
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (9): 1205-1212.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2024.09.016
• 论坛 • 上一篇
陈丽红1( ), 王妍1, 周翔天1, 郑俊克2, 闫小响1(
), 王妍1, 周翔天1, 郑俊克2, 闫小响1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-07-25
接受日期:2024-08-06
出版日期:2024-09-28
发布日期:2024-09-28
通讯作者:
闫小响,电子信箱:cardexyanxx@hotmail.com。作者简介:陈丽红(1981—),女,副研究员,博士;电子信箱:chenlihong@shsmu.edu.cn。
CHEN Lihong1( ), WANG Yan1, ZHOU Xiangtian1, ZHENG Junke2, YAN Xiaoxiang1(
), WANG Yan1, ZHOU Xiangtian1, ZHENG Junke2, YAN Xiaoxiang1( )
)
Received:2024-07-25
Accepted:2024-08-06
Online:2024-09-28
Published:2024-09-28
Contact:
YAN Xiaoxiang, E-mail: cardexyanxx@hotmail.com.摘要:
目的·基于医学领域国家自然科学基金青年科学基金项目资助率低的现状,对项目申请人展开深入调查,定量分析项目立项的影响因素,为进一步提升项目申报质量、加强青年医学人才培养提供数据参考和决策依据。方法·采用横断面调查法,选取上海交通大学医学院各二级学院及13所附属医院在2020—2022年有国家自然科学基金青年科学基金项目申报经历的申请人进行问卷调查,以项目申请结果为因变量,以申请人基本情况和申报情况等为自变量,通过Logistic逐步回归模型建模与分析。结果·对921名项目申请者的分析结果显示,学历(OR=1.86,95%CI 1.14~3.04)、毕业院校(OR=2.45,95%CI 1.47~4.08)、有较为充分的前期工作基础(OR=4.22,95%CI 2.44~7.29)、代表作平均影响因子(OR=1.10,95%CI 1.04~1.17)、申请书自评总分(OR=1.06,95%CI 1.04~1.08)是项目立项的主要影响因素。且项目获批者代表作平均影响因子和最高影响因子呈逐年递增的趋势。此外,青年医师和专职科研人员项目获批的影响因素不同,青年医师的毕业时间越长,获批率越低。结论·青年科学基金项目资助率低下,对科研成果的要求逐年提升,应注重前期积累,提高申请书撰写质量,并进一步采取措施,加强青年医学人才早期培养,完善分类培养举措,着力夯实研究基础。
中图分类号:
陈丽红, 王妍, 周翔天, 郑俊克, 闫小响. 国家自然科学基金青年科学基金项目立项的影响因素分析——以上海交通大学医学院为例[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(9): 1205-1212.
CHEN Lihong, WANG Yan, ZHOU Xiangtian, ZHENG Junke, YAN Xiaoxiang. Influencing factors of the approval of the Young Scientists Fund of National Natural Science Foundation of China: a case study of Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(9): 1205-1212.
