
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 614-623.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2025.05.010
收稿日期:2024-12-02
接受日期:2025-02-21
出版日期:2025-05-28
发布日期:2025-05-21
通讯作者:
金升元,副主任医师,博士;电子信箱:jsydll@sina.com。作者简介:赵建磊(1999—),男,硕士生;电子信箱:zjl0987vip@163.com。
ZHAO Jianlei1, ZHAO Jingqi1, LIU Chang2, HUANG Jingjun1, JIN Shengyuan1( )
)
Received:2024-12-02
Accepted:2025-02-21
Online:2025-05-28
Published:2025-05-21
Contact:
JIN Shengyuan, E-mail: jsydll@sina.com.摘要:
目的·利用系统评价比较治疗烧伤的清创过程中,水动力清创和常规清创在创面愈合时间、每1%总体表面积(total body surface area,TBSA)创面的清创时间、住院时间、术后7 d植皮存活率、二次清创率、术后3 d创面分泌物细菌培养阳性率以及术后感染发生率方面的差异,以期选择出针对需要清创的烧伤创面更加有效的清创方式。方法·检索PubMed、Embase、Web of Science、Cochrane Library、中国知网(CNKI)、中国生物医学文献服务系统(SinoMed)、维普中文期刊数据库及万方数据库,纳入水动力清创对比常规清创治疗烧伤的文献,检索语种为中文和英文,检索时限为建库至2024年10月1日,研究类型为随机对照试验(randomized controlled trial,RCT)。检索和筛选文献后,对纳入文献进行质量评价,并提取相关数据。定性资料和定量资料分别通过相对危险度(risk ratio,RR)和均数差(mean difference,MD)描述。使用RevMan5.4软件采用固定或随机效应模型制作森林图,使用Stata 14.0软件制作漏斗图以及进行Egger′s检验。结果·纳入15篇高质量RCT研究,包含需要清创的烧伤患者1 261例。分析结果显示:与常规清创组相比,水动力清创组术后的创面愈合时间(MD=-3.29,95%CI -3.88~-2.70,P<0.001)、每1% TBSA创面清创时间(MD=-0.63,95%CI -0.76~-0.50,P<0.001)、住院时间(MD=-4.22,95%CI -6.17~-2.28),P<0.001)明显缩短,术后7 d植皮存活率(MD=8.62,95%CI 7.21~10.04,P<0.001)明显升高,二次清创率(RR=0.21,95%CI 0.12~0.37,P<0.001)和术后3 d创面分泌物细菌培养阳性率(RR=0.30,95%CI 0.17~0.53,P<0.001)明显降低;2组术后感染发生率的差异无统计学意义(RR=1.06,95%CI 0.66~1.69,P=0.820)。结论·在烧伤创面治疗中,水动力清创与传统常规清创方式相比表现出更好的效果,具有清创和住院时间减少、二次清创需求降低、创面分泌物细菌培养阳性率降低以及植皮存活率提高的优势。
中图分类号:
赵建磊, 赵婧琦, 刘唱, 黄靖竣, 金升元. 水动力清创治疗烧伤的效果:随机对照试验的系统评价[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(5): 614-623.
ZHAO Jianlei, ZHAO Jingqi, LIU Chang, HUANG Jingjun, JIN Shengyuan. Efficacy of hydrodynamic debridement in the treatment of burns: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(5): 614-623.
