
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 1662-1670.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2025.12.012
• 综述 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2025-07-31
接受日期:2025-11-11
出版日期:2025-12-19
发布日期:2025-12-19
通讯作者:
冷一铭,助理研究员,博士;电子信箱:lyiming2010xy@126.com。基金资助:
QIN Zihao1, YUAN Hong1, LU Yao1, LENG Yiming1,2( )
)
Received:2025-07-31
Accepted:2025-11-11
Online:2025-12-19
Published:2025-12-19
Contact:
LENG Yiming, E-mail: lyiming2010xy@126.com.Supported by:摘要:
心血管损伤与修复依赖于多种细胞的募集、增殖与分化。CD34+细胞作为一类以分化簇34(cluster of differentiation 34,CD34)蛋白为标志物的异质性细胞群体,长期被视为心血管再生与修复的关键靶点。该类细胞可展现出高度的异质性与多向分化潜能,在特定的微环境信号调控下,能够分化为内皮细胞、平滑肌细胞、成纤维细胞、炎症细胞等多种谱系,在内皮修复、组织纤维化、免疫调节等过程中发挥重要作用。在心血管疾病中CD34+细胞可介导双重调控作用:既能促进组织修复与再生,又可能加剧病理损伤。尽管CD34⁺细胞疗法在心血管疾病中已具有良好的治疗潜力,但其向临床转化的过程仍面临诸多挑战与瓶颈。基于此,该文系统梳理了CD34⁺细胞的来源、分化轨迹与功能异质性,总结其在心血管基础研究与临床转化中的最新进展,旨在为深化疾病机制理解、开发新型精准治疗策略提供新视角。
中图分类号:
秦梓豪, 袁洪, 陆瑶, 冷一铭. CD34+细胞异质性在心血管损伤与修复中的多重角色[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(12): 1662-1670.
QIN Zihao, YUAN Hong, LU Yao, LENG Yiming. Multiple roles of CD34⁺ cell heterogeneity in cardiovascular injury and repair[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(12): 1662-1670.
| Cell subset | Distribution | Marker | Principal function |
|---|---|---|---|
| HSCs | Bone marrow, peripheral blood | Lin-, CD34+, CD38-, CD90+, CD45RA- | Hematopoiesis and long-term reconstitution |
| EPCs | Bone marrow, peripheral blood, vascular intima, multiple organs | CD34+, CD133+, VEGFR2+, CD31+, VE-cadherin+, vWF+, CD45- | Endothelial repair and angiogenesis |
| Inflammatory cells | Bone marrow, peripheral blood, tissues | CD45+ | Immune responses and inflammation |
| Fibroblasts | Interstitium across organs | CD34+, PDGFRα+, PI16+ (mouse) | Matrix production, tissue repair, and regulation of fibrosis |
| Fibroblast progenitors | Multiple organs | CD34+ Sca1+(mouse), PI16+ (mouse), POSTN+ | Differentiation into fibroblasts/myofibroblasts |
| SMCs | Multiple organs | αSMA+, MYH11+, SM22α+, CNN1+ | Contractility and vascular tone, and remodeling in injury/fibrosis |
