑶, 蒋时枫, 徐沁, 刘俊岭, 党素英, 樊雪梅. 靶向凝血因子FⅨa-FⅧa复合物结合位点的新型抗栓抗体[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(9): 1133-1141. |
| [7] | 刘俐, 耿子龙, 陈嘉焕, 张沙沙, 张冰. 血管内皮生长因子A调控人脐静脉内皮细胞miRNA的全基因表达谱分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(9): 1183-1189. |
| [8] | 胡静燕, 张琳, 张良. 人源核酸烷基化损伤修复酶ALKBH3在肿瘤进展和治疗中的作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(5): 684-689. |
| [9] | 吴则南, 张晨. 快感缺失的炎症机制研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(2): 241-245. |
| [10] | 贺 明,魏 倩,张颖婷. 铁死亡相关机制与其在肝脏相关疾病中作用的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(11): 1519-1523. |
| [11] | 吴若兰,张 越,俞润华,丁泽宇,黄 莺. 蛋白磷酸酶2A对机体能量代谢影响的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(11): 1530-1535. |
| [12] | 杨硕瑶1, 2,戚紫怡3,向 军4. 线粒体Lon蛋白酶及其相关疾病的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(5): 683-687. |
| [13] | 屈国君 1,陆元凤 2,李宇 1. PDGFRα下游新底物 CCT2对肿瘤细胞生长的影响及其机制[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2019, 39(1): 28-. |
| [14] | 董瑞 1,王英 1,王毓美 1,孙祖俊 1, 2,易静 1,杨洁 1. 人肺癌细胞系中SENP3介导p53的de-SUMO2/3修饰对其活性的调控作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2018, 38(7): 732-. |
| [15] | 刘进权1,谢冰2. BV8及其抗体与血管新生的关系[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2018, 38(4): 472-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||