
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (11): 1432-1442.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2025.11.003
• 前沿述评 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2025-05-07
接受日期:2025-06-06
出版日期:2025-11-28
发布日期:2025-12-03
通讯作者:
李本尚,主任医师,博士;电子信箱:libenshang@scmc.com.cn。Received:2025-05-07
Accepted:2025-06-06
Online:2025-11-28
Published:2025-12-03
Contact:
LI Benshang, E-mail: libenshang@scmc.com.cn.摘要:
嵌合抗原受体T细胞(chimeric antigen receptor T cell,CAR-T细胞)治疗通过基因工程改造T细胞,使其能够特异性识别并高效清除靶细胞,在B细胞淋巴瘤、白血病等血液系统恶性肿瘤的治疗中取得了突破性成就。基于该疗法独特的治疗原理,研究人员积极探索以拓展其在其他疾病领域的应用,其中,CAR-T细胞治疗在自身免疫性疾病(autoimmune disease,AID)的治疗中展现出巨大潜力并备受关注。目前,AID的传统治疗方案(如糖皮质激素、免疫抑制剂和生物制剂等)常面临疗效有限、缓解期短及长期毒性等诸多问题。相比之下,CAR-T细胞治疗凭借其精准靶向和可诱导持续无药物缓解的优势,成为AID极具前景的治疗策略。该文回顾CAR-T细胞治疗在多种AID中的临床前和临床研究进展,阐述该疗法清除致病性B细胞及重建免疫平衡的可行性。同时重点探讨CAR-T细胞治疗面临的主要挑战,包括不良反应、持久性不足及部分患者存在抵抗性等问题,并进一步从优化嵌合抗原受体(chimeric antigen receptor,CAR)结构、探索特异性靶点及开发通用型CAR-T细胞等方面提出应对策略,阐释其未来的发展方向,旨在为CAR-T细胞治疗在AID中的进一步开发和优化提供理论依据。
中图分类号:
王雪懿, 李本尚. CAR-T细胞治疗自身免疫性疾病的研究述评[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(11): 1432-1442.
WANG Xueyi, LI Benshang. Review of CAR-T cell therapy for autoimmune diseases[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(11): 1432-1442.
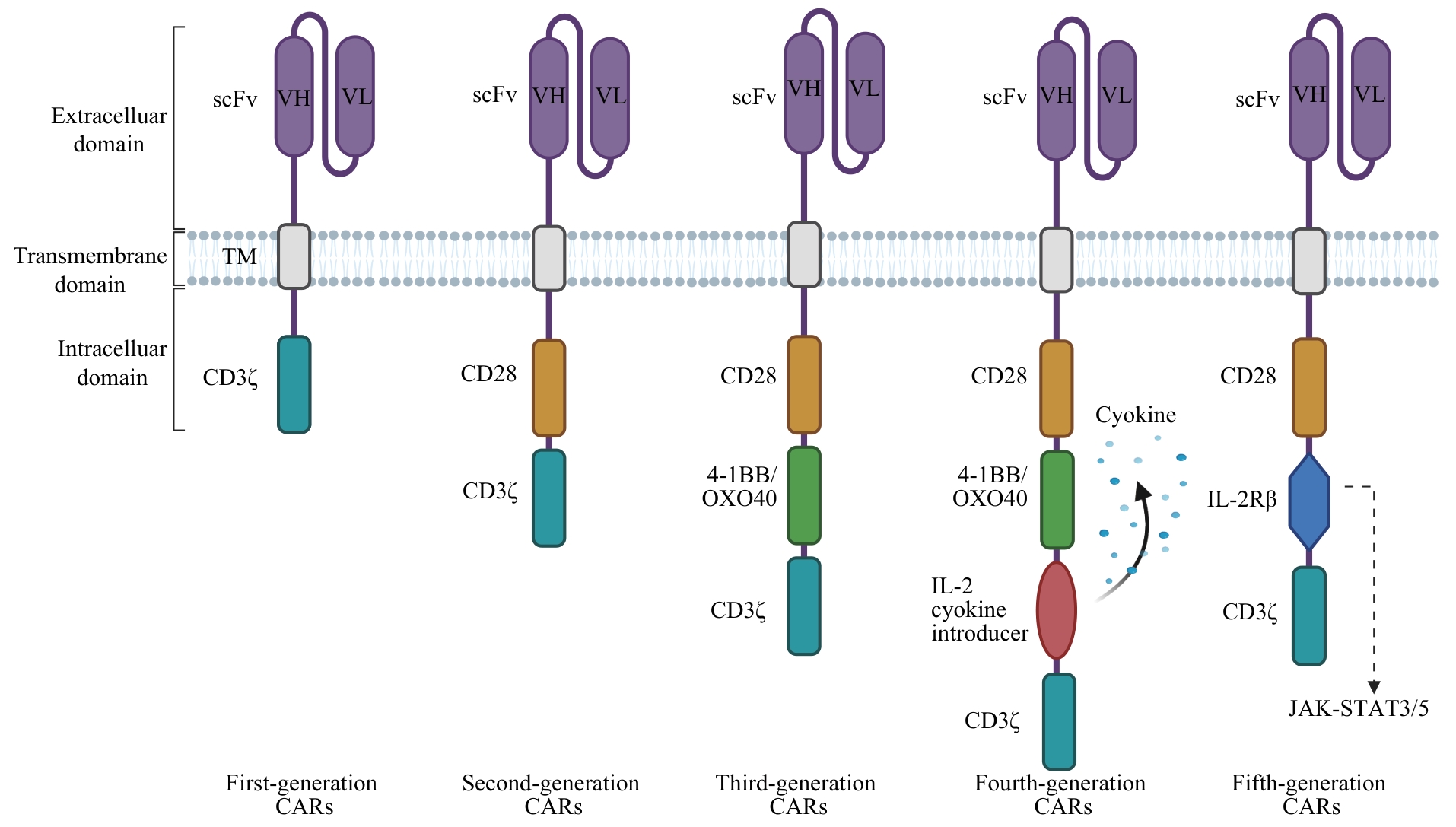
图1 5代CAR基本结构Note: VH—variable heavy chain; VL—variable light chain; TM—transmembrane domain; IL-2Rβ—Interleukin-2 receptor β.
