
Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science) ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (10): 1342-1352.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2025.10.009
• Clinical research • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Jia1, REN Lingjie1, SHI Minmin1, TANG Xiaomei1, MA Fangfang1, QIN Jiejie1,2( )
)
Received:2025-03-25
Accepted:2025-09-18
Online:2025-10-28
Published:2025-10-23
Contact:
QIN Jiejie
E-mail:qinjie2007@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
LIU Jia, REN Lingjie, SHI Minmin, TANG Xiaomei, MA Fangfang, QIN Jiejie. Identification and evaluation of COL12A1 as a novel serological diagnostic marker in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(10): 1342-1352.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://xuebao.shsmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2025.10.009
| Characteristic | Ruijin cohort Ⅰ (n=67) | CPTAC cohort (n=135) | Ruijin cohort Ⅱ | P2 value② | P3 value③ | P4 value④ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDAC (n=47) | Normal (n=75) | P1 value① | ||||||
| Age/year | 63 (56, 67) | 65 (60, 71) | 67 (56, 71) | 64 (56, 69) | 0.317 | 0.058 | 0.054 | 0.375 |
| Gender/n(%) | 0.634 | 0.331 | 0.810 | 0.280 | ||||
| Female | 33 (49.3) | 64 (47.4) | 20 (42.6) | 37 (49.3) | ||||
| Male | 34 (50.7) | 71 (52.6) | 27 (57.4) | 38 (50.7) | ||||
| Race/n(%) | ‒ | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| Black | 0 (0) | 2 (1.5) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||||
| White | 0 (0) | 30 (22.2) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||||
| Yellow | 67 (100) | 0 (0) | 47 (100) | 75 (100) | ||||
| NA | 0 (0) | 103 (76.3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||||
| TNM stage/n(%) | ‒ | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.380 | ||||
| Ⅰ | 20 (29.9) | 23 (17.0) | 5 (10.6) | ‒ | ||||
| Ⅱ | 47 (70.1) | 56 (41.5) | 17 (36.2) | ‒ | ||||
| Ⅲ | 0 (0) | 41 (30.4) | 18 (38.3) | ‒ | ||||
| Ⅳ | 0 (0) | 9 (6.7) | 7 (14.9) | ‒ | ||||
| NA | 0 (0) | 6 (4.4) | 0 (0) | ‒ | ||||
| T stage/n(%) | ‒ | 0.185 | 0.120 | 0.720 | ||||
| T1 | 10 (14.9) | 10 (7.4) | 4 (8.5) | ‒ | ||||
| T2 | 20 (29.9) | 83 (61.5) | 20 (42.6) | ‒ | ||||
| T3 | 37 (55.2) | 39 (28.9) | 7 (14.9) | ‒ | ||||
| T4 | 0 (0) | 1 (0.7) | 16 (34.0) | ‒ | ||||
| TX | 0 (0) | 2 (1.5) | 0 (0) | ‒ | ||||
| N stage/n(%) | ‒ | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.043 | ||||
| N0 | 44 (65.7) | 30 (22.2) | 12 (25.5) | ‒ | ||||
| N1 | 23 (34.3) | 51 (37.8) | 18 (38.3) | ‒ | ||||
| N2 | 0 (0) | 46 (34.1) | 14 (29.8) | ‒ | ||||
| NX | 0 (0) | 8 (5.9) | 3 (6.4) | ‒ | ||||
| M stage/n(%) | ‒ | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | ||||
| M0 | 67 (100) | 88 (65.2) | 40 (85.1) | ‒ | ||||
| M1 | 0 (0) | 8 (5.9) | 7 (14.9) | ‒ | ||||
| MX | 0 (0) | 39 (28.9) | 0 (0) | ‒ | ||||
Tab 1 Basic characteristics of the cohorts in the study
| Characteristic | Ruijin cohort Ⅰ (n=67) | CPTAC cohort (n=135) | Ruijin cohort Ⅱ | P2 value② | P3 value③ | P4 value④ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDAC (n=47) | Normal (n=75) | P1 value① | ||||||
