
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (3): 312-324.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2024.03.003
• 论著 · 基础研究 • 上一篇
王鑫1,2( ), 王晓霞3(
), 王晓霞3( ), 李彦庆1,2, 郑永鑫1,2, 乌杰2,4, 任猛2, 贾向东2, 许天祥2(
), 李彦庆1,2, 郑永鑫1,2, 乌杰2,4, 任猛2, 贾向东2, 许天祥2( )
)
收稿日期:2023-09-13
接受日期:2023-12-28
出版日期:2024-03-28
发布日期:2024-04-29
通讯作者:
许天祥
E-mail:1363166062@qq.com;xiaoxiawang_2012@163.com;122784509@qq.com
作者简介:王 鑫(1996—),男,硕士生;电子信箱:1363166062@qq.com基金资助:
WANG Xin1,2( ), WANG Xiaoxia3(
), WANG Xiaoxia3( ), LI Yanqing1,2, ZHENG Yongxin1,2, WU Jie2,4, REN Meng2, JIA Xiangdong2, XU Tianxiang2(
), LI Yanqing1,2, ZHENG Yongxin1,2, WU Jie2,4, REN Meng2, JIA Xiangdong2, XU Tianxiang2( )
)
Received:2023-09-13
Accepted:2023-12-28
Online:2024-03-28
Published:2024-04-29
Contact:
XU Tianxiang
E-mail:1363166062@qq.com;xiaoxiawang_2012@163.com;122784509@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的·利用生物信息学和免疫组织化学法探究在肺鳞状细胞癌(lung squamous cell carcinoma,LUSC)组织中香叶基香叶基焦磷酸合成酶(geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase 1,GGPS1)的表达及其临床意义。方法·首先从UCSC Xena平台下载LUSC组织与配对正常组织的转录组数据,使用R语言进行数据标准化和差异表达分析,并利用UALCAN数据库进行验证;采用UALCAN和LinkedOmics数据库分析LUSC患者中GGPS1表达与临床病理特征关系;利用Kaplan-Meier Plotter数据库探究LUSC患者GGPS1表达对预后的影响。应用最小绝对收缩和选择算子(least absolute shrinkage and selection operator,LASSO)回归分析筛选基因相关系数及风险评分。通过列线图和校正曲线评价GGPS1对LUSC的诊断价值。采用STRING、GeneMANIA数据库构建GGPS1蛋白质相互作用(protein-protein interaction,PPI)网络。运用R语言挑选与GGPS1相关差异基因,并进行基因本体论(Gene Ontology,GO)和京都基因和基因组百科全书(Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes,KEGG)富集分析。采用免疫组织化学法检测LUSC患者GGPS1表达情况,并分析其与临床病理特征和预后的相关性。结果·通过TIMER2.0数据库检索到GGPS1在多数肿瘤中表达均升高,且在LUSC中呈高表达。UCSC Xena、UALCAN数据库中GGPS1在LUSC的表达高于癌旁组织(均P<0.05)。UALCAN和LinkedOmics数据库发现GGPS1在指标分期较晚患者中的表达水平更高,且Kaplan-Meier Plotter数据库显示LUSC患者GGPS1高表达总生存期(overall survival,OS)较短(P<0.05)。基于LASSO回归评估LUSC患者有较好的风险预测效能。构建LUSC患者的个体化预测模型具有最佳预测准确度。GO、KEGG结果显示,GGPS1相关基因主要与蛋白质代谢、调节脂质和胆固醇代谢过程、尼古丁成瘾、磷脂酰肌醇3激酶(phosphatidylinositol3-kinase,PI3K)/蛋白激酶B(protein kinase B,AKT)/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR)、过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体(peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors,PPAR)信号通路等有关。GGPS1的代谢功能可能促进肿瘤发生。免疫组化结果提示GGPS1主要定位于细胞质中,且LUSC组织中表达高于癌旁组织(P<0.05),GGPS1高表达与LUSC患者肿瘤大小、淋巴结转移和TNM分期有关(均P<0.05),且GGPS1表达高的患者OS明显短于低表达者(P=0.000)。多因素Cox回归分析提示GGPS1可作为LUSC的独立预后因素。结论·相较于正常肺组织,GGPS1在LUSC中表达显著升高,尤其在肿瘤体积较大、淋巴结转移阳性及晚期的患者中表达升高更明显;且GGPS1过表达是LUSC患者预后差的独立预测因子。GGPS1有望成为新的LUSC诊治和预防的分子靶点。
中图分类号:
王鑫, 王晓霞, 李彦庆, 郑永鑫, 乌杰, 任猛, 贾向东, 许天祥. 香叶基香叶基焦磷酸合成酶在肺鳞状细胞癌中的表达及临床意义[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(3): 312-324.
WANG Xin, WANG Xiaoxia, LI Yanqing, ZHENG Yongxin, WU Jie, REN Meng, JIA Xiangdong, XU Tianxiang. Expression and clinical significance of geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase1 (GGPS1) in lung squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(3): 312-324.

