
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 204-210.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2025.02.009
• 论著 · 公共卫生 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-05-07
接受日期:2024-12-10
出版日期:2025-02-24
发布日期:2025-02-24
通讯作者:
苗雅
E-mail:linyijia2020@126.com;nning-my@163.com
作者简介:林祎嘉(1998—),女,硕士生;电子信箱:linyijia2020@126.com。
基金资助:
LIN Yijia( ), CHENG Lizhen, HU Tingjun, MIAO Ya(
), CHENG Lizhen, HU Tingjun, MIAO Ya( )
)
Received:2024-05-07
Accepted:2024-12-10
Online:2025-02-24
Published:2025-02-24
Contact:
MIAO Ya
E-mail:linyijia2020@126.com;nning-my@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的·采用两样本孟德尔随机化法(Mendelian randomization,MR)探究2型糖尿病(type 2 diabetes mellitus,T2DM)和认知功能障碍之间的因果关系。方法·从大规模全基因组关联研究(genome-wide association study,GWAS)汇总数据集中汇总与T2DM相关的工具变量,采用逆方差加权作为主要分析技术,以MR-Egger回归、加权中位数法和简单中位数法为辅,并联合应用meta分析对不同结局进行合并,分析T2DM与痴呆症、阿尔茨海默病(Alzheimer's disease,AD)和帕金森痴呆之间因果关系的可能性。采用MR-PRESSO整体测试和MR-Egger分析检查水平多效性。结果·遗传预测的T2DM与痴呆症(OR=1.11,95%CI 1.02~1.20,P=1.96×10-2)和AD(OR=1.16,95%CI 1.04~1.30,P=8.41×10-3)之间存在因果关系。meta分析支持T2DM与认知障碍的关联(OR=1.12,95%CI 1.05~1.20,P=4.22×10-4)。一系列敏感性分析提示不存在异质性和水平多效性。反向MR分析结果显示各种类型痴呆对T2DM没有明显的反向因果关系。结论·T2DM与多种痴呆症的患病风险呈正相关,提示T2DM可能是认知障碍的一个重要风险因素。
中图分类号:
林祎嘉, 程丽珍, 胡廷军, 苗雅. 基于孟德尔随机化法的2型糖尿病与认知障碍因果关系研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(2): 204-210.
LIN Yijia, CHENG Lizhen, HU Tingjun, MIAO Ya. Causal relationship between type 2 diabetes mellitus and cognitive impairment based on Mendelian randomization[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(2): 204-210.
| Phenotype | Sample size/n | Cases/n | Controls/n | Diagnostic criteria | Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2DM | 298 957 | 48 298 | 250 671 | Literature[ | European |
| Dementia | 216 771 | 7 284 | 209 487 | ICD-10: F00-F09 | European |
| AD | 218 792 | 3 899 | 214 893 | ICD-10: G30 | European |
