
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 535-544.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2022.04.017
收稿日期:2021-12-31
接受日期:2022-03-19
出版日期:2022-04-28
发布日期:2022-04-28
通讯作者:
陆舜,电子信箱:shunlu@sjtu.edu.cn。作者简介:陆文清(1998—),女,博士生;电子信箱:lwq817@sjtu.edu.cn基金资助:
LU Wenqing( ), MENG Zhouwenli(
), MENG Zhouwenli( ), YU Yongfeng, LU Shun(
), YU Yongfeng, LU Shun( )
)
Received:2021-12-31
Accepted:2022-03-19
Online:2022-04-28
Published:2022-04-28
Contact:
LU Shun, E-mail: shunlu@sjtu.edu.cn.Supported by:摘要:
表皮生长因子受体(epidermal growth factor receptor,EGFR)基因是非小细胞肺癌最常见的驱动基因。针对EGFR突变的酪氨酸激酶抑制剂(tyrosine kinase inhibitors,TKIs)是EGFR突变患者的一线治疗首选方案。虽然第一、二、三代TKIs已经广泛应用于临床,但无法避免的继发耐药和部分初治患者的原发耐药,仍旧给长线用药带来了巨大挑战。一代以及二代EGFR-TKIs的耐药机制研究较为清楚,包括T790M突变、MET扩增、ERBB2扩增、IGF1R上调、AXL活化等。第三代TKIs可克服前2代最常见的T790M突变,但是随其在临床应用的日益广泛,耐药问题正引起广泛的重视,相关机制和治疗策略目前仍在研究中。机制分为EGFR依赖性和非依赖性2种,包括靶基因突变、旁路信号通路激活、表型转化、表观遗传调控以及免疫抑制微环境等。第四代TKIs、联合治疗以及免疫治疗等都是潜在的耐药后治疗方式。
中图分类号:
陆文清, 孟周文理, 虞永峰, 陆舜. 非小细胞肺癌第三代表皮生长因子受体-酪氨酸激酶抑制剂的耐药机制及治疗策略[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(4): 535-544.
LU Wenqing, MENG Zhouwenli, YU Yongfeng, LU Shun. Resistance mechanisms and overcoming strategies of the third-generation EGFR-TKI in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2022, 42(4): 535-544.
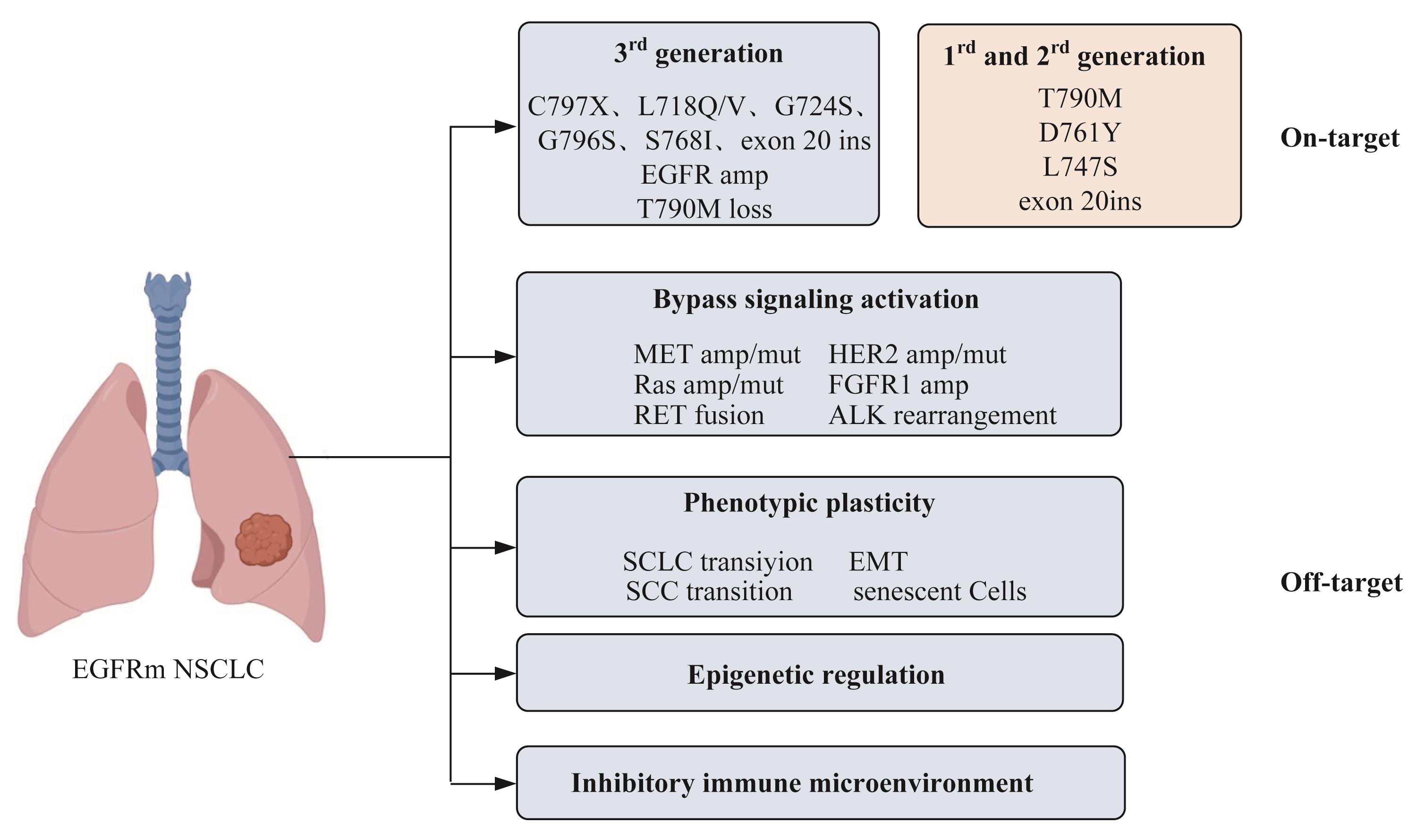
图1 EGFR-TKIs 的耐药机制Note:EGFRm NSCLC—EGFR-mutant NSCLC; ins—insertion; amp—amplification; mut—mutant.
Fig 1 Schematic diagram of resistance mechanisms of EGFR-TKIs
| 1 | SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. |
| 2 | WU L L, KE L P, ZHANG Z S, et al. Development of EGFR TKIs and options to manage resistance of third-generation EGFR TKI osimertinib: conventional ways and immune checkpoint inhibitors[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10: 602762. |
| 3 | YUN C H, MENGWASSER K E, TOMS A V, et al. The T790M mutation in EGFR kinase causes drug resistance by increasing the affinity for ATP[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2008, 105(6): 2070-2075. |
| 4 | BALAK M N, GONG Y X, RIELY G J, et al. Novel D761Y and common secondary T790M mutations in epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant lung adenocarcinomas with acquired resistance to kinase inhibitors[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2006, 12(21): 6494-6501. |
| 5 | COSTA D B, SCHUMER S T, TENEN D G, et al. Differential responses to erlotinib in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutated lung cancers with acquired resistance to gefitinib carrying the L747S or T790M secondary mutations[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2008, 26(7): 1182-1184. |
| 6 | ARCILA M E, NAFA K, CHAFT J E, et al. EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in lung adenocarcinomas: prevalence, molecular heterogeneity, and clinicopathologic characteristics[J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2013, 12(2): 220-229. |
| 7 | YU H A, ARCILA M E, REKHTMAN N, et al. Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2013, 19(8): 2240-2247. |
| 8 | ABOUNADER R, LATERRA J. Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor in brain tumor growth and angiogenesis[J]. Neuro-Oncology, 2005, 7(4): 436-451. |