| Study | Study design | Hydrosurgery debridement group | Conventional debridement group | Outcome | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Age/year | TBSA/% | n | Age/year | TBSA/% | |||
| NAWAR et al, 2022[ | RCT | 20 | 21.20±11.10 | 23.30±8.30 | 20 | 19.00±9.20 | 24.50±9.60 | ② |
| LEGEMAT et al, 2022[ | RCT | 137 | 42.89±25.47 | 8.41±7.49 | 137 | 42.89±25.47 | 8.41±7.49 | ⑦ |
| HYLAND et al, 2015[ | RCT | 30 | ‒ | ‒ | 31 | ‒ | ‒ | ⑦ |
| GRAVANTE et al, 2007[ | RCT | 42 | 46.00±26.90 | 25.00±14.00 | 45 | 50.00±28.40 | 23.00±16.00 | ① |
| GUO et al, 2022[ | RCT | 30 | ‒ | ‒ | 30 | ‒ | ‒ | ① |
| CHANG, 2022[ | RCT | 41 | 40.32±10.66 | ‒ | 42 | 40.56±10.72 | ‒ | ①②③④⑤ |
| JI et al, 2019[ | RCT | 40 | 44.23±6.23 | 19.38±5.68 | 40 | 44.28±6.24 | 18.75±6.05 | ①②③④⑤⑥ |
| LIU et al, 2016[ | RCT | 34 | 41.00±12.00 | 73.00±11.00 | 42 | 40.00±12.00 | 74.00±12.00 | ①②③④⑤ |
| LIU et al, 2024[ | RCT | 41 | 41.15±6.82 | 23.06±2.12 | 41 | 41.93±6.50 | 22.78±2.35 | ①②④⑥ |
| LIU et al, 2023[ | RCT | 60 | ‒ | ‒ | 60 | ‒ | ‒ | ①⑥ |
| QIU et al, 2022[ | RCT | 37 | 42.93±1.91 | 52.37±5.79 | 36 | 42.91±1.94 | 52.33±5.81 | ①②④ |
| WANG, 2021[ | RCT | 20 | 45.67±2.11 | 65.21±0.51 | 20 | 45.25±2.46 | 65.25±0.56 | ①⑦ |
| XIAO et al, 2016[ | RCT | 32 | 27.10±6.80 | ‒ | 32 | 28.00±7.40 | ‒ | ④ |
| XU et al, 2016[ | RCT | 37 | 44.00±27.00 | 37.00±14.00 | 41 | 50.00±19.00 | 34.00±16.00 | ⑥ |
| ZHANG, 2024[ | RCT | 21 | 44.57±7.70 | 66.86±9.64 | 22 | 43.59±9.89 | 67.18±8.61 | ①②③④⑤ |
表1 纳入文献的基本特征
Tab 1 Basic characteristics of the included studies on hydrosurgery debridement and conventional debridement