| Age/year | 63 (56, 67) | 65 (60, 71) | 67 (56, 71) | 64 (56, 69) | 0.317 | 0.058 | 0.054 | 0.375 |
| Gender/n(%) | 0.634 | 0.331 | 0.810 | 0.280 | ||||
| Female | 33 (49.3) | 64 (47.4) | 20 (42.6) | 37 (49.3) | ||||
| Male | 34 (50.7) | 71 (52.6) | 27 (57.4) | 38 (50.7) | ||||
| Race/n(%) | ‒ | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| Black | 0 (0) | 2 (1.5) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||||
| White | 0 (0) | 30 (22.2) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||||
| Yellow | 67 (100) | 0 (0) | 47 (100) | 75 (100) | ||||
| NA | 0 (0) | 103 (76.3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||||
| TNM stage/n(%) | ‒ | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.380 | ||||
| Ⅰ | 20 (29.9) | 23 (17.0) | 5 (10.6) | ‒ | ||||
| Ⅱ | 47 (70.1) | 56 (41.5) | 17 (36.2) | ‒ | ||||
| Ⅲ | 0 (0) | 41 (30.4) | 18 (38.3) | ‒ | ||||
| Ⅳ | 0 (0) | 9 (6.7) | 7 (14.9) | ‒ | ||||
| NA | 0 (0) | 6 (4.4) | 0 (0) | ‒ | ||||
| T stage/n(%) | ‒ | 0.185 | 0.120 | 0.720 | ||||
| T1 | 10 (14.9) | 10 (7.4) | 4 (8.5) | ‒ | ||||
| T2 | 20 (29.9) | 83 (61.5) | 20 (42.6) | ‒ | ||||
| T3 | 37 (55.2) | 39 (28.9) | 7 (14.9) | ‒ | ||||
| T4 | 0 (0) | 1 (0.7) | 16 (34.0) | ‒ | ||||
| TX | 0 (0) | 2 (1.5) | 0 (0) | ‒ | ||||
| N stage/n(%) | ‒ | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.043 | ||||
| N0 | 44 (65.7) | 30 (22.2) | 12 (25.5) | ‒ | ||||
| N1 | 23 (34.3) | 51 (37.8) | 18 (38.3) | ‒ | ||||
| N2 | 0 (0) | 46 (34.1) | 14 (29.8) | ‒ | ||||
| NX | 0 (0) | 8 (5.9) | 3 (6.4) | ‒ | ||||
| M stage/n(%) | ‒ | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | ||||
| M0 | 67 (100) | 88 (65.2) | 40 (85.1) | ‒ | ||||
| M1 | 0 (0) | 8 (5.9) | 7 (14.9) | ‒ | ||||
| MX | 0 (0) | 39 (28.9) | 0 (0) | ‒ | ||||
| Item | AUC | 95%CI | Accuracy/% | κ value | Sensitivity/% | Specificity/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All PDAC vs NHS | ||||||
| COL12A1 | 0.82 | 0.74‒0.90 | 82 | 0.63 | 81 | 83 |
| CA199 | 0.91 | 0.85‒0.96 | 88 | 0.75 | 89 | 87 |
| COL12A1+CA199 | 0.95 | 0.91‒0.99 | 92 | 0.83 | 94 | 91 |
| PDAC (Ⅰ‒Ⅱ stage) vs NHS | ||||||
| COL12A1 | 0.83 | 0.75‒0.92 | 81 | 0.53 | 77 | 83 |
| CA199 | 0.92 | 0.86‒0.97 | 88 | 0.69 | 91 | 87 |
| COL12A1+CA199 | 0.97 | 0.93‒0.99 | 92 | 0.79 | 95 | 91 |
| PDAC (T1-T2 stage) vs NHS | ||||||
| COL12A1 | 0.85 | 0.77‒0.93 | 83 | 0.59 | 83 | 83 |
| CA199 | 0.93 | 0.88‒0.98 | 89 | 0.73 | 96 | 87 |
| COL12A1+CA199 | 0.98 | 0.96‒1.00 | 92 | 0.80 | 96 | 91 |
| PDAC (N0 stage) vs NHS | ||||||
| COL12A1 | 0.84 | 0.75‒0.94 | 83 | 0.48 | 83 | 83 |
| CA199 | 0.92 | 0.86‒0.98 | 91 | 0.60 | 92 | 87 |
| COL12A1+CA199 | 0.97 | 0.94‒1.00 | 92 | 0.73 | 100 | 91 |
| PDAC (well-differentiated) vs NHS | ||||||
| COL12A1 | 0.80 | 0.69‒0.91 | 82 | 0.54 | 80 | 83 |
| CA199 | 0.89 | 0.79‒0.98 | 87 | 0.67 | 90 | 87 |
| COL12A1+CA199 | 0.94 | 0.85‒1.00 | 91 | 0.74 | 90 | 91 |
Tab 2 Complementary diagnostic value of COL12A1 to CA199 in the diagnosis of PDAC
