
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 422-432.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2022.04.004
收稿日期:2021-12-01
接受日期:2022-03-16
出版日期:2022-04-28
发布日期:2022-04-28
通讯作者:
余昕烊,电子信箱:yu_xinyoung@163.com。作者简介:吴侠霏(1997—),女,硕士生;电子信箱:cq_wxf@163.com。
基金资助:
WU Xiafei1( ), FANG Jie1, QI Hongbo1,2, YU Xinyang1(
), FANG Jie1, QI Hongbo1,2, YU Xinyang1( )
)
Received:2021-12-01
Accepted:2022-03-16
Online:2022-04-28
Published:2022-04-28
Contact:
YU Xinyang,E-mail: yu_xinyoung@163.com.Supported by:摘要:
目的·探究妊娠期糖尿病(gestational diabetes mellitus,GDM)对C57BL/6J子代成年鼠神经精神功能的影响。方法·将8周龄C57BL/6J小鼠随机分为GDM组和对照组,采用高脂饮食(high fat diet,HFD)诱导GDM模型,通过检测孕鼠空腹血糖、口服糖耐量实验(oral glucose tolerance test,OGTT)及胰岛素耐量实验(insulin tolerance test,ITT)指标验证模型是否诱导成功。子代正常饮食喂养至18周,进行开放旷场实验(open field test,OFT)、高架十字迷宫实验(elevated plus maze test,EPMT)、高架零迷宫实验(elevated zero maze test,EZMT)、强迫游泳实验(forced swimming test,FST)、悬尾实验(tail suspension test,TST)、糖水偏好实验(sucrose preference test,SPT)检测子代情绪行为。收集小鼠海马组织进行组织学验证。利用苏木精-伊红(hematoxylin-eosin,H-E)染色、镀银染色明确GDM组子代海马组织结构形态,免疫荧光染色检测神经元及星形胶质细胞标志阳性的细胞数量。利用实时定量PCR(real time quantitative PCR,RT-qPCR)检测海马区域多巴胺(dopamine,DA)、5-羟色胺(5-hydroxytryptamine,5-HT)、脑源性神经因子(brain-derived neural factor,BDNF)及cAMP反应元件结合蛋白(cAMP response element-binding protein,CREB)相关基因(Drd1、Htr2a、Bdnf、Creb1)的表达。多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,2组间差异采用独立样本t检验进行分析。结果·HFD诱导的C57BL/6J小鼠GDM模型表现为OGTT各时间点血糖值、曲线下面积(area under curve,AUC)明显升高,胰岛素耐量明显降低,证实GDM模型成功建立。子代OFT、EPMT、EZMT结果显示GDM组与对照组差异无统计学意义;FST、TST及SPT结果显示GDM组不动时间明显上升、糖水偏好百分比明显降低,且F1代雌性小鼠差异更为显著(P=0.000)。RT-qPCR结果显示,与对照组相比,GDM组Drd1、Htr2a、Bdnf表达量下降。H-E及镀银染色结果分析发现,GDM组海马组织结构没有明显变化,但免疫荧光结果提示GDM组神经元、星形胶质细胞数目下降。结论·GDM与C57BL/6J子代成年鼠神经精神障碍相关,其主要表现为子代成年期抑郁症倾向,不表现为焦虑症倾向。
中图分类号:
吴侠霏, 方婕, 漆洪波, 余昕烊. 妊娠期糖尿病对C57BL/6J子代成年鼠神经精神功能的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(4): 422-432.
WU Xiafei, FANG Jie, QI Hongbo, YU Xinyang. Neuropsychiatric effects of gestational diabetes mellitus in adult offspring in C57BL/6J mice[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2022, 42(4): 422-432.