图1 GGPS1 在泛癌中的表达Note: ACC—adrenocortical carcinoma; BLCA—bladder urothelial carcinoma; BRCA—breast invasive carcinoma; CESC—cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma; CHOL—cholangiocarcinoma; COAD—colon adenocarcinoma; DLBC—diffuse large B cell lymphoma; ESCA—esophageal carcinoma; GBM—glioblastoma multiforme; HNSC—head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; KICH—kidney chromophobe; KIRC—kidney renal clear cell carcinoma; KIRP—kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma; LAML—acute myeloid leukemia; LGG—brain lower grade glioma; LIHC—liver hepatocellular carcinoma; LUAD—lung adenocarcinoma; LUSC—lung squamous cell carcinoma; OV—ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma; PAAD—pancreatic adenocarcinoma; PCPG—pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma; PRAD—prostate adenocarcinoma; READ—rectum adenocarcinoma; SARC—sarcoma; SKCM—skin cutaneous melanoma; STAD—stomach adenocarcinoma; THCA—thyroid carcinoma; THYM—thymoma; UCEC—uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma; UCS—uterine carcinosarcoma. Blue represents normal tissue and red represents tumor tissue. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
Fig 1 The expression of GGPS1 in pan-carcinoma

图2 UCSC Xena和UALCAN数据库中 GGPS1 在LUSC和癌旁正常组织的差异表达Note: A. GGPS1 expression in the tumors and normal tissues. B. GGPS1 expression in the 49 pairs of tumors and normal tissues. C. The expression of GGPS1 in LUSC in UALCAN database. ①P=0.000, ②P=0.003.
Fig 2 Differential expression of GGPS1 in the LUSC and paracancerous normal tissues in the UCSC Xena and UALCAN databases

图3 UALCAN数据库中 GGPS1 表达与LUSC患者临床病理特征的关系Note: A. Comparison of GGPS1 expression between different stages of patients. B. Comparison of GGPS1 expression between different N stages of patients. ①P=0.000, ②P=0.001, ③P=0.027.
Fig 3 Relationship between GGPS1 expression and clinicopathological characteristics of LUSC patients in UALCAN database
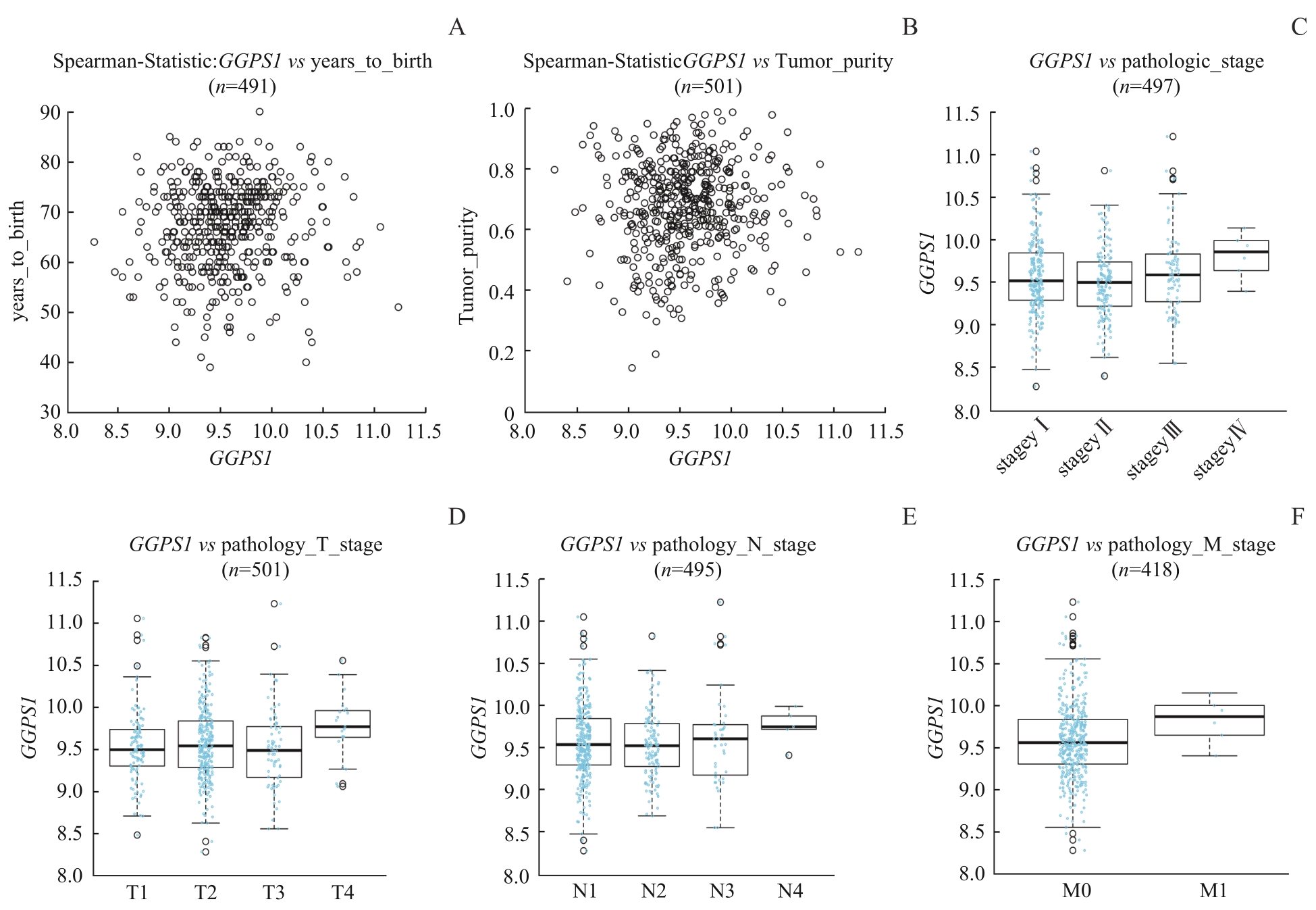
图4 LinkedOmics数据库中 GGPS1 表达与LUSC患者临床病理特征的关系Note: A. Expression level of GGPS1 of different ages. B. Expression level of GGPS1 in different tumor purity. C. Expression level of GGPS1 in different pathological grades. D. Expression level of GGPS1 in different T stages. E. Expression level of GGPS1 in different N stages. F. Expression level of GGPS1 in different M stages.
Fig 4 Relationship between GGPS1 expression and clinicopathological characteristics of LUSC patients in LinkedOmics database
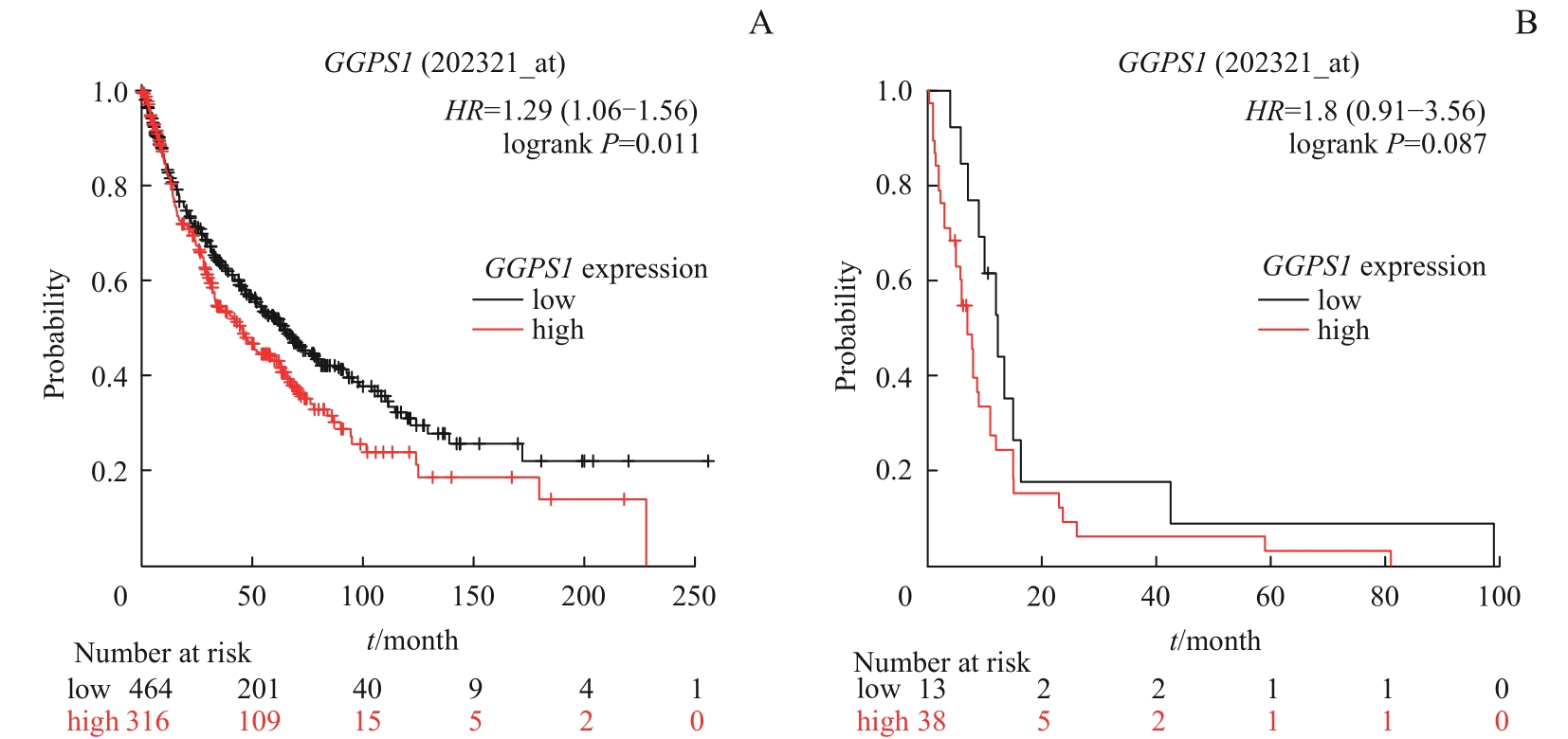
图5 Kaplan-Meier Plotter 数据库中 GGPS1 表达与LUSC患者预后的关系Note: A. Relationship between GGPS1 expression and overall survival. B. Relationship between GGPS1 expression and post progression survival.
