
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 373-380.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2025.03.015
收稿日期:2024-09-02
接受日期:2024-12-13
出版日期:2025-03-28
发布日期:2025-03-28
通讯作者:
熊 屏,主任医师,博士;电子信箱:xiong_ping_xp@163.com。作者简介:刘楚萱(1999—),女,硕士生;电子信箱:lcx1999takemone@163.com。
基金资助:
LIU Chuxuan( ), ZUO Jiaxin, XIONG Ping(
), ZUO Jiaxin, XIONG Ping( )
)
Received:2024-09-02
Accepted:2024-12-13
Online:2025-03-28
Published:2025-03-28
Contact:
XIONG Ping, E-mail: xiong_ping_xp@163.com.Supported by:摘要:
目的·基于超声评分参数及临床指标,构建鉴别原发性干燥综合征(primary Sjὅgren′s syndrome,PSS)与免疫球蛋白G4相关唾液腺炎(immunoglobulin G4-related sialadenitis,IgG4-RS)列线图并评估其性能。方法·回顾性选择2018年1月—2023年12月就诊于上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院的PSS患者141例和IgG4-RS患者31例。收集患者的超声评分参数,包括腮腺超声(parotid gland ultrasound,PGUS)评分、下颌下腺超声(submandibular gland ultrasound,SMGUS)评分、唾液腺超声(salivary gland ultrasound,SGUS)评分,及临床指标包括性别、年龄、抗SSB/La抗体、抗SSA/Ro60抗体、抗SSA/Ro52抗体、IgG、类风湿因子(rheumatoid factor,RF)。利用最小绝对收缩和选择算子(least absolute shrinkage and selection operator,LASSO)回归筛选出最优超声评分参数和临床指标,建立PSS和IgG4-RS的鉴别诊断列线图。通过bootstrap法进行模型的内部验证。分别采用受试者操作特征(receiver operator characteristic,ROC)曲线、校准曲线及决策曲线分析(decision curve analysis,DCA)评价模型的区分度、校准度及其在临床中的应用价值。结果·通过LASSO回归算法,共筛选出性别、年龄、抗SSA/Ro60抗体、抗SSA/Ro52抗体、PGUS评分、SMGUS评分6个变量,根据该6个指标建立列线图模型。该列线图模型的ROC曲线显示曲线下面积(area under the curve,AUC)为0.976,具有较强的区分度。bootstrap法内部重复抽样1 000次进行验证,平均绝对误差0.018,校准曲线表明预测值与实测值良好吻合。DCA表明该列线图具有一定的临床实用性。结论·基于超声评分参数及临床指标建立的列线图,在鉴别PSS和IgG4-RS方面展示了良好的区分度和校准度,有望为临床鉴别诊断2种疾病及制定相应治疗方案提供参考。
中图分类号:
刘楚萱, 左佳鑫, 熊屏. 基于超声评分参数及临床指标的列线图鉴别原发性干燥综合征与IgG4相关唾液腺炎[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(3): 373-380.
LIU Chuxuan, ZUO Jiaxin, XIONG Ping. A nomogram based on ultrasound scoring parameters and clinical indicators for differentiating primary Sjὅgren′s syndrome from IgG4-related sialadenitis[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(3): 373-380.
