
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (9): 1131-1144.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2023.09.007
收稿日期:2023-04-06
接受日期:2023-09-03
出版日期:2023-09-28
发布日期:2023-09-28
通讯作者:
麻 静,电子信箱:majing3436@163.com。作者简介:吴凯敏(1995—),女,硕士生;电子信箱:kaimin_wu2019@163.com。
基金资助:
WU Kaimin1( ), MA Jing1(
), MA Jing1( ), ZHAO Xuyun2(
), ZHAO Xuyun2( )
)
Received:2023-04-06
Accepted:2023-09-03
Online:2023-09-28
Published:2023-09-28
Contact:
MA Jing, E-mail: majing3436@163.com. #Co-responding authors.Supported by:摘要:
目的·研究间歇性禁食(intermittent fasting,IF)联合产热脂肪活化对小鼠肥胖的治疗和预防作用。方法·取8周龄雄性C57BL/6J正常小鼠以高脂饲料喂养4个月,构建肥胖小鼠模型作为肥胖治疗实验对象;另取8周龄雄性C57BL/6J正常小鼠作为肥胖预防实验对象。2种实验小鼠均分为对照组、隔日腹腔注射CL316243(β3-肾上腺素能受体激动剂,CL)组、IF组、IF联合隔日腹腔注射CL组。肥胖治疗实验小鼠与肥胖预防实验小鼠分别干预38 d和124 d,干预期间均以高脂饲料喂养。每2 d记录小鼠摄食量和体质量;实验结束后,检测小鼠外周血葡萄糖浓度,收集棕色脂肪组织(brown adipose tissue,BAT)、腹股沟白色脂肪组织(inguinal white adipose tissue,iWAT)、附睾白色脂肪组织(epididymal white adipose tissue,eWAT)和肝脏样本并称取质量,通过苏木精-伊红(H-E)染色观察脂肪组织和肝脏组织形态学的变化,采用实时荧光定量聚合酶链反应(RT-qPCR)分析脂肪组织和肝脏组织的产热基因、炎症基因,以及糖脂代谢相关基因的表达水平。结果·在肥胖治疗实验中,IF联合CL相较于单纯IF,可进一步减轻肥胖小鼠体质量并降低血糖(均P<0.05),减小eWAT和肝脏细胞内的脂滴(均P<0.05),促进eWAT与iWAT中产热基因解偶联蛋白1(uncoupling protein1,Ucp1)和细胞死亡诱导DFFA样效应蛋白α(cell death inducing DFFA like effector α,Cidea)的表达,上调eWAT与iWAT中脂肪酸氧化相关基因过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体α(peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α,Ppara)和烯酰辅酶A水合酶(enoyl-CoA hydratase and 3-hydroxyacyl CoA dehydrogenase,Ehhadh)的表达(均P<0.05);与对照组相比,IF联合CL还可抑制eWAT和肝脏中炎症相关的基因表达(均P<0.05),促进肝脏糖代谢相关基因表达(均P<0.05),但与单纯IF相比差异无统计学意义。在肥胖预防实验中,IF联合CL相较于单纯IF,可进一步减小eWAT和iWAT细胞内的脂滴,促进eWAT与iWAT中Ucp1和Cidea的表达,上调eWAT与iWAT中Ppara和Ehhadh的表达(均P<0.05);与对照组相比,IF联合CL还可抵抗高脂饮食诱导的体质量增长,以及改善血糖(均P<0.05),并抑制肝脏脂肪酸氧化相关基因的表达水平(均P<0.05),但与单纯IF相比差异无统计学意义。结论·在肥胖治疗与预防模型中,与单纯IF相比,IF联合产热脂肪活化均可减少脂肪组织中脂肪沉积,促进白色脂肪中产热基因及脂肪酸氧化基因的表达;但两者对体质量和血糖的联合作用在肥胖治疗模型中优于单纯IF,在预防模型中则无明显优势。
中图分类号:
吴凯敏, 麻静, 赵旭赟. 间歇性禁食联合产热脂肪活化防治小鼠肥胖作用研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(9): 1131-1144.
WU Kaimin, MA Jing, ZHAO Xuyun. Combined effects of intermittent fasting and thermogenic fat activation on the treatment and prevention of obesity in mice[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2023, 43(9): 1131-1144.
| Gene | Forward sequence (5′→3′) | Reverse sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Rplp0 | GAAACTGCTGCCTCACATCCG | GCTGGCACAGTGACCTCACACG |
| Ccl2 | AGGTCCCTGTCATGCTTCTG | TCTGGACCCATTCCTTCTTG |
| Ccl5 | TGCCCACGTCAAGGAGTATTT | TTCTCTGGGTTGGCACACACT |
| Il-1b | GAAATGCCACCTTTTGACAGTG | TGGATGCTCTCATCAGGACAG |
| Il-6 | AGTTGCCTTCTTGGGACTGA | TCCACGATTTCCCAGAGAAC |
| Ucp1 | GGCATTCAGAGGCAAATCAGCT | CAATGAACACTGCCACACCTC |
| Cidea | GCAGCCTGCAGGAACTTATCAGC | GATCATGAAATGCGTGTTGTCC |
| leptin | AGCAGTGCCTATCCAGAA | TGCCAGAGTCTGGTCCATCT |
| adiponectin | CAACTGAAGAGCTAGCTC | CTTAGGACCAAGAAGACCTG |
| Ppara | AGAGCCCCATCTGTCCTCTC | ACTGGTAGTCTGCAAAACCAAA |
| Pparg | CTGACCCAATGGTTGCTGAT | GGTGGAGATGCAGGTTCTAC |
| Ehhadh | CAGATGAAGCACTCAAGCTTG | ACCTTGGCAATGGCTTCTGCA |
