
Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science) ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (12): 1570-1578.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2024.12.010
• Public health • Previous Articles
XU Zujing1,2( ), JIANG Yining1,2, XU Jian1,2,3(
), JIANG Yining1,2, XU Jian1,2,3( )
)
Received:2024-05-03
Accepted:2024-09-30
Online:2024-12-28
Published:2024-12-28
Contact:
XU Jian
E-mail:tzxuzujing@163.com;sonia0616@sjtu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
XU Zujing, JIANG Yining, XU Jian. Relationship between prenatal mixed heavy metal/metalloid exposure and offspring cognitive and temperament development[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(12): 1570-1578.
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Maternal age/year | 29.39±3.41 |
| Maternal education level/n(%) | |
| Senior high school or below | 16 (11.50) |
| University or college | 105 (75.54) |
| Postgraduate | 18 (12.95) |
| Marital status/n(%) | |
| Married | 134 (96.40) |
| Single | 5 (3.60) |
| Occupation/n(%) | |
| Professional and technical personnel | 45 (32.37) |
| Administrative or management personnel | 30 (21.58) |
| Commercial personnel | 25 (17.99) |
| Others | 39 (28.06) |
| Family monthly income/n(%) | |
| <2 000 yuan | 6 (4.32) |
| 2 000‒5 000 yuan | 37 (26.62) |
| 5 000‒10 000 yuan | 54 (38.85) |
| >10 000 yuan | 42 (30.21) |
| Birth weight/kg | 3.47±0.42 |
| Gestational age/week | 39.27±1.36 |
| Child gender/n(%) | |
| Male | 56 (40.29) |
| Female | 83 (59.71) |
| Child age/month | 32.91±2.69 |
| DQ of GDS/score | |
| Gross motor | 108.36±11.05 |
| Fine motor | 100.47±13.32 |
| Language | 111.48±12.40 |
| Adaptive | 114.23±8.81 |
| Personal-social | 105.38±11.01 |
| Score of TTS/score | |
| Activity | 3.23±0.57 |
| Rhythm | 2.63±0.57 |
| Withdrawal | 2.94±0.77 |
| Adaptability | 2.90±0.58 |
| Reaction | 3.85±0.60 |
| Mood | 2.66±0.63 |
| Persistence | 2.86±0.66 |
| Attention | 3.72±0.53 |
| Threshold | 3.89±0.75 |
