
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (7): 847-858.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2024.07.006
• 论著 · 基础研究 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2023-12-15
接受日期:2024-06-18
出版日期:2024-07-28
发布日期:2024-07-28
通讯作者:
杜晓刚
E-mail:972478353@qq.com;cqmudxg@163.com
作者简介:魏云鑫(1996—),男,硕士生;电子信箱:972478353@qq.com。
基金资助:
WEI Yunxin( ), JIANG Xushun, CAI Mengyao, WEN Ruizhi, DU Xiaogang(
), JIANG Xushun, CAI Mengyao, WEN Ruizhi, DU Xiaogang( )
)
Received:2023-12-15
Accepted:2024-06-18
Online:2024-07-28
Published:2024-07-28
Contact:
DU Xiaogang
E-mail:972478353@qq.com;cqmudxg@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的·通过研究高糖环境下肾小球足细胞中软骨寡聚基质蛋白(cartilage oligomeric matrix protein,COMP)与自噬的关系,进一步阐明在高糖环境下足细胞受损的可能机制。方法·从GENE EXPRESSION OMNIBUS(GEO)数据库下载基因表达数据集GSE104948,使用GEO2R筛选差异表达基因(differentially expressed gene,DEG),并对筛选出来的DEG进行富集分析。将加权基因共表达网络分析(Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis,WGCNA)与STRING数据库构建 DEG的蛋白互作网络(protein protein interaction network,PPI)获得的相关性最高的关键基因(hub gene)取交集,并再次进行富集分析。体外培养条件永生性小鼠足细胞株,待其分化完全后,采用高糖刺激,Western blotting检测足细胞COMP、哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR)、微管相关蛋白1A/1B-轻链3(microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain3,LC3/MAP1LC3)等蛋白的表达。进一步通过抑制COMP的shRNA慢病毒载体感染足细胞以抑制COMP表达,并通过嘌呤霉素筛选稳定株,经Western blotting检测稳定株COMP、mTOR、LC3的表达,以观察COMP对自噬的影响。结果·共筛选出362个DEG进行后续分析。在这些DEG中,284个基因上调,78个基因下调。基因本体论(Gene Onotology,GO)术语分析结果显示,糖尿病肾病(diabetic nephropathy,DN)数据集中的DEG主要富集于细胞表面受体信号通路、受体结合等。主要富集的京都基因和基因组数据库(Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes,KEGG)通路包括细胞因子?细胞因子受体相互作用、磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase,PI3K)/蛋白激酶B(protein kinase B,PKB/AKT)信号通路等。WGCNA和PPI两部分hub基因取交集,验证了64个hub基因,再次用KEGG注释hub基因,发现大部分hub基因富集在“细胞外基质(extracellular matrix,ECM)?受体相互作用”和“PI3K/AKT信号通路”。在64个hub基因中,COMP呈显著高表达(logFC>2),而PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路是经典的自噬通路,提示COMP可能通过该通路影响细胞自噬。Western blotting结果显示,与甘露醇对照组、低糖组比较,高糖刺激下足细胞COMP表达明显升高。与对照组相比,高糖组LC3-Ⅱ的水平明显降低,表明高糖环境下足细胞的自噬启动受到了抑制。与阴性对照相比,敲低COMP的小鼠肾足细胞LC3-Ⅱ水平明显升高,mTOR随着COMP水平的降低也有所下降,表明抑制COMP有助于足细胞的自噬恢复。结论·DN患者的COMP高表达,高度富集于ECM受体和PI3K/AKT信号通路。高糖环境下小鼠肾足细胞自噬受到抑制,高糖诱导的足细胞COMP高表达可能是自噬抑制的关键因素,抑制COMP有助于小鼠肾足细胞的自噬恢复。
中图分类号:
魏云鑫, 蒋绪顺, 蔡梦瑶, 温睿智, 杜晓刚. COMP与糖尿病肾病自噬相关性分析及其功能验证[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(7): 847-858.
WEI Yunxin, JIANG Xushun, CAI Mengyao, WEN Ruizhi, DU Xiaogang. Correlation analysis of COMP and autophagy in diabetic nephropathy and its functional verification[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(7): 847-858.