| SMPCs | Multiple organs | Sca1+ (mouse), CD34+, PDGFRβ+ | Differentiation into SMCs and fibroblast-like lineages |
| MSCs | Bone marrow, adipose tissue, multiple organs | CD29+, CD44+, CD73+, CD90+, CD105+, CD34+ | Osteogenic, chondrogenic, and adipogenic differentiation |
表1 CD34⁺细胞及其分化细胞的组织分布、表型标志物与功能概览
Tab 1 Overview of tissue distribution, phenotypic markers, and functions of CD34⁺ cells and their differentiated lineages
| Cell subset | Distribution | Marker | Principal function |
|---|---|---|---|
| HSCs | Bone marrow, peripheral blood | Lin-, CD34+, CD38-, CD90+, CD45RA- | Hematopoiesis and long-term reconstitution |
| EPCs | Bone marrow, peripheral blood, vascular intima, multiple organs | CD34+, CD133+, VEGFR2+, CD31+, VE-cadherin+, vWF+, CD45- | Endothelial repair and angiogenesis |
| Inflammatory cells | Bone marrow, peripheral blood, tissues | CD45+ | Immune responses and inflammation |
| Fibroblasts | Interstitium across organs | CD34+, PDGFRα+, PI16+ (mouse) | Matrix production, tissue repair, and regulation of fibrosis |
| Fibroblast progenitors | Multiple organs | CD34+ Sca1+(mouse), PI16+ (mouse), POSTN+ | Differentiation into fibroblasts/myofibroblasts |
| SMCs | Multiple organs | αSMA+, MYH11+, SM22α+, CNN1+ | Contractility and vascular tone, and remodeling in injury/fibrosis |
| SMPCs | Multiple organs | Sca1+ (mouse), CD34+, PDGFRβ+ | Differentiation into SMCs and fibroblast-like lineages |
| MSCs | Bone marrow, adipose tissue, multiple organs | CD29+, CD44+, CD73+, CD90+, CD105+, CD34+ | Osteogenic, chondrogenic, and adipogenic differentiation |
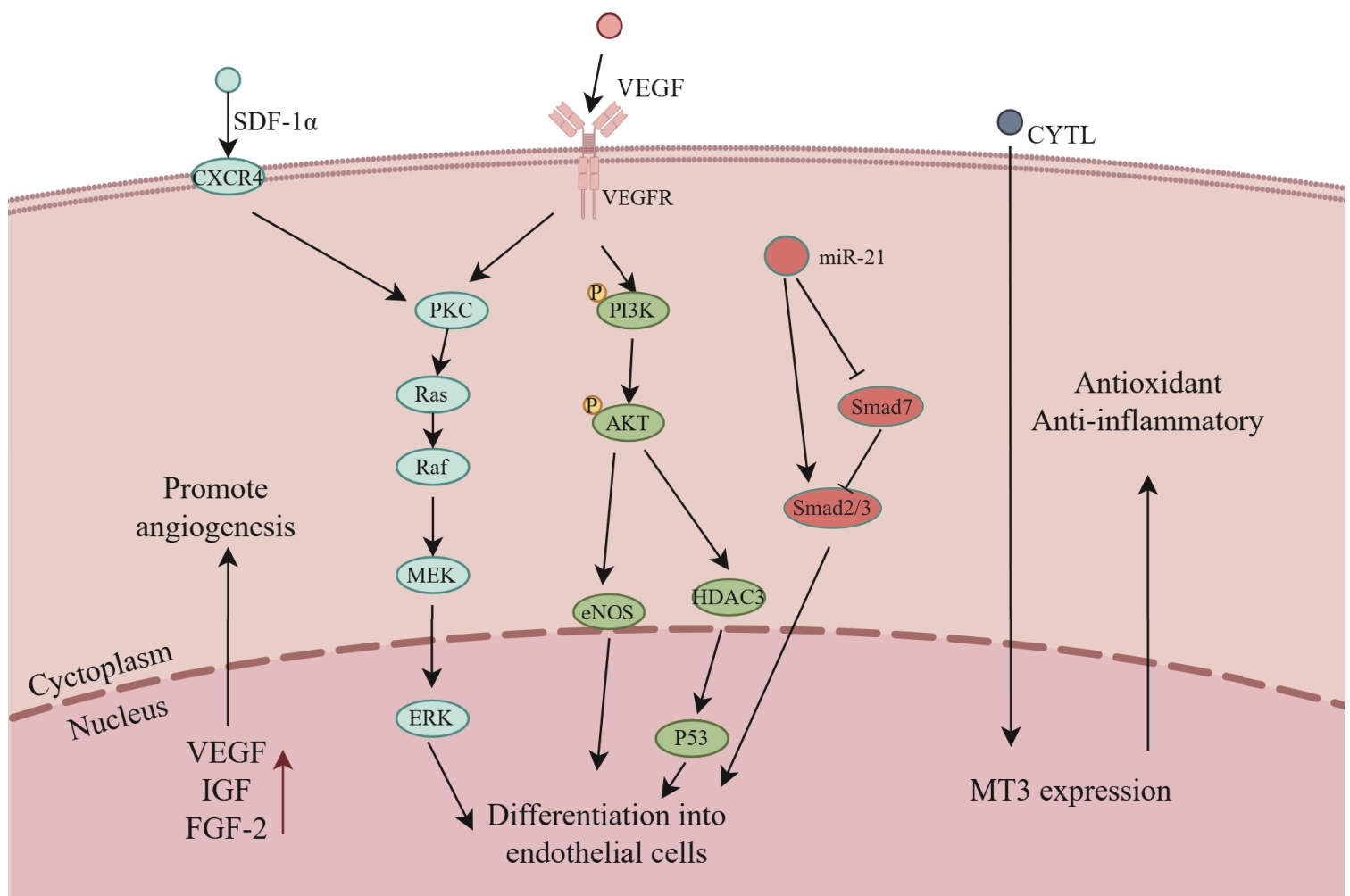
图2 CD34⁺细胞向内皮细胞分化的信号调控网络Note: CXCR4—C-X-C chemokine receptor 4; IGF—insulin-like growth factor; FGF-2—fibroblast growth factor 2; PKC—protein kinase C; Ras—rat sarcoma virus oncogene; Raf—rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma kinase; MEK—mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK—extracellular signal-regulated kinase; PI3K—phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT—protein kinase B; eNOS—endothelial nitric oxide synthase; P53—tumor protein p53; MT3—metallothionein 3.
