
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 459-467.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2025.04.008
收稿日期:2024-08-05
接受日期:2024-12-18
出版日期:2025-04-28
发布日期:2025-04-21
通讯作者:
沈 捷,主任医师,博士;电子信箱:she6nt@163.com。作者简介:陈 蓉(1999—),女,住院医师,硕士;电子信箱:rong1014@sjtu.edu.cn。
CHEN Rong, ZHANG Meng, ZHU Diqi, GUO Ying, SHEN Jie( )
)
Received:2024-08-05
Accepted:2024-12-18
Online:2025-04-28
Published:2025-04-21
Contact:
SHEN Jie, E-mail: she6t@163.com。摘要:
目的·评估抗中性粒细胞胞质抗体(anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody,ANCA)对川崎病(Kawasaki disease,KD)患儿并发冠状动脉病变(coronary artery lesion,CAL)的预测价值。方法·回顾性收集2018年1月至2024年5月上海交通大学医学院附属上海儿童医学中心收治的340例KD患儿的临床资料,按7∶3的比例随机分为训练集(n=237)和验证集(n=103)。通过单因素分析、最小绝对收缩和选择算法(least absolute shrinkage and selection operator,LASSO)筛选出CAL的危险因素,并将其纳入多因素Logistic回归分析,构建列线图预测模型。分别采用受试者操作特征(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)曲线、校准曲线及Hosmer-Lemeshow拟合优度检验、决策曲线分析(decision curve analysis,DCA)评价模型的区分度、校准度和临床适用性。根据Logistic回归方程中的自变量系数对各变量赋分,得到一个预测评分系统,并将其与目前3个常用评分系统(Kobayashi评分、Egami评分和Sano评分)的预测效能进行比较。结果·男性、低白蛋白血症、ANCA阳性和静脉注射免疫球蛋白抵抗是KD患儿发生CAL的危险因素,据此构建列线图预测模型。模型在训练集和验证集中的ROC曲线下面积分别为0.747(95%CI 0.667~0.821)和0.645(95%CI 0.500~0.794),表明模型预测效能良好;模型经校准曲线和Hosmer-Lemeshow拟合优度检验(训练集χ2 =5.105,P=0.746;验证集χ2 =13.549,P=0.094)验证,预测准确性良好;DCA显示模型具有一定的临床适用性。根据Logistic回归方程系数建立CAL的预测评分体系,与Kobayashi评分、Egami评分、Sano评分模型相比,其灵敏度(58.4%)和特异度(78.7%)均较高。结论·研究基于ANCA建立了一个可有效预测KD患儿发生CAL风险的评分模型,可为临床上早期识别高危患儿、制定个性化治疗方案和管理策略提供参考。
中图分类号:
陈蓉, 张锰, 朱荻绮, 郭颖, 沈捷. 基于抗中性粒细胞胞质抗体的列线图模型对川崎病患儿并发冠状动脉病变风险的预测作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(4): 459-467.
CHEN Rong, ZHANG Meng, ZHU Diqi, GUO Ying, SHEN Jie. Nomogram for predicting the risk of coronary artery lesions in patients with Kawasaki disease based on anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(4): 459-467.