| Study | Study design | Hydrosurgery debridement group | Conventional debridement group | Outcome | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Age/year | TBSA/% | n | Age/year | TBSA/% | |||
| NAWAR et al, 2022[ | RCT | 20 | 21.20±11.10 | 23.30±8.30 | 20 | 19.00±9.20 | 24.50±9.60 | ② |
| LEGEMAT et al, 2022[ | RCT | 137 | 42.89±25.47 | 8.41±7.49 | 137 | 42.89±25.47 | 8.41±7.49 | ⑦ |
| HYLAND et al, 2015[ | RCT | 30 | ‒ | ‒ | 31 | ‒ | ‒ | ⑦ |
| GRAVANTE et al, 2007[ | RCT | 42 | 46.00±26.90 | 25.00±14.00 | 45 | 50.00±28.40 | 23.00±16.00 | ① |
| GUO et al, 2022[ | RCT | 30 | ‒ | ‒ | 30 | ‒ | ‒ | ① |
| CHANG, 2022[ | RCT | 41 | 40.32±10.66 | ‒ | 42 | 40.56±10.72 | ‒ | ①②③④⑤ |
| JI et al, 2019[ | RCT | 40 | 44.23±6.23 | 19.38±5.68 | 40 | 44.28±6.24 | 18.75±6.05 | ①②③④⑤⑥ |
| LIU et al, 2016[ | RCT | 34 | 41.00±12.00 | 73.00±11.00 | 42 | 40.00±12.00 | 74.00±12.00 | ①②③④⑤ |
| LIU et al, 2024[ | RCT | 41 | 41.15±6.82 | 23.06±2.12 | 41 | 41.93±6.50 | 22.78±2.35 | ①②④⑥ |
| LIU et al, 2023[ | RCT | 60 | ‒ | ‒ | 60 | ‒ | ‒ | ①⑥ |
| QIU et al, 2022[ | RCT | 37 | 42.93±1.91 | 52.37±5.79 | 36 | 42.91±1.94 | 52.33±5.81 | ①②④ |
| WANG, 2021[ | RCT | 20 | 45.67±2.11 | 65.21±0.51 | 20 | 45.25±2.46 | 65.25±0.56 | ①⑦ |
| XIAO et al, 2016[ | RCT | 32 | 27.10±6.80 | ‒ | 32 | 28.00±7.40 | ‒ | ④ |
| XU et al, 2016[ | RCT | 37 | 44.00±27.00 | 37.00±14.00 | 41 | 50.00±19.00 | 34.00±16.00 | ⑥ |
| ZHANG, 2024[ | RCT | 21 | 44.57±7.70 | 66.86±9.64 | 22 | 43.59±9.89 | 67.18±8.61 | ①②③④⑤ |
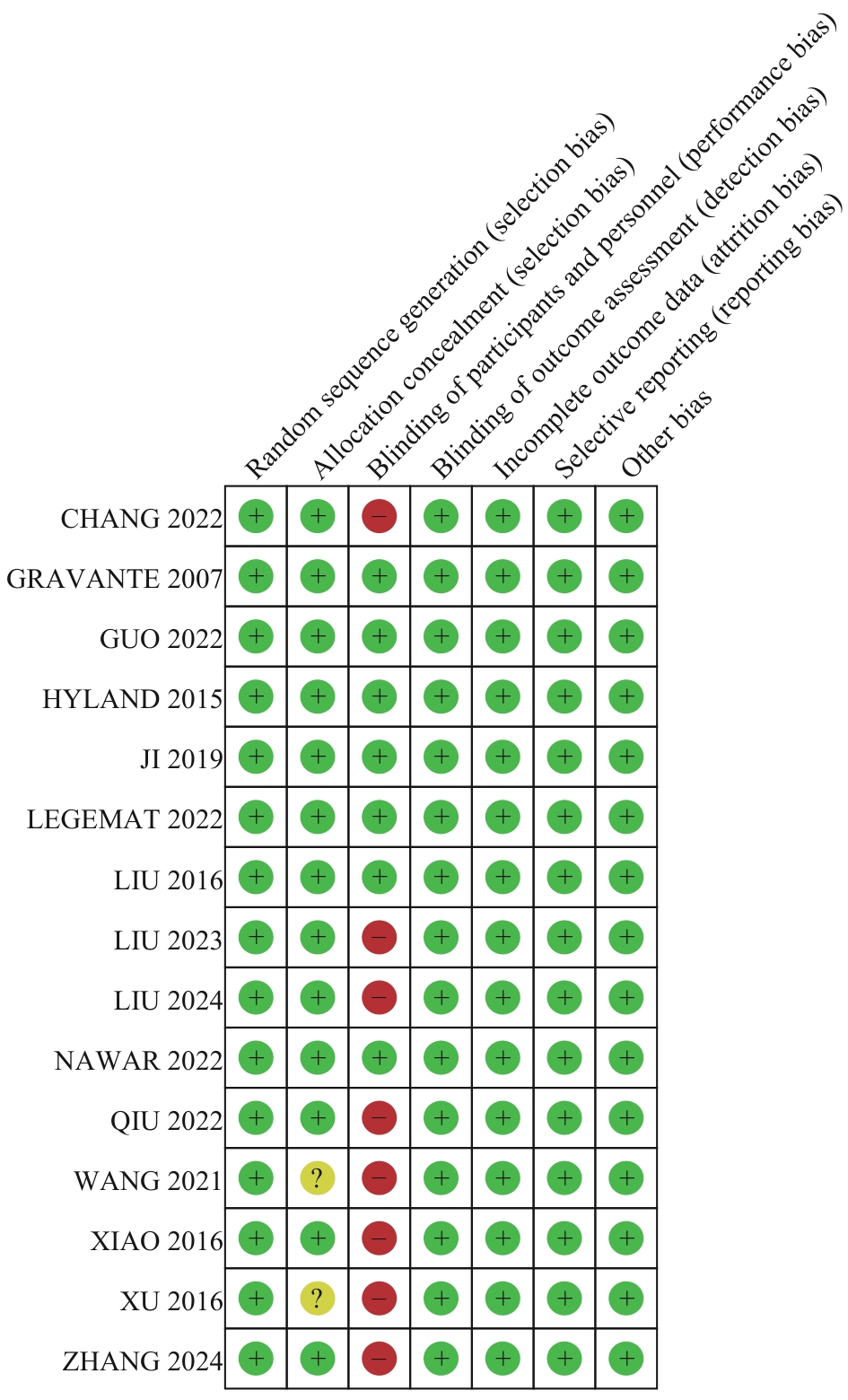
图2 纳入文献的风险偏倚评估Note: “+”—up to the standard; “-”—failure to meet the standard; “?”—not mentioned or described clearly in the literature.