| Gene | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | CACTGTCGAGTCGCGTCC | TCATCCATGGCGAACTGGTG |
| Drd1 | AGGTTGAGCAGGACATACGC | TTGCTTCTGGGCAATCCTGT |
| Htr2a | CTGATTCCTCTCTGTGCGCT | TCCAGCACGGTTGAAGTCTG |
| Bdnf | TAAACGTCCACGGACAAGGC | TCGTCAGACCTCTCGAACCT |
| Creb1 | GAAGAGACTTCTGCCCTCCG | GAAGAGACTTCTGCCCTCCC |
表1 RT-qPCR引物(5′→3′)
Tab 1 Primer sequence for RT-qPCR(5′→3′)
| Gene | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | CACTGTCGAGTCGCGTCC | TCATCCATGGCGAACTGGTG |
| Drd1 | AGGTTGAGCAGGACATACGC | TTGCTTCTGGGCAATCCTGT |
| Htr2a | CTGATTCCTCTCTGTGCGCT | TCCAGCACGGTTGAAGTCTG |
| Bdnf | TAAACGTCCACGGACAAGGC | TCGTCAGACCTCTCGAACCT |
| Creb1 | GAAGAGACTTCTGCCCTCCG | GAAGAGACTTCTGCCCTCCC |
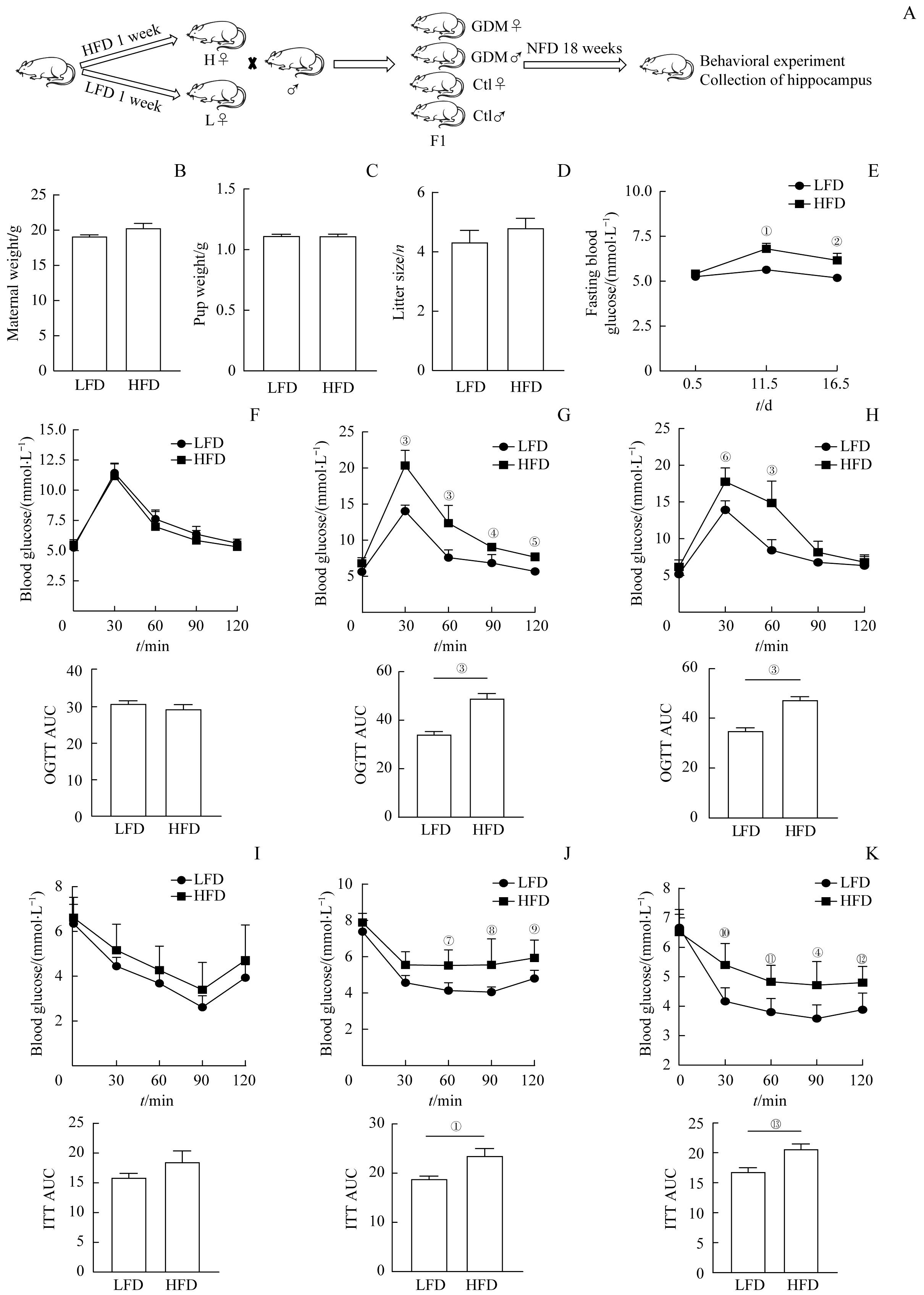
图1 高脂饮食诱导GDM模型Note: A. Experimental flow graph. B?D. E0.5d maternal weight (B), pup weight (C) and litter size (D) in the high-fat diet (HFD) and low-fat diet (LFD) feeding groups. E. Fasting blood glucose levels at 0.5, 11.5, and 16.5 days of gestation between groups. F?H. Comparison of blood glucose at each time point of OGTT and AUC between the HFD group and the LFD group at E0.5d (F), E11.5d (G), and E16.5d (H). I?K. Comparison of blood glucose at each time point of ITT and AUC between the HFD group and the LFD group at E0.5d (I), E11.5d (J), and E16.5d(K). n=6. ①P=0.015, ②P=0.042, ③P=0.000, ④P=0.004, ⑤P=0.009, ⑥P=0.000, ⑦P=0.007, ⑧P=0.003,⑨P=0.033, ⑩P=0.002, ?P=0.010, ?P=0.026, ?P=0.006, vs the LFD group.