| Variable | Approved group (n=582) | Unapproved group (n=339) | χ2/Z value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender/n(%) | 2.69 | 0.101 | ||
| Male | 213 (36.60) | 106 (31.27) | ||
| Female | 369 (63.40) | 233 (68.73) | ||
| Age/year | 31.00 (29.00, 33.00) | 32.00 (30.00, 34.00) | 170 944 | 0.000 |
| Educational background/n(%) | 125.09 | 0.000 | ||
| Bachelor | 0 (0) | 4 (1.18) | ||
| Master | 65 (11.17) | 142 (41.89) | ||
| Doctor | 517 (88.83) | 193 (56.93) | ||
| Graduate university/n(%) | 20.50 | 0.000 | ||
| 985 project university | 470 (80.76) | 237 (69.91) | ||
| Non-985 project university | 76 (13.06) | 84 (24.78) | ||
| Overseas university | 36 (6.19) | 18 (5.31) | ||
| Years of graduation/year | 1.00 (0, 3.00) | 2.00 (1.00, 6.00) | 182 530 | 0.000 |
| Postdoctoral experience/n(%) | 178 (30.58) | 50 (14.75) | 28.84 | 0.000 |
| Institution/n(%) | 2.22 | 0.136 | ||
| Affiliated hospital | 534 (91.75) | 320 (94.40) | ||
| College | 48 (8.25) | 19 (5.60) | ||
| Title of a professional post/n(%) | 12.74 | 0.002 | ||
| Junior and below | 381 (65.46) | 183 (53.98) | ||
| Intermediate | 180 (30.93) | 144 (42.48) | ||
| Senior | 21 (3.61) | 12 (3.54) | ||
| Job category/n(%) | 35.13 | 0.000 | ||
| Doctor | 361 (62.03) | 209 (61.65) | ||
| Full-time scientific researcher | 172 (29.55) | 61 (17.99) | ||
| Others | 49 (8.42) | 69 (20.35) | ||
| Number of applications/n(%) | 29.29 | 0.000 | ||
| 1 time | 319 (54.81) | 138 (40.83) | ||
| 2 times | 123 (21.13) | 116 (34.32) | ||
| 3 times | 98 (16.84) | 52 (15.38) | ||
| 4 or more times | 42 (7.22) | 33 (9.73) | ||
| Application department/n(%) | 4.12 | 0.127 | ||
| Department of Health Sciences | 504 (86.60) | 296 (87.32) | ||
| Department of Life Sciences | 44 (7.56) | 16 (4.72) | ||
| Other departments | 34 (5.84) | 27 (7.96) | ||
| Attributes of scientific questions/n(%) | 1.87 | 0.599 | ||
| Exploration and highlight originality | 63 (10.82) | 37 (10.91) | ||
| Cutting-edge area with the development of new methodology | 315 (54.12) | 171 (50.44) | ||
| Demand-driven bottleneck | 174 (29.90) | 116 (34.22) | ||
| Universal orientation and transdisciplinary convergence | 30 (5.15) | 15 (4.42) | ||
| Consistency of the application with the doctoral research/n(%) | 430 (73.88) | 143 (42.18) | 72.75 | 0.000 |
| Consistency between the application and supporting laboratory/n(%) | 521 (89.52) | 244 (71.98) | 42.68 | 0.000 |