Fig 2 Signal regulatory network governing the differentiation of CD34⁺ cells into endothelial cells
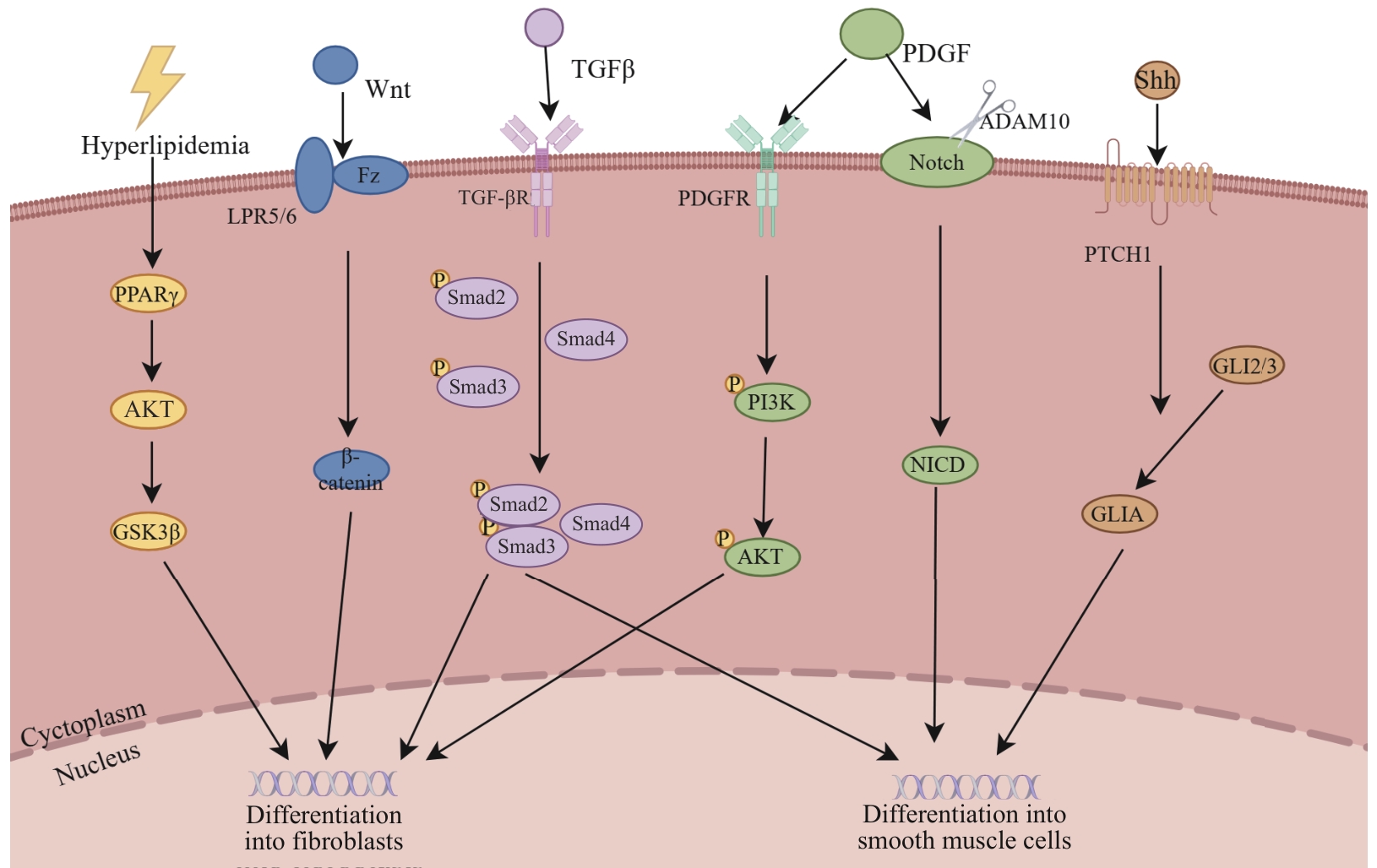
图3 CD34⁺细胞向平滑肌细胞和成纤维细胞分化的信号调控网络Note: PPARγ—peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ; GSK3β—glycogen synthase kinase 3β; Wnt—wingless-type MMTV integration site family member; Fz—frizzled receptor; LPR5/6—low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5/6; TGF-βR—transforming growth factor-β receptor; PDGFR—platelet-derived growth factor receptor; ADAM10—a disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 10; NICD—Notch intracellular domain; PTCH1—patched 1; GLIA—glioma-associated oncogene homolog A; GLI2/3—glioma-associated oncogene homolog 2/3.
