
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (7): 848-859.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2023.07.007
吴其谦( ), 胡燕琴, 陈迦勒, 李牧辰, 赵有淦, 伍静文(
), 胡燕琴, 陈迦勒, 李牧辰, 赵有淦, 伍静文( )
)
收稿日期:2023-01-11
接受日期:2023-06-20
出版日期:2023-07-28
发布日期:2023-07-28
通讯作者:
伍静文,电子信箱:zpwujw@shsmu.edu.cn。作者简介:吴其谦(1998—),男,硕士生;电子信箱:garrywuqiqian@163.com。
基金资助:
WU Qiqian( ), HU Yanqin, CHEN Jiale, LI Muchen, ZHAO Yougan, WU Jingwen(
), HU Yanqin, CHEN Jiale, LI Muchen, ZHAO Yougan, WU Jingwen( )
)
Received:2023-01-11
Accepted:2023-06-20
Online:2023-07-28
Published:2023-07-28
Contact:
WU Jingwen, E-mail: zpwujw@shsmu.edu.cn.Supported by:摘要:
目的·构建野生型(wild type,WT)小鼠和miR-34b/c-/-且miR-449-/-双敲除(double knockout,dKO)小鼠输卵管上皮类器官的培养体系,并进行表型验证。方法·利用酶消化法和差速贴壁法分离纯化WT小鼠和dKO小鼠输卵管上皮细胞,并利用免疫荧光法鉴定得到的输卵管上皮细胞的纯度;通过计数和直径测量比较WT小鼠和dKO小鼠输卵管上皮类器官数量、生长速度和生长大小;利用苏木精-伊红(hematoxylin-eosin,H-E)染色和透射电子显微镜(透射电镜)对输卵管上皮类器官进行形态和结构观察;采用免疫荧光法观察并统计纤毛细胞和分泌细胞在WT小鼠和dKO小鼠输卵管上皮类器官中的比例;采用免疫组织化学法、实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)和Western blotting检测分泌细胞、纤毛细胞相关基因在输卵管上皮类器官中的表达。结果·分离纯化得到的输卵管上皮细胞纯度较高。与WT小鼠相比,dKO小鼠输卵管上皮类器官生长更快,体积更大,数量也更多;但dKO小鼠输卵管上皮类器官发育较慢,于培养28 d时才出现上皮内陷,而WT小鼠的类器官于培养16 d时已经出现。H-E染色和透射电镜结果显示输卵管上皮类器官呈现出与在体输卵管类似的结构。免疫荧光检测显示dKO小鼠输卵管上皮类器官的纤毛细胞显著减少而分泌细胞显著增多(均P<0.05)。免疫组织化学法检测结果显示,dKO小鼠输卵管上皮类器官的分子表达模式与在体输卵管组织基本一致,即纤毛细胞标志物乙酰化微管蛋白α(Ac-α-tubulin)、叉头框J1(forkhead box J1,FOXJ1)表达减少,分泌细胞标志物配对盒8(paired box 8,PAX8)表达增加;RT-qPCR结果显示dKO小鼠输卵管上皮类器官中Foxj1和微管蛋白β4A(tubulin β class Ⅳa,Tubb4a)的mRNA水平均降低(均P<0.05),而Pax8 mRNA水平升高(P<0.05);Western blotting结果显示,dKO小鼠类器官中FOXJ1的蛋白表达水平显著降低,PAX8表达显著升高(均P<0.05)。结论·研究成功构建WT小鼠和dKO小鼠的输卵管上皮类器官培养体系,该体系可模拟小鼠在体输卵管的表型。
中图分类号:
吴其谦, 胡燕琴, 陈迦勒, 李牧辰, 赵有淦, 伍静文. 小鼠输卵管上皮类器官的构建及表型验证[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(7): 848-859.