Fig 1 High fat diet induced GDM model
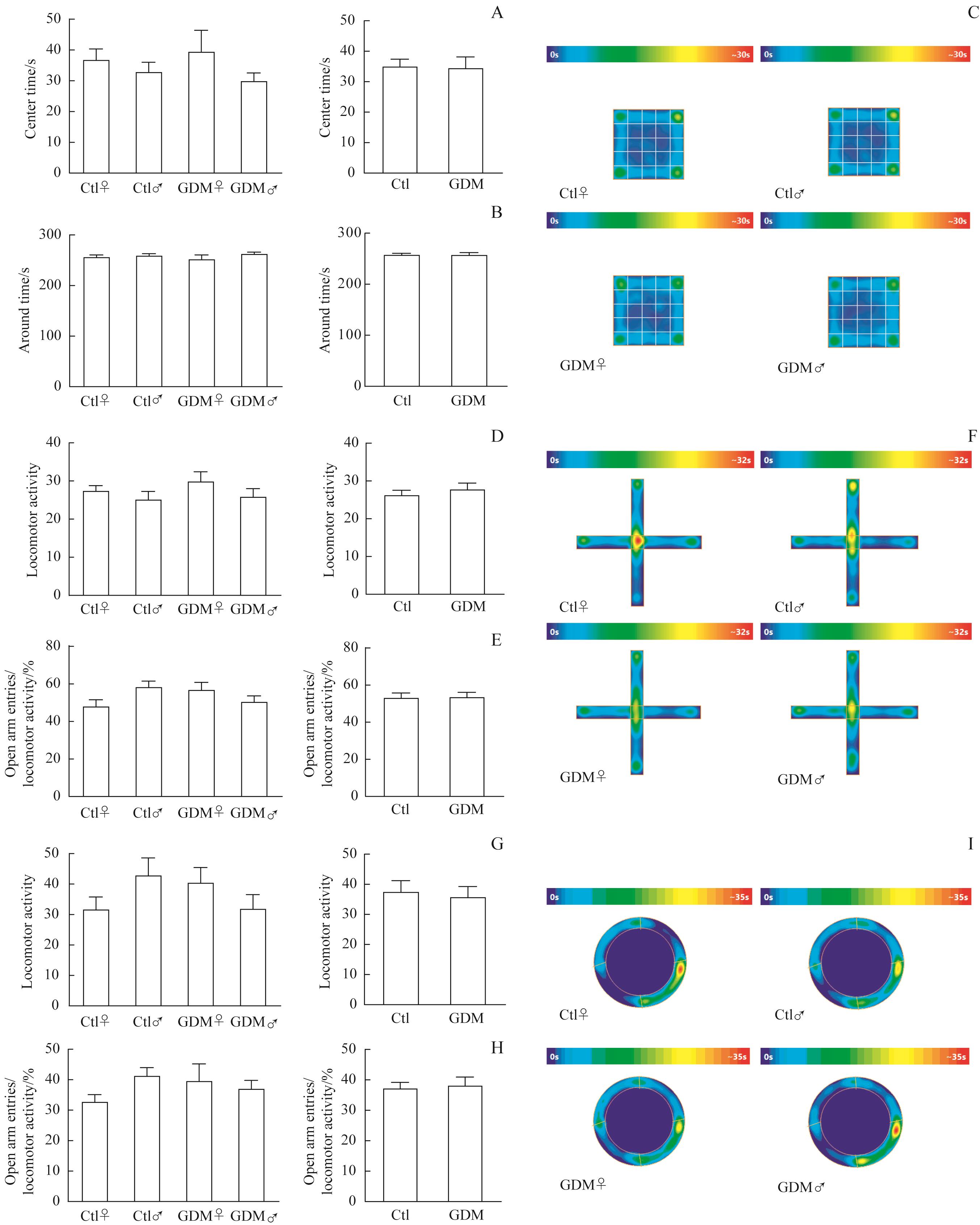
图2 GDM与成年子代鼠焦虑症无关Note: A?C. Open field test. The number of offspring entering the central region (A) and surrounding region (B) in the GDM and control groups (Ctl♀, n=12; Ctl♂, n=12; GDM♀, n=11; GDM♂, n=12). Thermal images of each group (C). D?F. The elevated plus maze test. The locomotor activity (D) and proportion of offspring mice entering open arms (E) in the GDM and control groups (Ctl♀, n=11; Ctl♂, n=11; GDM♀, n=10; GDM♂, n=11). Thermal images of each group (F). G?I. The elevated zero maze test. The locomotor activity (G) and proportion of offspring mice entering open arms (H) in the GDM and control groups (Ctl♀, n=11; Ctl♂, n=12; GDM♀, n=10; GDM♂, n=12). Thermal images of each group (I).