| Characteristic | PSS (n=141) | IgG4-RS (n=31) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender/n (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Male | 9(6.4) | 15(48.4) | |
| Female | 132(93.6) | 16(51.6) | |
| Age/year | 49.28±13.19 | 59.71±11.40 | <0.001 |
| Anti-SSB/La antibody/n (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Negative | 91(64.5) | 31(100.0) | |
| Positive | 50(35.5) | 0(0) | |
| Anti-SSA/Ro60 antibody/n (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Negative | 29(20.6) | 31(100.0) | |
| Positive | 112(79.4) | 0(0) | |
| Anti-SSA/Ro52 antibody/n (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Negative | 24(17.0) | 30(96.8) | |
| Positive | 117(83.0) | 1(3.2) | |
| IgG/g·L-1 | 18.55±5.12 | 21.55±10.86 | 0.142 |
| RF/n (%) | 0.003 | ||
| Negative | 63(44.7) | 23(74.2) | |
| Positive | 78(55.3) | 8(25.8) | |
| PGUS/score | 13.40±4.17 | 7.32±3.49 | <0.001 |
| SMGUS/score | 11.67±3.74 | 16.32±4.11 | <0.001 |
| SGUS/score | 25.07±6.54 | 23.65±5.08 | 0.256 |
表1 PSS和IgG4-RS患者的临床特征和超声评分参数
Tab 1 Clinical indicators and ultrasound scoring parameters of PSS and IgG4-RS patients
| Characteristic | PSS (n=141) | IgG4-RS (n=31) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender/n (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Male | 9(6.4) | 15(48.4) | |
| Female | 132(93.6) | 16(51.6) | |
| Age/year | 49.28±13.19 | 59.71±11.40 | <0.001 |
