
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 183-195.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2024.02.004
王莹1( ), 平立风2, 刘彤彤3, 刘珊珊4, 刘磊1(
), 平立风2, 刘彤彤3, 刘珊珊4, 刘磊1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-04-13
接受日期:2023-11-30
出版日期:2024-02-28
发布日期:2024-02-28
通讯作者:
刘 磊,电子信箱:2625260425@qq.com。作者简介:王 莹(1986—),女,副主任医师,硕士;电子信箱:taiyiwangying2009@163.com。
基金资助:
WANG Ying1( ), PING Lifeng2, LIU Tongtong3, LIU Shanshan4, LIU Lei1(
), PING Lifeng2, LIU Tongtong3, LIU Shanshan4, LIU Lei1( )
)
Received:2023-04-13
Accepted:2023-11-30
Online:2024-02-28
Published:2024-02-28
Contact:
LIU Lei, E-mail: 2625260425@qq.com.Supported by:摘要:
目的·探讨甲基莲心碱(neferine,Nef)对糖尿病肾病(diabetic nephropathy,DN)大鼠肾组织的作用及其相关机制。方法·采用高脂饲料喂食联合腹腔注射链脲佐菌素的方法构建DN模型大鼠,并将造模成功的大鼠随机分为DN组、Nef(低、中、高)剂量组、Nef高剂量+通路拮抗剂(AMD3100)组,每组10只。同时,选10只普通大鼠作为正常组。检测6组大鼠的空腹血糖(fasting blood glucose,FBG)、24 h尿蛋白、血清糖化血红蛋白(glycosylated hemoglobin,HbA1c)、血清肌酐(serum creatinine,Scr)、尿素氮(blood urea nitrogen,BUN)水平及肾指数。分别采用苏木精-伊红(hematoxylin-eosin,H-E)染色、马松(Masson)染色观察6组大鼠的肾组织的病理变化。采用硫代巴比妥酸(thiobarbituric acid,TBA)法检测肾组织丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA)含量,分别采用水溶性四氮唑(water soluble tetrazolium,WST-1)法、钼酸铵法检测肾组织超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)、过氧化氢酶(catalase,CAT)的活性。分别采用实时荧光定量PCR(quantitative real-time PCR,qPCR)和蛋白质印迹法(Western blotting)检测肾组织中基质细胞衍生因子-1(stromal cell-derived factor-1,SDF-1)、CXC趋化因子受体4(CXC chemokine receptor 4,CXCR4)的mRNA以及蛋白表达。采用高糖(30 mmol/L葡萄糖)诱导大鼠肾小管上皮细胞NRK-52E,以建立DN细胞模型。将该细胞分为对照组、高糖(HG)组、HG+Nef(低、中、高)剂量组(即HG+Nef-L、M、H组)、HG+Nef-H+AMD3100组。分别采用WST-1法、钼酸铵法检测模型细胞中SOD、CAT活性,采用TBA法检测MDA含量,分别采用qPCR、Western blotting检测SDF-1、CXCR4的mRNA及蛋白表达,采用CCK-8法、流式细胞术检测细胞活力和凋亡率。结果·与DN组比较,Nef(低、中、高)剂量组和Nef高剂量+AMD3100组大鼠的FBG、24 h尿蛋白、HbA1c、Scr、BUN水平以及肾指数、MDA水平均较低,SDF-1、CXCR4的mRNA和蛋白表达以及SOD、CAT活性均较高(均P<0.05),肾组织病理损伤、纤维化程度有所减轻,且均呈剂量依赖性;AMD3100能减弱高剂量Nef对DN大鼠的肾保护作用。与HG组比较,HG+Nef-L、M、H组NRK-52E细胞的活力,SOD、CAT活性,SDF-1、CXCR4的mRNA和蛋白表达均较高,MDA含量及凋亡率均较低(均P<0.05);AMD3100可逆转Nef-H对NRK-52E细胞损伤的保护作用。结论·Nef可能通过激活SDF-1/CXCR4信号通路来控制DN大鼠的血糖水平并提高其抗氧化能力,从而发挥肾保护作用。
中图分类号:
王莹, 平立风, 刘彤彤, 刘珊珊, 刘磊. 甲基莲心碱调节SDF-1/CXCR4信号通路对糖尿病肾病的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(2): 183-195.
WANG Ying, PING Lifeng, LIU Tongtong, LIU Shanshan, LIU Lei. Effect of neferine on diabetic nephropathy by regulating SDF-1/CXCR4 signal pathway[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(2): 183-195.