| 9 | GANDARA D R, LI T H, LARA P N, et al. Acquired resistance to targeted therapies against oncogene-driven non-small-cell lung cancer: approach to subtyping progressive disease and clinical implications[J]. Clin Lung Cancer, 2014, 15(1): 1-6. |
| 10 | SORIA J C, WU Y L, NAKAGAWA K, et al. Gefitinib plus chemotherapy versus placebo plus chemotherapy in EGFR-mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer after progression on first-line gefitinib (IMPRESS): a phase 3 randomised trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2015, 16(8): 990-998. |
| 11 | PARK K, YU C J, KIM S W, et al. First-line erlotinib therapy until and beyond response evaluation criteria in solid tumors progression in Asian patients with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: the ASPIRATION study[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2016, 2(3): 305-312. |
| 12 | YU H A, SIMA C S, HUANG J, et al. Local therapy with continued EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy as a treatment strategy in EGFR-mutant advanced lung cancers that have developed acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2013, 8(3): 346-351. |
| 13 | TAN C S, CHO B C, SOO R A. Treatment options for EGFR mutant NSCLC with CNS involvement-Can patients BLOOM with the use of next generation EGFR TKIs? [J]. Lung Cancer, 2017, 108: 29-37. |
| 14 | CROSS D A E, ASHTON S E, GHIORGHIU S, et al. AZD9291, an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer[J]. Cancer Discov, 2014, 4(9): 1046-1061. |
| 15 | MOK T S, WU Y L, AHN M J, et al. Osimertinib or platinum-pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-positive lung cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017, 376(7): 629-640. |
| 16 | RAMALINGAM S S, VANSTEENKISTE J, PLANCHARD D, et al. Overall survival with osimertinib in untreated, EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC[J]. N Engl J Med, 2020, 382(1): 41-50. |
| 17 | WU Y L, TSUBOI M, HE J, et al. Osimertinib in resected EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2020, 383(18): 1711-1723. |
| 18 | AHN M J, HAN J Y, LEE K H, et al. Lazertinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: results from the dose escalation and dose expansion parts of a first-in-human, open-label, multicentre, phase 1-2 study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2019, 20(12): 1681-1690. |
| 19 | SHI Y K, HU X S, ZHANG S C, et al. Efficacy, safety, and genetic analysis of furmonertinib (AST2818) in patients with EGFR T790M mutated non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase 2b, multicentre, single-arm, open-label study[J]. Lancet Respir Med, 2021, 9(8): 829-839. |
| 20 | SCHOENFELD A J, CHAN J M, RIZVI H, et al. Tissue-based molecular and histological landscape of acquired resistance to osimertinib given initially or at relapse in patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2019, 37(15_suppl): 9028. |
| 21 | WENG C H, CHEN L Y, LIN Y C, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) beyond EGFR mutations per se is a common mechanism for acquired resistance to EGFR TKI[J]. Oncogene, 2019, 38(4): 455-468. |
| 22 | NIEDERST M J, HU H C, MULVEY H E, et al. The allelic context of the C797S mutation acquired upon treatment with third-generation EGFR inhibitors impacts sensitivity to subsequent treatment strategies[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2015, 21(17): 3924-3933. |
