
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (3): 301-311.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2024.03.002
徐文晖( ), 杨畅, 李瑞卿, 卞京, 李夏伊, 郑磊贞(
), 杨畅, 李瑞卿, 卞京, 李夏伊, 郑磊贞( )
)
收稿日期:2023-05-14
接受日期:2024-03-19
出版日期:2024-03-28
发布日期:2024-03-28
通讯作者:
郑磊贞,电子信箱:zhengleizhen@xinhuamed.com.cn。作者简介:徐文晖(1998—),女,硕士生;电子信箱:xuwenhui98@126.com。
基金资助:
XU Wenhui( ), YANG Chang, LI Ruiqing, BIAN Jing, LI Xiayi, ZHENG Leizhen(
), YANG Chang, LI Ruiqing, BIAN Jing, LI Xiayi, ZHENG Leizhen( )
)
Received:2023-05-14
Accepted:2024-03-19
Online:2024-03-28
Published:2024-03-28
Contact:
ZHENG Leizhen, E-mail: zhengleizhen@xinhuamed.com.cn.Supported by:摘要:
目的·分析结直肠癌中干扰素调节因子3(interferon regulatory factor 3,IRF3)表达水平与临床病理特征及患者预后的关系,观察IRF3过表达对结直肠癌细胞增殖与侵袭能力的影响及其相关蛋白通路。方法·下载癌症基因组图谱(The Cancer Genome Atlas,TCGA)数据,分析IRF3表达水平与恶性肿瘤患者(肾癌、结直肠癌、肝癌、前列腺癌)预后的关系。采用免疫组织化学法检测10例结直肠癌或肾癌患者的癌组织与癌旁正常组织切片中IRF3表达水平的差异。针对IRF3蛋白的C端残基位点进行改造,构建拟磷酸化IRF3-5D(396/398/402/404/405-D)高表达的HEK-293T细胞。分别在细胞培养12、24 h时,采用TANK结合激酶1(TANK-binding kinase 1,TBK1)抑制剂进行处理,并采用蛋白质印迹法检测细胞IRF3、p-IRF3(Ser386)蛋白表达水平。采用RNA测序技术探索IRF3-5D高表达与肿瘤相关蛋白表达水平的相关性。构建野生型IRF3(IRF3-WT)和IRF3-5D过表达的结直肠癌细胞CT26、COLON26,采用细胞计数法、细胞划痕试验和克隆形成试验检测细胞增殖及迁移能力。结果·TCGA数据分析提示癌组织中IRF3蛋白表达水平与患者的不良预后呈正相关。癌症患者病理组织免疫组织化学法显示,结直肠癌、肾癌组织中IRF3的表达水平显著上调,且蛋白表达集中于细胞核内。TBK1抑制剂分别在细胞培养12、24 h时间点作用后,HEK-293T细胞p-IRF3(Ser386)蛋白表达减弱。RNA测序和蛋白质印迹法结果显示,多个与癌症预后不良相关的蛋白[IRF9、细胞程序性死亡-配体1(programmed cell death 1-ligand 1,PD-L1)等]表达水平在IRF3-5D高表达的条件下显著上调。结直肠癌细胞中过表达IRF3-5D,可导致癌细胞的增殖、迁移能力显著上调。结论·结直肠癌中IRF3表达水平与患者不良预后呈正相关。IRF3-5D蛋白在结直肠癌细胞内高表达后,促进癌细胞恶性生物学行为。此外,IRF3-5D依赖于TBK1介导的IRF3活化激活通路,并上调多个肿瘤相关蛋白的表达水平。
中图分类号:
徐文晖, 杨畅, 李瑞卿, 卞京, 李夏伊, 郑磊贞. 干扰素调节因子3促结直肠癌细胞增殖与侵袭相关探索[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(3): 301-311.
XU Wenhui, YANG Chang, LI Ruiqing, BIAN Jing, LI Xiayi, ZHENG Leizhen. Exploratory study of interferon regulatory factor 3 promoting proliferation and invasion related to colorectal cancer cells[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(3): 301-311.