| Variable | Training set (n=237) | Validation set (n=103) | P value① | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAL (n=58) | NCAL (n=179) | P value | CAL (n=19) | NCAL (n=84) | P value | |||
| Gender/n(%) | <0.001 | 0.682 | 0.897 | |||||
| Male | 45 (77.59) | 85 (47.49) | 12 (63.16) | 46 (54.76) | ||||
| Female | 13 (22.41) | 94 (52.51) | 7 (36.84) | 38 (45.24) | ||||
| Age/month | 30.00 (12.25,47.50) | 33.00 (18.00,56.50) | 0.148 | 29.00 (15.00,49.50) | 31.00 (18.75,52.50) | 0.702 | 0.781 | |
| Fever duration before IVIG/n(%) | 0.228 | 0.316 | 0.941 | |||||
| <5 d | 13 (22.41) | 26 (14.53) | 5 (26.32) | 13 (15.48) | ||||
| ≥5 d | 45 (77.59) | 153 (85.47) | 14 (73.68) | 71 (84.52) | ||||
| CRP/(mg·L-1) | 64.80 (37.95,103.03) | 63.40 (34.90,95.10) | 0.601 | 81.70 (51.60,109.70) | 61.60 (39.78,101.92) | 0.161 | 0.420 | |
| NEUT%/% | 66.26 (55.21,76.89) | 65.70 (53.70,76.78) | 0.895 | 68.21 (55.82,80.45) | 67.32 (52.11,74.67) | 0.280 | 0.933 | |
| HGB/(g·L-1) | 107.00 (101.00,115.00) | 110.00 (103.00,117.00) | 0.209 | 107.00 (101.00,112.50) | 110.50 (102.75,116.00) | 0.139 | 0.462 | |
| PLT/(×109·L-1) | 332.00 (227.50,452.50) | 336.00 (259.00,416.00) | 0.702 | 253.00 (219.50,338.00) | 329.50 (262.75,417.00) | 0.038 | 0.170 | |
| Na+/(mmol·L-1) | 135.60 (134.00,137.25) | 137.00 (135.00,138.65) | 0.010 | 136.00 (133.80,137.55) | 136.55 (135.00,138.15) | 0.190 | 0.922 | |
| ESR/(mm·h-1) | 65.50 (44.75,75.00) | 65.00 (48.00,81.00) | 0.531 | 66.00 (54.50,74.00) | 71.00 (54.50,87.00) | 0.655 | 0.120 | |
| Ferr/(ng·mL-1) | 171.25 (110.67,270.36) | 175.52 (130.20,241.20) | 0.712 | 252.60 (152.65,291.90) | 167.55 (136.88,272.72) | 0.241 | 0.177 | |
| ALT/(IU·L-1) | 27.50 (18.00,48.75) | 24.00 (15.50,59.50) | 0.356 | 30.00 (20.00,134.50) | 28.00 (18.75,60.00) | 0.540 | 0.215 | |
| AST/(IU·L-1) | 33.00 (27.00,47.75) | 33.00 (28.00,46.50) | 0.731 | 33.00 (28.00,70.00) | 34.00 (26.00,42.50) | 0.507 | 0.579 | |
| ALB/(g·L-1) | 34.62±4.36 | 3 6.66±3.98 | 0.002 | 35.22±2.87 | 36.04±4.59 | 0.326 | 0.586 | |
| TBIL/(μmol·L-1) | 8.80 (6.12,12.15) | 8.20 (5.60,11.45) | 0.352 | 9.10 (4.85,24.05) | 8.75 (6.65,11.72) | 0.953 | 0.264 | |
| NT-proBNP/(pg·mL-1) | 652.00 (185.50,2460.25) | 302.00 (104.00,984.00) | 0.014 | 291.00 (94.50,1528.50) | 406.00 (186.50,1189.75) | 0.792 | 0.691 | |