| 23 | TANG Z H, LU J J. Osimertinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer: mechanisms and therapeutic strategies[J]. Cancer Lett, 2018, 420: 242-246. |
| 24 | LE X N, PURI S, NEGRAO M V, et al. Landscape of EGFR-dependent and-independent resistance mechanisms to osimertinib and continuation therapy beyond progression in EGFR-mutant NSCLC[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 24(24): 6195-6203. |
| 25 | PELED N, ROISMAN L C, MIRON B, et al. Subclonal therapy by two EGFR TKIs guided by sequential plasma cell-free DNA in EGFR-mutated lung cancer[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2017, 12(7): e81-e84. |
| 26 | STARRETT J H, GUERNET A A, CUOMO M E, et al. Drug sensitivity and allele specificity of first-line osimertinib resistance EGFR mutations[J]. Cancer Res, 2020, 80(10): 2017-2030. |
| 27 | LIN Y T, TSAI T H, WU S G, et al. Complex EGFR mutations with secondary T790M mutation confer shorter osimertinib progression-free survival and overall survival in advanced non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Lung Cancer, 2020, 145: 1-9. |
| 28 | OXNARD G R, HU Y B, MILEHAM K F, et al. Assessment of resistance mechanisms and clinical implications in patients with EGFR T790M-positive lung cancer and acquired resistance to osimertinib[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2018, 4(11): 1527-1534. |
| 29 | LEE J Y, KIM H S, LEE B, et al. Genomic landscape of acquired resistance to third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR T790M-mutant non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Cancer, 2020, 126(11): 2704-2712. |
| 30 | PIOTROWSKA Z, NAGY R, FAIRCLOUGH S, et al. OA 09.01 characterizing the genomic landscape of EGFR C797S in lung cancer using ctDNA next-generation sequencing[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2017, 12(11): S1767. |
| 31 | WANG Z, YANG J J, HUANG J, et al. Lung adenocarcinoma harboring EGFR T790M and in trans C797S responds to combination therapy of first- and third-generation EGFR TKIs and shifts allelic configuration at resistance[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2017, 12(11): 1723-1727. |
| 32 | RAMALINGAM S S, CHENG Y, ZHOU C, et al. Mechanisms of acquired resistance to first-line osimertinib: preliminary data from the phase Ⅲ FLAURA study[J]. Ann Oncol, 2018, 29: viii740. |
| 33 | ENGELMAN J A, ZEJNULLAHU K, MITSUDOMI T, et al. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling[J]. Science, 2007, 316(5827): 1039-1043. |
| 34 | HSU C C, LIAO B C, LIAO W Y, et al. Exon 16-skipping HER2 as a novel mechanism of osimertinib resistance in EGFR L858R/T790M-positive non-small cell lung cancer[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2020, 15(1): 50-61. |
| 35 | HANAHAN D. Hallmarks of cancer: new dimensions[J]. Cancer Discov, 2022, 12(1): 31-46. |
| 36 | QUINTANAL-VILLALONGA Á, CHAN J M, YU H A, et al. Lineage plasticity in cancer: a shared pathway of therapeutic resistance[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2020, 17(6): 360-371. |
