
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 52-60.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2023.01.007
薛淋淋1( ), 李秉翰1, 常丽仙2, 李卫昆2, 刘春云2, 刘立2(
), 李秉翰1, 常丽仙2, 李卫昆2, 刘春云2, 刘立2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-09-01
接受日期:2022-12-09
出版日期:2023-01-28
发布日期:2023-01-28
通讯作者:
刘立
E-mail:18860230076@163.com;liuli197210@163.com
作者简介:薛淋淋(1993—),女,硕士生;电子信箱:18860230076@163.com。
基金资助:
XUE Linlin1( ), LI Binghan1, CHANG Lixian2, LI Weikun2, LIU Chunyun2, LIU Li2(
), LI Binghan1, CHANG Lixian2, LI Weikun2, LIU Chunyun2, LIU Li2( )
)
Received:2022-09-01
Accepted:2022-12-09
Online:2023-01-28
Published:2023-01-28
Contact:
LIU Li
E-mail:18860230076@163.com;liuli197210@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的·探讨丙型病毒性肝炎(丙肝)肝硬化失代偿期患者发生细菌感染的影响因素,建立列线图预测模型并进行评价。方法·回顾分析昆明市第三人民医院肝病科2020年1月—2021年12月因丙肝肝硬化住院的失代偿期患者574例,以是否发生细菌感染分为细菌感染组和非细菌感染组。收集患者的一般资料、入院合并症及实验室指标。经单因素分析、最小绝对收缩和选择算子(least absolute shrinkage and selection operator,LASSO)回归筛选变量,采用多因素Logistic回归分析影响因素,据此构建列线图模型并进行验证。采用决策曲线及临床影响曲线(clinical impact curve,CIC)评估模型的临床实际应用价值。结果·纳入患者中28.4%(163/574)的患者发生细菌感染,共191个部位,以自发性细菌性腹膜炎(86/191)和肺部细菌感染(79/191)为主;共分离培养出病原菌78株,以肺炎克雷伯菌(15/78)和大肠埃希菌(15/78)为主。多因素Logistic回归分析显示年龄≥60岁[比值比(odds ratio,OR)=2.054,95%置信区间(confidence interval,CI) 1.104~3.822,P=0.023]、女性(OR=1.701,95%CI 1.112~2.602,P=0.014)、腹水(OR=2.386,95%CI 1.601~3.557,P=0.000)、近2周有创操作史(OR=2.605,95%CI 1.368~4.960,P=0.004)、住院时间≥2周(OR=1.629,95%CI 1.098~2.416,P=0.015)是丙肝肝硬化失代偿期患者发生细菌感染的独立危险因素;输注人血白蛋白(OR=0.324,95%CI 0.194~0.542,P=0.000)和高总胆固醇(total cholesterol,CHOL;OR=0.675,95%CI 0.549~0.830,P=0.000)水平是其保护因素。用以上7个影响因素构建列线图模型,采用受试者工作特征曲线(receiver operator characteristic curve,ROC曲线)分析显示曲线下面积(area under the curve,AUC)为0.736,敏感度80.4%,特异度65.1%。Hosmer-lemeshow检验显示,模型具有较好的拟合度(χ2=9.030,P=0.340)。使用Bootstrap法内部重复抽样1 000次进行验证,平均绝对误差0.010,校正曲线和理想曲线基本拟合,预测值和实际值一致性较好。决策曲线显示列线图模型在高风险阈值(0.040~0.715)范围时,有着一定的临床实用性。CIC显示该列线图模型可进行高风险人群分层预测。结论·研究所构建的列线图模型具有较好的预测性、一致性和临床实用性,可为临床医师初步判断丙肝肝硬化失代偿期患者发生细菌感染的风险提供依据。
中图分类号:
薛淋淋, 李秉翰, 常丽仙, 李卫昆, 刘春云, 刘立. 丙型病毒性肝炎肝硬化失代偿期患者发生细菌感染的列线图预测模型构建及评价[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(1): 52-60.
XUE Linlin, LI Binghan, CHANG Lixian, LI Weikun, LIU Chunyun, LIU Li. Construction and evaluation of a nomogram prediction model for bacterial infection in patients with decompensated hepatitis C cirrhosis[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(1): 52-60.