| Medical-engineering science cross research/n(%) | 79 (13.57) | 42 (12.39) | 0.21 | 0.646 |
| Having participated in national projects such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China/n(%) | 485 (83.33) | 216 (63.72) | 43.95 | 0.000 |
| Other approved scientific research or talent projects before applying for Young Scientists Fund/n(%) | 289 (49.66) | 136 (40.12) | 6.99 | 0.008 |
| Previous experience in writing National Natural Science Foundation of China/n(%) | 326 (56.01) | 178 (52.51) | 0.65 | 0.421 |
| Sufficient foundation of previous work/n(%) | 551 (94.67) | 204 (60.18) | 168.27 | 0.000 |
| Number of representative papers | 2.00 (1.00, 3.00) | 2.00 (1.00, 3.00) | 142 365 | 0.000 |
| Average impact factor of representative papers | 6.15 (4.28, 9.53) | 3.88 (2.06, 5.90) | 89 105 | 0.000 |
| Highest impact factor of representative papers | 10.20 (6.60, 15.90) | 6.00 (4.00, 10.20) | 108 042 | 0.000 |
| Total self-evaluated score of the application/score | 86.00 (81.00, 90.00) | 75.00 (65.00, 81.00) | 82 262 | 0.000 |
表1 各项指标与青年科学基金项目是否立项的单因素分析(n=921)
Tab 1 Single factor analysis of the approval of the Young Scientists Fund (n=921)
| Variable | Approved group (n=582) | Unapproved group (n=339) | χ2/Z value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender/n(%) | 2.69 | 0.101 | ||
| Male | 213 (36.60) | 106 (31.27) | ||
| Female | 369 (63.40) | 233 (68.73) | ||
| Age/year | 31.00 (29.00, 33.00) | 32.00 (30.00, 34.00) | 170 944 | 0.000 |
| Educational background/n(%) | 125.09 | 0.000 | ||
| Bachelor | 0 (0) | 4 (1.18) | ||
| Master | 65 (11.17) | 142 (41.89) | ||
| Doctor | 517 (88.83) | 193 (56.93) | ||
| Graduate university/n(%) | 20.50 | 0.000 | ||
| 985 project university | 470 (80.76) | 237 (69.91) | ||
| Non-985 project university | 76 (13.06) | 84 (24.78) | ||
| Overseas university | 36 (6.19) | 18 (5.31) | ||
| Years of graduation/year | 1.00 (0, 3.00) | 2.00 (1.00, 6.00) | 182 530 | 0.000 |
| Postdoctoral experience/n(%) | 178 (30.58) | 50 (14.75) | 28.84 | 0.000 |
| Institution/n(%) | 2.22 | 0.136 | ||
| Affiliated hospital | 534 (91.75) | 320 (94.40) | ||
| College | 48 (8.25) | 19 (5.60) | ||
| Title of a professional post/n(%) | 12.74 | 0.002 | ||
| Junior and below | 381 (65.46) | 183 (53.98) | ||
| Intermediate | 180 (30.93) | 144 (42.48) | ||
| Senior | 21 (3.61) | 12 (3.54) | ||
| Job category/n(%) | 35.13 | 0.000 | ||