| PD | 216 895 | 267 | 216 628 | ICD-10: F02.3 | European |
表1 用于分析的研究和数据集的详细信息
Tab 1 Detailed information of studies and datasets used for analysis
| Phenotype | Sample size/n | Cases/n | Controls/n | Diagnostic criteria | Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2DM | 298 957 | 48 298 | 250 671 | Literature[ | European |
| Dementia | 216 771 | 7 284 | 209 487 | ICD-10: F00-F09 | European |
| AD | 218 792 | 3 899 | 214 893 | ICD-10: G30 | European |
| PD | 216 895 | 267 | 216 628 | ICD-10: F02.3 | European |
| SNP | Beta | SE | P value | R2/% | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs730497 | 0.041 3 | 0.008 4 | 3.07×10-8 | 0.05 | 24.17 |
| rs13133548 | 0.033 4 | 0.006 6 | 5.00×10-8 | 0.06 | 25.61 |
| rs9388489 | 0.034 5 | 0.006 7 | 1.19×10-8 | 0.06 | 26.51 |
| rs10906115 | -0.033 9 | 0.006 3 | 4.96×10-8 | 0.05 | 28.95 |
| rs1077394 | 0.036 9 | 0.006 8 | 3.92×10-8 | 0.06 | 29.45 |
| rs4812831 | 0.058 7 | 0.010 0 | 1.32×10-8 | 0.08 | 34.46 |
| rs16826069 | 0.046 5 | 0.007 9 | 6.97×10-9 | 0.07 | 34.65 |
| rs11063069 | 0.046 9 | 0.007 8 | 3.44×10-10 | 0.07 | 36.15 |
| rs4607103 | -0.041 5 | 0.006 9 | 6.76×10-10 | 0.07 | 36.17 |
| rs55834942 | -0.051 4 | 0.008 5 | 1.35×10-12 | 0.07 | 36.57 |
| rs738409 | 0.044 7 | 0.007 3 | 2.77×10-11 | 0.07 | 37.49 |
| rs4502156 | -0.040 0 | 0.006 5 | 9.55×10-11 | 0.08 | 37.87 |
| rs6905288 | 0.040 1 | 0.006 5 | 5.77×10-11 | 0.08 | 38.06 |
| rs243021 | 0.040 2 | 0.006 5 | 4.60×10-11 | 0.05 | 38.25 |
| rs4457053 | -0.046 6 | 0.007 5 | 3.68×10-13 | 0.08 | 38.61 |
| rs8042680 | 0.042 7 | 0.006 8 | 1.66×10-10 | 0.09 | 39.43 |
| rs10758593 | 0.039 3 | 0.006 2 | 2.56×10-11 | 0.08 | 40.18 |
| rs2796441 | --0.040 0 | 0.006 3 | 4.86×10-11 | 0.08 | 40.31 |
| rs6813195 | -0.046 1 | 0.007 0 | 1.53×10-12 | 0.09 | 43.37 |
| rs731839 | -0.044 3 | 0.006 7 | 7.42×10-13 | 0.09 | 43.72 |