Fig 2 Risk bias assessment of the included articles
| Outcome | Heterogeneity test | Effect Model | Meta-analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P value | I²/% | MD/RR (95%CI) | P value | ||
| Time to complete healing after graft | <0.001 | 68 | Random | -3.29 (-3.88, -2.70) | <0.001 |
| Time to debride 1% TBSA wound | 0.003 | 69 | Random | -0.63 (-0.76, -0.50) | <0.001 |
| Percentage of skin graft survival | 0.690 | 0 | Fixed | 8.62 (7.21, 10.04) | <0.001 |
| Secondary debridement rate | 0.980 | 0 | Fixed | 0.21 (0.12, 0.37) | <0.001 |
| Positive rate of bacterial culture of wound exudate at 3 d post-surgery | 0.990 | 0 | Random | 0.30 (0.17, 0.53) | <0.001 |
| Hospitalization duration | <0.001 | 92 | Random | -4.22 (-6.17, -2.28) | <0.001 |
| Postoperative infection rate | 0.810 | 0 | Random | 1.06 (0.66, 1.69) | 0.820 |
表2 水动力清创和常规清创治疗烧伤效果的分析
Tab 2 Analysis of the efficacy of hydrosurgery debridement and conventional debridement in the treatment of burns
| Outcome | Heterogeneity test | Effect Model | Meta-analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P value | I²/% | MD/RR (95%CI) | P value | ||
| Time to complete healing after graft | <0.001 | 68 | Random | -3.29 (-3.88, -2.70) | <0.001 |
| Time to debride 1% TBSA wound | 0.003 | 69 | Random | -0.63 (-0.76, -0.50) | <0.001 |
| Percentage of skin graft survival | 0.690 | 0 | Fixed | 8.62 (7.21, 10.04) | <0.001 |
| Secondary debridement rate | 0.980 | 0 | Fixed | 0.21 (0.12, 0.37) | <0.001 |
| Positive rate of bacterial culture of wound exudate at 3 d post-surgery | 0.990 | 0 | Random | 0.30 (0.17, 0.53) | <0.001 |
| Hospitalization duration | <0.001 | 92 | Random | -4.22 (-6.17, -2.28) | <0.001 |
| Postoperative infection rate | 0.810 | 0 | Random | 1.06 (0.66, 1.69) | 0.820 |
| Outcome | Number of studies/n | Fixed-effects model | Random-effects model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD/RR (95%CI) | P value | MD/RR (95%CI) | P value | ||
| Time to complete healing after graft | -3.11 (-3.43, -2.80) | <0.001 | -3.29 (-3.88, -2.70) | <0.001 | |
| Time to debride 1% TBSA wound | -0.65 (-0.71, -0.58) | <0.001 | -0.63 (-0.76, -0.50) | <0.001 | |
| Percentage of skin graft survival | 8.62 (7.21, 10.04) | <0.001 | 8.62 (7.21, 10.04) | <0.001 | |
| Secondary debridement rate | 0.21 (0.12, 0.37) | <0.001 | 0.22 (0.12, 0.39) | <0.001 | |
| Positive rate of bacterial culture of wound exudate at 3 d post-surgery | 0.30 (0.17, 0.53) | <0.001 | 0.30 (0.17, 0.53) | <0.001 | |
| Hospitalization duration | -3.86 (-4.38, -3.33) | <0.001 | -4.22 (-6.17, -2.28) | <0.001 | |
| Postoperative infection rate | 1.05 (0.65, 1.68) | 0.850 | 1.06 (0.66, 1.69) | 0.820 | |
表3 改变效应模型后meta分析结果
Tab 3 Meta-analysis results after altering the effect model
| Outcome | Number of studies/n | Fixed-effects model | Random-effects model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD/RR (95%CI) | P value | MD/RR (95%CI) | P value | ||