| 37 | MARCOUX N, GETTINGER S N, O'KANE G, et al. EGFR-mutant adenocarcinomas that transform to small-cell lung cancer and other neuroendocrine carcinomas: clinical outcomes[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2019, 37(4): 278-285. |
| 38 | QUINTANAL-VILLALONGA A, TANIGUCHI H, ZHAN Y A, et al. Multi-omic analysis of lung tumors defines pathways activated in neuroendocrine transformation[J]. Cancer Discov, 2021, 11(12):3028-3047. |
| 39 | KUO M H, LEE A C, HSIAO S H, et al. Cross-talk between SOX2 and TGFβ signaling regulates EGFR–TKI tolerance and lung cancer dissemination[J]. Cancer Res, 2020, 80(20): 4426-4438. |
| 40 | LOTSBERG M L, WNUK-LIPINSKA K, TERRY S, et al. AXL targeting abrogates autophagic flux and induces immunogenic cell death in drug-resistant cancer cells[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2020, 15(6): 973-999. |
| 41 | NILSSON M B, SUN H Y, ROBICHAUX J, et al. A YAP/FOXM1 axis mediates EMT-associated EGFR inhibitor resistance and increased expression of spindle assembly checkpoint components[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2020, 12(559): eaaz4589. |
| 42 | KURPPA K J, LIU Y, TO C, et al. Treatment-induced tumor dormancy through YAP-mediated transcriptional reprogramming of the apoptotic pathway[J]. Cancer Cell, 2020, 37(1): 104-122.e12. |
| 43 | WANG L H, DONG X Y, REN Y, et al. Targeting EHMT2 reverses EGFR-TKI resistance in NSCLC by epigenetically regulating the PTEN/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9(2): 129. |
| 44 | NAKAGAWA T, TAKEUCHI S, YAMADA T, et al. EGFR-TKI resistance due to BIM polymorphism can be circumvented in combination with HDAC inhibition[J]. Cancer Res, 2013, 73(8): 2428-2434. |
| 45 | PERALTA-ARRIETA I, TREJO-VILLEGAS O A, ARMAS-LÓPEZ L, et al. Failure to EGFR-TKI-based therapy and tumoural progression are promoted by MEOX2/GLI1-mediated epigenetic regulation of EGFR in the human lung cancer[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2022, 160: 189-205. |
| 46 | YANG L, HE Y T, DONG S, et al. Single-cell transcriptome analysis revealed a suppressive tumor immune microenvironment in EGFR mutant lung adenocarcinoma[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2022, 10(2): e003534. |
| 47 | PENG S L, WANG R, ZHANG X J, et al. EGFR-TKI resistance promotes immune escape in lung cancer via increased PD-L1 expression[J]. Mol Cancer, 2019, 18(1): 165. |
| 48 | WU S C, LUO M, TO K K W, et al. Intercellular transfer of exosomal wild type EGFR triggers osimertinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2021, 20(1): 17. |
| 49 | SHAH K N, BHATT R, ROTOW J, et al. Aurora kinase A drives the evolution of resistance to third-generation EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer[J]. Nat Med, 2019, 25(1): 111-118. |
| 50 | WANG S H, SONG Y P, LIU D L. EAI045: the fourth-generation EGFR inhibitor overcoming T790M and C797S resistance[J]. Cancer Lett, 2017, 385: 51-54. |
| 51 | TO C, JANG J, CHEN T, et al. Single and dual targeting of mutant EGFR with an allosteric inhibitor[J]. Cancer Discov, 2019, 9(7): 926-943. |
| 52 | LIU X L, ZHANG X Q, YANG L, et al. Preclinical evaluation of TQB3804, a potent EGFR C797S inhibitor[J]. Cancer Res 2019;79(13). |
