
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (12): 1569-1576.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2023.12.013
收稿日期:2023-06-07
接受日期:2023-11-30
出版日期:2023-12-28
发布日期:2024-02-01
通讯作者:
刘 敏,电子信箱:lm4104@shtrhospital.com。作者简介:陈子旋(1999—),男,傣族,硕士生;电子信箱:czixuan2023@126.com。
基金资助:
CHEN Zixuan( ), LI Dong, LIU Min(
), LI Dong, LIU Min( )
)
Received:2023-06-07
Accepted:2023-11-30
Online:2023-12-28
Published:2024-02-01
Contact:
LIU Min, E-mail: lm4104@shtrhospital.com.Supported by:摘要:
细胞焦亡是一种新的细胞程序性死亡方式,主要表现为细胞持续肿胀至破裂,进而释放出大量的炎症因子引起炎症反应。良性前列腺增生(benign prostatic hyperplasia,BPH)是老年男性最常发生的泌尿系统疾病,与激素变化和炎症反应密切相关。近年来,细胞焦亡在BPH的发生、发展中的作用引起了人们的关注。该文总结了细胞焦亡的机制,归纳了老年男性BPH的发病机制,并概述了细胞焦亡在BPH中的作用,以期为通过细胞焦亡寻找对BPH更有效的治疗措施提供新的思路。
中图分类号:
陈子旋, 李东, 刘敏. 细胞焦亡在老年男性良性前列腺增生中的作用综述[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(12): 1569-1576.
CHEN Zixuan, LI Dong, LIU Min. Review of the role of pyroptosis in benign prostatic hyperplasia in old males[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(12): 1569-1576.
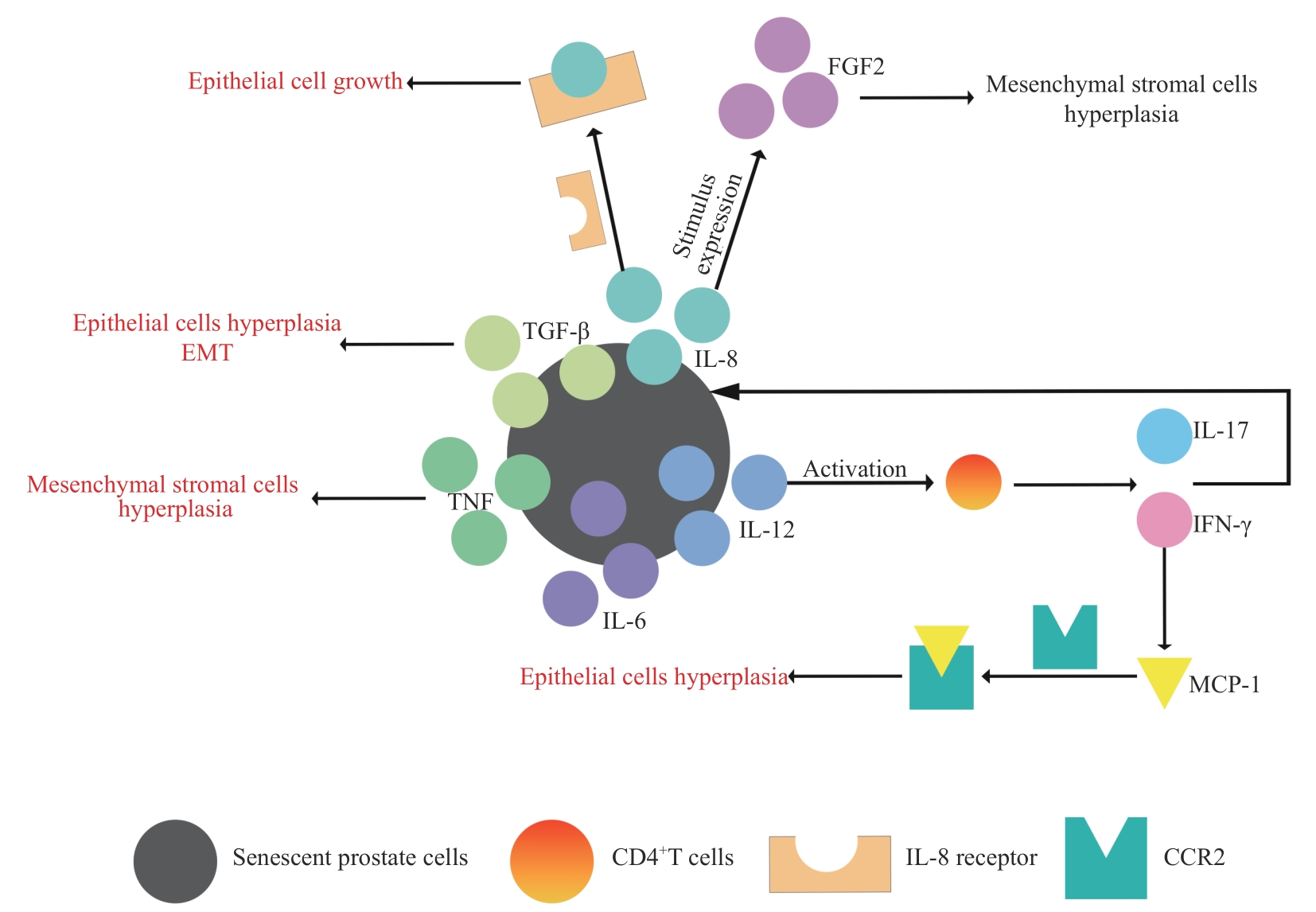
图1 炎症在老年男性BPH发病机制中的作用Note: EMT—epithelial-mesenchymal transition; TGF-β—transforming growth factor-β; TNF—tumor necrosis factor.
Fig 1 Role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of BPH in old males
| 1 | 张皓博, 赵宇楠, 杨学军. 细胞焦亡在椎间盘退变中的作用及治疗意义[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1445-1451. |
| ZHANG H B, ZHAO Y N, YANG X J. Role and therapeutic implications of pyroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1445-1451. | |
| 2 | ZHENG X T, CHEN W W, GONG F C, et al. The role and mechanism of pyroptosis and potential therapeutic targets in Sepsis: a review[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 711939. |
| 3 | NAIYILA X, LI J Z, HUANG Y, et al. A novel insight into the immune-related interaction of inflammatory cytokines in benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. J Clin Med, 2023, 12(5): 1821. |
| 4 | TRIPATHI U, MISRA A, TCHKONIA T, et al. Impact of senescent cell subtypes on tissue dysfunction and repair: importance and research questions[J]. Mech Ageing Dev, 2021, 198: 111548. |
| 5 | 李泽安, 谢俊佳, 陈君秀, 等. 微环境与良性前列腺增生发病机制的研究进展[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2022, 43(9): 717-720. |
| LI Z A, XIE J J, CHEN J X, et al. Role of microenvironment in the pathogenesis of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Chinese Journal of Urology, 2022, 43(9): 717-720. | |
| 6 | ZHAO M, GUO J, GAO Q H, et al. Relationship between pyroptosis-mediated inflammation and the pathogenesis of prostate disease[J]. Front Med (Lausanne), 2023, 10: 1084129. |
