
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (10): 1361-1371.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2025.10.011
收稿日期:2025-02-13
接受日期:2025-06-06
出版日期:2025-10-28
发布日期:2025-10-28
通讯作者:
韩邦旻,教授,博士;电子信箱:Hanbm@163.com。基金资助:
DUN Yiting, ZHAO Jing, FENG Chengling, LI Xingjian, CUI Di, HAN Bangmin( )
)
Received:2025-02-13
Accepted:2025-06-06
Online:2025-10-28
Published:2025-10-28
Contact:
HAN Bangmin, E-mail: Hanbm@163.com.Supported by:摘要:
目的·开发列线图预测模型和在线风险计算器,预测机器人辅助腹腔镜根治性前列腺切除术(robot-assisted radical prostatectomy,RARP)后患者尿控情况。方法·纳入2022年9月至2024年12月在上海交通大学医学院附属第一人民医院接受RARP手术且具备术前前列腺磁共振成像资料的604例前列腺癌患者。所有患者按照7∶3的比例随机重采样并分为训练集(n=420)和验证集(n=184)。自术后1个月起,每个月对患者的尿控情况进行随访。应用最小绝对收缩和选择算子回归(least absolute shrinkage and selection operator,LASSO)模型筛选预测特征;使用Logistic多因素回归分析建立从LASSO回归分析中选择的特征的预测模型;绘制受试者操作特征(receiver operator characteristic,ROC)曲线预测RARP术后患者尿控功能恢复情况;通过DeLong检验比较曲线下面积,评估模型的辨别力;通过校准曲线和决策曲线分析(decision curve analysis,DCA)评估模型的准确性和临床实用性。结果·根据患者术后的尿控随访数据,患者在术后3个月的尿控率为58.28%(352/604)。训练集的Logistic多因素回归分析结果显示,膜部尿道长度、右肛提肌厚度和术中失血量是术后早期(3个月)尿失禁的独立预测因素。基于该结果建立列线图预测模型。该模型显示出良好的区分度,训练集ROC曲线下面积为0.976(0.954,0.998),验证集ROC曲线下面积为0.977(0.945,1.000);DeLong检验证明训练集和验证集ROC曲线差异无统计学意义(P=0.949)。Hosmer-Lemeshow检验显示该模型具有良好的拟合优度(P=0.179)。DCA结果表明该列线图预测模型在临床上具有适用性。将列线图预测模型纳入在线计算器(
中图分类号:
敦译霆, 赵婧, 冯成领, 李行健, 崔迪, 韩邦旻. 机器人辅助腹腔镜根治性前列腺切除术后患者尿失禁的在线风险计算器和列线图预测模型[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(10): 1361-1371.
DUN Yiting, ZHAO Jing, FENG Chengling, LI Xingjian, CUI Di, HAN Bangmin. Online risk calculator and nomogram prediction model for urinary incontinence after robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(10): 1361-1371.
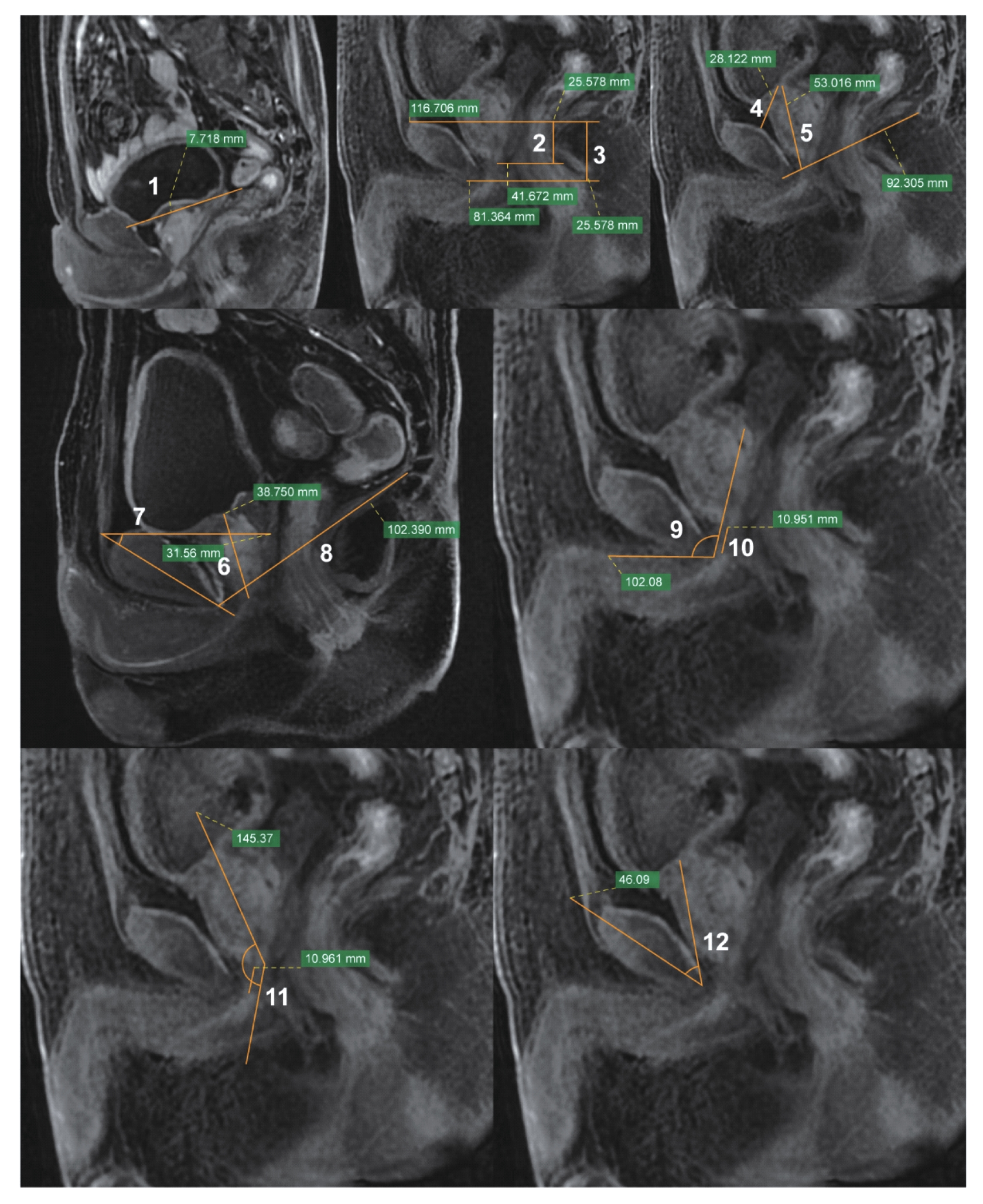
图1 MRI正中矢状图像Note: 1. IPPL; 2. Prostate apical depth; 3. Pubic height; 4. Distance from pubic symphysis to bladder neck; 5. Distance between the bladder neck and the pubococcygeous line; 6. Maximum prostate height; 7. Anteroposterior diameter of the middle pelvic plane; 8. Pubic symphysis angle; 9. Membranous urethra angle; 10. MUL; 11. Angle between the membranous urethra and the prostatic axis; 12. Pubourethral angle.