Fig 2 GDM not associated with anxiety disorders in adult offspring mice
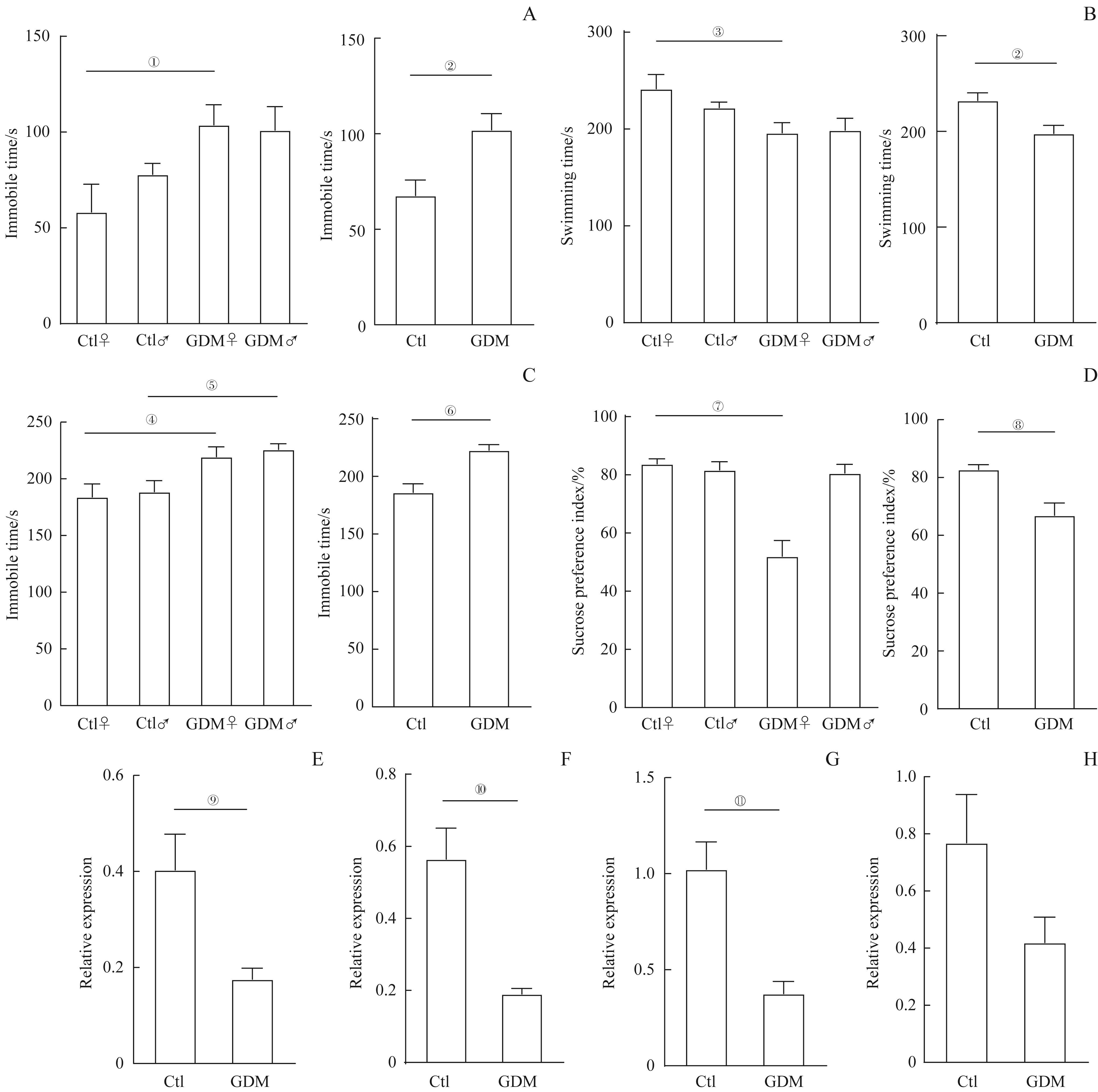
图3 GDM与成年子代鼠抑郁症相关Note: A/B. Forced swimming test. Comparison of immobility time (A) and swimming time (B) of offspring mice in the GDM and control groups (Ctl♀, n=12; Ctl♂, n=11; GDM♀, n=7; GDM♂, n=12). C. Tail suspension test. Comparison of immobility time of offspring mice in the GDM and control groups (Ctl♀, n=11; Ctl♂, n=9; GDM♀, n=10; GDM♂, n=11). D. Sucrose preference test. Comparison of preference of 1% sucrose of offspring mice in the GDM and control groups (Ctl♀, n=12; Ctl♂, n=12; GDM♀, n=11; GDM♂, n=12). E?H. The relative expression of Drd1 (E), Htr2α(F), Bdnf(G), and Creb1(H) in the hippocampi of offspring female mice in the two groups (n=6). ①P=0.043, ②P=0.006, ③P=0.031, ④P=0.048, ⑤P=0.041, ⑥P=0.000, ⑦P=0.000, ⑧P=0.001,⑨P=0.020,⑩P=0.002,?P=0.003, vs the control group.