| 7 | TANG R, XU J, ZHANG B, et al. Ferroptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis in anticancer immunity[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2020, 13(1): 110. |
| 8 | LI L S, JIANG M X, QI L, et al. Pyroptosis, a new bridge to tumor immunity[J]. Cancer Sci, 2021, 112(10): 3979-3994. |
| 9 | 郑小雁, 王星云, 张拥军. 抑制肺泡上皮细胞焦亡对支气管肺发育不良新生大鼠肺泡化阻滞的改善作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(2): 171-179. |
| ZHENG X Y, WANG X Y, ZHANG Y J. Improvement of alveolarization arrest in newborn rats with bronchopulmonary dysplasia via inhibiting alveolar epithelial cell pyroptosis[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao tong University:Medical Science, 2023, 43(2): 171-179. | |
| 10 | WEI X, XIE F, ZHOU X X, et al. Role of pyroptosis in inflammation and cancer[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2022, 19(9): 971-992. |
| 11 | RAO Z P, ZHU Y T, YANG P, et al. Pyroptosis in inflammatory diseases and cancer[J]. Theranostics, 2022, 12(9): 4310-4329. |
| 12 | HSU S K, LI C Y, LIN I L, et al. Inflammation-related pyroptosis, a novel programmed cell death pathway, and its crosstalk with immune therapy in cancer treatment[J]. Theranostics, 2021, 11(18): 8813-8835. |
| 13 | HU Z H, CHAI J J. Assembly and architecture of NLR resistosomes and inflammasomes[J]. Annu Rev Biophys, 2023, 52: 207-228. |
| 14 | MA Q. Pharmacological inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome: structure, molecular activation, and inhibitor-NLRP3 interaction[J]. Pharmacol Rev, 2023, 75(3): 487-520. |
| 15 | WEI Y N, YANG L, PANDEYA A, et al. Pyroptosis-induced inflammation and tissue damage[J]. J Mol Biol, 2022, 434(4): 167301. |
| 16 | YU P, ZHANG X, LIU N, et al. Pyroptosis: mechanisms and diseases[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2021, 6(1): 128. |
| 17 | WANG Y P, GAO W Q, SHI X Y, et al. Chemotherapy drugs induce pyroptosis through caspase-3 cleavage of a gasdermin[J]. Nature, 2017, 547(7661): 99-103. |
| 18 | ZHOU Z W, HE H B, WANG K, et al. Granzyme A from cytotoxic lymphocytes cleaves GSDMB to trigger pyroptosis in target cells[J]. Science, 2020, 368(6494): eaaz7548. |
| 19 | SARRIÓ D, MARTÍNEZ-VAL J, MOLINA-CRESPO Á, et al. The multifaceted roles of gasdermins in cancer biology and oncologic therapies[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2021, 1876(2): 188635. |
| 20 | OLTRA S S, COLOMO S, SIN L, et al. Distinct GSDMB protein isoforms and protease cleavage processes differentially control pyroptotic cell death and mitochondrial damage in cancer cells[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2023, 30(5): 1366-1381. |
