
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (8): 957-968.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2025.08.003
张宇琴1, 依力夏提·艾合买提1, 王艳丽1, 阳志2( ), 黄建1(
), 黄建1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-30
接受日期:2025-04-18
出版日期:2025-08-28
发布日期:2025-08-26
通讯作者:
黄 建,教授,博士;电子信箱:jyhuanj@shsmu.edu.cn基金资助:
ZHANG Yuqin1, AIHEMAITI Yilixiati1, WANG Yanli1, YANG Zhi2( ), HUANG Jian1(
), HUANG Jian1( )
)
Received:2025-03-30
Accepted:2025-04-18
Online:2025-08-28
Published:2025-08-26
Contact:
HUANG Jian, E-mail: jyhuanj@shsmu.edu.cnSupported by:摘要:
目的·探讨E3泛素连接酶膜相关锌指蛋白9(membrane-associated RING-CH 9,MARCH9)调控受体型蛋白质酪氨酸磷酸酶α(receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase alpha,RPTPα)泛素化修饰的分子机制及其生物学功能。方法·采用Western blotting鉴定RPTPα的泛素化修饰类型及MARCH9对其泛素化水平的调控作用;比较MARCH9野生型、MARCH9酶活突变体(MARCH9 S198A或MARCH9-HC/CC),以及shRNA介导的内源MARCH9敲低对RPTPα蛋白稳定性的影响;利用蛋白酶体抑制剂MG132、自噬抑制剂3-MA和溶酶体抑制剂氯喹(chloroquine,CQ)鉴定MARCH9介导的RPTPα泛素化降解类型;探究43 ℃热激促进RPTPα蛋白降解的可能机制;利用慢病毒载体构建MARCH9单敲低(H1299-shMARCH9)及MARCH9/RPTPα双敲低(H1299-shMARCH9-shRPTPα)的肺癌稳转细胞株,通过CCK-8细胞增殖、平板克隆形成和软琼脂克隆形成实验,评估MARCH9或RPTPα对肺癌细胞增殖与集落形成能力的影响;通过血管拟态形成实验和划痕实验检测MARCH9或RPTPα对肺癌细胞侵袭、迁移能力的影响;建立裸鼠皮下移植瘤模型评价MARCH9或RPTPα对肺癌细胞体内成瘤能力的影响;通过生物信息学方法比较MARCH9和RPTPα在肺癌患者中的表达差异与预后相关性。结果·RPTPα主要发生K63连接型多聚泛素化修饰,E3泛素连接酶MARCH9过表达显著增强其泛素化水平;过表达野生型MARCH9而非酶活突变体能显著降低RPTPα蛋白稳定性,而shRNA敲低内源MARCH9后RPTPα蛋白水平又会明显上升;CQ而非MG132或3-MA处理能增加RPTPα蛋白稳定性,提示MARCH9主要介导RPTPα的泛素化-溶酶体降解途径;43 ℃热激可以特异增强MARCH9-RPTPα相互作用并促进RPTPα蛋白降解。功能实验显示:与对照H1299细胞相比,H1299-shMARCH9细胞的RPTPα蛋白水平升高,细胞增殖速率加快,克隆形成和细胞侵袭能力均明显增强,裸鼠中成瘤能力也明显增强,而双敲低MARCH9/RPTPα的稳转细胞株又能逆转上述表型(均P<0.05)。生物信息学分析肺癌患者相关数据,显示RPTPα高表达与肺癌患者不良预后及肿瘤转移呈正相关,而MARCH9则为负相关。结论·MARCH9介导了磷酸酶RPTPα的K63型泛素化依赖的溶酶体降解过程。这一发现为开发靶向RPTPα的肿瘤治疗策略提供了新的依据。
中图分类号:
张宇琴, 依力夏提·艾合买提, 王艳丽, 阳志, 黄建. MARCH9介导磷酸酶RPTPα的泛素化降解[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(8): 957-968.
ZHANG Yuqin, AIHEMAITI Yilixiati, WANG Yanli, YANG Zhi, HUANG Jian. Ubiquitination and degradation of RPTPα mediated by MARCH9[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(8): 957-968.
