
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (9): 1169-1181.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2024.09.012
• 论著 · 临床研究 • 上一篇
吴其蓁( ), 刘启明(
), 刘启明( ), 柴烨子, 陶政宇, 王依楠, 郭欣宁, 姜萌(
), 柴烨子, 陶政宇, 王依楠, 郭欣宁, 姜萌( ), 卜军(
), 卜军( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-29
接受日期:2024-06-04
出版日期:2024-09-28
发布日期:2024-10-09
通讯作者:
姜萌,卜军
E-mail:wuqizhen@sjtu.edu.cn;090503liu@sjtu.edu.cn;jiangmeng0919@163.com;pujun310@hotmail.com
作者简介:吴其蓁(1997—),女,博士生;电子信箱:wuqizhen@sjtu.edu.cn基金资助:
WU Qizhen( ), LIU Qiming(
), LIU Qiming( ), CHAI Yezi, TAO Zhengyu, WANG Yinan, GUO Xinning, JIANG Meng(
), CHAI Yezi, TAO Zhengyu, WANG Yinan, GUO Xinning, JIANG Meng( ), PU Jun(
), PU Jun( )
)
Received:2024-01-29
Accepted:2024-06-04
Online:2024-09-28
Published:2024-10-09
Contact:
JIANG Meng,PU Jun
E-mail:wuqizhen@sjtu.edu.cn;090503liu@sjtu.edu.cn;jiangmeng0919@163.com;pujun310@hotmail.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的·通过机器学习方法,采用临床常见实验室指标及心脏彩色多普勒超声指标,在乳腺癌患者中探究早期识别并预测新辅助治疗后发生与代谢状态改变相关的心血管疾病高风险患者的方案。方法·连续入选2020年9月—2022年9月在上海交通大学医学院附属仁济医院乳腺外科确诊的原发性浸润性乳腺癌女性患者。收集并记录患者的一般情况、实验室检查结果及心脏彩色多普勒超声结果。经过特征提取后,分别应用梯度增强(gradient boost,GB)、支持向量机(support vector machine,SVM)、决策树(decision tree,DT)、K-近邻(K-nearest neighbour,KNN)及随机森林(random forest,RF)5种机器学习方法构建新辅助治疗后患者炎症代谢状态改变预测模型,并比较5种模型的预测性能。结果·最终纳入232例有效临床数据,其中135例为新辅助治疗前,97例为完成4个周期的新辅助治疗后。特征提取筛选出白细胞计数、血红蛋白、高密度脂蛋白、白细胞介素-2受体和白细胞介素-8这5项特征。在多特征分析中,白细胞计数+血红蛋白+高密度脂蛋白的受试者操作特征曲线下面积高于白细胞介素-2受体+白细胞介素-8(RF:0.928 vs 0.772;GB:0.900 vs 0.792;SVM:0.941 vs 0.764;KNN:0.907 vs 0.762;DT:0.799 vs 0.714),并且在RF、SVM、GB模型中的曲线下面积(0.928、0.941、0.900)及准确率(0.914、0.897、0.776)较高;与RF、GB模型(P=0.122,P=0.097)相比,SVM模型在训练集数据上校准度较好(P=0.394)。结论·SVM模型可通过纳入白细胞计数、血红蛋白、高密度脂蛋白、白细胞介素-2受体、白细胞介素-8这5项临床常见指标,在乳腺癌患者中建立早期预测新辅助治疗后代谢状态改变相关心血管疾病风险的预测模型,可能有助于临床上建立基于患者炎症代谢状态的个体化筛查方案。
中图分类号:
吴其蓁, 刘启明, 柴烨子, 陶政宇, 王依楠, 郭欣宁, 姜萌, 卜军. 机器学习预测乳腺癌新辅助治疗后炎症代谢状态改变的模型评价[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(9): 1169-1181.
WU Qizhen, LIU Qiming, CHAI Yezi, TAO Zhengyu, WANG Yinan, GUO Xinning, JIANG Meng, PU Jun. Evaluation of machine learning prediction of altered inflammatory metabolic state after neoadjuvant therapy for breast cancer[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2024, 44(9): 1169-1181.
| Indicator | All (n=232) | Patient before neoadjuvant therapy (n=135) | Patient after neoadjuvant therapy (n=97) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic parameter | |||
| Age/year | 47.00 (40.00, 55.00) | 46.00 (39.00, 54.50) | 48.00 (40.00, 56.00) |
| Height/m | 1.60 (1.58, 1.65) | 1.60 (1.58, 1.65) | 1.60 (1.58, 1.65) |
| Weight/kg | 60.00 (54.00, 67.78) | 59.00 (55.00, 66.25) | 60.00 (54.00, 68.00) |
| BMI/ (kg·m-2) | 22.87 (21.10, 25.39) | 22.66 (21.09, 24.96) | 23.10 (21.10, 25.50) |
| Systolic blood pressue/mmHg | 122.70±13.65 | 124.77±13.47 | 119.81±13.45 |
| Diastolic blood pressure/mmHg | 77.15±8.72 | 77.59±7.84 | 76.54±9.83 |