| rs972283 | 0.047 3 | 0.007 0 | 1.51×10-12 | 0.11 | 45.66 |
| rs1558902 | 0.046 1 | 0.006 7 | 2.13×10-10 | 0.10 | 47.34 |
| rs1531343 | 0.067 5 | 0.009 8 | 2.36×10-14 | 0.10 | 47.44 |
| rs35720761 | -0.072 1 | 0.010 4 | 8.31×10-16 | 0.10 | 48.06 |
| rs28265 | -0.088 5 | 0.012 6 | 4.45×10-14 | 0.38 | 49.33 |
| rs10842994 | -0.057 5 | 0.008 1 | 7.60×10-13 | 0.10 | 50.39 |
| rs58542926 | 0.083 6 | 0.011 6 | 3.36×10-15 | 0.10 | 51.94 |
| rs7202877 | -0.072 6 | 0.009 9 | 3.14×10-14 | 0.10 | 53.78 |
| rs7177055 | 0.052 8 | 0.007 2 | 5.65×10-14 | 0.13 | 53.78 |
| rs9379084 | -0.094 6 | 0.012 9 | 1.47×10-17 | 0.18 | 53.78 |
| rs459193 | 0.053 7 | 0.007 2 | 6.71×10-15 | 0.12 | 55.63 |
| rs8108269 | 0.054 3 | 0.007 2 | 5.15×10-16 | 0.13 | 56.88 |
| rs340874 | 0.048 6 | 0.006 3 | 1.41×10-15 | 0.10 | 59.51 |
| rs10244051 | 0.047 9 | 0.006 2 | 7.87×10-18 | 0.11 | 59.69 |
| rs60980157 | -0.061 5 | 0.007 9 | 6.63×10-16 | 0.14 | 60.60 |
| rs1359790 | -0.058 5 | 0.007 3 | 1.34×10-15 | 0.13 | 64.22 |
| rs1801282 | -0.091 6 | 0.011 0 | 2.68×10-19 | 0.17 | 69.34 |
| rs1260326 | 0.054 3 | 0.006 5 | 3.18×10-18 | 0.14 | 69.79 |
| rs516946 | 0.065 2 | 0.007 6 | 9.32×10-20 | 0.15 | 73.60 |
| rs1801212 | 0.063 0 | 0.007 3 | 7.09×10-21 | 0.15 | 74.48 |
| rs2943641 | 0.060 3 | 0.006 9 | 1.43×10-18 | 0.05 | 76.37 |
| rs12571751 | -0.055 9 | 0.006 2 | 3.14×10-22 | 0.16 | 81.29 |
| rs5219 | -0.063 0 | 0.006 5 | 1.52×10-22 | 0.18 | 93.94 |
| rs7501939 | -0.062 2 | 0.006 4 | 2.38×10-24 | 0.18 | 94.45 |
| rs11603334 | -0.088 1 | 0.009 0 | 1.72×10-24 | 0.20 | 95.82 |
| rs13389219 | -0.071 5 | 0.007 0 | 1.32×10-29 | 0.24 | 104.33 |
| rs11708067 | -0.083 9 | 0.007 8 | 9.32×10-31 | 0.23 | 115.70 |
| rs864745 | -0.070 1 | 0.006 5 | 2.87×10-30 | 0.24 | 116.31 |
| rs5015480 | -0.070 9 | 0.006 5 | 1.36×10-30 | 0.25 | 118.98 |
| rs10830963 | 0.082 9 | 0.007 2 | 9.44×10-30 | 0.28 | 132.57 |