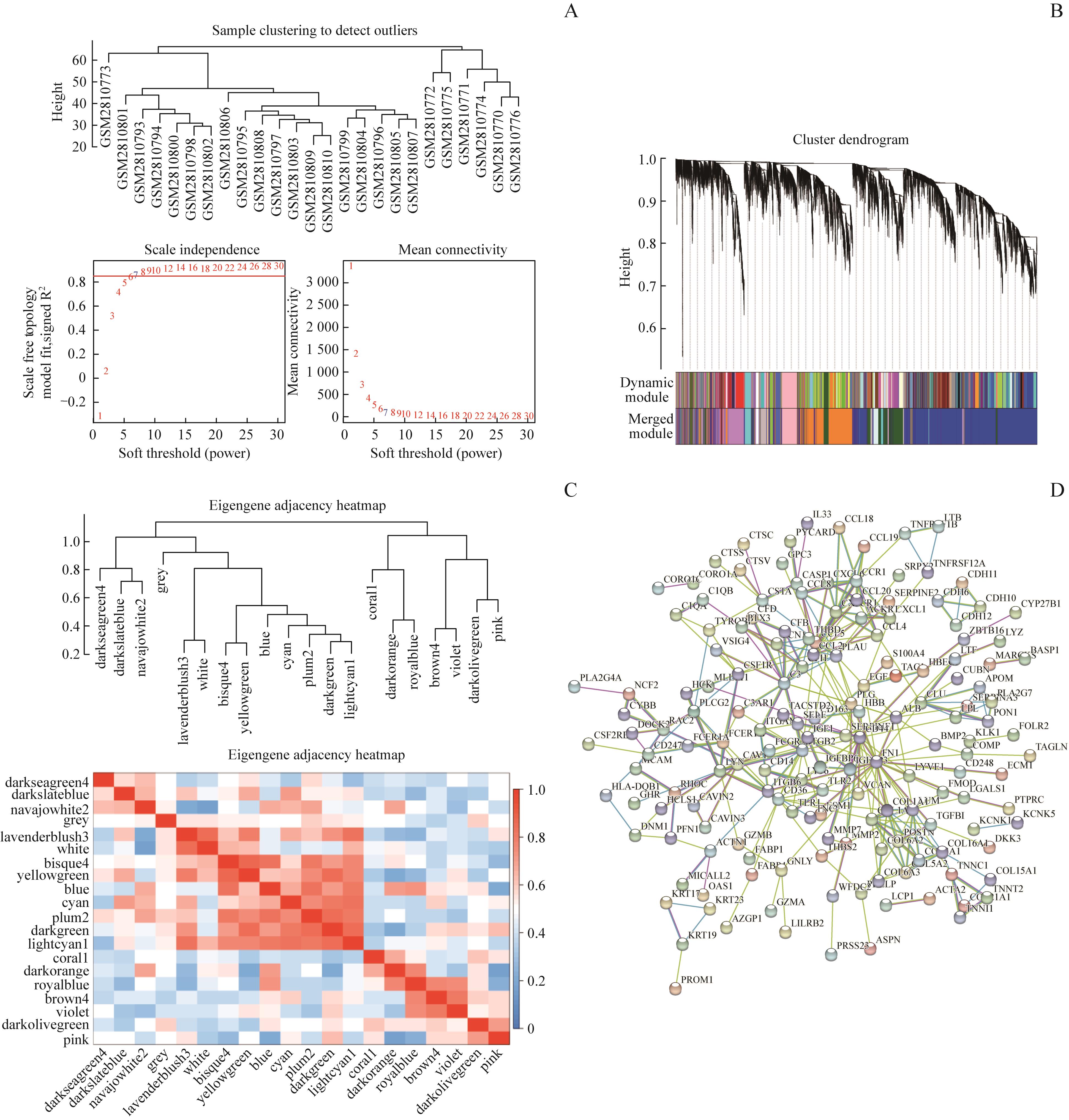
图1 WGCNA和PPI筛选hub基因Note: A. Soft threshold (power). B. Cluster dendrogram. C. Eigengene adjacency heatmap. D. Protein protein interaction network.
Fig 1 Hub genes screened by WGCNA and PPI
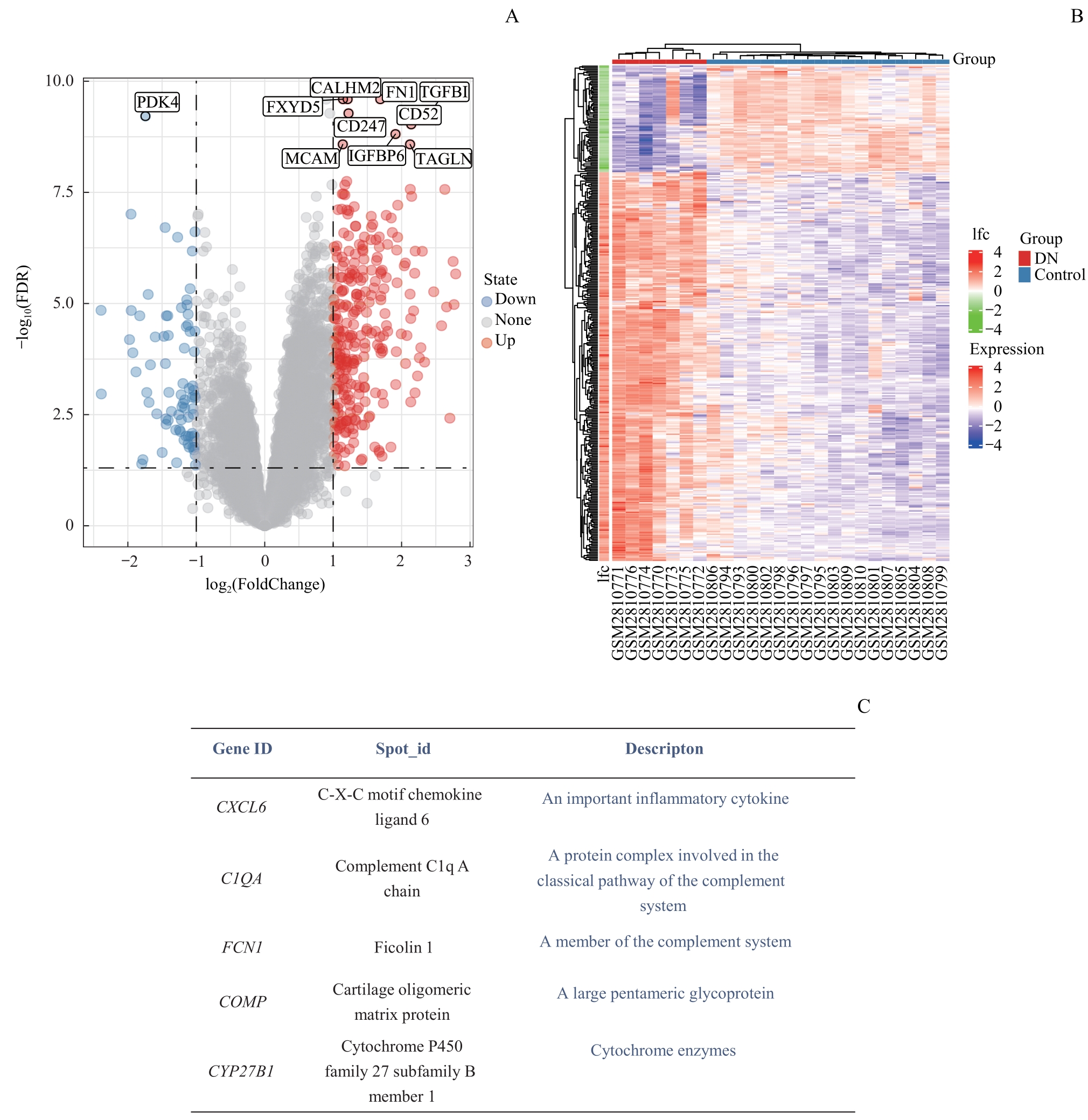
图2 差异表达基因筛选Note: A. Volcano map of differential expression genes. B. Heat map of differential expression genes. C. Significantly different expression genes and their definitions.