| IL-6/(pg·mL-1) | 74.51 (25.09,246.56) | 71.00 (33.11,169.65) | 0.402 | 74.39 (35.95,150.71) | 80.64 (24.84,167.78) | 0.875 | 0.905 | |
| Count of CD3+CD4+/n | 1 173.84 (694.43,1 779.17) | 1 183.81 (635.24,2 016.62) | 0.857 | 862.66 (396.05,1 269.99) | 1 110.01 (670.87,2 006.53) | 0.208 | 0.724 | |
| ANA/n(%) | 0.934 | 0.547 | 1.000 | |||||
| Positive | 12 (20.69) | 40 (22.35) | 5 (26.32) | 17 (20.24) | ||||
| Negative | 46 (79.31) | 139 (77.65) | 14 (73.68) | 67 (79.76) | ||||
| ANCA/n(%) | 0.007 | 0.002 | 0.946 | |||||
| Positive | 8 (13.79) | 6 (3.35) | 5 (36.32) | 2 (2.38) | ||||
| Negative | 50 (86.21) | 173 (96.65) | 14 (73.68) | 82 (97.62) | ||||
| IVIG resistance/n(%) | 0.008 | 0.031 | 0.846 | |||||
| Yes | 14 (24.14) | 17 (9.50) | 6 (31.58) | 9 (10.71) | ||||
| No | 44 (75.86) | 162 (90.50) | 13 (68.42) | 75 (89.29) | ||||
表1 训练集和验证集基线资料比较
Tab1 Comparison of baseline characteristics between the training set and validation set
| Variable | Training set (n=237) | Validation set (n=103) | P value① | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAL (n=58) | NCAL (n=179) | P value | CAL (n=19) | NCAL (n=84) | P value | |||
| Gender/n(%) | <0.001 | 0.682 | 0.897 | |||||
| Male | 45 (77.59) | 85 (47.49) | 12 (63.16) | 46 (54.76) | ||||
| Female | 13 (22.41) | 94 (52.51) | 7 (36.84) | 38 (45.24) | ||||
| Age/month | 30.00 (12.25,47.50) | 33.00 (18.00,56.50) | 0.148 | 29.00 (15.00,49.50) | 31.00 (18.75,52.50) | 0.702 | 0.781 | |
| Fever duration before IVIG/n(%) | 0.228 | 0.316 | 0.941 | |||||
| <5 d | 13 (22.41) | 26 (14.53) | 5 (26.32) | 13 (15.48) | ||||
| ≥5 d | 45 (77.59) | 153 (85.47) | 14 (73.68) | 71 (84.52) | ||||
| CRP/(mg·L-1) | 64.80 (37.95,103.03) | 63.40 (34.90,95.10) | 0.601 | 81.70 (51.60,109.70) | 61.60 (39.78,101.92) | 0.161 | 0.420 | |
| NEUT%/% | 66.26 (55.21,76.89) | 65.70 (53.70,76.78) | 0.895 | 68.21 (55.82,80.45) | 67.32 (52.11,74.67) | 0.280 | 0.933 | |
| HGB/(g·L-1) | 107.00 (101.00,115.00) | 110.00 (103.00,117.00) | 0.209 | 107.00 (101.00,112.50) | 110.50 (102.75,116.00) | 0.139 | 0.462 | |
| PLT/(×109·L-1) | 332.00 (227.50,452.50) | 336.00 (259.00,416.00) | 0.702 | 253.00 (219.50,338.00) | 329.50 (262.75,417.00) | 0.038 | 0.170 | |