图1 基于不同IRF3表达水平的Kaplan-Meier生存分析
Fig 1 Kaplan-Meier survival analysis based on different IRF3 expression levelsNote: A. Renal cancer. B. Colorectal cancer. C. Liver cancer. D. Prostate cancer.
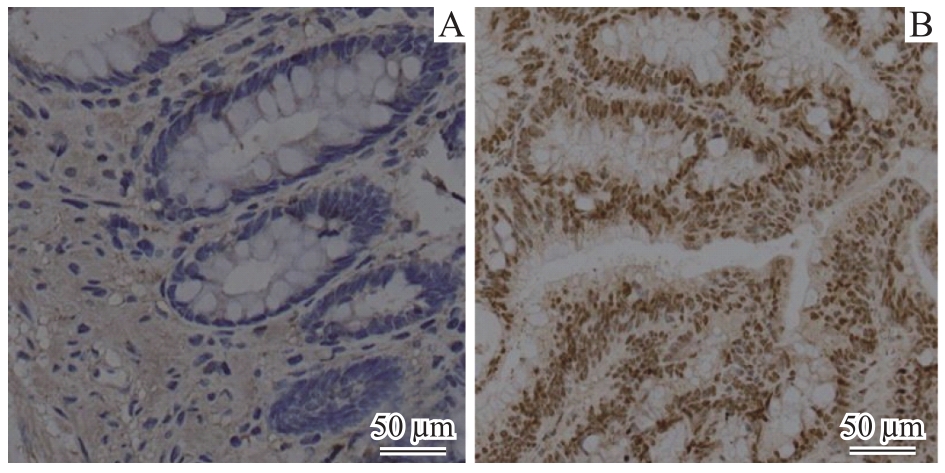
图2 肠癌患者癌组织与癌旁正常组织IRF3蛋白免疫组织化学对比(×20)
Fig 2 Comparison of immunohistochemical staining for IRF3 protein between cancerous and normal tissues adjacent to cancer in patients with colorectal cancer (×20)Note: A. Normal intestinal tissue adjacent to cancer. B. Cancerous tissue.
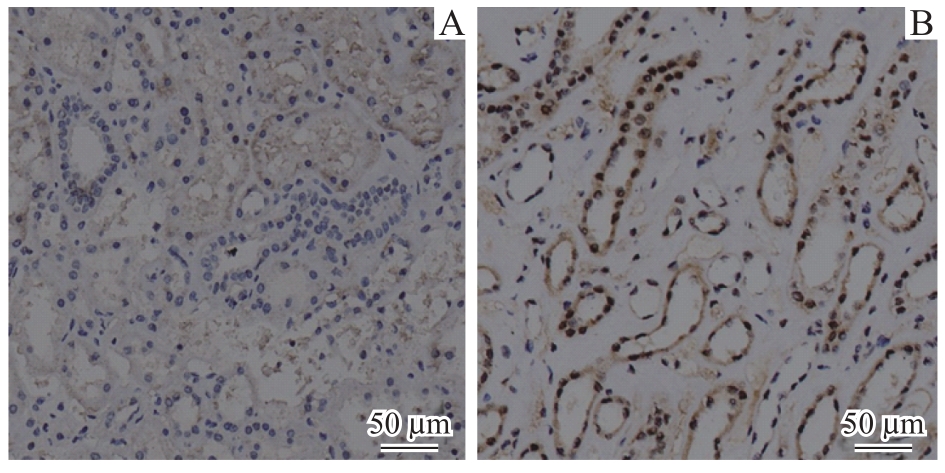
图3 肾癌患者癌组织与癌旁正常组织的IRF3免疫组织化学对比(×20)
Fig 3 Comparison of immunohistochemical staining for IRF3 protein between cancerous and normal tissues adjacent to cancer from patients with renal cancer (×20)Note: A. Normal kidney tissue adjacent to cancer. B. Cancerous tissue.