Fig 3 GDM associated with depression disorders of adult offspring mice
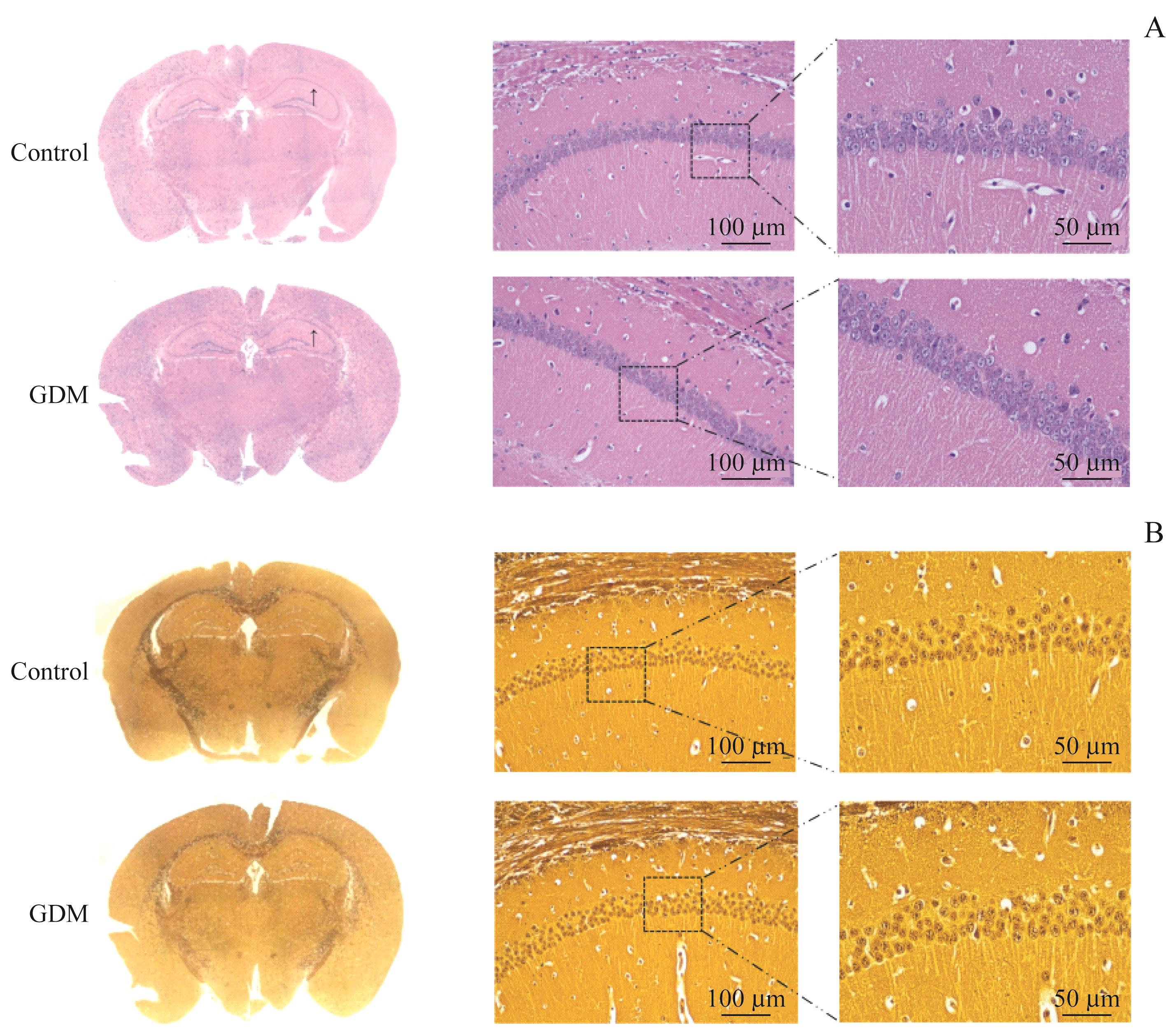
图4 GDM不改变子代小鼠海马组织结构Note: A/B. Images of murine hippocampus tissues stained with H-E staining (A) and silver staining (B) (scale bar=100 μm, 50 μm, respectively). The arrows indicating the enlarged areas in the right pictures.
Fig 4 GDM not affecting the hippocampal structure of offspring mice
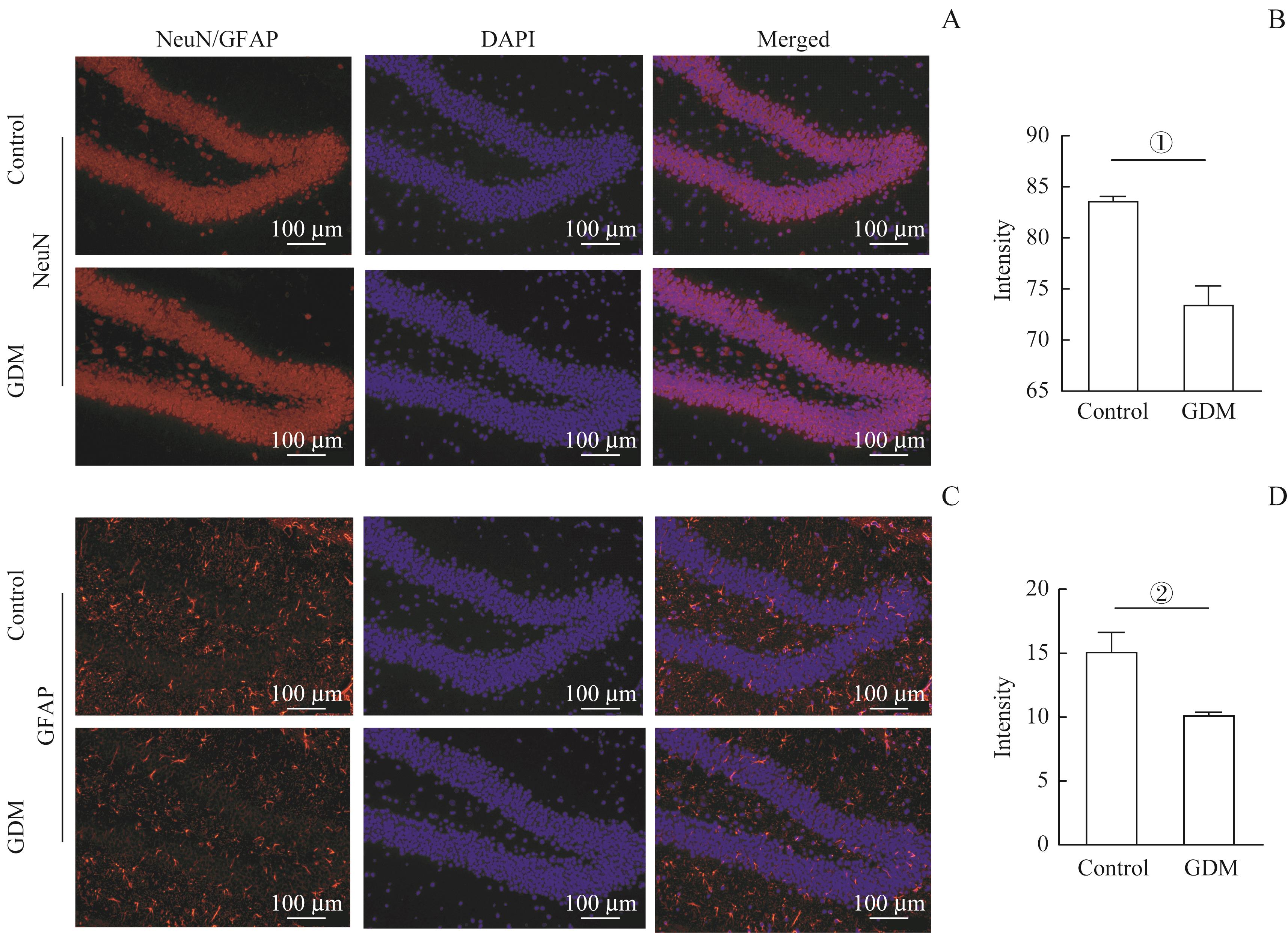
图5 GDM影响小鼠海马神经元发生Note: A/C. Representative immunofluorescent staining images of NeuN (A) and GFAP (C) positive cells in the hippocampi of the two groups. Scale bar=100 μm. B/D. Statistical analysis of the NeuN positive (B) or GFAP positive (D) cells in the hippocampus regions (n=3). ①P=0.005, ②P=0.030, vs the control group.
Fig 5 GDM affecting hippocampal neurongenesis
| 1 | 魏玉梅, 杨慧霞. 我国妊娠期糖尿病研究的发展与展望[J]. 中华围产医学杂志, 2018, 21(4): 218-220. |
| WEI Y M, YANG H X. Development and prospect of research on gestational diabetes mellitus in China[J]. Chin J Perinat Med, 2018, 21(4): 218-220. | |
| 2 | BOLTON J L, BILBO S D. Developmental programming of brain and behavior by perinatal diet: focus on inflammatory mechanisms[J]. Dialogues Clin Neurosci, 2014, 16(3): 307-320. |
| 3 | SOUSA R, TORRES Y S, FIGUEIREDO C P, et al. Consequences of gestational diabetes to the brain and behavior of the offspring[J]. An Acad Bras Cienc, 2018, 90(2 suppl 1): 2279-2291. |
| 4 | GAWLIŃSKA K, GAWLIŃSKI D, KOROSTYŃSKI M, et al. Maternal dietary patterns are associated with susceptibility to a depressive-like phenotype in rat offspring[J]. Dev Cogn Neurosci, 2021, 47: 100879. |
| 5 | FARAHVAR S, WALFISCH A, SHEINER E. Gestational diabetes risk factors and long-term consequences for both mother and offspring: a literature review[J]. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab, 2019, 14(1): 63-74. |
| 6 | NOMURA Y, MARKS D J, GROSSMAN B, et al. Exposure to gestational diabetes mellitus and low socioeconomic status: effects on neurocognitive development and risk of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in offspring[J]. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med, 2012, 166(4): 337-343. |
| 7 | 王晓瑜, 朱岷, 程昕然. 妊娠糖尿病对子代神经发育的研究进展[J]. 四川医学, 2020, 41(10): 1083-1089. |
| WANG X Y, ZHU M, CHENG X R. Research progress of gestational diabetes mellitus on offspring neurodevelopment[J]. Sichuan Med J, 2020, 41(10): 1083-1089. | |
| 8 | VAN LIESHOUT R J, VORUGANTI L P. Diabetes mellitus during pregnancy and increased risk of schizophrenia in offspring: a review of the evidence and putative mechanisms[J]. J Psychiatry Neurosci, 2008, 33(5): 395-404. |
