
上海交通大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (10): 1308-1319.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2025.10.006
收稿日期:2025-05-28
接受日期:2025-07-17
出版日期:2025-10-28
发布日期:2025-10-28
通讯作者:
马 柯,主任医师,教授,博士;电子信箱:marke72@163.com。基金资助:
YU Zhiyuan1, DONG Haiping1,2, GAO Nan1, MA Ke1( )
)
Received:2025-05-28
Accepted:2025-07-17
Online:2025-10-28
Published:2025-10-28
Contact:
MA Ke, E-mail: marke72@163.com.Supported by:摘要:
目的·开发一种多算法协同的计算生物学策略,构建吗啡耐受外周神经调控网络的预测模型,并筛选高置信度候选靶标。方法·构建不同吗啡用药时长的小鼠模型,采集其背根神经节(dorsal root ganglion,DRG)组织开展批量RNA测序,以表达矩阵为基础构建加权基因共表达网络,用于识别共表达基因模块。随后,通过整合加权基因共表达网络与差异表达基因(differentially expressed genes,DEGs)筛选候选基因,并对候选基因开展基因本体论(Gene Ontology,GO)、京都基因与基因组百科全书(Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes,KEGG)功能富集分析。同时,构建候选基因蛋白质相互作用(protein-protein interaction,PPI)网络并应用cytoHubba算法识别获得枢纽基因。整合最小绝对收缩与选择算子(least absolute shrinkage and selection operator,LASSO)回归、支持向量机递归特征消除(support vector machine recursive feature elimination,SVM-RFE)模型及随机森林(random forest,RF)模型3种机器学习算法筛选获得特征基因。最终通过基因集富集分析(gene set enrichment analysis,GSEA)验证枢纽基因和特征基因的功能特征。结果·加权基因共表达网络分析(weighted gene co-expression network analysis,WGCNA)鉴定出8 297个关键模块基因,结合DEGs筛选获得177个候选基因,功能富集分析显示它们显著参与离子通道调控及血管平滑肌收缩通路的生物学过程。结合PPI网络与3种机器学习算法,最终识别出4个特征基因[肌动蛋白γ2(actin γ2,smooth muscle,Actg2)、中心粒卷曲螺旋蛋白110(centriolar coiled-coil protein 110,Ccp110)、神经细胞黏附分子2(neural cell adhesion molecule 2,Ncam2)、硒结合蛋白1(selenium binding protein 1,Selenbp1)]及6个枢纽基因[肌动蛋白α2(actin α2,smooth muscle,Acta2)、血管性血友病因子(von Willebrand factor,Vwf)、细胞通信网络因子2(cellular communication network factor 2,Ccn2)、整合素β4(integrin β4,Itgb4)、整合素α11(integrin α11,Itga11)、TEK受体酪氨酸激酶(TEK receptor tyrosine kinase,Tek)]。结论·成功构建了多算法协同的吗啡耐受外周神经调控网络预测模型,共筛选出10个高置信度核心基因。
中图分类号:
禹志远, 董海平, 高楠, 马柯. 背根神经节吗啡耐受核心基因筛选与机制研究:加权基因共表达网络分析和机器学习的转录组学整合策略[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(10): 1308-1319.
YU Zhiyuan, DONG Haiping, GAO Nan, MA Ke. Identification and mechanistic analysis of core genes associated with morphine tolerance in dorsal root ganglion: an integrative transcriptomics approach using WGCNA and machine learning algorithms[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science), 2025, 45(10): 1308-1319.