| Item | Non-bacterial infection group (n=411) | Bacterial infection group (n=163) | χ2 /Z value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age≥60 years/n (%) | 32 (7.8) | 24 (14.7) | 6.283 | 0.012 |
| Gender/n (%) | 6.381 | 0.012 | ||
| Male | 304 (74.0) | 105 (64.4) | ||
| Female | 107 (26.0) | 58 (35.6) | ||
| Complication on admission/n (%) | ||||
| Diabetes | 74 (16.9) | 20 (12.0) | 2.803 | 0.094 |
| Hypertension | 107 (24.4) | 5 (3.0) | 1.926 | 0.588 |
| Upper gastrointestinal Hemorrhage | 19 (4.3) | 4 (2.4) | 1.427 | 0.232 |
| Ascites | 113 (25.7) | 81 (48.5) | 28.073 | 0.000 |
| Hepatorenal syndrome | 7 (1.6) | 5 (3.0) | 1.061 | 0.303 |
| Hepatic encephalopathy | 21 (4.8) | 10 (6.0) | 0.240 | 0.624 |
| Portal hypertensive Gastroenteropathy | 74 (16.9) | 24 (14.4) | 0.673 | 0.412 |
| Hyperammonemia | 24 (5.5) | 18 (10.8) | 4.660 | 0.031 |
| History of invasive procedures in the last two weeks/n (%)① | 29 (7.1) | 23 (14.1) | 7.050 | 0.008 |
| Infusing human serum albumin/n (%) | 134 (32.6) | 24(14.7) | 18.703 | 0.000 |
| Laboratory index | ||||
| WBC/(×109·L-1) | 4.0 (3.0, 5.2) | 4.6 (3.6, 6.2) | -3.920 | 0.000 |
| RBC/(×109·L-1) | 4.0 (3.2, 4.8) | 3.8 (3.0, 4.5) | -1.858 | 0.063 |
| PLT/(×109·L-1) | 76.0 (52.0, 110.0) | 71.0 (47.0, 104.0) | -0.917 | 0.359 |
| NEUT/(×109·L-1) | 2.3 (1.6, 3.3) | 3.0 (2.1, 4.4) | -4.730 | 0.000 |
| HGB/(g·L-1) | 124.0 (101.0, 145.0) | 121.3 (90.0, 145.0) | -1.817 | 0.069 |
| TP/(g·L-1) | 68.0 (60.8, 72.8) | 66.3 (58.2, 70.5) | -3.107 | 0.002 |
| ALB/(g·L-1) | 32.9 (28.0, 38.7) | 30.5 (24.9, 35.0) | -4.280 | 0.000 |
| PA/(mg·L-1) | 114.9 (93.1, 134.7) | 114.9 (76.6, 115.0) | -2.870 | 0.004 |
| GPT/(U·L-1) | 39.0 (24.0, 64.0) | 36.0 (23.0, 59.0) | -1.509 | 0.131 |
| GOT/(U·L-1) | 59.0 (36.0, 94.0) | 59.0 (36.0, 94.0) | -0.608 | 0.543 |
| TBIL/(μmol·L-1) | 28.3 (18.0, 45.5) | 36.0 (19.9, 69.4) | -2.728 | 0.006 |
| TAG/(mmol·L-1) | 1.2 (0.7, 4.1) | 1.1 (0.7, 4.1) | -0.496 | 0.620 |
| CHOL/(mmol·L-1) | 3.3 (2.7, 3.9) | 3.2 (2.4, 3.4) | -4.081 | 0.000 |
| HDL-C/(mmol·L-1) | 1.4 (1.0, 1.9) | 1.3 (0.9, 1.4) | -3.581 | 0.000 |
| LDL-C/(mmol·L-1) | 1.3 (0.8, 1.6) | 1.3 (0.8, 1.6) | -0.872 | 0.383 |
| UR/(mmol·L-1) | 4.7 (3.4, 6.3) | 5.3 (3.6, 7.4) | -1.590 | 0.112 |
| CREA/(mmol·L-1) | 65.0 (54.0, 79.0) | 71.0 (55.0, 90.0) | -3.100 | 0.002 |
| UA/(μmol·L-1) | 354.0 (276.0, 443.0) | 366.0 (303.0, 447.0) | -0.904 | 0.366 |
| LDH/(U·L-1) | 210.1 (156.0, 231.0) | 210.1 (159.0, 252.0) | -1.732 | 0.083 |
| PT/s | 15.1 (13.1, 16.8) | 15.1 (10.3, 17.8) | -0.393 | 0.694 |
| PTA/% | 58.0 (42.0, 71.0) | 54.7 (20.3, 68.0) | -1.937 | 0.053 |