| Time to complete healing after graft | -3.11 (-3.43, -2.80) | <0.001 | -3.29 (-3.88, -2.70) | <0.001 | |
| Time to debride 1% TBSA wound | -0.65 (-0.71, -0.58) | <0.001 | -0.63 (-0.76, -0.50) | <0.001 | |
| Percentage of skin graft survival | 8.62 (7.21, 10.04) | <0.001 | 8.62 (7.21, 10.04) | <0.001 | |
| Secondary debridement rate | 0.21 (0.12, 0.37) | <0.001 | 0.22 (0.12, 0.39) | <0.001 | |
| Positive rate of bacterial culture of wound exudate at 3 d post-surgery | 0.30 (0.17, 0.53) | <0.001 | 0.30 (0.17, 0.53) | <0.001 | |
| Hospitalization duration | -3.86 (-4.38, -3.33) | <0.001 | -4.22 (-6.17, -2.28) | <0.001 | |
| Postoperative infection rate | 1.05 (0.65, 1.68) | 0.850 | 1.06 (0.66, 1.69) | 0.820 | |
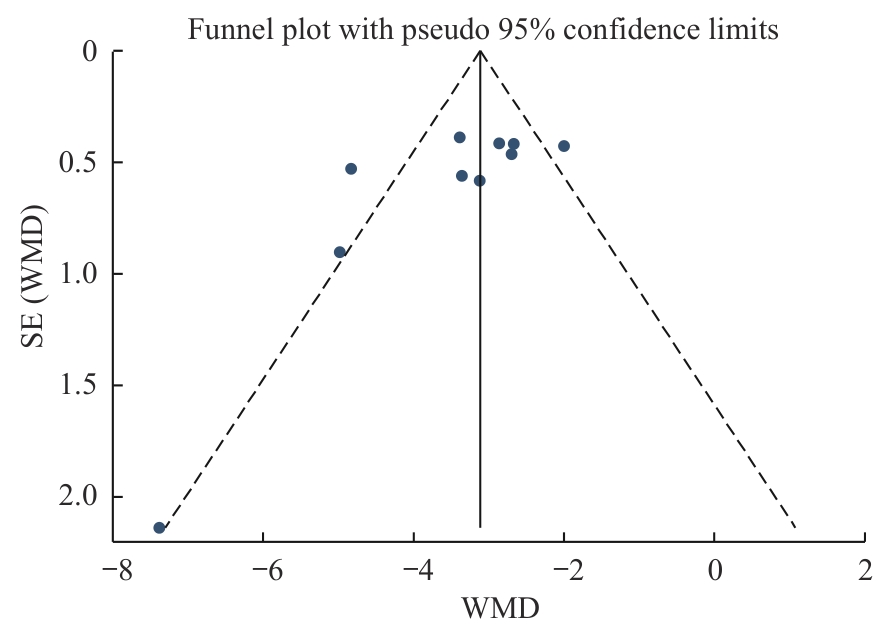
图11 创面愈合时间的发表偏倚漏斗图Note: SE‒standard error; WMD‒weighted mean difference.
Fig 11 Funnel plot of publication bias for time to complete healing after graft
| 1 | RADZIKOWSKA-BÜCHNER E, ŁOPUSZYŃSKA I, FLIEGER W, et al. An overview of recent developments in the management of burn injuries[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(22): 16357. |
| 2 | LEGEMATE C M, GOEI H, GOSTELIE O E, et al. Application of hydrosurgery for burn wound debridement: an 8-year cohort analysis[J]. Burns, 2019, 45(1): 88-96. |
| 3 | JESCHKE M G, VAN BAAR M E, CHOUDHRY M A, et al. Burn injury[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2020, 6(1): 11. |
| 4 | KAKAGIA D D, KARADIMAS E J. The efficacy of VersajetTM hydrosurgery system in burn surgery. A systematic review[J]. J Burn Care Res, 2018, 39(2): 188-200. |
| 5 | PIEPTU V, MIHAI A, GROZA C, et al. Burns in the emergency department: a one-year single center analysis on 355 cases[J]. Chirurgia (Bucur), 2020, 115(4): 486-492. |
| 6 | 邱琳峰. 水动力清创系统在四肢电弧烧伤清创中的应用[J]. 基层医学论坛, 2022, 26(32): 148-150. |
| QIU L F. The application of hydrodynamic debridement in the management of arc burns in limbs[J]. The Medical Forum, 2022, 26(32): 148-150. | |
| 7 | 刘功成, 阚朝辉, 盛嘉隽, 等. 水动力清创系统在严重烧伤患者大面积残余创面清创中的应用效果[J]. 中华烧伤杂志, 2016, 32(9): 549-554. |
| LIU G C, KAN Z H, SHENG J J, et al. Efficacy of a hydrosurgery system applied in the debridement of extensive residual wounds of patients with severe burn[J]. Chinese Journal of Burns, 2016, 32(9): 549-554. | |
| 8 | YUAN M Z, YIN M F, ZHANG L J, et al. Selective debridement of burn wounds using hydrosurgery system[J]. Int Wound J, 2020, 17(2): 300-309. |
| 9 | 阚朝辉, 刘功成, 朱世辉. 水动力清创系统在烧伤创面清创中的应用概况[J]. 第二军医大学学报, 2017, 38(4): 501-505. |
| KAN Z H, LIU G C, ZHU S H. Application of hydrosurgery system in debridement of burn wound: an overview[J]. Academic Journal of Second Military Medical University, 2017, 38(4): 501-505. | |
| 10 | JIANG Y, ZHOU P, LIU A Y, et al. Efficacy of hydrosurgical eschar excision following MEEK microskin grafting in patients with massive burns: a retrospective study of a single center[J]. Burns, 2024, 50(5): 1223-1231. |
