
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (8): 1081-1094.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2022.08.013
• 论著 · 临床研究 • 上一篇
仲麒( ), 黄雨捷, 张轶凡, 宋迎爽, 吴雅琴, 瞿方, 黄庆丰(
), 黄雨捷, 张轶凡, 宋迎爽, 吴雅琴, 瞿方, 黄庆丰( ), 胥春(
), 胥春( )
)
收稿日期:2022-03-17
接受日期:2022-06-17
出版日期:2022-08-12
发布日期:2022-08-12
通讯作者:
黄庆丰,胥春
E-mail:123281927@qq.com;hqfyy@163.com;imxuchun@163.com
作者简介:仲 麒(1996—),男,住院医师,学士;电子信箱:123281927@qq.com。
基金资助:
ZHONG Qi( ), HUANG Yujie, ZHANG Yifan, SONG Yingshuang, WU Yaqin, QU Fang, HUANG Qingfeng(
), HUANG Yujie, ZHANG Yifan, SONG Yingshuang, WU Yaqin, QU Fang, HUANG Qingfeng( ), XU Chun(
), XU Chun( )
)
Received:2022-03-17
Accepted:2022-06-17
Online:2022-08-12
Published:2022-08-12
Contact:
HUANG Qingfeng,XU Chun
E-mail:123281927@qq.com;hqfyy@163.com;imxuchun@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的·探究纤维桩修复上颌第一磨牙腭 面(palatal-occlusal,PO)和远中邻
面(palatal-occlusal,PO)和远中邻 面(distal-occlusal,DO)牙体缺损时适宜的修复策略。方法·建立上颌第一磨牙PO和DO 2种牙体缺损模型,每种缺损类型采用不放纤维桩(no post,NP)、腭根单纤维桩(palatal post,PP)、腭根及远颊根双纤维桩(palatal and distobuccal posts,PDP)、腭根及近颊根双纤维桩(palatal and mesiobuccal posts,PMP)以及三根管纤维桩(palatal, distobuccal and mesiobuccal posts,PDMP)5种不同策略进行全冠修复的有限元模型。若多桩组的纤维桩在树脂核内出现干扰,则将较细的桩于重叠处下方1 mm处水平截断。对各模型分别加载与牙体长轴平行的800 N垂直力和与牙体长轴呈45°角的225 N侧向力。通过有限元分析计算牙体组织和纤维桩内的等效应力及纤维桩-树脂水门汀、树脂水门汀-根管壁界面上的最大切应力。结果·对于牙体外表面的最大等效应力值,垂直载荷下PO缺损的PMP组和DO缺损的PDP组最小(分别为36.17 MPa、36.23 MPa),侧向载荷下PO缺损的PDMP组和DO缺损的PMP组最小(分别为40.47 MPa、42.05 MPa)。在2类牙体缺损中,置入纤维桩后根管内表面颈1/3的应力值普遍下降,中1/3的应力值普遍上升;腭根桩和近颊根桩中的最大等效应力值分别为垂直载荷和侧向载荷下的最高值(分别为60.75~71.29 MPa,45.91~51.82 MPa),相对应的纤维桩-树脂水门汀界面上最大切应力值也为相应载荷下的最高值(分别为11.26~12.93 MPa,12.38~13.03 MPa)。各组在垂直载荷下水门汀-根管壁界面上的最大切应力值相近(9.96~10.58 MPa),而在侧向载荷下PMP组和PDMP组水门汀-根管壁界面上的最大切应力值较高。结论·上颌第一磨牙应根据不同的牙体缺损类型采取不同的纤维桩修复策略:PO缺损宜采用腭根单纤维桩修复;DO缺损宜采用腭根加近颊根双纤维桩修复,同时控制垂直
面(distal-occlusal,DO)牙体缺损时适宜的修复策略。方法·建立上颌第一磨牙PO和DO 2种牙体缺损模型,每种缺损类型采用不放纤维桩(no post,NP)、腭根单纤维桩(palatal post,PP)、腭根及远颊根双纤维桩(palatal and distobuccal posts,PDP)、腭根及近颊根双纤维桩(palatal and mesiobuccal posts,PMP)以及三根管纤维桩(palatal, distobuccal and mesiobuccal posts,PDMP)5种不同策略进行全冠修复的有限元模型。若多桩组的纤维桩在树脂核内出现干扰,则将较细的桩于重叠处下方1 mm处水平截断。对各模型分别加载与牙体长轴平行的800 N垂直力和与牙体长轴呈45°角的225 N侧向力。通过有限元分析计算牙体组织和纤维桩内的等效应力及纤维桩-树脂水门汀、树脂水门汀-根管壁界面上的最大切应力。结果·对于牙体外表面的最大等效应力值,垂直载荷下PO缺损的PMP组和DO缺损的PDP组最小(分别为36.17 MPa、36.23 MPa),侧向载荷下PO缺损的PDMP组和DO缺损的PMP组最小(分别为40.47 MPa、42.05 MPa)。在2类牙体缺损中,置入纤维桩后根管内表面颈1/3的应力值普遍下降,中1/3的应力值普遍上升;腭根桩和近颊根桩中的最大等效应力值分别为垂直载荷和侧向载荷下的最高值(分别为60.75~71.29 MPa,45.91~51.82 MPa),相对应的纤维桩-树脂水门汀界面上最大切应力值也为相应载荷下的最高值(分别为11.26~12.93 MPa,12.38~13.03 MPa)。各组在垂直载荷下水门汀-根管壁界面上的最大切应力值相近(9.96~10.58 MPa),而在侧向载荷下PMP组和PDMP组水门汀-根管壁界面上的最大切应力值较高。结论·上颌第一磨牙应根据不同的牙体缺损类型采取不同的纤维桩修复策略:PO缺损宜采用腭根单纤维桩修复;DO缺损宜采用腭根加近颊根双纤维桩修复,同时控制垂直 力。
力。
中图分类号:
仲麒, 黄雨捷, 张轶凡, 宋迎爽, 吴雅琴, 瞿方, 黄庆丰, 胥春. 纤维桩修复上颌第一磨牙牙体缺损的三维有限元力学分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(8): 1081-1094.