| Anti-SSB/La antibody/n (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Negative | 91(64.5) | 31(100.0) | |
| Positive | 50(35.5) | 0(0) | |
| Anti-SSA/Ro60 antibody/n (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Negative | 29(20.6) | 31(100.0) | |
| Positive | 112(79.4) | 0(0) | |
| Anti-SSA/Ro52 antibody/n (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Negative | 24(17.0) | 30(96.8) | |
| Positive | 117(83.0) | 1(3.2) | |
| IgG/g·L-1 | 18.55±5.12 | 21.55±10.86 | 0.142 |
| RF/n (%) | 0.003 | ||
| Negative | 63(44.7) | 23(74.2) | |
| Positive | 78(55.3) | 8(25.8) | |
| PGUS/score | 13.40±4.17 | 7.32±3.49 | <0.001 |
| SMGUS/score | 11.67±3.74 | 16.32±4.11 | <0.001 |
| SGUS/score | 25.07±6.54 | 23.65±5.08 | 0.256 |
| Ultrasound/score | Intraobserver ICC (95%CI) | Interobserver ICC (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|
| PGUS | 0.944 (0.923‒0.959) | 0.927 (0.901‒0.947) |
| SMGUS | 0.943 (0.919‒0.959) | 0.918 (0.890‒0.939) |
| SGUS | 0.936 (0.903‒0.957) | 0.914 (0.879‒0.938) |
表2 超声评分参数的一致性分析
Tab 2 Agreement of ultrasound scoring parameters
| Ultrasound/score | Intraobserver ICC (95%CI) | Interobserver ICC (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|
| PGUS | 0.944 (0.923‒0.959) | 0.927 (0.901‒0.947) |
| SMGUS | 0.943 (0.919‒0.959) | 0.918 (0.890‒0.939) |
| SGUS | 0.936 (0.903‒0.957) | 0.914 (0.879‒0.938) |
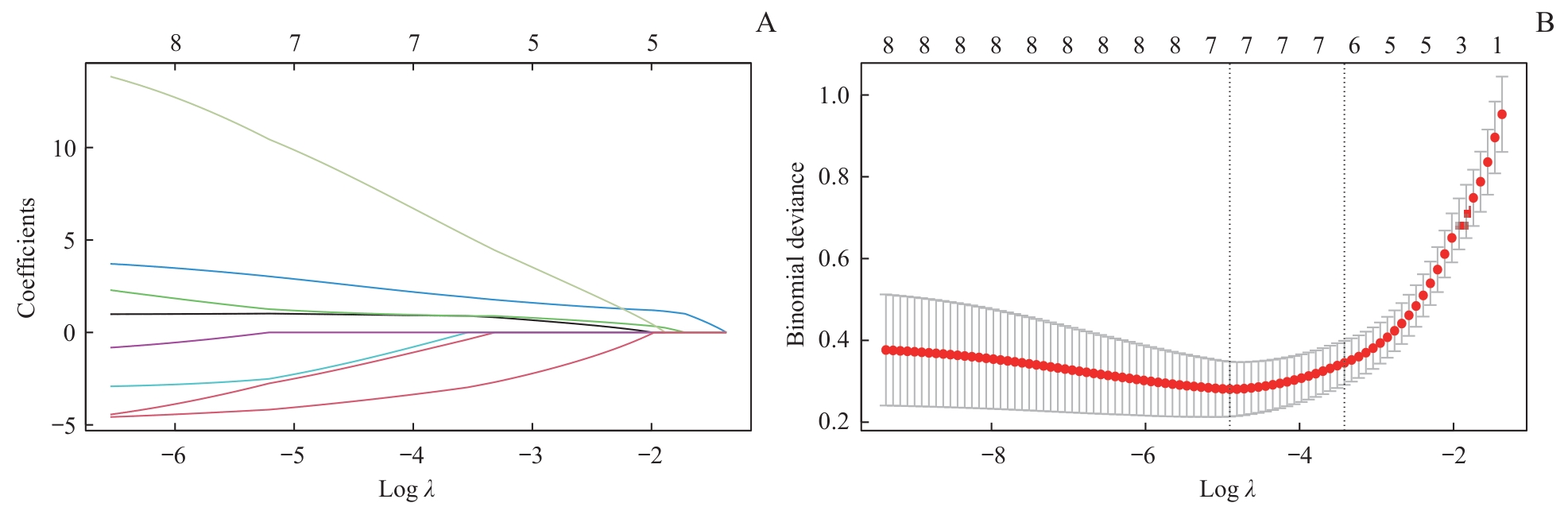