| Hmgcs2 | GACATCAACTCCCTGTGCCTG | GATGTCAGTGTTGCCTGAATC |
| Cidec | TCGACCTGTACAAGCTGAACCCT | AGGTGCCAAGCAGCATGTGACC |
| Srebp1c | GATGTGCGAACTGGACACAG | CATAGGGGGCGTCAAACAG |
| Fasn | GGAGGTGGTGATAGCCGGTAT | TGGGTAATCCATAGAGCCCAG |
| Scd1 | GCTGGAGTACGTCTGGAGGAA | TCCCGAAGAGGCAGGTGTAG |
| Dgat2 | GCGCTACTTCCGAGACTACTT | GGGCCTTATGCCAGGAAACT |
| Gck | AGGAGGCCAGTGTAAAGATGT | CTCCCAGGTCTAAGGAGAGAAA |
| Pfkl | TCCGCACCTACAACATCCAC | GGCTGGGATGACACACATGA |
| Hk2 | TGATCGCCTGCTTATTCACGG | AACCGCCTAGAAATCTCCAGA |
| Pkm | GCCGCCTGGACATTGACTC | CCATGAGAGAAATTCAGCCGAG |
| Glut1 | TCAAACATGGAACCACCGCTA | AAGAGGCCGACAGAGAAGGAA |
| Glut4 | GTGACTGGAACACTGGTCCTA | CCAGCCACGTTGCATTGTAG |
| Pepck | CATATGCTGATCCTGGGCATAAC | CAAACTTCATCCAGGCAATGTC |
| G6Pase | ACACCGACTACTACAGCAACAG | CCTCGAAAGATAGCAAGAGTAG |
表1 RT-qPCR引物序列
Tab 1 Primer sequences for RT-qPCR
| Gene | Forward sequence (5′→3′) | Reverse sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Rplp0 | GAAACTGCTGCCTCACATCCG | GCTGGCACAGTGACCTCACACG |
| Ccl2 | AGGTCCCTGTCATGCTTCTG | TCTGGACCCATTCCTTCTTG |
| Ccl5 | TGCCCACGTCAAGGAGTATTT | TTCTCTGGGTTGGCACACACT |
| Il-1b | GAAATGCCACCTTTTGACAGTG | TGGATGCTCTCATCAGGACAG |
| Il-6 | AGTTGCCTTCTTGGGACTGA | TCCACGATTTCCCAGAGAAC |
| Ucp1 | GGCATTCAGAGGCAAATCAGCT | CAATGAACACTGCCACACCTC |
| Cidea | GCAGCCTGCAGGAACTTATCAGC | GATCATGAAATGCGTGTTGTCC |
| leptin | AGCAGTGCCTATCCAGAA | TGCCAGAGTCTGGTCCATCT |
| adiponectin | CAACTGAAGAGCTAGCTC | CTTAGGACCAAGAAGACCTG |
| Ppara | AGAGCCCCATCTGTCCTCTC | ACTGGTAGTCTGCAAAACCAAA |
| Pparg | CTGACCCAATGGTTGCTGAT | GGTGGAGATGCAGGTTCTAC |
| Ehhadh | CAGATGAAGCACTCAAGCTTG | ACCTTGGCAATGGCTTCTGCA |
| Hmgcs2 | GACATCAACTCCCTGTGCCTG | GATGTCAGTGTTGCCTGAATC |
| Cidec | TCGACCTGTACAAGCTGAACCCT | AGGTGCCAAGCAGCATGTGACC |
| Srebp1c | GATGTGCGAACTGGACACAG | CATAGGGGGCGTCAAACAG |
| Fasn | GGAGGTGGTGATAGCCGGTAT | TGGGTAATCCATAGAGCCCAG |
| Scd1 | GCTGGAGTACGTCTGGAGGAA | TCCCGAAGAGGCAGGTGTAG |
| Dgat2 | GCGCTACTTCCGAGACTACTT | GGGCCTTATGCCAGGAAACT |
| Gck | AGGAGGCCAGTGTAAAGATGT | CTCCCAGGTCTAAGGAGAGAAA |
| Pfkl | TCCGCACCTACAACATCCAC | GGCTGGGATGACACACATGA |
| Hk2 | TGATCGCCTGCTTATTCACGG | AACCGCCTAGAAATCTCCAGA |
| Pkm | GCCGCCTGGACATTGACTC | CCATGAGAGAAATTCAGCCGAG |
| Glut1 | TCAAACATGGAACCACCGCTA | AAGAGGCCGACAGAGAAGGAA |
| Glut4 | GTGACTGGAACACTGGTCCTA | CCAGCCACGTTGCATTGTAG |
| Pepck | CATATGCTGATCCTGGGCATAAC | CAAACTTCATCCAGGCAATGTC |
| G6Pase | ACACCGACTACTACAGCAACAG | CCTCGAAAGATAGCAAGAGTAG |
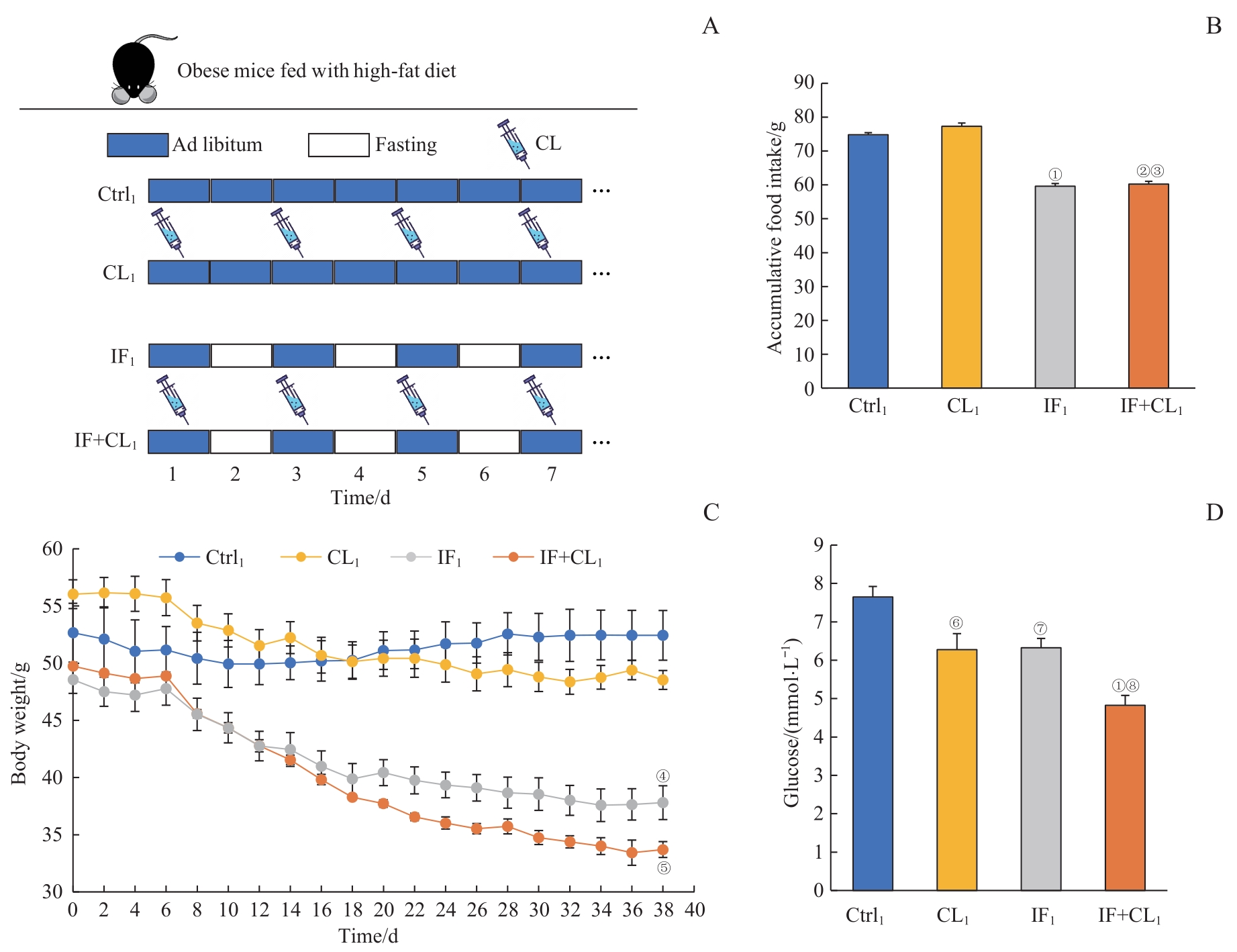
图1 间歇性禁食联合产热脂肪活化对肥胖小鼠体质量及血糖的影响Note: A. The schematic outline of the obesity treatment experiment. B. Accumulative food intake in four groups during intervention (38 d). C. Body weight in four groups during intervention. D. Blood glucose in four groups at the end of experiment. ①P=0.001, ②P=0.002, ④P=0.027, ⑥P=0.005, ⑦P=0.019, compared with the Ctrl1 group; ③P=0.002, compared with the CL1 group; ⑤P=0.049, ⑧P=0.010, compared with the IF1 group.