ZHONG Qi, HUANG Yujie, ZHANG Yifan, SONG Yingshuang, WU Yaqin, QU Fang, HUANG Qingfeng, XU Chun. Three-dimensional finite element analysis on fiber-reinforced composite post-restored maxillary first molar with tooth defect[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2022, 42(8): 1081-1094.

图2 不同修复策略的上颌第一磨牙牙体缺损修复模型(以PO牙体缺损为例)Note:A. NP group. B. PP group. C. PDP group. D. PMP group. E. PDMP group. DB—distobuccal; MB—mesiobuccal; P—palatal.
Fig 2 Models of restored maxillary first molar with tooth defect by different restoration strategy (PO defect for example)
| Component | Elastic modulus/MPa | Poisson ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Cancellous bone [ | 1 370 | 0.30 |
| Cortical bone [ | 13 700 | 0.30 |
| Dentin [ | 18 600 | 0.31 |
| Gutta-percha [ | 141.9 | 0.45 |
| Periodontal ligament [ | 68.9 | 0.45 |
| Resin cement (crown) [ | 18 300 | 0.30 |
| Resin composite (direct restoration) [ | 12 000 | 0.33 |
| Resin core build-up/Resin cement (post) [ | 16 440 | 0.26 |
| Zirconia ceramic crown [ | 200 000 | 0.33 |
| Quartz fiber-reinforced composite post [ | Ex =50 000, Ey =Ez =15 000 | 0.30 |
表1 材料及组织力学性能参数
Tab 1 Mechanical properties of materials and tooth tissues
| Component | Elastic modulus/MPa | Poisson ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Cancellous bone [ | 1 370 | 0.30 |
| Cortical bone [ | 13 700 | 0.30 |
| Dentin [ | 18 600 | 0.31 |
| Gutta-percha [ | 141.9 | 0.45 |
| Periodontal ligament [ | 68.9 | 0.45 |
| Resin cement (crown) [ | 18 300 | 0.30 |