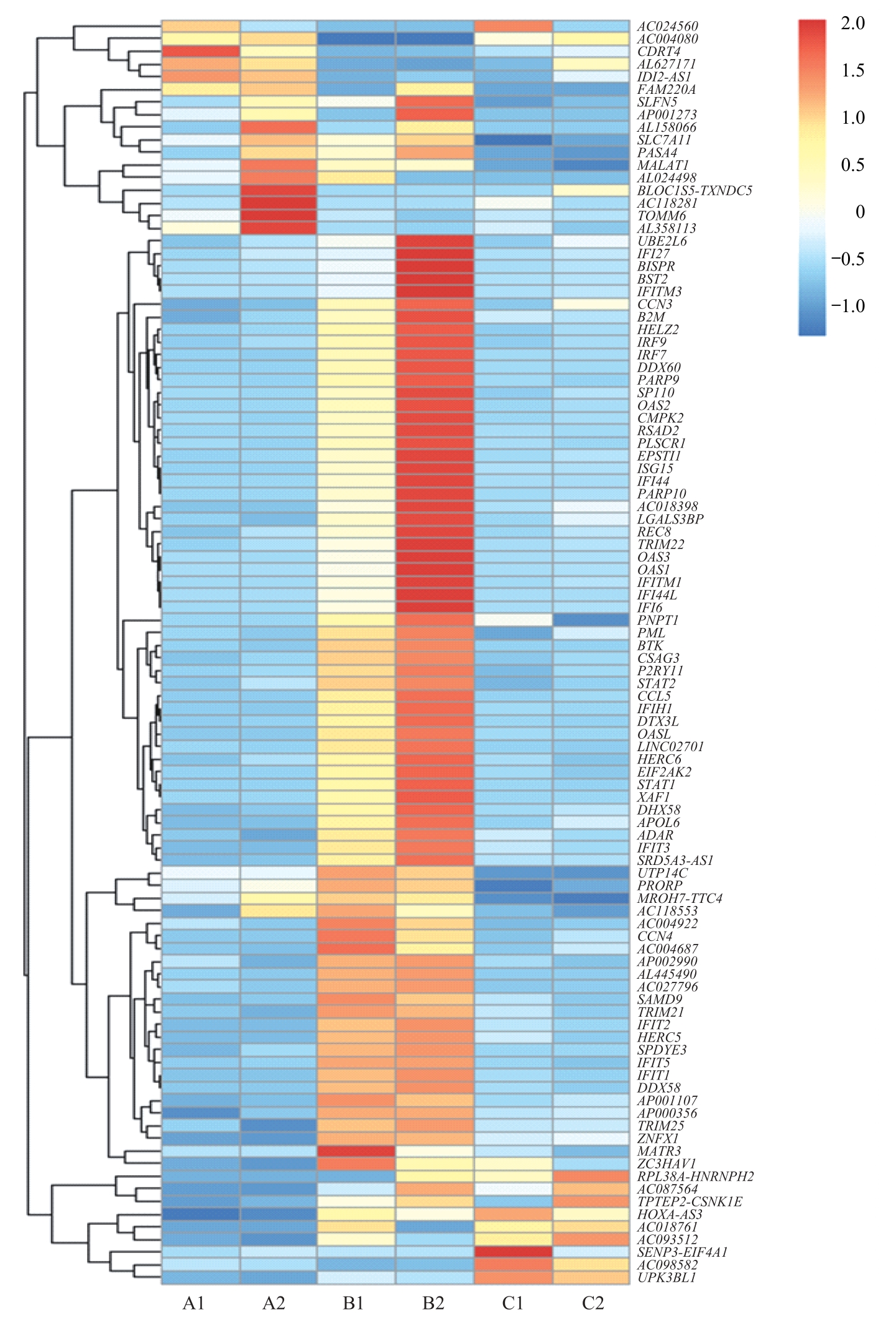
图5 3组间差异基因聚类热图Note: Horizontal coordinates are experimental groups. A1: IRF3-WT48 h, A2: IRF3-WT72 h; B1: IRF3-5D48 h, B2: IRF3-5D72 h; C1: IRF3-2A5D48 h, C2: IRF3-2A5D72 h. Vertical coordinates are the names of the major differential genes detected at the transcriptional level. Blue via white to red indicates low to high expression; red indicates high expression genes, and blue indicates low expression genes. CDRT4—CMT1A duplicated region transcript 4; SLFN5—recombinant Schlafen family member 5; RASA4—RAS p21 protein activator 4; MALAT-1—metastasis associated in lung denocarcinoma transcript 1; TOMM6—translocase of outer mitochondrial membrane 6; BISPR—BST2 interferon-stimulated positive regulator; IFITM3—interferon-induced transmembrane protein 3; CCN3—cellular communication network factor 3; B2M—β-2 microglobulin; HELZ2—helicase with zinc finger 2; IRF9—interferon regulatory factor 9; IRF7—interferon regulatory factor 7; DDX60—DExD/H-box helicase 60; PARP9—poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase family member 9; SP110—SP110 nuclear body protein; OAS2—2′-5′-oligoadenylate synthetase 2; CMPK2—cytidine monophosphate kinase 2; RSAD2—radical