| Primer | Forward sequence (5'→3') | Reverse sequence (5'→3') |
|---|---|---|
| Sdf-1 | GACGGTAAGCCAGTCAGCCT | CAGGTACCTCTGGATCCACT |
| Cxcr4 | ACGCACGACGTCTTCCAGTA | CCACCTGGTTCAACTCACTCC |
| β-actin | GCACCACACCTTCTACAATG | TGCTTGCTGATCCACATCTG |
表 1 qPCR引物序列
Tab 1 Primer sequence for qPCR
| Primer | Forward sequence (5'→3') | Reverse sequence (5'→3') |
|---|---|---|
| Sdf-1 | GACGGTAAGCCAGTCAGCCT | CAGGTACCTCTGGATCCACT |
| Cxcr4 | ACGCACGACGTCTTCCAGTA | CCACCTGGTTCAACTCACTCC |
| β-actin | GCACCACACCTTCTACAATG | TGCTTGCTGATCCACATCTG |
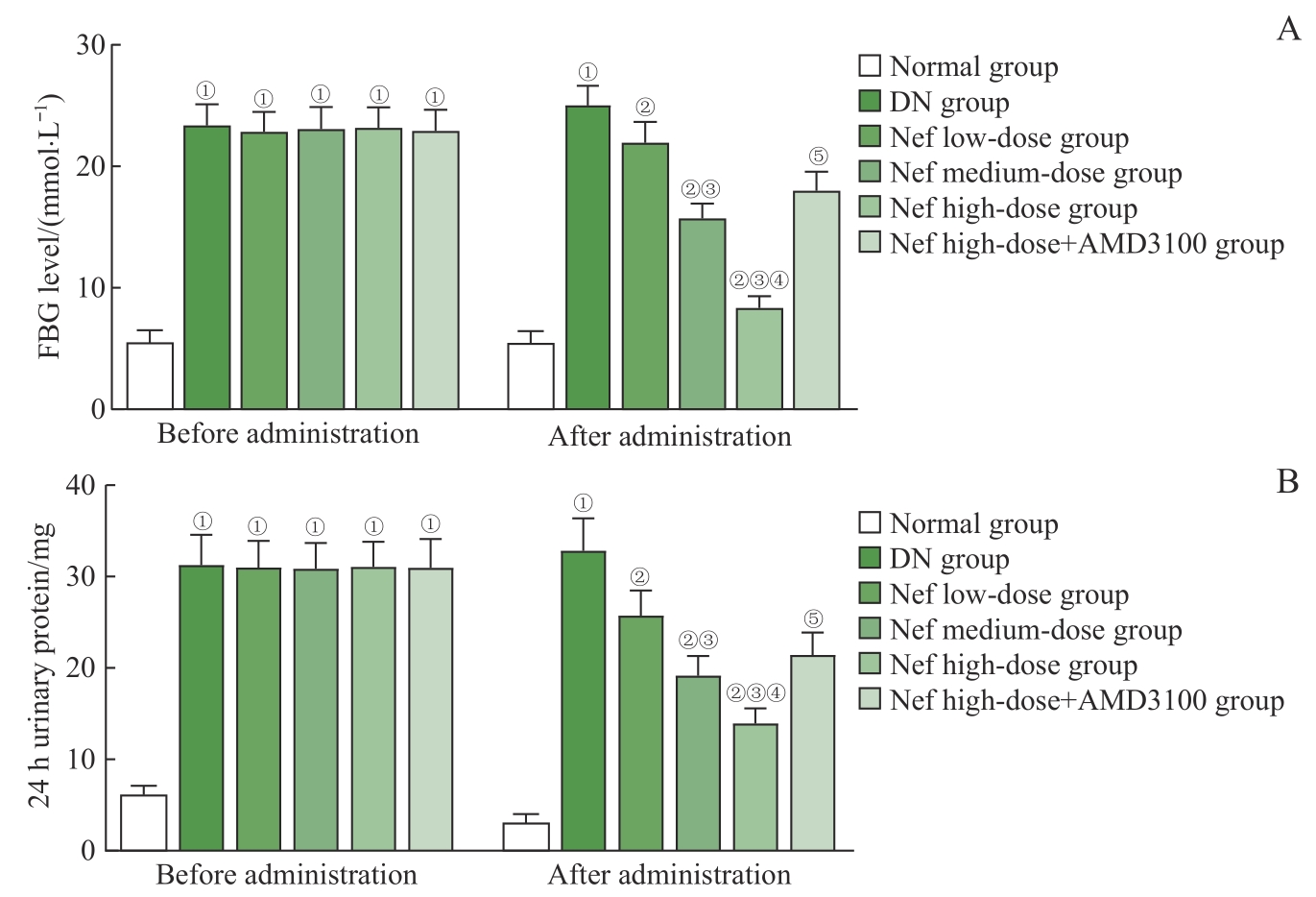
图1 各组大鼠FBG、24 h尿蛋白水平比较Note: A. FBG level. B. 24 h urinary protein level. ①P=0.000, compared with the normal group; ②P=0.000, compared with the DN group; ③P=0.000, compared with the Nef low-dose group; ④P=0.000, compared with the Nef medium-dose group; ⑤P=0.000, compared with the Nef high-dose group.
Fig 1 Comparison of the FBG and 24 h urinary protein levels of rats in each group
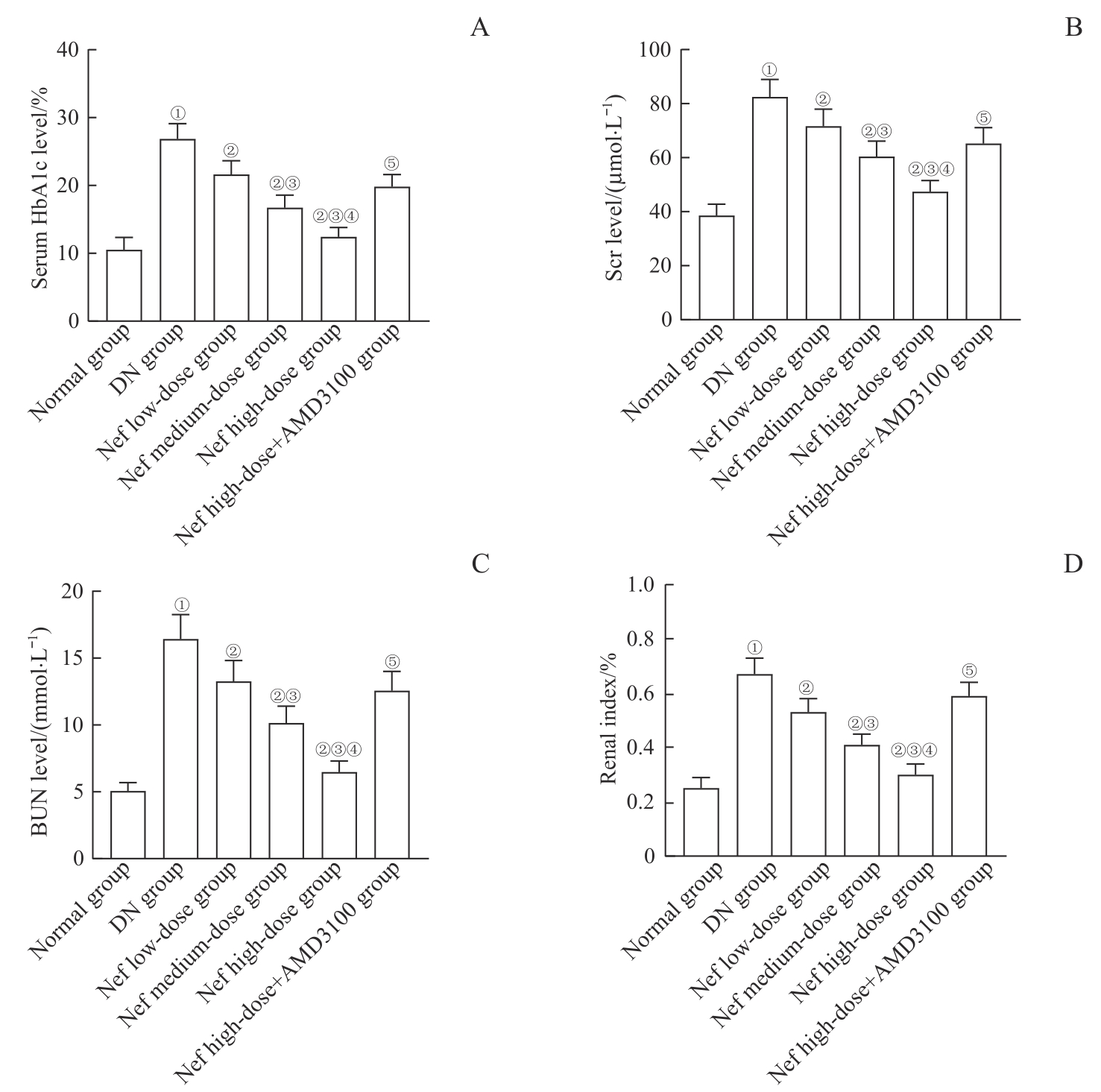