Fig 1 Basic structure of five generations of CARs
| Disease | Target antigen | CAR-T cell type | Experimental model | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLE | CD19 | anti-CD19 CAR-T | MRL/lpr mice, (NZB×NZW) F1 mice | [ |
| CD19 | anti-CD19 CAR-T | MRL/lpr mice | [ | |
| RA | antigenic FITC peptide | anti-FITC CAR-T | CIA mice | [ |
| CⅡ-specific autoimmune CD4+ T cells | DR1-CII CAR-T | CIA mice | [ | |
| T1DM | I-Ag7-B:9-23(R3) antigen complex | mAb287 CAR-T | NOD mice | [ |
| Insulin or IGPR-specific CD8⁺ T cells | Insulin/IGPR-reactive CAR-T | NOD mice | [ | |
| Pancreatic β cell-specific CD4⁺ T cells | 5MCAR-CTLs | NOD mice | [ | |
| Insulin | Insulin-specific CAR-Treg | NOD mice | [ | |
| HPi2 | HPi2 CAR-Treg | Human pancreatic β cell line, mouse β cell line | [ | |
| PV | Dsg3-specific B cells | Dsg3 CAAR-T | NSG-PV hybridoma model | [ |
| Dsg3-specific B cells | Dsg3 CAAR-T | Active immune PV mice, NSG-PV hybridoma model | [ | |
| UC | CEA | CEA CAR-Treg | CEA-transgenic mice, AOM-DSS-CRC model | [ |
| TNP | TNP-TPCR Treg | hapten-COL model | [ | |
| FliC | FliC CAR-Treg | DNBS-COL NSG model | [ | |
| MS | MOG | CARαMOG-FoxP3-Treg | EAE mice | [ |
| MOG and MBP | MOG/MBP CAR-Tregs | EAE mice | [ | |
| CD19 | anti-CD19 CAR-T | EAE mice | [ | |
| CD19 | anti-CD19 CAR-T | OSE mice | [ | |
| GVHD | HLA-A2 | HLA-A2 CAR-Treg | GVHD mice | [ |
| ANCA-AVV | CD19 | anti-CD19 CAR-T | MPO-AVV mice | [ |
| MG | anti-MuSK B cells | MuSK CAAR-T | NSG Nalm-6 xenografted mice, syngeneic MuSK EAMG mice | [ |
| NMDAR encephalitis | NMDAR autoantibodies | NMDAR CAAR-T | NSG xenograft model | [ |
表1 CAR-T细胞治疗AID的临床前试验
Tab 1 Preclinical trials of CAR-T cell treatment for AIDs
| Disease | Target antigen | CAR-T cell type | Experimental model | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLE | CD19 | anti-CD19 CAR-T | MRL/lpr mice, (NZB×NZW) F1 mice | [ |
| CD19 | anti-CD19 CAR-T | MRL/lpr mice | [ | |
| RA | antigenic FITC peptide | anti-FITC CAR-T | CIA mice | [ |
| CⅡ-specific autoimmune CD4+ T cells | DR1-CII CAR-T | CIA mice | [ | |
| T1DM | I-Ag7-B:9-23(R3) antigen complex | mAb287 CAR-T | NOD mice | [ |
| Insulin or IGPR-specific CD8⁺ T cells | Insulin/IGPR-reactive CAR-T | NOD mice | [ | |
| Pancreatic β cell-specific CD4⁺ T cells | 5MCAR-CTLs | NOD mice | [ | |
| Insulin | Insulin-specific CAR-Treg | NOD mice | [ | |
| HPi2 | HPi2 CAR-Treg | Human pancreatic β cell line, mouse β cell line | [ | |
| PV | Dsg3-specific B cells | Dsg3 CAAR-T | NSG-PV hybridoma model | [ |
| Dsg3-specific B cells | Dsg3 CAAR-T | Active immune PV mice, NSG-PV hybridoma model | [ | |
| UC | CEA | CEA CAR-Treg | CEA-transgenic mice, AOM-DSS-CRC model | [ |
| TNP | TNP-TPCR Treg | hapten-COL model | [ | |
| FliC | FliC CAR-Treg | DNBS-COL NSG model | [ | |
| MS | MOG | CARαMOG-FoxP3-Treg | EAE mice | [ |
| MOG and MBP | MOG/MBP CAR-Tregs | EAE mice | [ | |
| CD19 | anti-CD19 CAR-T | EAE mice | [ | |
| CD19 | anti-CD19 CAR-T | OSE mice | [ | |
| GVHD | HLA-A2 | HLA-A2 CAR-Treg | GVHD mice | [ |
| ANCA-AVV | CD19 | anti-CD19 CAR-T | MPO-AVV mice | [ |
| MG | anti-MuSK B cells | MuSK CAAR-T | NSG Nalm-6 xenografted mice, syngeneic MuSK EAMG mice | [ |
| NMDAR encephalitis | NMDAR autoantibodies | NMDAR CAAR-T | NSG xenograft model | [ |
| Disease | Target antigen | CAR-T cell source | Sample size/n | Disease status | Efficacy | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLE | CD19 | Autologous | 1 | Refractory | Drug-free remission in 44 d | [ |
| CD19 | Autologous | 5 | Refractory | Drug-free remission within 3 months | [ | |
| CD19 | Allogeneic | 3 | Refractory | Clinical remission in 12 months | [ | |
| BCMA & CD19 | Autologous | 1 | Refractory | Drug-free remission in 23 months | [ | |
| BCMA & CD19 | Autologous | 13 | Relapsed/refractory: 2. Refractory: 11 | 11 cases: drug-free remission in 12‒46 months | [ | |
| ASS | CD19 | Autologous | 1 | Refractory | Drug-free remission in 180 d | [ |