Fig 2 Differential expression genes screening
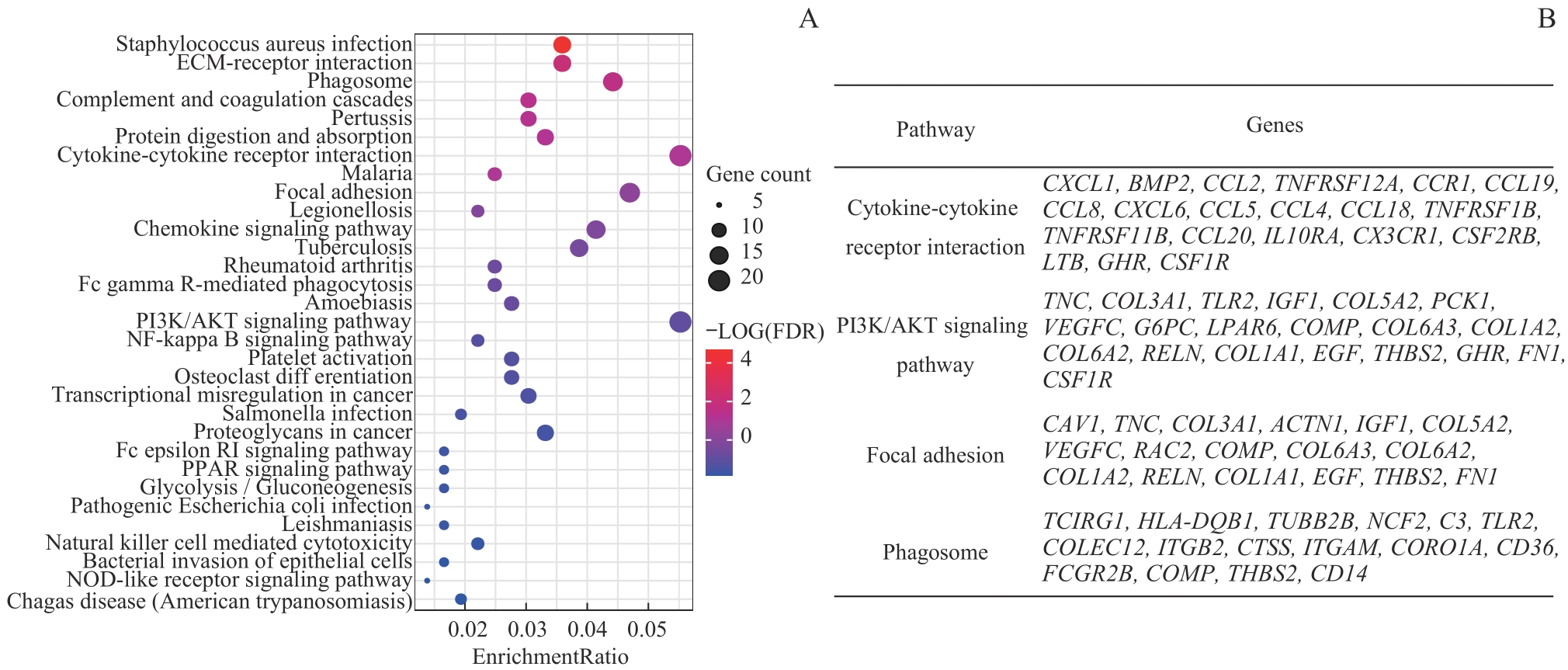
图3 差异基因KEGG分析Note: A. KEGG enriched gene bubble chart. B. Four signaling pathways with the most differentially enriched genes and corresponding differential expression genes.