| Primer | Forword (5′→3′) | Reverse (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| MARCH9-HA | CGCGGATCCGCCACCATGCTCAAGTCTCG GCTCCGCA | CCGGAATTCTCAAGCGTAGTCTGGGACGTCG TATGGGTAGACTGTAGTGACCCTCATGACA |
| MARCH9-H136A/C139S | TCAGCCCAGCCTCATCCGCTGGAT | GCCGTGCAGCGCACTGAGCCGT |
| MARCH9-CC152/155SS | TCAGCTACTTCAAGTACCAGGTCCTGGC | GCTCACTGCTCCAGGAGCCCCTCTCG |
| MARCH9-S198A | GCCATCTCCTGGCTCATCTGGTCCT | GGCAACCAGGAAGAGCGAGCCCAGA |
表1 PCR引物序列
Tab 1 Primers sequences for PCR
| Primer | Forword (5′→3′) | Reverse (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| MARCH9-HA | CGCGGATCCGCCACCATGCTCAAGTCTCG GCTCCGCA | CCGGAATTCTCAAGCGTAGTCTGGGACGTCG TATGGGTAGACTGTAGTGACCCTCATGACA |
| MARCH9-H136A/C139S | TCAGCCCAGCCTCATCCGCTGGAT | GCCGTGCAGCGCACTGAGCCGT |
| MARCH9-CC152/155SS | TCAGCTACTTCAAGTACCAGGTCCTGGC | GCTCACTGCTCCAGGAGCCCCTCTCG |
| MARCH9-S198A | GCCATCTCCTGGCTCATCTGGTCCT | GGCAACCAGGAAGAGCGAGCCCAGA |
| Name | Sequence (5'→3') |
|---|---|
| MARCH9 shRNA1 | CCGGGTCCAGATTGCTGCCATAGTTCTCGAGAACTATGGCAGCAATCTGGACTTTTTG |
| MARCH9 shRNA2 | CCGGGCAGTGGAAGGTCCTAAATTACTCGAGTAATTTAGGACCTTCCACTGCTTTTTG |
| MARCH9 shRNA3 | CCGGCCCTGGAGAGAACCGTCTTTACTCGAGTAAAGACGGTTCTCTCCAGGGTTTTTG |
表2 shRNA序列
Tab 2 Sequence of shRNA
| Name | Sequence (5'→3') |
|---|---|
| MARCH9 shRNA1 | CCGGGTCCAGATTGCTGCCATAGTTCTCGAGAACTATGGCAGCAATCTGGACTTTTTG |
| MARCH9 shRNA2 | CCGGGCAGTGGAAGGTCCTAAATTACTCGAGTAATTTAGGACCTTCCACTGCTTTTTG |
| MARCH9 shRNA3 | CCGGCCCTGGAGAGAACCGTCTTTACTCGAGTAAAGACGGTTCTCTCCAGGGTTTTTG |
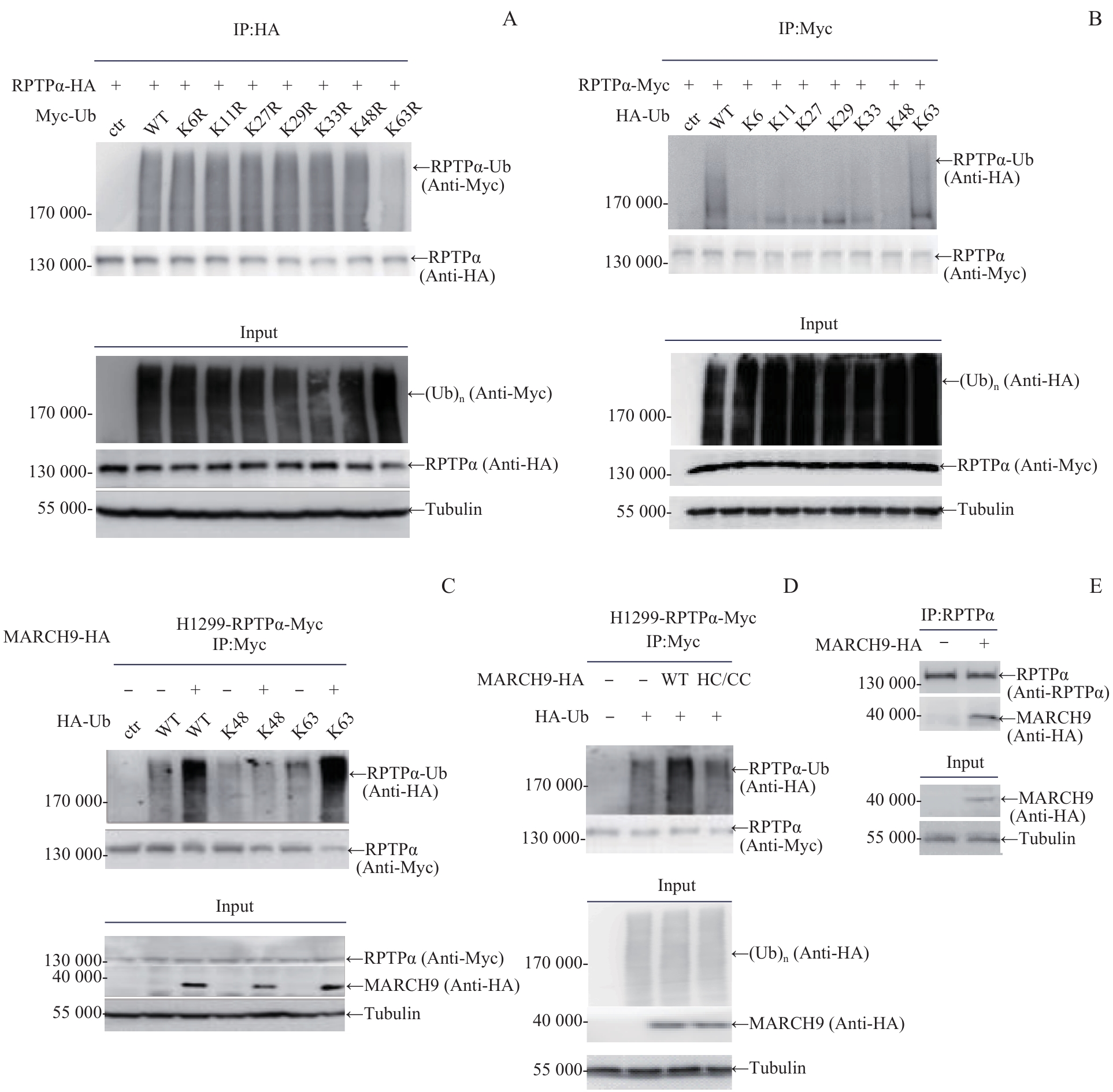
图1 MARCH9 介导的磷酸酶RPTPα K63连接型泛素化修饰Note: A. 293T cells were co-transfected with RPTPα-HA and single-point K/R Myc-Ub plasmid as indicated. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibody, followed by Western blotting analysis with anti-Myc antibody. B. 293T cells were co-transfected with RPTPα-Myc and K-only HA-Ub plasmid as indicated. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc antibody, followed by Western blotting analysis with anti-HA antibody. C. H1299-RPTPα-Myc stable cells were transfected with HA-Ub or HA-Ub KR as indicated, along with MARCH9-HA. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc antibody, followed by Western blotting analysis with anti-HA antibody. D. H1299-RPTPα-Myc stable cells were transfected with Flag-Ub alone, together with MARCH9-HA or MARCH9 HC-CC-HA. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc antibody, followed by Western blotting analysis with anti-Flag antibody. E. 293T cells were transfected with MARCH9-HA. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-RPTPα antibody, followed by Western blotting analysis with anti-HA antibody.