| 9 | VUONG B, ODERO G, ROZBACHER S, et al. Exposure to gestational diabetes mellitus induces neuroinflammation, derangement of hippocampal neurons, and cognitive changes in rat offspring[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2017, 14(1): 80. |
| 10 | BORA E, HARRISON B J, DAVEY C G, et al. Meta-analysis of volumetric abnormalities in cortico-striatal-pallidal-thalamic circuits in major depressive disorder[J]. Psychol Med, 2012, 42(4): 671-681. |
| 11 | HAYASAKA S, NAKAMURA M, NODA Y, et al. Lateralized hippocampal volume increase following high-frequency left prefrontal repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in patients with major depression[J]. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci, 2017, 71(11): 747-758. |
| 12 | SEXTON C E, MACKAY C E, EBMEIER K P. A systematic review and meta-analysis of magnetic resonance imaging studies in late-life depression[J]. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry, 2013, 21(2): 184-195. |
| 13 | DABELEA D, KNOWLER W C, PETTITT D J. Effect of diabetes in pregnancy on offspring: follow-up research in the Pima Indians[J]. J Matern Fetal Med, 2000, 9(1): 83-88. |
| 14 | LAWLOR D A, LICHTENSTEIN P, LÅNGSTRÖM N. Association of maternal diabetes mellitus in pregnancy with offspring adiposity into early adulthood: sibling study in a prospective cohort of 280,866 men from 248,293 families[J]. Circulation, 2011, 123(3): 258-265. |
| 15 | CANNON M, JONES P B, MURRAY R M. Obstetric complications and schizophrenia: historical and meta-analytic review[J]. Am J Psychiatry, 2002, 159(7): 1080-1092. |
| 16 | PANARIELLO F, FANELLI G, FABBRI C, et al. Epigenetic basis of psychiatric disorders: a narrative review[J]. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets, 2022, 21(4): 302-315. |
| 17 | KONG L H, CHEN X X, GISSLER M, et al. Relationship of prenatal maternal obesity and diabetes to offspring neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders: a narrative review[J]. Int J Obes (Lond), 2020, 44(10): 1981-2000. |
| 18 | JING Y H, SONG Y F, YAO Y M, et al. Retardation of fetal dendritic development induced by gestational hyperglycemia is associated with brain insulin/IGF-I signals[J]. Int J Dev Neurosci, 2014, 37: 15-20. |
| 19 | RIVERA H M, CHRISTIANSEN K J, SULLIVAN E L. The role of maternal obesity in the risk of neuropsychiatric disorders[J]. Front Neurosci, 2015, 9: 194. |
| 20 | PIAZZA F V, SEGABINAZI E, DE MEIRELES A L F, et al. Severe uncontrolled maternal hyperglycemia induces microsomia and neurodevelopment delay accompanied by apoptosis, cellular survival, and neuroinflammatory deregulation in rat offspring hippocampus[J]. Cell Mol Neurobiol, 2019, 39(3): 401-414. |
