
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (8): 1024-1033.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2022.08.007
收稿日期:2022-04-01
接受日期:2022-07-01
出版日期:2022-08-28
发布日期:2022-08-19
通讯作者:
黄 雷,电子信箱:leihuang@shsmu.edu.cn。作者简介:褚云开(1996—),男,硕士生;电子信箱:yunkaichu@126.com。
基金资助:
CHU Yunkai( ), LIAO Chunhua, DENG Huayun, HUANG Lei(
), LIAO Chunhua, DENG Huayun, HUANG Lei( )
)
Received:2022-04-01
Accepted:2022-07-01
Online:2022-08-28
Published:2022-08-19
Contact:
HUANG Lei, E-mail: leihuang@shsmu.edu.cn.Supported by:摘要:
目的·研究黏蛋白1(mucin1,MUC1)在不同肿瘤组织中的表达水平及其对患者生存期的影响;通过分析与MUC1存在相互作用的肿瘤相关蛋白的调控网络,预测MUC1参与肿瘤发生发展的可能机制。方法·使用GEPIA 2在线平台对MUC1在33种肿瘤中的mRNA水平,以及其与患者生存期的关系进行分析。在HEK293T细胞中转染MUC1-HA质粒,用HA抗体进行免疫共沉淀(co-immunoprecipitation,Co-IP)实验,对MUC1结合蛋白进行液相色谱-串联质谱(liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry,LCMS/MS)分析。使用String 11.5在线平台对MUC1结合蛋白的亚细胞定位、分子功能、涉及的疾病、参与的生物学过程以及这些蛋白之间的相互作用调控网络进行分析。结果·MUC1在乳腺癌、宫颈癌、弥漫性大B细胞瘤、多发性胶质细胞瘤、低级别脑胶质瘤、卵巢癌、胰腺癌、胸腺癌和子宫内膜癌等9种肿瘤中高表达;对这9种肿瘤中MUC1表达与生存期的关系分析发现,MUC1表达与生存期呈负相关,其中在乳腺癌、宫颈癌、多发性胶质细胞瘤、低级别脑胶质瘤、胰腺癌和胸腺癌等6种肿瘤中具有统计学意义。质谱分析共检测到526个MUC1结合蛋白,这些蛋白定位于细胞器、细胞质和膜结构最多;主要分子功能包括蛋白结合、离子结合和酶活性等;涉及的疾病有解剖实体性疾病、细胞增殖性疾病、代谢性疾病和癌症等;参与的生物学过程主要包括细胞应激、代谢、发育和生物合成等。MUC1结合蛋白主要参与代谢、癌症、cGMP-依赖cGMP的蛋白激酶(cGMP-dependent protein kinase,PKG)、肿瘤坏死因子(tumor necrosis factor,TNF)和细胞周期等信号通路;深入分析后发现,MUC1结合蛋白一方面大量参与到Wnt/β-catenin、Notch和cAMP等癌症相关信号通路,另一方面通过调控代谢、凋亡和细胞周期促进肿瘤的发生发展。结论·MUC1在多种肿瘤组织中高表达并与患者预后不良相关;MUC1通过蛋白相互作用参与调控细胞代谢和肿瘤相关信号通路。该研究创新性地发现多个新的MUC1结合蛋白,可为进一步研究MUC1生物学新功能奠定基础。
中图分类号:
褚云开, 廖春华, 邓华云, 黄雷. 黏蛋白1与肿瘤相关蛋白的调控网络研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(8): 1024-1033.
CHU Yunkai, LIAO Chunhua, DENG Huayun, HUANG Lei. Study of the regulatory network of MUC1 and tumor-associated proteins[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2022, 42(8): 1024-1033.