WU Qiqian, HU Yanqin, CHEN Jiale, LI Muchen, ZHAO Yougan, WU Jingwen. Establishment and phenotype verification of mouse oviductal epithelial organoids[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(7): 848-859.
| Primer | Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|
| Foxj1-F | AAGGAGGCAGAAATCCGGTG |
| Foxj1-R | TTGTAGCCTCCCTTGTGCAG |
| Pax8-F | CCCTTCGCCATAAAGCAGGA |
| Pax8-R | AGCATGGGGAAAGGCATTGA |
| Tubb4a-F | AACCCGGCACCATGGACTCTGT |
| Tubb4a-R | TGCCTGCTCCGGATTGACCAAATA |
| Ovgp1-F | TGGACCCCTTTCTTTGTACG |
| Ovgp1-R | TGGACAGCAGTGTTTTCAGC |
| Gapdh-F | TGGAAAGCTGTGGCGTGAT |
| Gapdh-R | GGGTAGGAACACGGAAGGC |
表1 实时荧光定量PCR引物序列
Tab 1 Primer sequences in RT-qPCR
| Primer | Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|
| Foxj1-F | AAGGAGGCAGAAATCCGGTG |
| Foxj1-R | TTGTAGCCTCCCTTGTGCAG |
| Pax8-F | CCCTTCGCCATAAAGCAGGA |
| Pax8-R | AGCATGGGGAAAGGCATTGA |
| Tubb4a-F | AACCCGGCACCATGGACTCTGT |
| Tubb4a-R | TGCCTGCTCCGGATTGACCAAATA |
| Ovgp1-F | TGGACCCCTTTCTTTGTACG |
| Ovgp1-R | TGGACAGCAGTGTTTTCAGC |
| Gapdh-F | TGGAAAGCTGTGGCGTGAT |
| Gapdh-R | GGGTAGGAACACGGAAGGC |