Fig 1 Effect of intermittent fasting combined with thermogenic fat activation on the body weight and blood glucose of obese mice
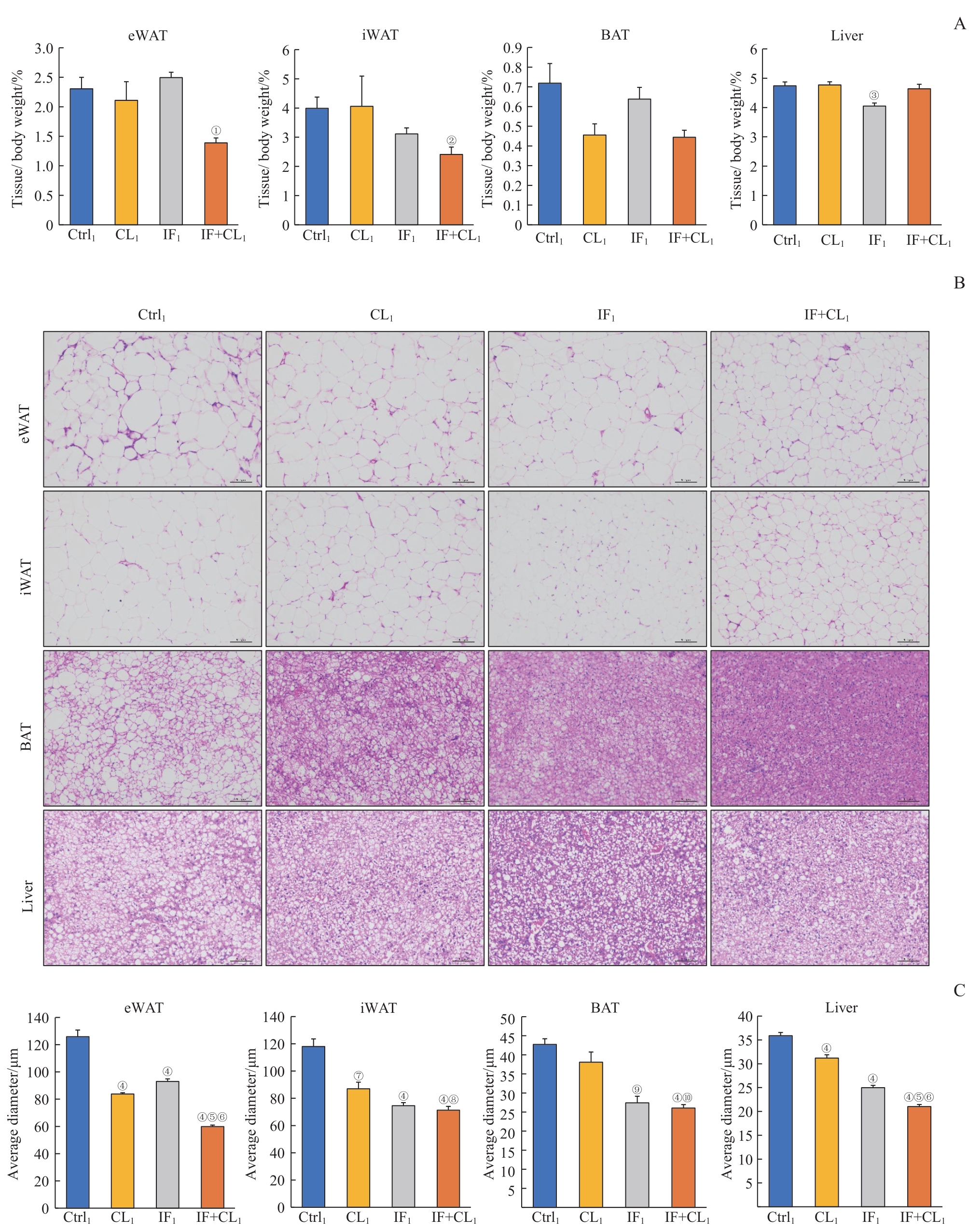
图2 间歇性禁食联合产热脂肪活化对肥胖小鼠脂肪和肝脏组织脂肪沉积的影响Note: A. The relative weight of eWAT, iWAT, BAT, and liver in the four groups. B. H-E staining of eWAT, iWAT, BAT, and liver sections in the four groups (×100). Scale bar=100 μm. C. The average diameters of the cells in eWAT, iWAT, BAT, and liver sections in the four groups. ①P=0.009, ②P=0.025, ③P=0.012, ④P=0.000, ⑦P=0.002, ⑨P=0.001, compared with the Ctrl1 group; ⑤P=0.000, ⑧P=0.020, ⑩P=0.010, compared with the CL1 group; ⑥P=0.000, compared with the IF1 group.
Fig 2 Effect of intermittent fasting combined with thermogenic fat activation on fat deposition in the fat and liver tissues of obese mice

图3 间歇性禁食联合产热脂肪活化对肥胖小鼠脂肪和肝脏组织炎症的影响Note: A. Inflammation genes in the eWAT analyzed by RT-qPCR. B. Inflammation genes in the liver analyzed by RT-qPCR. ①P=0.014, ②P=0.017, ③P=0.002, ④P=0.036, ⑤P=0.031. ⑥P=0.027, ⑦P=0.019, ⑧P=0.001, ⑨P=0.000, ⑩P=0.013, ?P=0.011, ?P=0.018, compared with the Ctrl1 group.