| 21 | JIN B R, KIM H J, NA J H, et al. Targeting benign prostate hyperplasia treatments: AR/TGF-β/NOX4 inhibition by apocynin suppresses inflammation and proliferation[J]. J Adv Res, 2023: S2090-S1232(23)00112-1. |
| 22 | TONG Y, ZHOU R Y. Review of the roles and interaction of androgen and inflammation in benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2020, 2020: 7958316. |
| 23 | HONG G L, KIM K H, KIM Y J, et al. Decreased mitophagy aggravates benign prostatic hyperplasia in aged mice through DRP1 and estrogen receptor α[J]. Life Sci, 2022, 309: 120980. |
| 24 | CANNARELLA R, CONDORELLI R A, BARBAGALLO F, et al. Endocrinology of the aging prostate: current concepts[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2021, 12: 554078. |
| 25 | AHEARN T U, PEISCH S, PETTERSSON A, et al. Expression of IGF/insulin receptor in prostate cancer tissue and progression to lethal disease[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2018, 39(12): 1431-1437. |
| 26 | CAO D H, SUN R N, PENG L, et al. Immune cell proinflammatory microenvironment and androgen-related metabolic regulation during benign prostatic hyperplasia in aging[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 842008. |
| 27 | BIRCH J, GIL J. Senescence and the SASP: many therapeutic avenues[J]. Genes Dev, 2020, 34(23/24): 1565-1576. |
| 28 | FIARD G, STAVRINIDES V, CHAMBERS E S, et al. Cellular senescence as a possible link between prostate diseases of the ageing male[J]. Nat Rev Urol, 2021, 18(10): 597-610. |
| 29 | LÓPEZ-OTÍN C, BLASCO M A, PARTRIDGE L, et al. Hallmarks of aging: an expanding universe[J]. Cell, 2023, 186(2): 243-278. |
| 30 | CAO Y, ZHANG H, TU G L, et al. The symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia patients with stromal-dominated hyperplasia nodules may be associated with prostate fibrosis[J]. Int J Gen Med, 2023, 16: 1181-1191. |
| 31 | ROYUELA M, DE MIGUEL M P, BETHENCOURT F R, et al. Transforming growth factor beta 1 and its receptor types Ⅰ and Ⅱ. Comparison in human normal prostate, benign prostatic hyperplasia, and prostatic carcinoma[J]. Growth Factors, 1998, 16(2): 101-110. |
| 32 | VICKMAN R E, AARON-BROOKS L, ZHANG R Y, et al. TNF is a potential therapeutic target to suppress prostatic inflammation and hyperplasia in autoimmune disease[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1): 2133. |