图1 MUC1 在不同肿瘤组织中的转录水平Note: Red indicates high expression of MUC1. Green indicates low expression of MUC1. Black indicates no significant difference. T—tumor tissue. N—normal tissue.CHOL—cholangiocarcinoma; COAD—colon adenocarcinoma; ESCA—esophageal carcinoma; HNSC—head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; KICH—kidney chromophobe; KIRC—kidney renal clear cell carcinoma; KIRP—kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma; LAML—acute myeloid leukemia; LIHC—liver hepatocellular carcinoma; LUAD—lung adenocarcinoma; LUSC—lung squamous cell carcinoma; MESO—mesothelioma; PCPG—pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma; PRAD—prostate adenocarcinoma; READ—rectum adenocarcinoma; SARC—sarcoma; SKCM—skin cutaneous melanoma; STAD—stomach adenocarcinoma; TGCT—testicular germ cell tumors; THCA—thyroid carcinoma; UCS—uterine carcinosarcoma; UVM—uveal melanoma.
Fig 1 Transcription levels of MUC1 in different tumor tissues
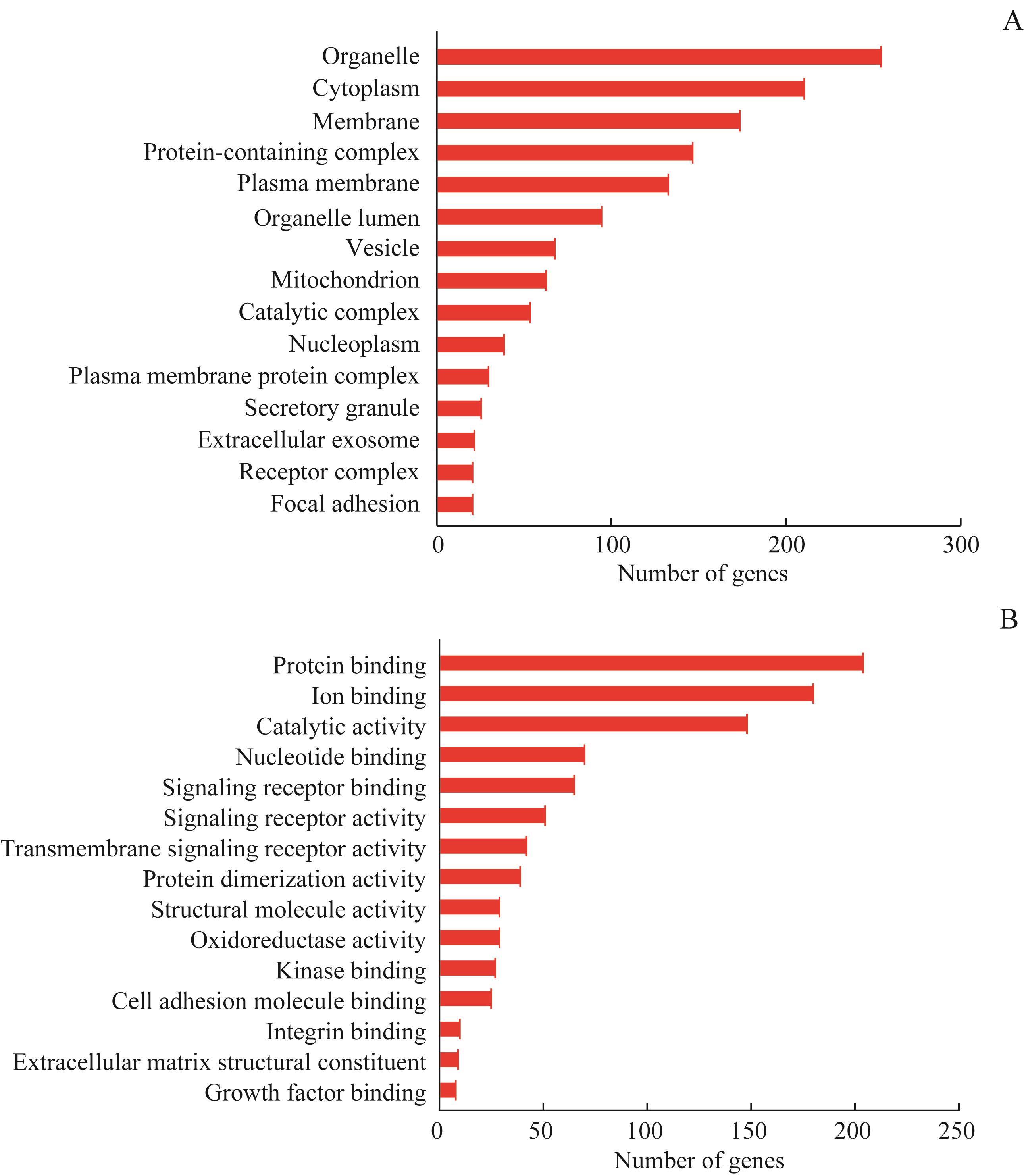
图3 MUC1结合蛋白的亚细胞定位和分子功能分析Note:A. Subcellular localization of MUC1-binding proteins. B. Molecular function of MUC1-binding proteins.