Fig 5 Relationship between GGPS1 expression and prognosis of LUSC patients in Kaplan-Meier Plotter database

图6 LUSC 患者LASSO回归分析与列线图的建立Note: A. Screening of candidate genes by LASSO-COX analysis. B. Relationship between risk score and overall survival. C. Effect of risk scores on survival outcomes. D. A nomogram for assessing the survival probability of 1-,2-, 3-,5- and 10-year for LUSC. E. Calibration curve of the prognostic risk model.
Fig 6 LASSO regression analyses and establishment of nomogram for LUSC patients
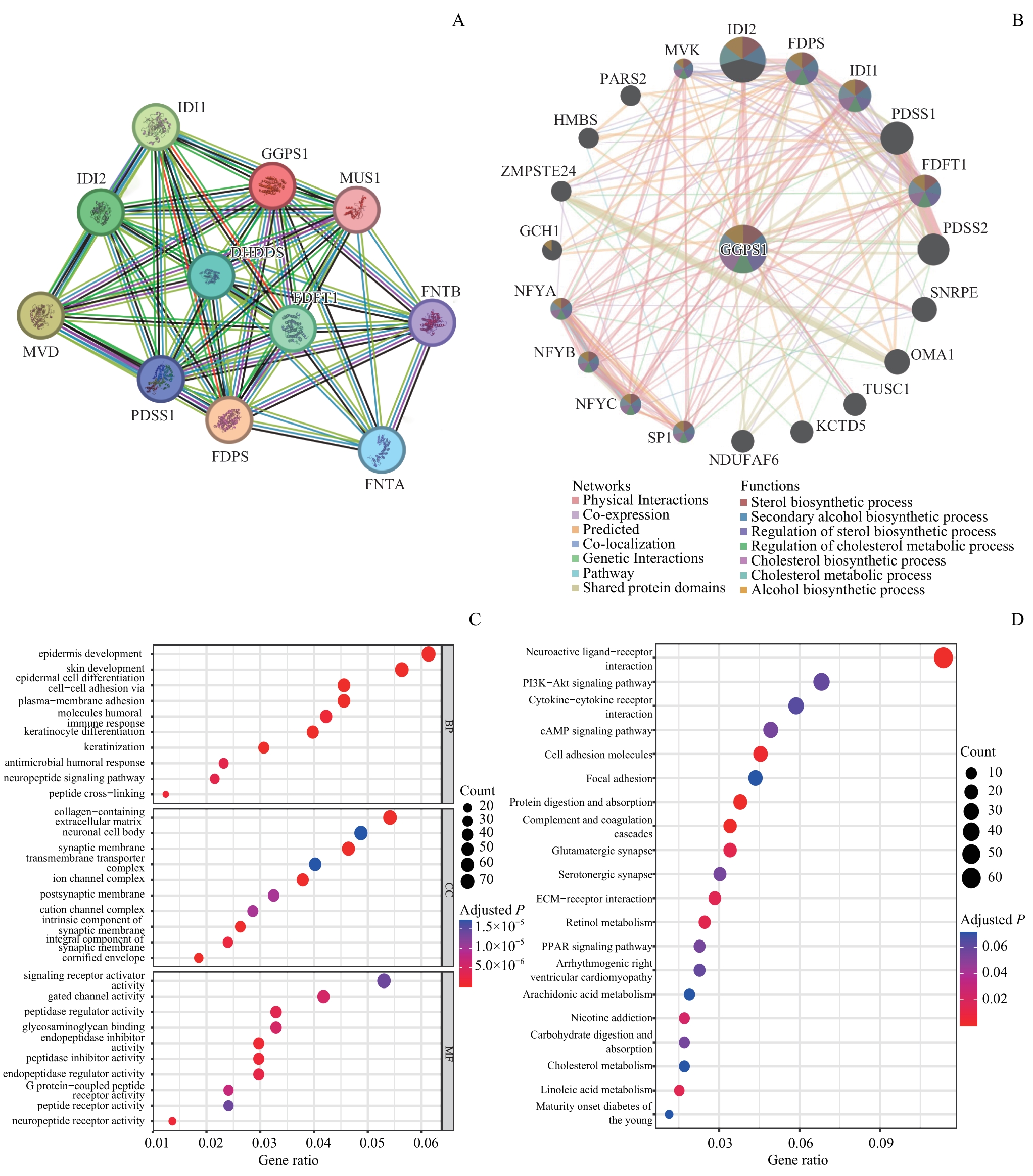
图7 GGPS1的PPI网络及GO、KEGG分析Note: A/B. PPI network analysis of STRING database (A) and GeneMANIA database (B). C/D. Bubble plot of GO enrichment analysis (C) and KEGG enrichment analysis (D). MVD—mevalonate diphosphate decarboxylase; DHDDS—dehydrodolichyl diphosphate synthase subunit; PDSS1—decaprenyl diphosphate dynthase subunit 1; FNTA—farnesyltransferase, CAAX