| Resin composite (direct restoration) [ | 12 000 | 0.33 |
| Resin core build-up/Resin cement (post) [ | 16 440 | 0.26 |
| Zirconia ceramic crown [ | 200 000 | 0.33 |
| Quartz fiber-reinforced composite post [ | Ex =50 000, Ey =Ez =15 000 | 0.30 |
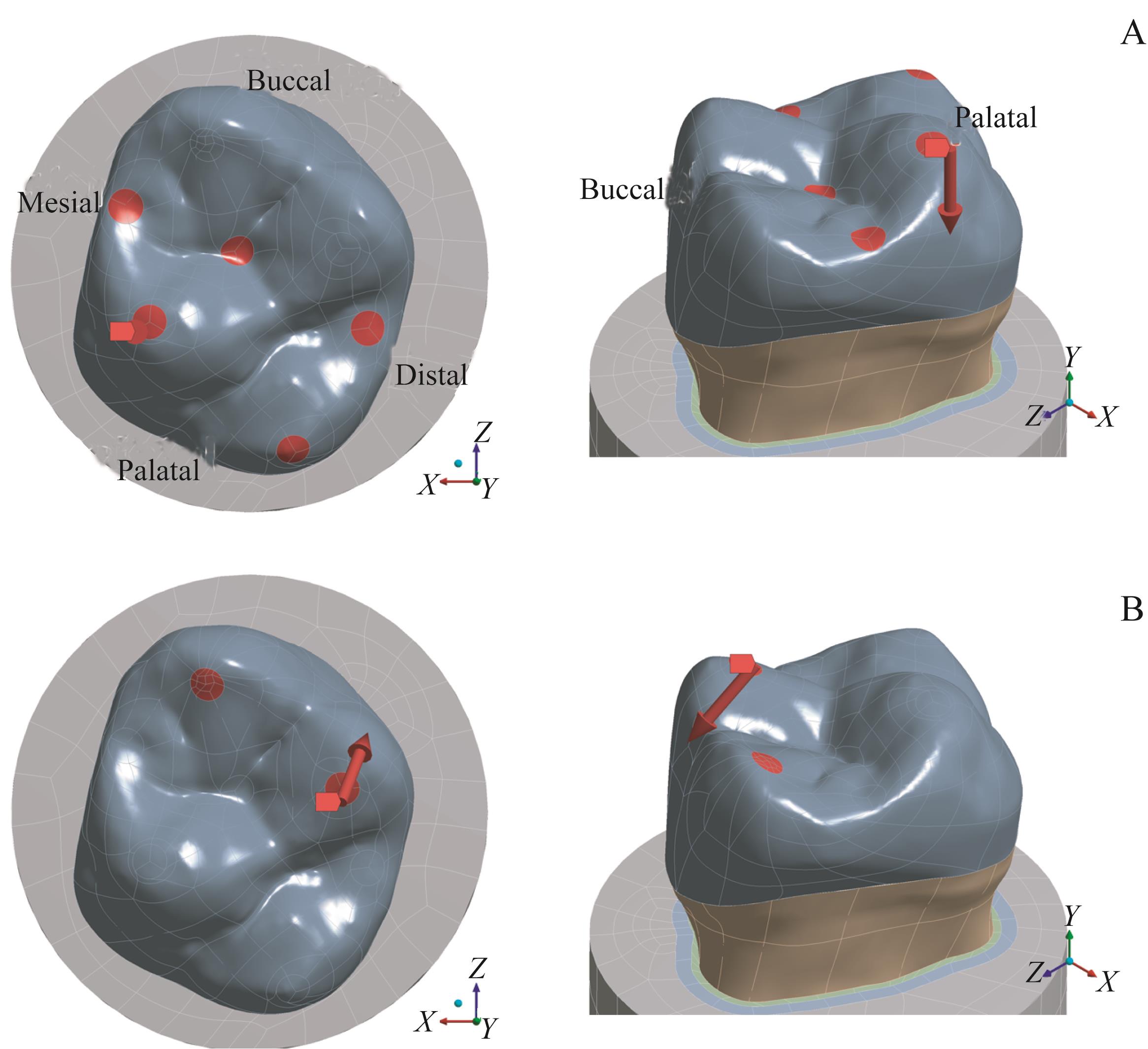
图3 加载位置及方向示意图Note:A. Vertical loading. The tooth was given an 800 N force parallel to the long axis (the direction of the 3D arrow) on the five points (red dots). B. Lateral loading. The tooth was given a 225 N force directed at 45° to the long axis (the direction of the 3D arrow) on the two points (red dots).
Fig 3 Schematics of the positions and directions of the loadings

图4 垂直载荷下牙体外表面的等效应力分布和最大等效应力值Note:A–F. PO defect. G–L: DO defect. A/G. NP group. B/H. PP group. C/I. PDP group. D/J. PMP group. E/K. PDMP group. F/L. The maximal equivalent stress (MES) in each group. The red arrows indicate the locations of maximum stress; the blue arrows indicate the locations of minimal stress; the yellow arrows indicate the stress concentration areas in furcation areas.
Fig 4 Equivalent stress distributions and MES on external surfaces of tooth tissues under vertical loading
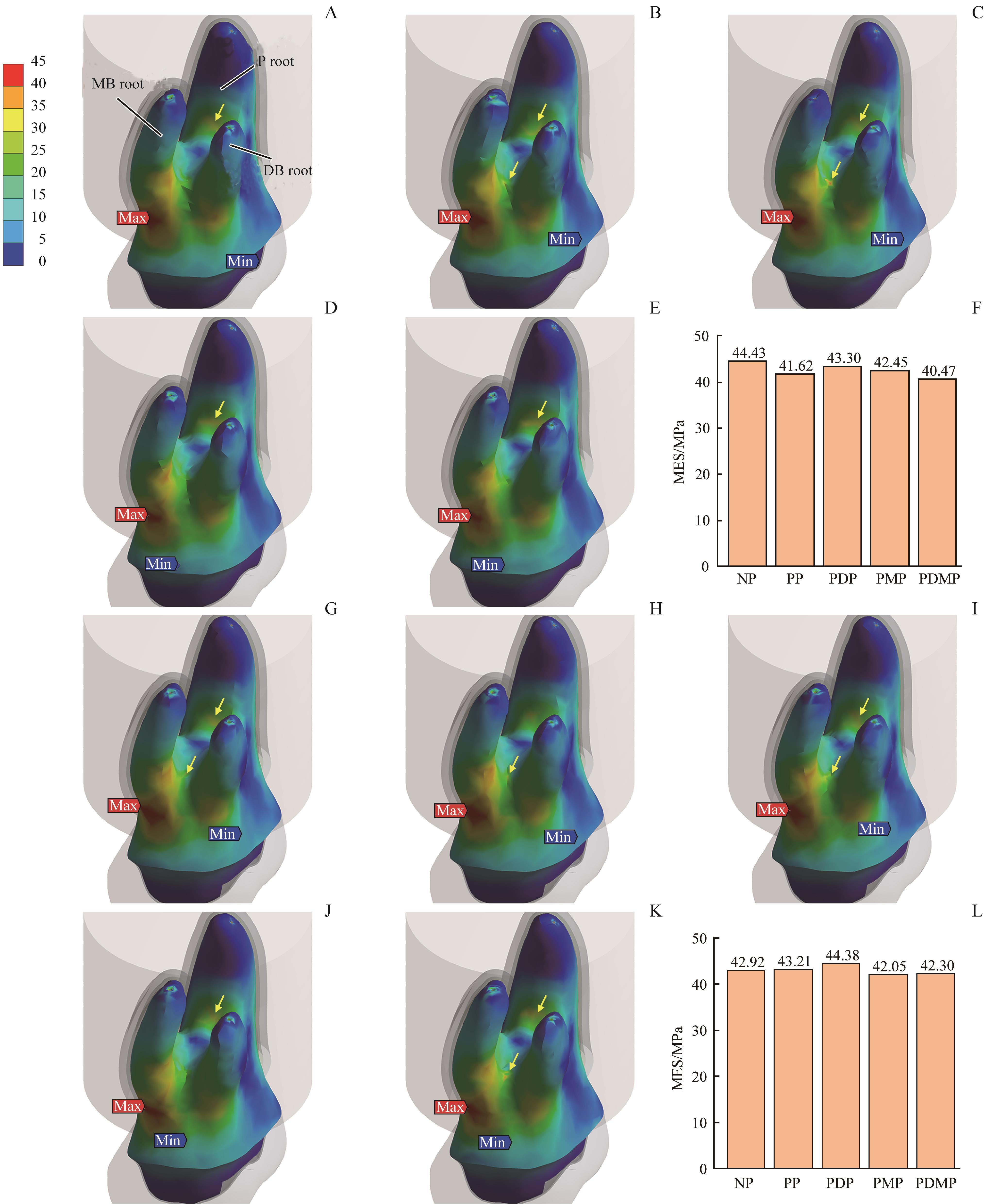
图5 侧向载荷下牙体外表面的等效应力分布和最大等效应力值Note:A–F. PO defect. G–L: DO defect. A/G. NP group. B/H. PP group. C/I. PDP group. D/J. PMP group. E/K. PDMP group. F/L. The MES in each group. The red arrows indicate the locations of maximum stress; the blue arrows indicate the locations of minimal stress; the yellow arrows indicate the stress concentration areas in furcation areas.