| 21 | KONG L H, NORSTEDT G, SCHALLING M, et al. The risk of offspring psychiatric disorders in the setting of maternal obesity and diabetes[J]. Pediatrics, 2018, 142(3): e20180776. |
| 22 | ORNOY A. Growth and neurodevelopmental outcome of children born to mothers with pregestational and gestational diabetes[J]. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev, 2005, 3(2): 104-113. |
| 23 | XIANG A H, WANG X H, MARTINEZ MP, et al. Maternal gestational diabetes mellitus, type 1 diabetes, and type 2 diabetes during pregnancy and risk of ADHD in offspring[J]. Diabetes Care, 2018, 41(12): 2502-2508. |
| 24 | VAN LIESHOUT R J, VORUGANTI L P. Diabetes mellitus during pregnancy and increased risk of schizophrenia in offspring: a review of the evidence and putative mechanisms[J]. J Psychiatry Neurosci, 2008, 33(5): 395-404. |
| 25 | RAMANATHAN M, JAISWAL A K, BHATTACHARYA S K. Hyperglycaemia in pregnancy: effects on the offspring behaviour with special reference to anxiety paradigms[J]. Indian J Exp Biol, 2000, 38(3): 231-236. |
| 26 | PENNA E, PIZZELLA A, CIMMINO F, et al. Neurodevelopmental disorders: effect of high-fat diet on synaptic plasticity and mitochondrial functions[J]. Brain Sci, 2020, 10(11): 805. |
| 27 | HASEBE K, KENDIG M D, MORRIS M J. Mechanisms underlying the cognitive and behavioural effects of maternal obesity[J]. Nutrients, 2021, 13(1): 240. |
| 28 | KINNEY B A, RABE M B, JENSEN R A, et al. Maternal hyperglycemia leads to gender-dependent deficits in learning and memory in offspring[J]. Exp Biol Med (Maywood), 2003, 228(2): 152-159. |
| 29 | HUERTA-CERVANTES M, PEÑA-MONTES D J, MONTOYA-PÉREZ R, et al. Gestational diabetes triggers oxidative stress in hippocampus and cerebral cortex and cognitive behavior modifications in rat offspring: age- and sex-dependent effects[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12(2): 376. |
| 30 | THION M S, LOW D, SILVIN A, et al. Microbiome influences prenatal and adult microglia in a sex-specific manner[J]. Cell, 2018, 172(3): 500-516.e16. |
| 31 | SALES V M, FERGUSON-SMITH A C, PATTI M E. Epigenetic mechanisms of transmission of metabolic disease across generations[J]. Cell Metab, 2017, 25(3): 559-571. |
| 32 | PINNEY S E, SIMMONS R A. Metabolic programming, epigenetics, and gestational diabetes mellitus[J]. Curr Diab Rep, 2012, 12(1): 67-74. |
| 33 | HUERTA-CERVANTES M, PEÑA-MONTES D J, LÓPEZ-VÁZQUEZ M Á, et al. Effects of gestational diabetes in cognitive behavior, oxidative stress and metabolism on the second-generation off-spring of rats[J]. Nutrients, 2021, 13(5): 1575. |