| Na+/(mmol·L-1) | 135.60 (134.00,137.25) | 137.00 (135.00,138.65) | 0.010 | 136.00 (133.80,137.55) | 136.55 (135.00,138.15) | 0.190 | 0.922 | |
| ESR/(mm·h-1) | 65.50 (44.75,75.00) | 65.00 (48.00,81.00) | 0.531 | 66.00 (54.50,74.00) | 71.00 (54.50,87.00) | 0.655 | 0.120 | |
| Ferr/(ng·mL-1) | 171.25 (110.67,270.36) | 175.52 (130.20,241.20) | 0.712 | 252.60 (152.65,291.90) | 167.55 (136.88,272.72) | 0.241 | 0.177 | |
| ALT/(IU·L-1) | 27.50 (18.00,48.75) | 24.00 (15.50,59.50) | 0.356 | 30.00 (20.00,134.50) | 28.00 (18.75,60.00) | 0.540 | 0.215 | |
| AST/(IU·L-1) | 33.00 (27.00,47.75) | 33.00 (28.00,46.50) | 0.731 | 33.00 (28.00,70.00) | 34.00 (26.00,42.50) | 0.507 | 0.579 | |
| ALB/(g·L-1) | 34.62±4.36 | 3 6.66±3.98 | 0.002 | 35.22±2.87 | 36.04±4.59 | 0.326 | 0.586 | |
| TBIL/(μmol·L-1) | 8.80 (6.12,12.15) | 8.20 (5.60,11.45) | 0.352 | 9.10 (4.85,24.05) | 8.75 (6.65,11.72) | 0.953 | 0.264 | |
| NT-proBNP/(pg·mL-1) | 652.00 (185.50,2460.25) | 302.00 (104.00,984.00) | 0.014 | 291.00 (94.50,1528.50) | 406.00 (186.50,1189.75) | 0.792 | 0.691 | |
| IL-6/(pg·mL-1) | 74.51 (25.09,246.56) | 71.00 (33.11,169.65) | 0.402 | 74.39 (35.95,150.71) | 80.64 (24.84,167.78) | 0.875 | 0.905 | |
| Count of CD3+CD4+/n | 1 173.84 (694.43,1 779.17) | 1 183.81 (635.24,2 016.62) | 0.857 | 862.66 (396.05,1 269.99) | 1 110.01 (670.87,2 006.53) | 0.208 | 0.724 | |
| ANA/n(%) | 0.934 | 0.547 | 1.000 | |||||
| Positive | 12 (20.69) | 40 (22.35) | 5 (26.32) | 17 (20.24) | ||||
| Negative | 46 (79.31) | 139 (77.65) | 14 (73.68) | 67 (79.76) | ||||
| ANCA/n(%) | 0.007 | 0.002 | 0.946 | |||||
| Positive | 8 (13.79) | 6 (3.35) | 5 (36.32) | 2 (2.38) | ||||
| Negative | 50 (86.21) | 173 (96.65) | 14 (73.68) | 82 (97.62) | ||||
| IVIG resistance/n(%) | 0.008 | 0.031 | 0.846 | |||||
| Yes | 14 (24.14) | 17 (9.50) | 6 (31.58) | 9 (10.71) | ||||
| No | 44 (75.86) | 162 (90.50) | 13 (68.42) | 75 (89.29) | ||||
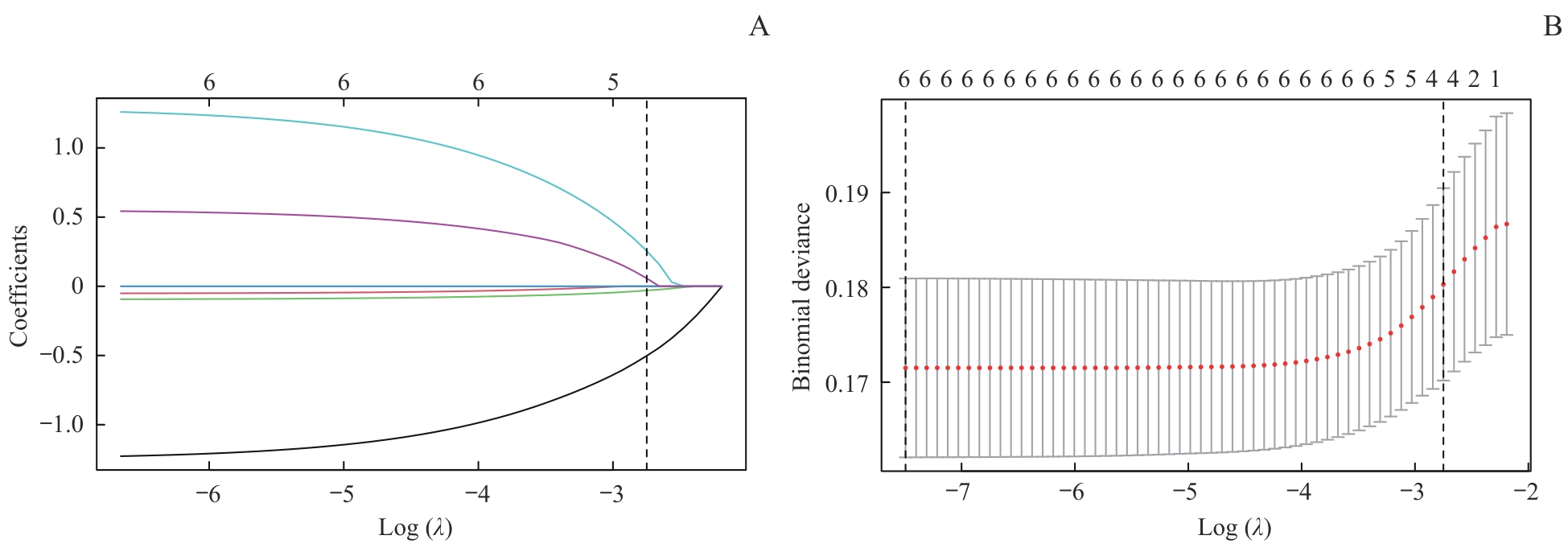
图2 训练集的LASSO回归模型风险因素筛选Note: A. LASSO coefficient profiles for 6 variables. B. A 9-fold cross-validation used in the LASSO regression. Dotted vertical lines represent the optimal values, determined using the minimum criteria (left dotted line) and the 1 standard error criterion (right dotted line). λmin=0.000 6, λ1se=0.064 0.