图1 通过LASSO回归算法筛选最优临床指标和超声参数Note: A. Path diagram of the LASSO coefficient. The ordinate represents the regression coefficients of different variables, while the lower abscissas shows the logarithm of the penalty coefficient (λ), and the upper abscissas shows the number of variables with non-zero coefficients corresponding to different log λ values. Different colored lines represent different variables. B. Cross-verification curve of LASSO regression. The ordinate represents binomial deviance. A smaller deviance indicates better model performance. The upper and lower abscissas are the same as in Figure A. The left dashed line in Figure B indicates the number of variables corresponding to the minimum λ (when the model fits best), and the number of variables is 7. The right dashed line indicates one standard error above the minimum λ (when the model performs relatively well), and the number of variables is 6.
Fig 1 Selection of clinical indicators and ultrasound data by LASSO regression
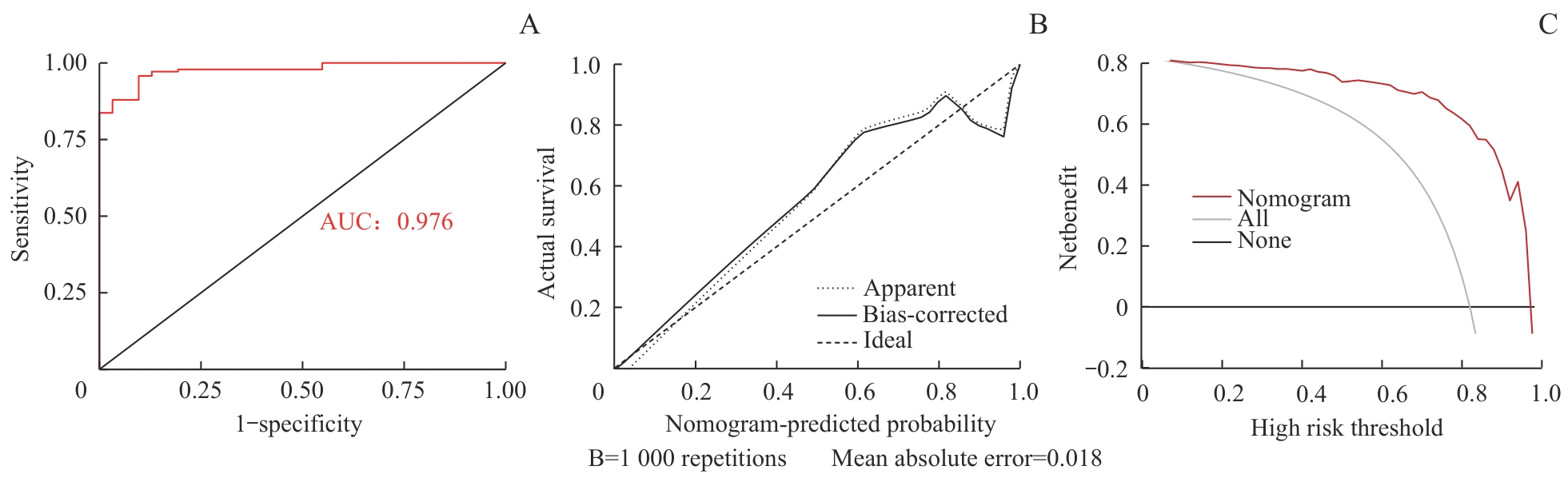
图3 列线图鉴别诊断的性能评估Note: A. ROC curve of the nomogram B. Calibration curve of the nomogram. The x-axis represents the predicted probabilities from the nomogram model, while the y-axis reflects the actual probabilities. The ideal line (black dashed line) indicates perfect calibration, while predicted probabilities align exactly with actual probabilities. The apparent line (gray dashed line) illustrates the observed