| 34 | ROOZENDAAL B, HAHN E L, NATHAN S V, et al. Glucocorticoid effects on memory retrieval require concurrent noradrenergic activity in the hippocampus and basolateral amygdala[J]. J Neurosci, 2004, 24(37): 8161-8169. |
| 35 | BORA E, FORNITO A, PANTELIS C, et al. Gray matter abnormalities in major depressive disorder: a meta-analysis of voxel based morphometry studies[J]. J Affect Disord, 2012, 138(1/2): 9-18. |
| 36 | MENARD C, PFAU M L, HODES G E, et al. Social stress induces neurovascular pathology promoting depression[J]. Nat Neurosci, 2017, 20(12): 1752-1760. |
| 37 | HARRISON P J. The neuropathology of primary mood disorder[J]. Brain, 2002, 125(Pt 7): 1428-1449. |
| [1] | 王思睿, 孔盖, 李惠, 钱禛颖, 崔慧茹, 唐莺莹. 经颅磁刺激治疗对抑郁症患者杏仁核及海马亚区体积的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(4): 434-442. |
| [2] | 陈深册, 陈依明, 王凡, 张梦珂, 杨惟杰, 吕洞宾, 洪武. 饮食干预治疗抑郁相关症状的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(8): 1050-1055. |
| [3] | 卢星宇, 徐一丹, 刘亦沁, 张骞仁, 董艳. 高脂饮食对孕期小鼠脂肪组织构成和炎症特征的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(8): 981-990. |
| [4] | 孙晨寅, 吴百川, 张慧凤, 方贻儒, 彭代辉. 体动记录仪评估抑郁症昼夜节律:一项系统综述和meta分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(5): 606-616. |
| [5] | 杨瑞君, 吕书红, 刘志业, 张新, 刘志浩. 中国5省初中生视屏时间和饮食行为与抑郁症状的关联[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(3): 358-364. |
| [6] | 马文琳, 林元杰, 金婷婷, 石薇, 蒋莉华, 赵莉. 初中生自我中心主义与非自杀性自伤的关系研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(8): 971-976. |
| [7] | 刘芊若, 方子晨, 吴宇涵, 钟羡欣, 国沐禾, 贾洁. 肠道菌群及其代谢产物与妊娠期糖尿病相关性的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(5): 641-647. |
| [8] | 徐一丹, 张骞仁, 卢星宇, 董艳. 高脂饮食孕鼠胎盘微环境特征及其意义[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(4): 397-405. |
| [9] | 张越, 瞿蕾, 谷沁, 朱亦清, 马莉莹, 孙文广. 妊娠期糖尿病孕妇尿酮体持续阳性对母婴临床结局的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(3): 314-319. |
| [10] | 葛玲玲, 黄洪军, 罗艳. 乳酰化修饰在疾病中的作用及机制研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(3): 374-379. |
| [11] | 李偲媛, 和申, 李华芳. 重度抑郁症中自噬通路及其关键标志物的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(10): 1324-1331. |
| [12] | 王婕, 吴慧, 卢凌鹏, 杨科峰, 祝捷, 周恒益, 姚蝶, 高雅, 冯宇婷, 刘玉红, 贾洁. 妊娠期糖尿病女性肠道菌群的变化特征及其与血糖、血脂和膳食的相关性[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(9): 1336-1346. |
| [13] | 高菲, 卢宇, 董书琴, 杨柳, 吴邵花, 韦静. 孕早期成纤维生长因子19亚族对妊娠期糖尿病的预测价值[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(7): 898-903. |
| [14] | 谷沁, 夏英倩, 朱亦清, 马莉莹, 瞿蕾, 孙文广. 妊娠期糖尿病孕妇一日门诊饮食个体化指导对血糖控制、体质量增速和妊娠结局的影响分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(2): 185-191. |
| [15] | 杨科峰, 贾洁, 丁天泽, 张硕, 李心怡, 祝捷, 刘玉红, 卢凌鹏, 吴慧. n⁃3多不饱和脂肪酸、汞与妊娠期糖尿病的关联[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(12): 1739-1744. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||