Fig 3 Subcellular localization and molecular function of MUC1-binding proteins
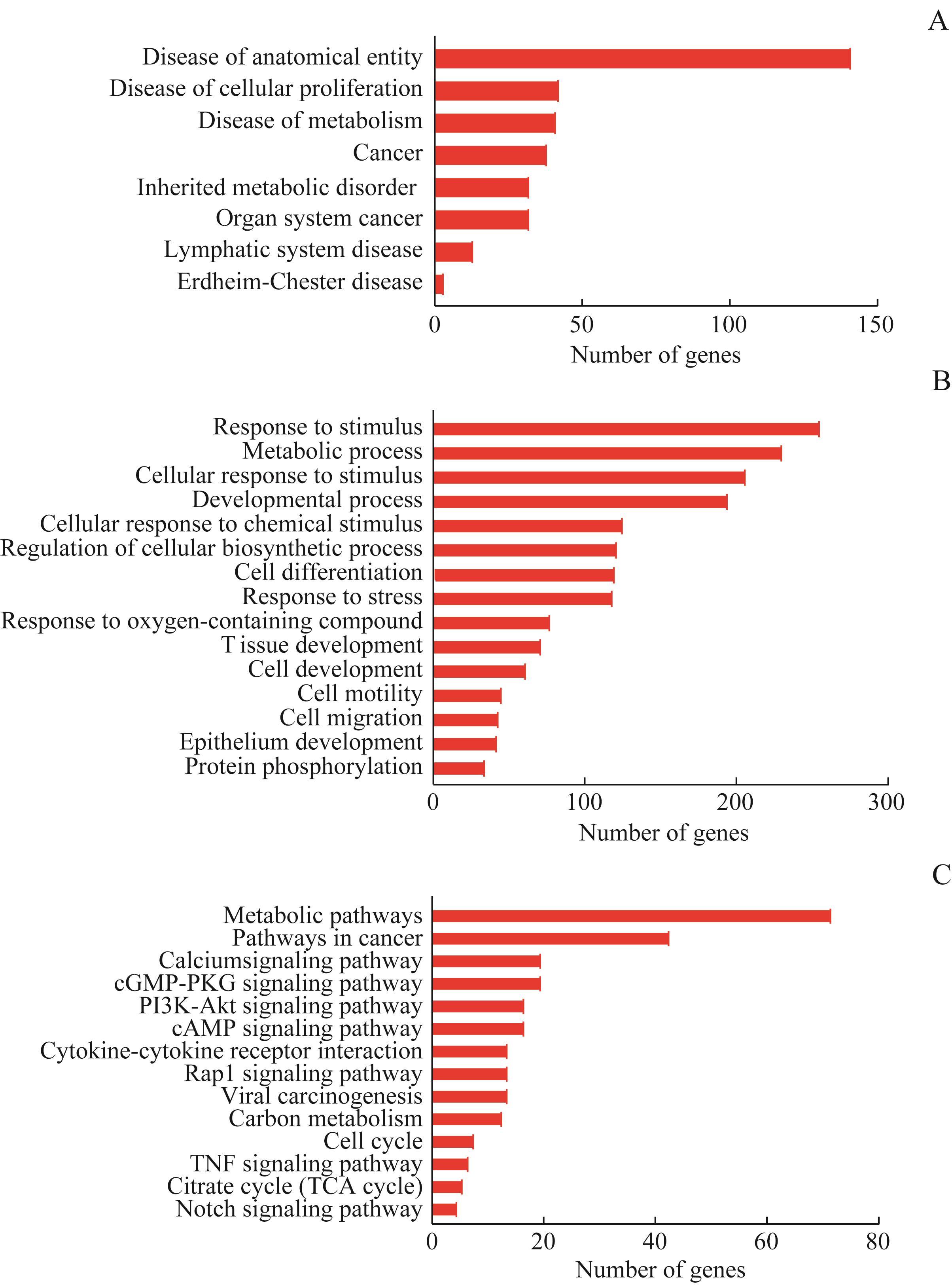
图4 与MUC1结合蛋白有关的疾病、生物学进程和信号通路Note:A. Diseases associated with MUC1-binding proteins. B. Biological processes associated with MUC1-binding proteins. C. Signaling pathways associated with MUC1-binding proteins.
Fig 4 Diseases, biological processes and signaling pathways associated with MUC1-binding proteins
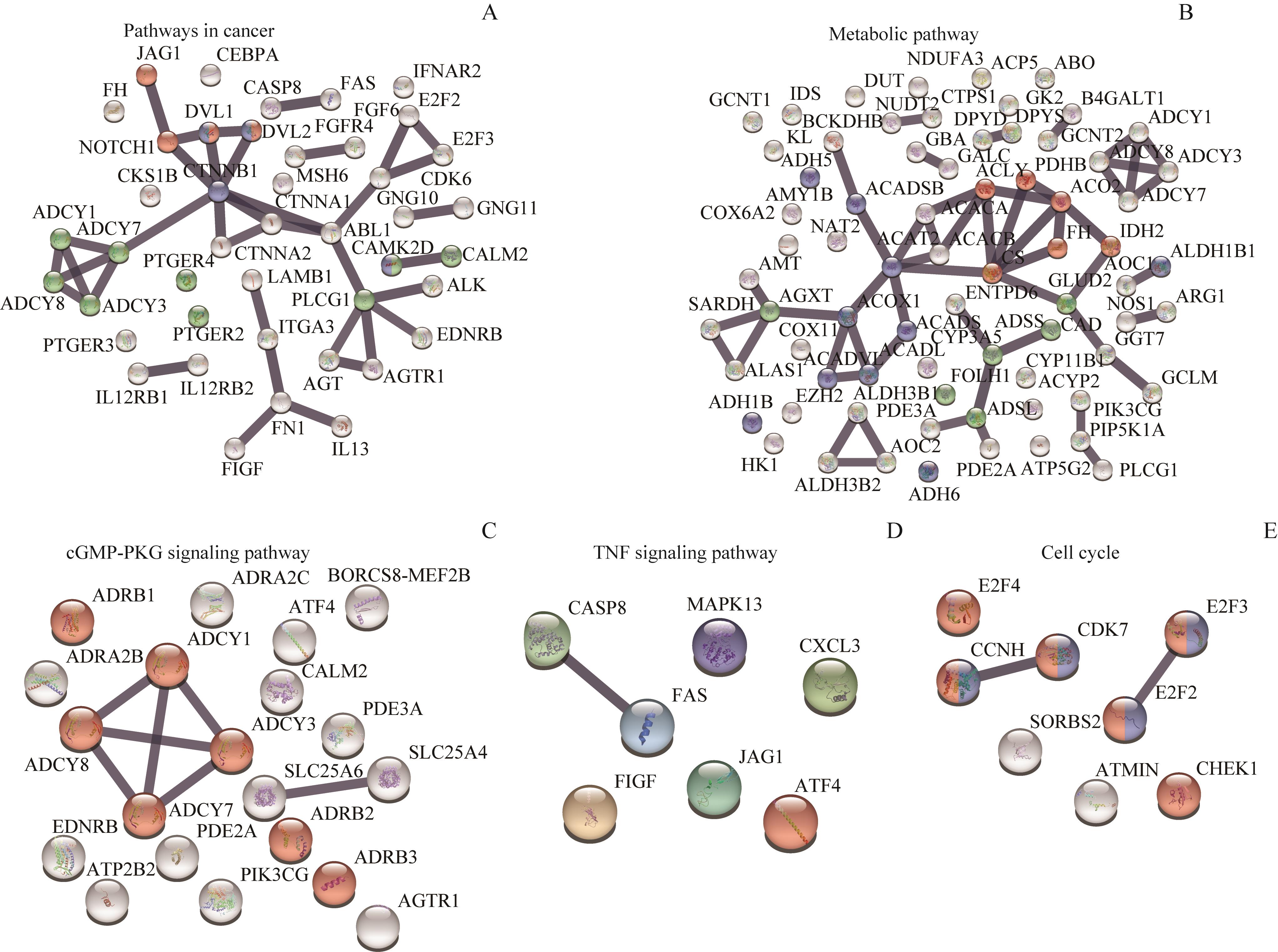
图5 MUC1结合蛋白参与的信号通路Note:A. Pathways in cancer. B. Metabolic pathway. C. cGMP-PKG signaling pathway. D. TNF signaling pathway. E. Cell cycle.
Fig 5 Signaling pathways of MUC1-binding proteins
| 1 | LI W, HAN Y, SUN C, et al. Novel insights into the roles and therapeutic implications of MUC1 oncoprotein via regulating proteins and non-coding RNAs in cancer[J]. Theranostics, 2022, 12(3): 999-1011. |
| 2 | LAKSHMANAN I, PONNUSAMY M P, MACHA M A, et al. Mucins in lung cancer: diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic implications [J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2015, 10(1): 19-27. |
| 3 | REN J, AGATA N, CHEN D, et al. Human MUC1 carcinoma-associated protein confers resistance to genotoxic anticancer agents[J]. Cancer Cell, 2004, 5(2): 163-175. |
| 4 | MORI Y, AKITA K, TANIDA S, et al. MUC1 protein induces urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) by forming a complex with NF-κB p65 transcription factor and binding to the uPA promoter, leading to enhanced invasiveness of cancer cells[J]. J Biol Chem, 2014, 289(51): 35193-35204. |
| 5 | LI Y, PANG Z, DONG X, et al. MUC1 induces M2 type macrophage influx during postpartum mammary gland involution and triggers breast cancer[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 9(3): 3446-3458. |
| 6 | RAJABI H, AHMAD R, JIN C, et al. MUC1-C oncoprotein confers androgen-independent growth of human prostate cancer cells[J]. Prostate, 2012, 72(15): 1659-1668. |