Fig 3 Effect of intermittent fasting combined with thermogenic fat activation on inflammation in the fat and liver tissues of obese mice

图4 间歇性禁食联合产热脂肪活化对肥胖小鼠白色脂肪组织代谢的影响Note: A. The expression of thermogenic genes in the eWAT analyzed by RT-qPCR. B. The expression of fatty acid oxidation genes in the eWAT analyzed by RT-qPCR. C. The expression of thermogenic genes in the iWAT analyzed by RT-qPCR. D. The expression of fatty acid oxidation genes in the iWAT analyzed by RT-qPCR. ①P=0.019, ②P=0.008, ④P=0.017, ⑤P=0.001, ⑧P=0.025, ⑨P=0.000, ⑩P=0.042, ?P=0.016, ?P=0.007, ?P=0.036, ?P=0.031, ?P=0.013, ?P=0.046, ?P=0.037, 22P=0.002, compared with the Ctrl1 group. ⑦P=0.004, ?P=0.037, 24P=0.003, compared with the CL1 group. ③P=0.010, ⑥P=0.002, ?P=0.003, ?P=0.049, 21P=0.037, 23P=0.000, 25P=0.001, compared with the IF1 group.
Fig 4 Effect of intermittent fasting combined with thermogenic fat activation on metabolism of white fat tissues in obese mice

图5 间歇性禁食联合产热脂肪活化对肥胖小鼠肝脏组织糖脂代谢的影响Note: A. The expression of fatty acid metabolism genes in the liver analyzed by RT-qPCR. B. The expression of gluconeogenesis and glycolysis genes in the liver analyzed by RT-qPCR. ①P=0.008, ②P=0.006, ③P=0.037, ④P=0.013. ⑤P=0.024, ⑥P=0.002, ⑦P=0.001, ⑧P=0.000, ⑨P=0.020, ⑩P=0.012, ?P=0.036, ?P=0.018, ?P=0.038, compared with the Ctrl1 group.
Fig 5 Effect of intermittent fasting combined with thermogenic fat activation on glucose and lipid metabolism in the liver tissue of obese mice
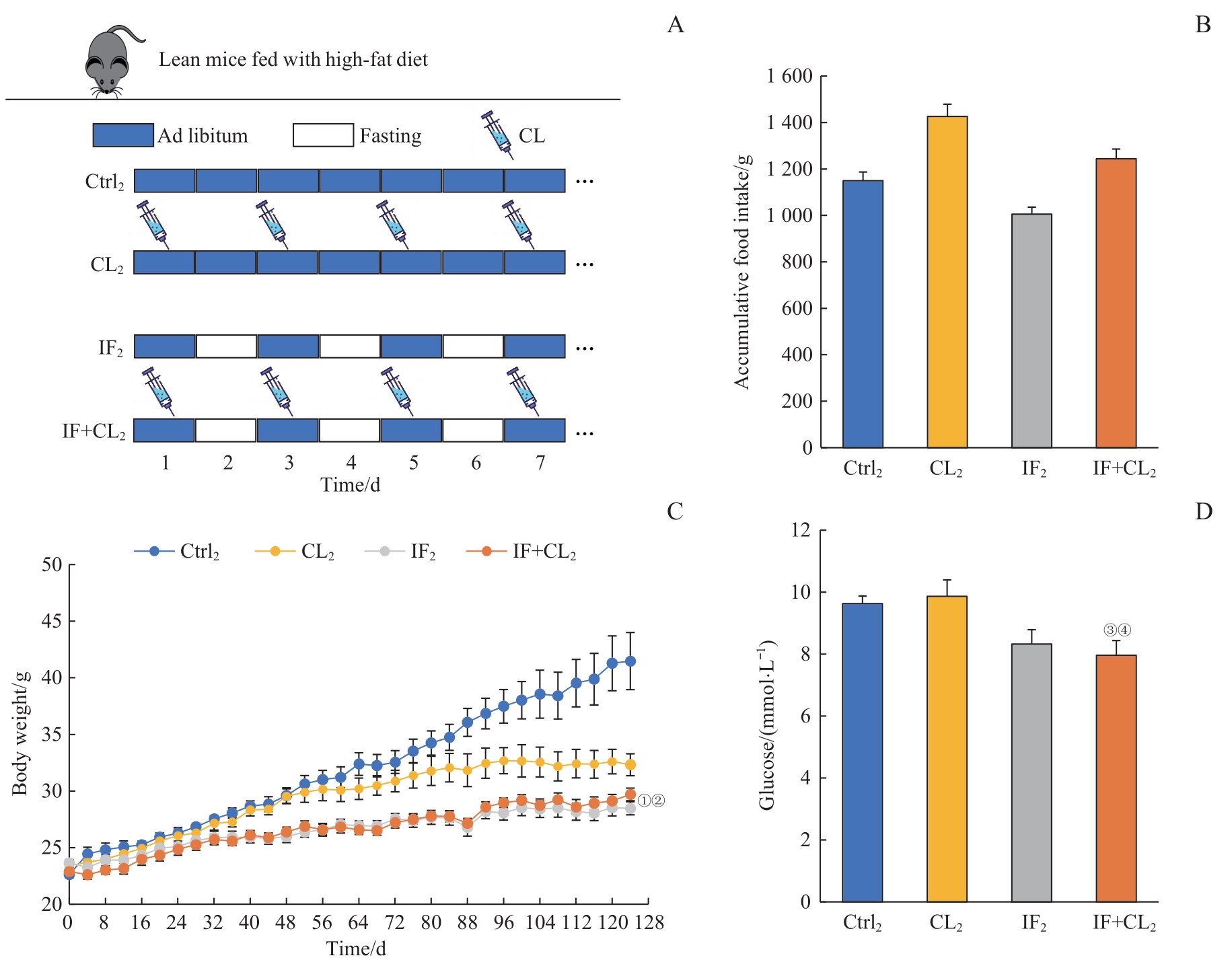
图6 间歇性禁食联合产热脂肪活化对高脂饮食引起的肥胖及血糖升高的预防作用Note: A. The schematic outline of the obesity prevention experiment. B. Accumulative food intake in four groups during intervention (124 d). C. Body weight in four groups during intervention. D. Blood glucose in four groups at the end of experiment. ①P=0.015, ③P=0.038, compared with the Ctrl2 group; ②P=0.023, ④P=0.045, compared with the CL2 group.
