
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 695-701.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2022.06.001
• 口腔外科专题 •
收稿日期:2022-03-02
接受日期:2022-05-30
出版日期:2022-06-28
发布日期:2022-08-19
通讯作者:
杨驰
E-mail:lucyhe119@163.com;yangchi63@hotmail.com
作者简介:何冬梅(1972—),女,教授,主任医师,博士;电子信箱:lucyhe119@163.com。
基金资助:Received:2022-03-02
Accepted:2022-05-30
Online:2022-06-28
Published:2022-08-19
Contact:
YANG Chi
E-mail:lucyhe119@163.com;yangchi63@hotmail.com
Supported by:摘要:
下颌骨髁突骨折在临床上常见,治疗不当会引起咬合紊乱、关节强直、生长发育受限等后遗症。该文结合文献回顾,总结了团队的诊治经验,旨在为临床医师提供参考。髁突骨折的影像学诊断特别是CT的冠状位图像重建是骨折分类和治疗的重要依据。按照骨折线的部位分为髁突(囊内)骨折、髁突颈部骨折和髁突下(基底部)骨折3类。其中囊内骨折又分为A、B、C、M 4种类型。髁突骨折的治疗包括非手术治疗和手术治疗。非手术治疗对咬合紊乱的患者可采用颌间弹性牵引的方式;手术治疗的绝对适应证是下颌支残端外脱位出关节窝的骨折,相对适应证是下颌支残端与关节窝接触的骨折、髁突颈部严重移位或脱位和基底部骨折。手术成功的关键点为:正确的手术入路,骨折的解剖复位和稳定的固定,术中对翼外肌附着和髁突表面软骨的保护,关节盘的复位。对于合并髁突骨折的下颌骨骨折进行复位和固定,要注意舌侧裂隙的关闭(以确保下颌骨宽度的恢复)和髁突在关节窝中的位置;当髁突骨折合并面中部骨折时应先复位固定髁突骨折和咬合关系,然后通过咬合复位固定上颌骨骨折。6岁以下的儿童髁突的自我改建能力较强,多用非手术治疗;随着年龄增长髁突的愈合改建能力逐渐减弱,12岁以上青少年的髁突接近成人,手术治疗适应证参考成人髁突骨折。
中图分类号:
何冬梅, 杨驰. 下颌骨髁突骨折的诊治方案:基于上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院颞下颌关节中心的经验[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(6): 695-701.
HE Dongmei, YANG Chi. Diagnosis and treatment protocol of mandibular condylar fracture: experience from the TMJ Center of Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2022, 42(6): 695-701.
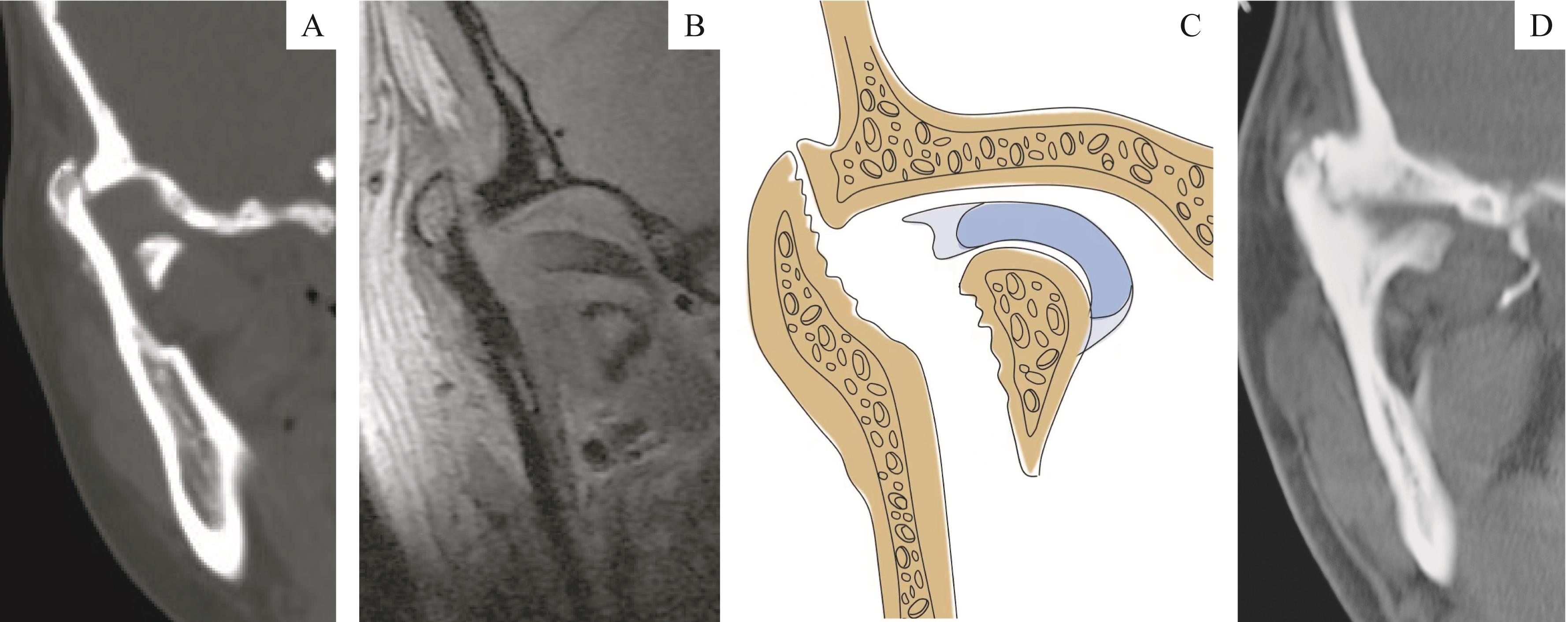