Fig 1 MRI mid-sagittal image
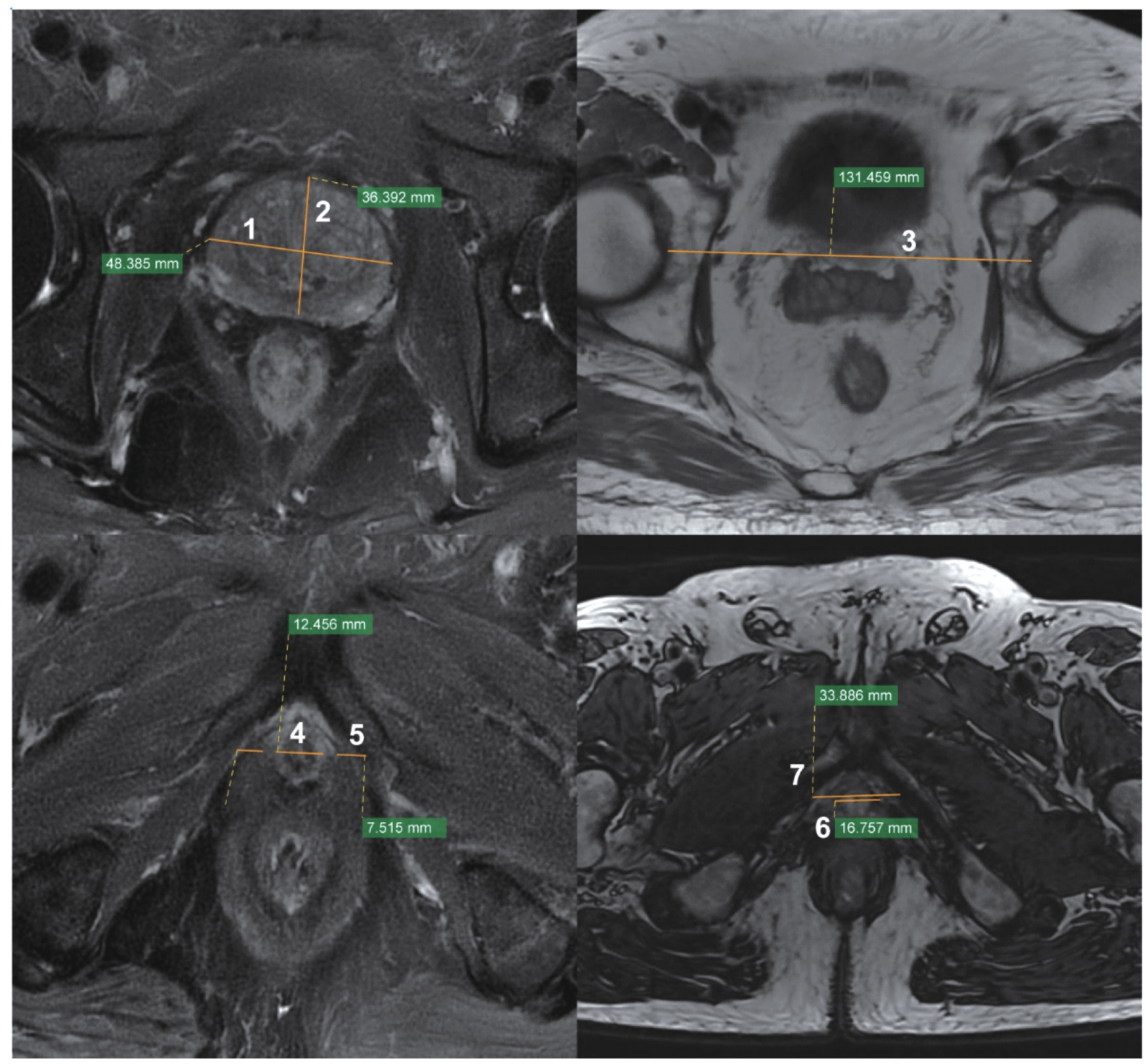
图2 MRI轴向图像Note: 1. Maximum prostate width; 2. Maximum prostate length; 3. Femoral bone width; 4. Urethral wall thickness; 5. Levator ani muscle thickness; 6. Average thickness of the levator ani muscle; 7. Lateral distance of the levator ani muscle.