Fig 6 Preventive effect of intermittent fasting combined with thermogenic fat activation on high-fat diet-induced obesity and hyperglycemia
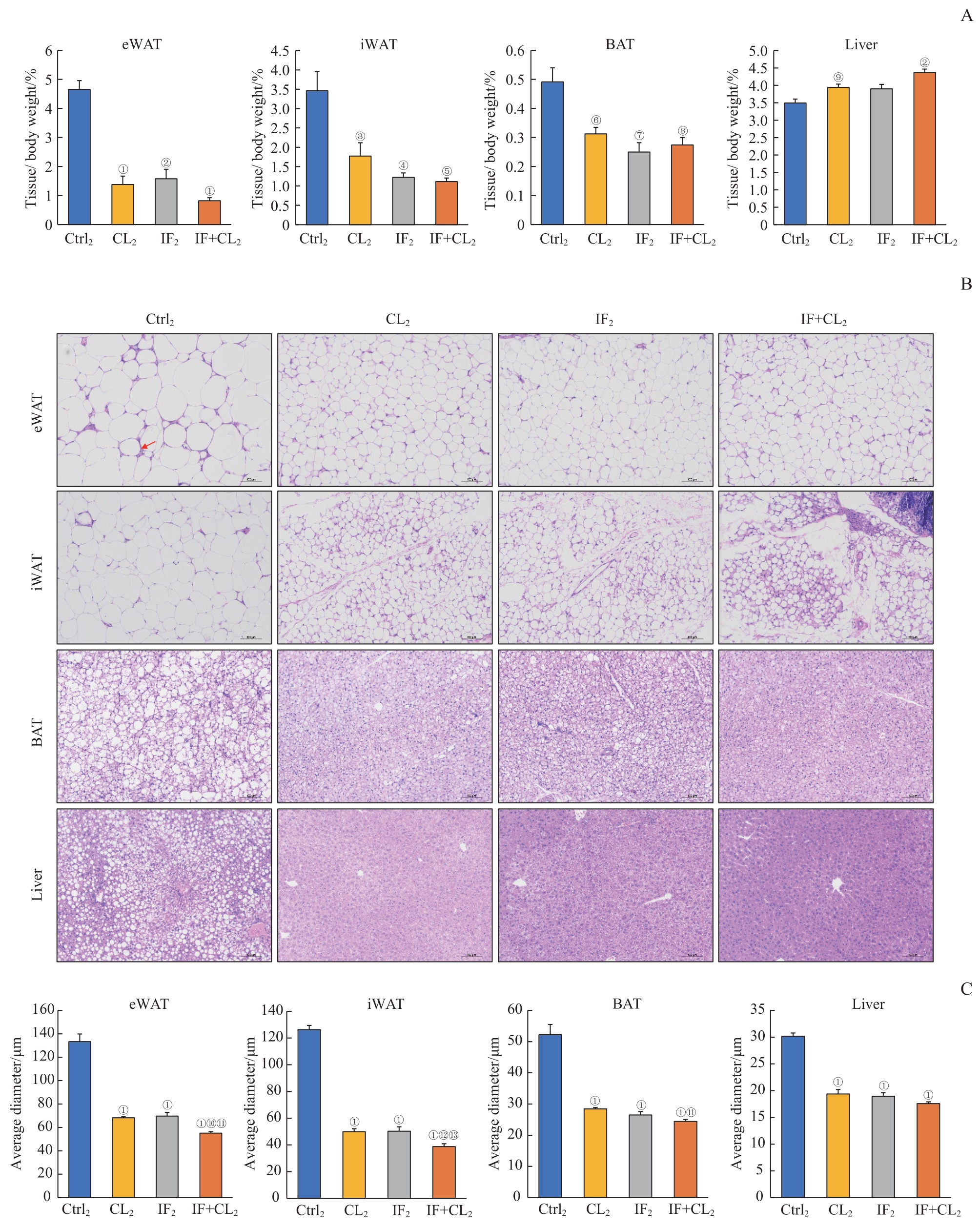
图7 间歇性禁食联合产热脂肪活化对高脂饮食诱导的脂肪和肝脏组织脂肪沉积的预防作用Note: A. The relative weight of eWAT, iWAT, BAT, and liver in the four groups. B. H-E staining of eWAT, iWAT, BAT and liver sections in the four groups (×100). Scale bar=100 μm. The arrow indicates the crown-like structure. C. The average diameters of the cells in eWAT, iWAT, BAT, and liver sections in the four groups. ①P=0.000, ②P=0.001, ③P=0.039, ④P=0.009, ⑤P=0.003, ⑥P=0.016, ⑦P=0.011, ⑧P=0.008, ⑨P=0.031, compared with the Ctrl2 group; ⑩P=0.001, ?P=0.016, compared with the IF2 group; ?P=0.000, ?P=0.005, compared with the CL2 group.
Fig 7 Preventive effect of intermittent fasting combined with thermogenic fat activation on high-fat diet-induced fat deposition in the fat and liver tissues
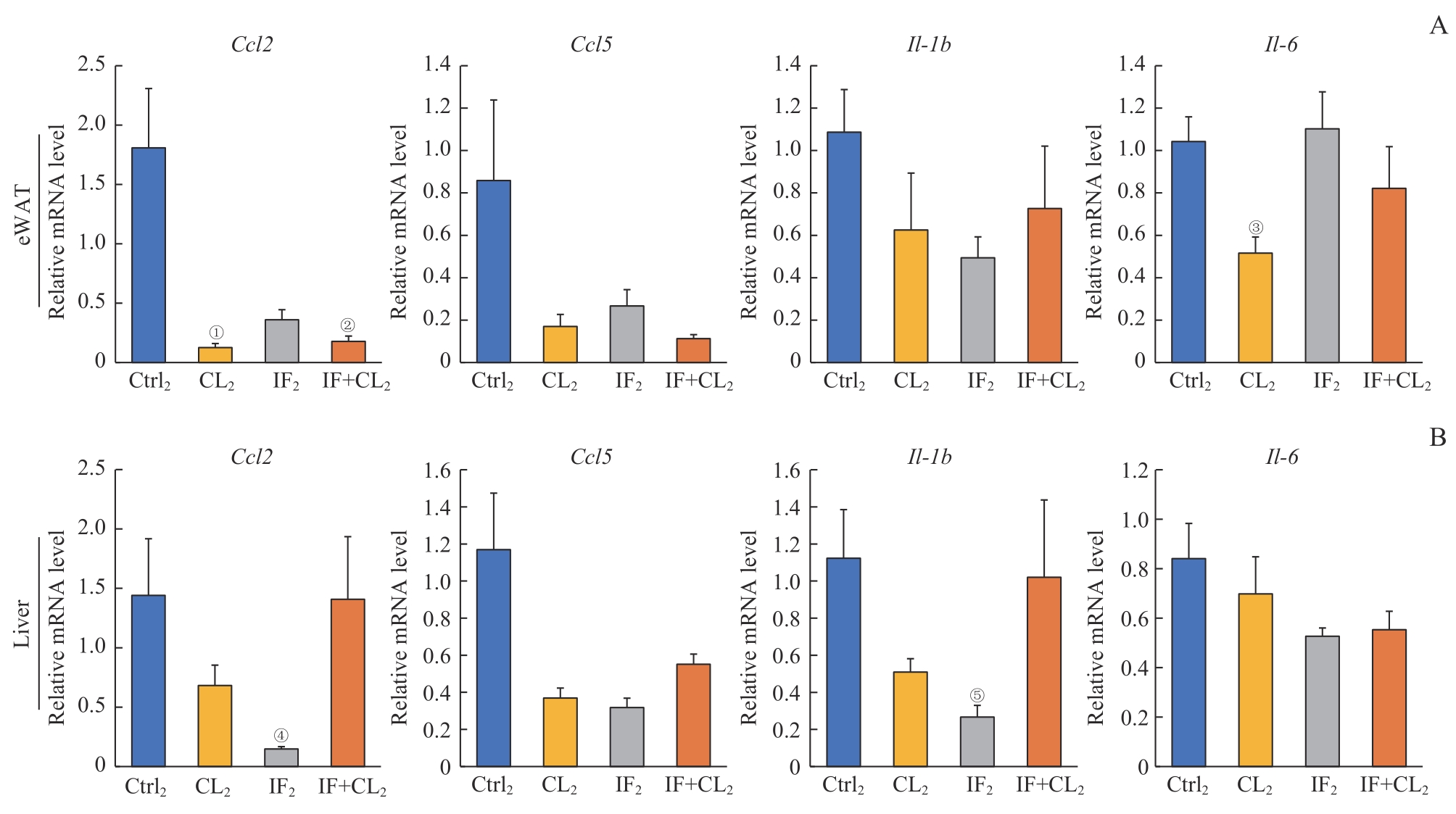
图8 间歇性禁食联合产热脂肪活化对高脂饮食诱导的脂肪和肝脏组织炎症的预防作用Note: A. Inflammation genes in the eWAT analyzed by RT-qPCR. B. Inflammation genes in the liver analyzed by RT-qPCR. ①P=0.024, ②P=0.028, ③P=0.010, ④P=0.040, ⑤P=0.039, compared with the Ctrl2 group.