Fig 5 Equivalent stress distributions and MES on external surfaces of tooth tissues under lateral loading
| Group | PO defect | DO defect | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical loading | Lateral loading | Vertical loading | Lateral loading | ||||||||||
| P | DB | MB | P | DB | MB | P | DB | MB | P | DB | MB | ||
| NP | |||||||||||||
| C | 16.22 | 14.72 | 13.62 | 12.97 | 24.17 | 16.85 | 14.83 | 11.75 | 13.83 | 23.48 | |||
| M | 24.27 | 16.22 | 13.68 | 19.13 | 25.85 | 22.81 | 15.96 | 13.25 | 19.97 | 26.08 | |||
| A | 24.07 | 11.83 | 23.67 | 11.25 | |||||||||
| PP | |||||||||||||
| C | 18.62 | 16.11 | 14.90 | 11.15 | 12.90 | 24.95 | 18.35 | 15.98 | 14.96 | 11.51 | 12.67 | 23.76 | |
| M | 16.11 | 13.76 | 19.54 | 15.98 | 12.73 | 19.11 | 24.89 | ||||||
| A | 26.66 | 11.22 | 17.51 | 23.73 | 10.84 | ||||||||
| PDP | |||||||||||||
| C | 18.47 | 15.47 | 11.44 | 13.46 | 23.43 | 18.31 | 18.70 | 14.59 | 11.11 | 13.51 | 23.61 | ||
| M | 13.48 | 19.60 | 13.01 | 20.41 | 25.85 | ||||||||
| A | 26.84 | 22.85 | 12.90 | 11.50 | 17.46 | 23.59 | 21.49 | 12.01 | |||||
| PMP | |||||||||||||
| C | 18.58 | 15.87 | 15.13 | 10.82 | 12.82 | 20.57 | 18.46 | 15.80 | 14.59 | 11.43 | 12.37 | 22.23 | |
| M | 15.73 | 21.63 | 19.45 | 15.80 | 20.06 | 20.20 | 32.36 | ||||||
| A | 31.43 | 14.27 | 27.90 | 27.72 | 11.97 | ||||||||
| PDMP | |||||||||||||
| C | 18.25 | 15.23 | 13.22 | 11.15 | 13.50 | 21.49 | 18.48 | 14.59 | 15.20 | 11.39 | 13.46 | 20.86 | |
| M | 22.22 | 35.26 | 19.73 | ||||||||||
| A | 23.90 | 23.81 | 10.98 | 20.02 | 23.72 | 22.31 | 15.32 | 11.63 | 20.00 | ||||
表2 纤维桩修复后各组根管内表面各区域最大等效应力值(MPa)
Tab 2 MES on internal surfaces of root canals after placing posts (MPa)
| Group | PO defect | DO defect | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical loading | Lateral loading | Vertical loading | Lateral loading | ||||||||||
| P | DB | MB | P | DB | MB | P | DB | MB | P | DB | MB | ||
| NP | |||||||||||||
| C | 16.22 | 14.72 | 13.62 | 12.97 | 24.17 | 16.85 | 14.83 | 11.75 | 13.83 | 23.48 | |||
| M | 24.27 | 16.22 | 13.68 | 19.13 | 25.85 | 22.81 | 15.96 | 13.25 | 19.97 | 26.08 | |||
| A | 24.07 | 11.83 | 23.67 | 11.25 | |||||||||
| PP | |||||||||||||
| C | 18.62 | 16.11 | 14.90 | 11.15 | 12.90 | 24.95 | 18.35 | 15.98 | 14.96 | 11.51 | 12.67 | 23.76 | |
| M | 16.11 | 13.76 | 19.54 | 15.98 | 12.73 | 19.11 | 24.89 | ||||||
| A | 26.66 | 11.22 | 17.51 | 23.73 | 10.84 | ||||||||
| PDP | |||||||||||||
| C | 18.47 | 15.47 | 11.44 | 13.46 | 23.43 | 18.31 | 18.70 | 14.59 | 11.11 | 13.51 | 23.61 | ||
| M | 13.48 | 19.60 | 13.01 | 20.41 | 25.85 | ||||||||
| A | 26.84 | 22.85 | 12.90 | 11.50 | 17.46 | 23.59 | 21.49 | 12.01 | |||||
| PMP | |||||||||||||
| C | 18.58 | 15.87 | 15.13 | 10.82 | 12.82 | 20.57 | 18.46 | 15.80 | 14.59 | 11.43 | 12.37 | 22.23 | |
| M | 15.73 | 21.63 | 19.45 | 15.80 | 20.06 | 20.20 | 32.36 | ||||||
| A | 31.43 | 14.27 | 27.90 | 27.72 | 11.97 | ||||||||
| PDMP | |||||||||||||
| C | 18.25 | 15.23 | 13.22 | 11.15 | 13.50 | 21.49 | 18.48 | 14.59 | 15.20 | 11.39 | 13.46 | 20.86 | |
| M | 22.22 | 35.26 | 19.73 | ||||||||||
| A | 23.90 | 23.81 | 10.98 | 20.02 | 23.72 | 22.31 | 15.32 | 11.63 | 20.00 | ||||

图6 纤维桩修复后各组根管内表面最大等效应力值相对直接冠修复时(NP组)的变化百分数Note:A. PO defect under vertical loading. B. PO defect under lateral loading. C. DO defect under vertical loading. D. DO defect under lateral loading.