Fig 2 MRI axial image
| Item | Total (n=604) | Training set (n=420) | Validation set (n=184) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPPL/mm | 0 (0, 7.21) | 0 (0, 7.28) | 0 (0, 5.29) | 0.800 |
| Prostatic apex shape/n(%) | 0.950 | |||
| Type A | 264 (43.71) | 180 (42.86) | 84 (45.65) | |
| Type B | 108 (17.88) | 76 (18.10) | 32 (17.39) | |
| Type D | 232 (38.41) | 164 (39.05) | 68 (36.96) | |
| Prostate apical depth/mm | 29.53 ± 5.65 | 29.57 ± 5.73 | 29.44 ± 5.53 | 0.895 |
| Pubic height/mm | 35.21 (32.81, 38.04) | 35.24 (33.04, 37.91) | 34.89 (32.65, 38.05) | 0.867 |
| Pubic symphysis to bladder neck distance/mm | 24.86 (22.18, 28.43) | 24.63 (22.13, 28.64) | 25.09 (22.51, 28.36) | 0.824 |
| Distance between the bladder neck and the pubococcygeous line/mm | 40.03 (35.37, 44.75) | 39.39 (35.35, 44.58) | 41.41 (36.5, 45.85) | 0.403 |
| Maximum prostate height/mm | 42.28 (37.92, 47.03) | 42.20 (37.38, 46.72) | 43.20 (38.18, 48.63) | 0.615 |
| Anteroposterior diameter of the middle pelvic plane/mm | 103.91±7.94 | 103.14±8.20 | 105.66±7.08 | 0.058 |
| Pubic symphysis angle/(°) | 33.63±5.30 | 33.62±5.32 | 33.64±5.32 | 0.978 |
| Membranous urethra angle/(°) | 115.70±7.89 | 116.12±8.08 | 114.73±7.45 | 0.305 |
| MUL/mm | 9.06 (6.54, 11.50) | 9.36 (6.70, 11.75) | 8.10 (6.23, 10.61) | 0.136 |
| Angle between membranous urethra and prostatic axis/(°) | 133.13 (127.26, 137.84) | 133.33 (126.42, 138.16) | 131.60 (128.39, 137.12) | 0.698 |
| Pubourethral angle/(°) | 60.62±8.73 | 60.86±8.86 | 60.08 ± 8.51 | 0.606 |
| Maximum prostate width/mm | 50.35 (45.99, 53.64) | 50.53 (45.99, 53.35) | 50.31 (46.01, 54.29) | 0.824 |
| Maximum prostate length/mm | 37.70 (33.41, 42.75) | 37.94 (33.48, 42.90) | 37.20 (33.17, 41.76) | 0.816 |
| Femoral bone width/mm | 117.44 ± 6.57 | 117.76 ± 6.90 | 116.72 ± 5.76 | 0.341 |
| Urethral wall thickness/mm | 16.99 (14.39, 19.43) | 17.14 (15.23, 19.39) | 16.37 (11.77, 19.73) | 0.350 |
| Left levator ani muscle thickness/mm | 20.13 (16.10, 22.22) | 20.58 (16.96, 22.39) | 19.27 (14.16, 21.96) | 0.134 |
| Right levator ani muscle thickness/mm | 19.91 (16.48, 21.73) | 20.11 (16.62, 21.89) | 18.91 (14.40, 21.40) | 0.216 |
| Average thickness of the levator ani muscle/mm | 20.08 (16.14, 21.99) | 20.27 (16.75, 22.11) | 19.12 (14.05, 21.76) | 0.176 |
| External distance of the levator ani muscle/mm | 55.87 (50.07, 60.86) | 56.61 (51.95, 61.44) | 54.49 (45.65, 59.66) | 0.128 |
| Age at surgery/year | 70 (67, 75) | 71 (67, 75) | 70 (68, 74) | 0.849 |
| Height/cm | 170.00 (167.00, 173.00) | 170.00 (166.00, 173.00) | 170.00 (167.62, 172.75) | 0.617 |
| Weight/kg | 70.00 (65.00, 74.95) | 70.00 (65.00, 75.00) | 68.00 (65.00, 71.88) | 0.232 |
| BMI/(kg·m-2) | 24.18±2.47 | 24.32±2.56 | 23.87±2.23 | 0.284 |
| Preoperative highest PSA/(ng·mL-1) | 10.70 (7.91, 17.00) | 11.10 (7.73, 17.00) | 10.70 (8.00, 16.85) | 0.832 |
| History of endocrine therapy/n(%) | 0.993 | |||
| No | 532 (88.08) | 372 (88.57) | 160 (86.96) | |
| Yes | 72 (11.92) | 48 (11.43) | 24 (13.04) | |
| DVC/n(%) | 0.647 | |||
| Suture | 520 (86.09) | 356 (84.76) | 164 (89.13) | |
| Preservation | 84 (13.91) | 64 (15.24) | 20 (10.87) | |
| NVB/n(%) | >0.999 | |||
| Bilateral extrafascial | 484 (80.13) | 336 (80.00) | 148 (80.43) | |
| Other ways | 120 (19.87) | 84 (20.00) | 36 (19.57) | |
| Modified anterior approach/n(%) | >0.999 | |||
| No | 592 (98.01) | 412 (98.10) | 180 (97.83) | |
| Yes | 12 (1.99) | 8 (1.90) | 4 (2.17) | |
| Reconstruction/n(%) | 0.726 | |||
| No | 388 (64.24) | 264 (62.86) | 124 (67.39) | |
| Yes | 216 (35.76) | 156 (37.14) | 60 (32.61) | |
| APA/n (%) | 0.553 | |||
| Preservation | 592 (98.01) | 408 (97.14) | 184 (100.00) | |
| Non-reservation | 12 (1.99) | 12 (2.86) | 0 (0) | |
| Lymph node dissection/n(%) | >0.999 | |||
| No | 516 (85.43) | 360 (85.71) | 156 (84.78) | |
| Yes | 88 (14.57) | 60 (14.29) | 28 (15.22) | |
| Intraoperative blood loss/mL | 50 (35, 100) | 50 (50, 100) | 50 (30, 80) | 0.434 |
| Gleason score/n(%) | 0.649 | |||