| CD19 | Autologous | 1 | Refractory | Drug-free remission in 150 d | [ | |
| CD19 | Autologous | 1 | Refractory | Clinical and serological remission in 240 d | [ | |
| SSc | CD19 | Autologous | 1 | Refractory | Clinical and serological remission in 6 months | [ |
| CD19 | Autologous | 3 | Refractory | Drug-free remission in 15 months | [ | |
| CD19 | Autologous | 1 | Refractory | Clinical and serological remission in 11 months | [ | |
| CD19 | Allogeneic | 2 | Refractory | Drug-free remission in 6 months | [ | |
| MS | CD19 | Autologous | 2 | Refractory | Clinical remission in 100 and 28 d | [ |
| NMOSD | BCMA | Autologous | 12 | Relapsed/refractory | 11 cases: Drug-free remission in 5.5 months | [ |
| MG | BCMA | Autologous | 14 | Refractory | Clinical remission within 6‒12 months | [ |
| CD19 | Autologous | 2 | Refractory | Clinical remission in 4 and 6 months | [ | |
| MMN | CD19 | Autologous | 1 | Refractory | Clinical and serological remission in 6 months | [ |
表2 CAR-T细胞治疗AID的临床实验
Tab 2 Clinical trials of CAR-T cell treatment for AIDs
| Disease | Target antigen | CAR-T cell source | Sample size/n | Disease status | Efficacy | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLE | CD19 | Autologous | 1 | Refractory | Drug-free remission in 44 d | [ |
| CD19 | Autologous | 5 | Refractory | Drug-free remission within 3 months | [ | |
| CD19 | Allogeneic | 3 | Refractory | Clinical remission in 12 months | [ | |
| BCMA & CD19 | Autologous | 1 | Refractory | Drug-free remission in 23 months | [ | |
| BCMA & CD19 | Autologous | 13 | Relapsed/refractory: 2. Refractory: 11 | 11 cases: drug-free remission in 12‒46 months | [ | |
| ASS | CD19 | Autologous | 1 | Refractory | Drug-free remission in 180 d | [ |
| CD19 | Autologous | 1 | Refractory | Drug-free remission in 150 d | [ | |
| CD19 | Autologous | 1 | Refractory | Clinical and serological remission in 240 d | [ | |
| SSc | CD19 | Autologous | 1 | Refractory | Clinical and serological remission in 6 months | [ |
| CD19 | Autologous | 3 | Refractory | Drug-free remission in 15 months | [ | |
| CD19 | Autologous | 1 | Refractory | Clinical and serological remission in 11 months | [ | |
| CD19 | Allogeneic | 2 | Refractory | Drug-free remission in 6 months | [ | |
| MS | CD19 | Autologous | 2 | Refractory | Clinical remission in 100 and 28 d | [ |
| NMOSD | BCMA | Autologous | 12 | Relapsed/refractory | 11 cases: Drug-free remission in 5.5 months | [ |
| MG | BCMA | Autologous | 14 | Refractory | Clinical remission within 6‒12 months | [ |
| CD19 | Autologous | 2 | Refractory | Clinical remission in 4 and 6 months | [ | |
| MMN | CD19 | Autologous | 1 | Refractory | Clinical and serological remission in 6 months | [ |
| Disease | Co-stimulatory molecule | Sample size/n | CRS | ICANS/n (%) | Hematologic toxicity/n (%) | Infection/ n (%) | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incidence/n (%) | Grade | Duration/d | |||||||
| SLE | 4-1BB | 1 | 0 (0) | — | — | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | UTI: 1 (100) | [ |
| 4-1BB | 5 | 3 (60) | Grade 1 | Median: 2 (2‒3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | URTI: 3 (60). Otitis: 1 (20) | [ | |
| CD28 | 3 | 0 (0) | — | — | 0 (0) | Thrombocytopenia: 1 (33) | URTI: 1 (33) | [ | |
CD28 (anti-BCMA), 4-1BB (anti-CD19) | 10 | 9 (90) | <grade 3 | Not reported | 0 (0) | Leucopenia: 5 (50). Neutropenia: 4 (40). Anemia: 5 (50). Lymphocytopenia: 4 (40) | COVID-19 infection: 8 (80). UTI: 1 (10) | [ | |
| ASS | 4-1BB | 1 | 1 (100) | Grade 1 | 3 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | Enteritis: 1 (100) | [ |
| 4-1BB | 1 | 1 (100) | Grade 1 | Not reported | 1 (100) | 0 (0) | Herpes simplex: 1 (100) | [ | |
| 4-1BB | 1 | 1 (100) | Grade 1 | 7 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | [ | |
| SSc | 4-1BB | 1 | 1 (100) | Grade 1 | 1 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | [ |
| 4-1 BB | 3 | 2 (67) | Grade 1 | Median: 5 (2‒7) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | Cellulitis: 1 (33). URTI: 1 (33) | [ | |