Fig 6 Percentage of MES changes in each group compared to NP group on the internal surfaces of root canals after placing posts
| Post | Group | PO defect | DO defect | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical loading | Lateral loading | Vertical loading | Lateral loading | ||
| Palatal canal | PP | 69.18 | 25.84 | 69.34 | 25.69 |
| PDP | 60.75 | 25.49 | 66.95 | 25.63 | |
| PMP | 65.00 | 25.22 | 71.29 | 25.37 | |
| PDMP | 65.50 | 25.43 | 63.78 | 25.44 | |
| Distobuccal canal | PDP | 42.50 | 26.29 | 39.73 | 27.50 |
| PDMP | 44.65 | 28.16 | 39.85 | 27.06 | |
| Mesiobuccal canal | PMP | 39.39 | 51.82 | 35.17 | 45.91 |
| PDMP | 36.27 | 49.31 | 27.06 | 48.91 | |
表3 各组纤维桩内最大等效应力值(MPa)
Tab 3 MES in the posts in each group (MPa)
| Post | Group | PO defect | DO defect | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical loading | Lateral loading | Vertical loading | Lateral loading | ||
| Palatal canal | PP | 69.18 | 25.84 | 69.34 | 25.69 |
| PDP | 60.75 | 25.49 | 66.95 | 25.63 | |
| PMP | 65.00 | 25.22 | 71.29 | 25.37 | |
| PDMP | 65.50 | 25.43 | 63.78 | 25.44 | |
| Distobuccal canal | PDP | 42.50 | 26.29 | 39.73 | 27.50 |
| PDMP | 44.65 | 28.16 | 39.85 | 27.06 | |
| Mesiobuccal canal | PMP | 39.39 | 51.82 | 35.17 | 45.91 |
| PDMP | 36.27 | 49.31 | 27.06 | 48.91 | |
| Post | Group | PO defect | DO defect | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical loading | Lateral loading | Vertical loading | Lateral loading | ||