| Heavy metal/metalloid level/(μg·dL-1) | |
| Mn | 3.32 (2.24, 4.63) |
| Pb | 3.60 (2.55, 4.35) |
| As | 2.03 (1.01, 3.35) |
| Cr | 1.78 (0.77, 2.52) |
Tab 1 Demographic and clinical characteristics of participants
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Maternal age/year | 29.39±3.41 |
| Maternal education level/n(%) | |
| Senior high school or below | 16 (11.50) |
| University or college | 105 (75.54) |
| Postgraduate | 18 (12.95) |
| Marital status/n(%) | |
| Married | 134 (96.40) |
| Single | 5 (3.60) |
| Occupation/n(%) | |
| Professional and technical personnel | 45 (32.37) |
| Administrative or management personnel | 30 (21.58) |
| Commercial personnel | 25 (17.99) |
| Others | 39 (28.06) |
| Family monthly income/n(%) | |
| <2 000 yuan | 6 (4.32) |
| 2 000‒5 000 yuan | 37 (26.62) |
| 5 000‒10 000 yuan | 54 (38.85) |
| >10 000 yuan | 42 (30.21) |
| Birth weight/kg | 3.47±0.42 |
| Gestational age/week | 39.27±1.36 |
| Child gender/n(%) | |
| Male | 56 (40.29) |
| Female | 83 (59.71) |
| Child age/month | 32.91±2.69 |
| DQ of GDS/score | |
| Gross motor | 108.36±11.05 |
| Fine motor | 100.47±13.32 |
| Language | 111.48±12.40 |
| Adaptive | 114.23±8.81 |
| Personal-social | 105.38±11.01 |
| Score of TTS/score | |
| Activity | 3.23±0.57 |
| Rhythm | 2.63±0.57 |
| Withdrawal | 2.94±0.77 |
| Adaptability | 2.90±0.58 |
| Reaction | 3.85±0.60 |
| Mood | 2.66±0.63 |
| Persistence | 2.86±0.66 |
| Attention | 3.72±0.53 |
| Threshold | 3.89±0.75 |
| Heavy metal/metalloid level/(μg·dL-1) | |
| Mn | 3.32 (2.24, 4.63) |
| Pb | 3.60 (2.55, 4.35) |
| As | 2.03 (1.01, 3.35) |
| Cr | 1.78 (0.77, 2.52) |
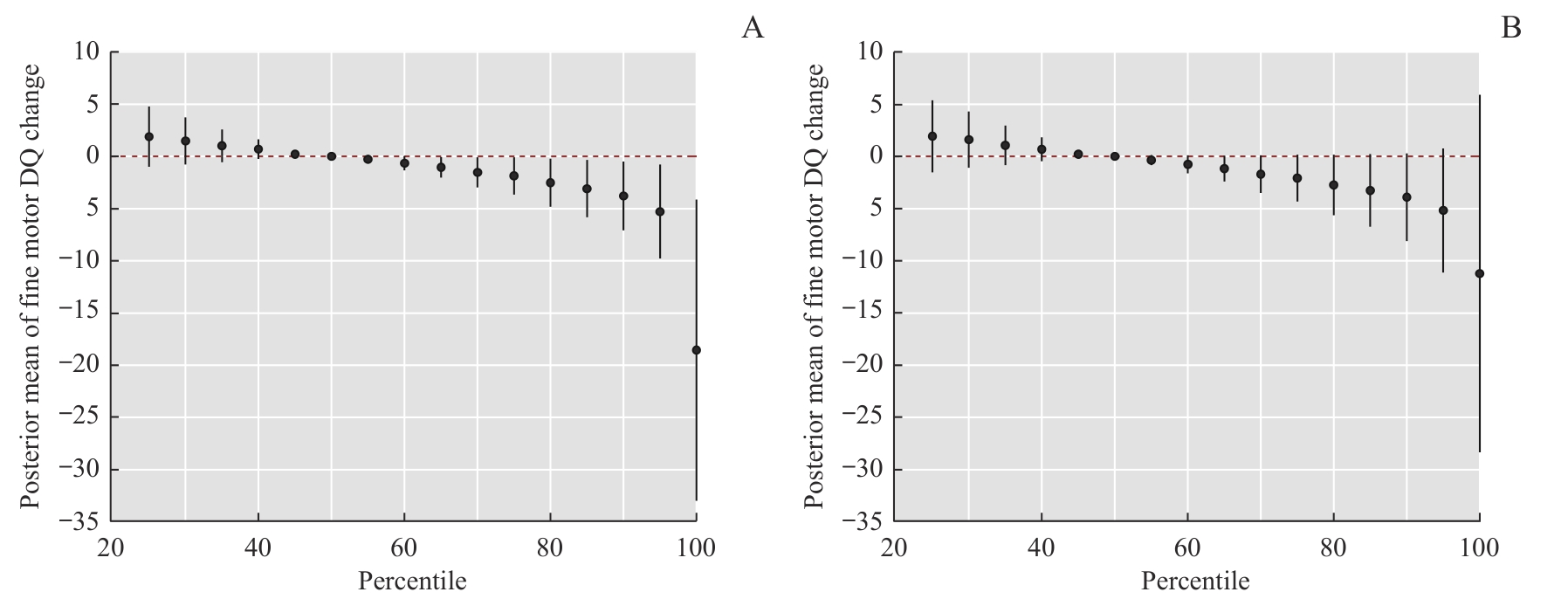
Fig 1 Total effect of prenatal maternal exposure to a combination of four heavy metals/metalloid on the fine motor development of children by the BKMR model
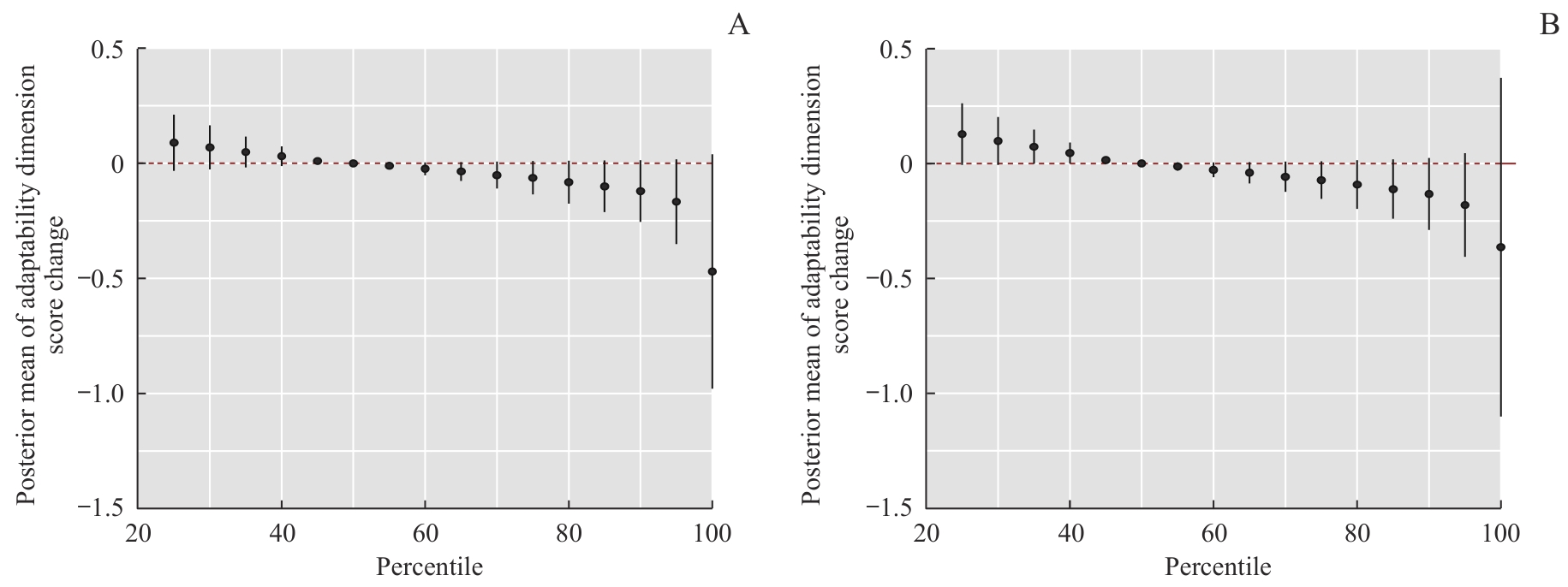
Fig 2 Total effect of prenatal maternal exposure to a combination of four heavy metals/metalloid on the adaptive dimension of the children by the BKMR model