| CD28 & 4-1BB | 1 | 1 (100) | Grade 1 | Not reported | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | [ | |
| CD28 | 2 | 0 (0) | — | — | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | [ | |
| MS | CD28 | 2 | 1 (50) | Grade 1 | 6 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | [ |
| NMOSD | 4-1BB | 12 | 12 (100) | Grade 1: 11. Grade 2: 1 | Median: 3.5 (1‒8) | 0 (0) | Leukopenia: 12 (100). Neutropenia: 12 (100). Anemia: 6 (50). Lymphocytopenia: 12 (100). Thrombocytopenia: 3 (25) | 7 (58) | [ |
| MG | Unknown | 14 | 0 (0) | — | — | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | [ |
| CD28 | 2 | 2 (100) | Grade 1: 1. Grade 2: 1 | Patient 1: 10. Patient 2: 9 | 1 (50) | 0 (0) | Tooth pulpitis: 1 (50) | [ | |
| MMN | CD28 | 1 | 1 (100) | Grade 2 | 3 | 1 (100) | Neutropenia: 1 (100) | 0 (0) | [ |
表3 CAR-T细胞治疗AID的相关不良反应
Tab 3 Adverse reactions related to CAR-T cell therapy for AIDs
| Disease | Co-stimulatory molecule | Sample size/n | CRS | ICANS/n (%) | Hematologic toxicity/n (%) | Infection/ n (%) | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incidence/n (%) | Grade | Duration/d | |||||||
| SLE | 4-1BB | 1 | 0 (0) | — | — | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | UTI: 1 (100) | [ |
| 4-1BB | 5 | 3 (60) | Grade 1 | Median: 2 (2‒3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | URTI: 3 (60). Otitis: 1 (20) | [ | |
| CD28 | 3 | 0 (0) | — | — | 0 (0) | Thrombocytopenia: 1 (33) | URTI: 1 (33) | [ | |
CD28 (anti-BCMA), 4-1BB (anti-CD19) | 10 | 9 (90) | <grade 3 | Not reported | 0 (0) | Leucopenia: 5 (50). Neutropenia: 4 (40). Anemia: 5 (50). Lymphocytopenia: 4 (40) | COVID-19 infection: 8 (80). UTI: 1 (10) | [ | |
| ASS | 4-1BB | 1 | 1 (100) | Grade 1 | 3 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | Enteritis: 1 (100) | [ |
| 4-1BB | 1 | 1 (100) | Grade 1 | Not reported | 1 (100) | 0 (0) | Herpes simplex: 1 (100) | [ | |
| 4-1BB | 1 | 1 (100) | Grade 1 | 7 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | [ | |
| SSc | 4-1BB | 1 | 1 (100) | Grade 1 | 1 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | [ |
| 4-1 BB | 3 | 2 (67) | Grade 1 | Median: 5 (2‒7) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | Cellulitis: 1 (33). URTI: 1 (33) | [ | |
| CD28 & 4-1BB | 1 | 1 (100) | Grade 1 | Not reported | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | [ | |
| CD28 | 2 | 0 (0) | — | — | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | [ | |
| MS | CD28 | 2 | 1 (50) | Grade 1 | 6 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | [ |
| NMOSD | 4-1BB | 12 | 12 (100) | Grade 1: 11. Grade 2: 1 | Median: 3.5 (1‒8) | 0 (0) | Leukopenia: 12 (100). Neutropenia: 12 (100). Anemia: 6 (50). Lymphocytopenia: 12 (100). Thrombocytopenia: 3 (25) | 7 (58) | [ |
| MG | Unknown | 14 | 0 (0) | — | — | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | [ |
| CD28 | 2 | 2 (100) | Grade 1: 1. Grade 2: 1 | Patient 1: 10. Patient 2: 9 | 1 (50) | 0 (0) | Tooth pulpitis: 1 (50) | [ | |
| MMN | CD28 | 1 | 1 (100) | Grade 2 | 3 | 1 (100) | Neutropenia: 1 (100) | 0 (0) | [ |
| [1] | LIU Y X, DONG M H, CHU Y H, et al. Dawn of CAR-T cell therapy in autoimmune diseases[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2024, 137(10): 1140-1150. |
| [2] | SU M, ZHAO C B, LUO S S. Therapeutic potential of chimeric antigen receptor based therapies in autoimmune diseases[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2022, 21(1): 102931. |
| [3] | POSNER J, BARRINGTON P, BRIER T, et al. Monoclonal antibodies: past, present and future[J]. Handb Exp Pharmacol, 2019, 260: 81-141. |
| [4] | PORTER D L, LEVINE B L, KALOS M, et al. Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells in chronic lymphoid leukemia[J]. N Engl J Med, 2011, 365(8): 725-733. |
| [5] | JUNE C H, O'CONNOR R S, KAWALEKAR O U, et al. CAR T cell immunotherapy for human cancer[J]. Science, 2018, 359(6382): 1361-1365. |