| rs2237895 | 0.079 7 | 0.006 6 | 1.83×10-38 | 0.31 | 145.82 |
| rs13266634 | -0.089 7 | 0.006 8 | 1.30×10-47 | 0.34 | 174.01 |
| rs4402960 | 0.091 9 | 0.006 6 | 8.31×10-49 | 0.38 | 193.88 |
| rs10965250 | -0.129 8 | 0.009 3 | 3.71×10-46 | 0.07 | 194.80 |
| rs7756992 | 0.107 3 | 0.006 7 | 1.33×10-61 | 0.09 | 256.48 |
| rs7903146 | 0.241 0 | 0.006 9 | 1.00×10-200 | 0.41 | 1 219.93 |
表2 筛选的SNP工具变量基本信息
Tab 2 Characteristics of instrumental variables for SNP
| SNP | Beta | SE | P value | R2/% | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs730497 | 0.041 3 | 0.008 4 | 3.07×10-8 | 0.05 | 24.17 |
| rs13133548 | 0.033 4 | 0.006 6 | 5.00×10-8 | 0.06 | 25.61 |
| rs9388489 | 0.034 5 | 0.006 7 | 1.19×10-8 | 0.06 | 26.51 |
| rs10906115 | -0.033 9 | 0.006 3 | 4.96×10-8 | 0.05 | 28.95 |
| rs1077394 | 0.036 9 | 0.006 8 | 3.92×10-8 | 0.06 | 29.45 |
| rs4812831 | 0.058 7 | 0.010 0 | 1.32×10-8 | 0.08 | 34.46 |
| rs16826069 | 0.046 5 | 0.007 9 | 6.97×10-9 | 0.07 | 34.65 |
| rs11063069 | 0.046 9 | 0.007 8 | 3.44×10-10 | 0.07 | 36.15 |
| rs4607103 | -0.041 5 | 0.006 9 | 6.76×10-10 | 0.07 | 36.17 |
| rs55834942 | -0.051 4 | 0.008 5 | 1.35×10-12 | 0.07 | 36.57 |
| rs738409 | 0.044 7 | 0.007 3 | 2.77×10-11 | 0.07 | 37.49 |
| rs4502156 | -0.040 0 | 0.006 5 | 9.55×10-11 | 0.08 | 37.87 |
| rs6905288 | 0.040 1 | 0.006 5 | 5.77×10-11 | 0.08 | 38.06 |
| rs243021 | 0.040 2 | 0.006 5 | 4.60×10-11 | 0.05 | 38.25 |
| rs4457053 | -0.046 6 | 0.007 5 | 3.68×10-13 | 0.08 | 38.61 |
| rs8042680 | 0.042 7 | 0.006 8 | 1.66×10-10 | 0.09 | 39.43 |
| rs10758593 | 0.039 3 | 0.006 2 | 2.56×10-11 | 0.08 | 40.18 |
| rs2796441 | --0.040 0 | 0.006 3 | 4.86×10-11 | 0.08 | 40.31 |
| rs6813195 | -0.046 1 | 0.007 0 | 1.53×10-12 | 0.09 | 43.37 |
| rs731839 | -0.044 3 | 0.006 7 | 7.42×10-13 | 0.09 | 43.72 |
| rs972283 | 0.047 3 | 0.007 0 | 1.51×10-12 | 0.11 | 45.66 |