Fig 2 Risk factors selection using a LASSO regression model in the training set
| Variable | B | SE | P value | OR | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | -1.259 | 0.362 | 0.001 | 0.283 | 0.135‒0.564 |
| ALB | -0.115 | 0.041 | 0.005 | 0.891 | 0.820‒0.964 |
| ANCA | 1.292 | 0.620 | 0.037 | 3.639 | 1.078‒12.740 |
| IVIG resistance | 0.653 | 0.437 | 0.135 | 1.922 | 0.800‒4.496 |
表2 训练集KD患儿合并CAL影响因素的Logistic回归分析
Tab 2 Logistic regression analysis of factors associated with CALs in patients with KD in the training set
| Variable | B | SE | P value | OR | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | -1.259 | 0.362 | 0.001 | 0.283 | 0.135‒0.564 |
| ALB | -0.115 | 0.041 | 0.005 | 0.891 | 0.820‒0.964 |
| ANCA | 1.292 | 0.620 | 0.037 | 3.639 | 1.078‒12.740 |
| IVIG resistance | 0.653 | 0.437 | 0.135 | 1.922 | 0.800‒4.496 |
| Variable | B | SE | P value | OR | 95%CI | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | -0.972 | 0.299 | 0.001 | 0.378 | 0.206‒0.670 | 5 |
| ALB<35 g·L-1 | 0.687 | 0.279 | 0.014 | 1.986 | 1.149‒3.441 | 3 |
| ANCA positivity | 1.550 | 0.507 | 0.002 | 4.711 | 1.758‒13.140 | 8 |
| IVIG resistance | 0.792 | 0.365 | 0.030 | 2.208 | 1.064‒4.481 | 4 |
表3 KD合并CAL影响因素的Logistic回归分析
Tab 3 Logistic regression analysis of factors associated with CALs in patients with KD
| Variable | B | SE | P value | OR | 95%CI | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | -0.972 | 0.299 | 0.001 | 0.378 | 0.206‒0.670 | 5 |
| ALB<35 g·L-1 | 0.687 | 0.279 | 0.014 | 1.986 | 1.149‒3.441 | 3 |
| ANCA positivity | 1.550 | 0.507 | 0.002 | 4.711 | 1.758‒13.140 | 8 |
| IVIG resistance | 0.792 | 0.365 | 0.030 | 2.208 | 1.064‒4.481 | 4 |
| Scoring model | AUC | 95%CI | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | Youden index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New score | 0.716 | 0.665‒0.764 | 0.584 | 0.787 | 44.6 | 86.6 | 0.372 |
| Kobayashi score | 0.549 | 0.494‒0.602 | 0.260 | 0.840 | 32.3 | 79.5 | 0.100 |
| Egami score | 0.556 | 0.502‒0.610 | 0.455 | 0.658 | 28.0 | 80.5 | 0.113 |
| Sano score | 0.537 | 0.483‒0.591 | 0.546 | 0.510 | 24.6 | 79.3 | 0.055 |
表4 4种评分系统对KD合并CAL的预测性能比较
Tab 4 Comparison of the predictive performance of 4 scoring systems for KD combined with CALs
| Scoring model | AUC | 95%CI | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | Youden index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New score | 0.716 | 0.665‒0.764 | 0.584 | 0.787 | 44.6 | 86.6 | 0.372 |
| Kobayashi score | 0.549 | 0.494‒0.602 | 0.260 | 0.840 | 32.3 | 79.5 | 0.100 |
| Egami score | 0.556 | 0.502‒0.610 | 0.455 | 0.658 | 28.0 | 80.5 | 0.113 |
| Sano score | 0.537 | 0.483‒0.591 | 0.546 | 0.510 | 24.6 | 79.3 | 0.055 |
| 1 | 中华医学会儿科学分会心血管学组, 中华医学会儿科学分会风湿学组,中华医学会儿科学分会免疫学组,等. 川崎病诊断和急性期治疗专家共识[J]. 中华儿科杂志,2022, 60(1): 6-13. |
| The Subspecialty Group of Cardiology, the Society of Pediatrics, Chinese Medical Association; the Subspecialty Group of Rheumatology, the Society of Pediatrics, Chinese Medical Association; the Subspecialty Group of Immunology, the Society of Pediatrics, Chinese Medical Association, et al. The expert consensus on diagnosis and acute-phase treatment of Kawasaki disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Pediatrics, 2022, 60(1): 6-13. | |
