
Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science) ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 129-137.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2025.02.001
• Basic research •
ZHANG Difan( ), WANG Minghui, ZHAO Jie, WAN Jiangbo, HUANG Fang(
), WANG Minghui, ZHAO Jie, WAN Jiangbo, HUANG Fang( ), HAO Siguo(
), HAO Siguo( )
)
Received:2024-05-20
Accepted:2024-10-14
Online:2025-02-28
Published:2025-02-28
Contact:
HUANG Fang, HAO Siguo
E-mail:zhangdifan121@163.com;huangfang335@163.com;haosiguo@xinhuamed.com.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
ZHANG Difan, WANG Minghui, ZHAO Jie, WAN Jiangbo, HUANG Fang, HAO Siguo. Anti-leukemia effect of B7 gene-modified leukemia cell-derived exosomes[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(2): 129-137.
| Gene | Forward primer (5'→3') | Reverse primer (5'→3') |
|---|---|---|
| Cd206 | GGGTTGCTATCACTCTCTATGC | TTTCTTGTCTGTTGCCGTAGTT |
| Il-10 | GACTTTAAGGGTTACCTGGGTTG | TCACATGCGCCTTGATGTCTG |
| Il-6 | ACTCACCTCTTCAGAACGAATTG | CCATCTTTGGAAGGTTCAGGTTG |
| Tnf-α | ACCAGCAGATGGGCTGTACC | GCGGAGAGGAGGCTGACTTT |
| Gadph | GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT | GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG |
Tab 1 Primer sequences for qPCR
| Gene | Forward primer (5'→3') | Reverse primer (5'→3') |
|---|---|---|
| Cd206 | GGGTTGCTATCACTCTCTATGC | TTTCTTGTCTGTTGCCGTAGTT |
| Il-10 | GACTTTAAGGGTTACCTGGGTTG | TCACATGCGCCTTGATGTCTG |
| Il-6 | ACTCACCTCTTCAGAACGAATTG | CCATCTTTGGAAGGTTCAGGTTG |
| Tnf-α | ACCAGCAGATGGGCTGTACC | GCGGAGAGGAGGCTGACTTT |
| Gadph | GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT | GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG |
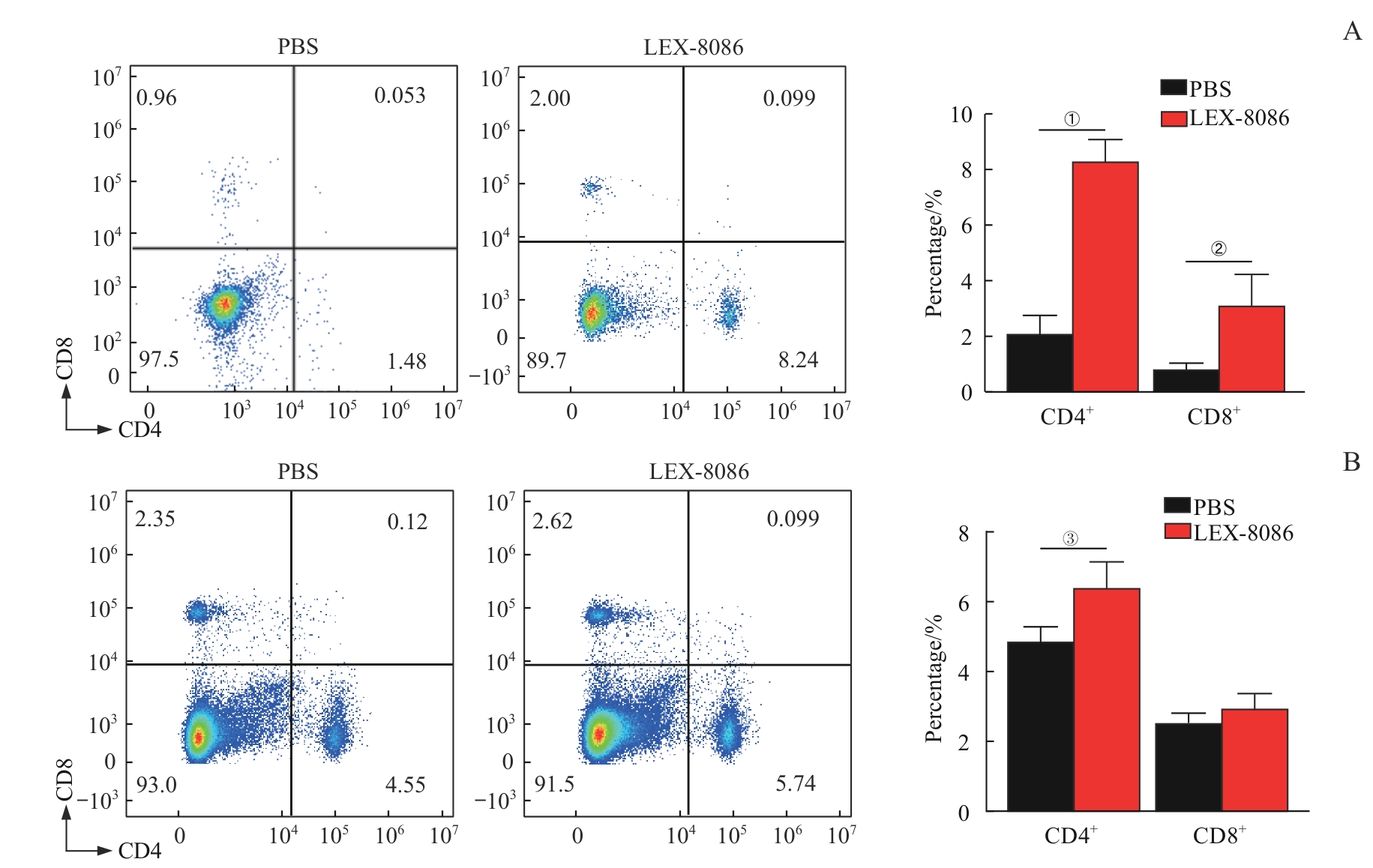
Fig 5 Proportions of CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells in the lymph nodes and spleens of DBA/2-leukemia tumor-bearing mice in the two groups determined by flow cytometry
| 1 | WHITESIDE T L. Tumor-derived exosomes and their role in cancer progression[J]. Adv Clin Chem, 2016, 74: 103-141. |
| 2 | SUN Z Y, XIE C Q, LIU H, et al. CD19 CAR-T cell therapy induced immunotherapy associated interstitial pneumonitis: a case report[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 778192. |
| 3 | RAJE N, BERDEJA J, LIN Y, et al. Anti-BCMA CAR T-cell therapy bb2121 in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2019, 380(18): 1726-1737. |
| 4 | OTT P A, HU Z T, KESKIN D B, et al. An immunogenic personal neoantigen vaccine for patients with melanoma[J]. Nature, 2017, 547(7662): 217-221. |
| 5 | SHEIH A, VOILLET V, HANAFI L A, et al. Clonal kinetics and single-cell transcriptional profiling of CAR-T cells in patients undergoing CD19 CAR-T immunotherapy[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 219. |
| 6 | CHEN G, HUANG A C, ZHANG W, et al. Exosomal PD-L1 contributes to immunosuppression and is associated with anti-PD-1 response[J]. Nature, 2018, 560(7718): 382-386. |