| Heart rate/ (beat ·min-1) | 78.19±5.56 | 77.63±5.32 | 78.96±5.87 |
| Accompanied by lymph node metastasis/n(%) | 72 (31.0) | 44 (32.6) | 28 (28.9) |
| Tumor location/n(%) | |||
| Left side | 113 (48.7) | 68 (50.4) | 45 (46.4) |
| Right side | 116 (50.0) | 65 (48.1) | 51 (52.6) |
| Bilateral | 3 (1.3) | 2 (1.5) | 1 (1.0) |
| Neoadjuvant treatment/n(%) | |||
| Paclitaxel+cisplatin | 26 (26.8) | ‒ | 26 (26.8) |
| Paclitaxel+cisplatin+trastuzumab | 21 (21.6) | ‒ | 21 (21.6) |
| Paclitaxel+cisplatin+apatinib | 35 (36.1) | ‒ | 35 (36.1) |
| Paclitaxel+cisplatin+pyrotinib | 15 (15.5) | ‒ | 15 (15.5) |
| Cardiovascular risk factor/n(%) | |||
| Coronary heart disease | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Hypertension | 52 (22.4) | 21 (15.6) | 31 (31.0) |
| Type 2 diabetes | 14 (6.0) | 6 (4.4) | 8 (8.2) |
| Hyperlipidemia | 26 (11.2) | 10 (7.4) | 16 (16.5) |
| Smoking | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Electrocardiographic parameter/n(%) | |||
| ST-T change | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (2.0) |
| QTc prolongation | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Echocardiographic parameter | |||
| AOD/mm | 30.00 (28.00, 32.00) | 30.00 (28.00, 32.00) | 31.00 (28.00, 32.00) |
| LAD/mm | 33.44±4.31 | 33.30±4.14 | 33.64±4.54 |
| LVEDD/mm | 44.62±3.30 | 44.66±3.35 | 44.57±3.24 |
| LVESD/mm | 28.00 (27.00, 30.00) | 28.00 (27.00, 30.00) | 29.00 (27.00, 30.00) |
| IVS/mm | 8.00 (7.00, 9.00) | 8.00 (7.00, 9.00) | 8.00 (7.00, 9.00) |
| LVPWT/mm | 8.00 (7.00, 8.00) | 8.00 (7.00, 8.00) | 8.00 (7.00, 9.00) |
| FS/% | 36.00 (34.00, 38.00) | 36.00 (34.00, 38.00) | 37.00 (35.00, 38.00) |
| EF/% | 65.00 (63.00, 68.00) | 65.00 (63.00, 68.00) | 66.00 (63.00, 69.00) |
| Laboratory examination parameter | |||
| WBC/ (×109·L-1) | 5.11 (4.04, 6.56) | 5.65 (4.68, 6.86) | 4.44 (3.50, 5.79)① |
| HB/ (g·L-1) | 120.00 (105.00, 129.00) | 127.00 (120.00, 133.00) | 105.00 (97.00, 117.00)① |
| HCT | 0.36 (0.32, 0.39) | 0.38 (0.36, 0.40) | 0.32 (0.29, 0.35)① |
| ST2/ (ng·mL-1) | 18.14 (13.83, 24.86) | 18.38 (13.75, 25.36) | 18.11 (14.25, 24.13) |
| BNP/ (pg·mL-1) | 19.00 (12.00, 32.00) | 19.00 (12.00, 31.00) | 21.00 (15.00, 35.00) |
| NT-proBNP/ (pg·mL-1) | 24.04 (10.00, 42.58) | 24.42 (10.00, 41.58) | 23.95 (10.48, 46.28) |
| TNI/ (ng·mL-1) | 0 (0, 0) | 0 (0, 0) | 0 (0, 0.01) |
| hsCRP/ (mg·L-1) | 0.71 (0.32, 1.41) | 0.70 (0.32, 1.42) | 0.86 (0.34, 1.40) |
| TC/ (mmol·L-1) | 4.48 (3.91, 5.16) | 4.52 (3.98, 5.24) | 4.42 (3.85, 4.99) |
| TAG/ (mmol·L-1) | 1.35 (0.86, 2.04) | 1.02 (0.74, 1.66) | 1.75 (1.27, 2.40)① |
| HDL/ (mmol·L-1) | 1.10 (0.87, 1.32) | 1.24 (1.04, 1.45) | 0.87 (0.75, 1.03)① |
| LDL/ (mmol·L-1) | 3.34 (2.82, 3.98) | 3.21 (2.76, 3.92) | 3.47 (2.94, 4.12) |
| NHDL/ (mmol·L-1) | 2.52 (2.16, 3.13) | 2.60 (2.21, 3.20) | 2.41 (2.05, 2.91)② |