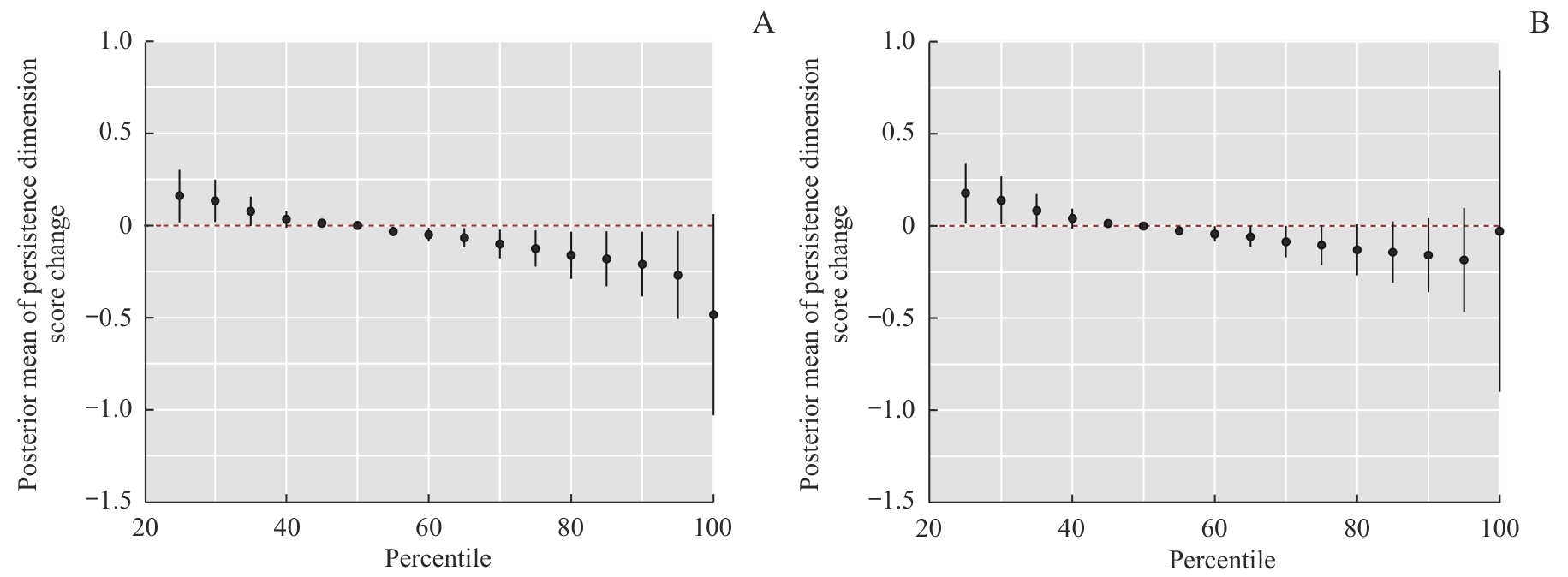
Fig 3 Total effect of prenatal maternal exposure to a combination of four heavy metals/metalloid on the persistence dimension of the children by the BKMR model
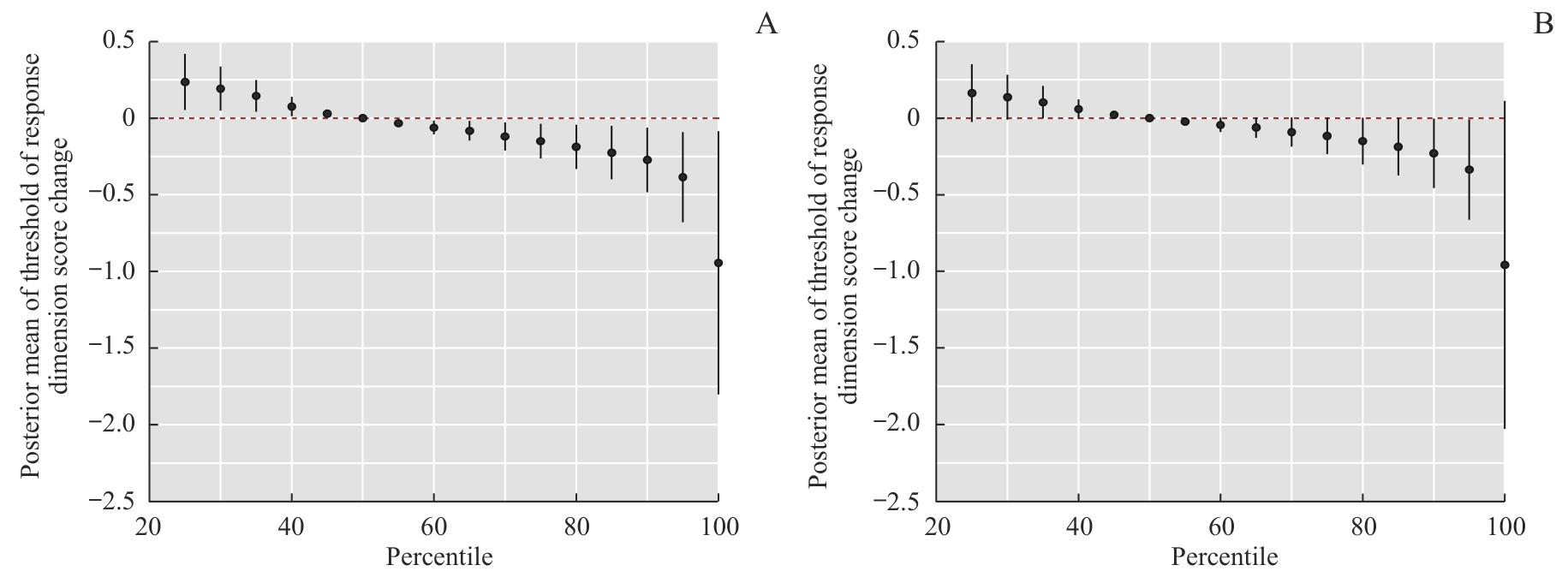
Fig 4 Total effect of prenatal maternal exposure to a combination of four heavy metals/metalloid on the threshold of response dimension of the children by the BKMR model
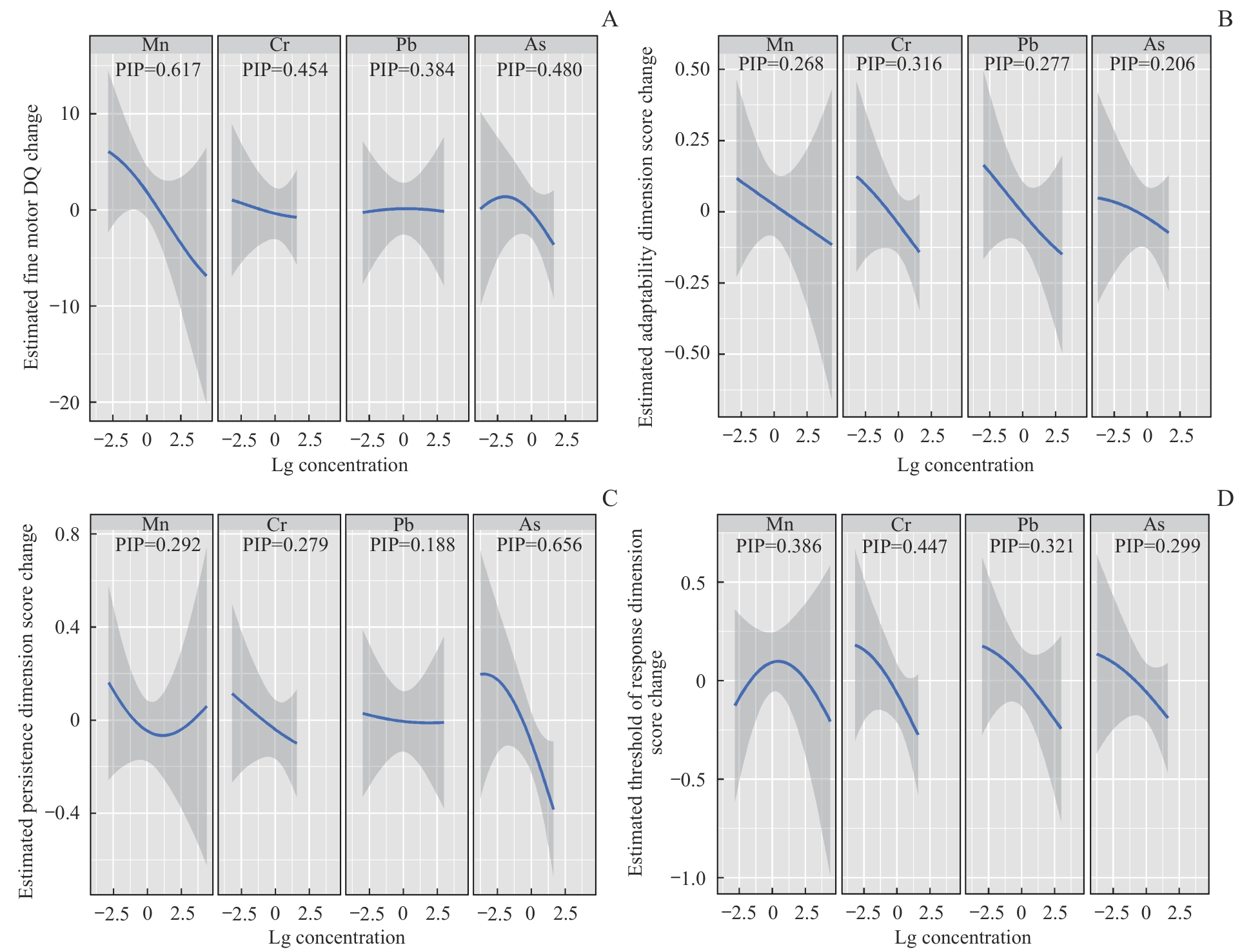
Fig 5 Analyses of the dominant effects of prenatal maternal exposure to the four heavy metals/metalloid on cognitive and temperament development in young children based on the BKMR model
| 1 | WITKOWSKA D, SŁOWIK J, CHILICKA K. Heavy metals and human health: possible exposure pathways and the competition for protein binding sites[J]. Molecules, 2021, 26(19): 6060. |
| 2 | DÓREA J G. Exposure to environmental neurotoxic substances and neurodevelopment in children from Latin America and the Caribbean[J]. Environ Res, 2021, 192: 110199. |
| 3 | WANG Y H, WANG Y Q, YAN C H. Gender differences in trace element exposures with cognitive abilities of school-aged children: a cohort study in Wujiang city, China[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, 2022, 29(43): 64807-64821. |
| 4 | JIA Z X, ZHANG H L, YU L, et al. Prenatal lead exposure, genetic factors, and cognitive developmental delay[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2023, 6(10): e2339108. |
| 5 | GUO J Q, WU C H, ZHANG J M, et al. Prenatal exposure to mixture of heavy metals, pesticides and phenols and IQ in children at 7 years of age: the SMBCS study[J]. Environ Int, 2020, 139: 105692. |
| 6 | KADAWATHAGEDARA M, MUCKLE G, QUÉNEL P, et al. Infant neurodevelopment and behavior in Guadeloupe after lead exposure and Zika maternal infection during pregnancy[J]. Neurotoxicology, 2023, 94: 135-146. |