图1 髁突骨折手术的绝对适应证:下颌支残端外脱位出关节窝Note:A. CT showed the ramus stump was dislocated out of the fossa. B. MRI of the same patient showed the articular disc was broken and displaced medially with the fracture fragment. C. The schematic diagram of figure B. D. CT showed the same patient without surgery treatment, whose bony fusion of the stump and fossa formed in the lateral side of the joint.
Fig 1 Absolute indication of condylar fracture surgery: ramus stump laterally dislocated out of the fossa
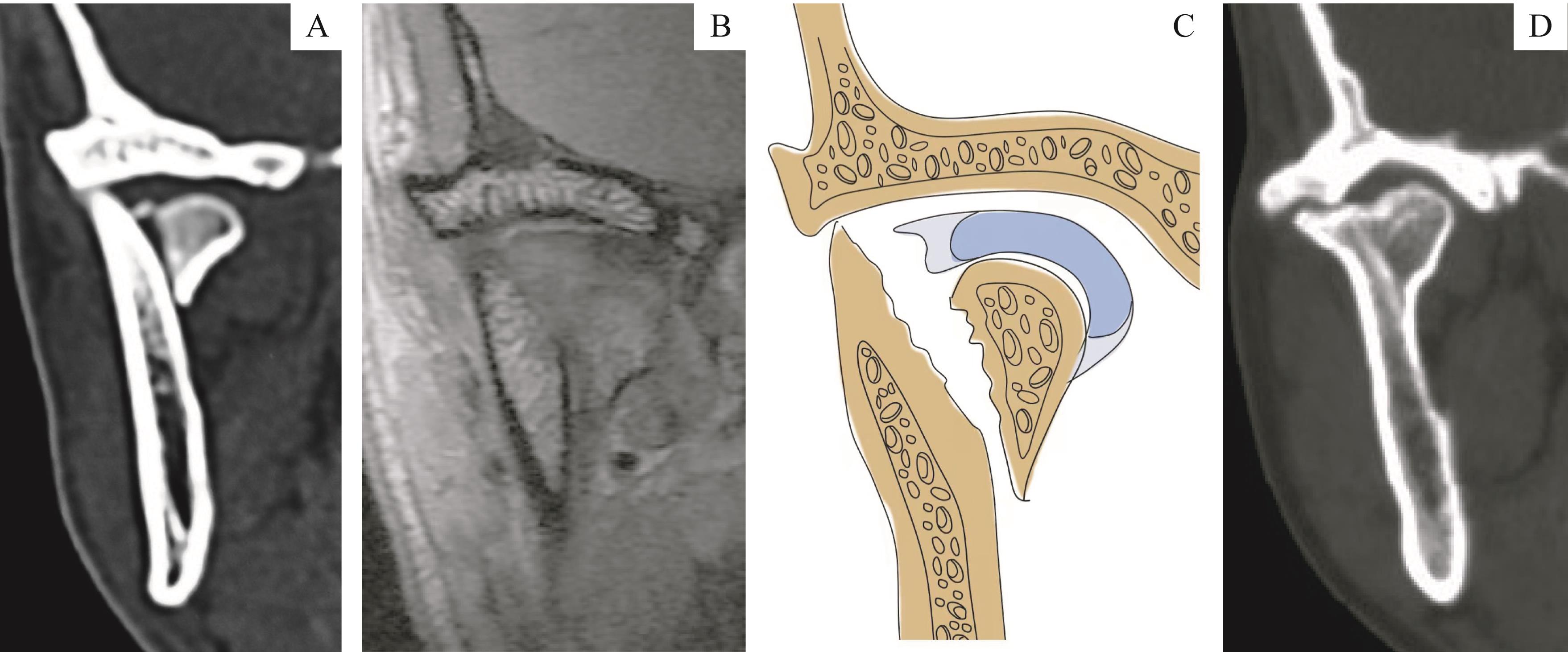
图2 髁突骨折手术的相对适应证之一:下颌支残端与关节窝接触Note:A. CT showed the ramus stump was attached to the fossa. B. MRI of the same patient showed the articular disc was perforated and displaced medially with the fracture