
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (7): 860-872.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2023.07.008
• 论著 · 基础研究 • 上一篇
杜少倩( ), 陶梦玉, 曹源, 王红霞, 胡孝渠, 范广建(
), 陶梦玉, 曹源, 王红霞, 胡孝渠, 范广建( ), 臧丽娟(
), 臧丽娟( )
)
收稿日期:2022-12-23
接受日期:2023-06-11
出版日期:2023-07-28
发布日期:2023-07-28
通讯作者:
范广建,臧丽娟
E-mail:dushaoqian@163.com;gjfan@shsmu.edu.cn;lou19941205@163.com
作者简介:杜少倩(1997—),女,硕士生;电子信箱:dushaoqian@163.com。
基金资助:
DU Shaoqian( ), TAO Mengyu, CAO Yuan, WANG Hongxia, HU Xiaoqu, FAN Guangjian(
), TAO Mengyu, CAO Yuan, WANG Hongxia, HU Xiaoqu, FAN Guangjian( ), ZANG Lijuan(
), ZANG Lijuan( )
)
Received:2022-12-23
Accepted:2023-06-11
Online:2023-07-28
Published:2023-07-28
Contact:
FAN Guangjian,ZANG Lijuan
E-mail:dushaoqian@163.com;gjfan@shsmu.edu.cn;lou19941205@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的·探究C-X-C模体趋化因子配体9(C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 9,CXCL9)表达对乳腺癌患者预后的影响及其与肿瘤浸润免疫细胞(tumor-infiltrating immune cell,TIIC)的相关性。方法·从癌症基因组图谱(The Cancer Genome Atlas,TCGA)数据库获得乳腺癌患者的1 100例癌组织和112例癌旁组织的转录组数据,并采用CIBERSORT反卷积算法分析乳腺癌免疫微环境中TIIC亚群比例及其对患者的预后影响。分别从TCGA数据库、ImmPort数据库和GEPIA2数据平台下载差异表达基因、免疫相关基因和乳腺癌预后相关基因,运用R语言分析该3类基因集的相交关系,以筛选目的基因。根据已下载的转录组数据,分析CXCL9的正相关基因、CXCL9 mRNA在乳腺癌组织和癌旁组织中的表达差异及其对患者预后的影响。利用STRING数据平台对CXCL9进行蛋白质相互作用(protein-protein interaction,PPI)网络分析,利用R语言对CXCL9正相关基因和PPI网络获得的互作蛋白对应的基因行基因本体数据库(Gene Ontology,GO)功能分析和京都基因与基因组百科全书(Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genome,KEGG)通路分析。