| 7 | LIU J Y, MARTIN L J, DINU I, et al. Interaction of prenatal bisphenols, maternal nutrients, and toxic metal exposures on neurodevelopment of 2-year-olds in the APrON cohort[J]. Environ Int, 2021, 155: 106601. |
| 8 | SKOGHEIM T S, WEYDE K V F, ENGEL S M, et al. Metal and essential element concentrations during pregnancy and associations with autism spectrum disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children[J]. Environ Int, 2021, 152: 106468. |
| 9 | STROUSTRUP A, HSU H H, SVENSSON K, et al. Toddler temperament and prenatal exposure to lead and maternal depression[J]. Environ Health, 2016, 15(1): 71. |
| 10 | BOBB J F, VALERI L, CLAUS HENN B, et al. Bayesian kernel machine regression for estimating the health effects of multi-pollutant mixtures[J]. Biostatistics, 2015, 16(3): 493-508. |
| 11 | ZHANG Y Q, DONG T Y, HU W Y, et al. Association between exposure to a mixture of phenols, pesticides, and phthalates and obesity: comparison of three statistical models[J]. Environ Int, 2019, 123: 325-336. |
| 12 | TAN Y X, FU Y Y, YAO H J, et al. Relationship between phthalates exposures and hyperuricemia in U.S. general population, a multi-cycle study of NHANES 2007‒2016[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2023, 859(Pt 1): 160208. |
| 13 | ZHAN W Q, QIU W, AO Y, et al. Environmental exposure to emerging alternatives of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and polycystic ovarian syndrome in women diagnosed with infertility: a mixture analysis[J]. Environ Health Perspect, 2023, 131(5): 57001. |
| 14 | YAO Q, VINTURACHE A, LEI X N, et al. Prenatal exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, fetal thyroid hormones, and infant neurodevelopment[J]. Environ Res, 2022, 206: 112561. |
| 15 | JIANG Y Q, WEI Y Y, GUO W H, et al. Prenatal titanium exposure and child neurodevelopment at 1 year of age: a longitudinal prospective birth cohort study[J]. Chemosphere, 2023, 311(Pt 1): 137034. |
| 16 | 洪琦, 周胜利, 姚凯南, 等. 幼儿气质量表的应用研究[J]. 中国儿童保健杂志, 2001, 9(3): 151-153. |