图2 各组大鼠血清HbA1c、Scr、BUN水平及肾指数比较Note: A. Serum HbA1c levels. B. Scr levels. C. BUN levels. D. Renal index. ①P=0.000, compared with the normal group; ②P=0.000, compared with the DN group; ③P=0.000, compared with the Nef low-dose group; ④P=0.000, compared with the Nef medium-dose group; ⑤P=0.000, compared with the Nef high-dose group.
Fig 2 Comparison of the serum HbA1c, Scr, BUN levels and renal index of rats in each group

图3 各组大鼠肾组织的病理形态观察 (H-E staining, ×200)Note: Blue arrows indicate glomerular hypertrophy; yellow arrows indicate vacuolar degeneration of renal tubular epithelial cells.
Fig 3 Observation of the pathological morphology of the renal tissues of rats in each group (H-E staining, ×200)
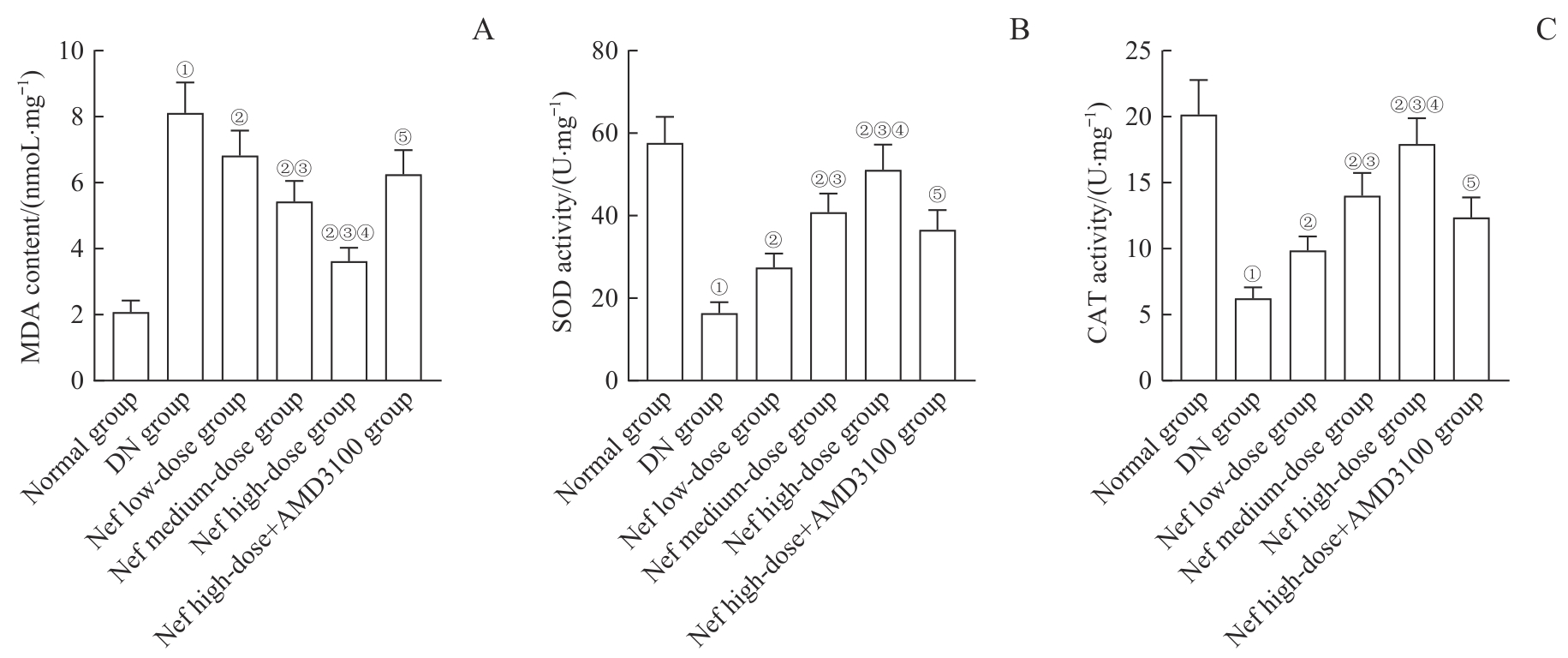
图5 各组大鼠肾组织中MDA含量及SOD、CAT活性比较Note: A. MDA content. B. SOD activity. C. CAT activity. ①P=0.000, compared with the normal group; ②P=0.000, compared with the DN group; ③P=0.000, compared with the Nef low-dose group; ④P=0.000, compared with the Nef medium-dose group; ⑤P=0.000, compared with the Nef high-dose group.