| Palatal canal | PP | 11.75 | 7.30 | 12.93 | 7.41 |
| PDP | 11.77 | 7.27 | 11.91 | 7.33 | |
| PMP | 11.39 | 7.49 | 11.26 | 7.33 | |
| PDMP | 11.50 | 7.27 | 12.92 | 7.40 | |
| Distobuccal canal | PDP | 7.91 | 6.94 | 8.09 | 7.03 |
| PDMP | 7.91 | 6.78 | 7.85 | 6.89 | |
| Mesiobuccal canal | PMP | 7.40 | 12.38 | 7.48 | 12.84 |
| PDMP | 7.73 | 13.00 | 7.57 | 13.03 | |
表4 纤维桩-树脂水门汀界面上最大切应力值(MPa)
Tab 4 Maximum shear stress on the post-cement interface (MPa)
| Post | Group | PO defect | DO defect | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical loading | Lateral loading | Vertical loading | Lateral loading | ||
| Palatal canal | PP | 11.75 | 7.30 | 12.93 | 7.41 |
| PDP | 11.77 | 7.27 | 11.91 | 7.33 | |
| PMP | 11.39 | 7.49 | 11.26 | 7.33 | |
| PDMP | 11.50 | 7.27 | 12.92 | 7.40 | |
| Distobuccal canal | PDP | 7.91 | 6.94 | 8.09 | 7.03 |
| PDMP | 7.91 | 6.78 | 7.85 | 6.89 | |
| Mesiobuccal canal | PMP | 7.40 | 12.38 | 7.48 | 12.84 |
| PDMP | 7.73 | 13.00 | 7.57 | 13.03 | |
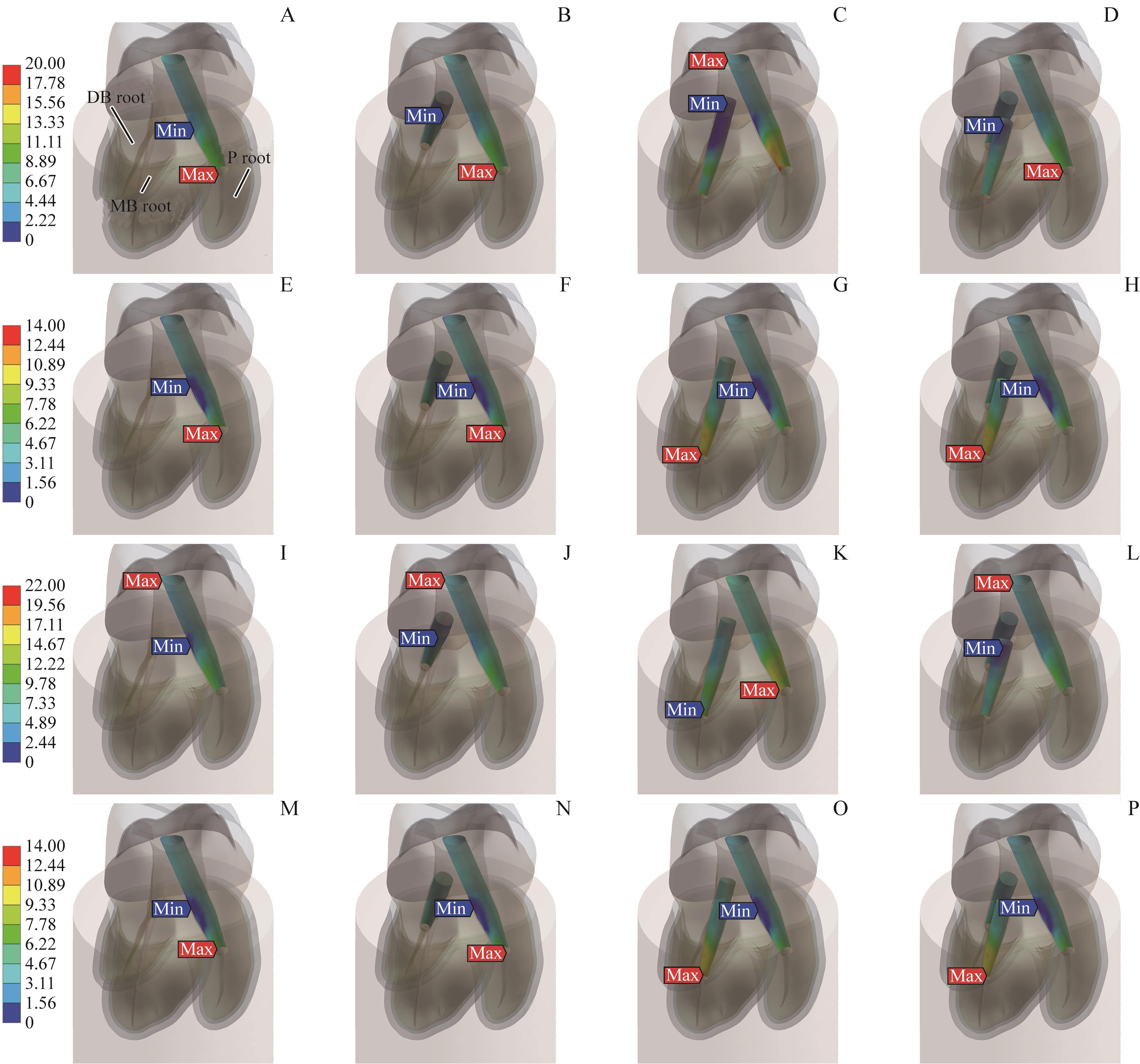
图7 2种载荷下纤维桩-树脂水门汀界面上的切应力分布Note:A–D. PO defect under vertical loading. E–H. PO defect under lateral loading. I–L. DO defect under vertical loading. M–P. DO defect under lateral loading. A/E/I/M. PP group. B/F/J/N. PDP group. C/J/K/O. PMP group. D/H/L/P. PDMP group. The red arrows indicate the locations of maximum stress; the blue arrows indicate the locations of minimal stress.