| rs1558902 | 0.046 1 | 0.006 7 | 2.13×10-10 | 0.10 | 47.34 |
| rs1531343 | 0.067 5 | 0.009 8 | 2.36×10-14 | 0.10 | 47.44 |
| rs35720761 | -0.072 1 | 0.010 4 | 8.31×10-16 | 0.10 | 48.06 |
| rs28265 | -0.088 5 | 0.012 6 | 4.45×10-14 | 0.38 | 49.33 |
| rs10842994 | -0.057 5 | 0.008 1 | 7.60×10-13 | 0.10 | 50.39 |
| rs58542926 | 0.083 6 | 0.011 6 | 3.36×10-15 | 0.10 | 51.94 |
| rs7202877 | -0.072 6 | 0.009 9 | 3.14×10-14 | 0.10 | 53.78 |
| rs7177055 | 0.052 8 | 0.007 2 | 5.65×10-14 | 0.13 | 53.78 |
| rs9379084 | -0.094 6 | 0.012 9 | 1.47×10-17 | 0.18 | 53.78 |
| rs459193 | 0.053 7 | 0.007 2 | 6.71×10-15 | 0.12 | 55.63 |
| rs8108269 | 0.054 3 | 0.007 2 | 5.15×10-16 | 0.13 | 56.88 |
| rs340874 | 0.048 6 | 0.006 3 | 1.41×10-15 | 0.10 | 59.51 |
| rs10244051 | 0.047 9 | 0.006 2 | 7.87×10-18 | 0.11 | 59.69 |
| rs60980157 | -0.061 5 | 0.007 9 | 6.63×10-16 | 0.14 | 60.60 |
| rs1359790 | -0.058 5 | 0.007 3 | 1.34×10-15 | 0.13 | 64.22 |
| rs1801282 | -0.091 6 | 0.011 0 | 2.68×10-19 | 0.17 | 69.34 |
| rs1260326 | 0.054 3 | 0.006 5 | 3.18×10-18 | 0.14 | 69.79 |
| rs516946 | 0.065 2 | 0.007 6 | 9.32×10-20 | 0.15 | 73.60 |
| rs1801212 | 0.063 0 | 0.007 3 | 7.09×10-21 | 0.15 | 74.48 |
| rs2943641 | 0.060 3 | 0.006 9 | 1.43×10-18 | 0.05 | 76.37 |
| rs12571751 | -0.055 9 | 0.006 2 | 3.14×10-22 | 0.16 | 81.29 |
| rs5219 | -0.063 0 | 0.006 5 | 1.52×10-22 | 0.18 | 93.94 |
| rs7501939 | -0.062 2 | 0.006 4 | 2.38×10-24 | 0.18 | 94.45 |
| rs11603334 | -0.088 1 | 0.009 0 | 1.72×10-24 | 0.20 | 95.82 |
| rs13389219 | -0.071 5 | 0.007 0 | 1.32×10-29 | 0.24 | 104.33 |
| rs11708067 | -0.083 9 | 0.007 8 | 9.32×10-31 | 0.23 | 115.70 |
| rs864745 | -0.070 1 | 0.006 5 | 2.87×10-30 | 0.24 | 116.31 |
| rs5015480 | -0.070 9 | 0.006 5 | 1.36×10-30 | 0.25 | 118.98 |
| rs10830963 | 0.082 9 | 0.007 2 | 9.44×10-30 | 0.28 | 132.57 |
| rs2237895 | 0.079 7 | 0.006 6 | 1.83×10-38 | 0.31 | 145.82 |