运用Spearman相关系数分析CXCL9 mRNA表达与TIIC亚群、免疫检查点相关基因的相关性。收集60例乳腺癌患者的石蜡组织样本并制成组织芯片,采用免疫组织化学染色(immunohistochemistry staining,IHC)分析芯片中CXCL9表达和CD8 + T细胞浸润的相关性。采用多重荧光免疫组织化学染色(multiplex immunohistochemistry staining,mIHC)分析芯片中乳腺癌组织间质内CXCL9+ 细胞的类型。采用Kaplan-Meier(KM)生存曲线分析CXCL9 mRNA表达、CD8+ T细胞浸润双因素对乳腺癌患者预后的影响。结果·CIBERSORT算法分析显示乳腺癌免疫微环境中TIIC亚群的分布比例差异大,其对患者的预后影响也大不相同。绘制上述3类基因集的韦恩图,筛选出目的基因CXCL9。获得与CXCL9正相关的前150个基因。在乳腺癌4种分子分型中CXCL9 mRNA的表达水平高于癌旁组织(均P=0.000),且其高表达与患者的良好预后相关(HR=0.624,P=0.013)。通过PPI网络分析共获得41个互作蛋白。GO和KEGG分析的结果显示,CXCL9及其相关基因主要富集在免疫调控相关的生物功能和通路。Spearman相关系数分析的结果显示,CXCL9 mRNA表达与CD8+ T细胞的浸润比例呈正相关,与M2型巨噬细胞的浸润比例呈负相关,且与多数免疫检查点基因的表达呈正相关(均P<0.05)。IHC实验结果显示,相较于癌旁组织,乳腺癌组织中CXCL9的表达较高,且伴随CD8 + T细胞浸润比例增加(P=0.000);mIHC结果发现,乳腺癌间质中CXCL9在部分CD68+ 肿瘤相关巨噬细胞和CD11c+ 树突状细胞内表达。KM生存曲线显示,当CXCL9高表达时,CD8+ T细胞高浸润才能延长乳腺癌患者的生存期。结论·CXCL9可作为乳腺癌患者良好预后的生物标志物,在乳腺癌微环境中CXCL9的高表达与CD8+ T细胞的浸润比例呈正相关并可能激活其抗肿瘤作用。同时,CXCL9的表达可能与肿瘤组织中募集淋巴细胞至肿瘤微环境发挥抗肿瘤免疫应答功能密切相关。
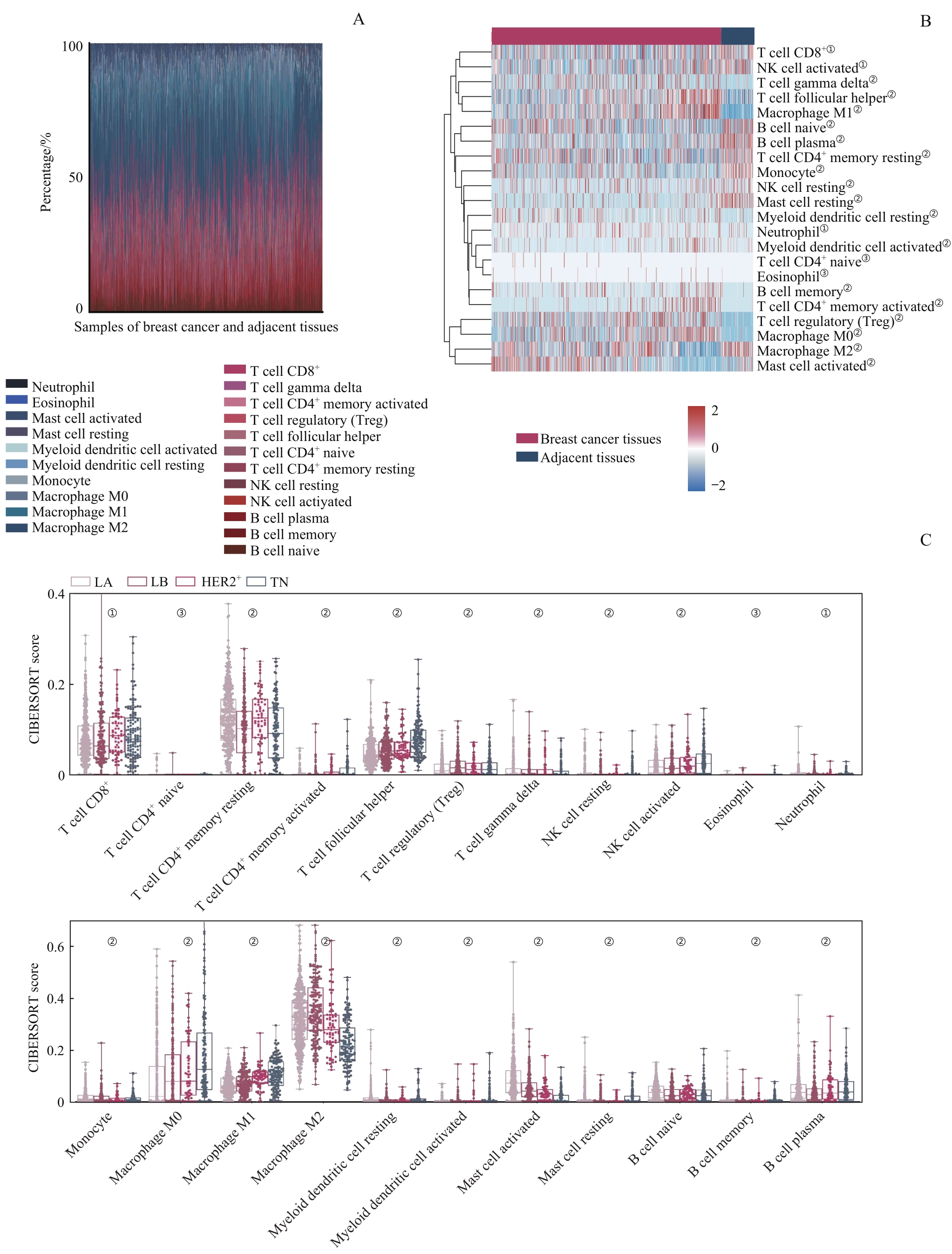
图1 乳腺癌TME中TIIC亚群的差异分析Note: A. Proportions of 22 TIIC subgroups in the microenvironment of breast cancer and adjacent tissues. B. Comparison of the distributions of TIIC subgroups in breast cancer tissues and adjacent tissues by heatmap (①P=0.010, ②P=0.001, ③P>0.05). C. Differential analysis of 22 types of TIICs in different molecular types of breast cancer (①P=0.010, ②P=0.001, ③P>0.05).