performance of the nomogram model, while the bias-corrected line (black solid line) shows the model′s performance after 1 000 repetitions of bootstrapping. C. DCA curve of the nomogram. The x-axis represents different probability thresholds, while the y-axis shows the net benefit. The black horizontal line indicates no intervention for any patients, the gray solid line represents intervention for all patients, and the red solid line reflects interventions guided by the nomogram.
Fig 3 Performance evaluation of the nomogram for differential diagnosis
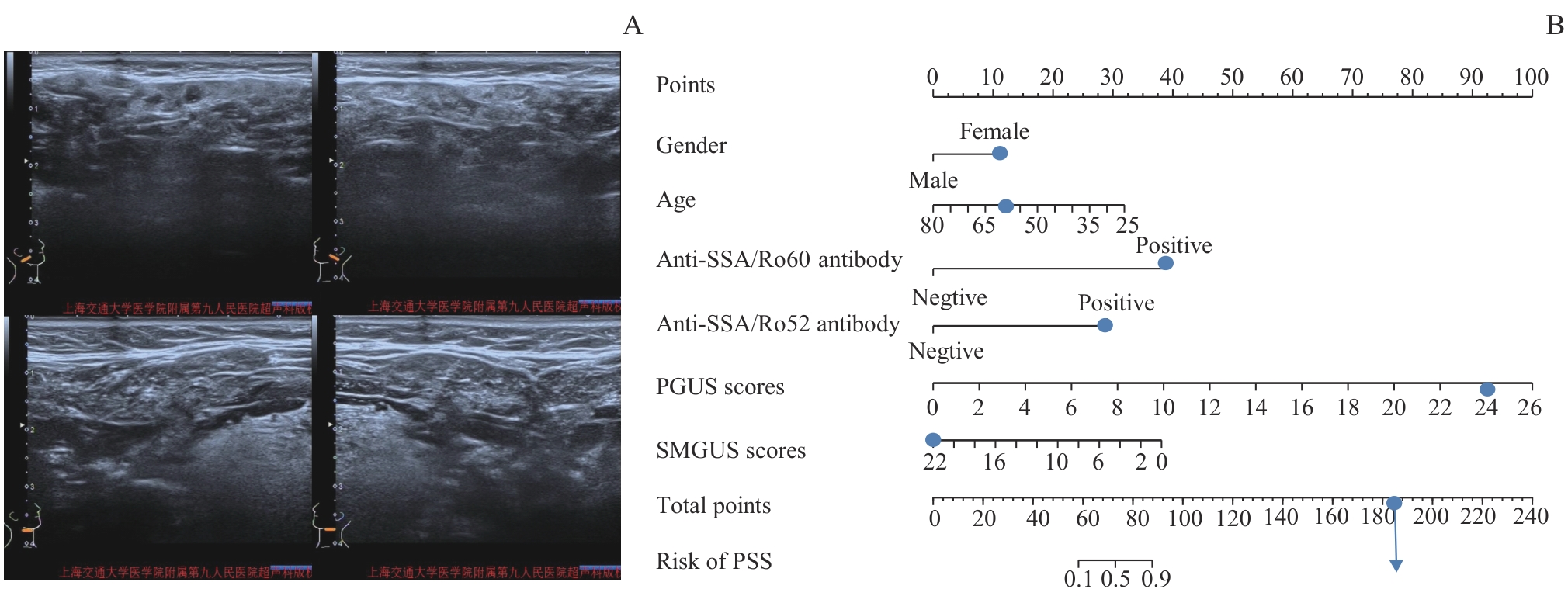
图4 列线图诊断PSS的实际应用Note: A 60-year-old female with PSS, positive for anti-SSA/Ro60 antibody and anti-SSA/Ro52 antibody. A. The ultrasound images of bilateral parotid gland showed a PGUS score of 24. The ultrasound images of bilateral submandibular gland showed a SMGUS score of 22. B. According to the nomogram, the prediction probability of PSS was greater than 90.00%.
Fig 4 Practical application of the nomogram in PSS diagnosis
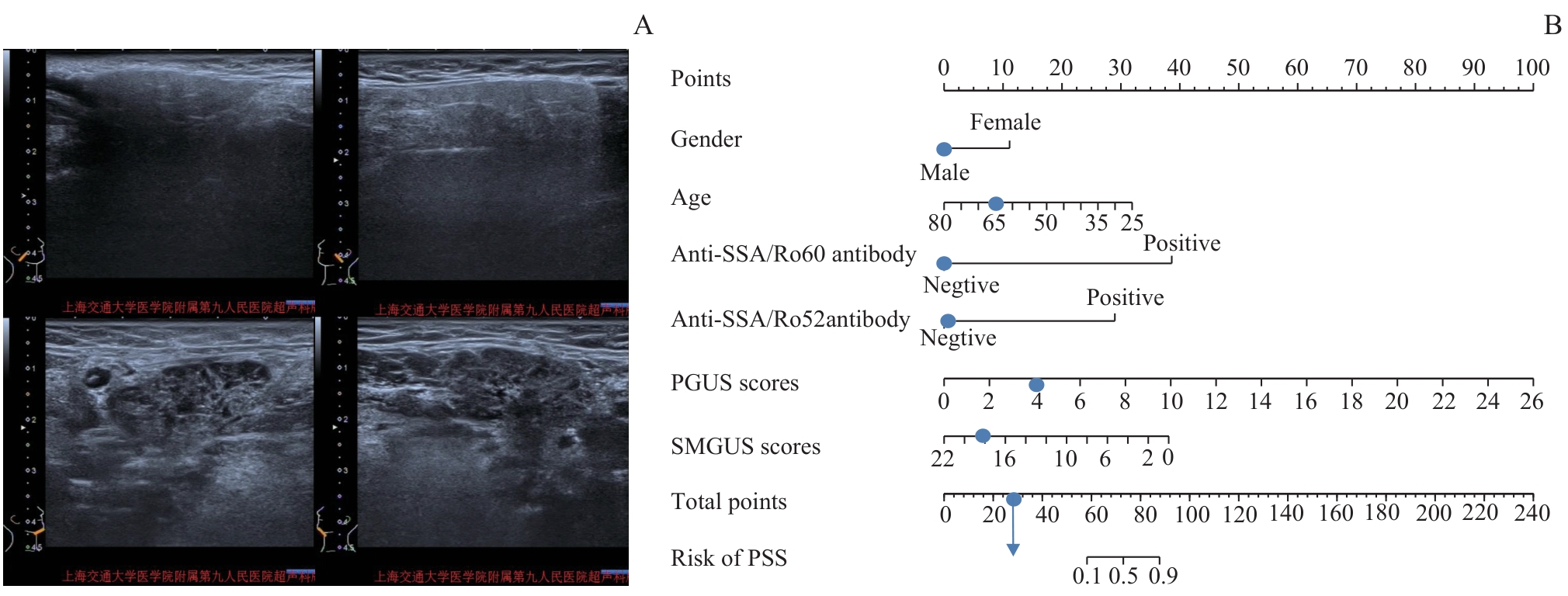
图5 列线图诊断IgG4-RS的实际应用Note: A 66-year-old male with IgG4-RS, negative for anti-SSA/Ro60 antibody and anti-SSA/Ro52 antibody. A. The ultrasound images of bilateral parotid gland showed a PGUS score of 4. The ultrasound images of bilateral submandibular gland showed a SMGUS score of 18. B. According to the nomogram, the prediction probability of PSS was less than 10.00%.