图1 WT小鼠和dKO小鼠输卵管上皮类器官形态学比较Note: A. Different genotypes of mice detected by PCR. Triple (miR-34b/c+/- and miR-449-/-), miR-449-/-, and dKO (miR-34b/c-/- and miR-449-/-). B. Primary culture of the oviductal epithelial cells (×400, scale bar=50 μm). C. Identification of the purity of the isolated oviductal epithelial cells using immunofluorescent staining. Ac-α-tubulin for showing ciliated cells, PAX8 for showing secretory cells, ACTA2 for showing smooth muscle cells, and vimentin for showing fibroblasts (×400, scale bar=50 μm). D. Phase contrast images of organoids formation and growth from WT mice and dKO mice (×100, scale bar=200 μm). E. The numbers of the organoids with different sizes were counted after 8 d. F. The numbers of the organoids with different sizes were counted after 16 d. G. The total numbers of organoids were counted after 8 d and 16 d. ①P=0.002, ②P=0.007, ③P=0.004, ④P=0.006, ⑤P=0.001, ⑥P=0.011, ⑦P=0.013, compared with the WT group.
Fig 1 Morphological comparison of oviductal epithelial organoids from WT mice and dKO mice
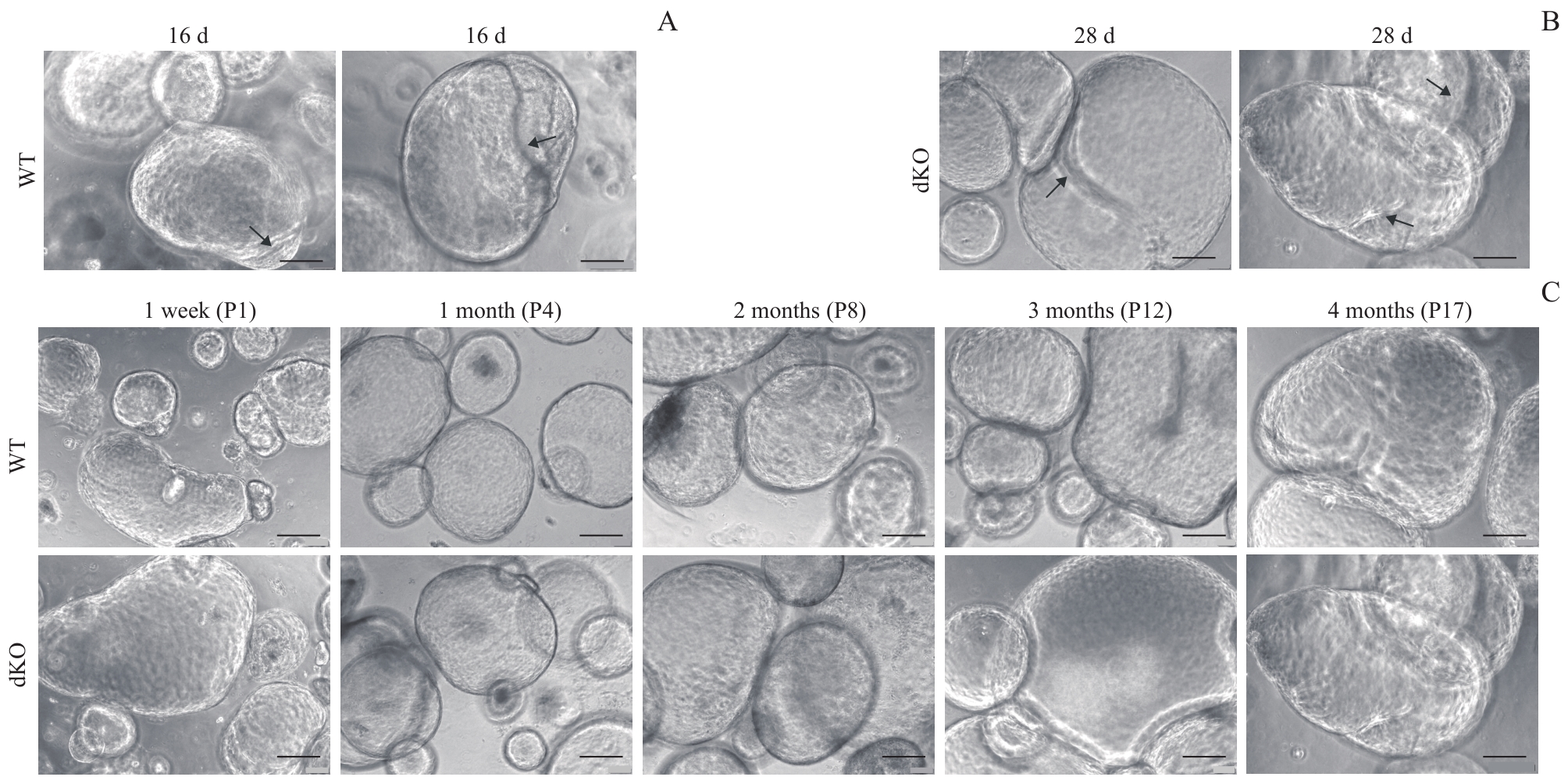
图2 输卵管上皮类器官的长期培养及传代Note: A/B. Representative mature organoids with epithelial invaginations and foldings (arrows) after 16 d of WT mice (A) and after 28 d of dKO mice (B) (×100, scale bar=200 μm). C. Oviductal epithelial organoids culture of WT mice and dKO mice could be maintainted at least for 4 months and 17 passages (P17) (×100, scale bar=200 μm).