| 6 | 64 (10.60) | 52 (12.38) | 12 (6.52) | |
| 7 | 364 (60.26) | 240 (57.14) | 124 (67.39) | |
| 8 | 52 (8.61) | 40 (9.52) | 12 (6.52) | |
| 9 | 124 (20.53) | 88 (20.95) | 36 (19.57) | |
| Tumor status of the apex margin/n(%) | 0.659 | |||
| Negative | 492 (81.46) | 348 (82.86) | 144 (78.26) | |
| Positive | 112 (18.54) | 72 (17.14) | 40 (21.74) | |
| Prostate volume/mm3 | 36.40 (25.73, 46.80) | 36.40 (26.75, 46.21) | 36.40 (24.52, 51.09) | 0.984 |
| Three-month postoperative urinary control/n(%) | 0.408 | |||
| Continence | 352 (58.28) | 256 (60.95) | 96 (52.17) | |
| Incontinence | 252 (41.72) | 164 (39.05) | 88 (47.83) | |
表1 训练集和验证集患者基线数据
Tab 1 Baseline characteristics of patients in the training and validation sets
| Item | Total (n=604) | Training set (n=420) | Validation set (n=184) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPPL/mm | 0 (0, 7.21) | 0 (0, 7.28) | 0 (0, 5.29) | 0.800 |
| Prostatic apex shape/n(%) | 0.950 | |||
| Type A | 264 (43.71) | 180 (42.86) | 84 (45.65) | |
| Type B | 108 (17.88) | 76 (18.10) | 32 (17.39) | |
| Type D | 232 (38.41) | 164 (39.05) | 68 (36.96) | |
| Prostate apical depth/mm | 29.53 ± 5.65 | 29.57 ± 5.73 | 29.44 ± 5.53 | 0.895 |
| Pubic height/mm | 35.21 (32.81, 38.04) | 35.24 (33.04, 37.91) | 34.89 (32.65, 38.05) | 0.867 |
| Pubic symphysis to bladder neck distance/mm | 24.86 (22.18, 28.43) | 24.63 (22.13, 28.64) | 25.09 (22.51, 28.36) | 0.824 |
| Distance between the bladder neck and the pubococcygeous line/mm | 40.03 (35.37, 44.75) | 39.39 (35.35, 44.58) | 41.41 (36.5, 45.85) | 0.403 |
| Maximum prostate height/mm | 42.28 (37.92, 47.03) | 42.20 (37.38, 46.72) | 43.20 (38.18, 48.63) | 0.615 |
| Anteroposterior diameter of the middle pelvic plane/mm | 103.91±7.94 | 103.14±8.20 | 105.66±7.08 | 0.058 |
| Pubic symphysis angle/(°) | 33.63±5.30 | 33.62±5.32 | 33.64±5.32 | 0.978 |
| Membranous urethra angle/(°) | 115.70±7.89 | 116.12±8.08 | 114.73±7.45 | 0.305 |
| MUL/mm | 9.06 (6.54, 11.50) | 9.36 (6.70, 11.75) | 8.10 (6.23, 10.61) | 0.136 |
| Angle between membranous urethra and prostatic axis/(°) | 133.13 (127.26, 137.84) | 133.33 (126.42, 138.16) | 131.60 (128.39, 137.12) | 0.698 |
| Pubourethral angle/(°) | 60.62±8.73 | 60.86±8.86 | 60.08 ± 8.51 | 0.606 |
| Maximum prostate width/mm | 50.35 (45.99, 53.64) | 50.53 (45.99, 53.35) | 50.31 (46.01, 54.29) | 0.824 |
| Maximum prostate length/mm | 37.70 (33.41, 42.75) | 37.94 (33.48, 42.90) | 37.20 (33.17, 41.76) | 0.816 |
| Femoral bone width/mm | 117.44 ± 6.57 | 117.76 ± 6.90 | 116.72 ± 5.76 | 0.341 |
| Urethral wall thickness/mm | 16.99 (14.39, 19.43) | 17.14 (15.23, 19.39) | 16.37 (11.77, 19.73) | 0.350 |
| Left levator ani muscle thickness/mm | 20.13 (16.10, 22.22) | 20.58 (16.96, 22.39) | 19.27 (14.16, 21.96) | 0.134 |
| Right levator ani muscle thickness/mm | 19.91 (16.48, 21.73) | 20.11 (16.62, 21.89) | 18.91 (14.40, 21.40) | 0.216 |
| Average thickness of the levator ani muscle/mm | 20.08 (16.14, 21.99) | 20.27 (16.75, 22.11) | 19.12 (14.05, 21.76) | 0.176 |
| External distance of the levator ani muscle/mm | 55.87 (50.07, 60.86) | 56.61 (51.95, 61.44) | 54.49 (45.65, 59.66) | 0.128 |
| Age at surgery/year | 70 (67, 75) | 71 (67, 75) | 70 (68, 74) | 0.849 |
| Height/cm | 170.00 (167.00, 173.00) | 170.00 (166.00, 173.00) | 170.00 (167.62, 172.75) | 0.617 |
| Weight/kg | 70.00 (65.00, 74.95) | 70.00 (65.00, 75.00) | 68.00 (65.00, 71.88) | 0.232 |
| BMI/(kg·m-2) | 24.18±2.47 | 24.32±2.56 | 23.87±2.23 | 0.284 |
| Preoperative highest PSA/(ng·mL-1) | 10.70 (7.91, 17.00) | 11.10 (7.73, 17.00) | 10.70 (8.00, 16.85) | 0.832 |
| History of endocrine therapy/n(%) | 0.993 | |||
| No | 532 (88.08) | 372 (88.57) | 160 (86.96) | |
| Yes | 72 (11.92) | 48 (11.43) | 24 (13.04) | |
| DVC/n(%) | 0.647 | |||
| Suture | 520 (86.09) | 356 (84.76) | 164 (89.13) | |
| Preservation | 84 (13.91) | 64 (15.24) | 20 (10.87) | |
| NVB/n(%) | >0.999 | |||
| Bilateral extrafascial | 484 (80.13) | 336 (80.00) | 148 (80.43) | |
| Other ways | 120 (19.87) | 84 (20.00) | 36 (19.57) | |