| 7 | JIN W, LIAO X, LV Y, et al. MUC1 induces acquired chemoresistance by upregulating ABCB1 in EGFR-dependent manner[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2017, 8(8): e2980. |
| 8 | LV Y, CANG W, LI Q, et al. Erlotinib overcomes paclitaxel-resistant cancer stem cells by blocking the EGFR-CREB/GRβ-IL-6 axis in MUC1-positive cervical cancer[J]. Oncogenesis, 2019, 8(12): 70. |
| 9 | RAINA D, KOSUGI M, AHMAD R, et al. Dependence on the MUC1-C oncoprotein in non-small cell lung cancer cells[J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2011, 10(5): 806-816. |
| 10 | HUANG L, REN J, CHEN D, et al. MUC1 cytoplasmic domain coactivates Wnt target gene transcription and confers transformation[J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2003, 2(6): 702-706. |
| 11 | HUANG L, CHEN D, LIU D, et al. MUC1 oncoprotein blocks glycogen synthase kinase 3β-mediated phosphorylation and degradation of β-catenin[J]. Cancer Res, 2005, 65(22): 10413-10422. |
| 12 | LI Y, YI H, YAO Y, et al. The cytoplasmic domain of MUC1 induces hyperplasia in the mammary gland and correlates with nuclear accumulation of β-catenin[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(4): e19102. |
| 13 | HUANG L, LIAO X, BECKETT M, et al. MUC1-C oncoprotein interacts directly with ATM and promotes the DNA damage response to ionizing radiation[J]. Genes Cancer, 2010, 1(3): 239-250. |
| 14 | LIAO C, YU L, PANG Z, et al. WWP1 targeting MUC1 for ubiquitin-mediated lysosomal degradation to suppress carcinogenesis[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2021, 6(1): 297. |
| 15 | SZKLARCZYK D, GABLE A L, LYON D, et al. STRING v11: protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2018, 47(D1): D607-D613. |
| 16 | ASTER J C, PEAR W S, BLACKLOW S C. The varied roles of Notch in cancer[J]. Annu Rev Pathol, 2017, 12: 245-275. |
| 17 | WANG Y, ZHAI S, XING J, et al. LncRNA GAS5 promotes abdominal aortic aneurysm formation through regulating the miR-185-5p/ADCY7 axis[J]. Anticancer Drugs, 2022, 33(3): 225-234. |