Fig 2 Long-term culture and passage of oviductal epithelial organoids
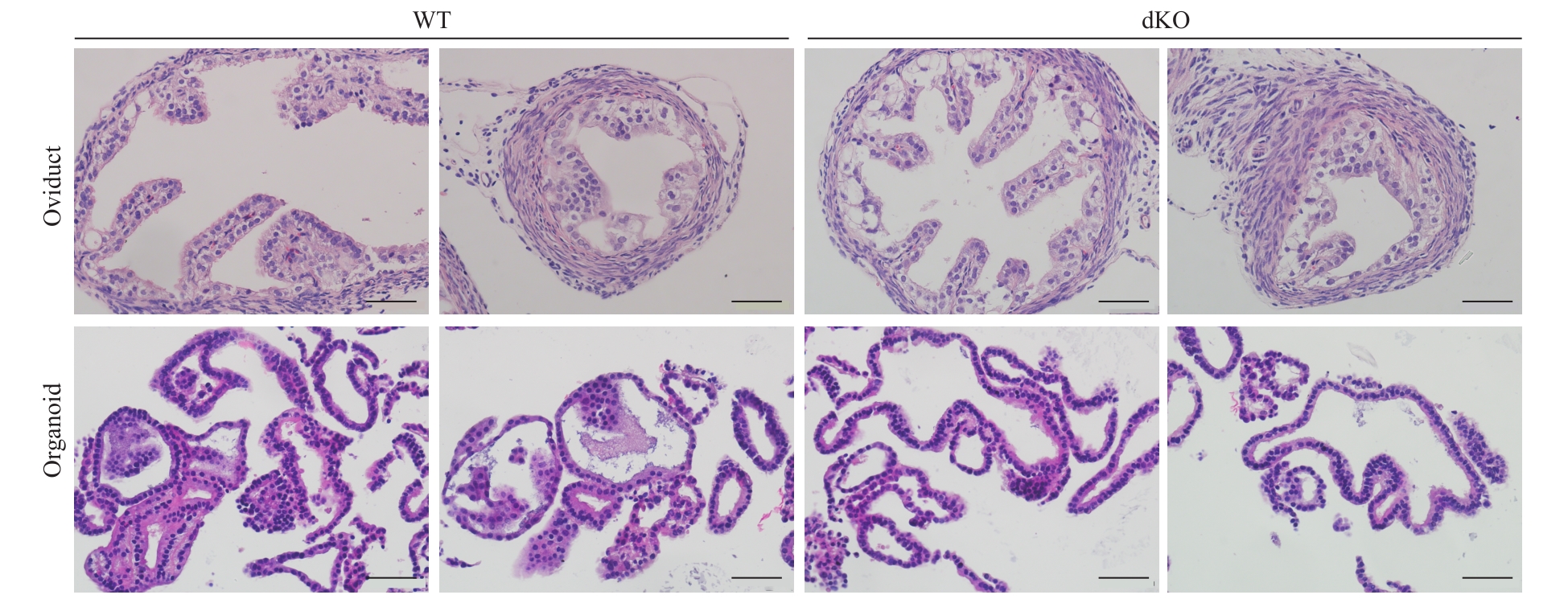
图3 光学显微镜下输卵管上皮类器官的结构(H-E染色, ×400)Note: Comparison of the histology structure of the oviducts and the oviductal epithelial organoids from WT mice and dKO mice after 2 months of culture (scale bar=50 μm).
Fig 3 Structure of the oviductal epithelial organoids under light microscopy (H-E staining, ×400)

图4 输卵管上皮类器官中纤毛细胞和分泌细胞的微观结构Note: A. Transmission electron microscopic images of the ciliated cells of oviductal epithelial organoids of WT mice and dKO mice after 2 months of culture (×10 000, scale bar=1 μm). The images on the right are the magnification ones in the dotted box on the left (×25 000, scale bar=500 nm). The white line showing the arrangement of the basal bodies, and the white arrows showing multiple disorganized centrioles. B. Transmission electron microscopic images of the secretory cells of oviductal epithelial organoids of WT mice and dKO mice after 2 months of culture (×10 000, scale bar=1 μm). The images on the right are the magnification ones in the dotted box on the left (×25 000, scale bar=500 nm). The white arrows showing the exocytosis granules by the secretory cells.
Fig 4 Microstructures of ciliated cells and secretory cells in the oviductal epithelial organoids