| 7 | AHMAD A. Epigenetic regulation of immunosuppressive tumor-associated macrophages through dysregulated microRNAs[J]. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2022, 124: 26-33. |
| 8 | NASERI M, BOZORGMEHR M, ZÖLLER M, et al. Tumor-derived exosomes: the next generation of promising cell-free vaccines in cancer immunotherapy[J]. Oncoimmunology, 2020, 9(1): 1779991. |
| 9 | KRACKHARDT A M, HARIG S, WITZENS M, et al. T-cell responses against chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells: implications for immunotherapy[J]. Blood, 2002, 100(1): 167-173. |
| 10 | TOWNSEND S E, ALLISON J P. Tumor rejection after direct costimulation of CD8+ T cells by B7-transfected melanoma cells[J]. Science, 1993, 259(5093): 368-370. |
| 11 | CHENG Q Z, KANG Y, YAO B, et al. Genetically engineered-cell-membrane nanovesicles for cancer immunotherapy[J]. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2023, 10(26): e2302131. |
| 12 | HU W W, HUANG F, NING L X, et al. Enhanced immunogenicity of leukemia-derived exosomes via transfection with lentiviral vectors encoding costimulatory molecules[J]. Cell Oncol (Dordr), 2020, 43(5): 889-900. |
| 13 | LI J Q, HUANG F, JIANG Y, et al. A novel costimulatory molecule gene-modified leukemia cell-derived exosome-targeted CD4+ T cell vaccine efficiently enhances anti-leukemia immunity[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 1043484. |
| 14 | JOHNSON B D, YAN X C, SCHAUER D W, et al. Dual expression of CD80 and CD86 produces a tumor vaccine superior to single expression of either molecule[J]. Cell Immunol, 2003, 222(1): 15-26. |
| 15 | VASILEVKO V, GHOCHIKYAN A, HOLTERMAN M J, et al. CD80 (B7-1) and CD86 (B7-2) are functionally equivalent in the initiation and maintenance of CD4+ T-cell proliferation after activation with suboptimal doses of PHA[J]. DNA Cell Biol, 2002, 21(3): 137-149. |
| 16 | SIVORI S, PENDE D, QUATRINI L, et al. NK cells and ILCs in tumor immunotherapy[J]. Mol Aspects Med, 2021, 80: 100870. |
| 17 | TRACY S I, VENKATESH H, HEKIM C, et al. Combining nilotinib and PD-L1 blockade reverses CD4+ T-cell dysfunction and prevents relapse in acute B-cell leukemia[J]. Blood, 2022, 140(4): 335-348. |
| 18 | DISTLER E, ALBRECHT J, BRUNK A, et al. Patient-individualized CD8⁺ cytolytic T-cell therapy effectively combats minimal residual leukemia in immunodeficient mice[J]. Int J Cancer, 2016, 138(5): 1256-1268. |
| [1] | HE Rui, YAN Kepeng, WANG Jing. Targeting folate cycle enhances effects of cancer immunotherapy by modulating myeloid-derived suppressor cells [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(8): 1011-1022. |
| [2] | HU Fei, CAI Xiaohan, CHENG Rui, JI Shiyu, MIAO Jiaxin, ZHU Yan, FAN Guangjian. Progress in translational research on immunotherapy for osteosarcoma [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(7): 814-821. |