Fig 5 Practical application of the nomogram in IgG4-RS diagnosis
| 1 | 俞光岩. 多发性唾液腺肿大的鉴别诊断及处理[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 1-4. |
| YU G Y. Differential diagnosis and management of multiple salivary gland enlargements[J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 1-4. | |
| 2 | NARVÁEZ J, SÁNCHEZ-FERNÁNDEZ S Á, SEOANE-MATO D, et al. Prevalence of Sjögren′s syndrome in the general adult population in Spain: estimating the proportion of undiagnosed cases[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 10627. |
| 3 | BRITO-ZERÓN P, RAMOS-CASALS M, BOSCH X, et al. The clinical spectrum of IgG4-related disease[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2014, 13(12): 1203-1210. |
| 4 | LÖHR J M, VUJASINOVIC M, ROSENDAHL J, et al. IgG4-related diseases of the digestive tract[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 19(3): 185-197. |
| 5 | FRAGOULIS G E, ZAMPELI E, MOUTSOPOULOS H M. IgG4-related sialadenitis and sjögren′s syndrome[J]. Oral Dis, 2017, 23(2): 152-156. |
| 6 | SEROR R, NOCTURNE G, MARIETTE X. Current and future therapies for primary Sjögren syndrome[J]. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2021, 17(8): 475-486. |
| 7 | HONG X, ZHANG Y Y, LI W, et al. Treatment of immunoglobulin G4-related sialadenitis: outcomes of glucocorticoid therapy combined with steroid-sparing agents[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2018, 20(1): 12. |
| 8 | 杜晶晶, 董兴红, 高洁, 等. 原发性干燥综合征患者抗SSB与其他实验室参数相关性研究[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2023, 20(16): 2395-2399. |
| DU J J, DONG X H, GAO J, et al. Correlations between anti-SSB and other laboratory parameters in patients with primary Sjögren′s syndrome[J]. Laboratory Medicine and Clinic,2023, 20(16): 2395-2399. | |
| 9 | 罗盈, 文章雪, 王子霞, 等. IgG4水平及IgG4/IgG比值对IgG4相关性疾病的临床价值[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2024, 45(7): 804-808. |
| LUO Y, WEN Z X, WANG Z X, et al. Clinical value of IgG4 level and IgG4/IgG ratioin in IgG4-related diseases[J]. International Journal of Laboratory Medicine, 2024, 45(7): 804-808. | |
| 10 | 蒋佳纯, 许世豪, 王晓冰, 等. 涎腺超声评分联合血清学指标诊断原发性干燥综合征的临床价值[J]. 中国现代医生, 2021, 59(31): 131-134, 193. |
| JIANG J C, XU S H, WANG X B, et al. Clinical value of salivary gland ultrasound scoring combined with serological indicators in diagnosis of primary sjögren′s syndrome[J]. China Modern Doctor, 2021, 59(31): 131-134, 193. | |
| 11 | CULVER L, SADLER R, SIMPSON D, et al. Elevated serum IgG4 levels in diagnosis, treatment response, organ involvement, and relapse in a prospective IgG4-related disease UK cohort[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2016, 111(5): 733-743. |
| 12 | 吴海兰, 王婧玲, 陈莉. 唾液腺超声评分系统在干燥综合征诊断中的应用进展[J]. 中国医学影像学杂志, 2022, 30(11): 1188-1191, 1196. |