| 11 | 徐风瑞, 乔亮, 李学川, 等. 水刀与削痂清创治疗中等面积深Ⅱ度烧伤创面的效果对比研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2016, 36(3): 354-358. |
| XU F R, QIAO L, LI X C, et al. Comparative study on the efficacy of water jet scalpel and tangential excision for debriding medium area deep second degree burn wounds[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2016, 36(3): 354-358. | |
| 12 | FUENMAYOR P, GOTTENGER R, PUJADAS Z, et al. Successful rhinophyma treatment utilizing the versajet Ⅱ hydrosurgery system: a case report and systematic review of the literature[J]. Cureus, 2024, 16(7): e63921. |
| 13 | LEGEMATE C M, KWA K A A, GOEI H, et al. Hydrosurgical and conventional debridement of burns: randomized clinical trial[J]. Br J Surg, 2022, 109(4): 332-339. |
| 14 | HYLAND E J, D'CRUZ R, MENON S, et al. Prospective, randomised controlled trial comparing Versajet™ hydrosurgery and conventional debridement of partial thickness paediatric burns[J]. Burns, 2015, 41(4): 700-707. |
| 15 | GUO Y F, SONG X G, SONG G R, et al. Application of hydrosurgical debridement and autologous skin cell suspension in the treatment of electric arc injury[J]. Burns Open, 2022, 6(1): 19-22. |
| 16 | GRAVANTE G, DELOGU D, ESPOSITO G, et al. Versajet hydrosurgery versus classic escharectomy for burn débridment: a prospective randomized trial[J]. J Burn Care Res, 2007, 28(5): 720-724. |
| 17 | CAO Y L, LIU Z C, CHEN X L. Efficacy of hydrosurgical excision combined with skin grafting in the treatment of deep partial-thickness and full-thickness burns: a two-year retrospective study[J]. Burns, 2023, 49(5): 1087-1095. |
| 18 | TANG X D, QIU L, WANG F, et al. Safety and efficacy of waterjet debridement vs. conventional debridement in the treatment of extremely severe burns: a retrospective analysis[J]. Burns, 2023, 49(8): 1926-1934. |
| 19 | GHOGOMU E A T, MAXWELL L J, BUCHBINDER R, et al. Updated method guidelines for cochrane musculoskeletal group systematic reviews and metaanalyses[J]. J Rheumatol, 2014, 41(2): 194-205. |
| 20 | 刘唱, 金春花, 罗银利, 等. 维拉帕米与曲安奈德对病理性瘢痕疗效及安全性的meta分析[J]. 中国皮肤性病学杂志, 2024, 38(1): 50-58. |
| LIU C, JIN C H, LUO Y L, et al. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of verapamil and triamcinolone acetonide in the treatment of pathological scar[J]. The Chinese Journal of Dermatovenereology, 2024, 38(1): 50-58. | |
| 21 | 尹杏杏, 谌天奇, 秦珊, 等. 瑞马唑仑和丙泊酚用于老年患者无痛胃肠镜检查安全性比较的meta分析[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志, 2024, 40(4): 393-400. |
| YIN X X, SHEN T Q, QIN S, et al. Comparison of the safety of remazolam and propofol for pain-free gastroscopy in elderly patients: a meta-analysis[J]. Journal of Clinical Anesthesiology, 2024, 40(4): 393-400. | |
| 22 | 肖宏涛, 田社民, 魏莹, 等. VERSAJETⅡ清创水刀系统治疗深Ⅱ度烧伤的疗效及安全性[J]. 临床医学, 2016, 36(11): 78-79. |
| XIAO H T, TIAN S M, WEI Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of VERSAJET Ⅱ hydrosurgery system in the treatment of deep partial-thickness burn wounds[J]. Clinical Medicine, 2016, 36(11): 78-79. | |