| FPG/ (mmol·L-1) | 4.95 (4.74, 5.26) | 4.88 (4.69, 5.24) | 5.05 (4.83, 5.29)④ |
| GOT/ (mmol·L-1) | 20.00 (16.00, 26.00) | 17.00 (14.00, 23.00) | 22.00 (19.00, 29.75) |
| GPT/ (mmol·L-1) | 19.00 (13.00, 29.50) | 15.00 (11.00, 27.00) | 24.00 (17.00, 34.00) |
| γ-GT/ (mmol·L-1) | 21.00 (14.00, 40.00) | 18.00 (12.00, 32.00) | 33.50 (17.00, 47.00) |
| IL-1β/ (pg·mL-1) | 5.00 (5.00, 5.00) | 5.00 (5.00, 5.00) | 5.00 (5.00, 5.00) |
| IL-2R/ (U·mL-1) | 330.00 (270.75, 424.75) | 295.00 (249.50, 369.50) | 399.00 (322.00, 508.00)① |
| IL-6/ (pg·mL-1) | 3.15 (2.21, 4.25) | 2.97 (2.12, 3.74) | 3.66 (2.68, 4.89)⑤ |
| IL-8/ (pg·mL-1) | 11.30 (7.72, 18.95) | 13.20 (8.81, 21.10) | 9.84 (7.06, 15.20)③ |
| IL-10/ (pg·mL-1) | 5.00 (5.00, 5.00) | 5.00 (5.00, 5.00) | 5.00 (5.00, 5.00) |
| TNF-α/ (pg·mL-1) | 6.53 (5.26, 7.86) | 6.01 (5.00, 7.02) | 7.33 (6.03, 8.60)① |
表1 乳腺癌新辅助治疗前及新辅助治疗后患者所有特征变量信息
Tab 1 All feature variable information of patients with breast cancer before and after neoadjuvant therapy
| Indicator | All (n=232) | Patient before neoadjuvant therapy (n=135) | Patient after neoadjuvant therapy (n=97) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic parameter | |||
| Age/year | 47.00 (40.00, 55.00) | 46.00 (39.00, 54.50) | 48.00 (40.00, 56.00) |
| Height/m | 1.60 (1.58, 1.65) | 1.60 (1.58, 1.65) | 1.60 (1.58, 1.65) |
| Weight/kg | 60.00 (54.00, 67.78) | 59.00 (55.00, 66.25) | 60.00 (54.00, 68.00) |
| BMI/ (kg·m-2) | 22.87 (21.10, 25.39) | 22.66 (21.09, 24.96) | 23.10 (21.10, 25.50) |
| Systolic blood pressue/mmHg | 122.70±13.65 | 124.77±13.47 | 119.81±13.45 |
| Diastolic blood pressure/mmHg | 77.15±8.72 | 77.59±7.84 | 76.54±9.83 |
| Heart rate/ (beat ·min-1) | 78.19±5.56 | 77.63±5.32 | 78.96±5.87 |
| Accompanied by lymph node metastasis/n(%) | 72 (31.0) | 44 (32.6) | 28 (28.9) |
| Tumor location/n(%) | |||
| Left side | 113 (48.7) | 68 (50.4) | 45 (46.4) |
| Right side | 116 (50.0) | 65 (48.1) | 51 (52.6) |
| Bilateral | 3 (1.3) | 2 (1.5) | 1 (1.0) |
| Neoadjuvant treatment/n(%) | |||
| Paclitaxel+cisplatin | 26 (26.8) | ‒ | 26 (26.8) |
| Paclitaxel+cisplatin+trastuzumab | 21 (21.6) | ‒ | 21 (21.6) |
| Paclitaxel+cisplatin+apatinib | 35 (36.1) | ‒ | 35 (36.1) |
| Paclitaxel+cisplatin+pyrotinib | 15 (15.5) | ‒ | 15 (15.5) |
| Cardiovascular risk factor/n(%) | |||
| Coronary heart disease | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Hypertension | 52 (22.4) | 21 (15.6) | 31 (31.0) |
| Type 2 diabetes | 14 (6.0) | 6 (4.4) | 8 (8.2) |
| Hyperlipidemia | 26 (11.2) | 10 (7.4) | 16 (16.5) |
| Smoking | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Electrocardiographic parameter/n(%) | |||
| ST-T change | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (2.0) |
| QTc prolongation | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Echocardiographic parameter | |||
| AOD/mm | 30.00 (28.00, 32.00) | 30.00 (28.00, 32.00) | 31.00 (28.00, 32.00) |