| Modified anterior approach/n(%) | >0.999 | |||
| No | 592 (98.01) | 412 (98.10) | 180 (97.83) | |
| Yes | 12 (1.99) | 8 (1.90) | 4 (2.17) | |
| Reconstruction/n(%) | 0.726 | |||
| No | 388 (64.24) | 264 (62.86) | 124 (67.39) | |
| Yes | 216 (35.76) | 156 (37.14) | 60 (32.61) | |
| APA/n (%) | 0.553 | |||
| Preservation | 592 (98.01) | 408 (97.14) | 184 (100.00) | |
| Non-reservation | 12 (1.99) | 12 (2.86) | 0 (0) | |
| Lymph node dissection/n(%) | >0.999 | |||
| No | 516 (85.43) | 360 (85.71) | 156 (84.78) | |
| Yes | 88 (14.57) | 60 (14.29) | 28 (15.22) | |
| Intraoperative blood loss/mL | 50 (35, 100) | 50 (50, 100) | 50 (30, 80) | 0.434 |
| Gleason score/n(%) | 0.649 | |||
| 6 | 64 (10.60) | 52 (12.38) | 12 (6.52) | |
| 7 | 364 (60.26) | 240 (57.14) | 124 (67.39) | |
| 8 | 52 (8.61) | 40 (9.52) | 12 (6.52) | |
| 9 | 124 (20.53) | 88 (20.95) | 36 (19.57) | |
| Tumor status of the apex margin/n(%) | 0.659 | |||
| Negative | 492 (81.46) | 348 (82.86) | 144 (78.26) | |
| Positive | 112 (18.54) | 72 (17.14) | 40 (21.74) | |
| Prostate volume/mm3 | 36.40 (25.73, 46.80) | 36.40 (26.75, 46.21) | 36.40 (24.52, 51.09) | 0.984 |
| Three-month postoperative urinary control/n(%) | 0.408 | |||
| Continence | 352 (58.28) | 256 (60.95) | 96 (52.17) | |
| Incontinence | 252 (41.72) | 164 (39.05) | 88 (47.83) | |
| Item | Continence (n=256) | Incontinence (n=164) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| IPPL/mm | 0 (0, 5.68) | 0 (0, 8.21) | 0.131 |
| Prostatic apex shape/n(%) | <0.001 | ||
| Type A | 52 (20.31) | 128 (78.05) | |
| Type B | 56 (21.88) | 20 (12.19) | |
| Type D | 148 (57.81) | 16 (9.76) | |
| Prostate apical depth/mm | 28.63±5.27 | 31.03±6.17 | 0.044 |
| Pubic height/mm | 35.3±3.36 | 35.64±4.30 | 0.667 |
| Pubic symphysis to bladder neck distance/mm | 24.30 (22.20, 28.00) | 25.27 (22.03, 29.93) | 0.395 |
| Distance between the bladder neck and the pubococcygeous line/mm | 39.10 (34.91, 43.24) | 41.46 (35.38, 45.39) | 0.329 |
| Maximum prostate height/mm | 39.55 (36.93, 46.39) | 45.15 (39.94, 50.65) | 0.011 |
| Anteroposterior diameter of the middle pelvic plane/mm | 103.48±7.48 | 102.61±9.30 | 0.618 |
| Pubic symphysis angle/(°) | 32.98±5.39 | 34.61±5.11 | 0.122 |
| Membranous urethra angle/(°) | 115.46±7.64 | 117.15 ± 8.72 | 0.312 |
| MUL/mm | 11.09 (9.42, 13.40) | 6.53 (6.04, 7.72) | < 0.001 |
| Angle between membranous urethra and prostatic axis/(°) | 132.55±9.69 | 133.80±9.51 | 0.517 |
| Pubourethral angle/(°) | 60.20±8.50 | 61.90±9.39 | 0.353 |
| Maximum prostate width/mm | 49.44 (44.75, 51.52) | 52.68 (49.38, 58.13) | < 0.001 |
| Maximum prostate length/mm | 36.50±7.12 | 41.56±7.02 | < 0.001 |
| Femoral bone width/mm | 118.99 (113.90, 121.32) | 116.69 (110.64, 120.89) | 0.051 |
| Urethral wall thickness/mm | 17.66±2.29 | 15.60±4.40 | 0.008 |
| Left levator ani muscle thickness/mm | 21.69 (20.39, 23.34) | 15.06 (12.82, 19.59) | < 0.001 |
| Right levator ani muscle thickness/mm | 21.42 (20.25, 22.82) | 15.36 (12.65, 17.84) | < 0.001 |
| Average thickness of the levator ani muscle/mm | 21.43 (20.29, 23.40) | 15.74 (12.37, 18.95) | < 0.001 |
| External distance of the levator ani muscle/mm | 58.52 (55.75, 62.95) | 50.80 (42.62, 55.50) | < 0.001 |
| Age at surgery/year | 70 (68, 75) | 71 (66, 75) | 0.911 |
| Height/cm | 170 (167, 174) | 170 (165, 173) | 0.280 |
| Weight/kg | 69.98±8.79 | 70.01±6.22 | 0.984 |
| BMI/(kg·m-2) | 24.17±2.88 | 24.54±1.99 | 0.440 |
| Preoperative highest PSA/(ng·mL-1) | 10.90 (7.73, 17.19) | 11.33 (8.20, 16.66) | 0.765 |
| History of endocrine therapy/n(%) | 0.761 | ||
| No | 224 (87.50) | 148 (90.24) | |
| Yes | 32 (12.50) | 16 (9.76) | |
| DVC/n(%) | 0.126 | ||
| Suture | 204 (79.69) | 152 (92.68) | |
| Preservation | 52 (20.31) | 12 (7.32) | |
| NVB/n(%) | 0.881 | ||
| Bilateral extrafascial | 208 (81.25) | 128 (78.05) | |
| Other ways | 48 (18.75) | 36 (21.95) | |
| Modified anterior approach/n(%) | >0.999 | ||
| No | 252 (98.44) | 160 (97.56) | |
| Yes | 4 (1.56) | 4 (2.44) | |
| Reconstruction/n(%) | >0.999 | ||