Fig 1 Differential analysis of TIIC subgroups in breast cancer TME

图3 目的基因的筛选Note: A. Volcano plot of DEGs between breast cancer tissues and adjacent tissues. B. Venn diagram of the target gene screened in the three gene sets.
Fig 3 Screening of target gene
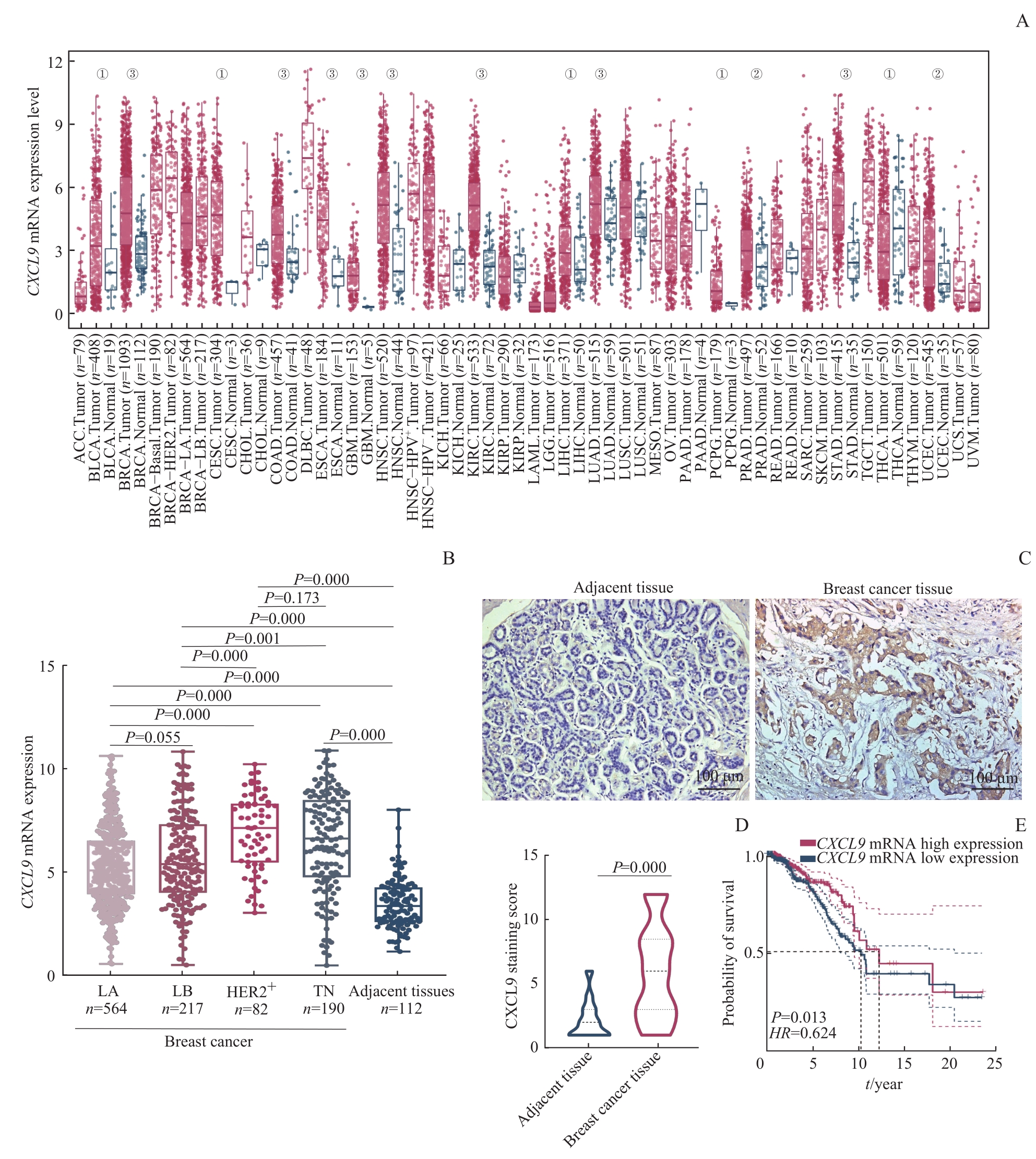
图4 目的基因的表达水平对乳腺癌患者的预后影响Note: A. Expression of CXCL9 mRNA in different types of tumor and their corresponding normal tissues (①P=0.050, ②P=0.010, ③P=0.001). ACC—adrenocortical carcinoma; BLCA—bladder urothelial carcinoma; BRCA—breast invasive carcinoma; CESC—cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma; CHOL—cholangiocarcinoma; COAD—colon adenocarcinoma; DLBC—lymphoid neoplasm diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; ESCA—esophageal carcinoma; GBM—glioblastoma multiforme; HNSC—head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; KICH—kidney chromophobe; KIRC—kidney renal clear cell carcinoma; KIRP—kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma; LAML—acute myeloid leukemia; LGG—brain lower grade glioma; LIHC—liver hepatocellular carcinoma; LUAD—lung adenocarcinoma; LUSC—lung squamous cell carcinoma; MESO—mesothelioma; OV—ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma; PAAD—pancreatic adenocarcinoma; PCPG—pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma; PRAD—prostate adenocarcinoma; READ—rectum adenocarcinoma; SARC—sarcoma; SKCM—skin cutaneous melanoma; STAD—stomach adenocarcinoma; TGCT—testicular germ cell tumor; THCA—thyroid carcinoma; THYM—thymoma; UCEC—uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma; UCS—uterine carcinosarcoma; UVM—uveal