| 33 | ALONSO-MAGDALENA P, BRÖSSNER C, REINER A, et al. A role for epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the etiology of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2009, 106(8): 2859-2863. |
| 34 | LI Q, HONG Y F, CHEN J, et al. Hypoxia-induced HIF-1α expression promotes neurogenic bladder fibrosis via EMT and pyroptosis[J]. Cells, 2022, 11(23): 3836. |
| 35 | WANG Z, ZHANG Y C, ZHAO C, et al. The miR-223-3p/MAP1B axis aggravates TGF-β-induced proliferation and migration of BPH-1 cells[J]. Cell Signal, 2021, 84: 110004. |
| 36 | JIA C Q, ZHANG Z Q, TANG J, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition induces GSDME transcriptional activation for inflammatory pyroptosis[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9: 781365. |
| 37 | BOSTWICK D G, EGEVAD L. Prostatic stromal proliferations: a review[J]. Pathology, 2021, 53(1): 12-25. |
| 38 | ZHANG C, ZHAI T Y, ZHU J H, et al. Research progress of antioxidants in oxidative stress therapy after spinal cord injury[J]. Neurochem Res, 2023, 48(12): 3473-3484. |
| 39 | MIAO C Y, ZHAO Y, CHEN Y, et al. Investigation of He's Yang Chao recipe against oxidative stress-related mitophagy and pyroptosis to improve ovarian function[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2023, 14: 1077315. |
| 40 | ZHANG C Y, LIN T J, NIE G H, et al. Cadmium and molybdenum co-induce pyroptosis via ROS/PTEN/PI3K/AKT axis in duck renal tubular epithelial cells[J]. Environ Pollut, 2021, 272: 116403. |
| 41 | REBELO A P, EIDHOF I, CINTRA V P, et al. Biallelic loss-of-function variations in PRDX3 cause cerebellar ataxia[J]. Brain, 2021, 144(5): 1467-1481. |
| 42 | JIANG M Y, HAN Z D, LI W J, et al. Mitochondrion-associated protein peroxiredoxin 3 promotes benign prostatic hyperplasia through autophagy suppression and pyroptosis activation[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(46): 80295-80302. |
| 43 | QUAN Y, XIN Y G, TIAN G E, et al. Mitochondrial ROS-modulated mtDNA: a potential target for cardiac aging[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2020, 2020: 9423593. |
| 44 | CHEN W F, HUANG X Q, PENG A X, et al. Kangquan recipe regulates the expression of BAMBI protein via the TGF- β/Smad signaling pathway to inhibit benign prostatic hyperplasia in rats[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2019, 2019: 6281819. |
| 45 | FUSCO F, CRETA M, DE NUNZIO C, et al. Progressive bladder remodeling due to bladder outlet obstruction: a systematic review of morphological and molecular evidences in humans[J]. BMC Urol, 2018, 18(1): 15. |