S-adenosyl methionine domain containing 2; IFI27—interferon alpha-inducible protein 27; BST-2—bone marrow stromal antigen 2; PLSCR1—phospholipid scramblase 1; EPSTI1—epithelial stromal interaction 1; PARP10—poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase family member 10; REC8—REC8 meiotic recombination protein; TRIM22—tripartite motif containing 22; PNPT1—polyribonucleotide nucleotidyltransferase 1; BTK—Bruton tyrosine kinase; STAT2—signal transducer and activator of transcription 2; DTX3L—deltex E3 ubiquitin ligase 3L; HERC6—HECT and RLD domain containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase family member 6; XAF1—XIAP-associated factor 1; DHX58—DExH-box helicase 58; APOL6—apolipoprotein L6; PRORP—protein-only RNase P catalytic subunit; CCN4—cellular communication network factor 4; SAMD9L—sterile α motif domain containing 9 like; TRIM21—tripartite-motif protein 21; DHX58—DExH-box helicase 58; ZNFX1—zinc finger NFX1-type containing 1; MATR3—matrin 3.
Fig 5 Heat map of differential gene clusterings between the three groups
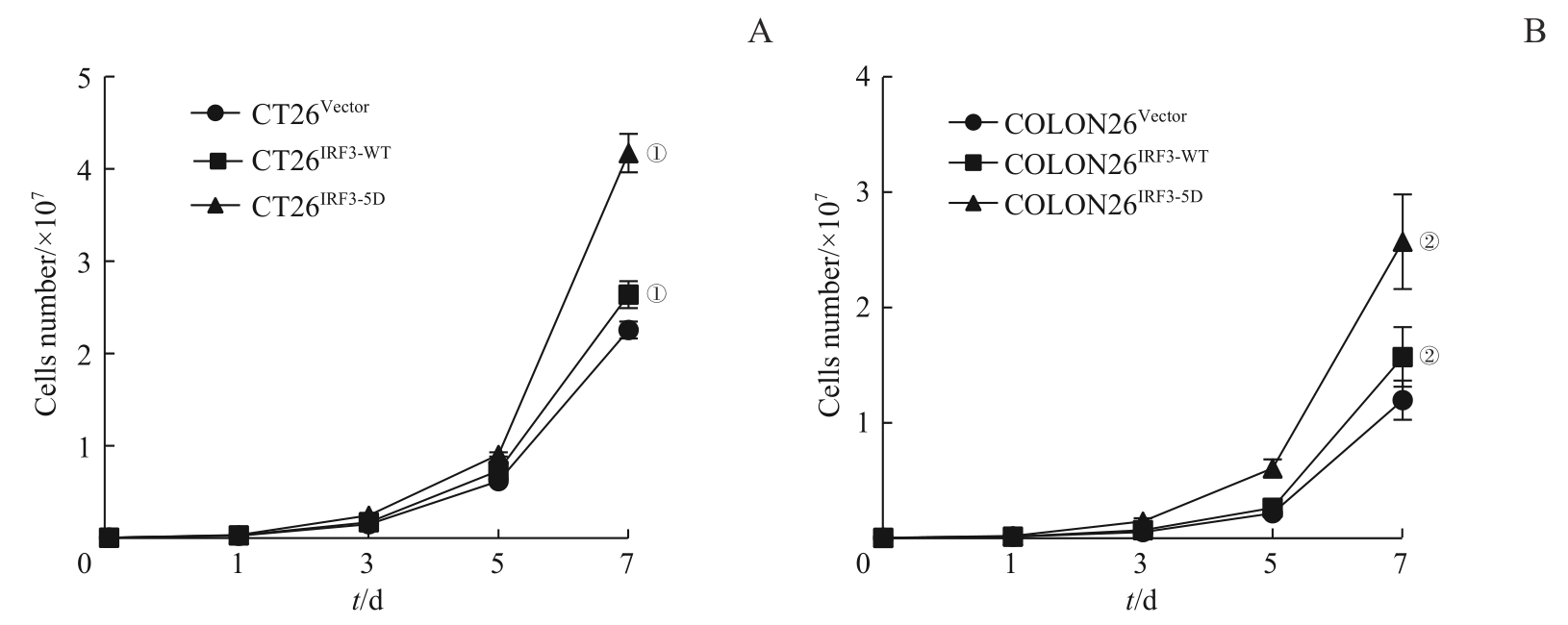
图8 3组CT26、COLON26细胞增殖能力对比Note: ①P=0.000, compared with CT26Vector; ②P=0.000, compared with COLON26Vector.