box, α; FNTB—farnesyltransferase, CAAX box, β; MVK—mevalonate kinase; PARS2—prolyl-TRNA synthetase 2, mitochondrial; SNRPE—small nuclear ribonucleoprotein polypeptide E; OMA1—OMA1 zinc metallopeptidase; HMBS—hydroxymethylbilane synthase; ZMPSTE24—zinc metallopeptidase STE24; GCH1—GTP cyclohydrolase 1; NFYA—nuclear transcription factor Y subunit α; NFYB—nuclear transcription factor Y subunit β; NFYC—nuclear transcription factor Y subunit γ; SP1—Sp1 transcription factor; NDUFAF6—NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase complex assembly factor 6; KCTD5—potassium channel tetramerization domain containing 5; TUSC1—tumor suppressor candidate 1.
Fig 7 PPI network and GO and KEGG analysis of GGPS1
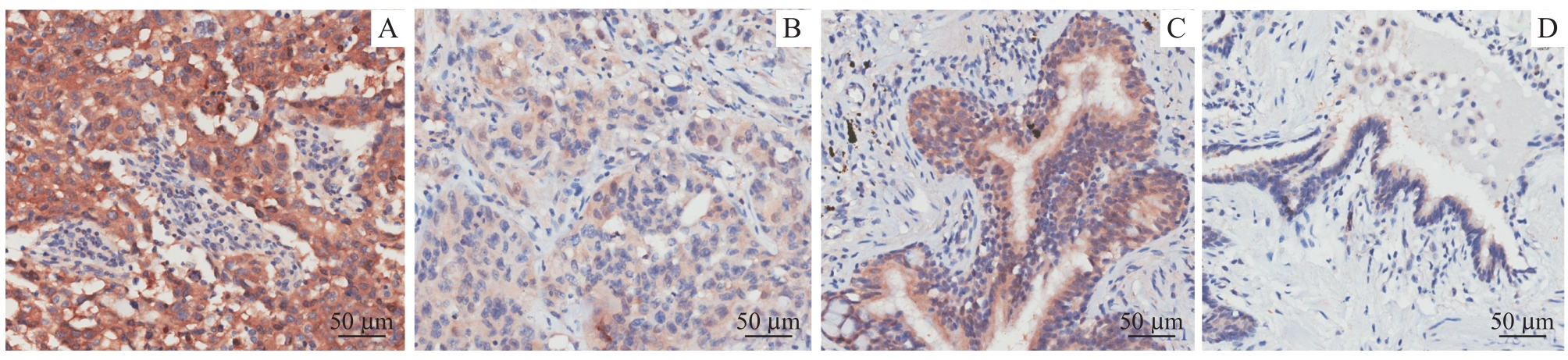
图8 LUSC及癌旁组织中GGPS1免疫组化染色(×200)Note: A/B. High expression (A) and low expression (B) of GGPS1 in cancer tissues. C/D. High expression (A) and low expression (B) of GGPS1 in adjacent tissues.