| 23 | 刘礼平, 邓涛, 朱鹏. 削痂清创与水刀清创治疗中面积深Ⅱ度烧伤创面的临床效果比较[J]. 中国医学创新, 2024, 21(15): 131-135. |
| LIU L P, DENG T, ZHU P. Comparison of clinical effects between scab removal and debridement and water knife debridement treatment for moderate area deep Ⅱ degree burn wounds[J]. Medical Innovation of China, 2024, 21(15): 131-135. | |
| 24 | 常刘. 水动力清创系统在烧伤患者创面清创中的应用效果[J]. 中国民康医学, 2022, 34(24): 44-47. |
| CHANG L. Application effects of hydrodynamic debridement system in wound debridement of burn patients[J]. Medical Journal of Chinese People's Health, 2022, 34(24): 44-47. | |
| 25 | 张彩云. 水动力清创系统在大面积烧伤残余创面治疗中的临床疗效观察[D]. 石家庄: 河北医科大学, 2024.ZHANG. Clinical efficacy observation of hydrosurgery system in the treatment of residual wounds with extensive burns[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Medical University, 2024. |
| 26 | 王菲. 水动力清创结合点状皮片移植治疗大面积烧伤残余创面疗效研究[J]. 中国伤残医学, 2021, 29(1): 44-46. |
| WANG F. Efficacy study of hydrosurgery debridement combined with punch graft skin transplantation in the treatment of large area burn residual wounds[J]. Chinese Journal of Trauma and Disability Medicine, 2021, 29(1): 44-46. | |
| 27 | 刘淑岩, 赵宇辉, 刘铁成, 等. 水刀与削痂清创治疗中等面积深Ⅱ度烧伤创面的效果对比[J]. 中华实验外科杂志, 2023, 40(5): 916. |
| LIU S Y, ZHAO Y H, LIU T C, et al. Comparative study on the effectiveness of water knife vs. scab debridement for medium area deep Ⅱ degree burn wounds[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Surgery, 2023, 40(5): 916. | |
| 28 | 季佳浩, 房贺, 钱李科, 等. 负压封闭引流联合水动力清创治疗深度烧伤临床疗效[J]. 临床军医杂志, 2019, 47(12): 1381-1382, 1384. |
| JI J H, FANG H, QIAN L K, et al. Clinical efficacy of negative pressure wound therapy combined with hydrosurgery debridement in the treatment of deep burns[J]. Clinical Journal of Medical Officers, 2019, 47(12): 1381-1382, 1384. | |
| 29 | NAWAR A, NOUH O M, SAAD A S, et al. Versajet™ versus knife excision for burn wound preparation: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Eur J Plast Surg, 2022, 45(5): 793-798. |
| 30 | WORMALD J C, WADE R G, DUNNE J A, et al. Hydrosurgical debridement versus conventional surgical debridement for acute partial-thickness burns[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2020, 9(9): CD012826. |
| 31 | 王磊, 蔡玉辉, 胡克苏, 等. 水动力清创系统用于深Ⅱ度烧伤创面治疗临床疗效的回顾性研究[J]. 中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版), 2021, 16(3): 245-250. |
| WANG L, CAI Y H, HU K S, et al. Retrospective study on the clinical effect of hydrosurgery system in the treatment of deep partial-thickness burn wound[J]. Chinese Journal of Injury Repair and Wound Healing (Electronic Edition), 2021, 16(3): 245-250 | |
| 32 | KWA K A, GOEI H, BREEDERVELD R S, et al. A systematic review on surgical and nonsurgical debridement techniques of burn wounds[J]. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg, 2019, 72(11): 1752-1762. |