| INR | 1.3 (1.2, 1.5) | 1.3 (1.2, 1.6) | -2.708 | 0.007 |
| AFP/(ng·mL-1) | 10.2 (5.2, 26.3) | 8.7 (3.8, 1 476.3) | -0.073 | 0.942 |
| ALP/(U·L-1) | 133.0 (99.0, 200.6) | 143.0 (98.0, 200.6) | -0.806 | 0.420 |
| IL-6/(pg·mL-1) | 21.0 (8.4, 64.5) | 62.7 (23.1, 64.5) | -5.908 | 0.000 |
| C1q/(mg·L-1) | 170.0 (142.0, 190.0) | 164.7 (140.0, 177.0) | -1.878 | 0.060 |
| hs-CRP/(mg·L-1) | 5.3 (0.8, 11.8) | 4.2 (0.8, 11.8) | -0.639 | 0.523 |
| Hospitalization time ≥2 weeks/n (%) | 177 (43.1) | 95 (58.3) | 10.839 | 0.001 |
表1 2组丙肝肝硬化失代偿期患者基线资料比较
Tab 1 Baseline data comparison between the two groups of patients with decompensated hepatitis C cirrhosis
| Item | Non-bacterial infection group (n=411) | Bacterial infection group (n=163) | χ2 /Z value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age≥60 years/n (%) | 32 (7.8) | 24 (14.7) | 6.283 | 0.012 |
| Gender/n (%) | 6.381 | 0.012 | ||
| Male | 304 (74.0) | 105 (64.4) | ||
| Female | 107 (26.0) | 58 (35.6) | ||
| Complication on admission/n (%) | ||||
| Diabetes | 74 (16.9) | 20 (12.0) | 2.803 | 0.094 |
| Hypertension | 107 (24.4) | 5 (3.0) | 1.926 | 0.588 |
| Upper gastrointestinal Hemorrhage | 19 (4.3) | 4 (2.4) | 1.427 | 0.232 |
| Ascites | 113 (25.7) | 81 (48.5) | 28.073 | 0.000 |
| Hepatorenal syndrome | 7 (1.6) | 5 (3.0) | 1.061 | 0.303 |
| Hepatic encephalopathy | 21 (4.8) | 10 (6.0) | 0.240 | 0.624 |
| Portal hypertensive Gastroenteropathy | 74 (16.9) | 24 (14.4) | 0.673 | 0.412 |
| Hyperammonemia | 24 (5.5) | 18 (10.8) | 4.660 | 0.031 |
| History of invasive procedures in the last two weeks/n (%)① | 29 (7.1) | 23 (14.1) | 7.050 | 0.008 |
| Infusing human serum albumin/n (%) | 134 (32.6) | 24(14.7) | 18.703 | 0.000 |
| Laboratory index | ||||
| WBC/(×109·L-1) | 4.0 (3.0, 5.2) | 4.6 (3.6, 6.2) | -3.920 | 0.000 |
| RBC/(×109·L-1) | 4.0 (3.2, 4.8) | 3.8 (3.0, 4.5) | -1.858 | 0.063 |
| PLT/(×109·L-1) | 76.0 (52.0, 110.0) | 71.0 (47.0, 104.0) | -0.917 | 0.359 |
| NEUT/(×109·L-1) | 2.3 (1.6, 3.3) | 3.0 (2.1, 4.4) | -4.730 | 0.000 |
| HGB/(g·L-1) | 124.0 (101.0, 145.0) | 121.3 (90.0, 145.0) | -1.817 | 0.069 |
| TP/(g·L-1) | 68.0 (60.8, 72.8) | 66.3 (58.2, 70.5) | -3.107 | 0.002 |
| ALB/(g·L-1) | 32.9 (28.0, 38.7) | 30.5 (24.9, 35.0) | -4.280 | 0.000 |
| PA/(mg·L-1) | 114.9 (93.1, 134.7) | 114.9 (76.6, 115.0) | -2.870 | 0.004 |
| GPT/(U·L-1) | 39.0 (24.0, 64.0) | 36.0 (23.0, 59.0) | -1.509 | 0.131 |
| GOT/(U·L-1) | 59.0 (36.0, 94.0) | 59.0 (36.0, 94.0) | -0.608 | 0.543 |
| TBIL/(μmol·L-1) | 28.3 (18.0, 45.5) | 36.0 (19.9, 69.4) | -2.728 | 0.006 |
| TAG/(mmol·L-1) | 1.2 (0.7, 4.1) | 1.1 (0.7, 4.1) | -0.496 | 0.620 |
| CHOL/(mmol·L-1) | 3.3 (2.7, 3.9) | 3.2 (2.4, 3.4) | -4.081 | 0.000 |