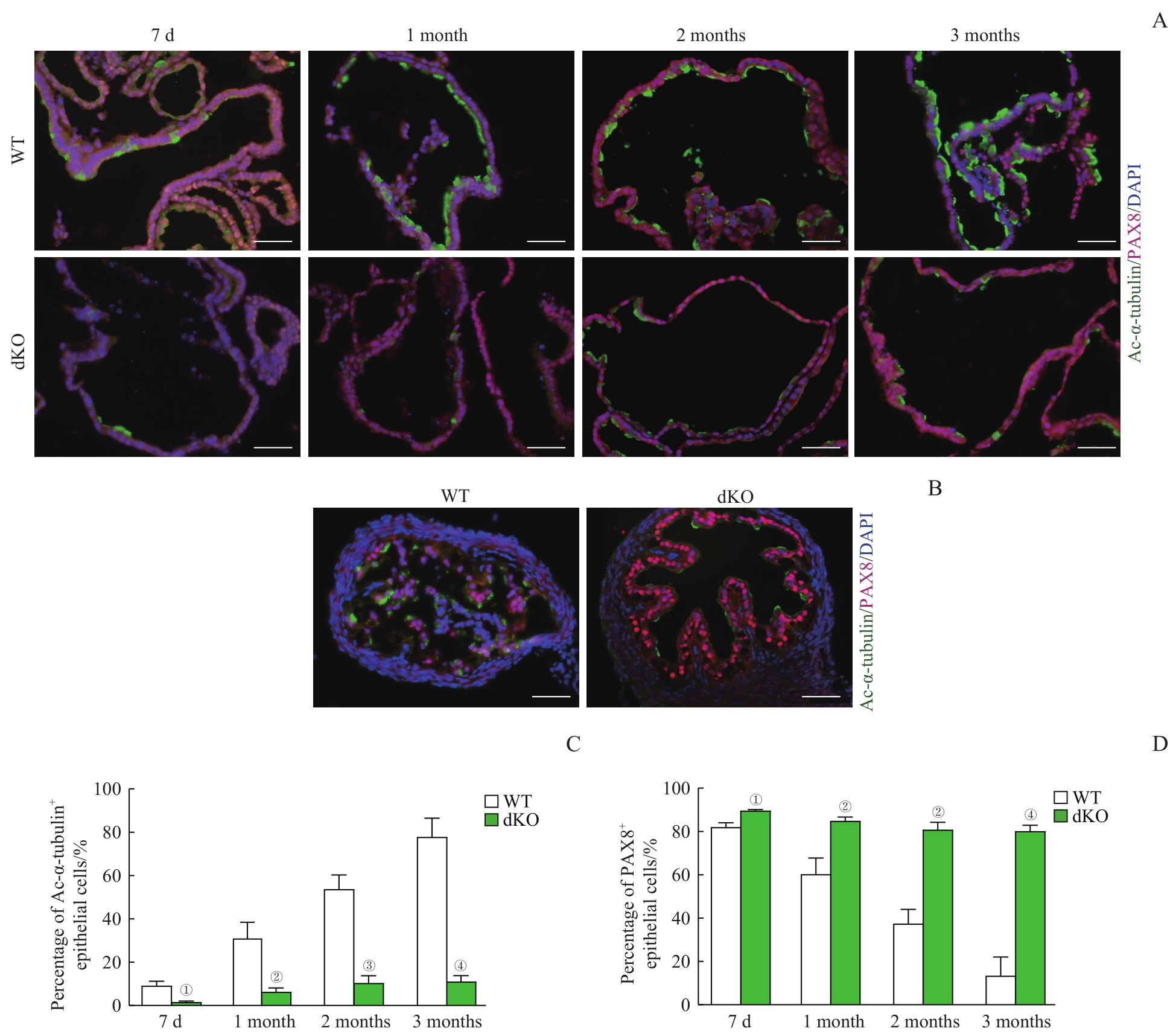
图5 输卵管上皮类器官的细胞构成Note: A/B. Co-immunofluorescent staining of Ac-α-tubulin (showing ciliated cells) and PAX8 (showing secretory cells) in the organoid sections (A) and the oviducts (B) of WT mice and dKO mice (×400, scale bar=50 μm). C/D. Quantification of ciliated cells (C) and secretory cells (D) of the organoids from WT mice and dKO mice across different culture time. ①P=0.004, ②P=0.005, ③P=0.001, ④P=0.000, compared with the WT group.
Fig 5 Cell composition of the oviductal epithelial organoids

图6 纤毛细胞与分泌细胞相关基因在输卵管上皮类器官中的表达Note: A. Expression and localization of Ac-α-tubulin, FOXJ1, and PAX8 in the oviductal tissues and oviductal epithelial organoids of WT mice and dKO mice using immunohistochemical staining (×400, scale bar=50 μm). B. The expression levels of ciliated cell- and secretory cell-related genes of the oviductal epithelial organoids from WT mice and dKO mice detected by RT-qPCR. Tubb4a and Foxj1 for ciliated cells. Pax8 and Ovgp1 for secretory cells. C?E. Western blotting analysis of FOXJ1 and PAX8 protein levels of oviductal epithelial organoids from WT mice and dKO mice (C) with quantitative analysis of FOXJ1 (D) and PAX8 (E). ①P=0.002, ②P=0.001, ③P=0.000, ④P=0.018, compared with the WT group..