Fig 3 Signaling regulatory network governing the differentiation of CD34⁺ cells into smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts
| [1] | MARVASTI T B, ALIBHAI F J, WEISEL R D, et al. CD34+ stem cells: promising roles in cardiac repair and regeneration[J]. Can J Cardiol, 2019, 35(10): 1311-1321. |
| [2] | ASAHARA T, MUROHARA T, SULLIVAN A, et al. Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis[J]. Science, 1997, 275(5302): 964-966. |
| [3] | AUGUSTIN H G, KOH G Y. A systems view of the vascular endothelium in health and disease[J]. Cell, 2024, 187(18): 4833-4858. |
| [4] | PRASAD M, CORBAN M T, HENRY T D, et al. Promise of autologous CD34+ stem/progenitor cell therapy for treatment of cardiovascular disease[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2020, 116(8): 1424-1433. |
| [5] | WANG X Y, WANG R L, JIANG L J, et al. Endothelial repair by stem and progenitor cells[J]. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 2022, 163: 133-146. |
| [6] | ALESSANDRI G, GIRELLI M, TACCAGNI G, et al. Human vasculogenesis ex vivo: embryonal aorta as a tool for isolation of endothelial cell progenitors[J]. Lab Investig, 2001, 81(6): 875-885. |
| [7] | JIANG L J, CHEN T, SUN S S, et al. Nonbone marrow CD34+ cells are crucial for endothelial repair of injured artery[J]. Circ Res, 2021, 129(8): e146-e165. |
| [8] | HU Y H, ZHANG Z Y, TORSNEY E, et al. Abundant progenitor cells in the adventitia contribute to atherosclerosis of vein grafts in ApoE-deficient mice[J]. J Clin Invest, 2004, 113(9): 1258-1265. |
| [9] | PU X Y, ZHU P W, ZHOU X H, et al. CD34+ cell atlas of main organs implicates its impact on fibrosis[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2022, 79(11): 576. |
| [10] | XU X D, ZHU P W, WANG H, et al. CD34+ PI16+ fibroblast progenitors aggravate neointimal lesions of allograft arteries via CCL11/CCR3-PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Theranostics, 2025, 15(6): 2523-2543. |
| [11] | WU H, YANG X P, CHEN T, et al. Aneurysm is restricted by CD34+ cell-formed fibrous collars through the PDGFRb-PI3K axis[J]. Adv Sci, 2025, 12(7): 2408996. |
| [12] | HASSANPOUR M, SALYBEKOV A A, KOBAYASHI S, et al. CD34 positive cells as endothelial progenitor cells in biology and medicine[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2023, 11: 1128134. |
| [13] | BAUMHETER S, SINGER M S, HENZEL W, et al. Binding of L-selectin to the vascular sialomucin CD34[J]. Science, 1993, 262(5132): 436-438. |
| [14] | ABUSAMRA D B, ALEISA F A, AL-AMOODI A S, et al. Not just a marker: CD34 on human hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells dominates vascular selectin binding along with CD44[J]. Blood Adv, 2017, 1(27): 2799-2816. |
| [15] | CHENG J, BAUMHUETER S, CACALANO G, et al. Hematopoietic defects in mice lacking the sialomucin CD34[J]. Blood, 1996, 87(2): 479-490. |
| [16] | SHI Q, RAFII S, WU M H, et al. Evidence for circulating bone marrow-derived endothelial cells[J]. Blood, 1998, 92(2): 362-367. |
| [17] | ASAHARA T, MASUDA H, TAKAHASHI T, et al. Bone marrow origin of endothelial progenitor cells responsible for postnatal vasculogenesis in physiological and pathological neovascularization[J]. Circ Res, 1999, 85(3): 221-228. |
| [18] | HORDYJEWSKA A, POPIOŁEK Ł, HORECKA A. Characteristics of hematopoietic stem cells of umbilical cord blood[J]. Cytotechnology, 2015, 67(3): 387-396. |
| [19] | TAO J P, CAO X J, YU B Q, et al. Vascular stem/progenitor cells in vessel injury and repair[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2022, 9: 845070. |
| [20] | ZHANG L, ISSA BHALOO S, CHEN T, et al. Role of resident stem cells in vessel formation and arteriosclerosis[J]. Circ Res, 2018, 122(11): 1608-1624. |
| [21] | FINA L, MOLGAARD H V, ROBERTSON D, et al. Expression of the CD34 gene in vascular endothelial cells[J]. Blood, 1990, 75(12): 2417-2426. |