| HDL-C/(mmol·L-1) | 1.4 (1.0, 1.9) | 1.3 (0.9, 1.4) | -3.581 | 0.000 |
| LDL-C/(mmol·L-1) | 1.3 (0.8, 1.6) | 1.3 (0.8, 1.6) | -0.872 | 0.383 |
| UR/(mmol·L-1) | 4.7 (3.4, 6.3) | 5.3 (3.6, 7.4) | -1.590 | 0.112 |
| CREA/(mmol·L-1) | 65.0 (54.0, 79.0) | 71.0 (55.0, 90.0) | -3.100 | 0.002 |
| UA/(μmol·L-1) | 354.0 (276.0, 443.0) | 366.0 (303.0, 447.0) | -0.904 | 0.366 |
| LDH/(U·L-1) | 210.1 (156.0, 231.0) | 210.1 (159.0, 252.0) | -1.732 | 0.083 |
| PT/s | 15.1 (13.1, 16.8) | 15.1 (10.3, 17.8) | -0.393 | 0.694 |
| PTA/% | 58.0 (42.0, 71.0) | 54.7 (20.3, 68.0) | -1.937 | 0.053 |
| INR | 1.3 (1.2, 1.5) | 1.3 (1.2, 1.6) | -2.708 | 0.007 |
| AFP/(ng·mL-1) | 10.2 (5.2, 26.3) | 8.7 (3.8, 1 476.3) | -0.073 | 0.942 |
| ALP/(U·L-1) | 133.0 (99.0, 200.6) | 143.0 (98.0, 200.6) | -0.806 | 0.420 |
| IL-6/(pg·mL-1) | 21.0 (8.4, 64.5) | 62.7 (23.1, 64.5) | -5.908 | 0.000 |
| C1q/(mg·L-1) | 170.0 (142.0, 190.0) | 164.7 (140.0, 177.0) | -1.878 | 0.060 |
| hs-CRP/(mg·L-1) | 5.3 (0.8, 11.8) | 4.2 (0.8, 11.8) | -0.639 | 0.523 |
| Hospitalization time ≥2 weeks/n (%) | 177 (43.1) | 95 (58.3) | 10.839 | 0.001 |
| Item | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95%CI) | P value | OR (95%CI) | P value | |
| Age≥60 years | 2.045 (1.164‒3.594) | 0.013 | 2.054 (1.104‒3.822) | 0.023 |
| Gender (female) | 1.569 (1.064‒2.316) | 0.023 | 1.701 (1.112‒2.602) | 0.014 |
| Diabetes | 1.567 (0.921‒2.666) | 0.098 | ‒ | ‒ |
| Hypertension | 1.167 (0.709‒1.918) | 0.544 | ‒ | ‒ |
| Hyperammonemia | 2.002 (1.055‒3.797) | 0.034 | ‒ | ‒ |
| Ascites | 2.605 (1.789‒3.793) | 0.000 | 2.386 (1.601‒3.557) | 0.000 |
| History of invasive procedures in the last two weeks① | 2.164 (1.211‒3.867) | 0.009 | 2.605 (1.386‒4.960) | 0.004 |
| Infusing human serum albumin | 0.357 (0.221‒0.577) | 0.000 | 0.324 (0.194‒0.542) | 0.000 |
| Laboratory index | ||||
| WBC | 1.187 (1.099‒1.282) | 0.000 | ‒ | ‒ |
| NEUT | 1.239 (1.131‒1.359) | 0.000 | ‒ | ‒ |
| HGB | 0.995 (0.990‒1.000) | 0.068 | ‒ | ‒ |
| TP | 0.980 (0.964‒0.997) | 0.018 | ‒ | ‒ |
| ALB | 0.952 (0.930‒0.975) | 0.000 | ‒ | ‒ |
| PA | 0.992 (0.988‒0.997) | 0.000 | ‒ | ‒ |
| TBIL | 1.007 (1.003‒1.010) | 0.000 | ‒ | ‒ |
| CHOL | 0.680 (0.559‒0.827) | 0.000 | 0.675 (0.549‒0.830) | 0.000 |
| HDL-C | 0.644 (0.485‒0.854) | 0.002 | ‒ | ‒ |
| LDL-C | 1.001 (1.000‒1.003) | 0.071 | ‒ | ‒ |
| CREA | 1.005 (1.001‒1.009) | 0.007 | ‒ | ‒ |
| IL-6 | 1.001 (1.000‒1.002) | 0.027 | ‒ | ‒ |
| C1q | 0.995 (0.992‒0.999) | 0.018 | ‒ | ‒ |
| LDH | 1.001 (1.000‒1.003) | 0.071 | ‒ | ‒ |
| INR | 1.015 (0.932‒1.107) | 0.727 | ‒ | ‒ |
| Hospitalization time ≥2 weeks | 1.847 (1.279‒2.677) | 0.001 | 1.629 (1.098‒2.416) | 0.015 |