| LAD/mm | 33.44±4.31 | 33.30±4.14 | 33.64±4.54 |
| LVEDD/mm | 44.62±3.30 | 44.66±3.35 | 44.57±3.24 |
| LVESD/mm | 28.00 (27.00, 30.00) | 28.00 (27.00, 30.00) | 29.00 (27.00, 30.00) |
| IVS/mm | 8.00 (7.00, 9.00) | 8.00 (7.00, 9.00) | 8.00 (7.00, 9.00) |
| LVPWT/mm | 8.00 (7.00, 8.00) | 8.00 (7.00, 8.00) | 8.00 (7.00, 9.00) |
| FS/% | 36.00 (34.00, 38.00) | 36.00 (34.00, 38.00) | 37.00 (35.00, 38.00) |
| EF/% | 65.00 (63.00, 68.00) | 65.00 (63.00, 68.00) | 66.00 (63.00, 69.00) |
| Laboratory examination parameter | |||
| WBC/ (×109·L-1) | 5.11 (4.04, 6.56) | 5.65 (4.68, 6.86) | 4.44 (3.50, 5.79)① |
| HB/ (g·L-1) | 120.00 (105.00, 129.00) | 127.00 (120.00, 133.00) | 105.00 (97.00, 117.00)① |
| HCT | 0.36 (0.32, 0.39) | 0.38 (0.36, 0.40) | 0.32 (0.29, 0.35)① |
| ST2/ (ng·mL-1) | 18.14 (13.83, 24.86) | 18.38 (13.75, 25.36) | 18.11 (14.25, 24.13) |
| BNP/ (pg·mL-1) | 19.00 (12.00, 32.00) | 19.00 (12.00, 31.00) | 21.00 (15.00, 35.00) |
| NT-proBNP/ (pg·mL-1) | 24.04 (10.00, 42.58) | 24.42 (10.00, 41.58) | 23.95 (10.48, 46.28) |
| TNI/ (ng·mL-1) | 0 (0, 0) | 0 (0, 0) | 0 (0, 0.01) |
| hsCRP/ (mg·L-1) | 0.71 (0.32, 1.41) | 0.70 (0.32, 1.42) | 0.86 (0.34, 1.40) |
| TC/ (mmol·L-1) | 4.48 (3.91, 5.16) | 4.52 (3.98, 5.24) | 4.42 (3.85, 4.99) |
| TAG/ (mmol·L-1) | 1.35 (0.86, 2.04) | 1.02 (0.74, 1.66) | 1.75 (1.27, 2.40)① |
| HDL/ (mmol·L-1) | 1.10 (0.87, 1.32) | 1.24 (1.04, 1.45) | 0.87 (0.75, 1.03)① |
| LDL/ (mmol·L-1) | 3.34 (2.82, 3.98) | 3.21 (2.76, 3.92) | 3.47 (2.94, 4.12) |
| NHDL/ (mmol·L-1) | 2.52 (2.16, 3.13) | 2.60 (2.21, 3.20) | 2.41 (2.05, 2.91)② |
| FPG/ (mmol·L-1) | 4.95 (4.74, 5.26) | 4.88 (4.69, 5.24) | 5.05 (4.83, 5.29)④ |
| GOT/ (mmol·L-1) | 20.00 (16.00, 26.00) | 17.00 (14.00, 23.00) | 22.00 (19.00, 29.75) |
| GPT/ (mmol·L-1) | 19.00 (13.00, 29.50) | 15.00 (11.00, 27.00) | 24.00 (17.00, 34.00) |
| γ-GT/ (mmol·L-1) | 21.00 (14.00, 40.00) | 18.00 (12.00, 32.00) | 33.50 (17.00, 47.00) |
| IL-1β/ (pg·mL-1) | 5.00 (5.00, 5.00) | 5.00 (5.00, 5.00) | 5.00 (5.00, 5.00) |
| IL-2R/ (U·mL-1) | 330.00 (270.75, 424.75) | 295.00 (249.50, 369.50) | 399.00 (322.00, 508.00)① |
| IL-6/ (pg·mL-1) | 3.15 (2.21, 4.25) | 2.97 (2.12, 3.74) | 3.66 (2.68, 4.89)⑤ |
| IL-8/ (pg·mL-1) | 11.30 (7.72, 18.95) | 13.20 (8.81, 21.10) | 9.84 (7.06, 15.20)③ |
| IL-10/ (pg·mL-1) | 5.00 (5.00, 5.00) | 5.00 (5.00, 5.00) | 5.00 (5.00, 5.00) |
| TNF-α/ (pg·mL-1) | 6.53 (5.26, 7.86) | 6.01 (5.00, 7.02) | 7.33 (6.03, 8.60)① |
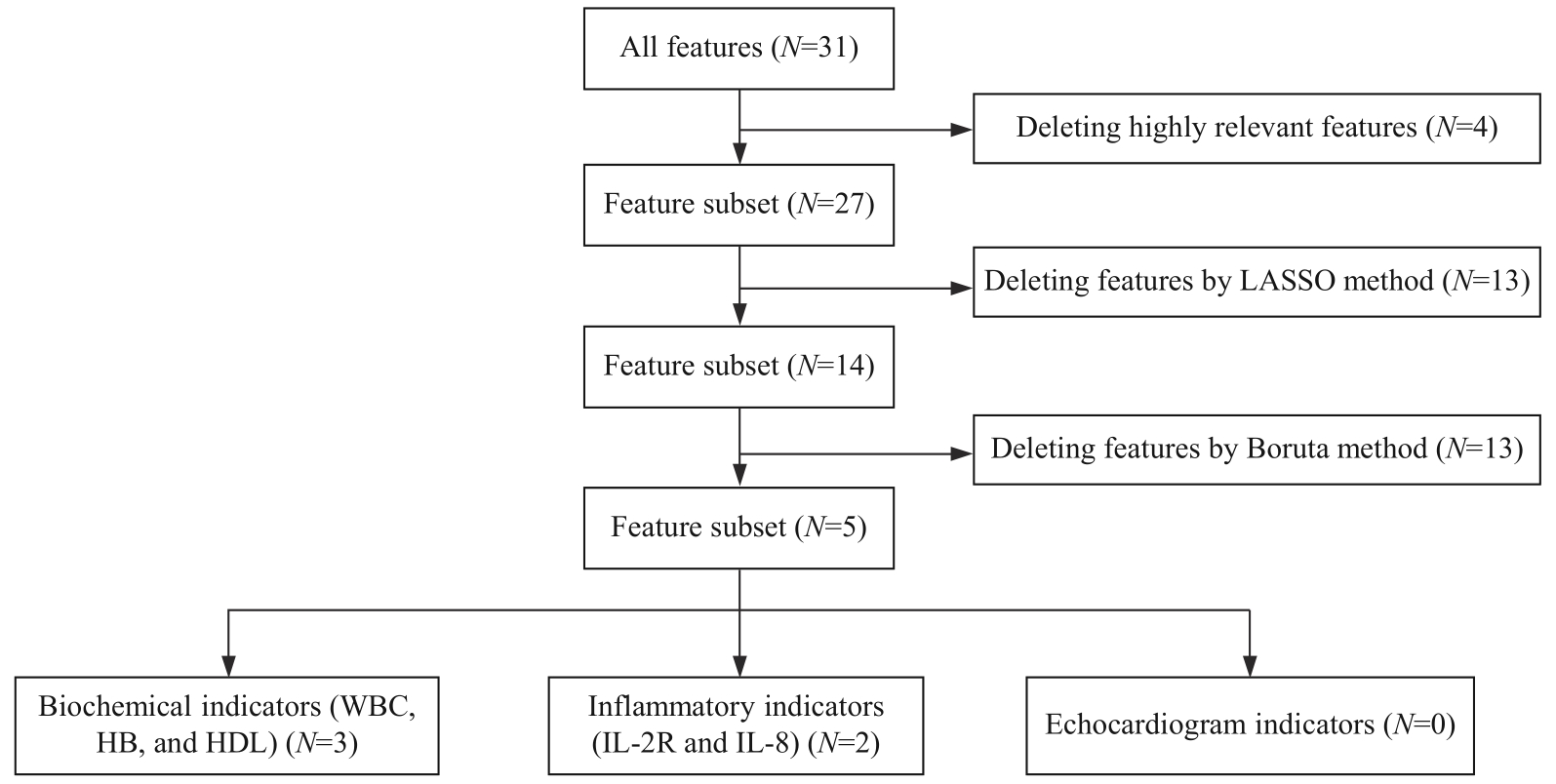
图2 乳腺癌新辅助治疗前后患者特征提取与特征分组流程图
Fig 2 Flowchart of feature extraction and feature grouping of patients with breast cancer before and after neoadjuvant therapy
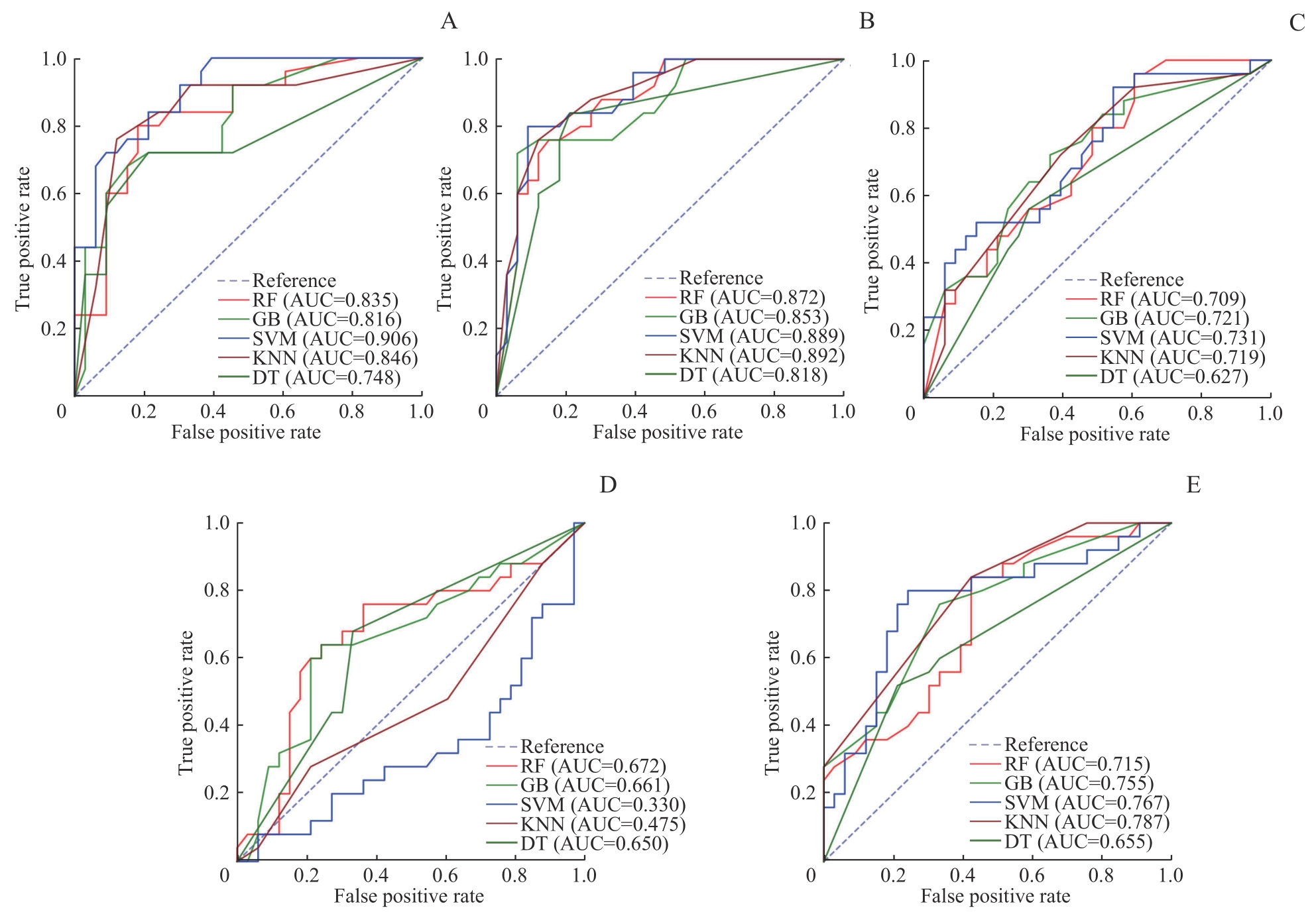
图3 乳腺癌新辅助治疗前后患者5种模型在测试集中的单特征分析ROC曲线Note: A. HB single-feature ROC curve. B. HDL single-feature ROC curve. C. IL-2R single-feature ROC curve. D. IL-8 single-feature ROC curve. E. WBC single-feature ROC curve.