| rs13266634 | -0.089 7 | 0.006 8 | 1.30×10-47 | 0.34 | 174.01 |
| rs4402960 | 0.091 9 | 0.006 6 | 8.31×10-49 | 0.38 | 193.88 |
| rs10965250 | -0.129 8 | 0.009 3 | 3.71×10-46 | 0.07 | 194.80 |
| rs7756992 | 0.107 3 | 0.006 7 | 1.33×10-61 | 0.09 | 256.48 |
| rs7903146 | 0.241 0 | 0.006 9 | 1.00×10-200 | 0.41 | 1 219.93 |
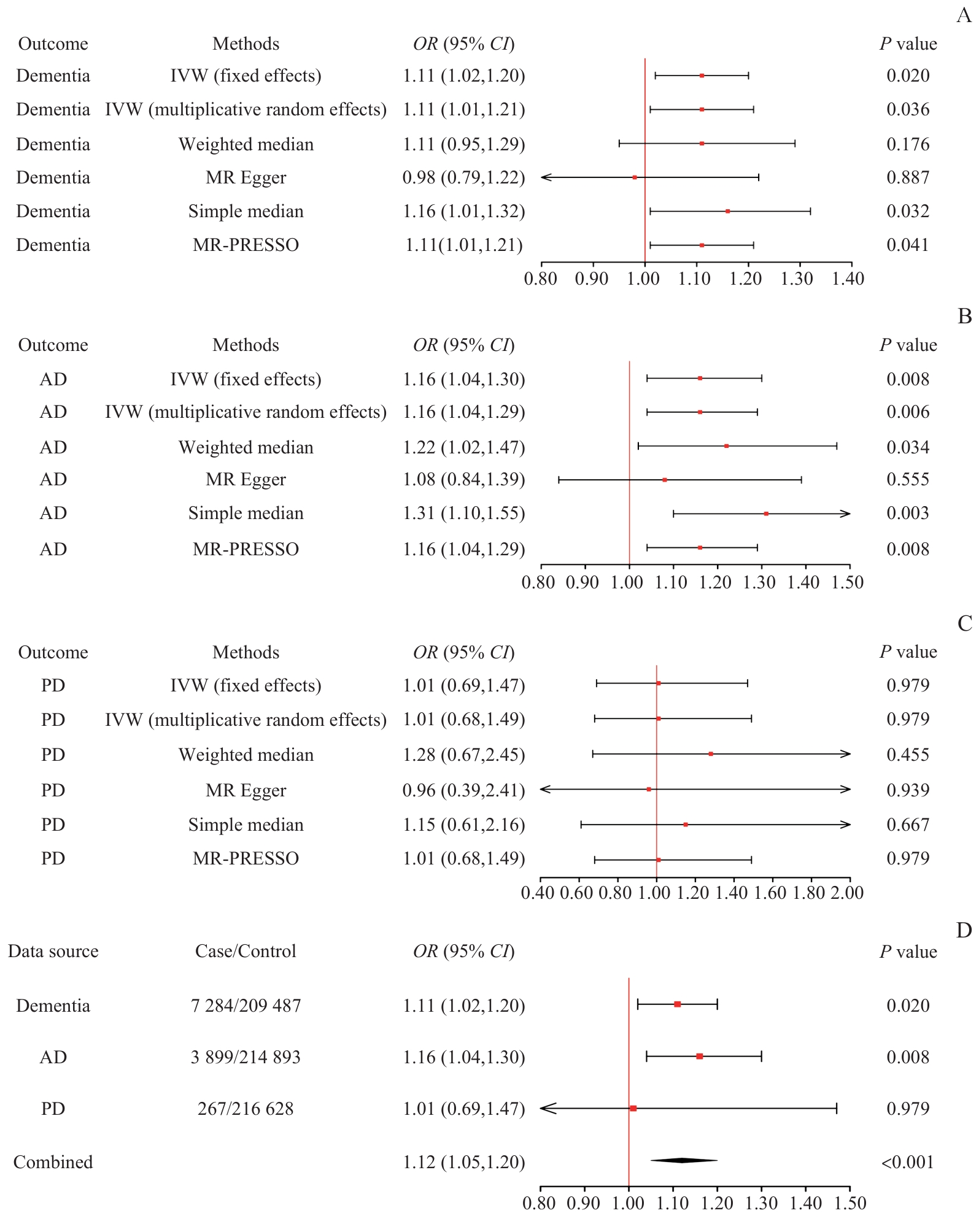
图1 遗传预测的T2DM对多种痴呆症影响的孟德尔随机化森林图分析Note: A. Forest plot showing the relationship between T2DM and all-cause dementia. B. Forest plot showing the relationship between T2DM and AD. C. Forest plot showing the relationship between T2DM and PD dementia. D. Forest plot of the meta-analysis examining T2DM and different types of dementia.
Fig 1 Mendelian randomization forest plot analysis of the genetically predicted effects of T2DM on multiple types of dementia
| Outcome | Heterogeneity | Pleiotropy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IVW Cochran's Q P value | MR-Egger Cochran's Q P value | MR-Egger intercept P value | MR-PRESSO global test P value | |
| Dementia | 0.115 | 0.125 | 0.247 | 0.136 |
| AD | 0.656 | 0.633 | 0.548 | 0.639 |
| PD | 0.382 | 0.346 | 0.922 | 0.368 |
表3 不同方法对异质性和多效性的评估
Tab 3 Evaluation of heterogeneity and directional pleiotropy using different methods
| Outcome | Heterogeneity | Pleiotropy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IVW Cochran's Q P value | MR-Egger Cochran's Q P value | MR-Egger intercept P value | MR-PRESSO global test P value | |
| Dementia | 0.115 | 0.125 | 0.247 | 0.136 |
| AD | 0.656 | 0.633 | 0.548 | 0.639 |
| PD | 0.382 | 0.346 | 0.922 | 0.368 |
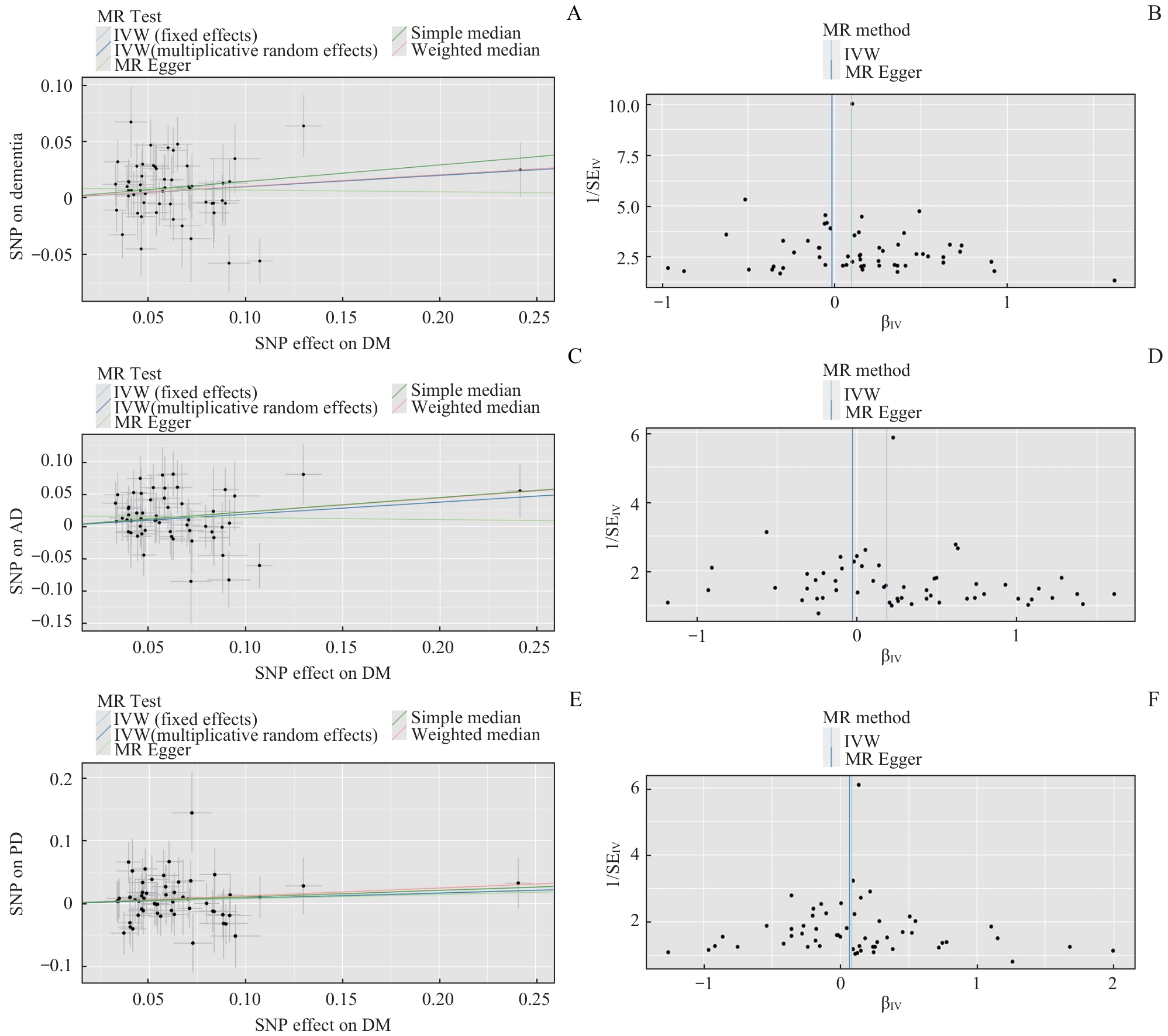
图2 孟德尔随机化散点图和漏斗图Note: A. Scatterplot of T2DM for all-cause dementia. B. Funnel plot of T2DM for all-cause dementia. C. Scatterplot of T2DM for AD. D. Funnel plot of T2DM for AD. E. Scatterplot of T2DM for PD dementia. F. Funnel plot of T2DM for PD dementia.