| 33 | HIHARA M, TAKEGAWA M, KAKUDO N, et al. A stylized two-stage debridement strategy using an electric dermatome and a Versajet™ hydrosurgery system for deep axillary burns[J]. J Surg Case Rep, 2022, 2022(10): rjac481. |
| 34 | 项俊, 吴红. 水动力清创系统对大面积烧伤残余创面愈合及炎症因子的影响[J]. 中国美容医学, 2021, 30(10): 25-28. |
| XIANG J, WU H. Effect of hydrodynamic debridement system on residual wound healing and inflammatory factors in large area burns[J]. Chinese Journal of Aesthetic Medicine, 2021, 30(10): 25-28. | |
| 35 | 王振君, 彭丽丽, 潘孙峰, 等. 新型削痂刀在深Ⅱ度烧伤创面早期治疗中的应用效果观察[J]. 浙江医学, 2022, 44(2): 154-157, 228-229. |
| WANG Z J, PENG L L, PAN S F, et al. Application of a novel eschar cutter in early treatment of deep second degree burn wounds[J]. Zhejiang Medical Journal, 2022, 44(2): 154-157, 228-229. | |
| 36 | PUTZER D, LECHNER R, CORACA-HUBER D, et al. The extent of environmental and body contamination through aerosols by hydro-surgical debridement in the lumbar spine[J]. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 2017, 137(6): 743-747. |
| [1] | 孙晨寅, 吴百川, 张慧凤, 方贻儒, 彭代辉. 体动记录仪评估抑郁症昼夜节律:一项系统综述和meta分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(5): 606-616. |
| [2] | 宋晨璐, 向军, 杨惠忠. 血清肝素结合蛋白对重度烧伤患者预后及脓毒症发生的早期预警价值[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(4): 474-481. |
| [3] | 杨越, 何开举, 宗家豪, 杨自逸, 吴向嵩, 龚伟. 细胞游离DNA在胆道癌诊断中的价值:一项meta分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(9): 1175-1185. |
| [4] | 陈惠, 朱唯一, 姚屹瑾. 调整左旋甲状腺素治疗剂量对甲状腺功能减退孕妇母婴结局影响的meta分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(7): 906-915. |
| [5] | 马卓然, 袁安彩, 蒋惠如, 陈潇雨, 张薇, 卜军. 脂质蓄积指数与中国成年人高血压关系的meta分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(4): 466-473. |
| [6] | 张媛媛, 吴安琪, 吴捷, 朱雅琪, 李梦瑶, 闫德修, 章雅青, 侯黎莉. 中青年癌症生存者重返工作干预方案的系统评价[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(3): 333-341. |
| [7] | 梁妍景, 黄楚贤, 李红艳, 侯黎莉. 维生素E对放疗或化疗导致的口腔黏膜炎有效性的meta分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(2): 208-214. |
| [8] | 杨玲, 侯黎莉, 赵燕, 陈卫宏, 张金凤, 毛艳. 口腔癌患者张口受限患病率的meta分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(1): 61-69. |
| [9] | 方芳, 台瑞, 余倩, 章雅青. 预康复对胃肠道择期手术患者术后恢复效果的系统评价[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(1): 70-78. |
| [10] | 董叫云, 宋菲, 陆树良, 刘琰, 田鸣. 制冷喷雾联合高分子水凝胶对急性烧伤创面的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(5): 562-569. |
| [11] | 陈卫宏, 侯黎莉, 杨玲, 毛艳, 张金凤. 冷冻疗法预防头颈癌患者放射性口腔黏膜炎的meta分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(5): 635-645. |
| [12] | 谭颖超, 杨珺玥, 王莉娜. 白细胞介素-1B-511C/T基因多态性与冠状动脉粥样硬化性心脏病关联的meta分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(2): 197-204. |
| [13] | 钱德伟, 周任, 关礼春, 张航, 虞敏. 吸入一氧化氮气体对外科手术后肾功能损伤和出血影响的meta分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(1): 95-100. |
| [14] | 王毅, 程诚, 沈红艳, 高红艳, 戴悦宁, 易正辉. 经颅磁刺激对阿尔茨海默病患者认知功能及伴痴呆的行为精神症状疗效的meta分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(7): 931-941. |
| [15] | 刘洁, 谢新民, 支雪梅, 陆静毅. 睡眠时间与糖尿病性视网膜病变风险关系的meta分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(11): 1502-1508. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||