Fig 1 MARCH9-mediated K63-linked ubiquitination of phosphatase RPTPα
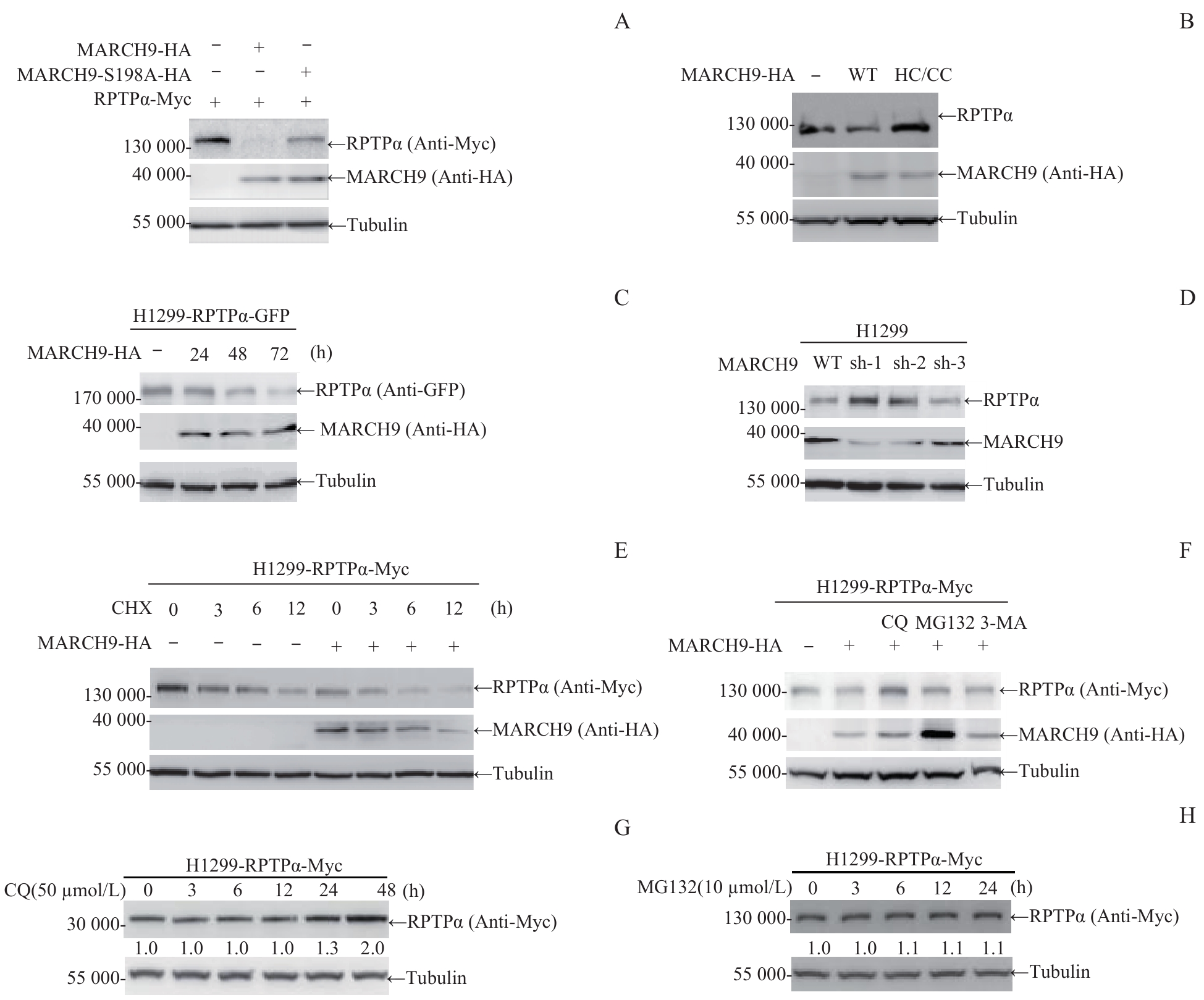
图2 MARCH9 介导的RPTPα蛋白质降解Note: A. 293T cells were transfected with RPTPα-Myc alone or co-transfected with MARCH9-HA or MARCH9 S198A-HA for 48 h. Cells were lysed and the ectopic RPTPα protein level was detected by Western blotting. B. 293T cells were transfected with MARCH9-HA or MARCH9 HC/CC-HA for 48 h. Cells were lysed and the endogenous RPTPα protein level was detected by Western blotting. C. H1299-RPTPα-GFP stable cells were transfected with MARCH9-HA for the indicated times. The ectopic RPTPα-GFP protein level was detected by Western blotting. D. MARCH9-knockdown H1299 stable cells were generated by polyclonal lenti-viral infections with the pLKO.1-shRNA. The endogenous RPTPα and MARCH9 protein levels were detected by Western blotting. E. H1299-RPTPα-Myc stable cells were transfected with MARCH9-HA for 24 h, followed by CHX (100 μg/mL) treatment for the indicated times. RPTPα protein stability was detected by Western blotting. Tubulin was used as a loading control. F. H1299-RPTPα-Myc stable cells were transfected with MARCH9-HA for 24 h, followed by treatment with CQ, MG132 or 3-MA for 6 h. Then the cells were lysed and the RPTPα protein level was detected by Western blotting. G/H. H1299-RPTPα-Myc stable cells were treated with CQ (50 μmol/L) or MG132 (10 μmol/L) for the indicated times. RPTPα protein stability was detected by Western blotting.