| [6] | BOYIADZIS M M, DHODAPKAR M V, BRENTJENS R J, et al. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T therapies for the treatment of hematologic malignancies: clinical perspective and significance[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2018, 6(1): 137. |
| [7] | LI X D, LI W, XU L P, et al. Chimeric antigen receptor-immune cells against solid tumors: structures, mechanisms, recent advances, and future developments[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2024, 137(11): 1285-1302. |
| [8] | YEKU O O, BRENTJENS R J. Armored CAR T-cells: utilizing cytokines and pro-inflammatory ligands to enhance CAR T-cell anti-tumour efficacy[J]. Biochem Soc Trans, 2016, 44(2): 412-418. |
| [9] | TANG X Y, SUN Y, ZHANG A, et al. Third-generation CD28/4-1BB chimeric antigen receptor T cells for chemotherapy relapsed or refractory acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a non-randomised, open-label phase Ⅰ trial protocol[J]. BMJ Open, 2016, 6(12): e013904. |
| [10] | LOCK D, MOCKEL-TENBRINCK N, DRECHSEL K, et al. Automated manufacturing of potent CD20-directed chimeric antigen receptor T cells for clinical use[J]. Hum Gene Ther, 2017, 28(10): 914-925. |
| [11] | TOKAREW N, OGONEK J, ENDRES S, et al. Teaching an old dog new tricks: next-generation CAR T cells[J]. Br J Cancer, 2019, 120(1): 26-37. |
| [12] | UTKARSH K, SRIVASTAVA N, KUMAR S, et al. CAR-T cell therapy: a game-changer in cancer treatment and beyond[J]. Clin Transl Oncol, 2024, 26(6): 1300-1318. |
| [13] | KIRIAKIDOU M, CHING C L. Systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2020, 172(11): ITC81-ITC96. |
| [14] | TEDDER T F, ENGEL P. CD20: a regulator of cell-cycle progression of B lymphocytes[J]. Immunol Today, 1994, 15(9): 450-454. |
| [15] | KANSAL R, RICHARDSON N, NEELI I, et al. Sustained B cell depletion by CD19-targeted CAR T cells is a highly effective treatment for murine lupus[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2019, 11(482): eaav1648. |
| [16] | JIN X X, XU Q, PU C F, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of anti-CD19 CAR-T cells in a mouse model of systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2021, 18(8): 1896-1903. |
| [17] | MOUGIAKAKOS D, KRÖNKE G, VÖLKL S, et al. CD19-targeted CAR T cells in refractory systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. N Engl J Med, 2021, 385(6): 567-569. |
| [18] | MACKENSEN A, MÜLLER F, MOUGIAKAKOS D, et al. Anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy for refractory systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Nat Med, 2022, 28(10): 2124-2132. |
| [19] | ZHANG W L, FENG J, CINQUINA A, et al. Treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus using BCMA-CD19 compound CAR[J]. Stem Cell Rev Rep, 2021, 17(6): 2120-2123. |
| [20] | OREN S, MANDELBOIM M, BRAUN-MOSCOVICI Y, et al. Vaccination against influenza in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: the effect of rituximab on the humoral response[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2008, 67(7): 937-941. |
| [21] | GOTTENBERG J E, RAVAUD P, BARDIN T, et al. Risk factors for severe infections in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with rituximab in the autoimmunity and rituximab registry[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2010, 62(9): 2625-2632. |
| [22] | ZHANG B, WANG Y, YUAN Y S, et al. In vitro elimination of autoreactive B cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients by universal chimeric antigen receptor T cells[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2021, 80(2): 176-184. |
| [23] | WHITTINGTON K B, PRISLOVSKY A, BEATY J, et al. CD8+ T cells expressing an HLA-DR1 chimeric antigen receptor target autoimmune CD4+ T cells in an antigen-specific manner and inhibit the development of autoimmune arthritis[J]. J Immunol, 2022, 208(1): 16-26. |
| [24] | MÜLLER F, BOELTZ S, KNITZA J, et al. CD19-targeted CAR T cells in refractory antisynthetase syndrome[J]. Lancet, 2023, 401(10379): 815-818. |