Fig 3 KEGG analysis of differential expression genes
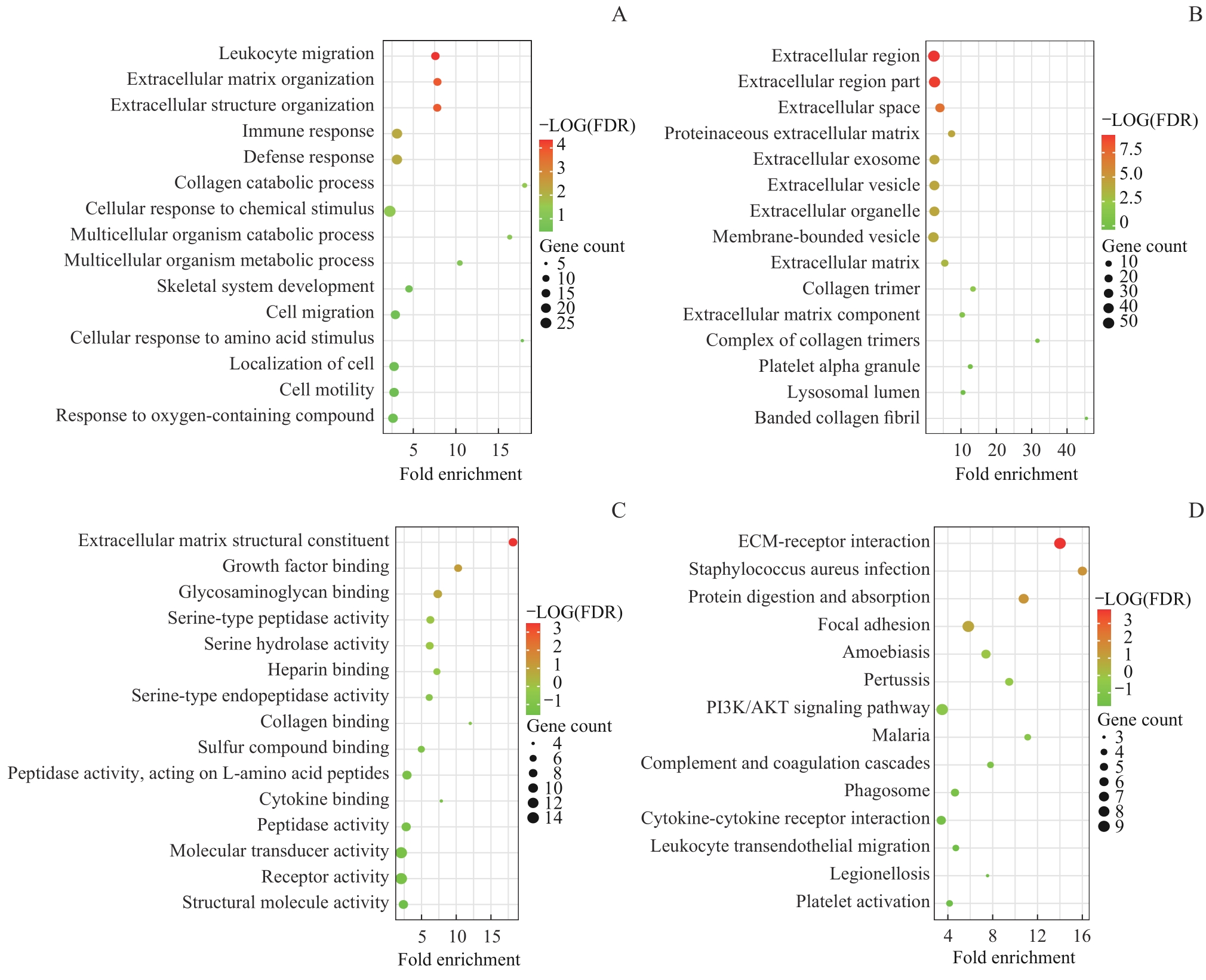
图4 Hub基因富集分析Note: A. Biological process (BP). B. Cell localization (CC). C. Molecular function (MF). D. Signaling pathway (KEGG).
Fig 4 Hub gene enrichment analysis
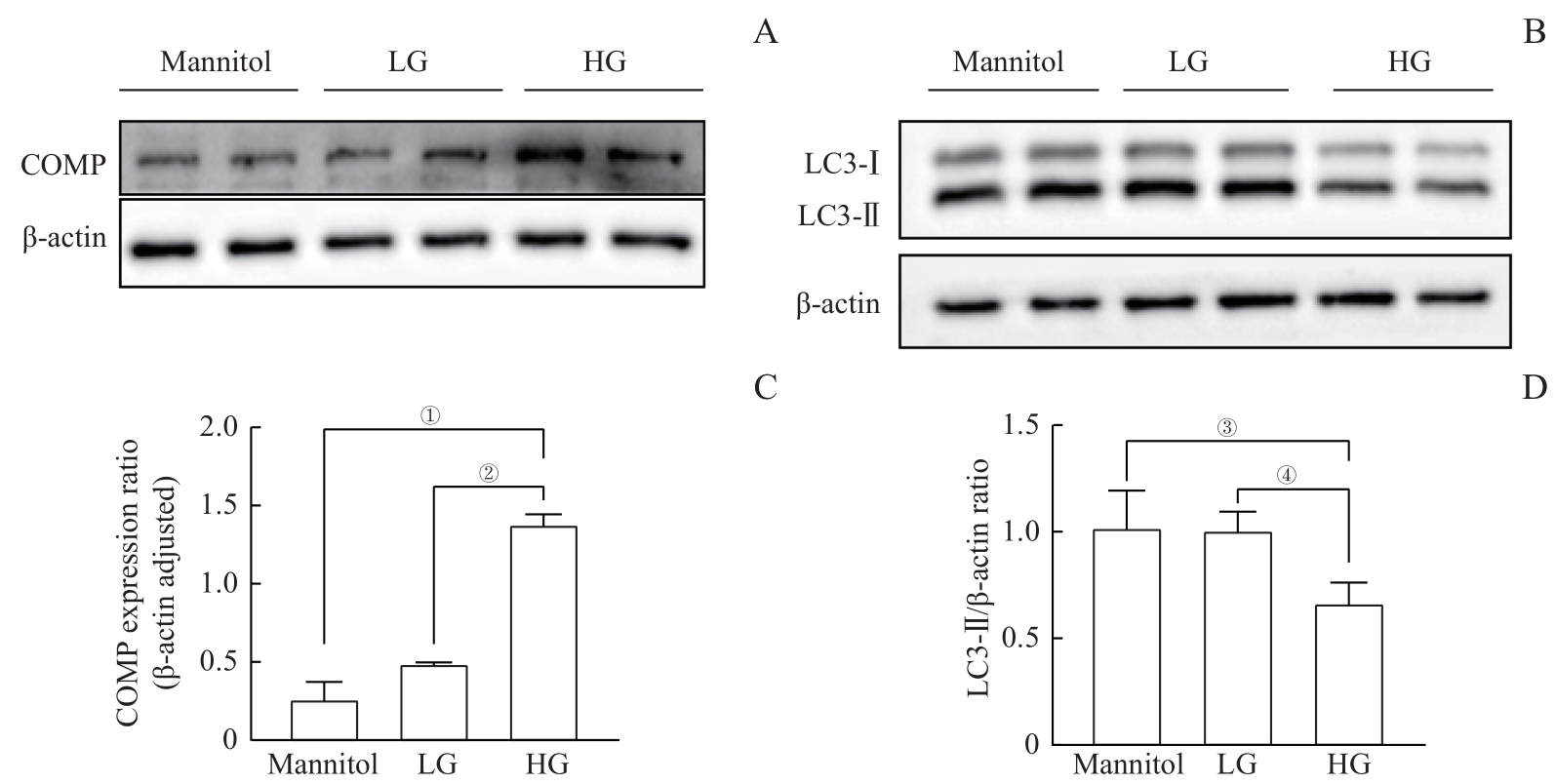
图5 高糖诱导的COMP过表达并抑制自噬Note: A. The Western blotting results showed that compared with the mannitol control group and the LG group, the expression of COMP significantly increased under high glucose condition. B. The Western blotting results showed that compared with the mannitol control group and the LG group, the expression of LC3-Ⅱ was significantly reduced under high glucose condition. C. Quantitative statistics were conducted on Figure A, and the mean±standard deviation of each group was 0.26±0.19 for the mannitol group, 0.49±0.01 for the LG group, and 1.38±0.11 for the HG group. ①P=0.008, ②P=0.011. D. Quantitative statistics were performed on Figure B. The mean±standard deviation of each group was 1.02±0.17 for the mannitol group, 1.01±0.09 for the LG group, and 0.67±0.10 for the HG group. ③P=0.007, ④P=0.000。
Fig 5 High glucose-induced COMP overexpressed and inhibited autophagy
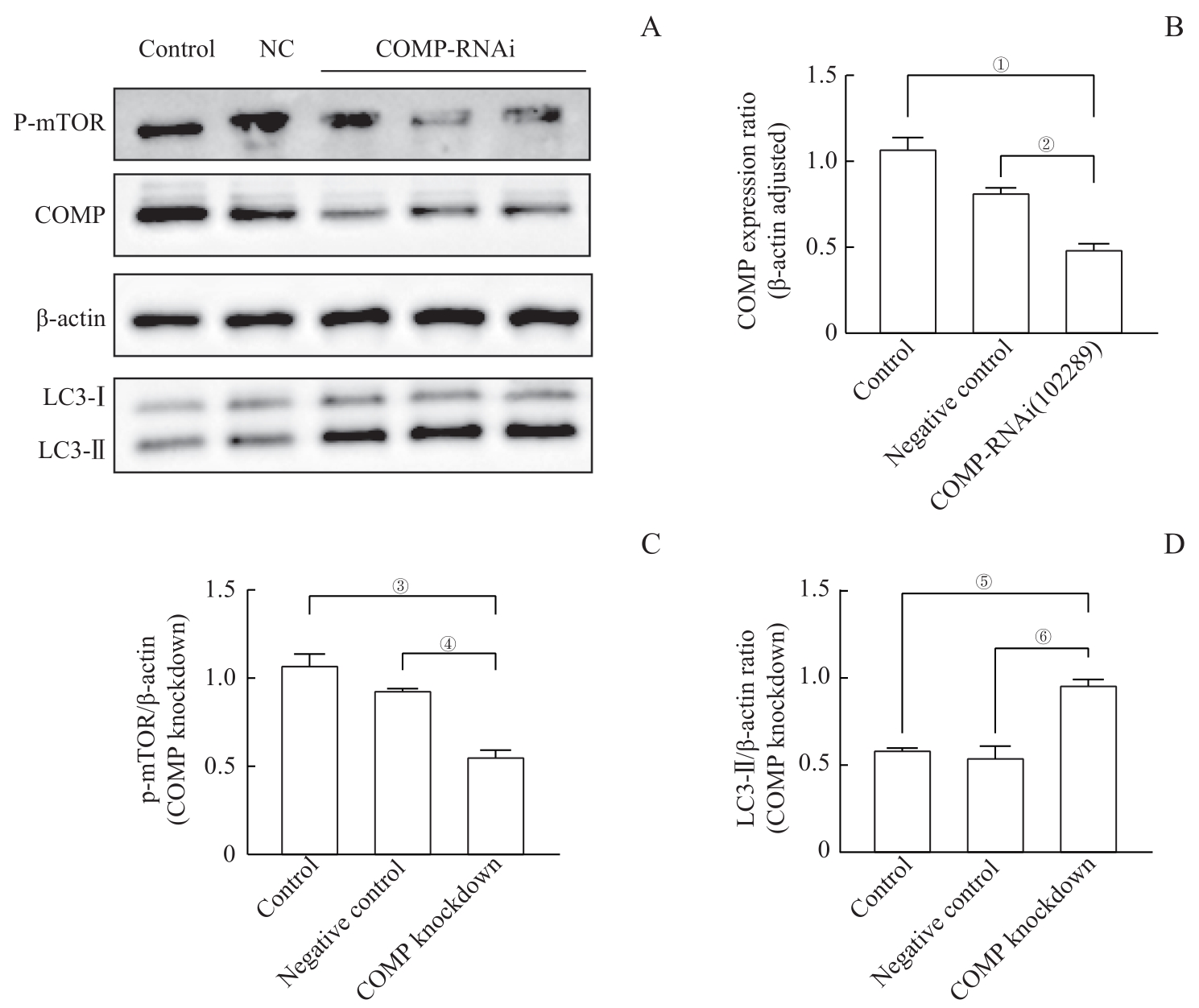
图6 敲低 COMP 水平促使足细胞mTOR表达降低和LC3-Ⅱ表达增加Note: A. The Western blotting results showed that in the cells infected with lentivirus, the expression of COMP was significantly reduced in the control group (control) and negative control group (NC), while the expression of p-mTOR was reduced and the expression of LC3-Ⅱ was significantly increased. B. The quantitative visualization view of COMP in Figure A shows that the mean±standard deviation of each group is 1.12±0.07 in the control group, 0.75±0.08 in the NC group, and 0.37±0.09 in the COMP RNAi (102289) group. ①P=0.000, ②P=0.004. C. The p-mTOR quantitative visualization view of Figure A shows mean±standard deviation for each group: 1.78±0.29 for the control group, 0.93±0.01 for the NC group, and 0.56±0.06 for the COMP RNAi (102289) group. ③P=0.005, ④P=0.018. D. The quantitative visualization view of LC3-Ⅱ in Figure A shows the mean±standard deviation of each group: 0.59±0.01 for the control group, 0.55±0.11 for the NC group, and 0.96±0.05 for the COMP RNAi (102289) group. ⑤P=0.007, ⑥P=0.003.
Fig 6 Knockdown of COMP levels reduced mTOR expression and increased LC3 expression in podocytes
| 1 | THOMAS M C, BROWNLEE M, SUSZTAK K, et al. Diabetic kidney disease[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2015, 1: 15018. |
| 2 | CAMERON J S. The discovery of diabetic nephropathy: from small print to centre stage[J]. J Nephrol, 2006, 19(Suppl 10): S75-S87. |
| 3 | ATKINS R C, ZIMMET P. Diabetic kidney disease: act now or pay later[J]. Kidney Int, 2010, 77(5): 375-377. |
| 4 | ZIYADEH F N, WOLF G. Pathogenesis of the podocytopathy and proteinuria in diabetic glomerulopathy[J]. Curr Diabetes Rev, 2008, 4(1): 39-45. |