fragment. C. The schematic diagram of figure B. D. CT showed the same patient without surgery treatment, whose ankylosis developed laterally to the displaced condyle.
Fig 2 One of the relative indications of condylar fracture surgery: the ramus stump contacting with the fossa
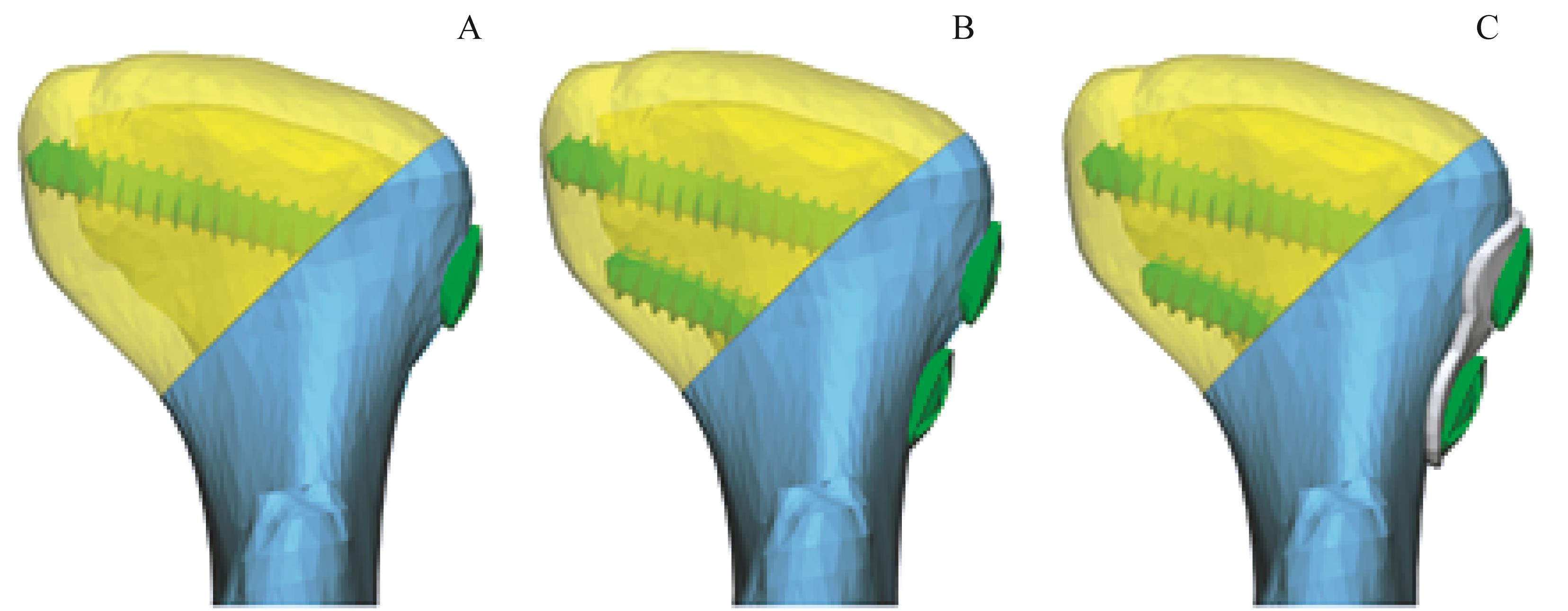
图3 髁突囊内骨折固定示意图Note:A. Single bicortical screw fixation. B. Fixation of two bicortical screws. C. Two bicortical screws with miniplate fixation for the condylar fracture with lateral defect.
Fig 3 Schematic diagrams of fixation of intracapsular condylar fractures
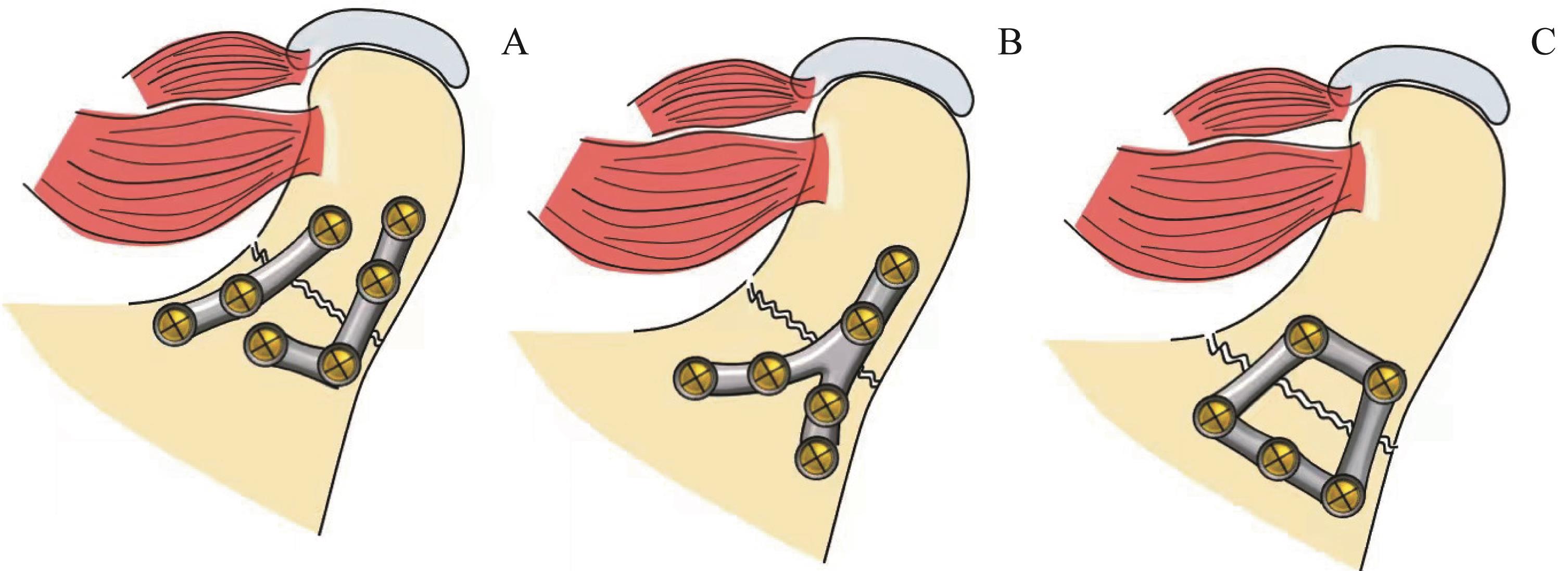
图4 髁突低位骨折的压力带和张力带固定示意图Note:A. Two mini-plates. B. A Y-shaped mini-plate. C. A trapezoid mini-plate.