| [25] | TAUBMANN J, KNITZA J, MÜLLER F, et al. Rescue therapy of antisynthetase syndrome with CD19-targeted CAR-T cells after failure of several B-cell depleting antibodies[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2024, 63(1): e12-e14. |
| [26] | PECHER A C, HENSEN L C, KLEIN R, et al. CD19-targeting CAR T cells for myositis and interstitial lung disease associated with antisynthetase syndrome[J]. JAMA, 2023, 329(24): 2154-2162. |
| [27] | ZHANG L, SOSINOWSKI T, COX A R, et al. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells targeting a pathogenic MHC class Ⅱ: peptide complex modulate the progression of autoimmune diabetes[J]. J Autoimmun, 2019, 96: 50-58. |
| [28] | FISHMAN S, LEWIS M D, SIEW L K, et al. Adoptive transfer of mRNA-transfected T cells redirected against diabetogenic CD8 T cells can prevent diabetes[J]. Mol Ther, 2017, 25(2): 456-464. |
| [29] | KOBAYASHI S, THELIN M A, PARRISH H L, et al. A biomimetic five-module chimeric antigen receptor (5MCAR) designed to target and eliminate antigen-specific T cells[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2020, 117(46): 28950-28959. |
| [30] | TENSPOLDE M, ZIMMERMANN K, WEBER L C, et al. Regulatory T cells engineered with a novel insulin-specific chimeric antigen receptor as a candidate immunotherapy for type 1 diabetes[J]. J Autoimmun, 2019, 103: 102289. |
| [31] | RADICHEV I A, YOON J, SCOTT D W, et al. Towards antigen-specific Tregs for type 1 diabetes: construction and functional assessment of pancreatic endocrine marker, HPi2-based chimeric antigen receptor[J]. Cell Immunol, 2020, 358: 104224. |
| [32] | ELLEBRECHT C T, BHOJ V G, NACE A, et al. Reengineering chimeric antigen receptor T cells for targeted therapy of autoimmune disease[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6295): 179-184. |
| [33] | LEE J M, LUNDGREN D K, MAO X M, et al. Antigen-specific B cell depletion for precision therapy of mucosal pemphigus vulgaris[J]. J Clin Invest, 2020, 130(12): 6317-6324. |
| [34] | BLAT D, ZIGMOND E, ALTEBER Z, et al. Suppression of murine colitis and its associated cancer by carcinoembryonic antigen-specific regulatory T cells[J]. Mol Ther, 2014, 22(5): 1018-1028. |
| [35] | ELINAV E, WAKS T, ESHHAR Z. Redirection of regulatory T cells with predetermined specificity for the treatment of experimental colitis in mice[J]. Gastroenterology, 2008, 134(7): 2014-2024. |
| [36] | BOARDMAN D A, WONG M Q, REES W D, et al. Flagellin-specific human CAR Tregs for immune regulation in IBD[J]. J Autoimmun, 2023, 134: 102961. |
| [37] | FRANSSON M, PIRAS E, BURMAN J, et al. CAR/FoxP3-engineered T regulatory cells target the CNS and suppress EAE upon intranasal delivery[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2012, 9: 112. |
| [38] | DE PAULA POHL A, SCHMIDT A, ZHANG A H, et al. Engineered regulatory T cells expressing myelin-specific chimeric antigen receptors suppress EAE progression[J]. Cell Immunol, 2020, 358: 104222. |
| [39] | GUPTA S, SIMIC M, SAGAN S A, et al. CAR-T cell-mediated B-cell depletion in central nervous system autoimmunity[J]. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm, 2023, 10(2): e200080. |
| [40] | MITSDOERFFER M, DI LIBERTO G, DÖTSCH S, et al. Formation and immunomodulatory function of meningeal B cell aggregates in progressive CNS autoimmunity[J]. Brain, 2021, 144(6): 1697-1710. |
| [41] | MACDONALD K G, HOEPPLI R E, HUANG Q, et al. Alloantigen-specific regulatory T cells generated with a chimeric antigen receptor[J]. J Clin Invest, 2016, 126(4): 1413-1424. |
| [42] | LODKA D, ZSCHUMMEL M, BUNSE M, et al. CD19-targeting CAR T cells protect from ANCA-induced acute kidney injury[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2024, 83(4): 499-507. |
| [43] | OH S, MAO X M, MANFREDO-VIEIRA S, et al. Precision targeting of autoantigen-specific B cells in muscle-specific tyrosine kinase myasthenia gravis with chimeric autoantibody receptor T cells[J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2023, 41(9): 1229-1238. |