| HONG Q, ZHOU S L, YAO K N, et al. The assessment of Toddler Temperament Scale[J]. Chinese Journal of Child Health Care, 2001, 9(3): 151-153. | |
| 17 | GIBBS M V, REEVES D, CUNNINGHAM C C. The application of temperament questionnaires to a British sample: issues of reliability and validity[J]. J Child Psychol Psychiatry, 1987, 28(1): 61-77. |
| 18 | ETTINGER A S, WENGROVITZ A G, PORTIE C, et al. Guidelines for the identification and management of lead exposure in pregnant and lactating women[S/OL]. Atlanta: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 2010[2024-09-19]. https://stacks.cdc.gov/view /cdc/147837. |
| 19 | ZINIA S S, YANG K H, LEE E J, et al. Effects of heavy metal exposure during pregnancy on birth outcomes[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1): 18990. |
| 20 | AL-SALEH I, SHINWARI N, MASHHOUR A, et al. Birth outcome measures and maternal exposure to heavy metals (lead, cadmium and mercury) in Saudi Arabian population[J]. Int J Hyg Environ Health, 2014, 217(2/3): 205-218. |
| 21 | CLAUS HENN B, SCHNAAS L, ETTINGER A S, et al. Associations of early childhood manganese and lead coexposure with neurodevelopment[J]. Environ Health Perspect, 2012, 120(1): 126-131. |
| 22 | SUN H, CHEN W, WANG D Y, et al. The effects of prenatal exposure to low-level cadmium, lead and selenium on birth outcomes[J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 108: 33-39. |
| 23 | MIYAZAKI J, IKEHARA S, TANIGAWA K, et al. Prenatal exposure to selenium, mercury, and manganese during pregnancy and allergic diseases in early childhood: the Japan environment and children's study[J]. Environ Int, 2023, 179: 108123. |
| 24 | FARÍAS P, HERNÁNDEZ-BONILLA D, MORENO-MACÍAS H, et al. Prenatal co-exposure to manganese, mercury, and lead, and neurodevelopment in children during the first year of life[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2022, 19(20): 13020. |