melanoma. B. Boxplot of CXCL9 mRNA expression in four molecular types of breast cancer and adjacent tissues. C/D. Observation (C) and statistical analysis (D) of differential expression of CXCL9 in breast cancer tissues and adjacent tissues by IHC. E. Detection of the effect of CXCL9 mRNA expression on prognosis of breast cancer patients by KM survival curve.
Fig 4 Effect of the expression of target genes on the prognosis of breast cancer patients

图5 CXCL9的PPI网络构建和 CXCL9 及其相关基因的GO功能分析和KEGG通路分析Note: A. PPI network of CXCL9. Red indicates proteins with CXCL9 interaction score >0.9, and blue indicates proteins with CXCL9 interaction score >0.7. PF4—platelet factor 4; PF4V1—platelet factor 4 variant 1; MAP2K3/6—dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3/6; GNAI2—guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i) subunit alpha-2; GNG2—guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(O) subunit gamma-2; GNB1—guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(T) subunit beta-1; SFTPC—surfactant protein C; CCR1—C-C chemokine receptor type 1; CXCR1—C-X-C chemokine receptor type 1; CX3CR1—CX3C chemokine receptor 1; CCL5—C-C motif chemokine ligand 5; DPP4—dipeptidyl peptidase-4; GPR29—chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 6; XCR1—chemokine XC receptor 1; C1QA/B—complement component 1, Q subcomponent, A chain/B chain; IDO1—indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1; SLAMF8—SLAM family member 8; ADAMDEC1—adam-like, decysin 1; GBP5—guanylate-binding protein 5. B/C. GO function analysis (B) and KEGG pathway analysis (C) of CXCL9 and its related genes.