| [44] | REINCKE S M, VON WARDENBURG N, HOMEYER M A, et al. Chimeric autoantibody receptor T cells deplete NMDA receptor-specific B cells[J]. Cell, 2023, 186(23): 5084-5097.e18. |
| [45] | WANG D D, WANG X B, TAN B H, et al. Allogeneic CD19-targeted CAR-T therapy in refractory systemic lupus erythematosus achieved durable remission[J]. Med, 2025: 100749. |
| [46] | WANG W J, HE S Z, ZHANG W L, et al. BCMA-CD19 compound CAR T cells for systemic lupus erythematosus: a phase 1 open-label clinical trial[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2024, 83(10): 1304-1314. |
| [47] | BERGMANN C, MÜLLER F, DISTLER J H W, et al. Treatment of a patient with severe systemic sclerosis (SSc) using CD19-targeted CAR T cells[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2023, 82(8): 1117-1120. |
| [48] | MÜLLER F, TAUBMANN J, BUCCI L, et al. CD19 CAR T-cell therapy in autoimmune disease: a case series with follow-up[J]. N Engl J Med, 2024, 390(8): 687-700. |
| [49] | MERKT W, FREITAG M, CLAUS M, et al. Third-generation CD19.CAR-T cell-containing combination therapy in Scl70+ systemic sclerosis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2024, 83(4): 543-546. |
| [50] | WANG X B, WU X, TAN B H, et al. Allogeneic CD19-targeted CAR-T therapy in patients with severe myositis and systemic sclerosis[J]. Cell, 2024, 187(18): 4890-4904.e9. |
| [51] | FISCHBACH F, RICHTER J, PFEFFER L K, et al. CD19-targeted chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy in two patients with multiple sclerosis[J]. Med, 2024, 5(6): 550-558.e2. |
| [52] | QIN C, TIAN D S, ZHOU L Q, et al. Anti-BCMA CAR T-cell therapy CT103A in relapsed or refractory AQP4-IgG seropositive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders: phase 1 trial interim results[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8(1): 5. |
| [53] | GRANIT V, BENATAR M, KURTOGLU M, et al. Safety and clinical activity of autologous RNA chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy in myasthenia gravis (MG-001): a prospective, multicentre, open-label, non-randomised phase 1b/2a study[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2023, 22(7): 578-590. |
| [54] | MOTTE J, SGODZAI M, SCHNEIDER-GOLD C, et al. Treatment of concomitant myasthenia gravis and Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome with autologous CD19-targeted CAR T cells[J]. Neuron, 2024, 112(11): 1757-1763.e2. |
| [55] | JHAVERI K S, SCHLAM I, HOLTZMAN N G, et al. Safety and efficacy of CAR T cells in a patient with lymphoma and a coexisting autoimmune neuropathy[J]. Blood Adv, 2020, 4(23): 6019-6022. |
| [56] | QI Y, ZHAO M, HU Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of CD19-specific CAR T cell-based therapy in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients with CNSL[J]. Blood, 2022, 139(23): 3376-3386. |
| [57] | HERNANI R, BENZAQUÉN A, SOLANO C. Toxicities following CAR-T therapy for hematological malignancies[J]. Cancer Treat Rev, 2022, 111: 102479. |
| [58] | OHNO R, NAKAMURA A. Advancing autoimmune rheumatic disease treatment: CAR-T cell therapies—evidence, safety, and future directions[J]. Semin Arthritis Rheum, 2024, 67: 152479. |
| [59] | WANG X, QI Y K, LI H J, et al. Impact of glucocorticoids on short-term and long-term outcomes in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma treated with CAR-T therapy[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 943004. |
| [60] | HUARTE E, O'CONNOR R S, PEEL M T, et al. Itacitinib (INCB039110), a JAK1 inhibitor, reduces cytokines associated with cytokine release syndrome induced by CAR T-cell therapy[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2020, 26(23): 6299-6309. |
| [61] | MESTERMANN K, GIAVRIDIS T, WEBER J, et al. The tyrosine kinase inhibitor dasatinib acts as a pharmacologic on/off switch for CAR T cells[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2019, 11(499): eaau5907. |