Fig 8 Immunohistochemical staining of GGPS1 in LUSC and adjacent tissues (×200)
| Expression | LUSC (n=90) | Normal (n=90) | χ2 | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GGPS1/n(%) | 8.193 | 0.004 | ||
| Low | 42 (46.7) | 61 (67.8) | ||
| High | 48 (53.3) | 29 (32.2) |
表1 GGPS1在中LUSC组织与癌旁正常肺组织表达差异
Tab 1 Differential expression of GGPS1 in LUSC and adjacent normal lung tissues
| Expression | LUSC (n=90) | Normal (n=90) | χ2 | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GGPS1/n(%) | 8.193 | 0.004 | ||
| Low | 42 (46.7) | 61 (67.8) | ||
| High | 48 (53.3) | 29 (32.2) |
| Characteristic | Total/n | GGPS1/n(%) | χ2 value | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low expression | High expression | ||||
| Gender | 1.213 | 0.271 | |||
| Male | 84 | 41 (48.8) | 43 (51.2) | ||
| Female | 6 | 1 (16.7) | 5 (83.3) | ||
| Age | 0.003 | 0.955 | |||
| ≤64 years old | 49 | 23 (46.9) | 26 (53.1) | ||
| >64 years old | 41 | 19 (46.3) | 22 (53.7) | ||
| History of smoking | 2.691 | 0.101 | |||
| No | 41 | 23 (56.1) | 18 (43.9) | ||
| Yes | 49 | 19 (38.8) | 30 (61.2) | ||
| Tumor location | 0.984 | 0.321 | |||
| Left | 40 | 21 (52.5) | 19 (47.5) | ||
| Right | 50 | 21 (42.0) | 29 (58.0) | ||
| Tumor size | 10.247 | 0.001 | |||
| ≤3 cm | 26 | 19 (73.1) | 7 (26.9) | ||
| >3 cm | 64 | 23 (35.9) | 41 (64.1) | ||
| Lymph node metastasis | 7.626 | 0.006 | |||
| No | 46 | 28 (60.9) | 18 (39.1) | ||
| Yes | 44 | 14 (31.8) | 30 (68.2) | ||
| TNM stage | 8.935 | 0.003 | |||
| Ⅰ~Ⅱ | 47 | 29 (61.7) | 18 (38.3) | ||
| Ⅲ~Ⅳ | 43 | 13 (30.2) | 30 (69.8) | ||
表2 GGPS1表达水平与LUSC临床病理特征的相关性
Tab 2 Correlation between GGPS1 expression level and clinicopathological characteristics of LUSC
| Characteristic | Total/n | GGPS1/n(%) | χ2 value | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low expression | High expression | ||||
| Gender | 1.213 | 0.271 | |||
| Male | 84 | 41 (48.8) | 43 (51.2) | ||
| Female | 6 | 1 (16.7) | 5 (83.3) | ||
| Age | 0.003 | 0.955 | |||
| ≤64 years old | 49 | 23 (46.9) | 26 (53.1) | ||
| >64 years old | 41 | 19 (46.3) | 22 (53.7) | ||
| History of smoking | 2.691 | 0.101 | |||
| No | 41 | 23 (56.1) | 18 (43.9) | ||
| Yes | 49 | 19 (38.8) | 30 (61.2) | ||
| Tumor location | 0.984 | 0.321 | |||
| Left | 40 | 21 (52.5) | 19 (47.5) | ||
| Right | 50 | 21 (42.0) | 29 (58.0) | ||
| Tumor size | 10.247 | 0.001 | |||
| ≤3 cm | 26 | 19 (73.1) | 7 (26.9) | ||
| >3 cm | 64 | 23 (35.9) | 41 (64.1) | ||
| Lymph node metastasis | 7.626 | 0.006 | |||
| No | 46 | 28 (60.9) | 18 (39.1) | ||
| Yes | 44 | 14 (31.8) | 30 (68.2) | ||
| TNM stage | 8.935 | 0.003 | |||
| Ⅰ~Ⅱ | 47 | 29 (61.7) | 18 (38.3) | ||
| Ⅲ~Ⅳ | 43 | 13 (30.2) | 30 (69.8) | ||
| Variable | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95%CI | P value | HR | 95%CI | P value | |
| Gender | 0.652 | 0.232‒1.837 | 0.419 | |||
| Age | 0.631 | 0.336‒1.185 | 0.152 | |||
| History of smoking | 2.054 | 1.054‒4.003 | 0.034 | 2.045 | 1.024‒4.086 | 0.043 |
| Tumor location | 0.878 | 0.468‒1.648 | 0.686 | |||
| Tumor size | 2.751 | 1.151‒6.574 | 0.023 | 1.621 | 0.639‒4.114 | 0.309 |
| Lymph node metastasis | 3.116 | 1.577‒6.157 | 0.001 | 4.039 | 1.257‒12.983 | 0.019 |
| TNM stage | 2.399 | 1.246‒4.619 | 0.009 | 0.473 | 0.147‒1.523 | 0.210 |
| GGPS1 expression | 3.872 | 1.834‒8.176 | 0.000 | 2.867 | 1.316‒6.242 | 0.008 |
表3 影响LUSC患者OS的Cox回归模型
Tab 3 Cox regression model affecting OS of LUSC patients
| Variable | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95%CI | P value | HR | 95%CI | P value | |
| Gender | 0.652 | 0.232‒1.837 | 0.419 | |||
| Age | 0.631 | 0.336‒1.185 | 0.152 | |||
| History of smoking | 2.054 | 1.054‒4.003 | 0.034 | 2.045 | 1.024‒4.086 | 0.043 |
| Tumor location | 0.878 | 0.468‒1.648 | 0.686 | |||
| Tumor size | 2.751 | 1.151‒6.574 | 0.023 | 1.621 | 0.639‒4.114 | 0.309 |
| Lymph node metastasis | 3.116 | 1.577‒6.157 | 0.001 | 4.039 | 1.257‒12.983 | 0.019 |
| TNM stage | 2.399 | 1.246‒4.619 | 0.009 | 0.473 | 0.147‒1.523 | 0.210 |
| GGPS1 expression | 3.872 | 1.834‒8.176 | 0.000 | 2.867 | 1.316‒6.242 | 0.008 |

图10 Cox回归分析森林图
Fig 10 Forest plot of Cox regression analysisNote: A. Univariate Cox regression analysis tree diagram. B. Multivariate Cox regression analysis tree diagram. HR>1 indicates disadvantageous factors.