Fig 5 Comparison of MDA content and SOD, CAT activity in renal tissues of rats in each group
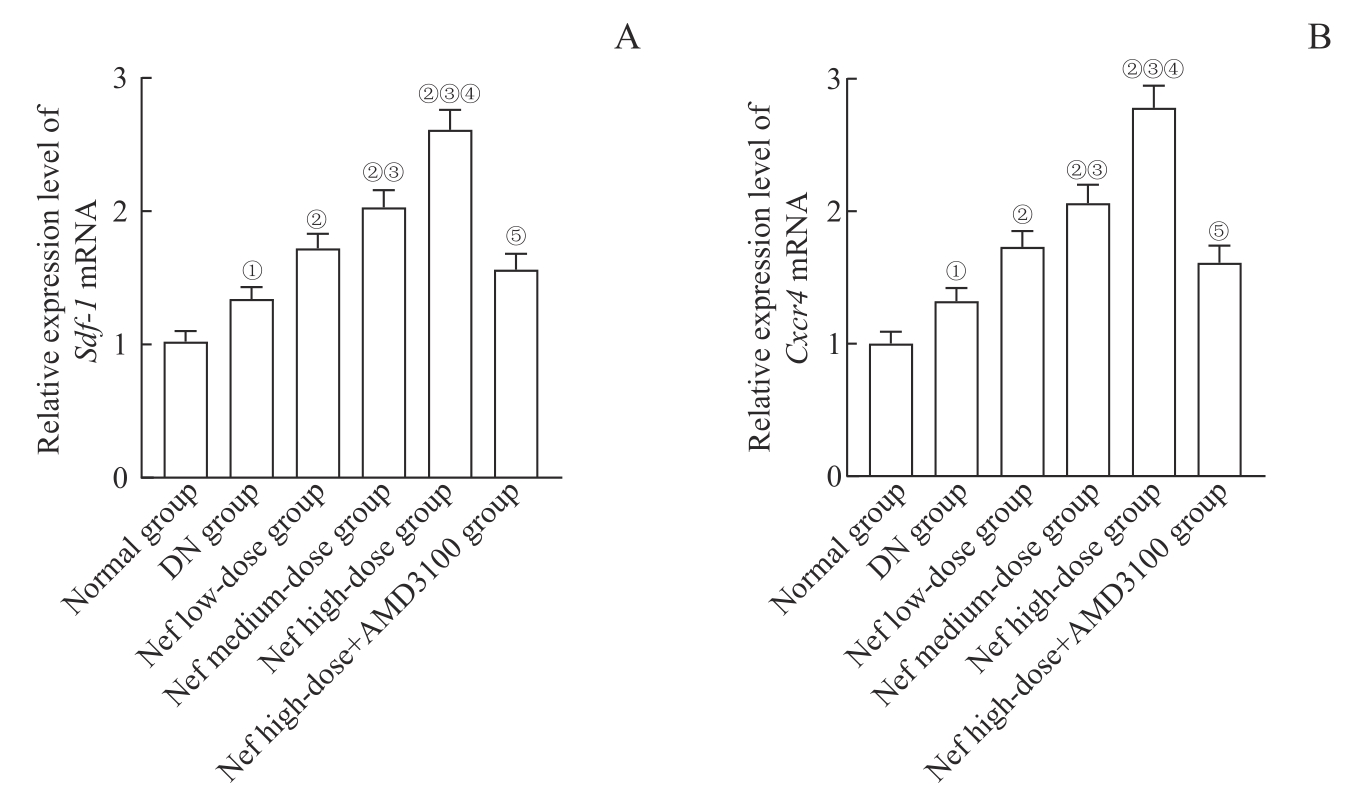
图6 各组大鼠肾组织中 Sdf-1 、 Cxcr4 mRNA表达比较Note: A. Relative expression of Sdf-1 mRNA. B. Relative expression of Cxcr4 mRNA. ①P=0.000, compared with the normal group; ②P=0.000, compared with the DN group; ③P=0.000, compared with the Nef low-dose group; ④P=0.000, compared with the Nef medium-dose group; ⑤P=0.000, compared with the Nef high-dose group.