Fig 4 Schematic diagrams of fixation of stress and tension bands in low condylar fractures
| 1 | MCLEOD N M, KEENAN M. Towards a consensus for classification of mandibular condyle fractures[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2021, 49(4): 251-255. |
| 2 | Consensus conference on open or closed management of condylar fractures. 12th ICOMS. Budapest, 1995[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 1998, 27(4): 243-267. |
| 3 | BOS R R, WARD BOOTH R P, DE BONT L G. Mandibular condyle fractures: a consensus[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 1999, 37(2): 87-89. |
| 4 | 张益. 中国颌面外科高年资医师髁突骨折治疗观点一致性的调查[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2010, 45(4): 196-202. |
| ZHANG Y. Condylar fracture and temporomandibular joint ankylosis[J]. Chin J Stomatol, 2010, 45(4): 196-202. | |
| 5 | NEFF A, CHOSSEGROS C, BLANC J L, et al. Position paper from the IBRA symposium on surgery of the head: the 2nd international symposium for condylar fracture osteosynthesis, Marseille, France 2012[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2014, 42(7): 1234-1249. |
| 6 | 黄国伟, 郑吉驷, 张善勇, 等. 曲面体层X线、CT和MRI在髁突骨折诊断中的应用比较[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2014, 49(7): 434-439. |
| HUANG G W, ZHENG J S, ZHANG S Y, et al. The value of paronamic radiograph, CT and MRI for the diagnosis of condylar fracture[J]. Chin J Stomatol, 2014, 49(7): 434-439. | |
| 7 | 姜滨, 陈敏洁, 张善勇, 等. 全景片诊断髁突骨折的应用价值[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志, 2009, 7(5): 397-400. |
| JIANG B, CHEN M J, ZHANG S Y, et al. The value of panoramic films in diagnosis of condylar fractures[J]. China J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2009, 7(5): 397-400. | |
| 8 | 何冬梅, 杨驰, 姜滨, 等. 下颌骨髁突囊内骨折不同治疗方法的冠状CT评价[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志, 2009, 7(6): 509-514. |
| HE D M, YANG C, JIANG B. Evaluation of the treatment for intracapsular condyle fracture of the mandible by coronal CT[J]. China J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2009, 7(6): 509-514. | |
| 9 | SCHIMMING R, ECKELT U, KITTNER T. The value of coronal computer tomograms in fractures of the mandibular condylar process[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod, 1999, 87(5): 632-639. |
| 10 | YANG X J, YAO Z D, HE D M, et al. Does soft tissue injury affect intracapsular condylar fracture healing?[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2015, 73(11): 2169-2180. |
| 11 | ZHENG J S, ZHANG S Y, YANG C, et al. Assessment of magnetic resonance images of displacement of the disc of the temporomandibular joint in different types of condylar fracture[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2016, 54(1): 74-79. |
| 12 | LINDAHL L. Condylar fractures of the mandible. Ⅰ. Classification and relation to age, occlusion, and concomitant injuries of teeth and teeth-supporting structures, and fractures of the mandibular body[J]. Int J Oral Surg, 1977, 6(1): 12-21. |
| 13 | LOUKOTA R A, ECKELT U, DE BONT L, et al. Subclassification of fractures of the condylar process of the mandible[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2005, 43(1): 72-73. |
| 14 | HLAWITSCHKA M, ECKELT U. Assessment of patients treated for intracapsular fractures of the mandibular condyle by closed techniques[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2002, 60(7): 784-792. |
| 15 | NEFF A, CORNELIUS C P, RASSE M, et al. The comprehensive AOCMF classification system: condylar process fractures—level 3 tutorial[J]. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr, 2014, 7(Suppl 1): S044-S058. |