表2 丙肝肝硬化失代偿期患者发生细菌感染的单因素及多因素Logistic回归分析结果
Tab 2 Results of univariate and multivariate Logistic regression analysis of bacterial infection in patients with decompensated hepatitis C cirrhosis
| Item | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95%CI) | P value | OR (95%CI) | P value | |
| Age≥60 years | 2.045 (1.164‒3.594) | 0.013 | 2.054 (1.104‒3.822) | 0.023 |
| Gender (female) | 1.569 (1.064‒2.316) | 0.023 | 1.701 (1.112‒2.602) | 0.014 |
| Diabetes | 1.567 (0.921‒2.666) | 0.098 | ‒ | ‒ |
| Hypertension | 1.167 (0.709‒1.918) | 0.544 | ‒ | ‒ |
| Hyperammonemia | 2.002 (1.055‒3.797) | 0.034 | ‒ | ‒ |
| Ascites | 2.605 (1.789‒3.793) | 0.000 | 2.386 (1.601‒3.557) | 0.000 |
| History of invasive procedures in the last two weeks① | 2.164 (1.211‒3.867) | 0.009 | 2.605 (1.386‒4.960) | 0.004 |
| Infusing human serum albumin | 0.357 (0.221‒0.577) | 0.000 | 0.324 (0.194‒0.542) | 0.000 |
| Laboratory index | ||||
| WBC | 1.187 (1.099‒1.282) | 0.000 | ‒ | ‒ |
| NEUT | 1.239 (1.131‒1.359) | 0.000 | ‒ | ‒ |
| HGB | 0.995 (0.990‒1.000) | 0.068 | ‒ | ‒ |
| TP | 0.980 (0.964‒0.997) | 0.018 | ‒ | ‒ |
| ALB | 0.952 (0.930‒0.975) | 0.000 | ‒ | ‒ |
| PA | 0.992 (0.988‒0.997) | 0.000 | ‒ | ‒ |
| TBIL | 1.007 (1.003‒1.010) | 0.000 | ‒ | ‒ |
| CHOL | 0.680 (0.559‒0.827) | 0.000 | 0.675 (0.549‒0.830) | 0.000 |
| HDL-C | 0.644 (0.485‒0.854) | 0.002 | ‒ | ‒ |
| LDL-C | 1.001 (1.000‒1.003) | 0.071 | ‒ | ‒ |
| CREA | 1.005 (1.001‒1.009) | 0.007 | ‒ | ‒ |
| IL-6 | 1.001 (1.000‒1.002) | 0.027 | ‒ | ‒ |
| C1q | 0.995 (0.992‒0.999) | 0.018 | ‒ | ‒ |
| LDH | 1.001 (1.000‒1.003) | 0.071 | ‒ | ‒ |
| INR | 1.015 (0.932‒1.107) | 0.727 | ‒ | ‒ |
| Hospitalization time ≥2 weeks | 1.847 (1.279‒2.677) | 0.001 | 1.629 (1.098‒2.416) | 0.015 |
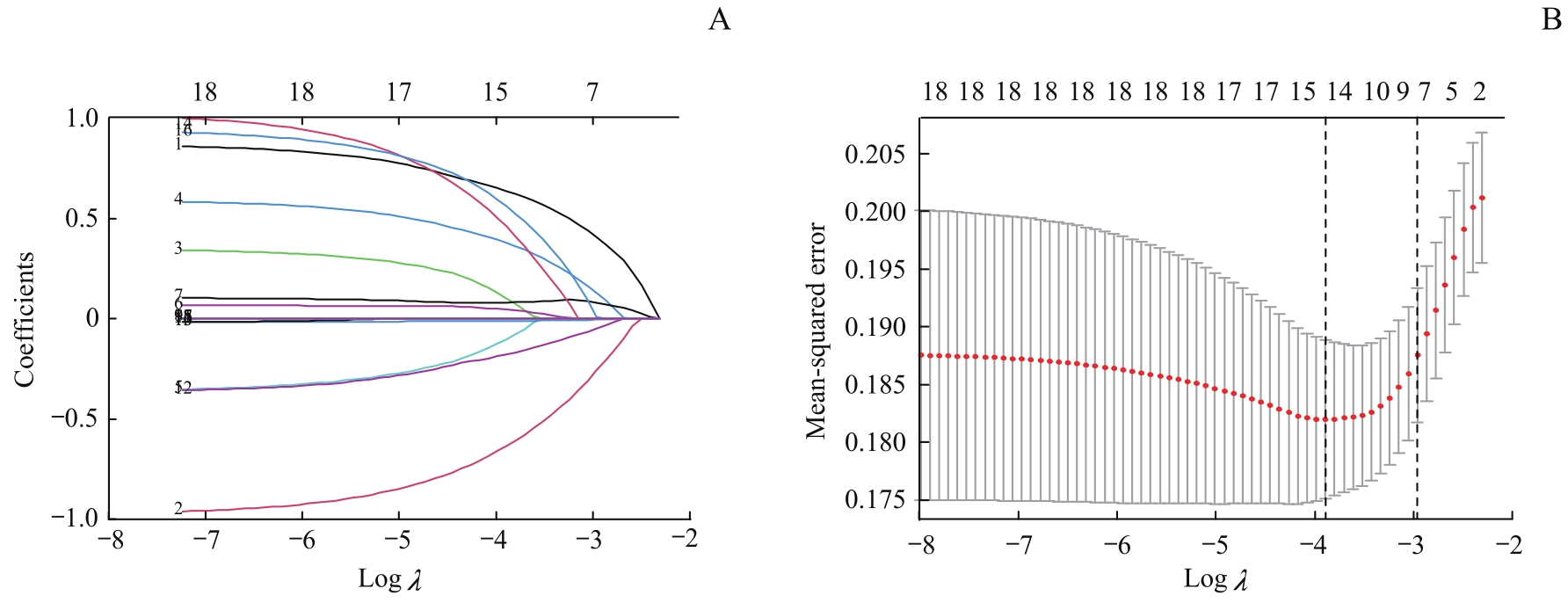
图1 丙肝肝硬化失代偿期患者发生细菌感染的LASSO回归模型Note: A. Path diagram of regression coefficient. The upper abscissas was the number of variables with non-zero coefficients in the model at this time, the lower abscissas was the logarithm of the penalty coefficient (λ), and the ordinate was the value of the coefficient. B. Cross-verification curve of LASSO regression. The upper and lower abscissas were the same as Fig A, and the ordinate was likelihood bias. The dotted line on the left of Fig B indicates the number of variables corresponding to the minimum λ (when the model has the highest fitting effect), and the number of variables was 14. The dotted line on the right indicates one standard error of the least λ (when the model has better fitting effect, fewer and simpler variables are included), and the number of variables was 7.