| 53 | SEQUIST L V, HAN J Y, AHN M J, et al. Osimertinib plus savolitinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive, MET-amplified, non-small-cell lung cancer after progression on EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors: interim results from a multicentre, open-label, phase 1b study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2020, 21(3): 373-386. |
| 54 | YU H A, GOLDBERG S B, LE X N, et al. Biomarker-directed phase Ⅱ platform study in patients with EGFR sensitizing mutation-positive advanced/metastatic non-small cell lung cancer whose disease has progressed on first-line osimertinib therapy (ORCHARD)[J]. Clin Lung Cancer, 2021, 22(6): 601-606. |
| 55 | WANG Y B, YANG N, ZHANG Y C, et al. Effective treatment of lung adenocarcinoma harboring EGFR-activating mutation, T790M, and Cis-C797S triple mutations by brigatinib and cetuximab combination therapy[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2020, 15(8): 1369-1375. |
| 56 | LA MONICA S, CRETELLA D, BONELLI M, et al. Trastuzumab emtansine delays and overcomes resistance to the third-generation EGFR-TKI osimertinib in NSCLC EGFR mutated cell lines[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2017, 36(1): 174. |
| 57 | LE X N, NILSSON M, GOLDMAN J, et al. Dual EGFR-VEGF pathway inhibition: a promising strategy for patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2021, 16(2): 205-215. |
| 58 | OXNARD G R, YANG J C H, YU H, et al. TATTON: a multi-arm, phase Ⅰb trial of osimertinib combined with selumetinib, savolitinib, or durvalumab in EGFR-mutant lung cancer[J]. Ann Oncol, 2020, 31(4): 507-516. |
| 59 | SOCINSKI M A, JOTTE R M, CAPPUZZO F, et al. Atezolizumab for first-line treatment of metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC[J]. N Engl J Med, 2018, 378(24): 2288-2301. |
| 60 | ZHANG J, ZHOU C, ZHAO Y, et al. MA11.06 A PII study of toripalimab, a PD-1 MAb, in combination with chemotherapy in EGFR+ advanced NSCLC patients failed to prior EGFR TKI therapies[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2019, 14(10): S292. |
| 61 | BURNETT H, EMICH H, CARROLL C, et al. Epidemiological and clinical burden of EGFR Exon 20 insertion in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic literature review[J]. PLoS One, 2021, 16(3): e0247620. |
| 62 | NORONHA V, CHOUGHULE A, PATIL V, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor exon 20 mutation in lung cancer: types, incidence, clinical features and impact on treatment[J]. Oncotargets Ther, 2017, 10: 2903-2908. |
| 63 | VAN VEGGEL B, DE LANGEN A J, HASHEMI S M S, et al. Afatinib and cetuximab in four patients with EGFR exon 20 insertion-positive advanced NSCLC[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2018, 13(8): 1222-1226. |
| 64 | PARK K, JOHN T, KIM S W, et al. Amivantamab (JNJ-61186372), an anti-EGFR-MET bispecific antibody, in patients with EGFR exon 20 insertion (exon20ins)-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2020, 38(15_suppl): 9512. |
| 65 | PARK K, HAURA E B, LEIGHL N B, et al. Amivantamab in EGFR exon 20 insertion-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer progressing on platinum chemotherapy: initial results from the CHRYSALIS phase Ⅰ study[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2021, 39(30): 3391-3402. |