| 5 | MIZUSHIMA N, KOMATSU M. Autophagy: renovation of cells and tissues[J]. Cell, 2011, 147(4): 728-741. |
| 6 | HE C C, KLIONSKY D J. Regulation mechanisms and signaling pathways of autophagy[J]. Annu Rev Genet, 2009, 43: 67-93. |
| 7 | KATAYAMA M, KAWAGUCHI T, BERGER M S, et al. DNA damaging agent-induced autophagy produces a cytoprotective adenosine triphosphate surge in malignant glioma cells[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2007, 14(3): 548-558. |
| 8 | RACANELLI A C, KIKKERS S A, CHOI A M K, et al. Autophagy and inflammation in chronic respiratory disease[J]. Autophagy, 2018, 14(2): 221-232. |
| 9 | BRAVO-SAN PEDRO J M, KROEMER G, GALLUZZI L. Autophagy and mitophagy in cardiovascular disease[J]. Circ Res, 2017, 120(11): 1812-1824. |
| 10 | DUANN P, LIANOS E A, MA J J, et al. Autophagy, innate immunity and tissue repair in acute kidney injury[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2016, 17(5): 662. |
| 11 | CHEN W T, HUNG K C, WEN M S, et al. Impaired leukocytes autophagy in chronic kidney disease patients[J]. Cardiorenal Med, 2013, 3(4): 254-264. |
| 12 | YASUDA-YAMAHARA M, KUME S, TAGAWA A, et al. Emerging role of podocyte autophagy in the progression of diabetic nephropathy[J]. Autophagy, 2015, 11(12): 2385-2386. |
| 13 | KUME S, THOMAS M C, KOYA D. Nutrient sensing, autophagy, and diabetic nephropathy[J]. Diabetes, 2012, 61(1): 23-29. |
| 14 | JIANG X S, CHEN X M, WAN J M, et al. Autophagy protects against palmitic acid-induced apoptosis in podocytes in vitro[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 42764. |
| 15 | YU S M W, BONVENTRE J V. Acute kidney injury and progression of diabetic kidney disease[J]. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis, 2018, 25(2): 166-180. |
| 16 | LIN Q S, BANU K, NI Z H, et al. Podocyte autophagy in homeostasis and disease[J]. J Clin Med, 2021, 10(6): 1184. |
| 17 | YANG D Y, LIVINGSTON M J, LIU Z W, et al. Autophagy in diabetic kidney disease: regulation, pathological role and therapeutic potential[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2018, 75(4): 669-688. |
| 18 | TAGAWA A, YASUDA M, KUME S, et al. Impaired podocyte autophagy exacerbates proteinuria in diabetic nephropathy[J]. Diabetes, 2016, 65(3): 755-767. |
| 19 | JIANG X S, XIANG X Y, CHEN X M, et al. Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase attenuates renal tubular mitochondrial dysfunction and ER stress by restoring autophagic flux in diabetic nephropathy[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(5): 385. |
| 20 | LENOIR O, JASIEK M, HÉNIQUE C, et al. Endothelial cell and podocyte autophagy synergistically protect from diabetes-induced glomerulosclerosis[J]. Autophagy, 2015, 11(7): 1130-1145. |
| 21 | LAPLANTE M, SABATINI D. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease[J]. Cell, 2012, 149(2): 274-293. |