Fig 2 MARCH9-mediated degradation of RPTPα protein
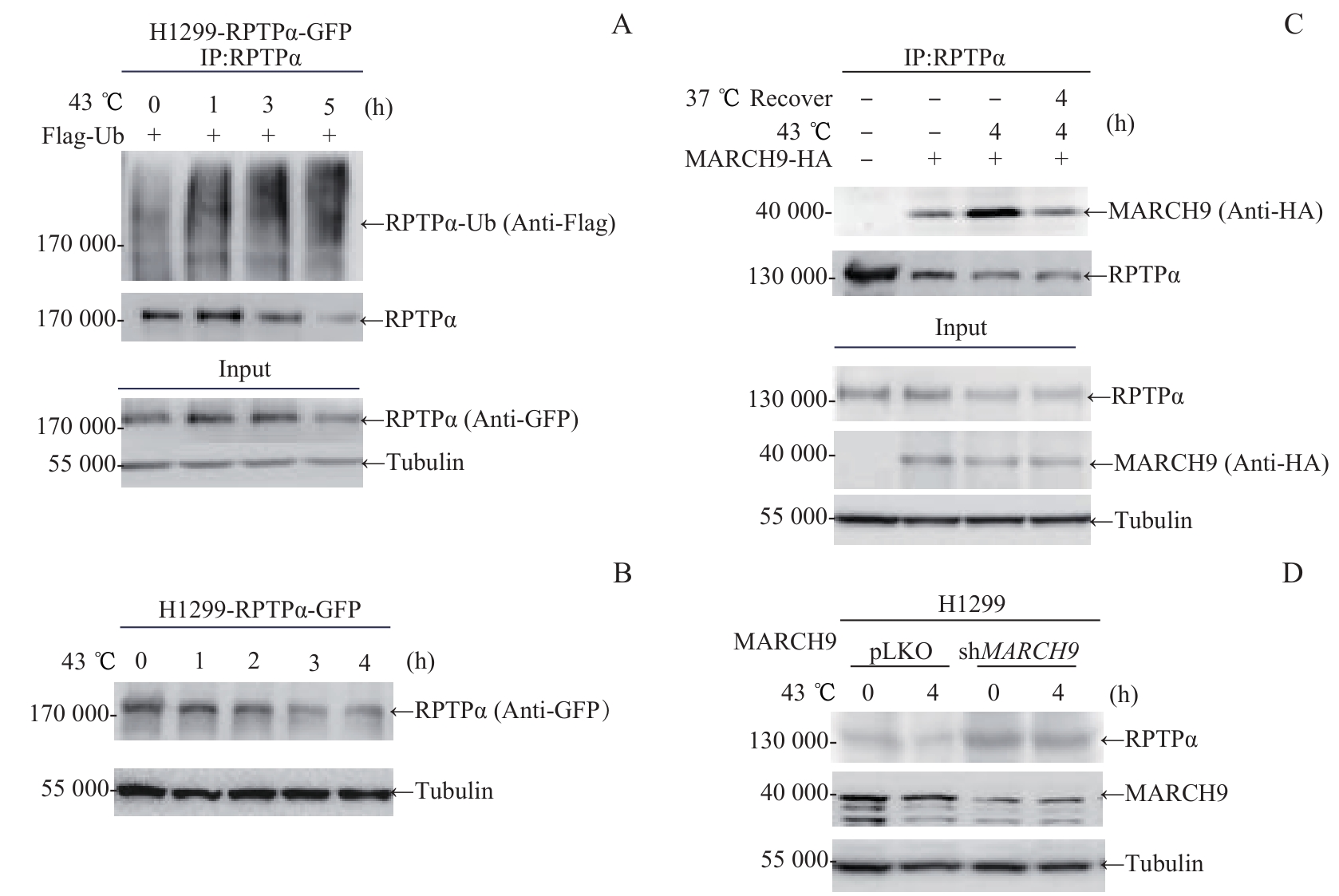
图3 热激-MARCH9 调控的RPTPα泛素化降解Note: A. H1299-RPTPα-GFP stable cells were transfected with Flag-Ub for 24 h. Cells were cultured at 43 ℃ for the indicated times, and lysed for immunoprecipitation with anti-RPTPα antibody, followed by Western blotting analysis with anti-Flag antibody. B. H1299-RPTPα-GFP stable cells were cultured at 43 ℃ for the indicated times. Then cells were lysed and the RPTPα protein level was analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-GFP antibody. C. 293T cells were transfected with MARCH9-HA for 48 h. Cells were cultured at 43 ℃ for 4 h alone, or followed by recovery at 37 ℃ for 4 h. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-RPTPα antibody, followed by Western blotting analysis with anti-HA antibody. D. MARCH9-shRNA H1299 stable cells and control H1299 cells were cultured at 43 ℃ for 4 h. The endogenous RPTPα and MARCH9 protein levels were detected by Western blotting.