Fig 6 Expression levels of ciliated cell- and secretory cell-related genes in oviductal epithelial organoids
| 1 | LI S, WINUTHAYANON W. Oviduct: roles in fertilization and early embryo development[J]. J Endocrinol, 2017, 232(1): R1-R26. |
| 2 | TALBOT P, SHUR B D, MYLES D G. Cell adhesion and fertilization: steps in oocyte transport, sperm-zona pellucida interactions, and sperm-egg fusion[J]. Biol Reprod, 2003, 68(1): 1-9. |
| 3 | KÖLLE S, DUBIELZIG S, REESE S, et al. Ciliary transport, gamete interaction, and effects of the early embryo in the oviduct: ex vivo analyses using a new digital videomicroscopic system in the cow[J]. Biol Reprod, 2009, 81(2): 267-274. |
| 4 | CHEN S, SCHOEN J. Air-liquid interface cell culture: from airway epithelium to the female reproductive tract[J]. Reprod Domest Anim, 2019, 54(Suppl 3): 38-45. |
| 5 | CUI Y T, ZHAO H Q, WU S W, et al. Human female reproductive system organoids: applications in developmental biology, disease modelling, and drug discovery[J]. Stem Cell Rev Rep, 2020, 16(6): 1173-1184. |
| 6 | KLASVOGT S, ZUSCHRATTER W, SCHMIDT A, et al. Air-liquid interface enhances oxidative phosphorylation in intestinal epithelial cell line IPEC-J2[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2017, 3: 17001. |
| 7 | ANDREI G, DURAFFOUR S, VAN DEN OORD J, et al. Epithelial raft cultures for investigations of virus growth, pathogenesis and efficacy of antiviral agents[J]. Antiviral Res, 2010, 85(3): 431-449. |
| 8 | LI D D, LI H, WANG Y, et al. Development and characterization of a polarized human endometrial cell epithelia in an air-liquid interface state[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2018, 9(1): 209. |
| 9 | LEVANON K, NG V, PIAO H Y, et al. Primary ex vivo cultures of human fallopian tube epithelium as a model for serous ovarian carcinogenesis[J]. Oncogene, 2010, 29(8): 1103-1113. |
| 10 | CHEN S, PALMA-VERA S E, KEMPISTY B, et al. In vitro mimicking of estrous cycle stages: dissecting the impact of estradiol and progesterone on oviduct epithelium[J]. Endocrinology, 2018, 159(9): 3421-3432. |
| 11 | ZHU M B, IWANO T, TAKEDA S. Fallopian tube basal stem cells reproducing the epithelial sheets in vitro-stem cell of fallopian epithelium[J]. Biomolecules, 2020, 10(9): 1270. |
| 12 | RAJAGOPAL M, TOLLNER T L, FINKBEINER W E, et al. Differentiated structure and function of primary cultures of monkey oviductal epithelium[J]. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim, 2006, 42(8/9): 248-254. |
| 13 | DVORAK A, TILLEY A E, SHAYKHIEV R, et al. Do airway epithelium air-liquid cultures represent the in vivo airway epithelium transcriptome?[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2011, 44(4): 465-473. |
| 14 | ALZAMIL L, NIKOLAKOPOULOU K, TURCO M Y. Organoid systems to study the human female reproductive tract and pregnancy[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2021, 28(1): 35-51. |
| 15 | ROSSI G, MANFRIN A, LUTOLF M P. Progress and potential in organoid research[J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2018, 19(11): 671-687. |
| 16 | CLEVERS H. Modeling development and disease with organoids[J]. Cell, 2016, 165(7): 1586-1597. |
| 17 | HUCH M, KNOBLICH J A, LUTOLF M P, et al. The hope and the hype of organoid research[J]. Development, 2017, 144(6): 938-941. |
| 18 | MEBARKI M, BENNACEUR A, BONHOMME-FAIVRE L. Human-cell-derived organoids as a new ex vivo model for drug assays in oncology[J]. Drug Discov Today, 2018, 23(4): 857-863. |
| 19 | KESSLER M, HOFFMANN K, BRINKMANN V, et al. The Notch and Wnt pathways regulate stemness and differentiation in human fallopian tube organoids[J]. Nat Commun, 2015, 6: 8989. |