Fig 3 ROC curves of single-feature analysis for five models in the test set for patients with breast cancer before and after neoadjuvant therapy
| Single feature | Model | AUC | Accuracy | Precision rate | Recall | F1 score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC | RF | 0.715 | 0.603 | 0.656 | 0.636 | 0.646 |
| GB | 0.755 | 0.655 | 0.659 | 0.818 | 0.730 | |
| SVM | 0.767 | 0.690 | 0.683 | 0.848 | 0.757 | |
| DT | 0.655 | 0.569 | 0.643 | 0.545 | 0.590 | |
| KNN | 0.787 | 0.690 | 0.703 | 0.788 | 0.743 | |
| HB | RF | 0.835 | 0.845 | 0.853 | 0.879 | 0.866 |
| GB | 0.816 | 0.759 | 0.788 | 0.788 | 0.788 | |
| SVM | 0.906 | 0.810 | 0.824 | 0.848 | 0.836 | |
| DT | 0.748 | 0.759 | 0.788 | 0.788 | 0.788 | |
| KNN | 0.846 | 0.793 | 0.862 | 0.758 | 0.806 | |
| HDL | RF | 0.872 | 0.810 | 0.824 | 0.848 | 0.836 |
| GB | 0.853 | 0.828 | 0.829 | 0.879 | 0.853 | |
| SVM | 0.889 | 0.845 | 0.833 | 0.909 | 0.870 | |
| DT | 0.818 | 0.759 | 0.771 | 0.818 | 0.794 | |
| KNN | 0.892 | 0.828 | 0.829 | 0.879 | 0.853 | |
| IL-2R | RF | 0.709 | 0.672 | 0.684 | 0.788 | 0.732 |
| GB | 0.721 | 0.655 | 0.710 | 0.667 | 0.688 | |
| SVM | 0.731 | 0.690 | 0.683 | 0.848 | 0.757 | |
| DT | 0.627 | 0.638 | 0.676 | 0.697 | 0.687 | |
| KNN | 0.719 | 0.655 | 0.651 | 0.848 | 0.737 | |
| IL-8 | RF | 0.672 | 0.603 | 0.692 | 0.545 | 0.610 |
| GB | 0.661 | 0.690 | 0.727 | 0.727 | 0.727 | |
| SVM | 0.330 | 0.569 | 0.569 | 1.000 | 0.725 | |
| DT | 0.650 | 0.672 | 0.733 | 0.667 | 0.698 | |
| KNN | 0.475 | 0.500 | 0.553 | 0.636 | 0.592 |
表2 乳腺癌新辅助治疗前后患者5种模型在测试集中的单特征变量预测性能比较
Tab 2 Comparison of the predictive performance of the five models for single-feature variables in the test set for patients with breast cancer before and after neoadjuvant therapy
| Single feature | Model | AUC | Accuracy | Precision rate | Recall | F1 score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC | RF | 0.715 | 0.603 | 0.656 | 0.636 | 0.646 |
| GB | 0.755 | 0.655 | 0.659 | 0.818 | 0.730 | |
| SVM | 0.767 | 0.690 | 0.683 | 0.848 | 0.757 | |
| DT | 0.655 | 0.569 | 0.643 | 0.545 | 0.590 | |
| KNN | 0.787 | 0.690 | 0.703 | 0.788 | 0.743 | |
| HB | RF | 0.835 | 0.845 | 0.853 | 0.879 | 0.866 |
| GB | 0.816 | 0.759 | 0.788 | 0.788 | 0.788 | |
| SVM | 0.906 | 0.810 | 0.824 | 0.848 | 0.836 | |
| DT | 0.748 | 0.759 | 0.788 | 0.788 | 0.788 | |
| KNN | 0.846 | 0.793 | 0.862 | 0.758 | 0.806 | |
| HDL | RF | 0.872 | 0.810 | 0.824 | 0.848 | 0.836 |
| GB | 0.853 | 0.828 | 0.829 | 0.879 | 0.853 | |
| SVM | 0.889 | 0.845 | 0.833 | 0.909 | 0.870 | |
| DT | 0.818 | 0.759 | 0.771 | 0.818 | 0.794 | |
| KNN | 0.892 | 0.828 | 0.829 | 0.879 | 0.853 | |
| IL-2R | RF | 0.709 | 0.672 | 0.684 | 0.788 | 0.732 |
| GB | 0.721 | 0.655 | 0.710 | 0.667 | 0.688 | |
| SVM | 0.731 | 0.690 | 0.683 | 0.848 | 0.757 | |
| DT | 0.627 | 0.638 | 0.676 | 0.697 | 0.687 | |
| KNN | 0.719 | 0.655 | 0.651 | 0.848 | 0.737 | |
| IL-8 | RF | 0.672 | 0.603 | 0.692 | 0.545 | 0.610 |