| 16 | HE D M, YANG C, CHEN M J, et al. Intracapsular condylar fracture of the mandible: our classification and open treatment experience[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2009, 67(8): 1672-1679. |
| 17 | YING B B, ZHANG Q Q, ZHU S S, et al. Outcomes of treatment for intracapsular fractures of the mandibular condyle: recommendation for a new classification[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2018, 56(2): 139-143. |
| 18 | ASSAEL L A. Open versus closed reduction of adult mandibular condyle fractures: an alternative interpretation of the evidence[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2003, 61(11): 1333-1339. |
| 19 | WANG B L, HE D M, YANG C, et al. Factors affecting the outcomes of non-surgical treatment for intracapsular condylar fractures[J]. Int J Clin Exp Med, 2016, 9(6): 10847-10855. |
| 20 | ELLIS E, THROCKMORTON G S. Treatment of mandibular condylar process fractures: biological considerations[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2005, 63(1): 115-134. |
| 21 | ELLIS E III. Complications of mandibular condyle fractures[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 1998, 27(4): 255-257. |
| 22 | ELLIS E III, SIMON P, THROCKMORTON G S. Occlusal results after open or closed treatment of fractures of the mandibular condylar process[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2000, 58(3): 260-268. |
| 23 | HE D M, CAI Y H, YANG C. Analysis of temporomandibular joint ankylosis caused by condylar fracture in adults[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2014, 72(4): 763.e1-763.e9. |
| 24 | HE D M, ELLIS E III, ZHANG Y. Etiology of temporomandibular joint ankylosis secondary to condylar fractures: the role of concomitant mandibular fractures[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2008, 66(1): 77-84. |
| 25 | SCHNEIDER M, ERASMUS F, GERLACH K L, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation versus closed treatment and mandibulomaxillary fixation of fractures of the mandibular condylar process: a randomized, prospective, multicenter study with special evaluation of fracture level[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2008, 66(12): 2537-2544. |
| 26 | ANDERSSON J, HALLMER F, ERIKSSON L. Unilateral mandibular condylar fractures: a 31-year follow-up of non-surgical treatment[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2007, 36(4): 310-314. |
| 27 | AL-MORAISSI E A, ELLIS E III. Surgical treatment of adult mandibular condylar fractures provides better outcomes than closed treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2015, 73(3): 482-493. |
| 28 | ZHANG X, LI K, HAN C, et al. Prognosis of diacapitular condylar fractures: a multivariate analysis[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2019, 57(10): 1019-1024. |
| 29 | CHANG S P, YANG Y, SHI L Q, et al. Modification of the measurement of the major variables in mandibular condylar fractures: angulation of sidewards displacement and shortening of the height of the ramus[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2018, 56(2): 113-119. |
| 30 | LI J, YANG H B, HAN L. Open versus closed treatment for unilateral mandibular extra-capsular condylar fractures: a meta-analysis[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2019, 47(7): 1110-1119. |