| [22] | MAJESKY M W, HORITA H, OSTRIKER A, et al. Differentiated smooth muscle cells generate a subpopulation of resident vascular progenitor cells in the adventitia regulated by Klf4[J]. Circ Res, 2017, 120(2): 296-311. |
| [23] | CORSELLI M, CHEN C W, SUN B, et al. The tunica adventitia of human arteries and veins as a source of mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Stem Cells Dev, 2012, 21(8): 1299-1308. |
| [24] | YU B Q, CHEN Q S, LE BRAS A, et al. Vascular stem/progenitor cell migration and differentiation in atherosclerosis[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2018, 29(2): 219-235. |
| [25] | DU L P, SUN X T, GONG H, et al. Single cell and lineage tracing studies reveal the impact of CD34+ cells on myocardial fibrosis during heart failure[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2023, 14(1): 33. |
| [26] | XU Q B, ZHANG Z Y, DAVISON F, et al. Circulating progenitor cells regenerate endothelium of vein graft atherosclerosis, which is diminished in ApoE-deficient mice[J]. Circ Res, 2003, 93(8): e76-e86. |
| [27] | HU Y H, DAVISON F, ZHANG Z Y, et al. Endothelial replacement and angiogenesis in arteriosclerotic lesions of allografts are contributed by circulating progenitor cells[J]. Circulation, 2003, 108(25): 3122-3127. |
| [28] | INGRAM D A, MEAD L E, MOORE D B, et al. Vessel wall-derived endothelial cells rapidly proliferate because they contain a complete hierarchy of endothelial progenitor cells[J]. Blood, 2005, 105(7): 2783-2786. |
| [29] | HAGENSEN M K, SHIM J, THIM T, et al. Circulating endothelial progenitor cells do not contribute to plaque endothelium in murine atherosclerosis[J]. Circulation, 2010, 121(7): 898-905. |
| [30] | FUJISAWA T, TURA-CEIDE O, HUNTER A, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells do not originate from the bone marrow[J]. Circulation, 2019, 140(18): 1524-1526. |
| [31] | LI Z W, SOLOMONIDIS E G, MELONI M, et al. Single-cell transcriptome analyses reveal novel targets modulating cardiac neovascularization by resident endothelial cells following myocardial infarction[J]. Eur Heart J, 2019, 40(30): 2507-2520. |
| [32] | DENG J C, NI Z C, GU W D, et al. Single-cell gene profiling and lineage tracing analyses revealed novel mechanisms of endothelial repair by progenitors[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2020, 77(24): 5299-5320. |
| [33] | SINGHAL M, LIU X T, INVERSO D, et al. Endothelial cell fitness dictates the source of regenerating liver vasculature[J]. J Exp Med, 2018, 215(10): 2497-2508. |
| [34] | WANG X R, BOVE A M, SIMONE G, et al. Molecular bases of VEGFR-2-mediated physiological function and pathological role[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8: 599281. |
| [35] | SCHNELLER D, HOFER-WARBINEK R, STURTZEL C, et al. Cytokine-like 1 is a novel proangiogenic factor secreted by and mediating functions of endothelial progenitor cells[J]. Circ Res, 2019, 124(2): 243-255. |
| [36] | SHAIK S, MARTIN E, HAYES D, et al. microRNA sequencing of CD34+ sorted adipose stem cells undergoing endotheliogenesis[J]. Stem Cells Dev, 2021, 30(5): 265-288. |
| [37] | SHVEDUNOVA M, AKHTAR A. Modulation of cellular processes by histone and non-histone protein acetylation[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2022, 23(5): 329-349. |
| [38] | ZENG L F, XIAO Q Z, MARGARITI A, et al. HDAC3 is crucial in shear- and VEGF-induced stem cell differentiation toward endothelial cells[J]. J Cell Biol, 2006, 174(7): 1059-1069. |
| [39] | GAO J, WANG Y H, LI W, et al. Loss of histone deacetylase 2 inhibits oxidative stress induced by high glucose via the HO-1/SIRT1 pathway in endothelial progenitor cells[J]. Gene, 2018, 678: 1-7. |