Fig 2 Scatterplot and funnel plot of Mendelian randomization
| 1 | DAMANIK J, YUNIR E. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and cognitive impairment[J]. Acta Med Indones, 2021, 53(2): 213-220. |
| 2 | BURILLO J, MARQUÉS P, JIMÉNEZ B, et al. Insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(5): 1236. |
| 3 | GUDALA K, BANSAL D, SCHIFANO F, et al. Diabetes mellitus and risk of dementia: a meta-analysis of prospective observational studies[J]. J Diabetes Investig, 2013, 4(6): 640-650. |
| 4 | THOMASSEN J Q, TOLSTRUP J S, BENN M, et al. Type-2 diabetes and risk of dementia: observational and Mendelian randomisation studies in 1 million individuals[J]. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci, 2020, 29: e118. |
| 5 | BENN M, NORDESTGAARD B G, TYBJÆRG-HANSEN A, et al. Impact of glucose on risk of dementia: Mendelian randomisation studies in 115, 875 individuals[J]. Diabetologia, 2020, 63(6): 1151-1161. |
| 6 | CHOHAN H, SENKEVICH K, PATEL R K, et al. Type 2 diabetes as a determinant of Parkinson's disease risk and progression[J]. Mov Disord, 2021, 36(6): 1420-1429. |
| 7 | Emdin C A, Khera A V, Kathiresan S. Mendelian randomization[J]. Jama, 2017, 318(19): 1925-1926. |
| 8 | LAWLOR D A, HARBORD R M, STERNE J A, et al. Mendelian randomization: using genes as instruments for making causal inferences in epidemiology[J]. Stat Med, 2008, 27(8): 1133-1163. |
| 9 | BURGESS S, BUTTERWORTH A, THOMPSON S G. Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data[J]. Genet Epidemiol, 2013, 37(7): 658-665. |
| 10 | DAVEY SMITH G, HEMANI G. Mendelian randomization: genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2014, 23(r1): R89-R98. |
| 11 | BURGESS S, SCOTT R A, TIMPSON N J, et al. Using published data in Mendelian randomization: a blueprint for efficient identification of causal risk factors[J]. Eur J Epidemiol, 2015, 30(7): 543-552. |
| 12 | MAHAJAN A, WESSEL J, WILLEMS S M, et al. Refining the accuracy of validated target identification through coding variant fine-mapping in type 2 diabetes[J]. Nat Genet, 2018, 50: 559-571. |
| 13 | KAMAT M A, BLACKSHAW J A, YOUNG R, et al. PhenoScanner V2: an expanded tool for searching human genotype-phenotype associations[J]. Bioinformatics, 2019, 35(22): 4851-4853. |
| 14 | LÖVDÉN M, FRATIGLIONI L, GLYMOUR M M, et al. Education and cognitive functioning across the life span[J]. Psychol Sci Public Interest, 2020, 21(1): 6-41. |
| 15 | RAMOS-LOYO J, GONZÁLEZ-GARRIDO A A, LLAMAS-ALONSO L A, et al. Sex differences in cognitive processing: an integrative review of electrophysiological findings[J]. Biol Psychol, 2022, 172: 108370. |
| 16 | SHIM H, CHASMAN D I, SMITH J D, et al. A multivariate genome-wide association analysis of 10 LDL subfractions, and their response to statin treatment, in 1868 Caucasians[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(4): e0120758. |
| 17 | BURGESS S, THOMPSON S G. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method[J]. Eur J Epidemiol, 2017, 32(5): 377-389. |
| 18 | BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, HAYCOCK P C, et al. Consistent estimation in Mendelian randomization with some invalid instruments using a weighted Median estimator[J]. Genet Epidemiol, 2016, 40(4): 304-314. |
| 19 | YUAN H, YANG W. Genetically determined serum uric acid and Alzheimer's disease risk[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2018, 65(4): 1259-1265. |
| 20 | VERBANCK M, CHEN C Y, NEALE B, et al. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases[J]. Nat Genet, 2018, 50: 693-698. |
| 21 | GRECO M F D, MINELLI C, SHEEHAN N A, et al. Detecting pleiotropy in Mendelian randomisation studies with summary data and a continuous outcome[J]. Stat Med, 2015, 34(21): 2926-2940. |
| 22 | BOWDEN J, DEL GRECO M F, MINELLI C, et al. A framework for the investigation of pleiotropy in two-sample summary data Mendelian randomization[J]. Stat Med, 2017, 36(11): 1783-1802. |
| 23 | HEMANI G, TILLING K, DAVEY SMITH G. Orienting the causal relationship between imprecisely measured traits using GWAS summary data[J]. PLoS Genet, 2017, 13(11): e1007081. |