| 25 | MARTINS A C, KRUM B N, QUEIRÓS L, et al. Manganese in the diet: bioaccessibility, adequate intake, and neurotoxicological effects[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2020, 68(46): 12893-12903. |
| 26 | MA C C, IWAI-SHIMADA M, TATSUTA N, et al. Health risk assessment and source apportionment of mercury, lead, cadmium, selenium, and manganese in Japanese women: an adjunct study to the Japan environment and children's study[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2020, 17(7): 2231. |
| 27 | HERNÁNDEZ-PELLÓN A, FERNÁNDEZ-OLMO I, LEDOUX F, et al. Characterization of manganese-bearing particles in the vicinities of a manganese alloy plant[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 175: 411-424. |
| 28 | 周燕婷. 广西锰暴露工人队列的随访及职业锰暴露对血液免疫学指标水平的影响[D]. 南宁: 广西医科大学, 2018. |
| ZHOU Y T. Follow-up of manganese-exposed workers cohort and effects of occupational manganese exposure on blood immunological indicators[D]. Nanning: Guangxi Medical University, 2018. | |
| 29 | 林鑫江, 杜登青, 陈思洽. 电子垃圾拆解区帕金森病患者血锰水平相关分析[J]. 中国现代药物应用, 2017, 11(18): 26-27. |
| LIN X J, DU D Q, CHEN S Q. Correlation analysis of blood manganese levels in Parkinson's disease patients in the electronic waste dismantling area[J]. Chinese Journal of Modern Drug Application, 2017, 11(18): 26-27. | |
| 30 | RODRIGUES E G, BELLINGER D C, VALERI L, et al. Neurodevelopmental outcomes among 2- to 3-year-old children in Bangladesh with elevated blood lead and exposure to arsenic and manganese in drinking water[J]. Environ Health, 2016, 15: 44. |
| 31 | CHUNG S E, CHEONG H K, HA E H, et al. Maternal blood manganese and early neurodevelopment: the mothers and children's environmental health (MOCEH) study[J]. Environ Health Perspect, 2015, 123(7): 717-722. |
| 32 | CAPARROS-GONZALEZ R A, GIMÉNEZ-ASENSIO M J, GONZÁLEZ-ALZAGA B, et al. Childhood chromium exposure and neuropsychological development in children living in two polluted areas in southern Spain[J]. Environ Pollut, 2019, 252(Pt B): 1550-1560. |
| 33 | 刘伟, 杨辉, 廖伟棠, 等. 电子垃圾拆解区儿童血铬水平与行为问题关系的研究[J]. 汕头大学医学院学报, 2011, 24(1): 26-29. |