| No | 160 (62.50) | 104 (63.41) | |
| Yes | 96 (37.50) | 60 (36.59) | |
| APA/n(%) | 0.279 | ||
| Preservation | 244 (95.31) | 164 (100.00) | |
| Non-reservation | 12 (4.69) | 0 (0) | |
| Lymph node dissection/n(%) | 0.713 | ||
| No | 224 (87.50) | 136 (82.93) | |
| Yes | 32 (12.50) | 28 (17.07) | |
| Intraoperative blood loss/mL | 50 (30, 80) | 80 (50, 100) | 0.003 |
| Gleason score/n(%) | 0.624 | ||
| 6 | 28 (10.94) | 24 (14.63) | |
| 7 | 144 (56.25) | 96 (58.54) | |
| 8 | 32 (12.50) | 8 (4.88) | |
| 9 | 52 (20.31) | 36 (21.95) | |
| Tumor status of the apex margin/n(%) | 0.802 | ||
| Negative | 216 (84.38) | 132 (80.49) | |
| Positive | 40 (15.62) | 32 (19.51) | |
| Prostate volume/mm3 | 36.40 (24.86, 47.33) | 37.44 (28.67, 43.68) | 0.517 |
表2 训练集患者术后早期尿失禁的单因素分析
Tab 2 Univariate analysis of early postoperative urinary incontinence in the training set
| Item | Continence (n=256) | Incontinence (n=164) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| IPPL/mm | 0 (0, 5.68) | 0 (0, 8.21) | 0.131 |
| Prostatic apex shape/n(%) | <0.001 | ||
| Type A | 52 (20.31) | 128 (78.05) | |
| Type B | 56 (21.88) | 20 (12.19) | |
| Type D | 148 (57.81) | 16 (9.76) | |
| Prostate apical depth/mm | 28.63±5.27 | 31.03±6.17 | 0.044 |
| Pubic height/mm | 35.3±3.36 | 35.64±4.30 | 0.667 |
| Pubic symphysis to bladder neck distance/mm | 24.30 (22.20, 28.00) | 25.27 (22.03, 29.93) | 0.395 |
| Distance between the bladder neck and the pubococcygeous line/mm | 39.10 (34.91, 43.24) | 41.46 (35.38, 45.39) | 0.329 |
| Maximum prostate height/mm | 39.55 (36.93, 46.39) | 45.15 (39.94, 50.65) | 0.011 |
| Anteroposterior diameter of the middle pelvic plane/mm | 103.48±7.48 | 102.61±9.30 | 0.618 |
| Pubic symphysis angle/(°) | 32.98±5.39 | 34.61±5.11 | 0.122 |
| Membranous urethra angle/(°) | 115.46±7.64 | 117.15 ± 8.72 | 0.312 |
| MUL/mm | 11.09 (9.42, 13.40) | 6.53 (6.04, 7.72) | < 0.001 |
| Angle between membranous urethra and prostatic axis/(°) | 132.55±9.69 | 133.80±9.51 | 0.517 |
| Pubourethral angle/(°) | 60.20±8.50 | 61.90±9.39 | 0.353 |
| Maximum prostate width/mm | 49.44 (44.75, 51.52) | 52.68 (49.38, 58.13) | < 0.001 |
| Maximum prostate length/mm | 36.50±7.12 | 41.56±7.02 | < 0.001 |
| Femoral bone width/mm | 118.99 (113.90, 121.32) | 116.69 (110.64, 120.89) | 0.051 |
| Urethral wall thickness/mm | 17.66±2.29 | 15.60±4.40 | 0.008 |
| Left levator ani muscle thickness/mm | 21.69 (20.39, 23.34) | 15.06 (12.82, 19.59) | < 0.001 |
| Right levator ani muscle thickness/mm | 21.42 (20.25, 22.82) | 15.36 (12.65, 17.84) | < 0.001 |
| Average thickness of the levator ani muscle/mm | 21.43 (20.29, 23.40) | 15.74 (12.37, 18.95) | < 0.001 |
| External distance of the levator ani muscle/mm | 58.52 (55.75, 62.95) | 50.80 (42.62, 55.50) | < 0.001 |
| Age at surgery/year | 70 (68, 75) | 71 (66, 75) | 0.911 |
| Height/cm | 170 (167, 174) | 170 (165, 173) | 0.280 |
| Weight/kg | 69.98±8.79 | 70.01±6.22 | 0.984 |
| BMI/(kg·m-2) | 24.17±2.88 | 24.54±1.99 | 0.440 |
| Preoperative highest PSA/(ng·mL-1) | 10.90 (7.73, 17.19) | 11.33 (8.20, 16.66) | 0.765 |
| History of endocrine therapy/n(%) | 0.761 | ||
| No | 224 (87.50) | 148 (90.24) | |
| Yes | 32 (12.50) | 16 (9.76) | |
| DVC/n(%) | 0.126 | ||
| Suture | 204 (79.69) | 152 (92.68) | |
| Preservation | 52 (20.31) | 12 (7.32) | |
| NVB/n(%) | 0.881 | ||
| Bilateral extrafascial | 208 (81.25) | 128 (78.05) | |
| Other ways | 48 (18.75) | 36 (21.95) | |
| Modified anterior approach/n(%) | >0.999 | ||
| No | 252 (98.44) | 160 (97.56) | |
| Yes | 4 (1.56) | 4 (2.44) | |
| Reconstruction/n(%) | >0.999 | ||
| No | 160 (62.50) | 104 (63.41) | |
| Yes | 96 (37.50) | 60 (36.59) | |
| APA/n(%) | 0.279 | ||
| Preservation | 244 (95.31) | 164 (100.00) | |
| Non-reservation | 12 (4.69) | 0 (0) | |
| Lymph node dissection/n(%) | 0.713 | ||
| No | 224 (87.50) | 136 (82.93) | |
| Yes | 32 (12.50) | 28 (17.07) | |
| Intraoperative blood loss/mL | 50 (30, 80) | 80 (50, 100) | 0.003 |
| Gleason score/n(%) | 0.624 | ||
| 6 | 28 (10.94) | 24 (14.63) | |
| 7 | 144 (56.25) | 96 (58.54) | |