Fig 6 Comparison of Sdf-1 and Cxcr4 mRNA expression in renal tissues of rats in each group
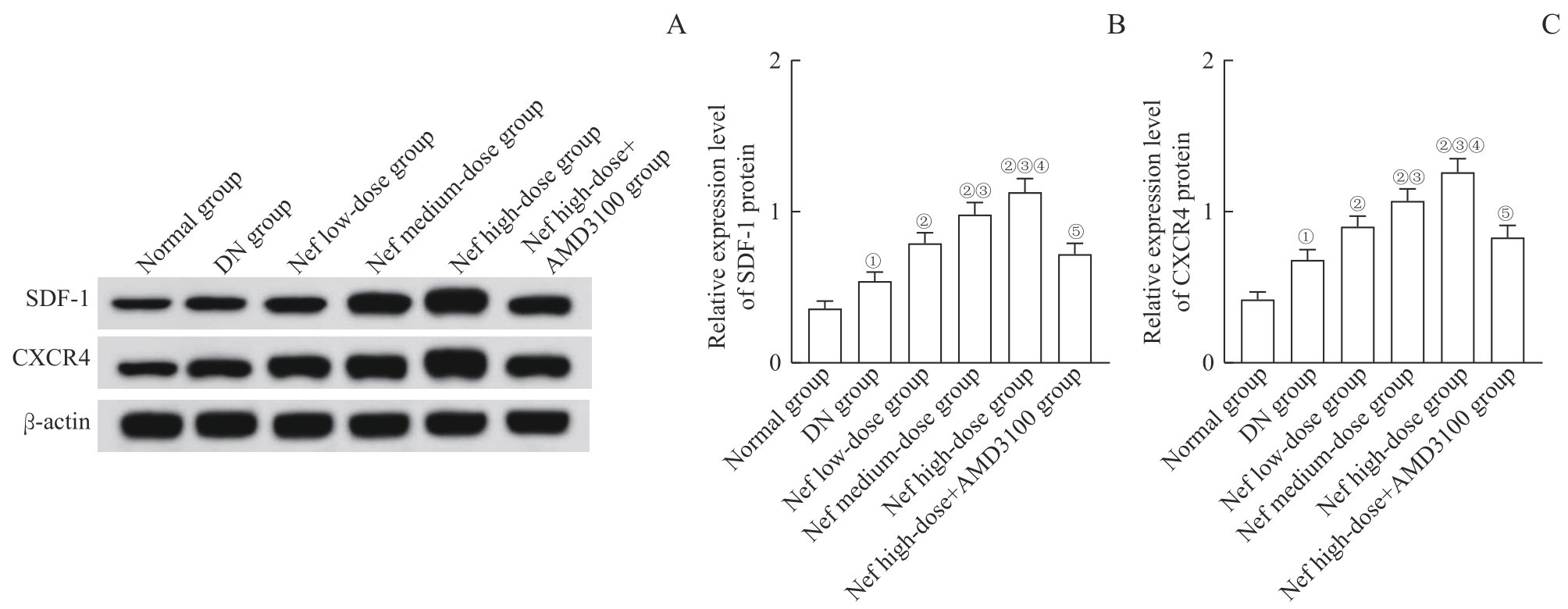
图7 各组大鼠肾组织中SDF-1、CXCR4蛋白表达Note: A. Western blotting analysis of SDF-1 and CXCR4 protein expression. B/C. Statistical analysis of relative expression of SDF-1 protein (B) and CXCR4 protein (C). ①P=0.000, compared with the normal group; ②P=0.000, compared with the DN group; ③P=0.000, compared with the Nef low-dose group; ④P=0.000, compared with the Nef medium-dose group; ⑤P=0.000, compared with the Nef high-dose group.
Fig 7 SDF-1 and CXCR4 protein expression in renal tissues of rats in each group

图8 各组NRK-52E细胞中MDA含量及SOD、CAT活性比较Note: A. MDA content. B. SOD activity. C. CAT activity. ①P=0.000, compared with the control group; ②P=0.000, compared with the HG group; ③P=0.000, compared with the HG+Nef-L group; ④P=0.000, compared with the HG+Nef-M group; ⑤P=0.000, compared with the HG+Nef-H group.
Fig 8 Comparison of MDA content and SOD, CAT activity in NRK-52E cells of each group

图9 各组NRK-52E细胞中 Sdf-1 、 Cxcr4 mRNA表达比较Note: A. Relative expression of Sdf-1 mRNA. B. Relative expression of Cxcr4 mRNA. ①P=0.000, compared with the control group; ②P=0.000, compared with the HG group; ③P=0.000, compared with the HG+Nef-L group; ④P=0.000, compared with the HG+Nef-M group; ⑤P=0.000, compared with the HG+Nef-H group.
Fig 9 Comparison of Sdf-1 and Cxcr4 mRNA expression in NRK-52E cells of each group
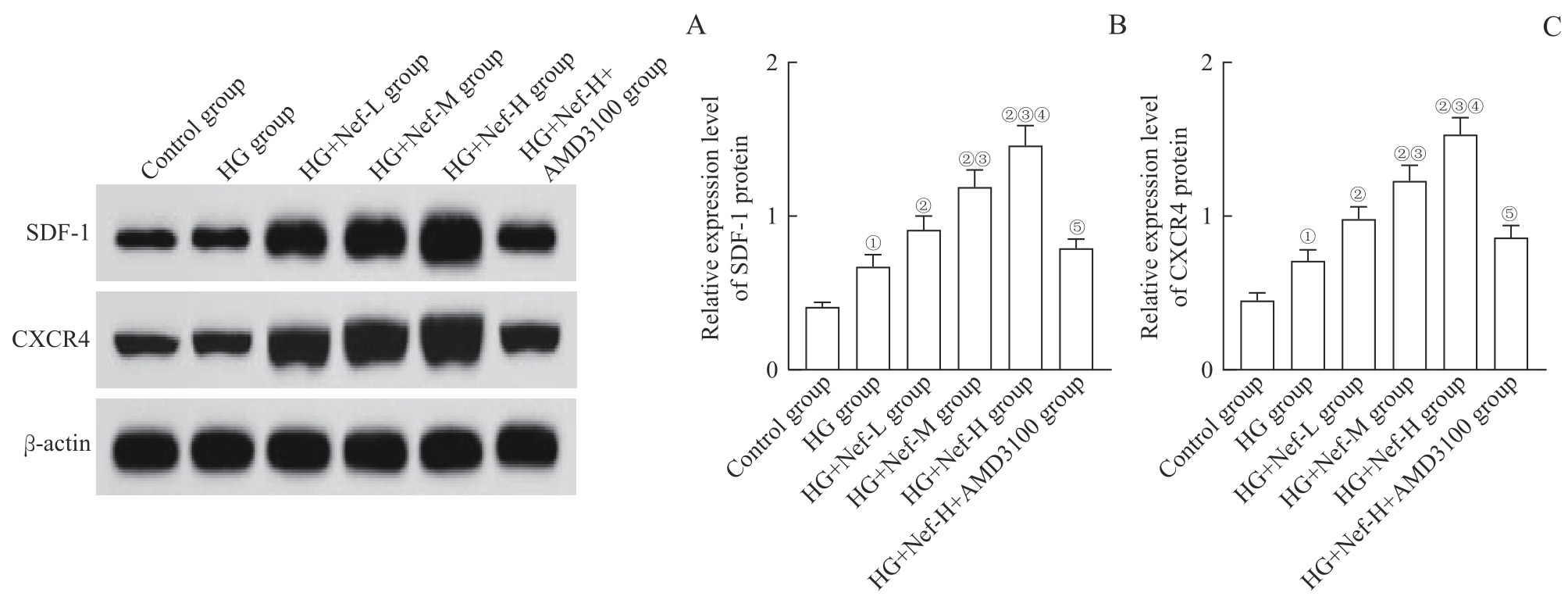
图10 各组NRK-52E细胞中SDF-1、CXCR4蛋白表达Note: A. Western blotting analysis of SDF-1 and CXCR4 protein expression. B/C. Statistical analysis of relative expression of SDF-1 protein (B) and CXCR4 protein (C). ①P=0.000, compared with the control group; ②P=0.000, compared with the HG group; ③P=0.000, compared with the HG+Nef-L group; ④P=0.000, compared with the HG+Nef-M group; ⑤P=0.000, compared with the HG+Nef-H group.