Fig 1 LASSO regression model of bacterial infection in patients with decompensated hepatitis C cirrhosis
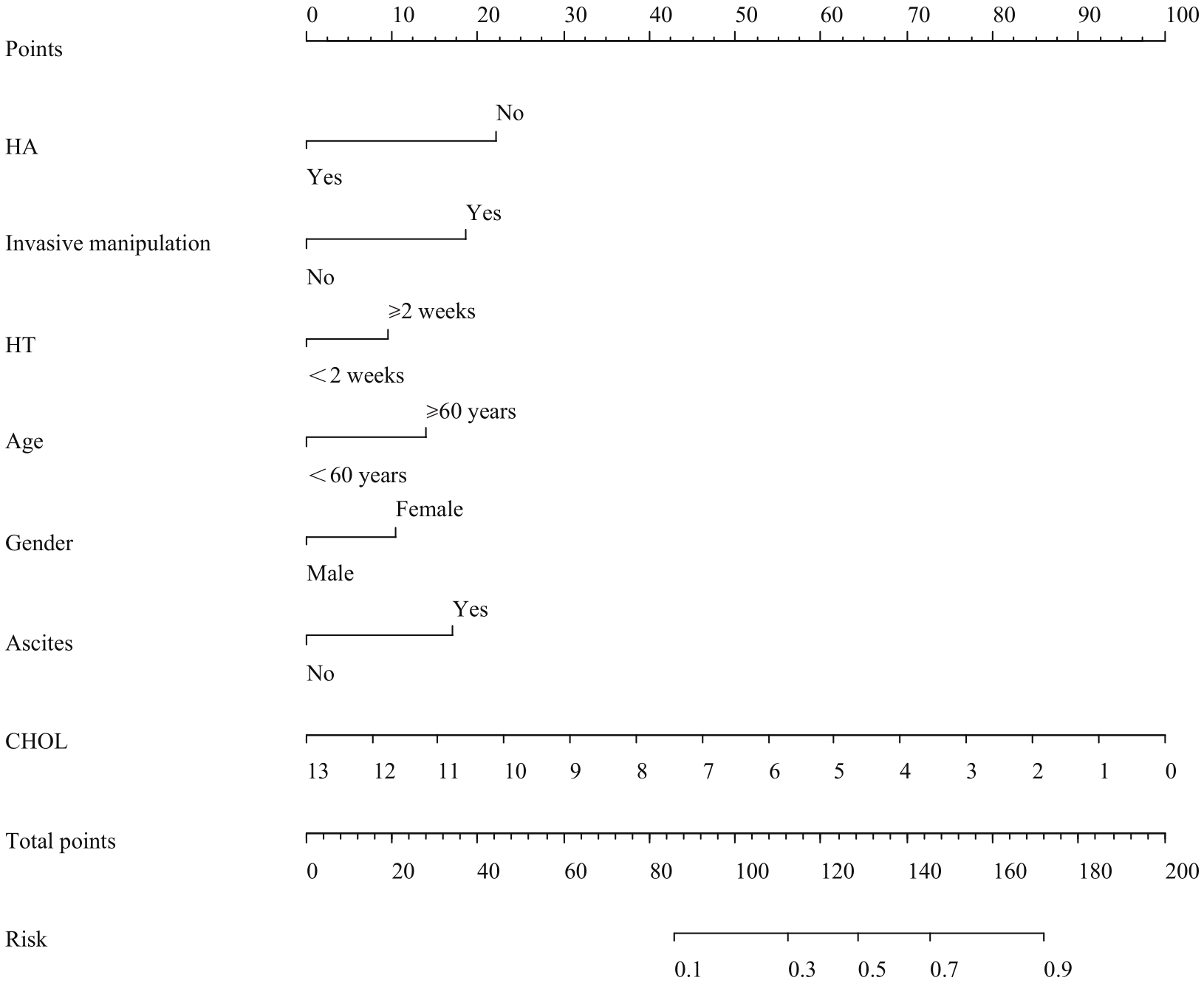
图2 丙肝肝硬化失代偿期患者发生细菌感染多因素Logistic回归分析的列线图Note: HA—human serum albumin was infused; HT—hospitalization time.
Fig 2 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of nomogram of bacterial infection in patients with decompensated hepatitis C cirrhosis
| 1 | 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委. 中国病毒性肝炎防治规划(2017—2020年)[EB/OL]. (2017-11-10)[2022-09-01]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/ewebeditor/uploadfile/2017/11/20171113134002475.pdf. |
| National Health Commission of the People′s Republic of China. Prevention and control plan of viral hepatitis in China (2017‒2020)[EB/OL]. (2017-11-10)[2022-09-01]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/ewebeditor/uploadfile/2017/11/20171113134002475.pdf. | |
| 2 | HEI F X, YE S D, DING G W, et al. Epidemiological analysis on reported hepatitis C cases in China from 2012 to 2016[J]. Biomed Environ Sci, 2018, 31(10): 773-776. |
| 3 | PIANO S, SINGH V, CARACENI P, et al. Epidemiology and effects of bacterial infections in patients with cirrhosis worldwide[J]. Gastroenterology, 2019, 156(5): 1368-1380.e10. |
| 4 | PLEGUEZUELO M, BENITEZ J M, JURADO J, et al. Diagnosis and management of bacterial infections in decompensated cirrhosis[J]. World J Hepatol, 2013, 5(1): 16-25. |
| 5 | FERNÁNDEZ J, PRADO V, TREBICKA J, et al. Multidrug-resistant bacterial infections in patients with decompensated cirrhosis and with acute-on-chronic liver failure in Europe[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 70(3): 398-411. |
| 6 | 中华医学会感染病学分会. 终末期肝病合并感染诊治专家共识(2021年版)[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2022, 30(2): 147-158. |
| Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment of end-stage liver disease complicated infection (2021 version)[J]. Chinese Journal of Hepatology, 2022, 30(2): 147-158. | |
| 7 | MIKUŁA T, SAPUŁA M, JABŁOŃSKA J, et al. Significance of heparin-binding protein and D-dimers in the early diagnosis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2018, 2018: 1969108. |
| 8 | SPAHR L, MORARD I, HADENGUE A, et al. Procalcitonin is not an accurate marker of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Hepato gastroenterology, 2001, 48(38): 502-505. |
| 9 | ZHU Y, CHENG H, MIN R, et al. Computed tomography images under the nomogram mathematical prediction model in the treatment of cerebral infarction complicated with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation and the impacts of virus infection[J]. Contrast Media Mol Imaging, 2022, 2022: 3950641. |
| 10 | LI S Y, YIN C H, CHEN J S, et al. A nomogram for predicting the development of serious bacterial infections in febrile term neonates: a single medical center experience in southern Taiwan[J]. Pediatr Neonatol, 2022, 63(6): 605-612. |
| 11 | XU X F, LI H W, SHENG Y J, et al. Nomogram for prediction of bronchial mucus plugs in children with Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 4579. |
| 12 | 中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会感染病学分会. 丙型肝炎防治指南(2019年版)[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2020, 23(1): S33-S52. |
| Chinese Society of Hepatology and Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for prevention and treatment of hepatitis C (2019 edition)[J]. Journal of Practical Hepatology, 2020, 23(1): S33-S52. | |