| 2 | de GRAEFF N, GROOT N, OZEN S, et al. European consensus-based recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of Kawasaki disease: the SHARE initiative[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2019, 58(4): 672-682. |
| 3 | JCS Joint Working Group. Guidelines for diagnosis and management of cardiovascular sequelae in Kawasaki disease (JCS 2013), digest version[J]. Circ J, 2014, 78(10): 2521-2562. |
| 4 | Newburger J W, Takahashi M, Burns J C. Kawasaki disease[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2016, 67(14): 1738-1749. |
| 5 | MCCRINDLE B W, ROWLEY A H, NEWBURGER J W, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a scientific statement for health professionals from the American heart association[J]. Circulation, 2017, 135(17): e927-e999. |
| 6 | BROGAN P, BURNS J C, CORNISH J, et al. Lifetime cardiovascular management of patients with previous Kawasaki disease[J]. Heart, 2020, 106(6): 411-420. |
| 7 | SCHULTE-PELKUM J, RADICE A, NORMAN G L, et al. Novel clinical and diagnostic aspects of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies[J]. J Immunol Res, 2014, 2014: 185416. |
| 8 | 中华医学会儿科学分会心血管学组, 中华医学会儿科学分会免疫学组. 川崎病冠状动脉病变的临床处理建议[J]. 中华儿科杂志, 2012, 50(10): 746-749. |
| The Subspecialty Group of Cardiology, the Society of Pediatrics, Chinese Medical Association; the Subspecialty Group of Rheumatology, the Society of Pediatrics, Chinese Medical Association. Recommendations for clinical management of Kawasaki disease with coronary arterial lesions[J]. Chinese Journal of Pediatrics, 2012, 50(10): 746-749. | |
| 9 | KOBAYASHI T, INOUE Y, TAKEUCHI K, et al. Prediction of intravenous immunoglobulin unresponsiveness in patients with Kawasaki disease[J]. Circulation, 2006, 113(22): 2606-2612. |
| 10 | EGAMI K, MUTA H, ISHII M, et al. Prediction of resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in patients with Kawasaki disease[J]. J Pediatr, 2006, 149(2): 237-240. |
| 11 | SANO T, KUROTOBI S, MATSUZAKI K, et al. Prediction of non-responsiveness to standard high-dose gamma-globulin therapy in patients with acute Kawasaki disease before starting initial treatment[J]. Eur J Pediatr, 2007, 166(2): 131-137. |
| 12 | PILANIA R K, BHATTARAI D, SINGH S. Controversies in diagnosis and management of Kawasaki disease[J]. World J Clin Pediatr, 2018, 7(1): 27-35. |
| 13 | TIAN J, LV H T, AN X J, et al. Endothelial microparticles induce vascular endothelial cell injury in children with Kawasaki disease[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2016, 20(9): 1814-1818. |
| 14 | LINDQUIST M E, HICAR M D. B cells and antibodies in Kawasaki disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(8): E1834. |
| 15 | TAKAHASHI K, OHARASEKI T, YOKOUCHI Y. Pathogenesis of Kawasaki disease[J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 2011, 164(Supplement 1): 20-22. |