Fig 10 SDF-1 and CXCR4 protein expression in NRK-52E cells of each group
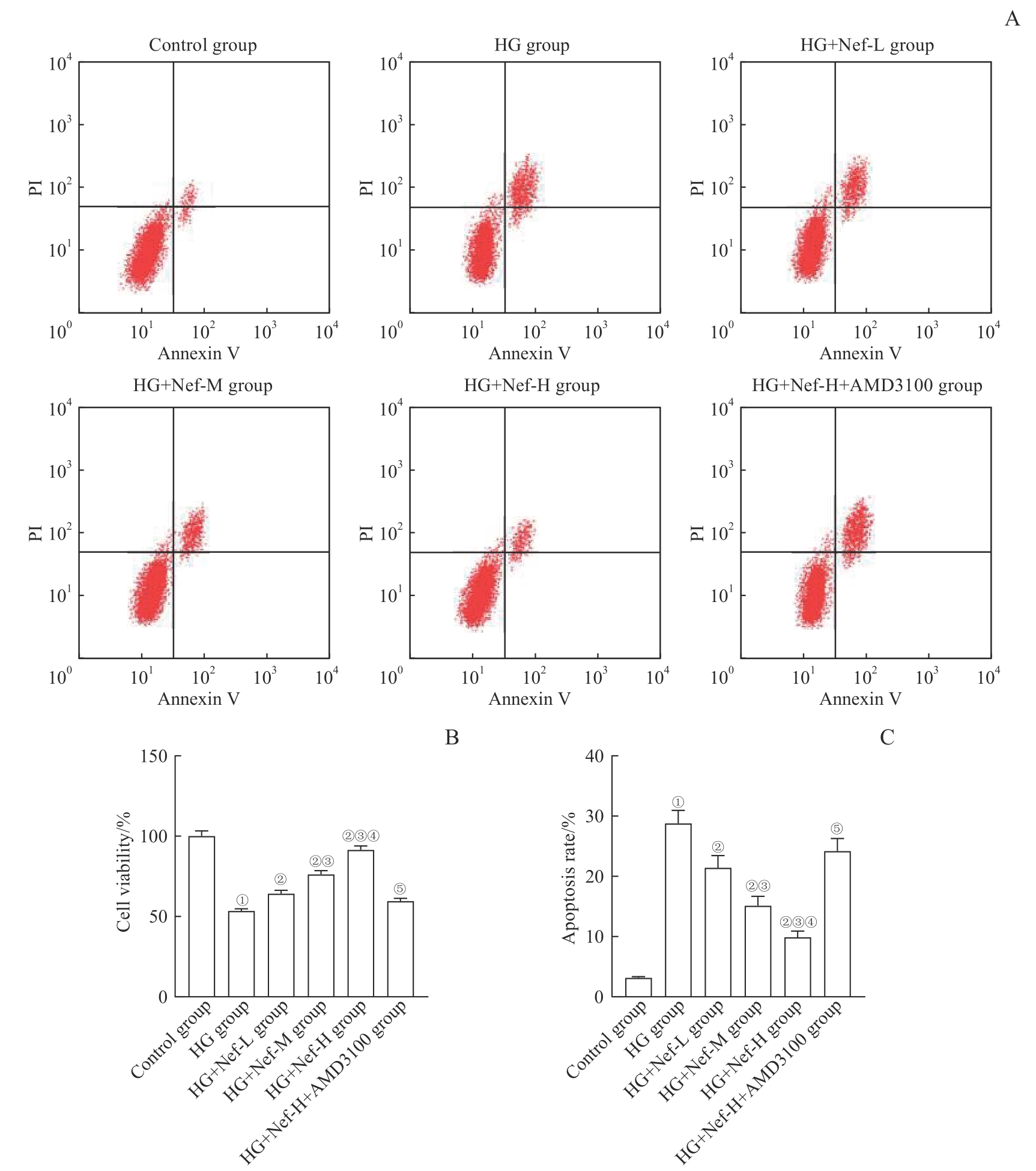
图11 各组NRK-52E细胞的活力及凋亡率比较Note: A. Detection of cell apoptosis by flow cytometry. B. Statistical analysis of cell viability. C. Statistical analysis of cell apoptosis rate. ①P=0.000, compared with the control group; ②P=0.000, compared with the HG group; ③P=0.000, compared with the HG+Nef-L group; ④P=0.000, compared with the HG+Nef-M group; ⑤P=0.000, compared with the HG+Nef-H group.