| WU H L, WANG J L, CHEN L. Application progress of salivary gland ultrasound scoring system in Sjögren′s syndrome[J].Chinese Journal of Medical Imaging, 2022, 30(11): 1188-1191, 1196. | |
| 13 | 刘杨, 程昉, 王艳玲, 等. 涎腺超声对原发性干燥综合征的诊断和评估价值[J]. 中华临床免疫和变态反应杂志, 2021, 15(5): 528-533. |
| LIU Y, CHEN F, WANG Y L, et al. Diagnostic and evaluation value of salivary gland ultrasonography in primary Sjögren′s syndrome[J]. Chinese Journal of Allergy & Clinical Immunology, 2021, 15(5): 528-533. | |
| 14 | 宁晓然, 王子乔, 张珊珊, 等. 超声评分系统在IgG4相关涎腺炎评估中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6): 1032-1035. |
| NING X R, WANG Z Q, ZHANG S S, et al. Application of ultrasonography scoring system in the assessment of IgG4-related sialadenitis[J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 1032-1035. | |
| 15 | NEGRINI S, EMMI G, GRECO M, et al. Sjögren′s syndrome: a systemic autoimmune disease[J]. Clin Exp Med, 2022, 22(1): 9-25. |
| 16 | UMEHARA H, OKAZAKI K, MASAKI Y, et al. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), 2011[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2012, 22(1): 21-30. |
| 17 | HOČEVAR A, AMBROŽIČ A, ROZMAN B, et al. Ultrasonographic changes of major salivary glands in primary Sjögren′s syndrome. Diagnostic value of a novel scoring system[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2005, 44(6): 768-772. |
| 18 | KOO T K, LI M Y. A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research[J]. J Chiropr Med, 2016, 15(2): 155-163. |
| 19 | ALENZI F, ALQAHTANI B, ALHAMAD E H, et al. Fatigue in Saudi patients with primary sjögren′s syndrome and its correlation with disease characteristics and outcome measures: a cross-sectional study[J]. Open Access Rheumatol, 2020, 12: 303-308.. |
| 20 | ZEHRFELD N, ABELMANN M, BENZ S, et al. Primary Sjögren′s syndrome independently promotes premature subclinical atherosclerosis[J]. RMD Open, 2024, 10(2): e003559. |
| 21 | MULLER R, EBBO M, HABERT P, et al. Thoracic manifestations of IgG4-related disease[J]. Respirology, 2023, 28(2): 120-131. |
| 22 | HONG X, LI W, XIE X Y, et al. Differential diagnosis of IgG4-related sialadenitis, primary Sjögren syndrome, and chronic obstructive submandibular sialadenitis[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2017, 55(2): 179-184. |
| 23 | CONTICINI E, D′ALESSANDRO R, BARDELLI M, et al. Routine IgG4 staining in minor salivary gland biopsy in a cohort of Italian Caucasian patients suffering from xerostomia[J]. Reumatologia, 2022, 60(1): 12-15. |
| 24 | 范文强, 吴洁, 马玲, 等. 抗SSA抗体、抗SSB抗体、抗α-胞衬蛋白抗体联合检测在干燥综合征诊断中价值探讨[J]. 中华生物医学工程杂志, 2017, 23(3): 239-243. |
| FAN W Q, WU J, MA L, et al. Value of combined detection of SSA antibody, anti-SSB antibody, and anti-α-fodrin antibody in diagnosis of Sjögren′s syndrome[J]. Chinese Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2017, 23(3): 239-243. | |