Fig 8 Comparison of growing capacity among three groups of CT26 and COLON26 cell
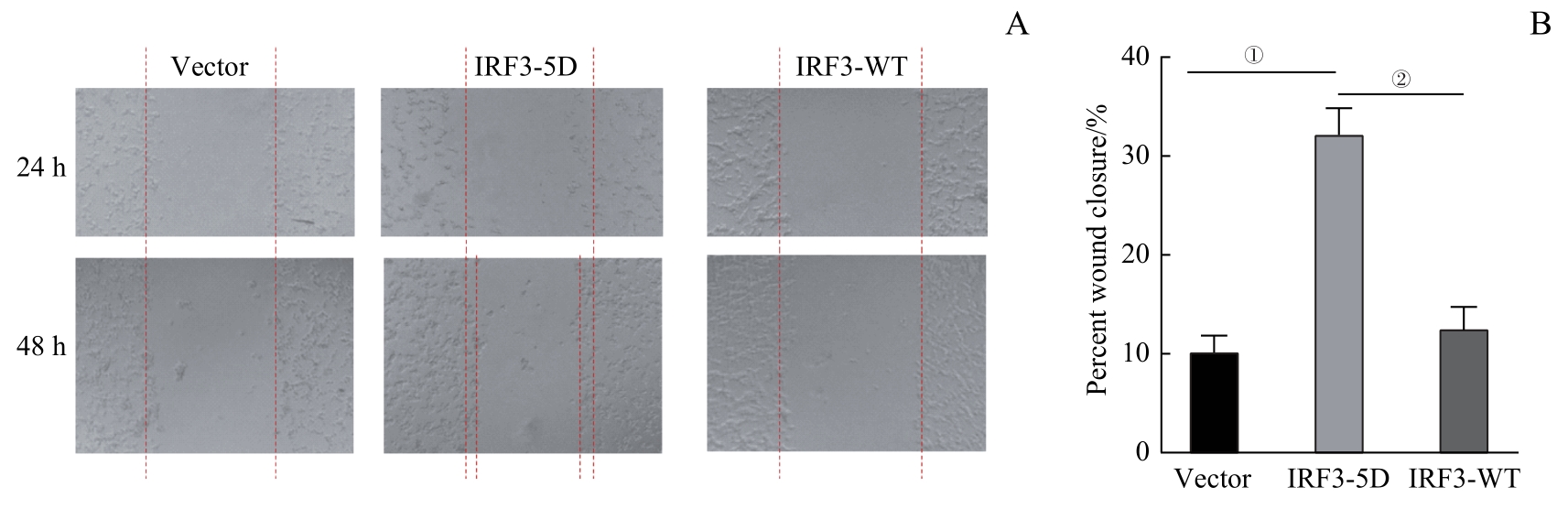
图9 3组CT26细胞转移侵袭能力对比Note: A. Detection of migration capacity of CT26 cells. B. Statistical analysis of CT26 cell wound closure percentage. ①P=0.000, compared between IRF3-5D andVector; ②P=0.000, compared between IRF3-5D and IRF3-WT.