Fig 7 Shear stress distributions on the post-cement interface under vertical and lateral loadings
| Group | PO defect | DO defect | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical loading | Lateral loading | Vertical loading | Lateral loading | |
| PP | 9.96 | 6.72 | 10.35 | 6.67 |
| PDP | 10.14 | 7.06 | 10.28 | 7.00 |
| PMP | 10.35 | 11.45 | 10.26 | 11.37 |
| PDMP | 10.58 | 11.29 | 10.38 | 11.54 |
表5 各组水门汀-根管壁界面上最大切应力值(MPa)
Tab 5 Maximum shear stress on the cement-canal interface in each group (MPa)
| Group | PO defect | DO defect | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical loading | Lateral loading | Vertical loading | Lateral loading | |
| PP | 9.96 | 6.72 | 10.35 | 6.67 |
| PDP | 10.14 | 7.06 | 10.28 | 7.00 |
| PMP | 10.35 | 11.45 | 10.26 | 11.37 |
| PDMP | 10.58 | 11.29 | 10.38 | 11.54 |
| 1 | YAMUNADEVI A, PRATIBHA R, RAJMOHAN M, et al. First molars in permanent dentition and their malformations in various pathologies: a review[J]. J Pharm Bioallied Sci, 2021, 13(Suppl 1): S23-S30. |
| 2 | 何三纲. 口腔解剖生理学[M]. 8版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2020. |
| HE S G. Oral anatomy and physiology[M]. 8th ed. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2020. | |
| 3 | 王兴. 第四次全国口腔健康流行病学调查报告[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2018. |
| WANG X. Report of the fourth national oral health epidemiological survey[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2018. | |
| 4 | 张文玲, 黄永丽, 赵勇. 牙齿折裂的相关因素分析和治疗[J]. 河南大学学报(医学版), 2015, 34(2): 123-125. |
| ZHANG W L, HUANG Y L, ZHAO Y. Analysis factors and treatment associated with fractured teeth[J]. J Henan Univ (Med Sci), 2015, 34(2): 123-125. | |
| 5 | 胡坤娥, 胡冬梅, 谭荣, 等. 影响后牙折裂的相关因素分析[J]. 中国美容医学, 2012, 21(17): 2235-2237. |
| HU K E, HU D M, TAN R, et al. Analysis of factors associated with posterior fractured teeth[J]. Chin J Aesthetic Med, 2012, 21(17): 2235-2237. | |
| 6 | ELIYAS S, JALILI J, MARTIN N. Restoration of the root canal treated tooth[J]. Br Dent J, 2015, 218(2): 53-62. |
| 7 | 牛光良. 纤维桩理论与实践[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2013. |
| NIU G L. Fiber post: current principles and practice[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2020. | |
| 8 | 乔玮. 桩核材料的临床应用与发展[J]. 包头医学院学报, 2011, 27(1): 136-138. |
| QIAO W. Clinical application and development of post-core materials[J]. J Baotou Med Coll, 2011, 27(1): 136-138. | |
| 9 | 杜珍, 汲平. 纤维桩的分类及性能特点[J]. 口腔颌面修复学杂志, 2007, 8(3): 227-228, 232. |
| DU Z, JI P. Classification and properties of fiber posts[J]. Chin J Prosthodont, 2007, 8(3): 227-228, 232. | |
| 10 | MARCHIONATTI A M E, WANDSCHER V F, RIPPE M P, et al. Clinical performance and failure modes of pulpless teeth restored with posts: a systematic review[J]. Braz Oral Res, 2017, 31: e64. |
| 11 | YANG A, LAMICHHANE A, XU C. Remaining coronal dentin and risk of fiber-reinforced composite post-core restoration failure: a meta-analysis[J]. Int J Prosthodont, 2015, 28(3): 258-264. |
| 12 | HARGREAVES K M, BERMAN L H. Cohen's pathways of the pulp expert consult[M]. 11th ed. St. Louis: Elsevier, 2015. |
| 13 | SCHWARTZ R S, ROBBINS J W. Post placement and restoration of endodontically treated teeth: a literature review[J]. J Endod, 2004, 30(5): 289-301. |
| 14 | YOON H G, OH H K, LEE D Y, et al. 3-D finite element analysis of the effects of post location and loading location on stress distribution in root canals of the mandibular 1st molar[J]. J Appl Oral Sci, 2018, 26: e20160406. |
| 15 | 赵莉, 李丽君, 赵克, 等. 不同桩核系统修复上颌第一磨牙的有限元分析[J]. 上海口腔医学, 2013, 22(6): 607-612. |
| ZHAO L, LI L J, ZHAO K, et al. Finite element analysis of first maxillary molars restored with different post and core materials[J]. Shanghai J Stomatol, 2013, 22(6): 607-612. | |
| 16 | 刘峰. 纤维桩修复技术[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2012. |
| LIU F. Fiber post restoration[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2012. | |
| 17 | ZHONG Q, HUANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Finite element analysis of maxillary first molar with a 4-wall defect and 1.5-mm-high ferrule restored with fiber-reinforced composite resin posts and resin core: the number and placement of the posts[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2022. DOI: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2022.01.029. |
| 18 | 王春艳. 龋病发生部位与年龄关系[J]. 内蒙古中医药, 2013, 32(25): 41. |
| WANG C Y. The relationship between caries location and age[J]. Inner Mong J Tradit Chin Med, 2013, 32(25): 41. | |
| 19 | 刘凡. 纤维桩性价比之王: Matchpost[Z/OL]. (2018-12-18) [2020-01-28]. https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/-eEbnPK3BbRby0JtpOxuIw. |
| LIU F. The king of cost performance in fiber posts: Matchpost[Z/OL]. (2018-12-18) [2020-01-28]. https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/-eEbn PK3BbRby0JtpOxuIw. | |