| Doctor | 361 (62.03) | 209 (61.65) | ||
| Full-time scientific researcher | 172 (29.55) | 61 (17.99) | ||
| Others | 49 (8.42) | 69 (20.35) | ||
| Number of applications/n(%) | 29.29 | 0.000 | ||
| 1 time | 319 (54.81) | 138 (40.83) | ||
| 2 times | 123 (21.13) | 116 (34.32) | ||
| 3 times | 98 (16.84) | 52 (15.38) | ||
| 4 or more times | 42 (7.22) | 33 (9.73) | ||
| Application department/n(%) | 4.12 | 0.127 | ||
| Department of Health Sciences | 504 (86.60) | 296 (87.32) | ||
| Department of Life Sciences | 44 (7.56) | 16 (4.72) | ||
| Other departments | 34 (5.84) | 27 (7.96) | ||
| Attributes of scientific questions/n(%) | 1.87 | 0.599 | ||
| Exploration and highlight originality | 63 (10.82) | 37 (10.91) | ||
| Cutting-edge area with the development of new methodology | 315 (54.12) | 171 (50.44) | ||
| Demand-driven bottleneck | 174 (29.90) | 116 (34.22) | ||
| Universal orientation and transdisciplinary convergence | 30 (5.15) | 15 (4.42) | ||
| Consistency of the application with the doctoral research/n(%) | 430 (73.88) | 143 (42.18) | 72.75 | 0.000 |
| Consistency between the application and supporting laboratory/n(%) | 521 (89.52) | 244 (71.98) | 42.68 | 0.000 |
| Medical-engineering science cross research/n(%) | 79 (13.57) | 42 (12.39) | 0.21 | 0.646 |
| Having participated in national projects such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China/n(%) | 485 (83.33) | 216 (63.72) | 43.95 | 0.000 |
| Other approved scientific research or talent projects before applying for Young Scientists Fund/n(%) | 289 (49.66) | 136 (40.12) | 6.99 | 0.008 |
| Previous experience in writing National Natural Science Foundation of China/n(%) | 326 (56.01) | 178 (52.51) | 0.65 | 0.421 |
| Sufficient foundation of previous work/n(%) | 551 (94.67) | 204 (60.18) | 168.27 | 0.000 |
| Number of representative papers | 2.00 (1.00, 3.00) | 2.00 (1.00, 3.00) | 142 365 | 0.000 |
| Average impact factor of representative papers | 6.15 (4.28, 9.53) | 3.88 (2.06, 5.90) | 89 105 | 0.000 |
| Highest impact factor of representative papers | 10.20 (6.60, 15.90) | 6.00 (4.00, 10.20) | 108 042 | 0.000 |
| Total self-evaluated score of the application/score | 86.00 (81.00, 90.00) | 75.00 (65.00, 81.00) | 82 262 | 0.000 |
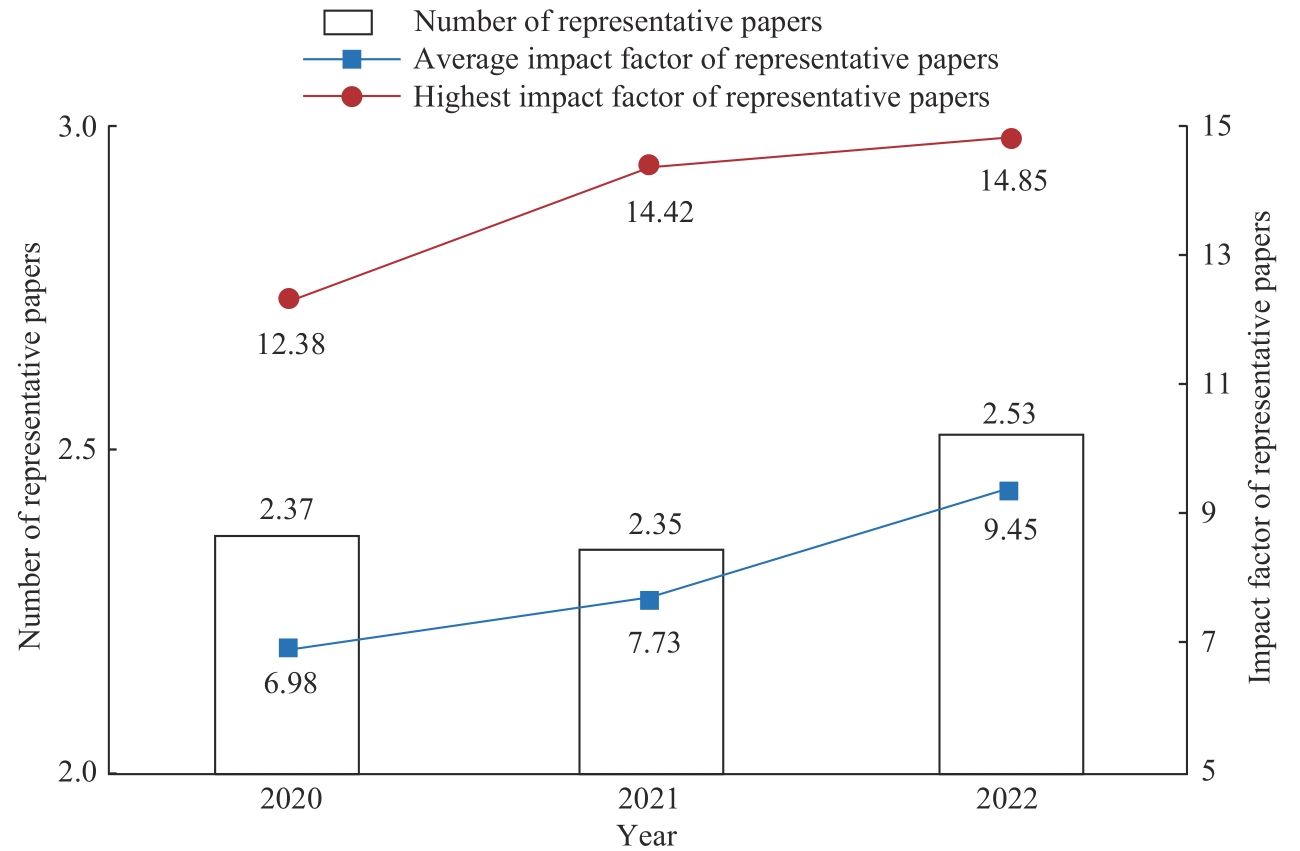
图1 青年科学基金项目获批者代表作的数量和质量变化Note: The number of approved Young Scientists Fund in 2020, 2021 and 2022 were 170, 191 and 221 respectively.