| 13 | PIANO S, TONON M, ANGELI P. Changes in the epidemiology and management of bacterial infections in cirrhosis[J]. Clin Mol Hepatol, 2021, 27(3): 437-445. |
| 14 | ALBILLOS A, DE GOTTARDI A, RESCIGNO M. The gut-liver axis in liver disease: pathophysiological basis for therapy[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 72(3): 558-577. |
| 15 | 吴柳, 洪灏, 李维正, 等. 肝硬化患者合并细菌感染的临床特征分析[J]. 中国感染与化疗杂志, 2020, 20(6): 601-606. |
| WU L, HONG H, LI W Z, et al. Clinical characteristics of bacterial infections in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy, 2020, 20(6): 601-606. | |
| 16 | 徐文倩, 吴瑶麒, 张近远, 等. 慢性肝病女性患者绝经后雌激素抗肝纤维化的作用机制[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2021, 37(10): 2425-2428. |
| XU W Q, WU Y Q, ZHANG J Y, et al. Mechanism of estrogen against liver fibrosis in postmenopausal women with chronic liver disease[J]. Journal of Clinical Hepatology, 2021, 37(10): 2425-2428. | |
| 17 | KLAIR J S, YANG J D, ABDELMALEK M F, et al. A longer duration of estrogen deficiency increases fibrosis risk among postmenopausal women with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2016, 64(1): 85-91. |
| 18 | MARTIN MATEOS R, ALBILLOS A. Sepsis in patients with cirrhosis awaiting liver transplantation: new trends and management[J]. Liver Transpl, 2019, 25(11): 1700-1709. |
| 19 | MARTÍNEZ J, HERNÁNDEZ-GEA V, RODRÍGUEZ-DE-SANTIAGO E, et al. Bacterial infections in patients with acute variceal bleeding in the era of antibiotic prophylaxis[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 75(2): 342-350. |
| 20 | 宫能凯, 全斌, 鲁俊, 等. 回归分析失代偿期肝硬化患者医院感染的危险因素[J]. 齐齐哈尔医学院学报, 2021, 42(9): 772-775. |
| GONG N K, QUAN B, LU J, et al. Analysis of the risk factors of nosocomial infection among patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis inpatients based on regression analysis[J]. Journal of Qiqihar Medical University, 2021, 42(9): 772-775. | |
| 21 | 徐升, 徐芳, 应丽园, 等. 肝硬化合并上消化道出血患者医院感染的病原学特点及影响因素研究[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2019, 29(1): 71-74. |
| XU S, XU F, YING L Y, et al. Etiological charateristics and influencing factor for nosocomial infection in liver cirrhosis patients complicated with upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage[J]. Chinese Journal of Nosocomiology, 2019, 29(1): 71-74. | |
| 22 | ARROYO V, ANGELI P, MOREAU R, et al. The systemic inflammation hypothesis: towards a new paradigm of acute decompensation and multiorgan failure in cirrhosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 74(3): 670-685. |
| 23 | NING Y X, KIM J K, MIN H K, et al. Cholesterol metabolites alleviate injured liver function and decrease mortality in an LPS-induced mouse model[J]. Metabolism, 2017, 71: 83-93. |
| 24 | 高鹏, 肖萍, 陈青锋, 等. 慢性乙型肝炎患者血脂水平的影响因素分析[J]. 第二军医大学学报, 2011, 32(12): 1375-1377. |
| GAO P, XIAO P, CHEN Q F, et al. Analysis of factors influencing serum lipids of patients with chronic hepatitis B infection[J]. Academic Journal of Second Military Medical University, 2011, 32(12): 1375-1377. | |
| 25 | DELGADO-COELLO B, BRIONES-ORTA M A, MACÍAS-SILVA M, et al. Cholesterol: recapitulation of its active role during liver regeneration[J]. Liver Int, 2011, 31(9): 1271-1284. |
| 26 | 薛永举, 杨丽, 朱玉, 等. 血清白蛋白、胆碱酯酶及凝血酶原活动度对病毒性肝炎肝硬化的诊断价值[J]. 蚌埠医学院学报, 2019, 44(3): 306-308, 313. |
| XUE Y J, YANG L, ZHU Y, et al. Value of the serum albumin, cholinesterase and prothrombin activity in the diagnosis of viral hepatitis cirrhosis[J]. Journal of Bengbu Medical College, 2019, 44(3): 306-308, 313. | |