| 20 | LI X X, KANG T, ZHAN D T, et al. Biomechanical behavior of endocrowns vs fiber post-core-crown vs cast post-core-crown for the restoration of maxillary central incisors with 1 mm and 2 mm ferrule height: a 3D static linear finite element analysis[J]. Medicine, 2020, 99(43): e22648. |
| 21 | GONZÁLEZ-LLUCH C, PÉREZ-GONZÁLEZ A. Analysis of the effect of design parameters and their interactions on the strength of dental restorations with endodontic posts, using finite element models and statistical analysis[J]. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin, 2016, 19(4): 428-439. |
| 22 | SAVYCHUK A, MANDA M, GALANIS C, et al. Stress generation in mandibular anterior teeth restored with different types of post-and-core at various levels of ferrule[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2018, 119(6): 965-974. |
| 23 | MAHMOUDI M, SAIDI A R, AMINI P, et al. Influence of inhomogeneous dental posts on stress distribution in tooth root and interfaces: three-dimensional finite element analysis[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2017, 118(6): 742-751. |
| 24 | DURMUŞ G, OYAR P. Effects of post core materials on stress distribution in the restoration of mandibular second premolars: a finite element analysis[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2014, 112(3): 547-554. |
| 25 | AUSIELLO P, CIARAMELLA S, MARTORELLI M, et al. Mechanical behavior of endodontically restored canine teeth: effects of ferrule, post material and shape[J]. Dent Mater, 2017, 33(12): 1466-1472. |
| 26 | JIANG Q Z, HUANG Y T, TU X R, et al. Biomechanical properties of first maxillary molars with different endodontic cavities: a finite element analysis[J]. J Endod, 2018, 44(8): 1283-1288. |
| 27 | CHIBA A, HATAYAMA T, KAINOSE K, et al. The influence of elastic moduli of core materials on shear stress distributions at the adhesive interface in resin built-up teeth[J]. Dent Mater J, 2017, 36(1): 95-102. |
| 28 | AROLA D D, REPROGEL R K. Tubule orientation and the fatigue strength of human dentin[J]. Biomaterials, 2006, 27(9): 2131-2140. |
| 29 | PLOTINO G, GRANDE N M, BEDINI R, et al. Flexural properties of endodontic posts and human root dentin[J]. Dent Mater, 2007, 23(9): 1129-1135. |
| 30 | KINNEY J H, MARSHALL S J, MARSHALL G W. The mechanical properties of human dentin: a critical review and re-evaluation of the dental literature[J]. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med, 2003, 14(1): 13-29. |
| 31 | 吴悦梅, 张富强, 宋宁, 等. 石英纤维根管桩复合材料的力学性能研究[J]. 上海口腔医学, 2006, 15(3): 304-307. |
| WU Y M, ZHANG F Q, SONG N, et al. Study on the mechanical properties of quartz fiber-reinforced composite for canal post[J]. Shanghai J Stomatol, 2006, 15(3): 304-307. | |
| 32 | ELSAKA S E, ELNAGHY A M. Bonding durability of titanium tetrafluoride treated glass fiber post with resin cement[J]. Dent Mater J, 2019, 38(2): 189-195. |
| 33 | CARDOSO G C, NAKANISHI L, ISOLAN C P, et al. Bond stability of universal adhesives applied to dentin using etch-and-rinse or self-etch strategies[J]. Braz Dent J, 2019, 30(5): 467-475. |
| [1] | 李晨琳, 李岩, 徐光宙. 预防性拔除下颌第三磨牙牙胚的临床研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(7): 893-897. |
| [2] | 陆叶平, 陈敏洁. 改良位点保留法拔除复杂下颌阻生第三磨牙对临床成骨愈合的作用初探[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(6): 729-734. |
| [3] | 傅娆, 刘川琪, 方斌, 黄如林, 李青峰, 谢芸. 改变扩张应力点在治疗皮肤软组织扩张器血运障碍中的应用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(2): 277-279. |
| [4] | 戴兆威, 彭伟伟, 杜 嵘, 朱亚琴. 2种机用镍钛系统对中度弯曲根管的疏通及成形能力研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(1): 89-. |
| [5] | 周知航 1*,毛懿 1*,陈旭卓 1*,张善勇 1,孙守福 2,甄锦泽 1. 新型锚固钉的抗力性分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2018, 38(8): 934-. |
| [6] | 喻金凤,胡赟,黄明娜,陈军,明叶,郑雷蕾. 骨性Ⅲ类错 伴下颌偏斜患者第一磨牙及其周围牙槽骨对称性的三维研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2018, 38(3): 288-. |
| [7] | 付梦辰,杨茜,王慧慧,李成皓,赵玉梅 . 可塑纤维桩对氢氧化钙作用后年轻恒牙抗折性能的影响#br#[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2017, 37(8): 1106-. |
| [8] | 何旭, 梁景平 . 不同年龄下颌单根管第一前磨牙根管形态的三维分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2016, 36(10): 1486-. |
| [9] | 鲍菁,谢明,焦婷. 牵张应力对人牙周膜成纤维细胞细胞外金属基质蛋白酶诱导剂表达的影响及相关信号通路的研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2015, 35(9): 1280-. |
| [10] | 董建辉,朱亚琴. 下颌阻生第三磨牙拔除难度的影响因素分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2014, 34(2): 254-. |
| [11] | 董建辉, 朱亚琴. 不同分牙方式拔除低位阻生下颌第三磨牙的临床效果分析[J]. , 2011, 31(2): 191-. |
| [12] | 金文忠, 黄庆丰, 魏 斌, 等. 近远中(牙合)支托对末端游离缺失修复应力分布的影响[J]. , 2009, 29(11): 1282-. |
| [13] | 魏 斌, 黄庆丰, 金文忠, 等. 套筒冠固位可摘局部义齿的建模及其力学特征分析[J]. , 2009, 29(11): 1285-. |
| [14] | 魏 斌, 陈 洁, 黄庆丰, 等. 套筒冠与卡环固位型义齿修复末端游离缺失的应力分布比较[J]. , 2009, 29(11): 1288-. |
| [15] | 黄庆丰, 金文忠, 张富强, 等. 精密附着体义齿修复下颌末端游离缺失的应力分析[J]. , 2009, 29(11): 1291-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 432
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 546
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||