Fig 1 Qualitative and quantitative change of the representative papers by approved Young Scientists Fund
| Variable | Assignment of value |
|---|---|
| Educational background | Bachelor=1, master=2, doctor=3 |
| Graduate university | 985 project university=1, non-985 project university=2, overseas university=3 |
| Postdoctoral experience | Yes=1, No=0 |
| Title of a professional post | Junior and below=1, intermediate=2, senior=3 |
| Job category | Doctor=1, full-time scientific researcher=2, others=3 |
| Number of applications | 1 time=1, 2 times=2, 3 times=3, 4 or more times=4 |
| Consistency of the application with the doctoral research | Yes=1, no=0 |
| Consistency between the application and supporting laboratory | Yes=1, no=0 |
| Medical-engineering science cross research | Yes=1, no=0 |
| Having participated in national projects such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China | Yes=1, no=0 |
| Other approved scientific research or talent projects before applying for Young Scientists Fund | Yes=1, no=0 |
| Sufficient foundation of previous work | Yes=1, no=0 |
表2 Logistic回归模型的分类变量赋值表
Tab 2 Categorical variable assignment for Logistic regression model
| Variable | Assignment of value |
|---|---|
| Educational background | Bachelor=1, master=2, doctor=3 |
| Graduate university | 985 project university=1, non-985 project university=2, overseas university=3 |
| Postdoctoral experience | Yes=1, No=0 |
| Title of a professional post | Junior and below=1, intermediate=2, senior=3 |
| Job category | Doctor=1, full-time scientific researcher=2, others=3 |
| Number of applications | 1 time=1, 2 times=2, 3 times=3, 4 or more times=4 |
| Consistency of the application with the doctoral research | Yes=1, no=0 |
| Consistency between the application and supporting laboratory | Yes=1, no=0 |
| Medical-engineering science cross research | Yes=1, no=0 |
| Having participated in national projects such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China | Yes=1, no=0 |
| Other approved scientific research or talent projects before applying for Young Scientists Fund | Yes=1, no=0 |
| Sufficient foundation of previous work | Yes=1, no=0 |
| Variable | Total number of surveyed applicants (n=921) | Doctor (n=570) | Full-time scientific researcher (n=233) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95%CI) | P value | OR (95%CI) | P value | OR (95%CI) | P value | |||
| Educational background | 1.86 (1.14‒3.04) | 0.014 | ||||||
Graduate university (985 project university vs non-985 project university) | 2.45 (1.47‒4.08) | 0.021 | ||||||
| Years of graduation | 0.89 (0.81‒0.97) | 0.008 | ||||||
| Having participated in national projects such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China | 2.03 (1.11‒3.71) | 0.022 | ||||||
| Sufficient foundation of previous work | 4.22 (2.44‒7.29) | 0.000 | 5.28 (2.56‒10.87) | 0.000 | 3.28 (1.05‒10.22) | 0.041 | ||
| Average impact factor of representative papers | 1.10 (1.04‒1.17) | 0.002 | 1.20 (1.10‒1.31) | 0.000 | 1.04 (1.00‒1.08) | 0.037 | ||