| 16 | del PRINCIPE D, PIETRAFORTE D, GAMBARDELLA L, et al. Pathogenetic determinants in Kawasaki disease: the haematological point of view[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2017, 21(4): 632-639. |
| 17 | 马乐, 杜忠东. 川崎病血管内皮细胞损伤机制的研究进展[J]. 中华儿科杂志, 2016, 54(2): 158-160. |
| MA L, DU Z D. Advances in the pathogenesis of vascular endothelial cells injury in Kawasaki disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Pediatrics, 2016, 54(2): 158-160. | |
| 18 | 中国医师协会风湿免疫科医师分会自身抗体检测专业委员会. 抗中性粒细胞胞浆抗体检测的临床应用专家共识[J].中华检验医学杂志, 2018, 41(9): 644-650. |
| The Committee of the Autoantibodies Detection of Rheumatology and Immunology Physicians Committee of Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Experts consensus on the clinical application of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies detection[J].Chinese Journal of Laboratory Medicine, 2018,41(9):644-650. | |
| 19 | LIBERAL R, MIELI-VERGANI G, VERGANI D. Clinical significance of autoantibodies in autoimmune hepatitis[J]. J Autoimmun, 2013, 46: 17-24. |
| 20 | 江志贵, 刘玲, 杨翠艳, 等. 抗中性粒细胞抗体在川崎病诊断中的价值[J]. 中国当代儿科杂志, 2012, 14(1): 45-47. |
| JIANG Z G, LIU L, YANG C Y, et al. Value of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody in diagnosis of Kawasaki disease[J].Chinese Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics, 2012, 14(1): 45-47. | |
| 21 | 刘坦, 孟晓峰, 杜世杰. 三种方法检测抗中性粒细胞胞浆抗体的比较分析[J]. 国际医药卫生导报, 2018, 24(4): 590-592. |
| LIU T, MENG X F, DU S J. Three methods for detecting antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies[J].International Medicine and Health Guildance News, 2018, 24(4): 590-592. | |
| 22 | van DER MOLEN R G, HAMANN D, JACOBS J F, et al. Anti-SSA antibodies are present in immunoglobulin preparations[J]. Transfusion, 2015, 55(4): 832-837. |
| 23 | BRIGHT P D, SMITH L, USHER J, et al. False interpretation of diagnostic serology tests for patients treated with pooled human immunoglobulin G infusions: a trap for the unwary[J]. Clin Med, 2015, 15(2): 125-129. |
| 24 | 赵建美, 王晓华. 川崎病患儿血清抗内皮细胞抗体和抗中性粒细胞胞浆抗体检测的临床意义[J]. 中国当代儿科杂志, 2014, 16(7): 740-744. |
| ZHAO J M, WANG X H. Clinical significance of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies and anti-endothelial cell antibodies in children with Kawasaki disease[J].Chinese Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics, 2014, 16(7): 740-744. | |
| 25 | RUAN Y, YE B, ZHAO X. Clinical characteristics of Kawasaki syndrome and the risk factors for coronary artery lesions in China[J]. Pediatr Infect Dis J, 2013, 32(10): e397-402. |
| 26 | PIAO J H, JIN L H, LV J, et al. Epidemiological investigation of Kawasaki disease in Jilin Province of China from 2000 to 2008[J]. Cardiol Young, 2010, 20(4): 426-432. |
| 27 | TAKEKOSHI N, KITANO N, TAKEUCHI T, et al. Analysis of age, sex, lack of response to intravenous immunoglobulin, and development of coronary artery abnormalities in children with Kawasaki disease in Japan[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2022, 5(6): e2216642. |
| 28 | KAYAPINAR O, OZDE C, KAYA A. Relationship between the reciprocal change in inflammation-related biomarkers (fibrinogen-to-albumin and hsCRP-to-albumin ratios) and the presence and severity of coronary slow flow[J]. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost, 2019, 25: 1076029619835383. |