Fig 8 Preventive effect of intermittent fasting combined with thermogenic fat activation on high-fat diet-induced inflammation in the fat and liver tissues
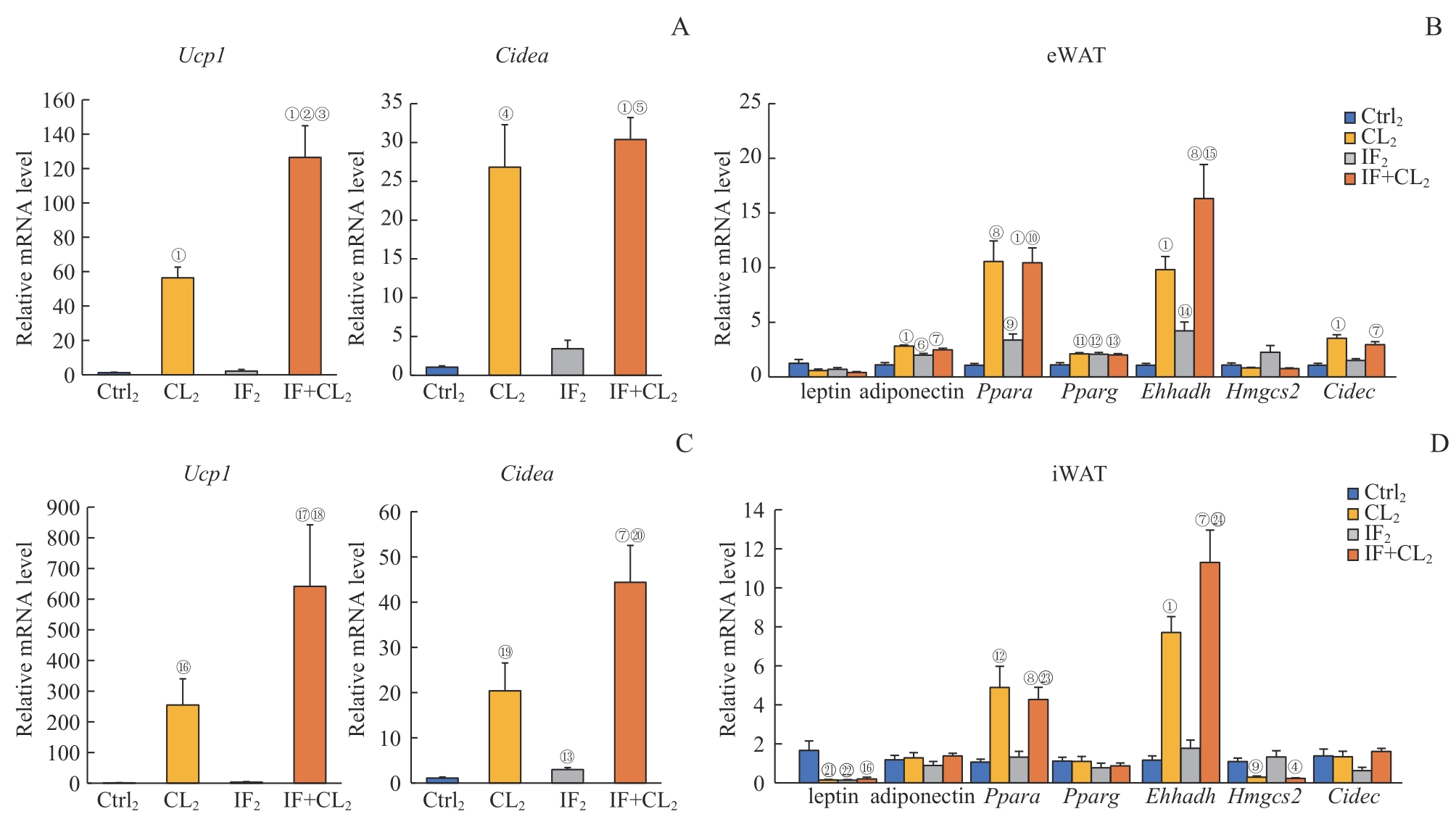
图9 间歇性禁食联合产热脂肪活化对高脂饮食小鼠白色脂肪组织代谢的影响Note: A. The expression of thermogenic genes in the eWAT analyzed by RT-qPCR. B. The expression of fatty acid oxidation genes in the eWAT analyzed by RT-qPCR. C. The expression of thermogenic genes in the iWAT analyzed by RT-qPCR. D. The expression of fatty acid oxidation genes in the iWAT analyzed by RT-qPCR. ①P=0.000, ④P=0.003, ⑥P=0.019, ⑦P=0.001, ⑧P=0.002, ⑨P=0.006, ?P=0.004, ?P=0.014, ?P=0.008, ?P=0.007, ?P=0.029, ?P=0.021, ?P=0.024, 21P=0.023, 22P=0.042, compared with the Ctrl2 group; ②P=0.001, ⑤P=0.000, ⑩P=0.006, ?P=0.020, ?P=0.041, ?P=0.005, 23P=0.010, 24P=0.003, compared with the IF2 group; ③P=0.012, compared with the CL2 group.