| Total self-evaluated score of the application | 1.06 (1.04‒1.08) | 0.000 | 1.06 (1.03‒1.08) | 0.000 | 1.09 (1.04‒1.14) | 0.000 | ||
表3 青年科学基金项目立项的多因素Logistic回归分析
Tab 3 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of the approved Young Scientists Fund
| Variable | Total number of surveyed applicants (n=921) | Doctor (n=570) | Full-time scientific researcher (n=233) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95%CI) | P value | OR (95%CI) | P value | OR (95%CI) | P value | |||
| Educational background | 1.86 (1.14‒3.04) | 0.014 | ||||||
Graduate university (985 project university vs non-985 project university) | 2.45 (1.47‒4.08) | 0.021 | ||||||
| Years of graduation | 0.89 (0.81‒0.97) | 0.008 | ||||||
| Having participated in national projects such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China | 2.03 (1.11‒3.71) | 0.022 | ||||||
| Sufficient foundation of previous work | 4.22 (2.44‒7.29) | 0.000 | 5.28 (2.56‒10.87) | 0.000 | 3.28 (1.05‒10.22) | 0.041 | ||
| Average impact factor of representative papers | 1.10 (1.04‒1.17) | 0.002 | 1.20 (1.10‒1.31) | 0.000 | 1.04 (1.00‒1.08) | 0.037 | ||
| Total self-evaluated score of the application | 1.06 (1.04‒1.08) | 0.000 | 1.06 (1.03‒1.08) | 0.000 | 1.09 (1.04‒1.14) | 0.000 | ||
| 1 | 中华人民共和国中央人民政府. 中共中央办公厅 国务院办公厅印发《关于进一步加强青年科技人才培养和使用的若干措施》[EB/OL]. [2024-02-05]. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/202308/content_ 6900456.htm. |
| The State Council of the People's Republic of China. The General Office of the Communist Party of China Central Committee and the General Office of the State Council “Several Measures to Further Strengthen the Training and Use of Young Scientific and Technological Talents” [EB/OL]. [2024-02-05]. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/202308/content_6900456.htm. | |
| 2 | 国家自然科学基金委员会.资助格局[EB/OL]. [2024-02-05]. https://www.nsfc.gov.cn/publish/portal0/jgsz/08/. |
| National Natural Science Foundation of China. Funding pattern[EB/OL]. [2024-02-05]. https://www.nsfc.gov.cn/publish/portal0/jgsz/08/. | |
| 3 | 唐靖, 张藜, 王新. 基础研究人才成长的沃土: 对国家自然科学基金人才类项目的历史回顾[J]. 中国科学基金, 2016, 30(5): 395-402. |
| TANG J, ZHANG L, WANG X. Fostering talents for basic research: a historical review of talent programs of NSFC[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2016, 30(5): 395-402. | |
| 4 | 乌云其其格. 加强支持与引导促进青年研究人员成长[J]. 中国科技奖励, 2012(11): 68-70. |
| WU Y Q Q G. Strengthening support and guidance to promote the growth of young researchers[J]. China Awards for Science and Technology, 2012(11): 68-70. | |
| 5 | 于璇, 游超, 黄锐, 等. 关于提升国家自然科学基金青年科学基金项目资助效益的探讨[J]. 中国科学基金, 2020, 34(3): 324-331. |
| YU X, YOU C, HUANG R, et al. Discussion on improvement of funding effectiveness on Young Scientists Fund of the NSFC[J].Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2020, 34(3): 324-331. | |
| 6 | 国家自然科学基金委员会. 年度报告[EB/OL]. [2024-02-05]. https://www.nsfc.gov.cn/publish/portal0/tab535/. |
| National Natural Science Foundation of China. Annual report[EB/OL]. [2024-02-05]. https://www.nsfc.gov.cn/publish/portal0/tab535/. | |