| [40] | HUANG C Y, LIN F Y, SHIH C M, et al. Moderate to high concentrations of high-density lipoprotein from healthy subjects paradoxically impair human endothelial progenitor cells and related angiogenesis by activating Rho-associated kinase pathways[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2012, 32(10): 2405-2417. |
| [41] | HUANG Z H, SUN A J. Metabolism, inflammation, and cardiovascular diseases from basic research to clinical practice[J]. Cardiol Plus, 2023, 8(1): 4-5. |
| [42] | TOUSOULIS D, ANDREOU I, ANTONIADES C, et al. Role of inflammation and oxidative stress in endothelial progenitor cell function and mobilization: therapeutic implications for cardiovascular diseases[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2008, 201(2): 236-247. |
| [43] | PASSMAN J N, DONG X R, WU S P, et al. A sonic hedgehog signaling domain in the arterial adventitia supports resident Sca1+ smooth muscle progenitor cells[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2008, 105(27): 9349-9354. |
| [44] | XIE Y, LU Y R, NI H, et al. Abstract 12723: smooth muscle-derived CD34+ cells after vascular injury contribute to vascular remodeling[C]//American Heart Association Scientific Sessions 2023. Philadelphia: American Heart Association, 2023. |
| [45] | YEH E T H, ZHANG S, WU H D, et al. Transdifferentiation of human peripheral blood CD34+-enriched cell population into cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, and smooth muscle cells in vivo[J]. Circulation, 2003, 108(17): 2070-2073. |
| [46] | HILL K L, OBRTLIKOVA P, ALVAREZ D F, et al. Human embryonic stem cell-derived vascular progenitor cells capable of endothelial and smooth muscle cell function[J]. Exp Hematol, 2010, 38(3): 246-257.e1. |
| [47] | NI Z C, DENG J C, POTTER C M F, et al. Recipient c-Kit lineage cells repopulate smooth muscle cells of transplant arteriosclerosis in mouse models[J]. Circ Res, 2019, 125(2): 223-241. |
| [48] | YANG F, CHEN Q S, YANG M, et al. Macrophage-derived MMP-8 determines smooth muscle cell differentiation from adventitia stem/progenitor cells and promotes neointima hyperplasia[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2020, 116(1): 211-225. |
| [49] | HELDIN C H, WESTERMARK B. Mechanism of action and in vivo role of platelet-derived growth factor[J]. Physiol Rev, 1999, 79(4): 1283-1316. |
| [50] | WU Y, SHEN Y, KANG K, et al. Effects of estrogen on growth and smooth muscle differentiation of vascular wall-resident CD34+ stem/progenitor cells[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2015, 240(2): 453-461. |
| [51] | ROSS J J, HONG Z G, WILLENBRING B, et al. Cytokine-induced differentiation of multipotent adult progenitor cells into functional smooth muscle cells[J]. J Clin Invest, 2006, 116(12): 3139-3149. |
| [52] | PESCE M, DUDA G N, FORTE G, et al. Cardiac fibroblasts and mechanosensation in heart development, health and disease[J]. Nat Rev Cardiol, 2023, 20(5): 309-324. |
| [53] | BUECHLER M B, PRADHAN R N, KRISHNAMURTY A T, et al. Cross-tissue organization of the fibroblast lineage[J]. Nature, 2021, 593(7860): 575-579. |
| [54] | XIE J, JIANG L J, WANG J Z, et al. Multilineage contribution of CD34+ cells in cardiac remodeling after ischemia/reperfusion injury[J]. Basic Res Cardiol, 2023, 118(1): 17. |
| [55] | DU L P, WANG X Y, GUO Y, et al. Altered lipid metabolism promoting cardiac fibrosis is mediated by CD34+ cell-derived FABP4+ fibroblasts[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2024, 56(8): 1869-1886. |
| [56] | WU J, MONTANIEL K R C, SALEH M A, et al. Origin of matrix-producing cells that contribute to aortic fibrosis in hypertension[J]. Hypertension, 2016, 67(2): 461-468. |
| [57] | SONG Y W, YANG J Y, LI T R, et al. CD34+ cell-derived fibroblast-macrophage cross-talk drives limb ischemia recovery through the OSM-ANGPTL signaling axis[J]. Sci Adv, 2023, 9(15): eadd2632. |