| LIU W, YANG H, LIAO W T, et al. Study on blood chromium levels and behavior effects of children in electronic waste recycling area[J]. Journal of Shantou University Medical College, 2011, 24(1): 26-29. | |
| 34 | 伍晓艳. 孕期7种有害金属元素单独和联合暴露的母婴健康效应关联评价: 出生队列研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽医科大学, 2018. |
| WU X Y. The individual and combined effect of prenatal exposure to harmful metals on adverse maternal and infants outcomes: a birth-cohort study[D]. Hefei: Anhui Medical University, 2018. | |
| 35 | CHEN H, ZHANG H L, WANG X, et al. Prenatal arsenic exposure, arsenic metabolism and neurocognitive development of 2-year-old children in low-arsenic areas[J]. Environ Int, 2023, 174: 107918. |
| [1] | CHENG Xiaomeng, ZHANG Yan, GAO Yu, TIAN Ying. Progress in cumulative risk assessment of human health from combined exposure to environmental pollutants [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(8): 1037-1043. |
| [2] | ZHANG Yiyi, NI Changyu, JIN Ying, HE Yaping, FENG Nannan. Effect of hypertension and dyslipidemia on cognition of urban elderly residents [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(7): 907-914. |
| [3] | ZHANG Qinjie, HUANG Sui, TAN Haoyue, ZHOU Xiang, WANG Junyi, LIU Yuzi, WEN Wen, GUO Jia, WU Hao, JIA Huan. Establishment and verification of auditory brainstem implant vocoder model [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(10): 1279-1286. |
| [4] | LIU Taotao, LIU Xiaoli, WU Jingying, NI Ruilong, ZHANG Mengyuan, JI Duxin, ZHANG Mei, CAO Li. Clinical and genetic characteristics of adult cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(5): 592-599. |
| [5] | WU Yujing, GUO Qian, LIU Xiaohua, LI Guanjun. Progress in relationship between chronotype and technology addiction and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(4): 487-494. |
| [6] | CHEN Liqi, XUE Zhuowei, WU Qingkai. Review of MRI-based three-dimensional digital model reconstruction of female pelvic floor organs [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2022, 42(3): 381-386. |