| 66 | CHO B C, LEE K H, CHO E K, et al. 1258O Amivantamab (JNJ-61186372), an EGFR-MET bispecific antibody, in combination with lazertinib, a 3rd-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), in advanced EGFR NSCLC[J]. Ann Oncol, 2020, 31: S813. |
| 67 | LE X N, GOLDMAN J, CLARKE J, et al. Abstract CT081: poziotinib activity and durability of responses in previously treated EGFR exon 20 NSCLC patients: a Phase 2 study[C]//Tumor Biology. American Association for Cancer Research, 2020: 80(16). |
| 68 | GONZALVEZ F, VINCENT S, BAKER T E, et al. Mobocertinib (TAK-788): a targeted inhibitor of EGFR exon 20 insertion mutants in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Cancer Discov, 2021, 11(7): 1672-1687. |
| 69 | FELIP E, BARLESI F, BESSE B, et al. Phase 2 study of the HSP-90 inhibitor AUY922 in previously treated and molecularly defined patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2018, 13(4): 576-584. |
| 70 | PARK H R, KIM T M, LEE Y, et al. Acquired resistance to third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with de novo EGFRT790M-mutant NSCLC[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2021, 16(11): 1859-1871. |
| 71 | ROBICHAUX J P, LE X N, VIJAYAN R S K, et al. Structure-based classification predicts drug response in EGFR-mutant NSCLC[J]. Nature, 2021, 597(7878): 732-737. |
| [1] | 梁效宁, 石亭旺, 陈云丰. 小菌落变异株的致病机制及治疗研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(6): 784-791. |
| [2] | 邹沛辰, 刘鸿宇, 阿衣娜扎尔·艾合买提, 朱亮, 唐亚斌, 雷绘敏. 索托拉西布获得性耐药肺癌细胞的代谢轮廓分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(2): 138-149. |
| [3] | 张先洲, 杜凤麟, 吴雷, 任逸喆, 赵明娜, 娄加陶. OGT通过ERK信号通路促进非小细胞肺癌增殖的机制研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(10): 1288-1297. |
| [4] | 朱鸣阳, 许元元, 任江浩, 黄嘉正, 李若楠, 谭强. 以磨玻璃结节为表现的肺腺癌亚肺叶切除研究综述[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(7): 922-927. |
| [5] | 刘晨茜, 韩林, 杨轶, 周韩, 刘亚云, 盛德乔. GPR87通过激活RHO/ROCK通路促进非小细胞肺癌的侵袭和迁移[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(12): 1514-1525. |
| [6] | 黄华艳, 徐张闻笛, 夏立亮, 虞永峰, 陆舜. 表皮生长因子受体突变型晚期非小细胞肺癌免疫治疗的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(5): 611-618. |
| [7] | 赵卓明, 刘振浩, 鲁曼曼, 张钰, 许林锋, 谢鹭. 基于TCR组库分析流程的非小细胞肺癌特征分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(12): 1520-1528. |
| [8] | 赵富茂, 彭玫, 彭晓露, 舒韦韦, 彭丽. 鲍曼不动杆菌在环境美罗培南浓度变化时耐药性的改变及其机制[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(11): 1396-1407. |
| [9] | 廖雅慧, 刘丽云, 朱泓睿, 林厚文, 严继舟, 孙凡. 海绵来源的smenospongine通过抑制非小细胞肺癌细胞中的EGFR-Akt-ABCG2信号通路抑制顺铂耐药[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(8): 997-1007. |
| [10] | 刘子杨, 王小文, 陈力. lncRNA GK-IT1通过调控醛缩酶A影响非小细胞肺癌细胞的恶性进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(5): 591-601. |
| [11] | 李若楠, 陈小科, 许元元, 谭强. ⅠB~ⅢA期非小细胞肺癌患者术后辅助靶向治疗研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(11): 1612-1619. |
| [12] | 张宇, 吴晓渊, 管丽华, 刘译远, 彭星月, 谢海燕, 胡玮, 郝可可, 夏宁, 陆国军, 侯志波. 高通量药物敏感性筛选系统在非小细胞肺癌伴恶性胸腔积液治疗中的应用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(1): 82-89. |
| [13] | 凌徐心仪, 张瑶, 钟华. 非小细胞肺癌免疫治疗获益人群筛选的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(8): 1114-1119. |
| [14] | 马韵芳, 潘丽娜, 李圳, 高蓓莉, 胡家安, 徐志红. 司美替尼下调KRAS G12V突变型非小细胞肺癌细胞PD-L1水平的探索性研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(6): 741-748. |
| [15] | 徐建华, 江萍, 邓炯. ATP结合盒蛋白G超家族成员2在肺癌中的表达及意义[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(6): 830-833. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||