| 25 | 喻晓雯, 王琴, 冯婧, 等. 原发性干燥综合征的自身抗体研究进展[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2018, 34(2): 301-305. |
| YU X W, WANG Q, FENG J, et al. Advances in research on autoantibodies of primary sjögren′s syndrome[J]. Chinese Journal of Immunology, 2018, 34(2): 301-305. | |
| 26 | ABDEL RAZEK A A K, MUKHERJI S. Imaging of sialadenitis[J]. Neuroradiol J, 2017, 30(3): 205-215. |
| 27 | MOSSEL E, VAN GINKEL M S, HAACKE E A, et al. Histopathology, salivary flow and ultrasonography of the parotid gland: three complementary measurements in primary Sjögren′s syndrome[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2022, 61(6): 2472-2482. |
| 28 | ZHOU M Z, LIU Y Y, ZHANG S S, et al. Diagnostic value of a novel salivary gland ultrasound scoring system in IgG4-related sialadenitis[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2025, 64(2): 747-755. |
| [1] | 陈蓉, 张锰, 朱荻绮, 郭颖, 沈捷. 基于抗中性粒细胞胞质抗体的列线图模型对川崎病患儿并发冠状动脉病变风险的预测作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(4): 459-467. |
| [2] | 敦译霆, 赵婧, 冯成领, 李行健, 崔迪, 韩邦旻. 机器人辅助腹腔镜根治性前列腺切除术后患者尿失禁的在线风险计算器和列线图预测模型[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(10): 1361-1371. |
| [3] | 陆佳萍, 刘醒, 张林杉, 赵琳, 张敏, 李小英, 刘玥隽. 腹部脂肪面积与2型糖尿病患者胰岛β细胞第一时相分泌功能的关系[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(1): 42-50. |
| [4] | 姚莉, 田沃土, 曹立. 以神经系统损伤为首发症状的2例原发性干燥综合征报道[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(6): 795-800. |
| [5] | 杨婧偊, 陈留宝, 王康太, 杨兴智, 于海涛. 基于实验室指标的系统性红斑狼疮鉴别诊断列线图的构建及评估[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(2): 204-211. |
| [6] | 邓青松, 张长青, 陶诗聪. 烟酰胺代谢相关基因与骨关节炎的关系探索[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(2): 145-160. |
| [7] | 闫文月, 李强. 发热伴血小板减少综合征与肾综合征出血热的诊断与鉴别诊断的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(11): 1457-1462. |
| [8] | 薛淋淋, 李秉翰, 常丽仙, 李卫昆, 刘春云, 刘立. 丙型病毒性肝炎肝硬化失代偿期患者发生细菌感染的列线图预测模型构建及评价[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(1): 52-60. |
| [9] | 邹弋华, 彭婕, 赵培泉. 先天性视盘凹陷性异常的临床特征与治疗研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(2): 230-234. |
| [10] | 王晔恺, 陈位, 杨颍辉, 吴静泽, 王和平, 姚燕珍, 鲍舟君. 骨折后手术患者异位骨化风险的nomogram临床评分系统的建立[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(2): 166-172. |
| [11] | 徐莹, 褚以忞, 杨大明, 李吉, 张海芹, 彭海霞. 基于差异表达基因组合构建高度微卫星不稳定结直肠癌转移预测模型[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(9): 1197-1206. |
| [12] | 于洁, 李凡. 超声造影应用于诊断膀胱良恶性肿瘤的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(3): 396-399. |
| [13] | 刘芳芳, 包关水, 闫梦侠. 基于列线图的原发性头痛辅助决策模型的构建[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(10): 1323-1329. |
| [14] | 吕恒宇,黄 晨,夏 翔,赵 刚. 预测根治性胃癌切除术后并发症危险因素的列线图模型的建立[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(7): 894-900. |
| [15] | 何春明,尹 航,唐 健,丁一宗,傅于捷,赵晓菁. 基于SEER数据库的老年肺癌术后患者预后模型构建与内部验证[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(11): 1554-1561. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||