| 1 | SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. |
| 2 | 国家卫生健康委办公厅. 原发性肺癌诊疗指南(2022年版)[J]. 协和医学杂志, 2022, 13(4): 549-570. |
| General Office of National Health Commission. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of primary lung cancer (2022 edition)[J]. Union Medical Journal, 2022, 13(4): 549-570. | |
| 3 | LAZZARI C, KARACHALIOU N, GREGORC V, et al. Second-line therapy of squamous non-small cell lung cancer: an evolving landscape[J]. Expert Rev Respir Med, 2017, 11(6): 469-479. |
| 4 | ERICSSON J, GREENE J M, CARTER K C, et al. Human geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase: isolation of the cDNA, chromosomal mapping and tissue expression[J]. J Lipid Res, 1998, 39(9): 1731-1739. |
| 5 | KUZUGUCHI T, MORITA Y, SAGAMI I, et al. Human geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase. cDNA cloning and expression[J]. J Biol Chem, 1999, 274(9): 5888-5894. |
| 6 | 王鑫, 许天祥, 李彦庆等. GGPPS及其抑制剂在肿瘤中的研究进展[J]. 生命的化学, 2023, 43(6): 831-840. |
| WANG X, XU T X, LI Y Q, et al. Research progress of GGPPS and its inhibitors in tumors[J]. Chemistry of Life, 2023, 43(6): 831-840. | |
| 7 | LI T W, FU J X, ZENG Z X, et al. TIMER2.0 for analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2020, 48(W1): W509-W514. |
| 8 | CHANDRASHEKAR D S, KARTHIKEYAN S K, KORLA P K, et al. UALCAN: an update to the integrated cancer data analysis platform[J]. Neoplasia, 2022, 25: 18-27. |
| 9 | NAGY Á, LÁNCZKY A, MENYHÁRT O, et al. Validation of miRNA prognostic power in hepatocellular carcinoma using expression data of independent datasets[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 9227. |
| 10 | SZKLARCZYK D, KIRSCH R, KOUTROULI M, et al. The STRING database in 2023: protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2023, 51(D1): D638-D646. |
| 11 | FRANZ M, RODRIGUEZ H, LOPES C, et al. GeneMANIA update 2018[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2018, 46(W1): W60-W64. |
| 12 | BADE B C, DELA CRUZ C S. Lung cancer 2020: epidemiology, etiology, and prevention[J]. Clin Chest Med, 2020, 41(1): 1-24. |
| 13 | MANASWIYOUNGKUL P, DE ARAUJO E D, GUNNING P T. Targeting prenylation inhibition through the mevalonate pathway[J]. RSC Med Chem, 2020, 11(1): 51-71. |
| 14 | KAIYRZHANOV R, PERRY L, ROCCA C, et al. GGPS1-associated muscular dystrophy with and without hearing loss[J]. Ann Clin Transl Neurol, 2022, 9(9): 1465-1474. |
| 15 | YU D C, LIU J, CHEN J, et al. GGPPS1 predicts the biological character of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis[J]. BMC Cancer, 2014, 14: 248. |
| 16 | ZHAO D D, YUAN J, CHENG Q, et al. Evidence for a role of geranylgeranylation in renal angiomyolipoma and renal epithelioid angiomyolipoma[J]. Oncol Lett, 2019, 17(2): 1523-1530. |
| 17 | WEISSENRIEDER J S, REILLY J E, NEIGHBORS J D, et al. Inhibiting geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthesis reduces nuclear androgen receptor signaling and neuroendocrine differentiation in prostate cancer cell models[J]. Prostate, 2019, 79(1): 21-30. |
| 18 | HUANG K, HAN L, XU H M, et al. The prognostic role and metabolic function of GGPS1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Front Mol Biosci, 2023, 10: 1109403. |
| 19 | HANEY S L, VARNEY M L, CHHONKER Y S, et al. Inhibition of geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase is a novel therapeutic strategy for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. Oncogene, 2019, 38(26): 5308-5320. |
| 20 | HANEY S L, VARNEY M L, WILLIAMS J T, et al. Geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase inhibitor and proteasome inhibitor combination therapy in multiple myeloma[J]. Exp Hematol Oncol, 2022, 11(1): 5. |