Fig 5 PPI network construction of CXCL9 and GO functional analysis and KEGG pathway analysis of CXCL9 and its related genes
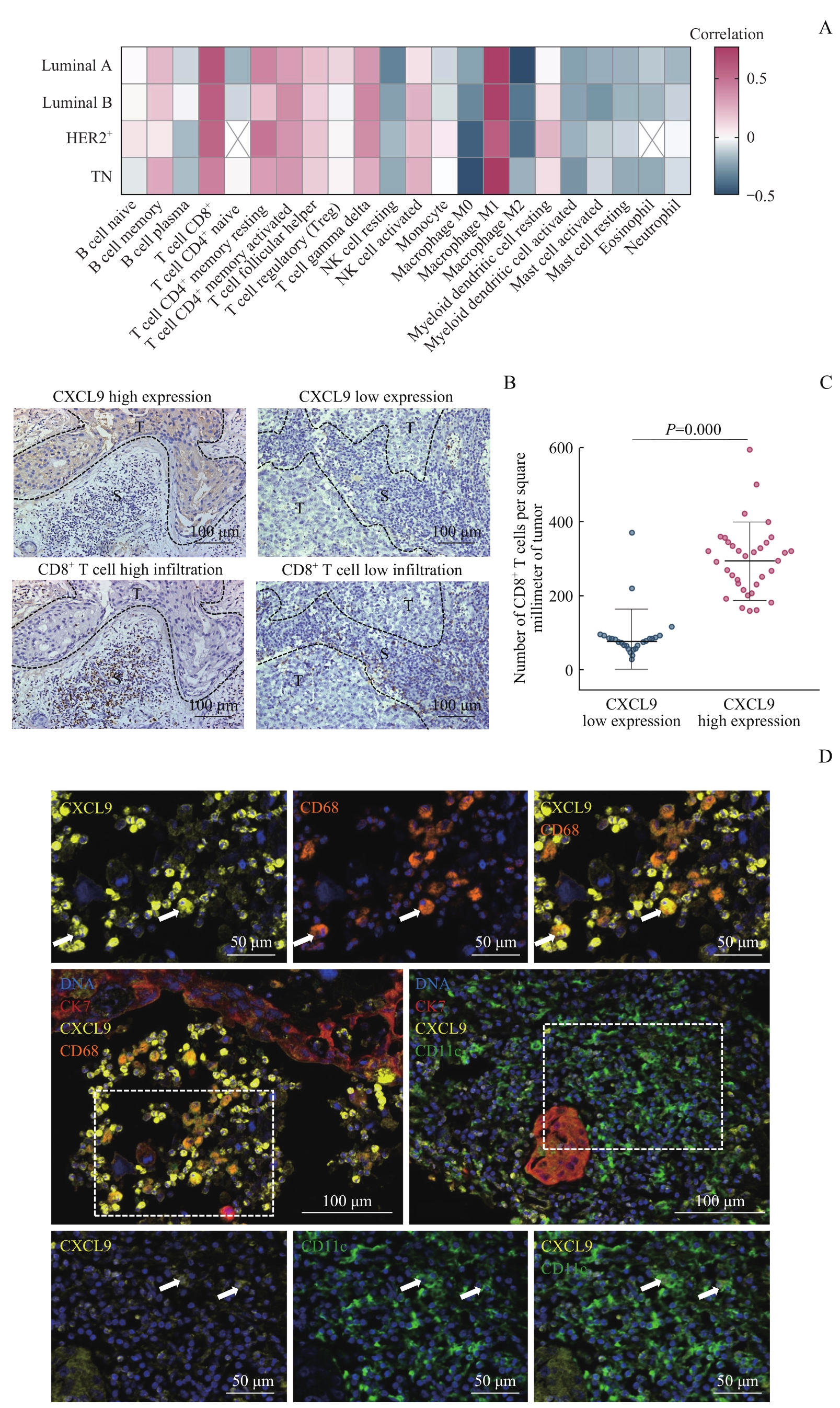
图6 乳腺癌中 CXCL9 mRNA表达与TIIC浸润水平的相关性分析Note: A. Spearman correlation analysis of TIICs infiltration ratio and CXCL9 mRNA expression. B. Observation of the relationship between CXCL9 expression and CD8+ T cells infiltration ratio by IHC. S—stroma; T—tumor. C. Correlation between CXCL9 expression and the number of CD8+ T cells infiltration by beeswarm plot. D. Fluorescence images of CXCL9+ cell species in breast cancer interstitium. Yellow indicates CXCL9, orange indicates CD68, green indicates CD11c, red indicates CK7, and blue indicates DNA. The left dashed box indicates the field of upper 3 small figures, and the right one indicates the field of lower 3 small figures. The arrows indicate CXCL9+CD68+ cells or CXCL9+CD11c+ cells.