| 22 | WULLSCHLEGER S, LOEWITH R, HALL M N. TOR signaling in growth and metabolism[J]. Cell, 2006, 124(3): 471-484. |
| 23 | HAY N, SONENBERG N. Upstream and downstream of mTOR[J]. Genes Dev, 2004, 18(16): 1926-1945. |
| 24 | INOKI K, MORI H, WANG J Y, et al. mTORC1 activation in podocytes is a critical step in the development of diabetic nephropathy in mice[J]. J Clin Invest, 2011, 121(6): 2181-2196. |
| 25 | XIAO T L, GUAN X, NIE L, et al. Rapamycin promotes podocyte autophagy and ameliorates renal injury in diabetic mice[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2014, 394(1): 145-154. |
| 26 | GÖDEL M, HARTLEBEN B, HERBACH N, et al. Role of mTOR in podocyte function and diabetic nephropathy in humans and mice[J]. J Clin Invest, 2011, 121(6): 2197-2209. |
| 27 | CINÀ D P, ONAY T, PALTOO A, et al. Inhibition of MTOR disrupts autophagic flux in podocytes[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2012, 23(3): 412-420. |
| 28 | POSEY K L, COUSTRY F, HECHT J T. Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein: compopathies and beyond[J]. Matrix Biol, 2018, 71/72: 161-173. |
| 29 | LI Q, WANG C, WANG Y F, et al. HSCs-derived COMP drives hepatocellular carcinoma progression by activating MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 37(1): 231. |
| 30 | ASANUMA K, MUNDEL P. The role of podocytes in glomerular pathobiology[J]. Clin Exp Nephrol, 2003, 7(4): 255-259. |
| 31 | LI Y, PAN Y, CAO S R, et al. Podocyte EGFR inhibits autophagy through upregulation of Rubicon in type 2 diabetic nephropathy[J]. Diabetes, 2021, 70(2): 562-576. |
| 32 | KAWACHI H, MIYAUCHI N, SUZUKI K, et al. Role of podocyte slit diaphragm as a filtration barrier[J]. Nephrology (Carlton), 2006, 11(4): 274-281. |
| 33 | ANIL KUMAR P, WELSH G I, SALEEM M A, et al. Molecular and cellular events mediating glomerular podocyte dysfunction and depletion in diabetes mellitus[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2014, 5: 151. |
| 34 | LIN J S, SUSZTAK K. Podocytes: the weakest link in diabetic kidney disease?[J]. Curr Diab Rep, 2016, 16(5): 45. |
| 35 | NAGATA M. Podocyte injury and its consequences[J]. Kidney Int, 2016, 89(6): 1221-1230. |
| 36 | WIGGINS J E, GOYAL M, SANDEN S K, et al. Podocyte hypertrophy, “adaptation,” and “decompensation” associated with glomerular enlargement and glomerulosclerosis in the aging rat: prevention by calorie restriction[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2005, 16(10): 2953-2966. |
| 37 | PAGTALUNAN M E, MILLER P L, JUMPING-EAGLE S, et al. Podocyte loss and progressive glomerular injury in type II diabetes[J]. J Clin Invest, 1997, 99(2): 342-348. |
| 38 | SUSZTAK K, RAFF A C, SCHIFFER M, et al. Glucose-induced reactive oxygen species cause apoptosis of podocytes and podocyte depletion at the onset of diabetic nephropathy[J]. Diabetes, 2006, 55(1): 225-233. |