| 21 | HANEY S L, FENG D, CHHONKER Y S, et al. Evaluation of geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase inhibition as a novel strategy for the treatment of osteosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma[J]. Drug Dev Res, 2023, 84(1): 62-74. |
| 22 | WANG X X, XU W J, ZHAN P, et al. Overexpression of geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase contributes to tumour metastasis and correlates with poor prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2018, 22(4): 2177-2189. |
| 23 | BIAN X L, LIU R, MENG Y, et al. Lipid metabolism and cancer[J]. J Exp Med, 2021, 218(1): e20201606. |
| 24 | ZHANG C J, ZHU N, LI H F, et al. New dawn for cancer cell death: emerging role of lipid metabolism[J]. Mol Metab, 2022, 63: 101529. |
| 25 | 胡婵婵, 范毅, 徐源, 等. 脂质代谢在肺癌发生发展及诊疗领域中的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(12): 1766-1771. |
| HU C C, FAN Y, XU Y, et al. Lipid metabolism and lung cancer: emerging roles in occurrence, progression, diagnosis and treatment[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2022, 42(12): 1766-1771. | |
| 26 | ERSHOV P, KALUZHSKIY L, MEZENTSEV Y, et al. Enzymes in the cholesterol synthesis pathway: interactomics in the cancer context[J]. Biomedicines, 2021, 9(8): 895. |
| 27 | XU H, WANG Q S, SUN Q, et al. In type 2 diabetes induced by cigarette smoking, activation of p38 MAPK is involved in pancreatic β-cell apoptosis[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, 2018, 25(10): 9817-9827. |
| 28 | SHEN N, GONG T, WANG J D, et al. Cigarette smoke-induced pulmonary inflammatory responses are mediated by EGR-1/GGPPS/MAPK signaling[J]. Am J Pathol, 2011, 178(1): 110-118. |
| 29 | CHANG W H, LAI A G. The pan-cancer mutational landscape of the PPAR pathway reveals universal patterns of dysregulated metabolism and interactions with tumor immunity and hypoxia[J]. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2019, 1448(1): 65-82. |
| [1] | 邓青松, 张长青, 陶诗聪. 烟酰胺代谢相关基因与骨关节炎的关系探索[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(2): 145-160. |
| [2] | 杜少倩, 陶梦玉, 曹源, 王红霞, 胡孝渠, 范广建, 臧丽娟. CXCL9在乳腺癌中的表达及其与肿瘤免疫浸润特征的相关性研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(7): 860-872. |
| [3] | 李清林, 王文波, 刘伟. 肌腱去应力退化机制的生物信息学分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(5): 560-570. |
| [4] | 韩夏夏, 蒋扬, 顾霜霜, 戴黛, 沈南. 系统性红斑狼疮患者免疫细胞代谢通路转录组分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(9): 1197-1207. |
| [5] | 靳步, 袁颖, 陈婉玉, 徐浒东, 黄晓蕾, 何佳璐, 于红. 基于GEO数据库探索miRNA靶基因通过泛素化参与食管鳞状细胞癌[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(4): 464-471. |
| [6] | 龚其雨, 陈磊. 多组学数据解析循环及浸润性B细胞在结直肠癌免疫微环境中的作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(4): 472-481. |
| [7] | 许静轩, 杜少倩, 曹源, 王红霞, 黄伟翼. MMP14在胰腺癌中的表达及其与肿瘤免疫微环境特征的相关性研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(3): 312-322. |
| [8] | 王建茹, 彭广操, 朱明军. 基于GEO数据库和生物信息学分析筛选小鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤相关的潜在枢纽基因[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(1): 51-62. |
| [9] | 刘俐, 耿子龙, 陈嘉焕, 张沙沙, 张冰. 血管内皮生长因子A调控人脐静脉内皮细胞miRNA的全基因表达谱分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(9): 1183-1189. |
| [10] | 徐莹, 褚以忞, 杨大明, 李吉, 张海芹, 彭海霞. 基于差异表达基因组合构建高度微卫星不稳定结直肠癌转移预测模型[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(9): 1197-1206. |
| [11] | 宣贝贝, 龚赛楠, 刘佳丽, 全权, 孟雨, 牟晓玲. DNA聚合酶θ在子宫内膜癌中的表达及其临床意义[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(9): 1207-1214. |
| [12] | 陈盛, 严志龙, 吴晔明, 徐敏, 顾松, 马靖. HIF-1α/SHH信号通路在神经母细胞瘤中的表达及临床意义[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(8): 1056-1061. |
| [13] | 刘音, 杨涛, 谢裕赛, 王玉柱. 基于GEO数据库筛选狼疮性肾炎的关键基因和信号通路[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(6): 749-755. |
| [14] | 杨鹿笛, 王高明, 胡仁豪, 蒋小华, 崔然. 生物信息学方法筛选胰腺癌进展相关的核心基因[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(5): 571-578. |
| [15] | 顾琦晟, 张米粒, 曹灿, 李继坤. 基于TCGA数据库分析胃癌可变剪接与肿瘤免疫的关系[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(4): 448-458. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||