| 8 | 32 (12.50) | 8 (4.88) | |
| 9 | 52 (20.31) | 36 (21.95) | |
| Tumor status of the apex margin/n(%) | 0.802 | ||
| Negative | 216 (84.38) | 132 (80.49) | |
| Positive | 40 (15.62) | 32 (19.51) | |
| Prostate volume/mm3 | 36.40 (24.86, 47.33) | 37.44 (28.67, 43.68) | 0.517 |
| Item | Log λ |
|---|---|
| Prostatic apex shape | -0.519 |
| Prostate apical depth | 0 |
| Maximum prostate height | 0.043 |
| MUL | -0.343 |
| Maximum prostate width | 0 |
| Maximum prostate length | 0.031 |
| Urethral wall thickness | 0 |
| Left levator ani muscle thickness | 0 |
| Right levator ani muscle thickness | -0.486 |
| Average thickness of the levator ani muscle | 0 |
| External distance of the levator ani muscle | 0 |
| Intraoperative blood loss | 0.014 |
表3 基于LASSO回归的预测变量筛选
Tab 3 Predictor selection based on LASSO regression
| Item | Log λ |
|---|---|
| Prostatic apex shape | -0.519 |
| Prostate apical depth | 0 |
| Maximum prostate height | 0.043 |
| MUL | -0.343 |
| Maximum prostate width | 0 |
| Maximum prostate length | 0.031 |
| Urethral wall thickness | 0 |
| Left levator ani muscle thickness | 0 |
| Right levator ani muscle thickness | -0.486 |
| Average thickness of the levator ani muscle | 0 |
| External distance of the levator ani muscle | 0 |
| Intraoperative blood loss | 0.014 |
| Item | Coef | S.E. | Z value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prostatic apex shape type B | -2.296 | 1.340 | -1.710 | 0.087 |
| Prostatic apex shape type D | -0.845 | 1.299 | -0.650 | 0.515 |
| Maximum prostate height | 0.153 | 0.108 | 1.420 | 0.156 |
| MUL | -0.523 | 0.258 | -2.020 | 0.043 |
| Maximum prostate length | 0.015 | 0.099 | 0.150 | 0.878 |
| Right levator ani muscle thickness | -0.756 | 0.234 | -3.230 | 0.001 |
| Intraoperative blood loss | 0.027 | 0.013 | 2.110 | 0.035 |
表4 术后早期尿失禁发生的多因素 Logistic回归分析
Tab 4 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of early postoperative urinary incontinence
| Item | Coef | S.E. | Z value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prostatic apex shape type B | -2.296 | 1.340 | -1.710 | 0.087 |
| Prostatic apex shape type D | -0.845 | 1.299 | -0.650 | 0.515 |
| Maximum prostate height | 0.153 | 0.108 | 1.420 | 0.156 |
| MUL | -0.523 | 0.258 | -2.020 | 0.043 |
| Maximum prostate length | 0.015 | 0.099 | 0.150 | 0.878 |
| Right levator ani muscle thickness | -0.756 | 0.234 | -3.230 | 0.001 |
| Intraoperative blood loss | 0.027 | 0.013 | 2.110 | 0.035 |
| [1] | DIAO X Y, GUO C, JIN Y K, et al. Cancer situation in China: an analysis based on the global epidemiological data released in 2024[J]. Cancer Commun (Lond), 2025, 45(2): 178-197. |
| [2] | RUAN X H, STACIA CHUN T T, HUANG D, et al. Outcomes of radical prostatectomy in a 20-year localized prostate cancer single institution series in China[J]. Asian J Androl, 2023, 25(3): 345-349. |
| [3] | COSTELLO A J. Considering the role of radical prostatectomy in 21st century prostate cancer care[J]. Nat Rev Urol, 2020, 17(3): 177-188. |
| [4] | FICARRA V, NOVARA G, ARTIBANI W, et al. Retropubic, laparoscopic, and robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a systematic review and cumulative analysis of comparative studies[J]. Eur Urol, 2009, 55(5): 1037-1063. |
| [5] | WALZ J, EPSTEIN J I, GANZER R, et al. A critical analysis of the current knowledge of surgical anatomy of the prostate related to optimisation of cancer control and preservation of continence and erection in candidates for radical prostatectomy: an update[J]. Eur Urol, 2016,70(2):301-311. |
| [6] | FICARRA V, NOVARA G, ROSEN R C, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of studies reporting urinary continence recovery after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy[J]. Eur Urol, 2012, 62(3): 405-417. |
| [7] | CENTEMERO A, RIGATTI L, GIRAUDO D, et al. Preoperative pelvic floor muscle exercise for early continence after radical prostatectomy: a randomised controlled study[J]. Eur Urol, 2010, 57(6): 1039-1043. |