| 7 | 郭美荣, 彭洁, 赵伟, 等. 中国高层次科技人才成长过程及特征分析: 以“国家杰出青年科学基金” 获得者为例[J]. 科技管理研究, 2011, 31(1): 135-138. |
| GUO M R, PENG J, ZHAO W, et al. Analysis on the high-level sci-tech talents′ characteristics and growth experience in China: taking the winners of NSFDYS for example[J]. Science and Technology Management Research, 2011, 31(1): 135-138. | |
| 8 | 刘超, 李东, 鲍锦涛, 等. “优青” 对青年科技人才成长的促进作用及相关管理举措探讨[J]. 中国科学基金, 2018, 32(4): 387-392. |
| LIU C, LI D, BAO J T, et al. Analysis of the role of “Outstanding Young Scientists Foundation” in promoting the growth of young scientists and related administrative initiatives[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2018, 32(4): 387-392. | |
| 9 | 张楠楠, 于璇, 肖瑜, 等. 医学领域优秀青年科学基金项目资助情况及项目负责人成长特征分析[J]. 中国科学基金, 2019, 33(6): 623-627. |
| ZHANG N N, YU X, XIAO Y, et al. Analysis on the situation and characteristics of Excellent Young Scientists Fund in medical science[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2019, 33(6): 623-627. | |
| 10 | 王剑斌, 安维东, 何彦, 等. 青年科研人才成长特征与资助策略优化研究[J]. 中国科学基金, 2023, 37(3): 488-495. |
| WANG J B, AN W D, HE Y, et al. Research on the growth characteristics of Young Scientific Research Talents and the optimization of funding strategy[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2023, 37(3): 488-495. | |
| 11 | EBADI A, SCHIFFAUEROVA A. How to boost scientific production? A statistical analysis of research funding and other influencing factors[J]. Scientometrics, 2016, 106(3): 1093-1116. |
| 12 | BOL T, DE VAAN M, VAN DE RIJT A. The Matthew effect in science funding[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2018, 115(19): 4887-4890. |
| 13 | WANG Y, JONES B F, WANG D S. Early-career setback and future career impact[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 4331. |
| 14 | LI D, AGHA L. Research funding. Big names or big ideas: do peer-review panels select the best science proposals?[J]. Science, 2015, 348(6233): 434-438. |
| 15 | 乌云其其格. 发达国家如何培养卓越研究人才[J]. 中国人才(上半月), 2015(1): 58-59. |
| WU Y Q Q G. How developed countries can cultivate outstanding research talents [J]. Chinese Talents, 2015(1): 58-59. | |
| 16 | 闫小响. 新时代卓越青年医学人才培养的思考[J]. 中国科学基金, 2024, 38(3): 557-558. |
| YAN X X. Thoughts on the cultivation of outstanding young medical talents in the new era[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2024, 38(3): 557-558. | |
| 17 | 王震坤, 陈刚, 王子伟. 某大型医院申请国家自然科学基金医学部项目获批情况定量分析[J]. 中国医院, 2022, 26(8): 58-61. |
| WANG Z K, CHEN G, WANG Z W. Quantitative analysis on influencing factors on project approval of Medical Science Department of National Natural Science Foundation of China in a large general hospital[J]. Chinese Hospitals, 2022, 26(8): 58-61. | |
| 18 | 吴凡, 汪玲. 深化临床医学教育改革培养造就服务健康中国需求的卓越医师[J]. 中国卫生资源, 2023, 26(6): 625-627. |
| WU F, WANG L. Deepening the reform of clinical medical education and cultivating outstanding physicians who serve the needs of a healthy China[J]. China Health Resources, 2023, 26(6): 625-627. | |
| 19 | 吴凡, 汪玲. 构建新时代 “MD+PhD” 医学教育新模式[J]. 中国卫生资源, 2021, 24(2): 111-115. |