| GB | 0.661 | 0.690 | 0.727 | 0.727 | 0.727 | |
| SVM | 0.330 | 0.569 | 0.569 | 1.000 | 0.725 | |
| DT | 0.650 | 0.672 | 0.733 | 0.667 | 0.698 | |
| KNN | 0.475 | 0.500 | 0.553 | 0.636 | 0.592 |
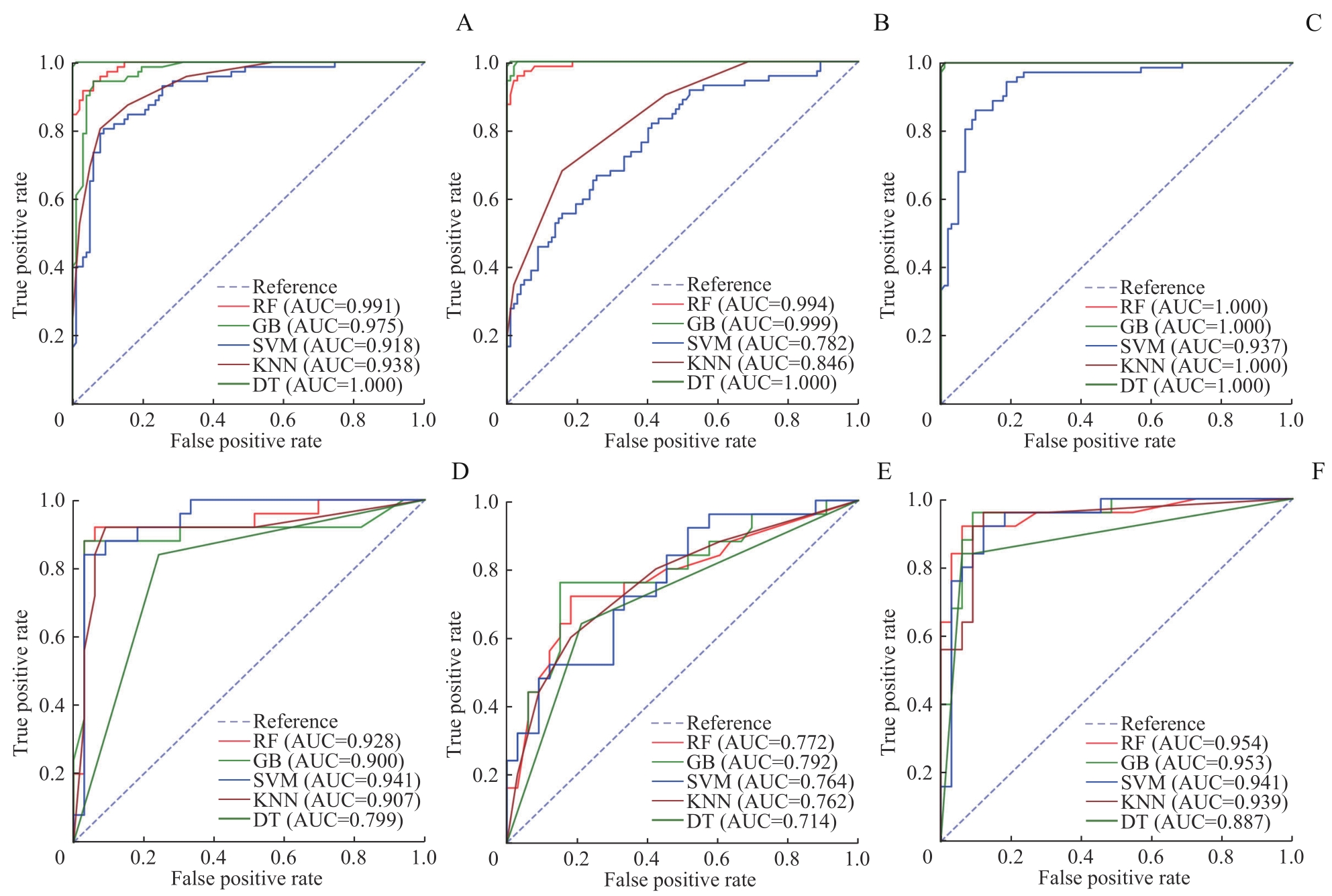
图4 乳腺癌新辅助治疗前后患者的5种模型的多特征分析ROC曲线Note: A?C. ROC curves of training group (A. WBC+HB+HDL multi-feature ROC curve; B. IL-2R+IL-8 multi-feature ROC curve; C. All features multi-feature ROC curve). D?F. ROC curves of testing group (D. WBC+HB+HDL multi-feature ROC curve; E. IL-2R+IL-8 multi-feature ROC curve; F. All features multi-feature ROC curve).
Fig 4 ROC curves of multi-feature analysis for five models for patients with breast cancer before and after neoadjuvant therapy
| Multi-feature | Model | AUC | Accuracy | Precision rate | Recall | F1 value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC+HB+HDL | RF | 0.928 | 0.914 | 0.938 | 0.909 | 0.923 |
| GB | 0.900 | 0.776 | 0.885 | 0.697 | 0.780 | |
| SVM | 0.941 | 0.897 | 0.909 | 0.909 | 0.909 | |
| DT | 0.799 | 0.793 | 0.862 | 0.758 | 0.806 | |
| KNN | 0.907 | 0.897 | 0.886 | 0.939 | 0.912 | |
| IL-2R+IL-8 | RF | 0.772 | 0.776 | 0.763 | 0.879 | 0.817 |
| GB | 0.792 | 0.793 | 0.818 | 0.818 | 0.818 | |
| SVM | 0.764 | 0.707 | 0.690 | 0.879 | 0.773 | |
| DT | 0.714 | 0.707 | 0.735 | 0.758 | 0.746 | |
| KNN | 0.762 | 0.724 | 0.730 | 0.818 | 0.771 | |
| All features | RF | 0.954 | 0.897 | 0.909 | 0.909 | 0.909 |
| GB | 0.953 | 0.914 | 0.967 | 0.879 | 0.921 | |
| SVM | 0.941 | 0.879 | 0.882 | 0.909 | 0.896 | |
| DT | 0.887 | 0.862 | 0.857 | 0.909 | 0.882 | |
| KNN | 0.939 | 0.862 | 0.903 | 0.848 | 0.875 |
表3 乳腺癌新辅助治疗前后患者的5种模型在测试集中的多特征变量预测性能比较
Tab 3 Comparison of the predictive performance of the five models for multi-feature variables in the test set for patients with breast cancer before and after neoadjuvant therapy
| Multi-feature | Model | AUC | Accuracy | Precision rate | Recall | F1 value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC+HB+HDL | RF | 0.928 | 0.914 | 0.938 | 0.909 | 0.923 |
| GB | 0.900 | 0.776 | 0.885 | 0.697 | 0.780 | |
| SVM | 0.941 | 0.897 | 0.909 | 0.909 | 0.909 | |
| DT | 0.799 | 0.793 | 0.862 | 0.758 | 0.806 | |
| KNN | 0.907 | 0.897 | 0.886 | 0.939 | 0.912 | |
| IL-2R+IL-8 | RF | 0.772 | 0.776 | 0.763 | 0.879 | 0.817 |
| GB | 0.792 | 0.793 | 0.818 | 0.818 | 0.818 | |
| SVM | 0.764 | 0.707 | 0.690 | 0.879 | 0.773 | |
| DT | 0.714 | 0.707 | 0.735 | 0.758 | 0.746 | |
| KNN | 0.762 | 0.724 | 0.730 | 0.818 | 0.771 | |
| All features | RF | 0.954 | 0.897 | 0.909 | 0.909 | 0.909 |
| GB | 0.953 | 0.914 | 0.967 | 0.879 | 0.921 | |
| SVM | 0.941 | 0.879 | 0.882 | 0.909 | 0.896 | |
| DT | 0.887 | 0.862 | 0.857 | 0.909 | 0.882 | |
| KNN | 0.939 | 0.862 | 0.903 | 0.848 | 0.875 |
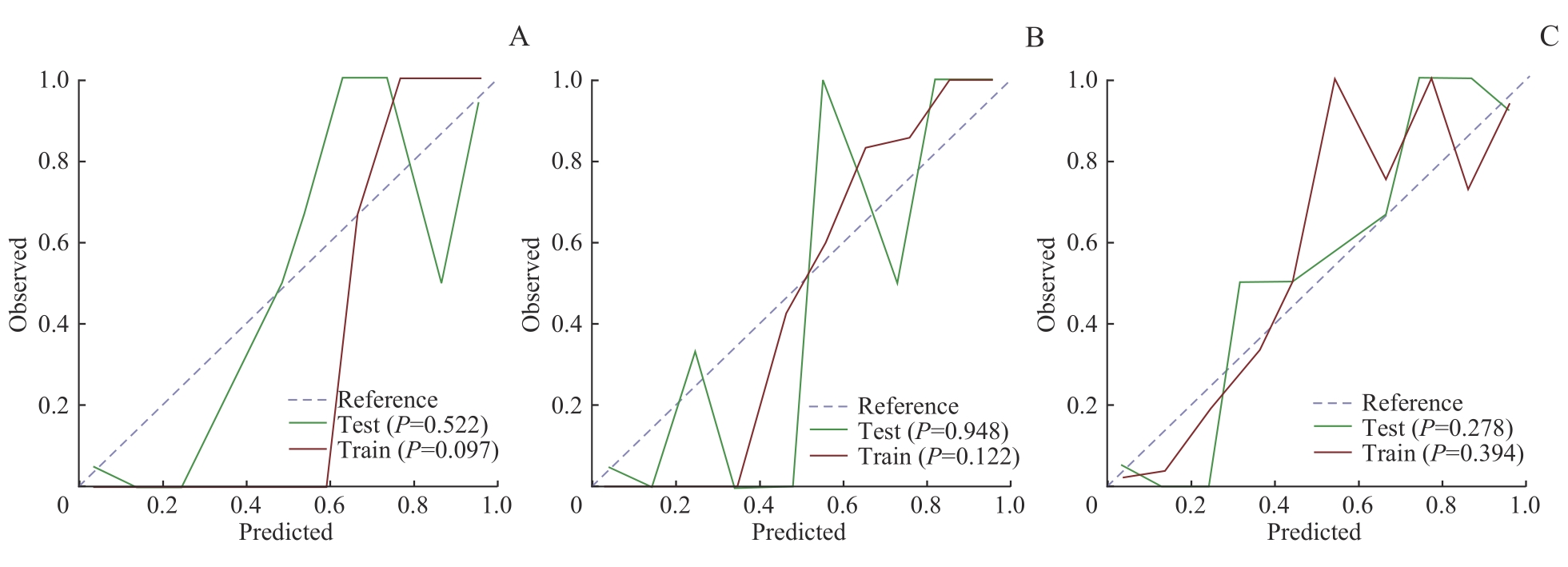
图5 所有特征组GB、RF、SVM模型的校准曲线Note: A. GB model calibration curve. B. RF model calibration curve. C. SVM model calibration curve.