| [3] | DING Yanling, LI Jie, YUAN Jun, LI Yan. Research progress in targeted therapies of chronic lymphocytic leukemia [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(2): 264-270. |
| [4] | LIU Jiayu, HUANG Fang, HAO Siguo. A case of chronic myelomonocytic leukemia complicated with immune thrombocytopenia [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(2): 287-290. |
| [5] | TANG Sijie, MI Jianqing. Clinical advances in antibody-drug conjugates for hematological malignancies [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(12): 1607-1614. |
| [6] | KONG Ruxin, ZHOU Yaqun, WEI Tingyi, LEI Ming. Function and mechanism of cancer-testis antigen CT63 in chronic myeloid leukemia [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(11): 1347-1358. |
| [7] | FANG Xinyue, SHI Lan, XIA Siyi, WANG Jiaxuan, WU Yingli, HE Kejun. Research progress in Menin-MLL interaction and its inhibitors in MLL-rearranged leukemia [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(10): 1287-1298. |
| [8] | ZHOU Haixia, ZHANG Jing. Research progress of m6A methylation modification in regulating tumor immunity [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(1): 137-144. |
| [9] | CUI Zhiyan, CHEN Yao, TAO Yue, SHEN Shuhong, LI Hui. Effects of PRPS1 I72 mutations on drug resistance in acute lymphoblastic leukemia and its mechanisms [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(8): 977-987. |
| [10] | WU Qiqi, WANG Hao, LIN Li, YAN Bo, ZHANG Shulin. miR-185-5p facilitates intracellular Mycobacterium growth via inhibiting macrophage autophagy [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(6): 699-708. |
| [11] | LI Ying, TAN Yangxia, YIN Hongxin, JIANG Yanling, CHEN Li, MENG Guoyu. Research progress in the pathogenesis and prognosis of ZNF384 fusion subtype acute leukemia [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(5): 631-640. |
| [12] | FU Lirong, ZHANG Chen. Advances in the role of circular RNA in schizophrenia [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(11): 1445-1449. |
| [13] | HOU Shumin, SHAO Jingbo. Research progress in clinical characteristics, diagnosis and prognosis of TdT-negative lymphoblastic lymphoma/acute lymphoblastic leukemia [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(1): 120-124. |
| [14] | LU Yu, WANG Hao, BA Qian. Role of gut microbiota in hepatocellular carcinoma: cancer occurrence, progresses and treatments [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2022, 42(7): 939-944. |
| [15] | JIN Lei, XU Wenbin, YE Chenjing, YAN Hua. Prophylactic antifungal effect of posaconazole on patients with hematological malignant tumor undergoing chemotherapy [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2022, 42(6): 792-796. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 85
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 160
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||