| 20 | XIE Y, PARK E S, XIANG D X, et al. Long-term organoid culture reveals enrichment of organoid-forming epithelial cells in the fimbrial portion of mouse fallopian tube[J]. Stem Cell Res, 2018, 32: 51-60. |
| 21 | WU J W, BAO J Q, KIM M, et al. Two miRNA clusters, miR-34b/c and miR-449, are essential for normal brain development, motile ciliogenesis, and spermatogenesis[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2014, 111(28): E2851-E2857. |
| 22 | YUAN S Q, WANG Z Q, PENG H Y, et al. Oviductal motile cilia are essential for oocyte pickup but dispensable for sperm and embryo transport[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2021, 118(22): e2102940118. |
| 23 | LOUKAS I, SKAMNELOU M, TSARIDOU S, et al. Fine-tuning multiciliated cell differentiation at the post-transcriptional level: contribution of miR-34/449 family members[J]. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc, 2021, 96(5): 2321-2332. |
| 24 | MERCEY O, POPA A, CAVARD A, et al. Characterizing isomiR variants within the microRNA-34/449 family[J]. FEBS Lett, 2017, 591(5): 693-705. |
| 25 | LABIDI-GALY S I, PAPP E, HALLBERG D, et al. High grade serous ovarian carcinomas originate in the fallopian tube[J]. Nat Commun, 2017, 8(1): 1093. |
| 26 | PERETS R, WYANT G A, MUTO K W, et al. Transformation of the fallopian tube secretory epithelium leads to high-grade serous ovarian cancer in Brca;Tp53;Pten models[J]. Cancer Cell, 2013, 24(6): 751-765. |
| 27 | ISHIGURO T, OHATA H, SATO A, et al. Tumor-derived spheroids: relevance to cancer stem cells and clinical applications[J]. Cancer Sci, 2017, 108(3): 283-289. |
| 28 | ZHANG S, DOLGALEV I, ZHANG T, et al. Both fallopian tube and ovarian surface epithelium are cells-of-origin for high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 5367. |
| [1] | 周亦凝, 叶之韵, 陈慧文, 谢欣宜, 周薇, 宋忠臣. Th17细胞特异性敲除Stat3对牙周炎小鼠焦虑抑郁样行为的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(7): 838-845. |
| [2] | 陈勇羽, 黄益仁, 陈哲逸, 周冰倩, 陈诗宇, 郑英霞. 丝氨酸蛋白酶抑制因子1在胃癌中的表达及其促进胃癌发展的作用机制[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(2): 150-160. |
| [3] | 黄勤, 黄缨, 李文. 输卵管复合妊娠的超声检查时间探讨[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(12): 1545-1551. |
| [4] | 施泽纶, 王青, 何雯, 傅唯佳, 王颖雯, 韩晓, 张晓波. 纳米塑料诱导肺泡Ⅱ型上皮细胞DNA损伤加重重症哮喘[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(11): 1391-1405. |
| [5] | 颜丽, 汪央, 刘小奕, 潘漪莲, 朱旻蛟, 刘璟蓝, 张健. 输卵管整形与输卵管切除治疗双侧输卵管重度积水不孕女性长期妊娠结局的比较[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(6): 728-737. |
| [6] | 徐瀛濂, 田静, 张翔, 赵顺英. 气道上皮细胞在哮喘发病机制中的作用研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(5): 619-623. |
| [7] | 郑小雁, 王星云, 张拥军. 抑制肺泡上皮细胞焦亡对支气管肺发育不良新生大鼠肺泡化阻滞的改善作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(2): 171-179. |
| [8] | 谢林, 程烨, 郑琦敏, 张熙, 付莉莉, 陈敏, 王怡, 梅长林, 谢静远, 顾向晨. 淫羊藿苷对急性肾损伤向慢性肾脏病转化小鼠模型的预防性保护作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(1): 8-19. |
| [9] | 解昕轶, 杨钰萌, 王少薇, 孙娜, 史传道, 刘启玲, 张荣强, 李俊杰. 新型冠状病毒(SARS-COV-2)感染后人嗅觉神经上皮细胞的基因组调控网络研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(11): 1524-1533. |
| [10] | 周冰倩, 韩丽, 陈哲逸, 陈诗宇, 郑英霞. 蛋白精氨酸甲基转移酶5在肺癌中的表达及其促进肺癌的作用机制[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(8): 1009-1016. |
| [11] | 周天浩, 辛肇晨, 杜少倩, 曹源, 许静轩, 劳曾红, 王红霞. 乳腺癌类器官共培养技术的建立和优化[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(8): 1017-1024. |
| [12] | 王钰婷1, 2,刘锦燕2,史 册1,赵珺涛1, 2,项明洁1, 2. 白念珠菌ERG3基因敲除及其对耐药性的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(2): 163-. |
| [13] | 吕亚男,顾青,李东丽,宫媛媛. 叶黄素对转化生长因子 -β2诱导的视网膜色素上皮细胞 上皮 -间质转化的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2019, 39(6): 571-. |
| [14] | 王凌霄,刘婷婷,杨晓辉,姚智卿,蔡慧珍. 枸杞多糖对髓样分化因子 88基因敲除小鼠 2型糖尿病模型炎症因子的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2019, 39(2): 136-. |
| [15] | 刘霞,余维,余丹,陈娟,骆小华,李兵. 腺病毒介导的 siRNA 沉默PNUTS 基因对喉癌 Hep-2 细胞增殖、侵袭的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2018, 38(2): 161-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||