| 18 | KINKL N, HAGEMAN G S, SAHEL J A, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) and candidate signaling molecule distribution within rat and human retina[J]. Mol Vis, 2002, 8: 149-160. |
| 19 | MARTÍNEZ-REYES I, CHANDEL N S. Mitochondrial TCA cycle metabolites control physiology and disease[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 102. |
| 20 | ROMEO S. ACAT2 as a novel therapeutic target to treat fatty liver disease[J]. J Intern Med, 2022, 292(2): 175-176. |
| 21 | VAMECQ J, ANDREOLETTI P, EL KEBBAJ R, et al. Peroxisomal acyl-CoA oxidase type 1: anti-inflammatory and anti-aging properties with a special emphasis on studies with LPS and argan oil as a model transposable to aging[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2018, 2018: 6986984. |
| 22 | RODIONOV R N, JARZEBSKA N, WEISS N, et al. AGXT2: a promiscuous aminotransferase[J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2014, 35(11): 575-582. |
| 23 | PLAITAKIS A, LATSOUDIS H, SPANAKI C. The human GLUD2 glutamate dehydrogenase and its regulation in health and disease[J]. Neurochem Int, 2011, 59(4): 495-509. |
| 24 | PIAZZA G A, WARD A, CHEN X, et al. PDE5 and PDE10 inhibition activates cGMP/PKG signaling to block Wnt/β-catenin transcription, cancer cell growth, and tumor immunity[J]. Drug Discov Today, 2020, 25(8): 1521-1527. |
| 25 | ZOU T, LIU J, SHE L, et al. A perspective profile of ADCY1 in cAMP signaling with drug-resistance in lung cancer[J]. J Cancer, 2019, 10(27): 6848-6857. |
| 26 | GAO Z, LEI W I, LEE L T O. The role of neuropeptide-stimulated cAMP-EPACs signalling in cancer cells[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(1): 311. |
| 27 | DONG Y, CHEN H, GAO J, et al. Molecular machinery and interplay of apoptosis and autophagy in coronary heart disease[J]. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 2019, 136: 27-41. |