Fig 9 Comparison of invasive ability among three groups of CT26 cells

图10 3组COLON26细胞生长活力对比Note: Initial cell number laid down was 500 and 2 000. A. Colony formation of COLON26 cells. B. Statistical analysis of clone formation rate of COLON26 cells. ①P=0.000, compared between IRF3-5D and Vector; ②P=0.000, compared between IRF3-5D and IRF3-WT; ③P=0.001, compared between IRF3-5D and Vector; ④P=0.001, compared between IRF3-5D and IRF3-WT.
Fig 10 Comparison of cell viability among three groups of COLON26 cells
| 1 | SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. |
| 2 | 周雄, 胡明, 李子帅, 等. 2020年全球及中国结直肠癌流行状况分析[J]. 海军军医大学学报, 2022, 43(12): 1356-1364. |
| ZHOU X, HU M, LI Z S, et al. Colorectal cancer in the world and China in 2020: an analysis of epidemic status[J]. Academic Journal of Naval Medical University, 2022, 43(12): 1356-1364. | |
| 3 | 李建, 张尧, 胡登敏, 等. 1990—2019年中国人群早发性结直肠癌疾病负担及变化趋势分析[J]. 现代预防医学, 2022, 49(19): 3468-3473. |
| LI J, ZHANG Y, HU D M, et al. Disease burden and its time trends of early-onset colorectal cancer in China, 1990—2019[J]. Modern Preventive Medicine, 2022, 49(19): 3468-3473. | |
| 4 | ZHOU W K, WANG J M, WANG X, et al. Degradation of HDAC10 by autophagy promotes IRF3-mediated antiviral innate immune responses[J]. Sci Signal, 2022, 15(765): eabo4356. |
| 5 | ZHANG Q, LIU S D, ZHANG C S, et al. AMPK directly phosphorylates TBK1 to integrate glucose sensing into innate immunity[J]. Mol Cell, 2022, 82(23): 4519-4536.e7. |
| 6 | SUN X C, XIN S Y, LI W Y, et al. Discovery of Notch pathway-related genes for predicting prognosis and tumor microenvironment status in bladder cancer[J]. Front Genet, 2022, 13: 928778. |
| 7 | SONG J, ZHAO W, ZHANG X, et al. Mutant RIG-Ⅰ enhances cancer-related inflammation through activation of circRIG-Ⅰ signaling[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13: 7096. |
| 8 | SHAN S H, NIU J P, YIN R P, et al. Peroxidase from foxtail millet bran exerts anti-colorectal cancer activity via targeting cell-surface GRP78 to inactivate STAT3 pathway[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2022, 12(3): 1254-1270. |
| 9 | SAIKRUANG W, ANG YAN PING L, ABE H, et al. The RNA helicase DDX3 promotes IFNB transcription via enhancing IRF-3/p300 holocomplex binding to the IFNB promoter[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12(1): 3967. |
| 10 | OKAMURA K, NAGAYAMA S, TATE T, et al. Lymphocytes in tumor-draining lymph nodes co-cultured with autologous tumor cells for adoptive cell therapy[J]. J Transl Med, 2022, 20(1): 241. |
| 11 | PASCOLUTTI R, YETURU L, PHILIPPIN G, et al. ATP128 clinical therapeutic cancer vaccine activates NF-κB and IRF3 pathways through TLR4 and TLR2 in human monocytes and dendritic cells[J]. Cancers, 2022, 14(20): 5134. |
| 12 | LIU J, JI Q L, CHENG F, et al. The lncRNAs involved in regulating the RIG-Ⅰ signaling pathway[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2022, 12: 1041682. |
| 13 | YANG Y Y, CAO X Y, HUANG L S, et al. RNF19a inhibits antiviral immune response to RNA viruses through degradation of TBK1[J]. Mol Immunol, 2022, 143: 1-6. |
| 14 | 寻鲁宁, 王冲, 沈成凤, 等. 1990—2019年中国结直肠癌发病趋势分析及预测模型比较[J]. 中国肿瘤, 2023, 32(4): 279-286. |
| XUN L N, WANG C, SHEN C F, et al. Prediction of colorectal cancer incidence in China with three different models based on trends from 1990 to 2019[J]. China Cancer, 2023, 32(4): 279-286. | |