| Item | AUC | 95%CI | Accuracy/% | κ value | Sensitivity/% | Specificity/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All PDAC vs NHS | ||||||
| COL12A1 | 0.82 | 0.74‒0.90 | 82 | 0.63 | 81 | 83 |
| CA199 | 0.91 | 0.85‒0.96 | 88 | 0.75 | 89 | 87 |
| COL12A1+CA199 | 0.95 | 0.91‒0.99 | 92 | 0.83 | 94 | 91 |
| PDAC (Ⅰ‒Ⅱ stage) vs NHS | ||||||
| COL12A1 | 0.83 | 0.75‒0.92 | 81 | 0.53 | 77 | 83 |
| CA199 | 0.92 | 0.86‒0.97 | 88 | 0.69 | 91 | 87 |
| COL12A1+CA199 | 0.97 | 0.93‒0.99 | 92 | 0.79 | 95 | 91 |
| PDAC (T1-T2 stage) vs NHS | ||||||
| COL12A1 | 0.85 | 0.77‒0.93 | 83 | 0.59 | 83 | 83 |
| CA199 | 0.93 | 0.88‒0.98 | 89 | 0.73 | 96 | 87 |
| COL12A1+CA199 | 0.98 | 0.96‒1.00 | 92 | 0.80 | 96 | 91 |
| PDAC (N0 stage) vs NHS | ||||||
| COL12A1 | 0.84 | 0.75‒0.94 | 83 | 0.48 | 83 | 83 |
| CA199 | 0.92 | 0.86‒0.98 | 91 | 0.60 | 92 | 87 |
| COL12A1+CA199 | 0.97 | 0.94‒1.00 | 92 | 0.73 | 100 | 91 |
| PDAC (well-differentiated) vs NHS | ||||||
| COL12A1 | 0.80 | 0.69‒0.91 | 82 | 0.54 | 80 | 83 |
| CA199 | 0.89 | 0.79‒0.98 | 87 | 0.67 | 90 | 87 |
| COL12A1+CA199 | 0.94 | 0.85‒1.00 | 91 | 0.74 | 90 | 91 |
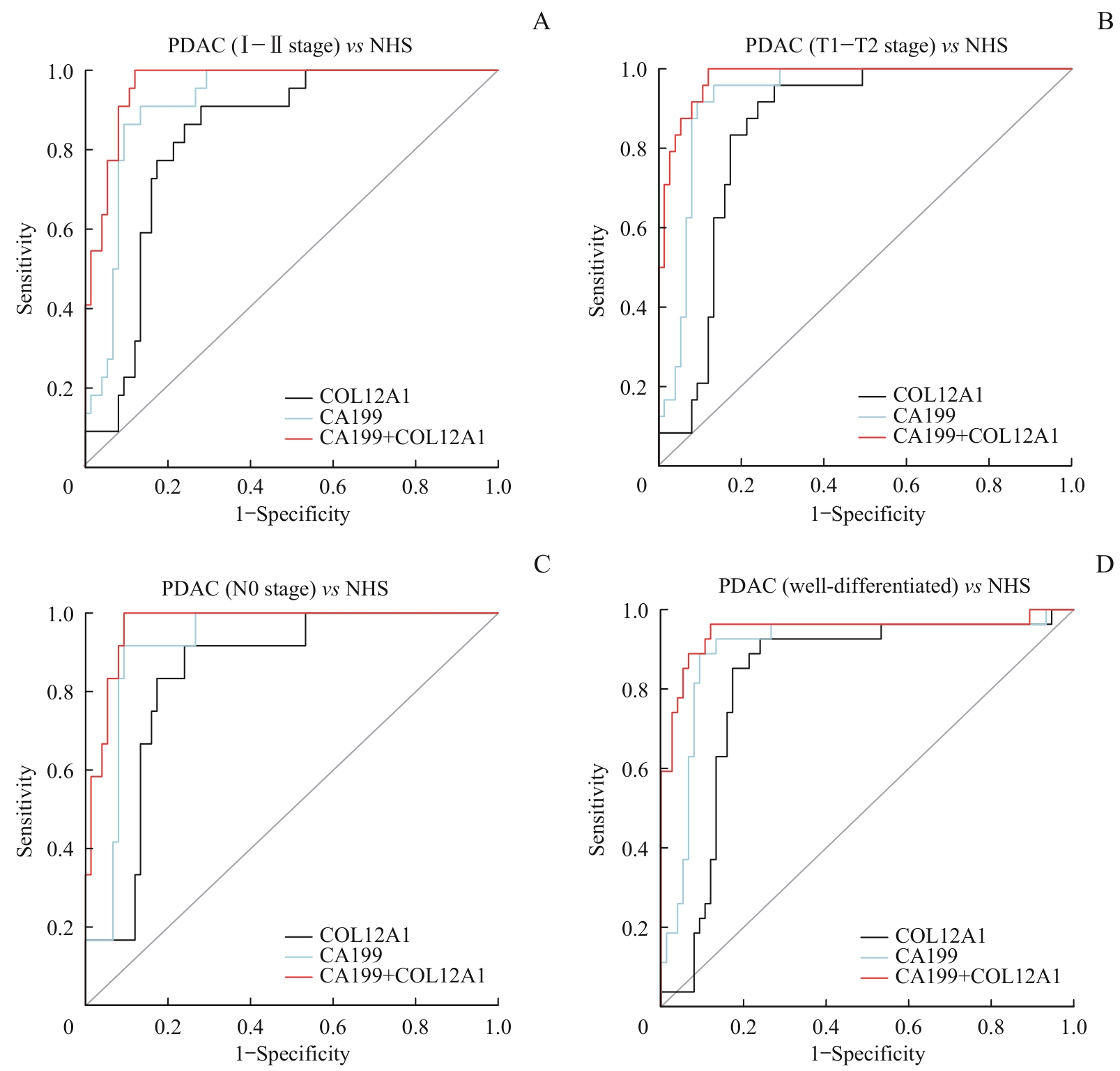
Fig 4 Diagnostic performance of COL12A1, CA199, and their combination in the subgroups of PDAC patients based on TNM stage, differentiation, T stage, and N stage
| [1] | SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. |
| [2] | RYAN D P, HONG T S, BARDEESY N. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2014, 371(11): 1039-1049. |
| [3] | 佟陈昀颢. 中国大陆地区胰腺癌回顾性临床流行病学研究[D]. 北京: 北京协和医学院, 2024. |
| TONG C Y H. A retrospective clinical epidemiology study of pancreatic cancer in mainland China[D]. Beijing: Peking Union Medical College, 2024. | |
| [4] | MIZRAHI J D, SURANA R, VALLE J W, et al. Pancreatic cancer[J]. Lancet, 2020, 395(10242): 2008-2020. |
| [5] | 胡斌, 宋少莉. 胰腺癌的治疗进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2015, 35(3): 445-449. |
| HU B, Song S L. Progresses of treatment of pancreatic cancer[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2015, 35(3): 445-449. | |
| [6] | LUO G P, JIN K Z, DENG S M, et al. Roles of CA19-9 in pancreatic cancer: biomarker, predictor and promoter[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2021, 1875(2): 188409. |
| [7] | BOYD L N C, ALI M, COMANDATORE A, et al. Prediction model for early-stage pancreatic cancer using routinely measured blood biomarkers[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2023, 6(8): e2331197. |
| [8] | HICKS D, FARSANI G T, LAVAL S, et al. Mutations in the collagen Ⅻ gene define a new form of extracellular matrix-related myopathy[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2014, 23(9): 2353-2363. |
| [9] | ZHANG Y P, WANG H X, GAO Z C, et al. COL12A1 promotes osteosarcoma progression via the FAK/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway[J]. Curr Mol Med, 2024. DOI:10.2174/0115665240322280240903111159. |
| [10] | YAN Y L, LIANG Q J, LIU Y H, et al. COL12A1 as a prognostic biomarker links immunotherapy response in breast cancer[J]. Endocr Relat Cancer, 2023, 30(5): e230012. |