Fig 6 Correlation between CXCL9 mRNA expression and TIICs infiltration ratio in breast cancer
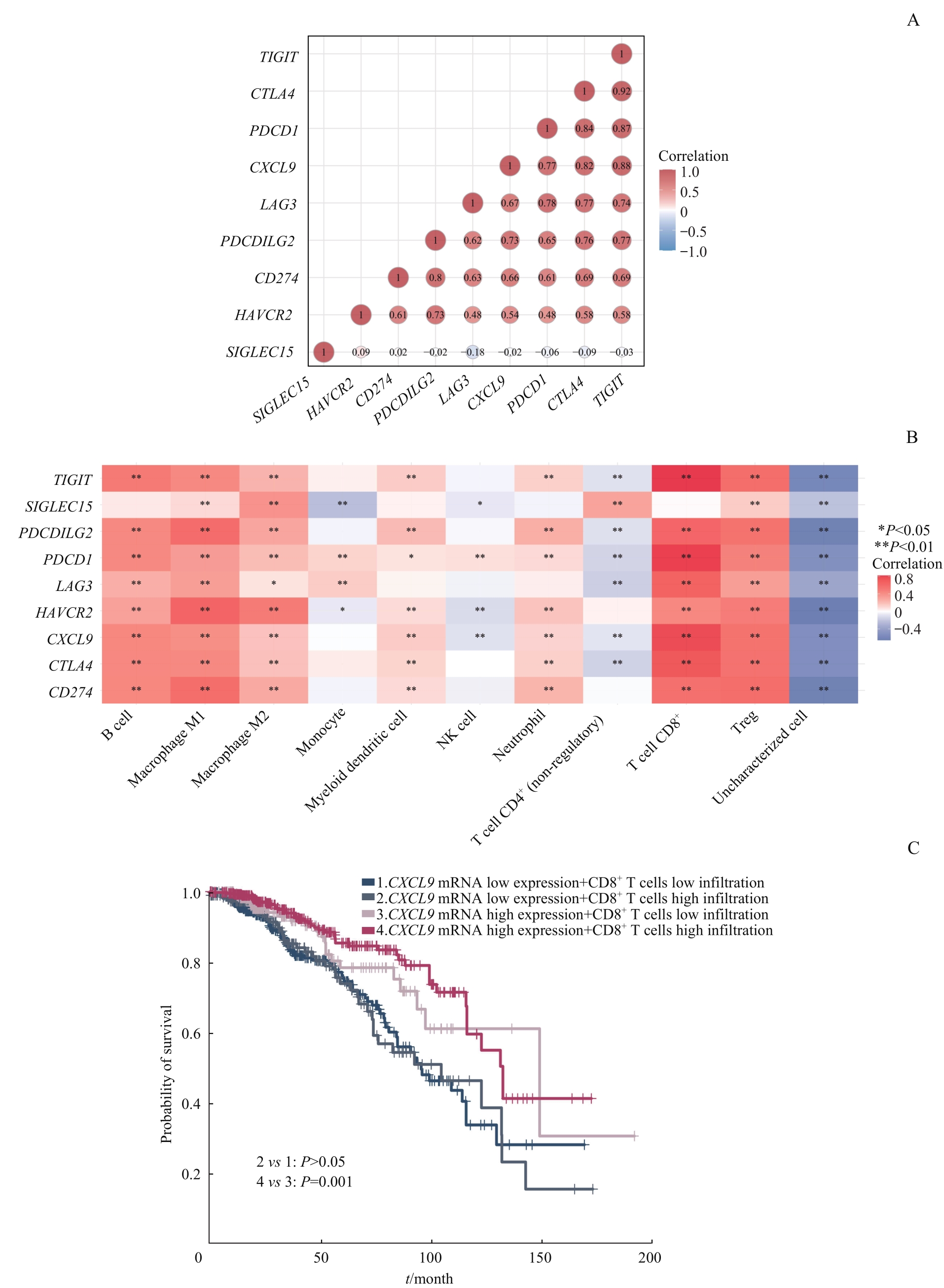
图7 CXCL9 mRNA表达水平和CD8+ T细胞浸润比例对乳腺癌患者预后的影响Note: A. Correlation between CXCL9 mRNA and immune checkpoint genes. B. Heatmap of various TIICs infiltration ratio in relation to CXCL9 and immune checkpoint genes. C. Effect of combination of high and low expression of CXCL9 mRNA and high and low infiltration of CD8+ T cells on the prognosis of breast cancer patients.