| [7] | Yi-kun MEI, Jing-cong TAN, An-jun WANG, Hui WANG, Ning-ning LIU. Advances in cell wall structure and Candida albicans-host interaction [J]. JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE), 2021, 41(9): 1246-1251. |
| [8] | Qian-long ZHANG, Ying TIAN. Progress in the influence of prenatal exposure to phthalates on placental function and its mechanism [J]. JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE), 2021, 41(9): 1261-1266. |
| [9] | Ya-jie ZHU, Hui LIN, Xi CHEN, Yi-ran ZHAO, Xin-mei LIU, He-feng HUANG. Change of cortisol level in umbilical cord blood of neonates delivered by gestational diabetes mellitus mothers and its influence on offspring health [J]. JOURNAL OF SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY (MEDICAL SCIENCE), 2021, 41(1): 49-54. |
| [10] | YU Qi1, 2, LIU Meng-xue3, YANG Jie3, LIU Kun1, 2, XU Xun1, 2. Automated analysis of microaneurysm lesions in standard seven-field color fundus photography [J]. , 2019, 39(6): 598-. |
| [11] | JIANG Ya-qin1, 2, WANG Zuo-wei2,JIE Yong2,YI Zheng-hui1#, WANG Ji-jun1# . Effect of social cognition and interactive training on rehabilitation of schizophrenic patients in community [J]. , 2018, 38(3): 310-. |
| [12] | ZENG Long-hui, MENG Guo-yu. Saf pili and biofilm formation [J]. , 2018, 38(2): 125-. |
| [13] | WEI Zhen-yu, WU Dan-hong . Research progresses of apelin in nervous system [J]. , 2017, 37(5): 704-. |
| [14] | SUN Jun-yan, LAI Dong-mei. Effects of ovarian function and menopausal hormone therapy on cognitive function [J]. , 2016, 36(9): 1368-. |
| [15] | GU Xie-cheng, WANG Yi-chen, CAI Bo, et al. Condom usage of unmarried female migrant workers in Shanghai and relevant influencing factors [J]. , 2015, 35(7): 1051-. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 182
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 269
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||