Fig 5 Calibration curves of the three models of GB, RF and SVM for all feature sets
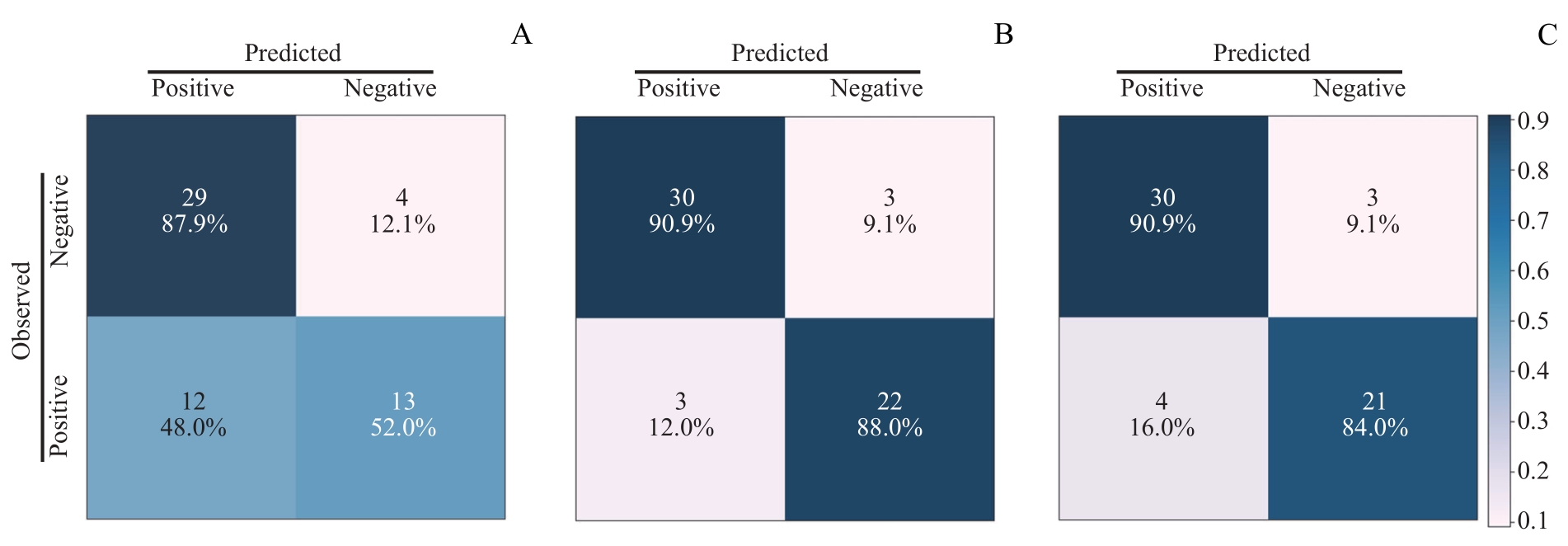
图7 SVM模型中3个多特征分析组的混淆矩阵Note: A. Confusion matrix of IL-2R+IL-8 in SVM moedl. B. Confusion matrix of WBC+HB+HDL in SVM model. C. Confusion matrix of all features (WBC+HB+HDL+IL-2R+IL-8) in SVM model.