| 39 | YI M X, ZHANG L, LIU Y, et al. Autophagy is activated to protect against podocyte injury in adriamycin-induced nephropathy[J]. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2017, 313(1): F74-F84. |
| 40 | PARZYCH K R, KLIONSKY D J. An overview of autophagy: morphology, mechanism, and regulation[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2014, 20(3): 460-473. |
| 41 | QI Y Y, ZHOU X J, CHENG F J, et al. Increased autophagy is cytoprotective against podocyte injury induced by antibody and interferon-α in lupus nephritis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2018, 77(12): 1799-1809. |
| 42 | SUN M Y, WANG S J, LI X Q, et al. CXCL6 promotes renal interstitial fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy by activating JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2019, 10: 224. |
| 43 | ZHENG S T, SHEN T X, LIU Q, et al. CXCL6 fuels the growth and metastases of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells both in vitro and in vivo through upregulation of PD-L1 via activation of STAT3 pathway[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2021, 236(7): 5373-5386. |
| 44 | JUN W D, MAKINO H. Inflammation and the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy[J]. Clin Sci (Lond), 2013, 124(3): 139-152. |
| 45 | SAMSU N. Diabetic nephropathy: challenges in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2021, 2021: 1497449. |
| 46 | THOMAS M C, GROOP P H, TRYGGVASON K. Towards understanding the inherited susceptibility for nephropathy in diabetes[J]. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens, 2012, 21(2): 195-202. |
| 47 | FREEDMAN B I, BOSTROM M, DAEIHAGH P, et al. Genetic factors in diabetic nephropathy[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2007, 2(6): 1306-1316. |
| 48 | VUGA L J, MILOSEVIC J, PANDIT K, et al. Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(12): e83120. |
| 49 | MAGDALENO F, ARRIAZU E, DE GALARRETA M R, et al. Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein participates in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 65(5): 963-971. |
| 50 | HOLDEN P, MEADOWS R S, CHAPMAN K L, et al. Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein interacts with type IX collagen, and disruptions to these interactions identify a pathogenetic mechanism in a bone dysplasia family[J]. J Biol Chem, 2001, 276(8): 6046-6055. |
| 51 | TAN K M, DUQUETTE M, JOACHIMIAK A, et al. The crystal structure of the signature domain of cartilage oligomeric matrix protein: implications for collagen, glycosaminoglycan and integrin binding[J]. FASEB J, 2009, 23(8): 2490-2501. |
| 52 | CHEN F H, HERNDON M E, PATEL N, et al. Interaction of cartilage oligomeric matrix protein/thrombospondin 5 with aggrecan[J]. J Biol Chem, 2007, 282(34): 24591-24598. |
| 53 | DI CESARE P E, CHEN F S, MOERGELIN M, et al. Matrix-matrix interaction of cartilage oligomeric matrix protein and fibronectin[J]. Matrix Biol, 2002, 21(5): 461-470. |