| 15 | FANG X L, XU J F, JIN K T, et al. Combining of immunotherapeutic approaches with chemotherapy for treatment of gastric cancer: achievements and limitations[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2023, 118: 110062. |
| 16 | FANG G D, XU D L, ZHANG T, et al. Biological functions, mechanisms, and clinical significance of circular RNA in colorectal cancer[J]. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 1138481. |
| 17 | UHLÉN M, BJÖRLING E, AGATON C, et al. A human protein atlas for normal and cancer tissues based on antibody proteomics[J]. Mol Cell Proteomics, 2005, 4(12): 1920-1932. |
| 18 | TIEDT R, KING F J, STAMM C, et al. Integrated CRISPR screening and drug profiling identifies combination opportunities for EGFR, ALK, and BRAF/MEK inhibitors[J]. Cell Rep, 2023, 42(4): 112297. |
| 19 | WANG H Q, CUI B M, YAN H Y, et al. Targeting 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase against EV-A71 replication by upregulating interferon response[J]. Antivir Res, 2023, 209: 105497. |
| 20 | RUAN J Y, ZHANG P, ZHANG Q Q, et al. Colorectal cancer inhibitory properties of polysaccharides and their molecular mechanisms: a review[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2023, 238: 124165. |
| 21 | YAN X L, ZHENG W W, GENG S, et al. Cytokine receptor-like factor 3 negatively regulates antiviral immunity by promoting the degradation of TBK1 in teleost fish[J]. J Virol, 2023, 97(1): e0179222. |
| 22 | YANG S, JIN S H, XIAN H F, et al. Metabolic enzyme UAP1 mediates IRF3 pyrophosphorylation to facilitate innate immune response[J]. Mol Cell, 2023, 83(2): 298-313.e8. |
| 23 | JING T, ZHAO B Y, XU P B, et al. The structural basis of IRF-3 activation upon phosphorylation[J]. J Immunol, 2020, 205(7): 1886-1896. |
| 24 | KUHL N, LINDER A, PHILIPP N, et al. STING agonism turns human T cells into interferon-producing cells but impedes their functionality[J]. EMBO Rep, 2023, 24(3): e55536. |
| 25 | YUM S, LI M H, FANG Y, et al. TBK1 recruitment to STING activates both IRF3 and NF-κB that mediate immune defense against tumors and viral infections[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2021, 118(14): e2100225118. |
| 26 | GAO Q Z, ZHOU R, MENG Y, et al. Long noncoding RNA CMPK2 promotes colorectal cancer progression by activating the FUBP3-c-Myc axis[J]. Oncogene, 2020, 39(19): 3926-3938. |
| 27 | YANG L Q, HU H Y, HAN Y, et al. CpG-binding protein CFP1 promotes ovarian cancer cell proliferation by regulating BST2 transcription[J]. Cancer Gene Ther, 2022, 29(12): 1895-1907. |
| 28 | YANG J Q, ZHANG Q, WANG J L, et al. Dynamic profiling of immune microenvironment during pancreatic cancer development suggests early intervention and combination strategy of immunotherapy[J]. EBioMedicine, 2022, 78: 103958. |
| 29 | XU S S, LIU Y C, MA H S, et al. A novel signature integrated of immunoglobulin, glycosylation and anti-viral genes to predict prognosis for breast cancer[J]. Front Genet, 2022, 13: 834731. |
| 30 | YANG C S, JIVIDEN K, KAMATA T, et al. Androgen signaling uses a writer and a reader of ADP-ribosylation to regulate protein complex assembly[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 2705. |
| 31 | WANG L D, SUN X D, HE J N, et al. Functions and molecular mechanisms of deltex family ubiquitin E3 ligases in development and disease[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9: 706997. |