| [58] | CHEN D X, LI K, WEI L L, et al. Neointimal hyperplasia after endoluminal injury in mice is dependent on tissue factor- and angiopoietin-2 dependent interferon gamma production by fibrocytes and macrophages[J]. Front Immunol, 2024, 15: 1345199. |
| [59] | VAN AMERONGEN M J, BOU-GHARIOS G, ER P P, et al. Bone marrow-derived myofibroblasts contribute functionally to scar formation after myocardial infarction[J]. J Pathol, 2008, 214(3): 377-386. |
| [60] | QIN L, LIU N, BAO C L M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells in fibrotic diseases: the two sides of the same coin[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2023, 44(2): 268-287. |
| [61] | LI X Y, SUN H, LI D, et al. CD34+ synovial fibroblasts exhibit high osteogenic potential in synovial chondromatosis[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 2024, 397(1): 37-50. |
| [62] | DAMIANO G, RINALDI R, POMPILIO G, et al. Liraglutide prevents hyperglycemia-induced senescence and proinflammatory monocyte differentiation in CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells[C]// Frontiers in CardioVascular Biomedicine 2024. Amsterdam: European Society of Cardiology, 2024. |
| [63] | LI Y, LIU Z X, HAN X M, et al. Dynamics of endothelial cell generation and turnover in arteries during homeostasis and diseases[J]. Circulation, 2024, 149(2): 135-154. |
| [64] | RATAJCZAK J, KUCIA M, MIERZEJEWSKA K, et al. Paracrine proangiopoietic effects of human umbilical cord blood-derived purified CD133+ cells: implications for stem cell therapies in regenerative medicine[J]. Stem Cells Dev, 2013, 22(3): 422-430. |
| [65] | MATHIYALAGAN P, LIANG Y X, KIM D, et al. Angiogenic mechanisms of human CD34+ stem cell exosomes in the repair of ischemic hindlimb[J]. Circ Res, 2017, 120(9): 1466-1476. |
| [66] | MAUSE S F, RITZEL E, DECK A, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells modulate the phenotype of smooth muscle cells and increase their neointimal accumulation following vascular injury[J]. Thromb Haemost, 2022, 122(3): 456-469. |
| [67] | SHUDO Y, COHEN J E, MACARTHUR J W, et al. Spatially oriented, temporally sequential smooth muscle cell-endothelial progenitor cell bi-level cell sheet neovascularizes ischemic myocardium[J]. Circulation, 2013, 128(11_suppl_1): S59-S68. |
| [68] | CARNEIRO G D, SIELSKI M S, VIEIRA C P, et al. Administration of endothelial progenitor cells accelerates the resolution of arterial thrombus in mice[J]. Cytotherapy, 2019, 21(4): 444-459. |
| [69] | JARAJAPU Y P R, HAZRA S, SEGAL M, et al. Vasoreparative dysfunction of CD34+ cells in diabetic individuals involves hypoxic desensitization and impaired autocrine/paracrine mechanisms[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(4): e93965. |
| [70] | LIM A A, POUYABAHAR D, ASHRAF M, et al. Single-cell transcriptome analysis reveals CD34 as a marker of human sinoatrial node pacemaker cardiomyocytes[J]. Nat Commun, 2024, 15: 10206. |
| [71] | EPPINGA R N, HAGEMEIJER Y, BURGESS S, et al. Identification of genomic loci associated with resting heart rate and shared genetic predictors with all-cause mortality[J]. Nat Genet, 2016, 48(12): 1557-1563. |
| [72] | RIGATO M, AVOGARO A, FADINI G P. Levels of circulating progenitor cells, cardiovascular outcomes and death: a meta-analysis of prospective observational studies[J]. Circ Res, 2016, 118(12): 1930-1939. |
| [73] | LIU C T, GUO J Y, CHOU R H, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells and major adverse cardiovascular events in patients receiving elective coronary angiography[J]. Cardiol Plus, 2023, 8(1): 37-45. |
| [74] | OZCAN I, TOYA T, CORBAN M T, et al. Circulating progenitor cells are associated with plaque progression and long-term outcomes in heart transplant patients[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2022, 118(7): 1703-1712. |