| 29 | 张玉坤, 黄春华, 杨蕾, 等. 血清白蛋白、血沉、血小板/淋巴细胞比值、中性粒细胞/淋巴细胞比值与川崎病患儿冠脉病变程度的关系[J]. 中国医师杂志, 2023, 25(1): 23-27. |
| ZHANG Y K, HUANG C H, YANG L, et al. The relationship between albumin, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, platelet/lymphocyte ratio, neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio and the degree of coronary artery disease in children with Kawasaki disease[J]. Journal of Chinese Physician, 2023, 25(1): 23-27. | |
| 30 | ARQUES S. Human serum albumin in cardiovascular diseases[J]. Eur J Intern Med, 2018, 52: 8-12. |
| 31 | FUKAZAWA R, KOBAYASHI J, AYUSAWA M, et al. JCS/JSCS 2020 guideline on diagnosis and management of cardiovascular sequelae in Kawasaki disease[J]. Circ J, 2020, 84(8): 1348-1407. |
| 32 | XIE T, WANG Y, FU S, et al. Predictors for intravenous immunoglobulin resistance and coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease[J]. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J, 2017, 15(1): 17. |
| [1] | 陈佳莹, 褚以忞, 彭海霞. 结直肠癌无进展生存时间预测模型及影响因素研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(3): 324-334. |
| [2] | 刘楚萱, 左佳鑫, 熊屏. 基于超声评分参数及临床指标的列线图鉴别原发性干燥综合征与IgG4相关唾液腺炎[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(3): 373-380. |
| [3] | 敦译霆, 赵婧, 冯成领, 李行健, 崔迪, 韩邦旻. 机器人辅助腹腔镜根治性前列腺切除术后患者尿失禁的在线风险计算器和列线图预测模型[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(10): 1361-1371. |
| [4] | 陆佳萍, 刘醒, 张林杉, 赵琳, 张敏, 李小英, 刘玥隽. 腹部脂肪面积与2型糖尿病患者胰岛β细胞第一时相分泌功能的关系[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(1): 42-50. |
| [5] | 邓青松, 张长青, 陶诗聪. 烟酰胺代谢相关基因与骨关节炎的关系探索[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(2): 145-160. |
| [6] | 杨婧偊, 陈留宝, 王康太, 杨兴智, 于海涛. 基于实验室指标的系统性红斑狼疮鉴别诊断列线图的构建及评估[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(2): 204-211. |
| [7] | 田晓梵, 董怡, 楼文晖, 张琪, 邱艺杰, 左丹, 王文平. 基于超声剪切波弹性成像参数与临床风险因素的术后胰瘘改良预测模型[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(4): 437-444. |
| [8] | 冯佳丽, 彭宇, 段君凯. 川崎病相关微RNA的功能机制及生物标志物研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(2): 256-260. |
| [9] | 张锰, 崔青, 朱荻绮, 张玉奇, 钟玉敏, 沈捷. 川崎病合并冠状动脉病变患儿21例冠状动脉造影复查分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(12): 1535-1541. |
| [10] | 薛淋淋, 李秉翰, 常丽仙, 李卫昆, 刘春云, 刘立. 丙型病毒性肝炎肝硬化失代偿期患者发生细菌感染的列线图预测模型构建及评价[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(1): 52-60. |
| [11] | 夏坤健, 邓林林, 王琳. 乳腺癌化学治疗致肝损伤预测模型的构建及其评价[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(4): 502-509. |
| [12] | 王晔恺, 陈位, 杨颍辉, 吴静泽, 王和平, 姚燕珍, 鲍舟君. 骨折后手术患者异位骨化风险的nomogram临床评分系统的建立[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(2): 166-172. |
| [13] | 徐莹, 褚以忞, 杨大明, 李吉, 张海芹, 彭海霞. 基于差异表达基因组合构建高度微卫星不稳定结直肠癌转移预测模型[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(9): 1197-1206. |
| [14] | 岳犇, 王高明, 杨鹿笛, 崔然, 郁丰荣. 胃癌患者预后相关微RNA预测模型的构建及其应用价值探讨[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(11): 1436-1445. |
| [15] | 奚黎婷, 朱锦舟, 虞晨燕, 倪柳菁, 许春芳, 吴爱荣. 急性非静脉曲张性上消化道出血患者再出血预测模型和新型评分系统的构建[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(11): 1491-1497. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||