| 28 | MCILWAIN D R, BERGER T, MAK T W. Caspase functions in cell death and disease[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2013, 5(4): a008656. |
| 29 | YUE J, LÓPEZ J M. Understanding MAPK signaling pathways in apoptosis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(7): E2346. |
| 30 | PIWARSKI S A, THOMPSON C, CHAUDHRY A R, et al. The putative endogenous AHR ligand ITE reduces JAG1 and associated NOTCH1 signaling in triple negative breast cancer cells[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2020, 174: 113845. |
| 31 | FUJII W, NISHIMURA T, KANO K, et al. CDK7 and CCNH are components of CDK-activating kinase and are required for meiotic progression of pig oocytes[J]. Biol Reprod, 2011, 85(6): 1124-1132. |
| 32 | DEGREGORI J. The genetics of the E2F family of transcription factors: shared functions and unique roles[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2002, 1602(2): 131-150. |
| 33 | REN J, BHARTI A, RAINA D, et al. MUC1 oncoprotein is targeted to mitochondria by heregulin-induced activation of c-Src and the molecular chaperone HSP90[J]. Oncogene, 2006, 25(1): 20-31. |
| 34 | AHMAD R, ALAM M, RAJABI H, et al. The MUC1-C oncoprotein binds to the BH3 domain of the pro-apoptotic BAX protein and blocks BAX function[J]. J Biol Chem, 2012, 287(25): 20866-20875. |
| 35 | FRUMAN D A, CHIU H, HOPKINS B D, et al. The PI3K pathway in human disease[J]. Cell, 2017, 170(4): 605-635. |
| 36 | CUI C, MERRITT R, FU L, et al. Targeting calcium signaling in cancer therapy[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2017, 7(1): 3-17. |
| 37 | JIN C, RAJABI H, PITRODA S, et al. Cooperative interaction between the MUC1-C oncoprotein and the Rab31 GTPase in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(7): e39432. |
| 38 | RAJABI H, HIRAKI M, TAGDE A, et al. MUC1-C activates EZH2 expression and function in human cancer cells[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 7481. |