Fig 7 Effect of CXCL9 mRNA expression level and CD8+ T cells infiltration ratio on the prognosis of breast cancer patients
| 1 | SIEGEL R L, MILLER K D, FUCHS H E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2022[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2022, 72(1): 7-33. |
| 2 | SCHMID P, ADAMS S, RUGO H S, et al. Atezolizumab and nab-paclitaxel in advanced triple-negative breast cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2018, 379(22): 2108-2121. |
| 3 | FRANZOI M A, DE AZAMBUJA E. Atezolizumab in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: IMpassion130 and 131 trials-how to explain different results?[J]. ESMO Open, 2020, 5(6): e001112. |
| 4 | CORTES J, CESCON D W, RUGO H S, et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus placebo plus chemotherapy for previously untreated locally recurrent inoperable or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (KEYNOTE-355): a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 clinical trial[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10265): 1817-1828. |
| 5 | GOODING A J, ZHANG B, GUNAWARDANE L, et al. The lncRNA BORG facilitates the survival and chemoresistance of triple-negative breast cancers[J]. Oncogene, 2019, 38(12): 2020-2041. |
| 6 | GONÇALVES H, GUERRA M R, DUARTE CINTRA J R, et al. Survival study of triple-negative and non-triple-negative breast cancer in a Brazilian cohort[J]. Clin Med Insights Oncol, 2018, 12: 1179554918790563. |
| 7 | 杨芳, 于雁. 肿瘤微环境: 肿瘤转移的关键因素[J]. 中国肺癌杂志, 2015, 18(1): 48-54. |
| YANG F, YU Y. Tumor microenvironment: the critical element of tumor metastasis[J]. Chinese Journal of Lung Cancer, 2015, 18(1): 48-54. | |
| 8 | JIA Q, WANG A, YUAN Y, et al. Heterogeneity of the tumor immune microenvironment and its clinical relevance[J]. Exp Hematol Oncol, 2022, 11(1): 24. |
| 9 | JIA Q, WU W, WANG Y, et al. Local mutational diversity drives intratumoral immune heterogeneity in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1): 5361. |
| 10 | OHTANI H. Focus on TILs: prognostic significance of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in human colorectal cancer[J]. Cancer Immun, 2007, 7: 4. |
| 11 | BULE P, AGUIAR S I, AIRES-DA-SILVA F, et al. Chemokine-directed tumor microenvironment modulation in cancer immunotherapy[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(18): 9804. |
| 12 | HARLIN H, MENG Y, PETERSON A C, et al. Chemokine expression in melanoma metastases associated with CD8+ T-cell recruitment[J]. Cancer Res, 2009, 69(7): 3077-3085. |
| 13 | MESSINA J L, FENSTERMACHER D A, ESCHRICH S, et al. 12-Chemokine gene signature identifies lymph node-like structures in melanoma: potential for patient selection for immunotherapy?[J]. Sci Rep, 2012, 2: 765. |
| 14 | FRIDMAN W H, PAGÈS F, SAUTÈS-FRIDMAN C, et al. The immune contexture in human tumours: impact on clinical outcome[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2012, 12(4): 298-306. |
| 15 | TENG M W, NGIOW S F, RIBAS A, et al. Classifying cancers based on T-cell infiltration and PD-L1[J]. Cancer Res, 2015, 75(11): 2139-2145. |
| 16 | GALON J, BRUNI D. Approaches to treat immune hot, altered and cold tumours with combination immunotherapies[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2019, 18(3): 197-218. |
| 17 | GARRIDO F, APTSIAURI N, DOORDUIJN E M, et al. The urgent need to recover MHC class Ⅰ in cancers for effective immunotherapy[J]. Curr Opin Immunol, 2016, 39: 44-51. |
| 18 | BONAVENTURA P, SHEKARIAN T, ALCAZER V, et al. Cold tumors: a therapeutic challenge for immunotherapy[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 168. |
| 19 | WHERRY E J, KURACHI M. Molecular and cellular insights into T cell exhaustion[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2015, 15(8): 486-499. |
| 20 | RIBAS A, WOLCHOK J D. Cancer immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade[J]. Science, 2018, 359(6382): 1350-1355. |
| 21 | NEWMAN A M, LIU C L, GREEN M R, et al. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles[J]. Nat Methods, 2015, 12(5): 453-457. |