| [75] | HENRY T D, LOSORDO D W, TRAVERSE J H, et al. Autologous CD34+ cell therapy improves exercise capacity, angina frequency and reduces mortality in no-option refractory angina: a patient-level pooled analysis of randomized double-blinded trials[J]. Eur Heart J, 2018, 39(23): 2208-2216. |
| [76] | SUNG P H, LI Y C, LEE M S, et al. Intracoronary injection of autologous CD34+ cells improves one-year left ventricular systolic function in patients with diffuse coronary artery disease and preserved cardiac performance: a randomized, open-label, controlled phase Ⅱ clinical trial[J]. J Clin Med, 2020, 9(4): 1043. |
| [77] | DEN DEKKER W K, HOUTGRAAF J H, ONUMA Y, et al. Final results of the HEALING ⅡB trial to evaluate a bio-engineered CD34 antibody coated stent (GenousTM Stent) designed to promote vascular healing by capture of circulating endothelial progenitor cells in CAD patients[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2011, 219(1): 245-252. |
| [78] | JAKOBSEN L, CHRISTIANSEN E H, FREEMAN P, et al. Randomized clinical comparison of the dual-therapy CD34 antibody-covered sirolimus-eluting combo stent with the sirolimus-eluting orsiro stent in patients treated with percutaneous coronary intervention: the SORT OUT X trial[J]. Circulation, 2021, 143(22): 2155-2165. |
| [79] | JAGUSZEWSKI M, ALOYSIUS R, WANG W, et al. The REMEDEE-OCT study: an evaluation of the bioengineered COMBO dual-therapy CD34 antibody-covered sirolimus-eluting coronary stent compared with a cobalt-chromium everolimus-eluting stent in patients with acute coronary syndromes: insights from optical coherence tomography imaging analysis[J].JACC Cardiovasc Interv, 2017, 10(5): 489-499. |
| [1] | 马会华, 闫奎坡, 刘刚, 徐亚洲, 张磊, 孙彦琴. 肠道微生物群与心血管疾病的因果关系评价:双向孟德尔随机化分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(12): 1606-1619. |
| [2] | 李萍, 蒋惠如, 叶梦月, 王雅玉, 陈潇雨, 袁安彩, 徐文杰, 戴慧敏, 陈曦, 闫小响, 涂圣贤, 郑元琦, 张薇, 卜军. 基于上海社区老年人群队列的心血管疾病和恶性肿瘤的危险因素流行特征分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(5): 617-625. |
| [3] | 何志洁, 何津春, 张燕培, 王耀东, 王占科. 基于垂直密度梯度离心全自动血脂谱检测法的家族性高三酰甘油血症家系血脂亚组分分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(4): 482-489. |
| [4] | 张彤, 田雪, 左颖婷, 郑曼琪, 张怡君, 吴寿岭, 陈朔华, 马高亭, 佟旭, 王安心, 莫大鹏. 无传统危险因素人群中TyG指数与心脑血管疾病的关系[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(3): 267-274. |
| [5] | 蔡明琪, 陈焱, 林开斌, 黄冬. 生长分化因子11在心血管疾病中的作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(6): 834-838. |
| [6] | 孙敏, 张冬颖. 钠-葡萄糖共转运蛋白2抑制剂对2型糖尿病患者心血管保护作用的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(3): 391-395. |
| [7] | 代华杰, 禤立平, 项家丽, 林泓, 赵志云, 王天歌, 李勉, 徐瑜, 陆洁莉, 王卫庆, 毕宇芳, 徐敏. 上海市社区中老年人群健康的血管衰老和心血管疾病患病风险的相关性研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(2): 223-227. |
| [8] | 陆言巧,沈 兰,何 奔. 人工智能在心血管疾病的辅助诊疗中的应用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(2): 259-. |
| [9] | 张夏,郑雷蕾,刘艳,明叶,何昊珏,胡赟. 聚 (左旋乳酸 -己内酯 )/明胶静电纺丝支架对大鼠骨髓 来源内皮祖细胞成血管分化的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2018, 38(5): 499-. |
| [10] | 季海英,尤纱纱,曹惠敏,何斌. PCSK9 抑制剂降低低密度脂蛋白胆固醇的临床研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2018, 38(2): 212-. |
| [11] | 岳丹丹,魏珍玉,陈昕,王岬琰,卢文美,钟萍3,吴丹红 . 循环内皮祖细胞对急性缺血性脑卒中预后的预测价值[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2017, 37(7): 964-. |
| [12] | 赵丹丹,顾燕云,王计秋,胡春秀,洪洁,张翼飞,SPREAD-DIMCAD 研究组 . 基线脂代谢谱特征对降糖药物干预再发心血管事件影响的预测研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2017, 37(6): 744-. |
| [13] | 闵丹燕,陆晓蓉,李振元,严豪,张敏芳,王琴,袁江姿,倪兆慧,方炜. 低T 3 综合征可预测腹膜透析患者的不良预后[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2017, 37(11): 1501-. |
| [14] | 高金丽,彭魁,倪衡如,黄小琳,毕宇芳,徐敏. 上海社区中老年人群代谢综合征与心血管疾病患病风险相关性研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2016, 36(9): 1341-. |
| [15] | 程 棣,林 琳,杜 瑞,陆洁莉. Omega-3脂肪酸与心血管疾病[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2016, 36(8): 1231-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||