| [11] | 张文姣. COL12A1在胰腺癌中的表达与临床病理特征及预后的关系[D]. 青岛: 青岛大学, 2024. |
| ZHANG W J. The expression of COL12A1 in pancreatic cancer and its relationship with clinicopathological features and prognosis[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University, 2024. | |
| [12] | KRUG K, JAEHNIG E J, SATPATHY S, et al. Proteogenomic landscape of breast cancer tumorigenesis and targeted therapy[J]. Cell, 2020, 183(5): 1436-1456.e31. |
| [13] | JIANG L X, QIN J J, DAI Y T, et al. Prospective observational study on biomarkers of response in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. Nat Med, 2024, 30(3): 749-761. |
| [14] | RITCHIE M E, PHIPSON B, WU D, et al. Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2015, 43(7): e47. |
| [15] | FANG H, KNEZEVIC B, BURNHAM K L, et al. XGR software for enhanced interpretation of genomic summary data, illustrated by application to immunological traits[J]. Genome Med, 2016, 8(1): 129. |
| [16] | DELONG E R, DELONG D M, CLARKE-PEARSON D L. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach[J]. Biometrics, 1988, 44(3): 837-845. |
| [17] | CAO L W, HUANG C, ZHOU D C, et al. Proteogenomic characterization of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. Cell, 2021, 184(19): 5031-5052.e26. |
| [18] | AMIN M B, EDGE S, GREENE F L. AJCC cancer staging manual[M]. 8th ed. New York: Springer, 2017: 327-335. |
| [19] | DOU Y C, KATSNELSON L, GRITSENKO M A, et al. Proteogenomic insights suggest druggable pathways in endometrial carcinoma[J]. Cancer Cell, 2023, 41(9): 1586-1605.e15. |
| [20] | 李宝宝. 基于蛋白质组学技术筛选脑膜瘤诊断的血清学潜在生物标志物的研究[D]. 延安: 延安大学, 2022. |
| LI B B. Screening serological diagnosis of meningioma based on proteomic techniques studies on potential biomarkers[D]. Yan'an: Yan'an University, 2022. | |
| [21] | GERECKE D R, OLSON P F, KOCH M, et al. Complete primary structure of two splice variants of collagen Ⅻ, and assignment of alpha 1 (Ⅻ) collagen (COL12A1), alpha 1 (Ⅸ) collagen (COL9A1), and alpha 1 (ⅩⅨ) collagen (COL19A1) to human chromosome 6q12-q13[J]. Genomics, 1997, 41(2): 236-242. |
| [22] | XU S S, XU H X, WANG W Q, et al. The role of collagen in cancer: from bench to bedside[J]. J Transl Med, 2019, 17(1): 309. |
| [23] | TIAN C X, HUANG Y, CLAUSER K R, et al. Suppression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma growth and metastasis by fibrillar collagens produced selectively by tumor cells[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 2328. |
| [24] | GELSE K, PÖSCHL E, AIGNER T. Collagens: structure, function, and biosynthesis[J]. Adv Drug Deliv Rev, 2003, 55(12): 1531-1546. |
| [25] | NISSEN N I, KARSDAL M, WILLUMSEN N. Collagens and cancer associated fibroblasts in the reactive stroma and its relation to cancer biology[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 38(1): 115. |
| [26] | THORLACIUS-USSING J, JENSEN C, MADSEN E A, et al. Type ⅩⅩ collagen is elevated in circulation of patients with solid tumors[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(8): 4144. |