Fig 3 Heat shock and MARCH9-mediated ubiquitination degradation of RPTPα
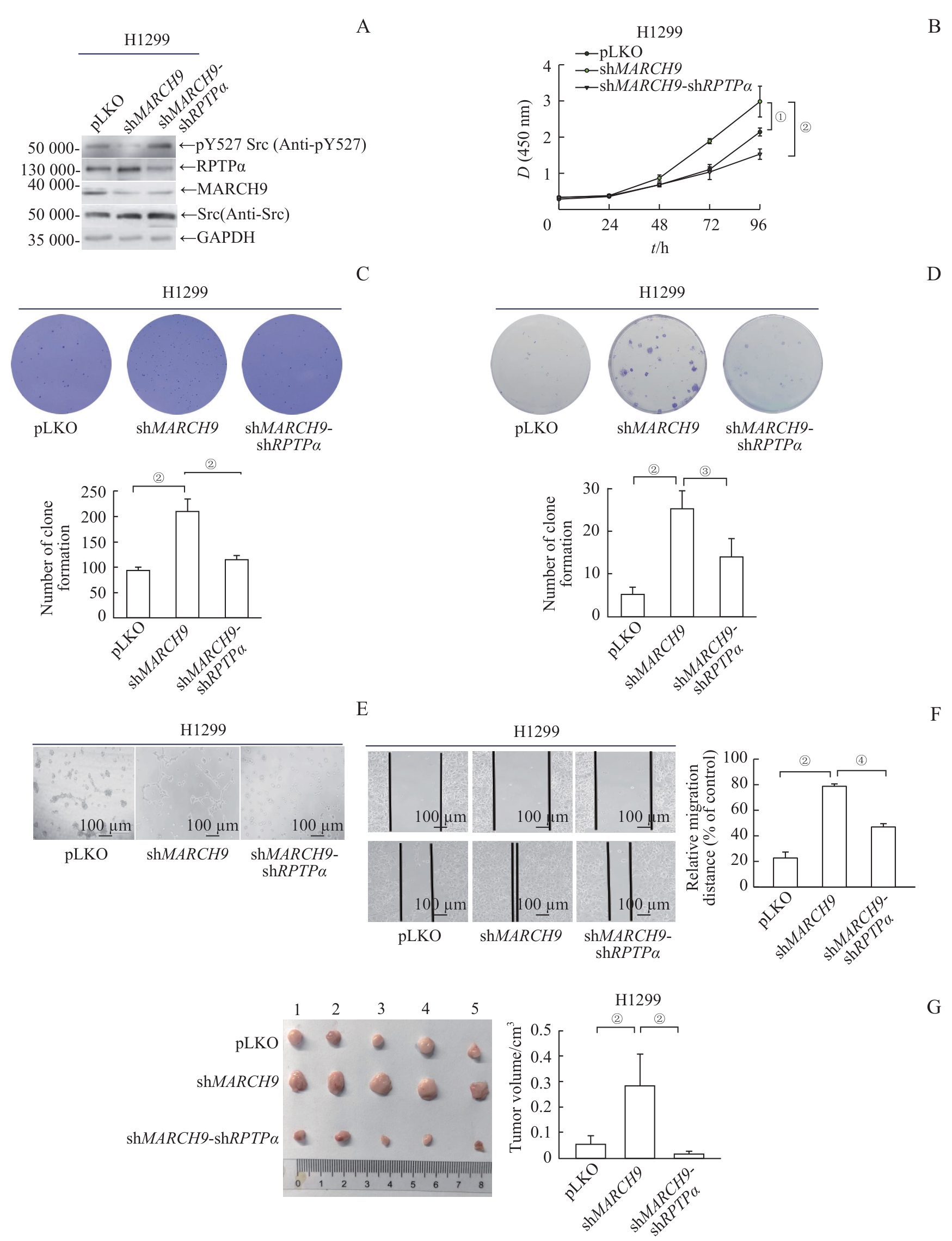
图4 MARCH9 介导的RPTPα降解抑制肿瘤细胞的恶性转化Note: A. MARCH9-shRNA or MARCH9-shRNA/RPTPα-shRNA H1299 stable cell lines were generated by a lenti-viral system. Endogenous levels of Src pY527, RPTPα and MARCH9 proteins were detected by Western blotting. B. Growth curves of H1299 stable cells expressing vector, MARCH9-shRNA, or MARCH9-shRNA/RPTPα-shRNA were measured using the CCK-8 assay. Data are presented as x±s. Statistical significance was determined by Student's t-test (n=6). C. Soft-agar colony formation assays of H1299 stable cells expressing vector, MARCH9-shRNA, or MARCH9-shRNA/RPTPα-shRNA. Representative images of six replicates are shown, and colony numbers were quantified (n=6). Data are presented as x±s. The significance was determined by Student's t-test. D. H1299 stable cells expressing vector, MARCH9-shRNA, or MARCH9-shRNA/RPTPα-shRNA were seeded at 300 cells well and cultured for 15 d. The number of colonies was scored and representative images are shown. Quantification of clones for each group (n=3) is presented as x±s. The significance was determined by Student's t-test. E. Vasculogenic mimicry assays of H1299 stable cells expressing vector, MARCH9-shRNA, or MARCH9-shRNA/RPTPα-shRNA. The representative photographs of cell morphology were taken. F. Wound healing assay of H1299 stable cells expressing vector, MARCH9-shRNA, or MARCH9-shRNA/RPTPα-shRNA. Representative images were taken at 0 h and 14 h time points. G. Tumor images (left) of male BALB/c nude mice subcutaneously injected with suspension H1299 stable cells expressing vector, MARCH9-shRNA, or MARCH9-shRNA/RPTPα-shRNA (3×106 cells/mouse). Xenografted tumors were taken out, dissected, and weighed after 4 weeks. Quantification of tumors for each group (n=5) is shown (right). Data are presented as x¯±s. The significance was determined by Student's t-test. ①P=0.006, ②P<0.001, ③P=0.010, ④P=0.003.