| 31 | ELLIS E III, THROCKMORTON G S, PALMIERI C. Open treatment of condylar process fractures: assessment of adequacy of repositioning and maintenance of stability[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2000, 58(1): 27-34. |
| 32 | HE D M, YANG C, CHEN M J, et al. Modified preauricular approach and rigid internal fixation for intracapsular condyle fracture of the mandible[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2010, 68(7): 1578-1584. |
| 33 | SCHÖN R, FAKLER O, GELLRICH N C, et al. Five-year experience with the transoral endoscopically assisted treatment of displaced condylar mandible fractures[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2005, 116(1): 44-50. |
| 34 | BU L T, CHEN Q, HUANG K, et al. Evaluation of internal fixation techniques for condylar head fractures: a finite element analysis and comparison[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2022, 133(5): e96-e104. |
| 35 | 冯智强, 杨驰, 何冬梅, 等. 339例下颌骨髁突骨折回顾分析[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志, 2009, 7(3): 209-212. |
| FENG Z Q, YANG C, HE D M, et al. Fractures of the mandibular condyle: a retrospective study of 339 cases[J]. China J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2009, 7(3): 209-212. | |
| 36 | 何冬梅, 杨驰. 单(双)侧髁突骨折与合并颌骨骨折的治疗原则[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2009, 44(12): 725-727. |
| HE D M, YANG C. Treatment differences between unilateral and bilateral condylar fractures of the mandible and combined maxillary fractures[J]. Chin J Stomatol, 2009, 44(12): 725-727. | |
| 37 | 冯智强, 何冬梅, 杨驰. 儿童髁突骨折诊断和治疗的现状与展望[J]. 口腔颌面外科杂志, 2008, 18(6): 439-442. |
| FENG Z Q, HE D M, YANG C. Current status and prospects on the diagnosis and treatment of mandibular condyle fractures in children[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2008, 18(6): 439-442. | |
| 38 | 胡敏, 王燕一, 张立海, 等. 手术与非手术治疗儿童下颌骨髁状突骨折的疗效比较[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2010, 24(12): 1440-1443. |
| HU M, WANG Y Y, ZHANG L H, et al. Comparative effectiveness of surgical and non-surgical treatment for pediatric mandibular condylar fractures[J]. Chin J Repara Reconstr Surg, 2010, 24(12): 1440-1443. | |
| 39 | 韩晶, 李智, 周海华, 等. 儿童髁突骨折治疗方法的临床评价与分析[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2014, 49(8): 486-490. |
| HAN J, LI Z, ZHOU H H, et al. Clinical evaluation of open and close treatment in pediatric condylar fractures[J]. Chin J Stomatol, 2014, 49(8): 486-490. | |
| 40 | 王航, 周伟, 安金刚, 等. 儿童髁突骨折临床特点及保守治疗的疗效观察[J]. 现代口腔医学杂志, 2020, 34(4): 227-231. |
| WANG H, ZHOU W, AN J G, et al. Clinical characteristics of pediatric mandibular condylar fractures and the outcomes of closed treatment[J]. J Modern Stomatol, 2020, 34(4): 227-231. | |
| 41 | ZHOU H H, LV K, YANG R T, et al. Abduction of the condyle head leads to condylar resorption: a radiologic study in children with intracapsular fractures[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2019, 123: 168-174. |
| 42 | 朱妍菲, 唐艳梅, 孙蕙珺, 等. 144例儿童髁突骨折闭合性治疗回顾分析[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志, 2017, 15(4): 329-333. |
| ZHU Y F, TANG Y M, SUN H J, et al. Nonsurgical management of condylar fractures in children: a retrospective study of 144 cases[J]. China J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2017, 15(4): 329-333. | |
| 43 | 唐艳梅, 徐兵, 聂萍, 等. 正畸辅助儿童髁突囊内骨折外脱位伴下颌后缩的闭合性治疗[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志, 2015, 13(6): 550-553. |