| [27] | WILLUMSEN N, ALI S M, LEITZEL K, et al. Collagen fragments quantified in serum as measures of desmoplasia associate with survival outcome in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 19761. |
| [28] | SONG Y, WANG L, WANG K D, et al. COL12A1 acts as a novel prognosis biomarker and activates cancer-associated fibroblasts in pancreatic cancer through bioinformatics and experimental validation[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2023, 15(5): 1480. |
| [29] | WERNER S, CHEN H D, TAO S, et al. Systematic review: serum autoantibodies in the early detection of gastric cancer[J]. Int J Cancer, 2015, 136(10): 2243-2252. |
| [30] | PEPE M S, ETZIONI R, FENG Z, et al. Phases of biomarker development for early detection of cancer[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2001, 93(14): 1054-1061. |
| [31] | SONG J, SOKOLL L J, PASAY J J, et al. Identification of serum biomarker panels for the early detection of pancreatic cancer[J]. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 2019, 28(1): 174-182. |
| [32] | 李祥苏, 王冬冬, 吴旭东. 血清MUC5AC和CA199联合检测在胰腺癌诊断中的作用[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2022, 30(5): 852-855. |
| LI X S, WANG D D, WU X D. Evaluation of serum MUC5AC in combination with CA199 for the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer[J]. Journal of Modern Oncology, 2022, 30(5): 852-855. | |
| [33] | KIM J, BAMLET W R, OBERG A L, et al. Detection of early pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with thrombospondin-2 and CA19-9 blood markers[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2017, 9(398): eaah5583. |
| [34] | LEI X F, JIA S Z, YE J, et al. Application values of detection of serum CA199, CA242 and CA50 in the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer[J]. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents, 2017, 31(2): 383-388. |
| [35] | DONG D, JIA L, ZHANG L F, et al. Periostin and CA242 as potential diagnostic serum biomarkers complementing CA19.9 in detecting pancreatic cancer[J]. Cancer Sci, 2018, 109(9): 2841-2851. |
| [36] | HUANG B W, HUANG H R, ZHANG S T, et al. Artificial intelligence in pancreatic cancer[J]. Theranostics, 2022, 12(16): 6931-6954. |
| [1] | XU Hanwen, CHEN Moxin, LIANG Xiaoyi, SHU Qin, NIE Wanqin, YANG Xuefeng, SHEN Minxuan, LI Xiaojing, CAO Yu, LI Lin. Research progress on intelligent diagnosis of eye diseases based on facial photos [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(9): 1249-1255. |
| [2] | HUANG Xin, LIU Jiahui, YE Jingwen, QIAN Wenli, XU Wanxing, WANG Lin. Development and clinical application of a machine learning-driven model for metabolite-based diagnosis of small cell lung cancer [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(8): 1009-1016. |
| [3] | LIU Chuxuan, ZUO Jiaxin, XIONG Ping. A nomogram based on ultrasound scoring parameters and clinical indicators for differentiating primary Sjὅgren′s syndrome from IgG4-related sialadenitis [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(3): 373-380. |