| 39 | MA J, RUBIN B K, VOYNOW J A. Mucins, mucus, and goblet cells[J]. Chest, 2018, 154(1): 169-176. |
| 40 | PARK J A, PARK S, CHOI J K, et al. Inhibition of MUC1-C increases ROS and cell death in mouse embryonic stem cells[J]. Int J Stem Cells, 2021, 14(2): 180-190. |
| 41 | HAGIWARA M, YASUMIZU Y, YAMASHITA N, et al. MUC1-C activates the BAF (mSWI/SNF) complex in prostate cancer stem cells[J]. Cancer Res, 2021, 81(4): 1111-1122. |
| 42 | AGATA N, AHMAD R, KAWANO T, et al. MUC1 oncoprotein blocks death receptor-mediated apoptosis by inhibiting recruitment of caspase-8[J]. Cancer Res, 2008, 68(15): 6136-6144. |
| 43 | CHEN Q, LI D, REN J, et al. MUC1 activates JNK1 and inhibits apoptosis under genotoxic stress[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2013, 440(1): 179-183. |
| 44 | SUN C C, ZHOU Q, HU W, et al. Transcriptional E2F1/2/5/8 as potential targets and transcriptional E2F3/6/7 as new biomarkers for the prognosis of human lung carcinoma[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2018, 10(5): 973-987. |
| 45 | TAN P Y, WEN L J, LI H N, et al. miR-548c-3p inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of human breast cancer cell by targeting E2F3[J]. Cytotechnology, 2020, 72(5): 751-761. |
| 46 | TYAGI A, AGARWAL C, AGARWAL R. Inhibition of retinoblastoma protein (Rb) phosphorylation at serine sites and an increase in Rb-E2F complex formation by silibinin in androgen-dependent human prostate carcinoma LNCaP cells: role in prostate cancer prevention[J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2002, 1(7): 525-532. |
| 47 | EVAN G I, VOUSDEN K H. Proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer[J]. Nature, 2001, 411(6835): 342-348. |
| [1] | 木尔扎特·艾麦提, 张业骞, 刘涛, 白龙, 张浩宇, 倪博, 关玉静, 王书昌, 顾佳毅, 朱纯超, 夏翔, 张子臻. 机器人与腹腔镜辅助近端胃切除联合双肌瓣吻合治疗早期胃上部癌的近期效果对比[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(7): 874-882. |