Fig 9 Effect of intermittent fasting combined with thermogenic fat activation on metabolism of white fat tissues in mice on a high-fat diet
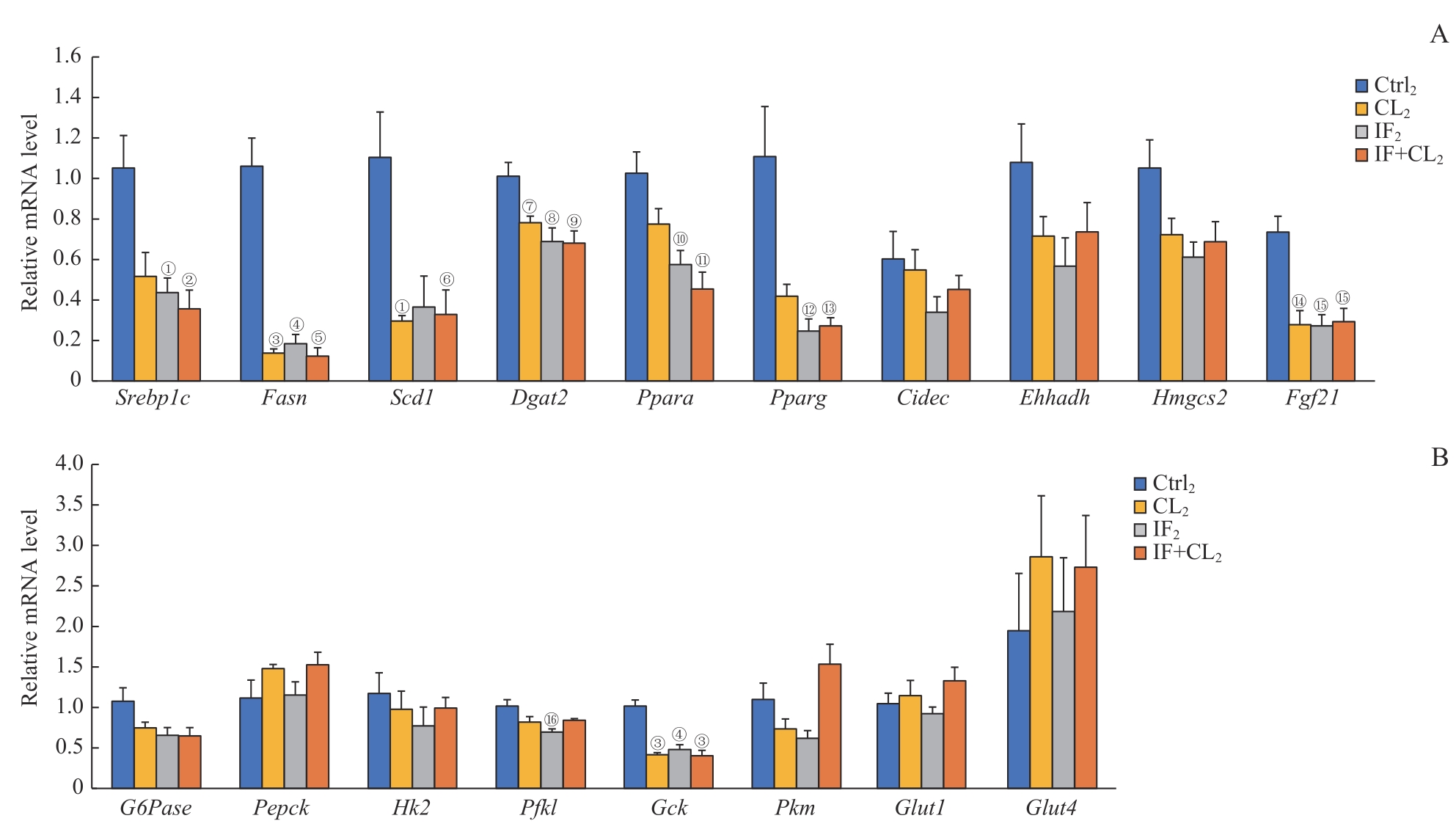
图10 间歇性禁食联合产热脂肪活化对高脂饮食小鼠肝脏组织糖脂代谢的影响Note: A. The expression of fatty acid metabolism genes in the liver analyzed by RT-qPCR. B. The expression of gluconeogenesis and glycolysis genes in the liver analyzed by RT-qPCR. ①P=0.025, ②P=0.010, ③P=0.001, ④P=0.002, ⑤P=0.000, ⑥P=0.026, ⑦P=0.040, ⑧P=0.021, ⑨P=0.011, ⑩P=0.020, ?P=0.005, ?P=0.031, ?P=0.018, ?P=0.017, ?P=0.008, ?P=0.022, compared with the Ctrl2 group.