Fig 11 Comparison of NRK-52E cell activity and apoptosis rate in each group
| 1 | SAGOO M K, GNUDI L. Diabetic nephropathy: an overview[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2020, 2067: 3-7. |
| 2 | SAMSU N. Diabetic nephropathy: challenges in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2021, 2021: 1497449. |
| 3 | SHI Y, RIESE D J 2nd, SHEN J Z. The role of the CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 chemokine axis in cancer[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11: 574667. |
| 4 | SONG A N, JIANG A N, XIONG W, et al. The role of CXCL12 in kidney diseases: a friend or foe?[J]. Kidney Dis (Basel), 2021, 7(3): 176-185. |
| 5 | ZHANG Q Z, HE L, DONG Y, et al. Sitagliptin ameliorates renal tubular injury in diabetic kidney disease via STAT3-dependent mitochondrial homeostasis through SDF-1α/CXCR4 pathway[J]. FASEB J, 2020, 34(6): 7500-7519. |
| 6 | ZHANG T T, JIANG J G. Active ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of diabetes and diabetic complications[J]. Expert Opin Investig Drugs, 2012, 21(11): 1625-1642. |
| 7 | BHARATHI PRIYA L, HUANG C Y, HU R M, et al. An updated review on pharmacological properties of neferine: a bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid from Nelumbo nucifera[J]. J Food Biochem, 2021, 45(12): e13986. |
| 8 | CEVIK M, GOBEKA H H, AYDEMIR O. Effects of neferine on retinal tissue in experimental diabetic rat model[J]. Int Ophthalmol, 2023, 43(1): 249-260. |
| 9 | LI J, CHOU H Y, LI L, et al. Wound healing activity of neferine in experimental diabetic rats through the inhibition of inflammatory cytokines and Nrf-2 pathway[J]. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol, 2020, 48(1): 96-106. |
| 10 | 李莉, 李松, 曹萌, 等. MiR-146a-5p对高脂饮食/链脲佐菌素诱导的糖尿病肾病大鼠肾组织的保护作用[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2021, 44(2): 108-113. |
| LI L, LI S, CAO M, et al. Protective effect of miR-146a-5p on renal tissue in high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Anatomy, 2021, 44(2): 108-113. | |
| 11 | SINGH L, RANA S, MEHAN S. Role of adenylyl cyclase activator in controlling experimental diabetic nephropathy in rats[J]. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol, 2018, 10(5): 144-153. |
| 12 | 张培培, 夏虹, 鲁科达, 等. 加味黄风汤对糖尿病肾病模型大鼠肾组织8-OHdG表达的影响[J]. 浙江中西医结合杂志, 2020, 30(8): 618-622, 696. |
| ZHANG P P, XIA H, LU K D, et al. Effect of modified Huangfeng decoction on the expression of 8-OHdG in renal tissue of diabetic nephropathy rats[J]. Zhejiang Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, 2020, 30(8): 618-622, 696. | |
| 13 | WANG Y Y, WANG S Z, WANG R, et al. Neferine exerts antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis by inhibiting the MAPK and NF-κB/IκBα pathways[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2021, 2021: 4136019. |
| 14 | 叶泽华, 夏煜琦, 李柏均, 等. CXCR4在草酸钙晶体致肾损伤及纤维化中的作用和机制[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2022, 43(4): 285-290. |
| YE Z H, XIA Y Q, LI B J, et al. The role and mechanism of CXCR4 in renal injury and fibrosis caused by calcium oxalate crystals[J]. Chinese Journal of Urology, 2022, 43(4): 285-290. | |
| 15 | TAN H T, CHEN J X, LI Y C, et al. Glabridin, a bioactive component of licorice, ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by regulating ferroptosis and the VEGF/Akt/ERK pathways[J]. Mol Med, 2022, 28(1): 58. |
| 16 | BHARATHI PRIYA L, BASKARAN R, HUANG C Y, et al. Neferine modulates IGF-1R/Nrf2 signaling in doxorubicin treated H9c2 cardiomyoblasts[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2018, 119(2): 1441-1452. |
| 17 | 李建坤, 苏红宁. CXCR4对PDGF-BB诱导的血管平滑肌细胞增殖、迁移的影响及白藜芦醇的抑制作用[J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2019, 30(7): 766-770. |
| LI J K, SU H N. The role of CXCR4 in proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells and the inhibition of resveratrol[J]. Traditional Chinese Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacology, 2019, 30(7): 766-770. | |
| 18 | SELBY N M, TAAL M W. An updated overview of diabetic nephropathy: diagnosis, prognosis, treatment goals and latest guidelines[J]. Diabetes Obes Metab, 2020, 22(Suppl 1): 3-15. |
| 19 | LI S J, ZHANG Y Y, ZHANG J, et al. Neferine exerts ferroptosis-inducing effect and antitumor effect on thyroid cancer through Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1 inhibition[J]. J Oncol, 2022, 2022: 7933775. |
| 20 | LIN T Y, HUNG C Y, CHIU K M, et al. Neferine, an alkaloid from lotus seed embryos, exerts antiseizure and neuroprotective effects in a kainic acid-induced seizure model in rats[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(8): 4130. |
| 21 | YOUSIF HUSSIN ALIMAM H, ABDELATEIF HUSSEIN W, IBRAHIM S, et al. Blood glucose, HbA1c level, and its correlation with VEGF-A (+405G/C) polymorphism as biomarker predicts the risk of retinopathy and nephropathy in type 2 diabetic patients[J]. Rep Biochem Mol Biol, 2022, 11(3): 421-429. |
| 22 | 李燕菲. 糖尿病患者HbA1c、β2-MG、α1-MG、尿微量白蛋白/肌酐变化及与早期肾功能损害的关系分析[J]. 医学理论与实践, 2023, 36(2): 293-295. |