| 27 | 文关良. 肝炎肝硬化患者血清CHE、ALB、CHO水平检测在肝功能评估中的临床应用价值[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2017, 14(18): 2741-2742. |
| GUAN W L. Clinical application value of serum CHE, ALB and CHO levels in liver function assessment of patients with hepatitis cirrhosis[J]. Laboratory Medicine and Clinic, 2017, 14(18): 2741-2742. | |
| 28 | DESCHÊNES M, VILLENEUVE J P. Risk factors for the development of bacterial infections in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 1999, 94(8): 2193-2197. |
| 29 | 谭立明, 丁耀东, 陈娟娟, 等. C1q在自身免疫性疾病中的临床意义[J]. 检验医学, 2017, 32(8): 686-690. |
| TAN L M, DING Y D, CHEN J J, et al. Complement 1q determination for autoimmune diseases[J]. Laboratory Medicine, 2017, 32(8): 686-690. | |
| 30 | ZHANG Q, SHI B X, WU L. Characteristics and risk factors of infections in patients with HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure: a retrospective study[J]. PeerJ, 2022, 10: e13519. |
| 31 | 杨慧玲, 刘小静, 何英利, 等. 失代偿期乙型肝炎肝硬化患者发生医院感染临床特点及危险因素分析[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2020, 23(1): 78-81. |
| YANG H L, LIU X J, HE Y L, et al.Clinical characteristics of and risk factors for nosocomial infections in patients with hospitalized decompensated hepatitis B liver cirrhosis[J]. Journal of Practical Hepatology, 2020, 23(1): 78-81. | |
| 32 | CHINA L, FREEMANTLE N, FORREST E, et al. A randomized trial of albumin infusions in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2021, 384(9): 808-817. |
| [1] | 朱月悦, 张锦文, 马锐翔, 陈彩莲, 林羿, 刘晓瑞. 产后血栓性疾病的危险因素分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(4): 415-421. |
| [2] | 张彤, 田雪, 左颖婷, 郑曼琪, 张怡君, 吴寿岭, 陈朔华, 马高亭, 佟旭, 王安心, 莫大鹏. 无传统危险因素人群中TyG指数与心脑血管疾病的关系[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(3): 267-274. |
| [3] | 王晔恺, 陈位, 杨颍辉, 吴静泽, 王和平, 姚燕珍, 鲍舟君. 骨折后手术患者异位骨化风险的nomogram临床评分系统的建立[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(2): 166-172. |
| [4] | 李爱求, 张潇潇, 姜允丽, 肖艳赏, 丁国栋, 吴蓓蓉, 董晓艳. 学龄前儿童反复喘息的相关危险因素分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(10): 1435-1440. |
| [5] | 徐莹, 褚以忞, 杨大明, 李吉, 张海芹, 彭海霞. 基于差异表达基因组合构建高度微卫星不稳定结直肠癌转移预测模型[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(9): 1197-1206. |
| [6] | 丁远森, 王枫, 孙家悦, 邵正威, 邹德荣, 陆家瑜. 不同年龄2型糖尿病患者牙周健康流行病学调查[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(2): 217-222. |
| [7] | 刘芳芳, 包关水, 闫梦侠. 基于列线图的原发性头痛辅助决策模型的构建[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(10): 1323-1329. |
| [8] | 马银珠*,陆光华*,钟 娜,王海红,和 申,赵 雪,江海峰,王 振. 酒精所致精神病性障碍男性患者临床特征及危险因素[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(9): 1256-1262. |
| [9] | 徐 慧,刘 芳. 早发冠状动脉粥样硬化性心脏病相关危险因素的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(8): 1148-1151. |
| [10] | 吕恒宇,黄 晨,夏 翔,赵 刚. 预测根治性胃癌切除术后并发症危险因素的列线图模型的建立[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(7): 894-900. |
| [11] | 倪 坤1,赵利敏1,李晓艳1,时海波2. 城市1岁以下婴儿急性中耳炎临床特点与危险因素分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(7): 923-928. |
| [12] | 张柳蕙,张 旭,王嘉璐,亢晓丽. 外斜视矫正术后的连续性内斜视危险因素与治疗的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(7): 974-979. |
| [13] | 周悦玲,丁 峰. 肾结石的危险因素与诊断评估研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(5): 688-692. |
| [14] | 崔 羽,冉娟娟,王 益,顾 平. 血清25-羟基维生素D水平与脑白质疏松症的相关性研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(2): 231-. |
| [15] | 何春明,尹 航,唐 健,丁一宗,傅于捷,赵晓菁. 基于SEER数据库的老年肺癌术后患者预后模型构建与内部验证[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(11): 1554-1561. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||