| 54 | FU Y, KONG W. Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein: matricellular and matricrine signaling in cardiovascular homeostasis and disease[J]. Curr Vasc Pharmacol, 2017, 15(3): 186-196. |
| 55 | WISŁOWSKA M, JABŁOŃSKA B. Serum cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) in rheumatoid arthritis and knee osteoarthritis[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2005, 24(3): 278-284. |
| 56 | HUA W, HUANG H Z, TAN L T, et al. CD36 mediated fatty acid-induced podocyte apoptosis via oxidative stress[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(5): e0127507. |
| 57 | HUANG Y Q, XIA J H, ZHENG J G, et al. Deficiency of cartilage oligomeric matrix protein causes dilated cardiomyopathy[J]. Basic Res Cardiol, 2013, 108(5): 374. |
| [1] | 王鑫, 王晓霞, 李彦庆, 郑永鑫, 乌杰, 任猛, 贾向东, 许天祥. 香叶基香叶基焦磷酸合成酶在肺鳞状细胞癌中的表达及临床意义[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(3): 312-324. |
| [2] | 邓青松, 张长青, 陶诗聪. 烟酰胺代谢相关基因与骨关节炎的关系探索[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(2): 145-160. |
| [3] | 王莹, 平立风, 刘彤彤, 刘珊珊, 刘磊. 甲基莲心碱调节SDF-1/CXCR4信号通路对糖尿病肾病的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(2): 183-195. |
| [4] | 贾君杰, 邢海帆, 张群子, 刘奇烨, 汪年松, 范瑛. 缺氧诱导因子-1α抑 制剂YC-1改善糖尿病肾病小鼠肾脏损伤的机制研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(9): 1089-1098. |
| [5] | 高楠, 郝璨, 马冰洁, 靳天, 马柯, 刘晓明. 转位分子蛋白经由Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1通路激活自噬缓解大鼠糖尿病神经病理性疼痛[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(8): 988-996. |
| [6] | 杜少倩, 陶梦玉, 曹源, 王红霞, 胡孝渠, 范广建, 臧丽娟. CXCL9在乳腺癌中的表达及其与肿瘤免疫浸润特征的相关性研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(7): 860-872. |
| [7] | 吴淇琦, 汪豪, 林砺, 晏博, 张舒林. miR-185-5p通过抑制巨噬细胞自噬促进胞内分枝杆菌生长[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(6): 699-708. |
| [8] | 金芳全, 樊成虎, 唐晓栋, 陈彦同, 齐兵献. 线粒体功能障碍与骨质疏松症相关性研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(6): 761-767. |
| [9] | 李清林, 王文波, 刘伟. 肌腱去应力退化机制的生物信息学分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(5): 560-570. |
| [10] | 陈奕馨, 程丽珍, 林祎嘉, 苗雅. 2型糖尿病脑病小鼠海马中转录因子EB活性与自噬功能的变化[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(2): 162-170. |
| [11] | 李偲媛, 和申, 李华芳. 重度抑郁症中自噬通路及其关键标志物的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(10): 1324-1331. |
| [12] | 吴佳晋, 钟晨, 李大伟, 陈若洋, 瞿俊文, 张明. 甲基转移酶3调控pri-miR-21甲基化修饰在糖尿病肾病肾脏纤维化中的作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(1): 1-7. |
| [13] | 王雪敏, 王亚楠, 牛爱琴, 叶英, 李飞. 微RNA-30b-5p通过靶向Atg5抑制多囊卵巢综合征大鼠卵巢颗粒细胞自噬[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(1): 20-28. |
| [14] | 韩夏夏, 蒋扬, 顾霜霜, 戴黛, 沈南. 系统性红斑狼疮患者免疫细胞代谢通路转录组分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(9): 1197-1207. |
| [15] | 靳步, 袁颖, 陈婉玉, 徐浒东, 黄晓蕾, 何佳璐, 于红. 基于GEO数据库探索miRNA靶基因通过泛素化参与食管鳞状细胞癌[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(4): 464-471. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 340
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||