| LI Y F. Changes of HbA1c, β2-MG, α1-MG, urinary microalbumin/creatinine and their relationship with early renal function impairment in patients with diabetes mellitus[J]. The Journal of Medical Theory and Practice, 2023, 36(2): 293-295. | |
| 23 | 司珩, 李梦檀. HbAlc、CK及FBG联合检测在糖尿病微血管病变诊断中的应用[J]. 医药论坛杂志, 2021, 42(2): 138-140, 145. |
| SI H, LI M T. Application of HbAlc, CK and FBG combined detection in the diagnosis of diabetic microangionopathy[J]. Journal of Medical Forum, 2021, 42(2): 138-140, 145. | |
| 24 | LI H H, CHEN W H, CHEN Y S, et al. Neferine attenuates acute kidney injury by inhibiting NF-κB signaling and upregulating klotho expression[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2019, 10: 1197. |
| 25 | HERNANDEZ L F, EGUCHI N, WHALEY D, et al. Anti-oxidative therapy in diabetic nephropathy[J]. Front Biosci (Schol Ed), 2022, 14(2): 14. |
| 26 | MA X J, MA J R, LENG T, et al. Advances in oxidative stress in pathogenesis of diabetic kidney disease and efficacy of TCM intervention[J]. Ren Fail, 2023, 45(1): 2146512. |
| 27 | TANG Y S, ZHAO Y H, ZHONG Y, et al. Neferine inhibits LPS-ATP-induced endothelial cell pyroptosis via regulation of ROS/NLRP3/caspase-1 signaling pathway[J]. Inflamm Res, 2019, 68(9): 727-738. |
| 28 | ZHANG X, LIAO Y, YE T. Correlations of SDF-1 and CXCR4 levels with caspase-3 expression in the retina of rats after optic nerve injury[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2020, 13(8): 2058-2064. |
| 29 | SIDDIQI F S, CHEN L H, ADVANI S L, et al. CXCR4 promotes renal tubular cell survival in male diabetic rats: implications for ligand inactivation in the human kidney[J]. Endocrinology, 2015, 156(3): 1121-1132. |
| 30 | TAKASHIMA S, FUJITA H, FUJISHIMA H, et al. Stromal cell-derived factor-1 is upregulated by dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition and has protective roles in progressive diabetic nephropathy[J]. Kidney Int, 2016, 90(4): 783-796. |
| 31 | TANG W M, PANJA S, JOGDEO C M, et al. Study of renal accumulation of targeted polycations in acute kidney injury[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2022, 23(5): 2064-2074. |
| 32 | CHEN L H, ADVANI S L, THAI K, et al. SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling preserves microvascular integrity and renal function in chronic kidney disease[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(3): e92227. |
| 33 | YANG J, ZHU F M, WANG X H, et al. Continuous AMD3100 treatment worsens renal fibrosis through regulation of bone marrow derived pro-angiogenic cells homing and T-cell-related inflammation[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(2): e0149926. |
| 34 | 魏萍, 薛春苗, 潘霖, 等. 甲基莲心碱对胰岛素抵抗的HepG2细胞降糖的影响[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2020, 19(12): 1283-1286. |
| WEI P, XUE C M, PAN L, et al. Effects of neferine on hypoglycemia of insulin-resistant HepG2 cells[J]. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, 2020, 19(12): 1283-1286. |
| [1] | 万宏劲, 胡逸斌, 王昕, 张凯, 秦安, 马培翔, 马辉, 赵杰. 甲基莲心碱通过KEAP1/NRF2/GPX4和NF-κB信号通路减轻椎间盘退行性变[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(3): 261-270. |
| [2] | 王博恩, 陈思远, 施晴, 张慕晨, 易红梅, 董磊, 王黎, 程澍, 许彭鹏, 赵维莅. 肾脏累及的弥漫性大B细胞淋巴瘤患者临床病理特征[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(9): 1162-1168. |
| [3] | 魏云鑫, 蒋绪顺, 蔡梦瑶, 温睿智, 杜晓刚. COMP与糖尿病肾病自噬相关性分析及其功能验证[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(7): 847-858. |
| [4] | 李玉, 张羽. 慢性肾脏病患者不良妊娠结局的危险因素分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(5): 560-566. |
| [5] | 贾君杰, 邢海帆, 张群子, 刘奇烨, 汪年松, 范瑛. 缺氧诱导因子-1α抑 制剂YC-1改善糖尿病肾病小鼠肾脏损伤的机制研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(9): 1089-1098. |
| [6] | 吴佳晋, 钟晨, 李大伟, 陈若洋, 瞿俊文, 张明. 甲基转移酶3调控pri-miR-21甲基化修饰在糖尿病肾病肾脏纤维化中的作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(1): 1-7. |
| [7] | 谢林, 程烨, 郑琦敏, 张熙, 付莉莉, 陈敏, 王怡, 梅长林, 谢静远, 顾向晨. 淫羊藿苷对急性肾损伤向慢性肾脏病转化小鼠模型的预防性保护作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(1): 8-19. |
| [8] | 赖秀秀, 朱青燕, 谈佳奇, 杨令, 朱琰, 周公民. 小剂量非布司他改善无症状高尿酸血症高龄患者肾功能的临床研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(7): 885-892. |
| [9] | 王亚琨, 许佳瑞, 吴茜茜, 张晓华, 朱迎春, 白寿军. 医养结合综合干预对上海郊区老年慢性肾脏病患者生活质量和精神状态的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(7): 904-910. |
| [10] | 魏珊, 纪鸥洋, 陈志豪, 黄泽慧, 李璞, 方均燕, 刘英莉. 慢性肾脏病患者安全用药知信行量表的编制及信度、效度分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(12): 1729-1738. |
| [11] | 邢海帆, 范瑛. 单细胞RNA测序应用于肾小球疾病研究的进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(10): 1458-1465. |
| [12] | 张佳思, 邹春波, 卢宇, 陈茜, 张伟亚, 何姣姣. 血脂蛋白磷脂酶A2和中性粒细胞明胶酶相关脂质运载蛋白在诊断早期糖尿病肾病中的价值[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(6): 770-775. |
| [13] | 周丝丝, 巩格言, 马佳莉, 高雯颖, 张莹. 慢性肾脏病患儿-家长过渡期准备与双方生活质量的互依关系分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(12): 1588-1595. |
| [14] | 姜梦迪, 张文. 糖尿病肾病中的组蛋白修饰与靶向干预的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(1): 103-107. |
| [15] | 陈胜男,申 燕. 不对称二甲基精氨酸在慢性肾脏病患者动脉粥样硬化发生和发展中的作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(8): 1131-1136. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||