| [62] | MORRIS E C, NEELAPU S S, GIAVRIDIS T, et al. Cytokine release syndrome and associated neurotoxicity in cancer immunotherapy[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2022, 22(2): 85-96. |
| [63] | HAROON A, MUHSEN I N, ABID M B, et al. Infectious complications and preventative strategies following chimeric antigen receptor T-cells (CAR-T cells) therapy for B-cell malignancies[J]. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther, 2022, 15(3): 153-158. |
| [64] | ABRAMSON J S, LIA PALOMBA M, GORDON L I, et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel for patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): a multicentre seamless design study[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10254): 839-852. |
| [65] | GHILARDI G, PARUZZO L, SVOBODA J, et al. Bendamustine lymphodepletion before axicabtagene ciloleucel is safe and associates with reduced inflammatory cytokines[J]. Blood Adv, 2024, 8(3): 653-666. |
| [66] | HILL J A, GIRALT S, TORGERSON T R, et al. CAR-T: and a side order of IgG, to go?—Immunoglobulin replacement in patients receiving CAR-T cell therapy[J]. Blood Rev, 2019, 38: 100596. |
| [67] | MAHMOUDJAFARI Z, HAWKS K G, HSIEH A A, et al. American society for blood and marrow transplantation pharmacy special interest group survey on chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy administrative, logistic, and toxicity management practices in the United States[J]. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant, 2019, 25(1): 26-33. |
| [68] | GU T, ZHU M, HUANG H, et al. Relapse after CAR-T cell therapy in B-cell malignancies: challenges and future approaches[J]. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B, 2022, 23(10): 793-811. |
| [69] | FLUGEL C L, MAJZNER R G, KRENCIUTE G, et al. Overcoming on-target, off-tumour toxicity of CAR T cell therapy for solid tumours[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2023, 20(1): 49-62. |
| [70] | HUDECEK M, SOMMERMEYER D, KOSASIH P L, et al. The nonsignaling extracellular spacer domain of chimeric antigen receptors is decisive for in vivo antitumor activity[J]. Cancer Immunol Res, 2015, 3(2): 125-135. |
| [71] | WU W, ZHOU Q P, MASUBUCHI T, et al. Multiple signaling roles of CD3ε and its application in CAR-T cell therapy[J]. Cell, 2020, 182(4): 855-871.e23. |
| [72] | SUN C, MAHENDRAVADA A, BALLARD B, et al. Safety and efficacy of targeting CD138 with a chimeric antigen receptor for the treatment of multiple myeloma[J]. Oncotarget, 2019, 10(24): 2369-2383. |
| [73] | NOCTURNE G, MARMONTEL O, DI FILIPPO M, et al. Efficacy of daratumumab in refractory primary Sjögren disease[J]. RMD Open, 2023, 9(3): e003464. |
| [74] | ROCCATELLO D, FENOGLIO R, CANIGGIA I, et al. Daratumumab monotherapy for refractory lupus nephritis[J]. Nat Med, 2023, 29(8): 2041-2047. |
| [75] | AGHAJANIAN H, KIMURA T, RURIK J G, et al. Targeting cardiac fibrosis with engineered T cells[J]. Nature, 2019, 573(7774): 430-433. |
| [76] | LIN H L, CHENG J L, MU W, et al. Advances in universal CAR-T cell therapy[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 744823. |
| [1] | 唐珺倩, 李本尚. 儿童高危细胞遗传学B系急性淋巴细胞白血病治疗新进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(10): 1390-1399. |
| [2] | 丁艳玲, 李杰, 袁军, 李燕. 慢性淋巴细胞白血病靶向治疗的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(2): 264-270. |
| [3] | 杨婧偊, 陈留宝, 王康太, 杨兴智, 于海涛. 基于实验室指标的系统性红斑狼疮鉴别诊断列线图的构建及评估[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(2): 204-211. |
| [4] | 李悦华, 李青峰, 谢芸. 脂肪来源间充质干细胞在自身免疫性疾病中的应用进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(8): 1131-1138. |
| [5] | 那迪娜·帕尔哈提null, 严妍, 车千纪, 罗菁, 刘鑫男, 李斌. 嵌合抗原受体T细胞疗法在胶质母细胞瘤中的应用与展望[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(7): 982-986. |
| [6] | 赵初娴,高 峰,戎 殳,尚明花 . 狼疮性肾炎合并 Castleman 病 1 例报道及文献复习[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2017, 37(12): 1710-. |
| [7] | 缪 怡, 胡朝英, 钱 柳, 等. 类风湿性关节炎免疫学研究进展[J]. , 2011, 31(7): 1035-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