Fig 10 Effect of intermittent fasting combined with thermogenic fat activation on glucose and lipid metabolism in the liver tissue of mice on a high-fat diet
| 1 | WANG W S, SEALE P. Control of brown and beige fat development[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2016, 17(11): 691-702. |
| 2 | HARMS M, SEALE P. Brown and beige fat: development, function and therapeutic potential[J]. Nat Med, 2013, 19(10): 1252-1263. |
| 3 | SAKERS A, DE SIQUEIRA M K, SEALE P, et al. Adipose-tissue plasticity in health and disease[J]. Cell, 2022, 185(3): 419-446. |
| 4 | WOLFRUM C, GERHART-HINES Z. Fueling the fire of adipose thermogenesis[J]. Science, 2022, 375(6586): 1229-1231. |
| 5 | HAO L, SCOTT S, ABBASI M, et al. Beneficial metabolic effects of mirabegron in vitro and in high-fat diet-induced obese mice[J]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2019, 369(3): 419-427. |
| 6 | PERES VALGAS DA SILVA C, CALMASINI F, ALEXANDRE E C, et al. The effects of mirabegron on obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance are associated with brown adipose tissue activation but not beiging in the subcutaneous white adipose tissue[J]. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol, 2021, 48(11): 1477-1487. |
| 7 | FINLIN B S, MEMETIMIN H, ZHU B B, et al. The β3-adrenergic receptor agonist mirabegron improves glucose homeostasis in obese humans[J]. J Clin Invest, 2020, 130(5): 2319-2331. |
| 8 | O'MARA A E, JOHNSON J W, LINDERMAN J D, et al. Chronic mirabegron treatment increases human brown fat, HDL cholesterol, and insulin sensitivity[J]. J Clin Invest, 2020, 130(5): 2209-2219. |
| 9 | PUTMAN A K, CONTRERAS G A, MOTTILLO E P. Thermogenic adipose redox mechanisms: potential targets for metabolic disease therapies[J]. Antioxidants (Basel), 2023, 12(1): 196. |
| 10 | VARADY K A, CIENFUEGOS S, EZPELETA M, et al. Clinical application of intermittent fasting for weight loss: progress and future directions[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2022, 18(5): 309-321. |
| 11 | CATENACCI V A, PAN Z X, OSTENDORF D, et al. A randomized pilot study comparing zero-calorie alternate-day fasting to daily caloric restriction in adults with obesity[J]. Obesity (Silver Spring), 2016, 24(9): 1874-1883. |
| 12 | VARADY K A, BHUTANI S, KLEMPEL M C, et al. Alternate day fasting for weight loss in normal weight and overweight subjects: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Nutr J, 2013, 12(1): 146. |
| 13 | HARVIE M N, PEGINGTON M, MATTSON M P, et al. The effects of intermittent or continuous energy restriction on weight loss and metabolic disease risk markers: a randomized trial in young overweight women[J]. Int J Obes (Lond), 2011, 35(5): 714-727. |
| 14 | LIU D Y, HUANG Y, HUANG C, et al. Calorie restriction with or without time-restricted eating in weight loss[J]. N Engl J Med, 2022, 386(16): 1495-1504. |
| 15 | CHO A R, MOON J Y, KIM S, et al. Effects of alternate day fasting and exercise on cholesterol metabolism in overweight or obese adults: a pilot randomized controlled trial[J]. Metabolism, 2019, 93: 52-60. |
| 16 | TREPANOWSKI J F, KROEGER C M, BARNOSKY A, et al. Effect of alternate-day fasting on weight loss, weight maintenance, and cardioprotection among metabolically healthy obese adults: a randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA Intern Med, 2017, 177(7): 930-938. |
| 17 | KLEMPEL M C, BHUTANI S, FITZGIBBON M, et al. Dietary and physical activity adaptations to alternate day modified fasting: implications for optimal weight loss[J]. Nutr J, 2010, 9: 35. |
| 18 | DE CABO R, MATTSON M P. Effects of intermittent fasting on health, aging, and disease[J]. N Engl J Med, 2019, 381(26): 2541-2551. |
| 19 | LIU B, PAGE A J, HUTCHISON A T, et al. Intermittent fasting increases energy expenditure and promotes adipose tissue browning in mice[J]. Nutrition, 2019, 66: 38-43. |
| 20 | MARINHO T S, ORNELLAS F, AGUILA M B, et al. Browning of the subcutaneous adipocytes in diet-induced obese mouse submitted to intermittent fasting[J]. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2020, 513: 110872. |
| 21 | LI G, XIE C, LU S, et al. Intermittent fasting promotes white adipose browning and decreases obesity by shaping the gut microbiota[J]. Cell Metab, 2017, 26(4): 672-685.e4. |
| 22 | HEPLER C, WEIDEMANN B J, WALDECK N J, et al. Time-restricted feeding mitigates obesity through adipocyte thermogenesis[J]. Science, 2022, 378(6617): 276-284. |
| 23 | YONESHIRO T, AITA S, MATSUSHITA M, et al. Brown adipose tissue, whole-body energy expenditure, and thermogenesis in healthy adult men[J]. Obesity (Silver Spring), 2011, 19(1): 13-16. |
| 24 | SPONTON C H, DE LIMA-JUNIOR J C, LEIRIA L O. What puts the heat on thermogenic fat: metabolism of fuel substrates[J]. Trends Endocrinol Metab, 2022, 33(8): 587-599. |
| 25 | EZPELETA M, GABEL K, CIENFUEGOS S, et al. Effect of alternate day fasting combined with aerobic exercise on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Cell Metab, 2023, 35(1): 56-70.e3. |
| 26 | GUREVICH-PANIGRAHI T, PANIGRAHI S, WIECHEC E, et al. Obesity: pathophysiology and clinical management[J]. Curr Med Chem, 2009, 16(4): 506-521. |
| 27 | BEL J S, TAI T C, KHAPER N, et al. Mirabegron: the most promising adipose tissue beiging agent[J]. Physiol Rep, 2021, 9(5): e14779. |
| [1] | 李倩玉, 钱逸斐, 李松玲, 朱子俊, 覃雯莉, 刘艳丰, 邱必军. Zeste 12抑制基因在肝细胞癌中的功能及机制[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(9): 1138-1148. |
| [2] | 王静怡, 邓佳丽, 朱仪, 丁心怡, 郭嘉婧, 王中领. 新型pH响应性锰基纳米探针用于乳腺癌铁死亡及磁共振成像实验研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(9): 1183-1193. |
| [3] | 江怡, 黄晨浩, 李祉良, 吴珺玮, 赵任, 张弢. 1例KRAS突变的结直肠癌患者术前接受化疗联合免疫治疗的效果报道[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(9): 1256-1260. |
| [4] | 何苏荟, 赵银龙, 张家毓. 端粒酶基因治疗对压力超负荷心力衰竭小鼠的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(8): 949-956. |
| [5] | 林桐, 陶怡, 金诗炜, 孙淼, 糜坚青. 血浆置换联合经典化学治疗对多发性骨髓瘤患者肾功能的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(7): 823-828. |
| [6] | 孟靖, 谢玉婷, 左佳鑫, 熊屏. 纳米工程化T细胞体系的构建及其对口腔鳞状细胞癌的体外治疗研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(7): 866-873. |
| [7] | 陈子旋, 刘敏. 肾细胞癌免疫细胞治疗的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(7): 916-925. |
| [8] | 高欣洁, 刘艳, 王大威. 地中海贫血基因治疗研究进展及思考[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(5): 540-548. |
| [9] | 张钲佳, 李小敏, 周鑫, 马海荣, 艾松涛. 高阶磁共振功能成像评估骨与软组织肿瘤价值初探[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(5): 585-596. |
| [10] | 李文妙, 邢莉, 潘英瑜, 黄滢, 杨国访, 刘德达. 下颌第一磨牙根管直径和锥度的锥形束CT测量分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(5): 597-604. |
| [11] | 禹恺, 帅哲玮, 黄洪军, 罗艳. 小胶质细胞在中枢神经系统炎症性疾病中的作用和机制研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(5): 630-638. |
| [12] | 黄周轩, 邵静波. 慢性原发性免疫性血小板减少症的治疗研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(4): 508-516. |
| [13] | 周至宜, 赵浩, 缪亦锋, 朱池豪, 杨溪, 王思源, 冯军峰, 邱永明. 全神经内镜技术在后颅窝病变手术中的应用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(3): 365-372. |
| [14] | 张涤凡, 王明慧, 赵洁, 万江波, 黄方, 郝思国. B7基因修饰的白血病细胞外泌体的抗白血病效应[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(2): 129-137. |
| [15] | 朱涵菁, 郭艳, 殷弘凡, 王贝贝, 谢娟, 杨艳. 前列腺癌内分泌治疗患者体重管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(2): 194-203. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||