| [2] | 杨娜, 刘俊丽, 白静, 杨思怡, 韩继明, 张华华. HENMT1通过激活PI3K-AKT-mTOR信号通路促进胃癌的增殖与迁移[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(6): 717-726. |
| [3] | 汤开然, 冯成领, 韩邦旻. 基于单细胞测序与转录组测序构建M2巨噬细胞基因相关的前列腺癌预后模型[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(5): 549-561. |
| [4] | 张钲佳, 李小敏, 周鑫, 马海荣, 艾松涛. 高阶磁共振功能成像评估骨与软组织肿瘤价值初探[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(5): 585-596. |
| [5] | 万宏劲, 胡逸斌, 王昕, 张凯, 秦安, 马培翔, 马辉, 赵杰. 甲基莲心碱通过KEAP1/NRF2/GPX4和NF-κB信号通路减轻椎间盘退行性变[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(3): 261-270. |
| [6] | 马秀珍, 周妮, 郭思琪, 王源媛, 麦平. 大麻素受体1通过Gαi/o/RhoA信号通路促进急性肺损伤小鼠巨噬细胞M1极化[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(2): 161-168. |
| [7] | 张博源, 姚志荣. 紫外线诱导的DNA损伤促进皮肤恶性肿瘤发生的研究现状[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(2): 228-232. |
| [8] | 刘佳, 任灵杰, 施敏敏, 唐笑梅, 马芳芳, 秦洁洁. COL12A作为一种新型的胰腺导管腺癌血清诊断标志物的鉴定与评价[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(10): 1342-1352. |
| [9] | PANDIT Roshan, 卢君瑶, 何立珩, 包玉洁, 季萍, 陈颖盈, 许洁, 王颖. 肿瘤坏死因子-α在新型冠状病毒感染合并肾损伤中的作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(1): 1-10. |
| [10] | 木司塔巴·木台力甫, 王俊杰, 钱云臻, 陈溯源, 邵达, 张志刚, 李冬雪. 预免疫策略结合mVenus-p27K-系统构建休眠肿瘤小鼠模型[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(9): 1104-1114. |
| [11] | 何蕊, 颜克鹏, 王静. 靶向髓源性抑制细胞的叶酸循环增强肿瘤免疫治疗效果研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(8): 1011-1022. |
| [12] | 胡飞, 蔡晓涵, 程睿, 季诗雨, 苗嘉欣, 朱晏, 范广建. 骨肉瘤免疫微环境及其免疫治疗临床转化研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(7): 814-821. |
| [13] | 张烨晟, 杨易静, 黄依雯, 施珑玙, 王曼媛, 陈思思. 肿瘤微环境免疫细胞调节肿瘤细胞耐药性的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(7): 830-838. |
| [14] | 李萍, 蒋惠如, 叶梦月, 王雅玉, 陈潇雨, 袁安彩, 徐文杰, 戴慧敏, 陈曦, 闫小响, 涂圣贤, 郑元琦, 张薇, 卜军. 基于上海社区老年人群队列的心血管疾病和恶性肿瘤的危险因素流行特征分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(5): 617-625. |
| [15] | 王梦婷, 陈怡楠, 轩辕欣阳, 袁海花. 肺癌恶性胸腔积液来源肿瘤细胞的小鼠PDX模型构建及实验验证[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(4): 435-443. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||