| 22 | FRANCESCHINI A, SZKLARCZYK D, FRANKILD S, et al. STRING v9.1: protein-protein interaction networks, with increased coverage and integration[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2013, 41(database issue): D808-D815. |
| 23 | ADAMS S, GATTI-MAYS M E, KALINSKY K, et al. Current landscape of immunotherapy in breast cancer: a review[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2019, 5(8): 1205-1214. |
| 24 | NANDA R, CHOW L Q, DEES E C, et al. Pembrolizumab in patients with advanced triple-negative breast cancer: phase Ⅰb KEYNOTE-012 study[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2016, 34(21): 2460-2467. |
| 25 | ADAMS S, LOI S, TOPPMEYER D, et al. Pembrolizumab monotherapy for previously untreated, PD-L1-positive, metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: cohort B of the phase Ⅱ KEYNOTE-086 study[J]. Ann Oncol, 2019, 30(3): 405-411. |
| 26 | WALSER T C, MA X, KUNDU N, et al. Immune-mediated modulation of breast cancer growth and metastasis by the chemokine Mig (CXCL9) in a murine model[J]. J Immunother, 2007, 30(5): 490-498. |
| 27 | YU L, YANG X, XU C, et al. Comprehensive analysis of the expression and prognostic value of CXC chemokines in colorectal cancer[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2020, 89(Pt B): 107077. |
| 28 | BRONGER H, KRAEFT S, SCHWARZ-BOEGER U, et al. Modulation of CXCR3 ligand secretion by prostaglandin E2 and cyclooxygenase inhibitors in human breast cancer[J]. Breast Cancer Res, 2012, 14(1): R30. |
| 29 | Pein M, Insua-Rodríguez J, Hongu T, et al. Metastasis-initiating cells induce and exploit a fibroblast niche to fuel malignant colonization of the lungs[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 1494. |
| 30 | DANGAJ D, BRUAND M, GRIMM A J, et al. Cooperation between constitutive and inducible chemokines enables T cell engraftment and immune attack in solid tumors[J]. Cancer Cell, 2019, 35(6): 885-900.e10. |
| [1] | 曹源, 王红霞, 朱灜, 李军建. 四次跨膜蛋白1在乳腺癌中的表达及其促进乳腺癌进展的作用机制[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(3): 293-300. |
| [2] | 杨笑萱, 朱珊, 钱程, 储晓英. 术中使用小剂量右美托咪定对乳腺癌手术患者预后的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(2): 194-200. |
| [3] | 夏坤健, 邓林林, 王琳. 乳腺癌化学治疗致肝损伤预测模型的构建及其评价[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(4): 502-509. |
| [4] | 许静轩, 杜少倩, 曹源, 王红霞, 黄伟翼. MMP14在胰腺癌中的表达及其与肿瘤免疫微环境特征的相关性研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(3): 312-322. |
| [5] | 张郁瑭, 金奕婕, 张凤春, 徐迎春. 乳腺癌合并新型冠状病毒肺炎感染患者的抗肿瘤合理化诊疗方案探讨[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(12): 1745-1750. |
| [6] | 苏俊澄, 王禹铮, 唐雷, 徐迎春, 张凤春. 乳腺癌脑转移患者的临床病理特征及预后的影响因素分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(11): 1562-1568. |
| [7] | 孙亚蒙, 马晔, 郭润生. 乳腺癌组织样本中 HER2基因拷贝数的检测分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(11): 1589-1597. |
| [8] | 王禹铮, 苏俊澄, 唐雷, 徐迎春, 张凤春. 单周紫杉醇联合顺铂一线治疗转移性乳腺癌的效果和安全性的回顾性研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(10): 1420-1427. |
| [9] | 王建茹, 彭广操, 朱明军. 基于GEO数据库和生物信息学分析筛选小鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤相关的潜在枢纽基因[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(1): 51-62. |
| [10] | 陈翠, 金叶, 王琳, 李红丽, 万财凤, 姜立新. 30例乳腺化生性癌的多种影像学对比分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(1): 70-76. |
| [11] | 刘俐, 耿子龙, 陈嘉焕, 张沙沙, 张冰. 血管内皮生长因子A调控人脐静脉内皮细胞miRNA的全基因表达谱分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(9): 1183-1189. |
| [12] | 周天浩, 辛肇晨, 杜少倩, 曹源, 许静轩, 劳曾红, 王红霞. 乳腺癌类器官共培养技术的建立和优化[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(8): 1017-1024. |
| [13] | 季艳杰, 罗浩, 蔡海燕, 刘欣宇, 金诗佳, 粟深月, 徐含章, 雷虎, 吴英理. CDDO-Me对三阴性乳腺癌细胞泛素特异性蛋白酶2a活性及细胞增殖的抑制作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(8): 1025-1032. |
| [14] | 王成志, 邓华云, 庞智, 黄雷. MUC1在HER2阳性乳腺癌发病中的作用及机制研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(7): 839-848. |
| [15] | 张海燕, 储晓英. 非阿片类镇痛药应用在全身麻醉喉罩置入的乳腺癌保乳手术中的可行性[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(5): 637-641. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 3595
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 1235
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||