Fig 4 MARCH9-mediated degradation of RPTPα suppresses the oncogenic potential of tumor cells
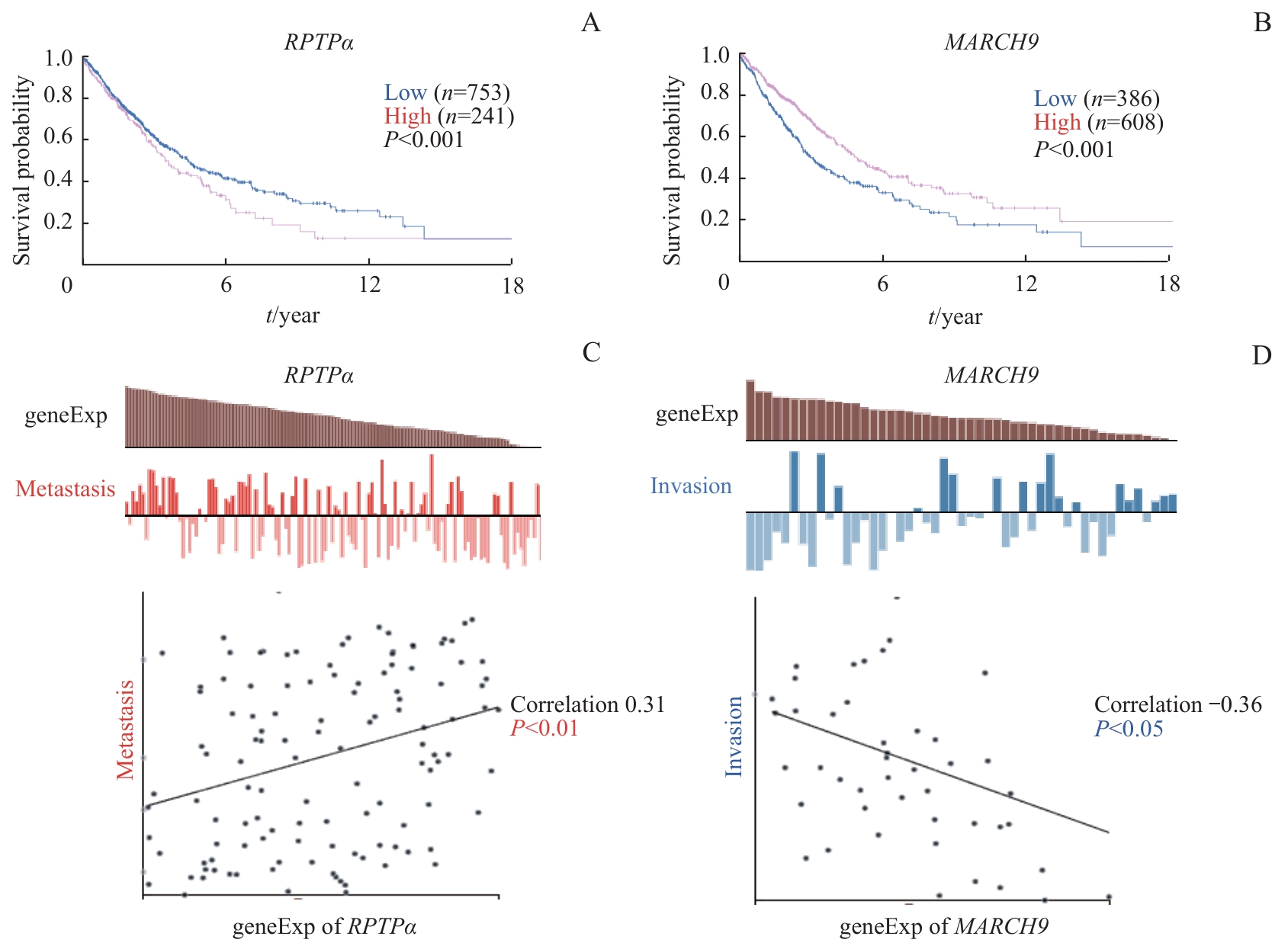
图5 RPTPα 、 MARCH9 与肺癌相关性的生物信息学分析Note: A.Correlation between RPTPα mRNA level and overall survival in human lung cancer. B. Correlation between MARCH9 mRNA level and overall survival in human lung cancer. C. Correlation between RPTPα mRNA level and lung cancer metastasis. D. Correlation between MARCH9 mRNA level and lung cancer invasion.