| [4] | DU Fang, ZHOU Lingyun, CHEN Jiao, LIU Danbo, XIANG Hongxian, CHEN Haifei. A case report of relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma with multifocal extramedullary infiltration and pulmonary adenocarcinoma [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(1): 122-128. |
| [5] | MUTAILIFU Musitaba, WANG Junjie, QIAN Yunzhen, CHEN Suyuan, SHAO Da, ZHANG Zhigang, LI Dongxue. A dormant cancer mouse model established by combining preimmune strategy with mVenus-p27K - system [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(9): 1104-1114. |
| [6] | GUO Yonglin, CHEN Moxin, LIU Zheyuan, LI Yifei, WANG Ziqi, SHU Qin, LI Lin. Progress in diagnosis and treatment of strabismus based on artificial intelligence technology [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(3): 393-398. |
| [7] | YANG Jingyu, CHEN Liubao, WANG Kangtai, YANG Xingzhi, YU Haitao. Establishment and evaluation of nomogram for differential diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus based on laboratory indications [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(2): 204-211. |
| [8] | CHEN Suyuan, Mutailifu Musitaba, LI Dongxue, ZHANG Zhigang. Expression of adhesion G protein-coupled receptor F1 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its mechanism of promoting cancer progression [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(1): 23-34. |
| [9] | YANG Yue, HE Kaiju, ZONG Jiahao, YANG Ziyi, WU Xiangsong, GONG Wei. Diagnostic value of cell-free DNA to biliary tract cancers: a meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(9): 1175-1185. |
| [10] | WANG Yingwen, LI Xiaoling, DAI Jiajia, LIU Fang, HUANG Jianfeng, WANG Libo, ZHANG Xiaobo, FENG Rui. Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors of severe asthma in children: a single-center prospective cohort study [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(6): 665-672. |
| [11] | DANG Xiangyang, TANG Yuyi, LI Weiguo, LIU Enmei. Diagnostic value of fractional exhaled nitric oxide in predicting cough variant asthma in children with chronic cough: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(6): 680-688. |
| [12] | LI Ying, TAN Yangxia, YIN Hongxin, JIANG Yanling, CHEN Li, MENG Guoyu. Research progress in the pathogenesis and prognosis of ZNF384 fusion subtype acute leukemia [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(5): 631-640. |
| [13] | PAN Hong, LIAO Yingna, GAI Yanzhi, QIAN Liheng, NIE Huizhen. Expression of sorting nexin 1 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its mechanism in promoting PDAC progress [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(3): 278-292. |
| [14] | FENG Jiali, PENG Yu, DUAN Junkai. Progress in functional mechanisms and biomarkers of miRNA related to Kawasaki disease [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(2): 256-260. |
| [15] | YAN Wenyue, LI Qiang. Research progress in diagnosis and differential diagnosis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome and hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(11): 1457-1462. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||