| TANG Y M, XU B, NIE P, et al. Closed treatment of pediatric dislocated intracapsular condylar fractures with mandibular retrusion using orthodontic appliance[J]. China J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2015, 13(6): 550-553. | |
| 44 | 朱妍菲, 唐艳梅, 孙蕙珺, 等. 2~15岁单侧髁突骨折患者保守治疗后颌骨对称性的三维评价[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2018, 53(5): 318-323. |
| ZHU Y F, TANG Y M, SUN H J, et al. Facial symmetry after conservative treatment of unilateral condylar fracture in children: a three-dimensional study[J]. Chin J Stomatol, 2018, 53(5): 318-323. | |
| 45 | 杜常欣, 徐兵, 朱妍菲, 等. 65例儿童髁突囊内骨折保守治疗临床预后的Helkimo指数评价[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志, 2020, 18(5): 421-426. |
| DU C X, XU B, ZHU Y F, et al. Evaluation of clinical prognosis of condylar intracapsular fractures in 65 children with conservative treatment using Helkimo index[J]. China J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2020, 18(5): 421-426. | |
| 46 | WALKER R V. Condylar fractures: nonsurgical management[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 1994, 52(11): 1185-1188. |
| 47 | LI L Z, FENG Z Q, MA R, et al. The comparative study of mandibular ramus growth with different treatment methods for intracapsular condylar fracture[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2013, 24(2): 657-670. |
| 48 | FENG Z Q, LI L Z, HE D M, et al. Role of retention of the condylar cartilage in open treatment of intracapsular condylar fractures in growing goats: three-dimensional computed tomographic analysis[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2012, 50(6): 523-527. |
| [1] | 吕拥芬, 李嫔. 21-羟化酶缺乏症的分子诊断及临床意义[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(5): 557-561. |
| [2] | 邓露, 李佳怡. 点阵CO2激光治疗女性压力性尿失禁的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(5): 685-689. |
| [3] | 王衍鸿, 韩稷钰, 万大千. 下肢外骨骼机器人对关节镜下半月板修补术后患者功能重建的治疗效果[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(3): 337-343. |
| [4] | 林艳艳, 许岩, 李慧. 儿童急性淋巴细胞白血病化学治疗常规药物耐药机制的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(2): 211-217. |
| [5] | 邹弋华, 彭婕, 赵培泉. 先天性视盘凹陷性异常的临床特征与治疗研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(2): 230-234. |
| [6] | 陈炜, 刘颖斌. 肝门部胆管癌综合治疗的进展与争议[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(1): 1-8. |
| [7] | 张宇, 吴晓渊, 管丽华, 刘译远, 彭星月, 谢海燕, 胡玮, 郝可可, 夏宁, 陆国军, 侯志波. 高通量药物敏感性筛选系统在非小细胞肺癌伴恶性胸腔积液治疗中的应用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(1): 82-89. |
| [8] | 李莉莎, 李建辉, 何斌, 吴楠楠, 朱同玉, 郭晓奎, 陈峥宏. 噬菌体治疗泛耐药肺炎克雷伯菌肺部感染的临床应用及效果初探[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(9): 1272-1276. |
| [9] | 熊雷, 易茜, 许明芳, 陈健. MRPL12在肺腺癌中的表达和预后分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(8): 1033-1040. |
| [10] | 周珺珺, 赵洁, 汤静燕, 蒋马伟, 马秀梅, 白永瑞. Ⅲ~Ⅳ期神经母细胞瘤患儿放射治疗预后因素分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(8): 1051-1055. |
| [11] | 李静威, 王俐文, 蒋玲曦, 詹茜, 陈皓, 沈柏用. 胰腺癌免疫抑制性肿瘤微环境研究综述[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(8): 1103-1108. |
| [12] | 凌徐心仪, 张瑶, 钟华. 非小细胞肺癌免疫治疗获益人群筛选的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(8): 1114-1119. |
| [13] | 陈博, 赵鹏军. 儿童室性早搏诱发心肌病的危险因素及其干预策略[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(7): 977-981. |
| [14] | 马韵芳, 潘丽娜, 李圳, 高蓓莉, 胡家安, 徐志红. 司美替尼下调KRAS G12V突变型非小细胞肺癌细胞PD-L1水平的探索性研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(6): 741-748. |
| [15] | 朱嘉莳, 李红, 邵静波, 张娜, 杨静薇, 陈凯, 王真, 蒋慧. 急性淋巴细胞白血病儿童治疗失败原因的分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(6): 764-769. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 4508
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 1795
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