Fig 5 Bioinformatics analysis of RPTPα, MARCH9, and their association with lung cancer
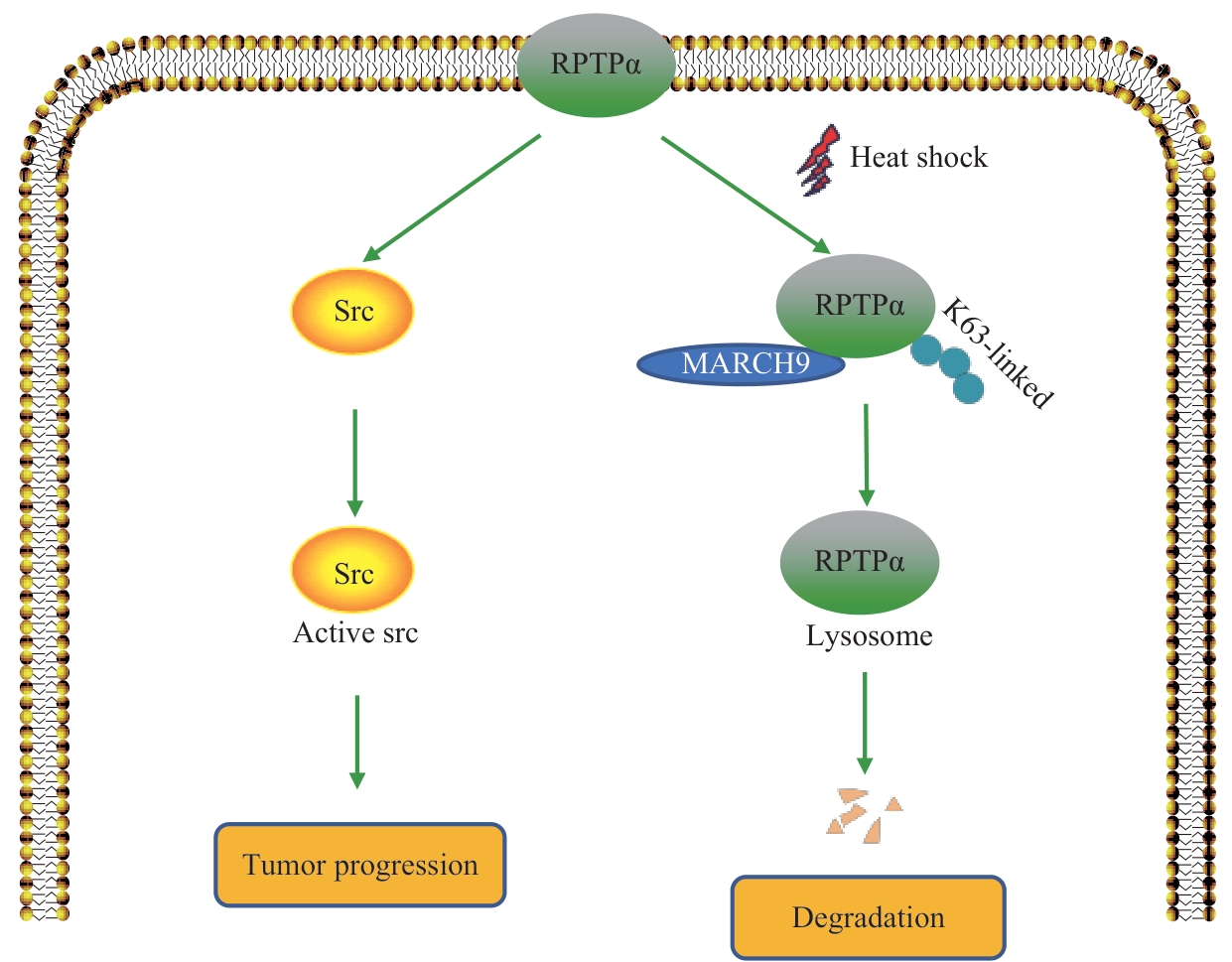
图6 MARCH9 介导RPTPα泛素化降解的工作模型Note: A schematic model. RPTPα promotes tumor progression by dephosphorylating Src pY527 and activating Src kinase. Heat shock promotes the binding of the ubiquitin E3 ligase MARCH9 to RPTPα and enhances its K63-linked ubiquitination and degradation, thereby antagonizing the RPTPα-Src signaling pathway.
Fig 6 Working model of MARCH9-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of RPTPα
| [1] | SAP J, D'EUSTACHIO P, GIVOL D, et al. Cloning and expression of a widely expressed receptor tyrosine phosphatase[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1990, 87(16): 6112-6116. |
| [2] | ZHENG X M, WANG Y, FALLEN C J. Cell transformation and activation of pp60c-src by overexpression of a protein tyrosine phosphatase[J]. Nature, 1992, 359(6393): 336-339. |
| [3] | ZHENG X M, RESNICK R J, SHALLOWAY D. A phosphotyrosine displacement mechanism for activation of Src by PTPα[J]. EMBO J, 2000, 19(5): 964-978. |
| [4] | VACARU A M, DEN HERTOG J. Serine dephosphorylation of receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase α in mitosis induces Src binding and activation[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2010, 30(12): 2850-2861. |
| [5] | PALLEN C J. Protein tyrosine phosphatase alpha (PTPα): a Src family kinase activator and mediator of multiple biological effects[J]. Curr Top Med Chem, 2003, 3(7): 821-835. |
| [6] | TABITI K, SMITH D R, GOH H S, et al. Increased mRNA expression of the receptor-like protein tyrosine phosphatase α in late stage colon carcinomas[J]. Cancer Lett, 1995, 93(2): 239-248. |
| [7] | BERNDT A, LUO X, BÖHMER F D, et al. Expression of the transmembrane protein tyrosine phosphatase RPTPα in human oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Histochem Cell Biol, 1999, 111(5): 399-403. |
| [8] | KRNDIJA D, SCHMID H, EISMANN J L, et al. Substrate stiffness and the receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase α regulate spreading of colon cancer cells through cytoskeletal contractility[J]. Oncogene, 2010, 29(18): 2724-2738. |
| [9] | ARDINI E, AGRESTI R, TAGLIABUE E, et al. Expression of protein tyrosine phosphatase α (RPTPα) in human breast cancer correlates with low tumor grade, and inhibits tumor cell growth in vitro and in vivo[J]. Oncogene, 2000, 19(43): 4979-4987. |
| [10] | ZHENG X M, RESNICK R J, SHALLOWAY D. Apoptosis of estrogen-receptor negative breast cancer and colon cancer cell lines by PTPα and Src RNAi[J]. Int J Cancer, 2008, 122(9): 1999-2007. |
| [11] | ANDERSON K S, CRAMER D W, SIBANI S, et al. Autoantibody signature for the serologic detection of ovarian cancer[J]. J Proteome Res, 2015, 14(1): 578-586. |
| [12] | FANG J Y, ZHANG Y Q, HUANG C H, et al. Glucose-mediated N-glycosylation of RPTPα affects its subcellular localization and Src activation[J]. Oncogene, 2023, 42(14): 1058-1071. |
| [13] | RAIBORG C, STENMARK H. The ESCRT machinery in endosomal sorting of ubiquitylated membrane proteins[J]. Nature, 2009, 458(7237): 445-452. |
| [14] | LIN H, LI S, SHU H B. The membrane-associated MARCH E3 ligase family: emerging roles in immune regulation[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 1751. |
| [15] | HÖR S, ZIV T, ADMON A, et al. Stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture and differential plasma membrane proteome quantitation identify new substrates for the MARCH9 transmembrane E3 ligase[J]. Mol Cell Proteomics, 2009, 8(8): 1959-1971. |