| WU F, WANG L. Constructing a new “MD+PhD” model of medical education in the new era[J]. China Health Resources, 2021, 24(2): 111-115. | |
| 20 | 马麟, 孔菲, 程方骁, 等. 学科交叉融合发展的探索与实践——以生命科学领域为例[J]. 大学与学科, 2021(4): 100-107. |
| MA L, KONG F, CHENG F X, et al. Exploration and practice of interdisciplinary integration development: taking the field of life sciences as an example[J]. Universities and Disciplines, 2021(4): 100-107. | |
| 21 | 张皓, 杨玉辉, 王凯, 等. 高等医学院校青年科研培训体制探索与实践: 以国家自然科学基金申报为例[J]. 中国高等医学教育, 2012(6): 20-21. |
| ZHANG H, YANG Y H, WANG K, et al. Exploration and practice of youth research training system in higher medical colleges: taking the application for National Natural Science Foundation of China as an example[J]. China Higher Medical Education, 2012(6): 20-21. | |
| 22 | 辜承慰, 罗惠文, 董涵琼, 等. 基于间隔时间系数的独立医科大学青年人才成长路径分析: 以国家自然科学基金项目为例[J]. 中国科学基金, 2022, 36(2): 301-308. |
| GU C W, LUO H W, DONG H Q, et al. Analysis on the growth path of young talents in independent medical university based on interval time coefficient: a case study of National Natural Science Foundation of China[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2022, 36(2): 301-308. |
| [1] | 陆晔峰, 高磊青, 倪晓筱, 富晶晶. 儿童肝移植术后早期血糖及血脂的多时间点监测与影响因素分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(4): 443-451. |
| [2] | 陈佳莹, 褚以忞, 彭海霞. 结直肠癌无进展生存时间预测模型及影响因素研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(3): 324-334. |
| [3] | 傅艺玲, 吴茜, 罗晓庆, 吴艾泓, 夏雪兰, 郑敏. 晚期癌症患者预立医疗照护计划参与行为影响因素的系统综述[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(4): 482-493. |
| [4] | 罗晨, 沈玲, 王传伟, 顾佳妮, 王瑾, 赵黎, 黄帅. 腹腔镜结直肠癌根治术后患者早期下床活动现状及影响因素[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(9): 1201-1210. |
| [5] | 王晓玉, 彭银辉, 马文琳, 姚博爽, 李一凡, 赵莉, 杨春霞. 新冠疫情大流行期间儿童及青少年新发焦虑症状的纵向研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(8): 963-970. |
| [6] | 台瑞, 方芳, 毛晶珏, 周霞. 永久性肠造口患者造口适应水平影响因素分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(11): 1423-1429. |
| [7] | 崔培荣, 倪雪萍, 宗明灿, 忻笑, 江雨露, 李贤华. 老年慢性病患者健康信息寻求行为现状及影响因素路径分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(6): 805-812. |
| [8] | 许莉, 杨艳, 陈菡芬, 姜萌, 卜军. 急性心肌梗死患者于心脏康复中心就诊的影响因素及效果评价[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(5): 646-652. |
| [9] | 何烨, 方芳. 非体外循环冠状动脉搭桥患者术前糖化血红蛋白水平与术后谵妄的关系[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(1): 21-27. |
| [10] | 蔡羽莹, 刘焰. 生活质量评估量表及心理评估工具在干眼症人群中的应用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(9): 1252-1255. |
| [11] | 吴志山, 黄润, 梁丽萍, 朱宇婷, 郑乔木, 姜丽萍. ICU老年患者术后谵妄发生的特征及影响因素分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(12): 1580-1586. |
| [12] | 吴圣佳1, 2,李贤华3,康 磊2,忻 笑4,倪雪萍5,宋 婷1. 冠状动脉旁路移植术后中青年患者社会参与水平及影响因素的调查研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(2): 247-. |
| [13] | 张素群,倪琛,盛美萍,汪云. 体外受精-胚胎移植术中单胚胎移植与双胚胎移植的妊娠结局及影响因素分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2019, 39(6): 642-. |
| [14] | 路会萍*,吴李娜*,汪海娅. 社区门诊老年高血压患者自测健康调查及其影响因素分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2019, 39(10): 1194-. |
| [15] | 何亚平 1,楼玮群 2,陈杰灵 2,周箴 3,朱静芬 1,简红 3. 病程12个月及以上非小细胞肺癌患者生活质量评估及影响因素研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2018, 38(7): 775-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||