| 32 | BOLIS M, PARONI G, FRATELLI M, et al. All-trans retinoic acid stimulates viral mimicry, interferon responses and antigen presentation in breast-cancer cells[J]. Cancers, 2020, 12(5): 1169. |
| 33 | AHMED S F, BUETOW L, GABRIELSEN M, et al. DELTEX2 C-terminal domain recognizes and recruits ADP-ribosylated proteins for ubiquitination[J]. Sci Adv, 2020, 6(34): eabc0629. |
| 34 | LO P K, YAO Y, LEE J S, et al. LIPG signaling promotes tumor initiation and metastasis of human basal-like triple-negative breast cancer[J]. eLife, 2018, 7: e31334. |
| 35 | ZHOU Y J, LI G L, WANG J Y, et al. PD-L1: expression regulation[J]. Blood Sci, 2023, 5(2): 77-91. |
| 36 | ROTMAN J, DEN OTTER L A S, BLEEKER M C G, et al. PD-L1 and PD-L2 expression in cervical cancer: regulation and biomarker potential[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 596825. |
| 37 | WU Y L, CHEN W Y, XU Z P, et al. PD-L1 distribution and perspective for cancer immunotherapy-blockade, knockdown, or inhibition[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 2022. |
| 38 | SHEN X, ZHAO B. Efficacy of PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitors and PD-L1 expression status in cancer: meta-analysis[J]. BMJ, 2018, 362: k3529. |
| 39 | WANG X, TENG F F, KONG L, et al. PD-L1 expression in human cancers and its association with clinical outcomes[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2016, 9: 5023-5039. |
| [1] | 黄紫晗, 黄心智. 单细胞RNA测序在骨再生研究中的应用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(8): 1053-1058. |
| [2] | 朱晗懿, 石欢, 俞创奇, 郑凌艳. 白介素-1β在极重症口腔颌面部感染中的预警价值及机制初探[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(6): 661-672. |
| [3] | 禹恺, 帅哲玮, 黄洪军, 罗艳. 小胶质细胞在中枢神经系统炎症性疾病中的作用和机制研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(5): 630-638. |
| [4] | 罗文, 吕明君, 张珍, 张雪, 姚志荣. 自噬在皮肤黑色素瘤中的双重效应及耐药中的作用研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(2): 233-240. |
| [5] | 唐珺倩, 李本尚. 儿童高危细胞遗传学B系急性淋巴细胞白血病治疗新进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(10): 1390-1399. |
| [6] | 张勇, 李伟宏, 程志鹏, 王斌, 王思珩, 王毓斌. 受体相互作用蛋白激酶1调节癌症进展和免疫反应的研究现状[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(6): 788-794. |
| [7] | 司春婴, 王建茹, 李晓辉, 王永霞, 关怀敏. 基于单细胞测序技术解析冠状动脉粥样硬化患者平滑肌细胞的细胞间通信及关键基因[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(2): 169-182. |
| [8] | 丁艳玲, 李杰, 袁军, 李燕. 慢性淋巴细胞白血病靶向治疗的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(2): 264-270. |
| [9] | 唐思洁, 糜坚青. 抗体药物偶联物在血液肿瘤中的临床应用研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(12): 1607-1614. |
| [10] | 方馨悦, 石岚, 夏思易, 王佳璇, 吴英理, 何珂骏. Menin-MLL蛋白相互作用及相关抑制剂在MLL基因重排白血病中应用的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(10): 1287-1298. |
| [11] | 周婉桢, 滕银成. 非经典Wnt通路在卵巢癌中的作用与潜在治疗意义研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(8): 1056-1063. |
| [12] | 梅艳青, 韩雨洁, 翁文筠, 张蕾, 唐玉杰. 靶向抑制CDK12/13在高级别胶质瘤中的体外治疗效果和作用分子机制探究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(5): 545-559. |
| [13] | 徐瀛濂, 田静, 张翔, 赵顺英. 气道上皮细胞在哮喘发病机制中的作用研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(5): 619-623. |
| [14] | 魏兰懿, 薛晓川, 陈君君, 杨全军, 王梦月, 韩永龙. 骨肉瘤免疫微环境中肿瘤相关巨噬细胞及其靶向治疗的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(5): 624-630. |
| [15] | 刘铁鑫, 林俊卿, 郑宪友. 靶向亚细胞结构治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(2): 230-236. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||