| [16] | LUO Q, LIU Q Q, CHENG H C, et al. Nondegradable ubiquitinated ATG9A organizes Golgi integrity and dynamics upon stresses[J]. Cell Rep, 2022, 40(7): 111195. |
| [17] | TAN C, BYRNE E F X, AH-CANN C, et al. A serine in the first transmembrane domain of the human E3 ubiquitin ligase MARCH9 is critical for down-regulation of its protein substrates[J]. J Biol Chem, 2019, 294(7): 2470-2485. |
| [18] | HAGLUND K, DIKIC I. The role of ubiquitylation in receptor endocytosis and endosomal sorting[J]. J Cell Sci, 2012, 125(Pt 2): 265-275. |
| [19] | HUANG F T, KIRKPATRICK D, JIANG X J, et al. Differential regulation of EGF receptor internalization and degradation by multiubiquitination within the kinase domain[J]. Mol Cell, 2006, 21(6): 737-748. |
| [20] | LIU H, CHEN B, LIU L L, et al. The role of MARCH9 in colorectal cancer progression[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 906897. |
| [21] | SHEN Q M, WANG H Y, XU S. MARCH9 suppresses lung adenocarcinoma progression by downregulating ICAM-1[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 50(1): 92-107. |
| [22] | LUO M, MENG Z P, MOROISHI T, et al. Heat stress activates YAP/TAZ to induce the heat shock transcriptome[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2020, 22(12): 1447-1459. |
| [23] | NICE T J, DENG W W, COSCOY L, et al. Stress-regulated targeting of the NKG2D ligand Mult1 by a membrane-associated RING-CH family E3 ligase[J]. J Immunol, 2010, 185(9): 5369-5376. |
| [1] | 那迪娜·帕尔哈提, 张鹏善, 徐亦天, 陈赟琪, 黄陈. 人去泛素化酶圆柱瘤蛋白截短体质粒的构建及其对胃癌细胞表型的调控研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(9): 1149-1160. |
| [2] | 黄昕, 刘家辉, 叶敬文, 钱文莉, 许万星, 王琳. 基于机器学习的小细胞肺癌代谢分子诊断模型的建立和临床应用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(8): 1009-1016. |
| [3] | 邹沛辰, 刘鸿宇, 阿衣娜扎尔·艾合买提, 朱亮, 唐亚斌, 雷绘敏. 索托拉西布获得性耐药肺癌细胞的代谢轮廓分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(2): 138-149. |
| [4] | 张先洲, 杜凤麟, 吴雷, 任逸喆, 赵明娜, 娄加陶. OGT通过ERK信号通路促进非小细胞肺癌增殖的机制研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(10): 1288-1297. |
| [5] | 蔡单, 黄晶. 非经典型多梳抑制复合物1.6的电镜结构分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(9): 1136-1145. |
| [6] | 朱鸣阳, 许元元, 任江浩, 黄嘉正, 李若楠, 谭强. 以磨玻璃结节为表现的肺腺癌亚肺叶切除研究综述[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(7): 922-927. |
| [7] | 王梦婷, 陈怡楠, 轩辕欣阳, 袁海花. 肺癌恶性胸腔积液来源肿瘤细胞的小鼠PDX模型构建及实验验证[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(4): 435-443. |
| [8] | 刘晨茜, 韩林, 杨轶, 周韩, 刘亚云, 盛德乔. GPR87通过激活RHO/ROCK通路促进非小细胞肺癌的侵袭和迁移[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(12): 1514-1525. |
| [9] | 黄华艳, 徐张闻笛, 夏立亮, 虞永峰, 陆舜. 表皮生长因子受体突变型晚期非小细胞肺癌免疫治疗的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(5): 611-618. |
| [10] | 赵卓明, 刘振浩, 鲁曼曼, 张钰, 许林锋, 谢鹭. 基于TCR组库分析流程的非小细胞肺癌特征分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(12): 1520-1528. |
| [11] | 邹菁华, 宫淼淼, 沈瑛. KRAS4AG12C和KRAS4BG12C对人肺上皮细胞生长和运动的作用差异及机制研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(8): 1016-1023. |
| [12] | 赵珂珂, 蒋蓓蓓, 张璐, 王凌云, 张亚平, 解学乾. 超低剂量平扫CT深度学习图像重建评价肺部病灶的可行性[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(8): 1062-1069. |
| [13] | 廖雅慧, 刘丽云, 朱泓睿, 林厚文, 严继舟, 孙凡. 海绵来源的smenospongine通过抑制非小细胞肺癌细胞中的EGFR-Akt-ABCG2信号通路抑制顺铂耐药[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(8): 997-1007. |
| [14] | 刘子杨, 王小文, 陈力. lncRNA GK-IT1通过调控醛缩酶A影响非小细胞肺癌细胞的恶性进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(5): 591-601. |
| [15] | 靳步, 袁颖, 陈婉玉, 徐浒东, 黄晓蕾, 何佳璐, 于红. 基于GEO数据库探索miRNA靶基因通过泛素化参与食管鳞状细胞癌[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(4): 464-471. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||