| [8] | SCHIFANO N, CAPOGROSSO P, TUTOLO M, et al. How to prevent and manage post-prostatectomy incontinence: a review[J]. World J Mens Health, 2021, 39(4): 581-597. |
| [9] | TUTOLO M, BRUYNEEL L, VAN DER AA F, et al. A novel tool to predict functional outcomes after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy and the value of additional surgery for incontinence[J]. BJU Int, 2021, 127(5): 575-584. |
| [10] | ZHANG F, CHU H L, HAO Y C, et al. Preoperative predictive model of early urinary continence recovery after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy[J]. World J Urol, 2023, 41(1): 59-65. |
| [11] | GU Z R, ZHENG Z T, ZHANG W T, et al. The development and assessment of a predicting nomogram for the recovery of immediate urinary continence following laparoscopic radical prostatectomy[J]. Front Surg, 2023, 9: 1071093. |
| [12] | PARK J J, HONG Y, KWON A, et al. Efficacy of surgical treatment for post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence: a systematic review and network meta-analysis[J]. Int J Surg, 2023, 109(3): 401-411. |
| [13] | LARDAS M, GRIVAS N, DEBRAY T P A, et al. Patient- and tumour-related prognostic factors for urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy for nonmetastatic prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Eur Urol Focus, 2022, 8(3): 674-689. |
| [14] | GACCI M, DE NUNZIO C, SAKALIS V, et al. Latest evidence on post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence[J]. J Clin Med, 2023, 12(3): 1190. |
| [15] | KOHJIMOTO Y, YAMASHITA S, KIKKAWA K, et al. The association of length of the resected membranous urethra with urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy[J]. Urol J, 2020, 17(2): 146-151. |
| [16] | WANG M, DENG R Q, WANG L, et al. Association between 3D membranous urethral parameters and urinary continence recovery after RARP[J]. Eur J Med Res, 2024, 29(1): 165. |
| [17] | SONG C, DOO C K, HONG J H, et al. Relationship between the integrity of the pelvic floor muscles and early recovery of continence after radical prostatectomy[J]. J Urol, 2007, 178(1): 208-211. |
| [1] | 汤开然, 冯成领, 韩邦旻. 基于单细胞测序与转录组测序构建M2巨噬细胞基因相关的前列腺癌预后模型[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(5): 549-561. |
| [2] | 陈蓉, 张锰, 朱荻绮, 郭颖, 沈捷. 基于抗中性粒细胞胞质抗体的列线图模型对川崎病患儿并发冠状动脉病变风险的预测作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(4): 459-467. |
| [3] | 刘楚萱, 左佳鑫, 熊屏. 基于超声评分参数及临床指标的列线图鉴别原发性干燥综合征与IgG4相关唾液腺炎[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(3): 373-380. |
| [4] | 朱涵菁, 郭艳, 殷弘凡, 王贝贝, 谢娟, 杨艳. 前列腺癌内分泌治疗患者体重管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(2): 194-203. |
| [5] | 陆佳萍, 刘醒, 张林杉, 赵琳, 张敏, 李小英, 刘玥隽. 腹部脂肪面积与2型糖尿病患者胰岛β细胞第一时相分泌功能的关系[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(1): 42-50. |
| [6] | 蔡人杰, 徐明. KHSRP通过ANK3调节前列腺癌细胞对雄激素的反应性[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(4): 417-426. |
| [7] | 邓青松, 张长青, 陶诗聪. 烟酰胺代谢相关基因与骨关节炎的关系探索[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(2): 145-160. |
| [8] | 杨婧偊, 陈留宝, 王康太, 杨兴智, 于海涛. 基于实验室指标的系统性红斑狼疮鉴别诊断列线图的构建及评估[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(2): 204-211. |
| [9] | 朱涵菁, 殷弘凡, 尤思洁, 杨艳. 前列腺癌患者内分泌治疗相关不良反应的潜在剖面分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(9): 1186-1193. |
| [10] | 严叶青, 梁胜, 杨斌, 邹仁健, 马玉飞, 蔡利生, 王辉, 傅宏亮. 18F-MD-PSMA PET/CT显像在中高危前列腺癌初始分期中的应用价值[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(7): 873-881. |
| [11] | 饶琳, 张琳娜, 袁嘉琪, 卢邦春. 产后盆底肌训练对改善盆底功能的效果分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(3): 308-313. |
| [12] | 杨万里, 宋娟, 李兵, 劳一敏. CBX8抑制前列腺癌细胞侵袭的机制研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(12): 1507-1519. |
| [13] | 薛淋淋, 李秉翰, 常丽仙, 李卫昆, 刘春云, 刘立. 丙型病毒性肝炎肝硬化失代偿期患者发生细菌感染的列线图预测模型构建及评价[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(1): 52-60. |
| [14] | 邓露, 李佳怡. 点阵CO2激光治疗女性压力性尿失禁的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(5): 685-689. |
| [15] | 王慧, 赵莹, 温丽蓉, 曹军, 羊继平, 原永明. 前列腺癌患者血液中PSA、TAP、MACC1的表达及其诊断价值[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(4): 496-501. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||