| 24 | BRION M J, SHAKHBAZOV K, VISSCHER P M. Calculating statistical power in Mendelian randomization studies[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2013, 42(5): 1497-1501. |
| 25 | HEMANI G, ZHENG J, ELSWORTH B, et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome[J]. Elife, 2018, 7: e34408. |
| 26 | YAVORSKA O O, BURGESS S. MendelianRandomization: an R package for performing Mendelian randomization analyses using summarized data[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2017, 46(6): 1734-1739. |
| 27 | XUE M, XU W, OU Y N, et al. Diabetes mellitus and risks of cognitive impairment and dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 144 prospective studies[J]. Ageing Res Rev, 2019, 55: 100944. |
| 28 | LAI H T M, CHANG K, SHARABIANI M T A, et al. Twenty-year trajectories of cardio-metabolic factors among people with type 2 diabetes by dementia status in England: a retrospective cohort study[J]. Eur J Epidemiol, 2023, 38(7): 733-744. |
| 29 | DAO L, CHOI S, FREEBY M. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and cognitive function: understanding the connections[J]. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes, 2023, 30(1): 7-13. |
| 30 | LUO A, XIE Z, WANG Y, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus-associated cognitive dysfunction: advances in potential mechanisms and therapies[J]. Neurosci Biobehav Rev, 2022, 137: 104642. |
| 31 | ABI SALEH R, LIRETTE S T, BENJAMIN E J, et al. Mediation effects of diabetes and inflammation on the relationship of obesity to cognitive impairment in African Americans[J]. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2022, 70(10): 3021-3029. |
| 32 | XU W L, QIU C X, WAHLIN A, et al. Diabetes mellitus and risk of dementia in the Kungsholmen Project: a 6-year follow-up study[J]. Neurology, 2004, 63(7): 1181-1186. |
| 33 | GOEDERT M. NEURODEGENERATION. Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases: the prion concept in relation to assembled Aβ, tau, and α-synuclein[J]. Science, 2015, 349(6248): 1255555. |
| [1] | 陆佳萍, 刘醒, 张林杉, 赵琳, 张敏, 李小英, 刘玥隽. 腹部脂肪面积与2型糖尿病患者胰岛β细胞第一时相分泌功能的关系[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(1): 42-50. |
| [2] | 刘美志, 王子杨, 姜雅宁, 弥萌, 孙永宁. 番泻苷A对2型糖尿病小鼠动脉粥样硬化斑块形成及5-羟色胺信号分子表达的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(8): 991-998. |
| [3] | 杜亚格, 卢言慧, 安宇, 宋颖, 郑婕. 肠道菌群在糖尿病认知功能障碍中的作用机制及靶向干预的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(4): 494-500. |
| [4] | 张新燕, 李涵, 冉慧, 苏青, 张洪梅. 2型糖尿病患者血清SUMO1水平与高甘油三酯血症相关性研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(10): 1266-1272. |
| [5] | 吴凌恒, 陈建雄, 张梦娇, 沙蕾, 曹萌萌, 沈崔琴, 杜联芳, 李朝军. 血糖控制不理想对2型糖尿病患者亚临床心肌收缩功能的影响研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(8): 1024-1031. |
| [6] | 高雄, 张秋霞, 杨苗苗, 罗玮, 王月刚, 修建成. 房颤与认知障碍的因果关系:一项孟德尔随机化研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(11): 1359-1365. |
| [7] | 张蓉, 陆丽, 王亚昕, 董文倩, 张宇, 周健. 糖尿病患者血糖波动异常与认知功能障碍关系的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(2): 235-240. |
| [8] | 张静静, 祝超瑜, 肖元元, 蒋伏松, 高清歌, 方云云, 魏丽. 胰高血糖素样肽1受体基因rs3765467变异与2型糖尿病的关联研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(9): 1215-1221. |
| [9] | 张佳思, 邹春波, 卢宇, 陈茜, 张伟亚, 何姣姣. 血脂蛋白磷脂酶A2和中性粒细胞明胶酶相关脂质运载蛋白在诊断早期糖尿病肾病中的价值[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(6): 770-775. |
| [10] | 孙敏, 张冬颖. 钠-葡萄糖共转运蛋白2抑制剂对2型糖尿病患者心血管保护作用的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(3): 391-395. |
| [11] | 丁远森, 王枫, 孙家悦, 邵正威, 邹德荣, 陆家瑜. 不同年龄2型糖尿病患者牙周健康流行病学调查[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(2): 217-222. |
| [12] | 罗 钢,崔永晨,曹 越,张俊峰. 手术创伤对2型糖尿病小鼠术后认知功能和脑葡萄糖代谢的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(11): 1468-1472. |
| [13] | 贾芷莹 1, 2,董旻晔 1, 2,施贞夙 2, 3,金春林 4,李国红 1, 2. 基于机器学习的轻度认知功能障碍筛查研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2019, 39(8): 908-. |
| [14] | 王婷婷 1, 2,李明杰 1,林宁 1,钮忆欣 1,简蔚霞 1,苏青 1. 血清高尿酸水平与住院糖尿病患者白蛋白尿短期进展的关系研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2019, 39(7): 754-. |
| [15] | 高玮 1,王雪姣 2,甄琴 2,丁晓颖 2,徐浣白 2,王育璠 2,彭永德 2. 2型糖尿病患者心率变异性降低的危险因素分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2019, 39(6): 629-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 214
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 174
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||