Fig 7 Confusion matrices for the three multi-feature analysis groups in SVM model
| 1 | SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. |
| 2 | BRAY F, LAVERSANNE M, SUNG H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024, 74(3): 229-263. |
| 3 | RAMIN C, SCHAEFFER M L, ZHENG Z, et al. All-Cause and cardiovascular disease mortality among breast cancer survivors in CLUE Ⅱ, a long-standing community-based cohort[J].J Natl Cancer Inst, 2021, 113(2): 137-145. |
| 4 | JOHNSON K W, TORRES SOTO J, GLICKSBERG B S, et al. Artificial intelligence in cardiology[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2018, 71(23): 2668-2679. |
| 5 | OIKONOMOU E K, KHERA R. Machine learning in precision diabetes care and cardiovascular risk prediction[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2023, 22(1): 259. |
| 6 | YANG H Z, YU B X, OUYANG P, et al. Machine learning-aided risk prediction for metabolic syndrome based on 3 years study[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12(1): 2248. |
| 7 | WANG G, ZHANG Y, LI S, et al. A machine learning-based prediction model for cardiovascular risk in women with preeclampsia[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2021, 8: 736491. |
| 8 | BETANCUR J, COMMANDEUR F, MOTLAGH M, et al. Deep learning for prediction of obstructive disease from fast myocardial perfusion SPECT: a multicenter study[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging, 2018, 11(11): 1654-1663. |
| 9 | ALAA A M, BOLTON T, DI ANGELANTONIO E, et al. Cardiovascular disease risk prediction using automated machine learning: a prospective study of 423, 604 UK Biobank participants[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(5): e0213653. |
| 10 | PUJADAS E R, RAISI-ESTABRAGH Z, SZABO L, et al. Prediction of incident cardiovascular events using machine learning and CMR radiomics[J]. Eur Radiol, 2023, 33(5): 3488-3500. |
| 11 | TAWFIQ E, SELAK V, ELWOOD J M, et al. Performance of cardiovascular disease risk prediction equations in more than 14 000 survivors of cancer in New Zealand primary care: a validation study[J]. Lancet, 2023, 401(10374): 357-365. |
| 12 | MENG M, ZHAO C. Application of support vector machines to a small-sample prediction[J]. Adv Petrol Explor Dev, 2015, 2(10): 72-75. |
| 13 | MUHAMMAD S, FAN T, HAI Y, et al. Reigniting hope in cancer treatment: the promise and pitfalls of IL-2 and IL-2R targeting strategies[J]. Mol Cancer, 2023, 22(1): 121. |
| 14 | HERNANDEZ R, PÕDER J, LAPORTE K M, et al. Engineering IL-2 for immunotherapy of autoimmunity and cancer[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2022, 22(10): 614-628. |
| 15 | BAGGIOLINI M, CLARK-LEWIS I. Interleukin-8, a chemotactic and inflammatory cytokine[J]. FEBS Lett, 1992, 307(1): 97-101. |
| 16 | LIU Y Y, ZHOU N N, ZHOU L, et al. IL-2 regulates tumor-reactive CD8+ T cell exhaustion by activating the aryl hydrocarbon receptor[J]. Nat Immunol, 2021, 22(3): 358-369. |
| 17 | LIU Q, LI A, TIAN Y, et al. The CXCL8-CXCR1/2 pathways in cancer[J]. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 2016, 31: 61-71. |
| 18 | SINGH J K, SIMÕES B M, HOWELL S J, et al. Recent advances reveal IL-8 signaling as a potential key to targeting breast cancer stem cells[J]. Breast Cancer Res, 2013, 15(4): 210. |
| 19 | AHMED S, MOHAMED H T, EL-HUSSEINY N, et al. IL-8 secreted by tumor associated macrophages contribute to lapatinib resistance in HER2-positive locally advanced breast cancer via activation of Src/STAT3/ERK1/2-mediated EGFR signaling[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res, 2021, 1868(6): 118995. |
| 20 | PAN K, XU C, CHEN C, et al. Soluble interleukin-2 receptor combined with interleukin-8 is a powerful predictor of future adverse cardiovascular events in patients with acute myocardial infarction[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2023, 10: 1110742. |
| 21 | BOUCHENTOUF M, WILLIAMS P, FORNER K A, et al. Interleukin-2 enhances angiogenesis and preserves cardiac function following myocardial infarction[J]. Cytokine, 2011, 56(3): 732-738. |
| 22 | APOSTOLAKIS S, VOGIATZI K, AMANATIDOU V, et al. Interleukin 8 and cardiovascular disease[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2009, 84(3): 353-360. |
| 23 | KIM C S, PARK H S, KAWADA T, et al. Circulating levels of MCP-1 and IL-8 are elevated in human obese subjects and associated with obesity-related parameters[J]. Int J Obes, 2006, 30(9): 1347-1355. |
| 24 | ZHAO H, HUANG R, JIANG M, et al. Myocardial tissue-level characteristics of adults with metabolically healthy obesity[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging, 2023, 16(7): 889-901. |
| 25 | QU F, CHEN R, PENG Y, et al. Assessment of the predictive role of serum lipid profiles in breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy[J]. J Breast Cancer, 2020, 23(3): 246-258. |
| 26 | TAHMASSEBI A, WENGERT G J, HELBICH T H, et al. Impact of machine learning with multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging of the breast for early prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy and survival outcomes in breast cancer patients[J]. Invest Radiol, 2019, 54(2): 110-117. |
| 27 | SHI Z, HUANG X, CHENG Z, et al. MRI-based quantification of intratumoral heterogeneity for predicting treatment response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer[J]. Radiology, 2023, 308(1): e222830. |
| [1] | 许万星, 王琳, 郭巧梅, 王薛庆, 娄加陶. 多模态肺结节诊断模型的临床验证及应用价值探索[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(8): 1030-1036. |
| [2] | 韩依杉, 徐梓淇, 陶梦玉, 范广建, 余波. PRMT6促进乳腺癌细胞的增殖和迁移[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(8): 999-1010. |
| [3] | 杜少倩, 陶梦玉, 曹源, 王红霞, 胡孝渠, 范广建, 臧丽娟. CXCL9在乳腺癌中的表达及其与肿瘤免疫浸润特征的相关性研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(7): 860-872. |
| [4] | 马奔, 赵成, 束翌俊, 董平. CT影像组学在胃肠道间质瘤中的应用进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(7): 923-930. |
| [5] | 曹源, 王红霞, 朱灜, 李军建. 四次跨膜蛋白1在乳腺癌中的表达及其促进乳腺癌进展的作用机制[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(3): 293-300. |
| [6] | 杨笑萱, 朱珊, 钱程, 储晓英. 术中使用小剂量右美托咪定对乳腺癌手术患者预后的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(2): 194-200. |
| [7] | 王斓茜, 马官荣, 姜咏竹, 常秀林, 方廖琼, 白晋. 大肠埃希菌外膜囊泡对乳腺癌细胞增殖及荷瘤小鼠肿瘤生长的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(10): 1245-1254. |
| [8] | 夏坤健, 邓林林, 王琳. 乳腺癌化学治疗致肝损伤预测模型的构建及其评价[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(4): 502-509. |
| [9] | 张郁瑭, 金奕婕, 张凤春, 徐迎春. 乳腺癌合并新型冠状病毒肺炎感染患者的抗肿瘤合理化诊疗方案探讨[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(12): 1745-1750. |
| [10] | 苏俊澄, 王禹铮, 唐雷, 徐迎春, 张凤春. 乳腺癌脑转移患者的临床病理特征及预后的影响因素分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(11): 1562-1568. |
| [11] | 孙亚蒙, 马晔, 郭润生. 乳腺癌组织样本中 HER2基因拷贝数的检测分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(11): 1589-1597. |
| [12] | 王禹铮, 苏俊澄, 唐雷, 徐迎春, 张凤春. 单周紫杉醇联合顺铂一线治疗转移性乳腺癌的效果和安全性的回顾性研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(10): 1420-1427. |
| [13] | 李欣, 范青. 机器学习在抑郁症患者面部特征研究中的应用进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(1): 124-129. |
| [14] | 陈翠, 金叶, 王琳, 李红丽, 万财凤, 姜立新. 30例乳腺化生性癌的多种影像学对比分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(1): 70-76. |
| [15] | 周天浩, 辛肇晨, 杜少倩, 曹源, 许静轩, 劳曾红, 王红霞. 乳腺癌类器官共培养技术的建立和优化[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(8): 1017-1024. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 943
|
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||