| 46 | WANG K, CHEN L, YANG J, et al. Urethral meatus stricture BOO stimulates bladder smooth muscle cell proliferation and pyroptosis via IL‑1β and the SGK1‑NFAT2 signaling pathway[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2020, 22(1): 219-226. |
| 47 | KUSTRIMOVIC N, BOMBELLI R, BACI D, et al. Microbiome and prostate cancer: a novel target for prevention and treatment[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(2): 1511. |
| 48 | BERTHELOOT D, LATZ E, FRANKLIN B S. Necroptosis, pyroptosis and apoptosis: an intricate game of cell death[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2021, 18(5): 1106-1121. |
| [1] | 王治琪, 王莹. 儿童炎症性肠病相关贫血的诊治研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(9): 1232-1238. |
| [2] | 赛提尔古丽·克然木, 钱蕾, 丁思怡, 哈娜提·马合力木汗, 杨雪儿, 贾浩. 精氨酸代谢调控间充质干细胞功能的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(7): 910-915. |
| [3] | 赵心雨, 张文超, 陈旭卓, 宋佳琪, 黄慧, 张善勇. 亚精胺对脂多糖诱导的小鼠颅骨炎症性骨溶解的作用研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(6): 673-683. |
| [4] | 韩龙传, 李悦, 邹智慧, 罗静, 李若伊, 张颖婷, 唐欣欣, 田丽红, 陆宇恒, 黄莺, 贺明, 付寅坤. 磷脂酰乙醇胺引起内质网应激促进巨噬细胞衰老及肝损伤[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(6): 693-704. |
| [5] | 杨乐, 周怡, 王钶韵, 赖娅莉. 大黄素改善阿尔茨海默病认知障碍、内质网应激和神经炎症的研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(6): 727-734. |
| [6] | 张星语, 李若谷. 主动脉瘤单细胞转录组的系统性分析与探索[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(6): 735-744. |
| [7] | 禹恺, 帅哲玮, 黄洪军, 罗艳. 小胶质细胞在中枢神经系统炎症性疾病中的作用和机制研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(5): 630-638. |
| [8] | 万宏劲, 胡逸斌, 王昕, 张凯, 秦安, 马培翔, 马辉, 赵杰. 甲基莲心碱通过KEAP1/NRF2/GPX4和NF-κB信号通路减轻椎间盘退行性变[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(3): 261-270. |
| [9] | 邓佳丽, 郭嘉婧, 王静怡, 丁心怡, 朱仪, 王中领. 自组装载药纳米探针用于乳腺癌焦亡增敏及化学交换饱和转移成像研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(3): 271-281. |
| [10] | PANDIT Roshan, 卢君瑶, 何立珩, 包玉洁, 季萍, 陈颖盈, 许洁, 王颖. 肿瘤坏死因子-α在新型冠状病毒感染合并肾损伤中的作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(1): 1-10. |
| [11] | 王晓红, 方贻儒. 双相障碍神经炎症机制的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(1): 107-112. |
| [12] | 陈铭豪, 刘沛雨, 王旋, 吴一想, 江玉瑾, 张朝阳, 张敬法. 糖尿病视网膜病变的药物治疗研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(7): 822-829. |
| [13] | 夏西茜, 丁珂珂, 张慧恒, 彭旭飞, 孙昳旻, 唐雅珺, 汤晓芳. 肠道菌群介导胆汁酸影响炎症性肠病的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(7): 839-846. |
| [14] | 曾德洁, 陈增辉, 丁乾坤, 孙夏青, 孙琪, 赵士兵. 天然来源的多糖在干预神经发育障碍中的应用前景[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(6): 779-787. |
| [15] | 郑梦奕, 毛家亮, 邹治国, 张瑞雷, 张厚, 李世光. 全身免疫炎症指数及躯体化症状评分对首发心梗PCI术后发生院内主要不良心血管事件的预测价值[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(3): 334-341. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||