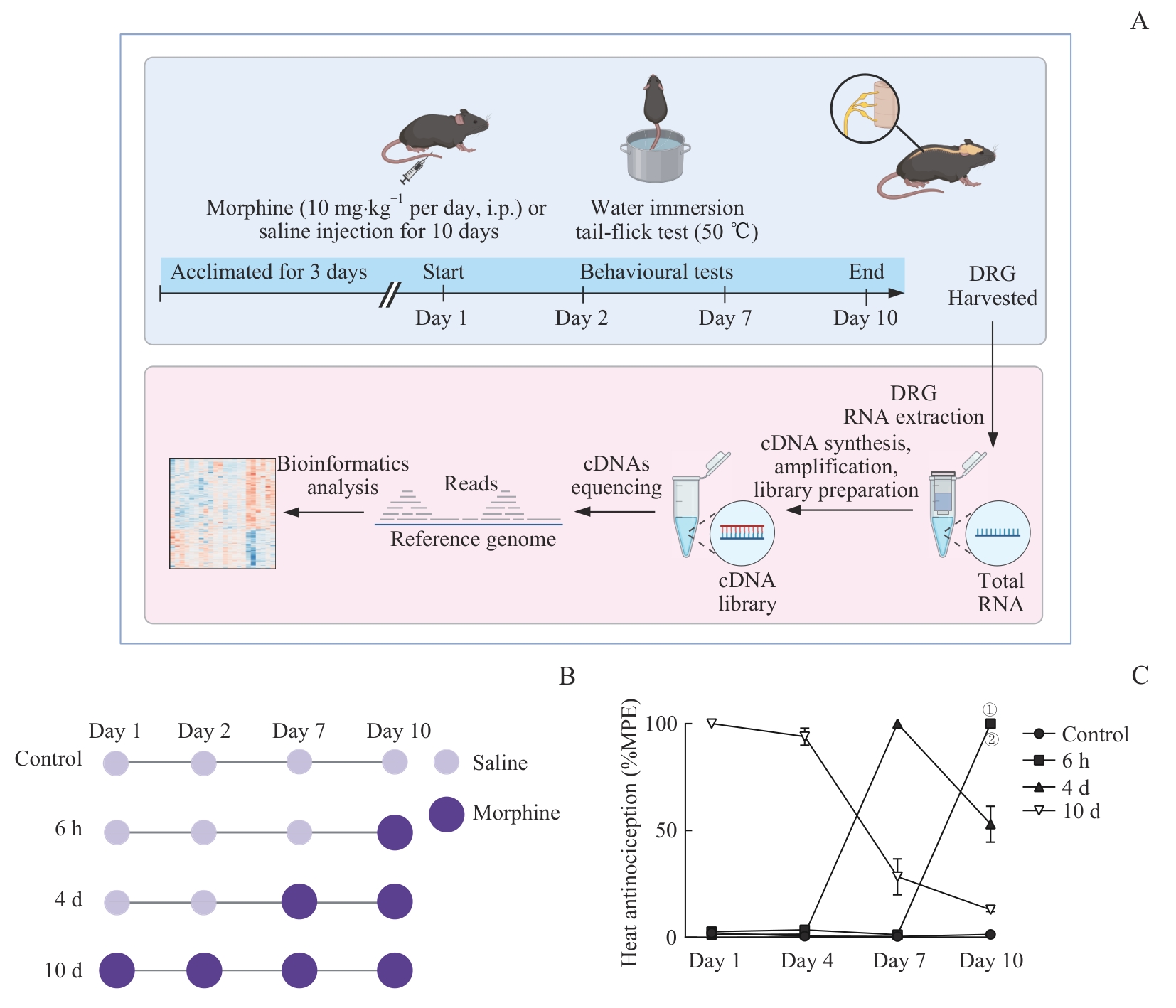
图2 不同吗啡用药时长小鼠模型的建立与行为学评估Note: A. Schematic diagram showing the overall experimental workflow. B. Morphine administration protocols for different treatment durations. C. Comparison of MPE% in the tail-flick test among groups. Control (n=6), 6 h (n=5), 4 d (n=6), 10 d (n=5). ①P=0.004, 6 h vs Control group; ②P=0.008, 6 h vs 10 d group (Kolmogorov-Smirnov test). i.p.—intraperitoneal injection.
Fig 2 Establishment and behavioral evaluation of mouse models with different morphine administration durations
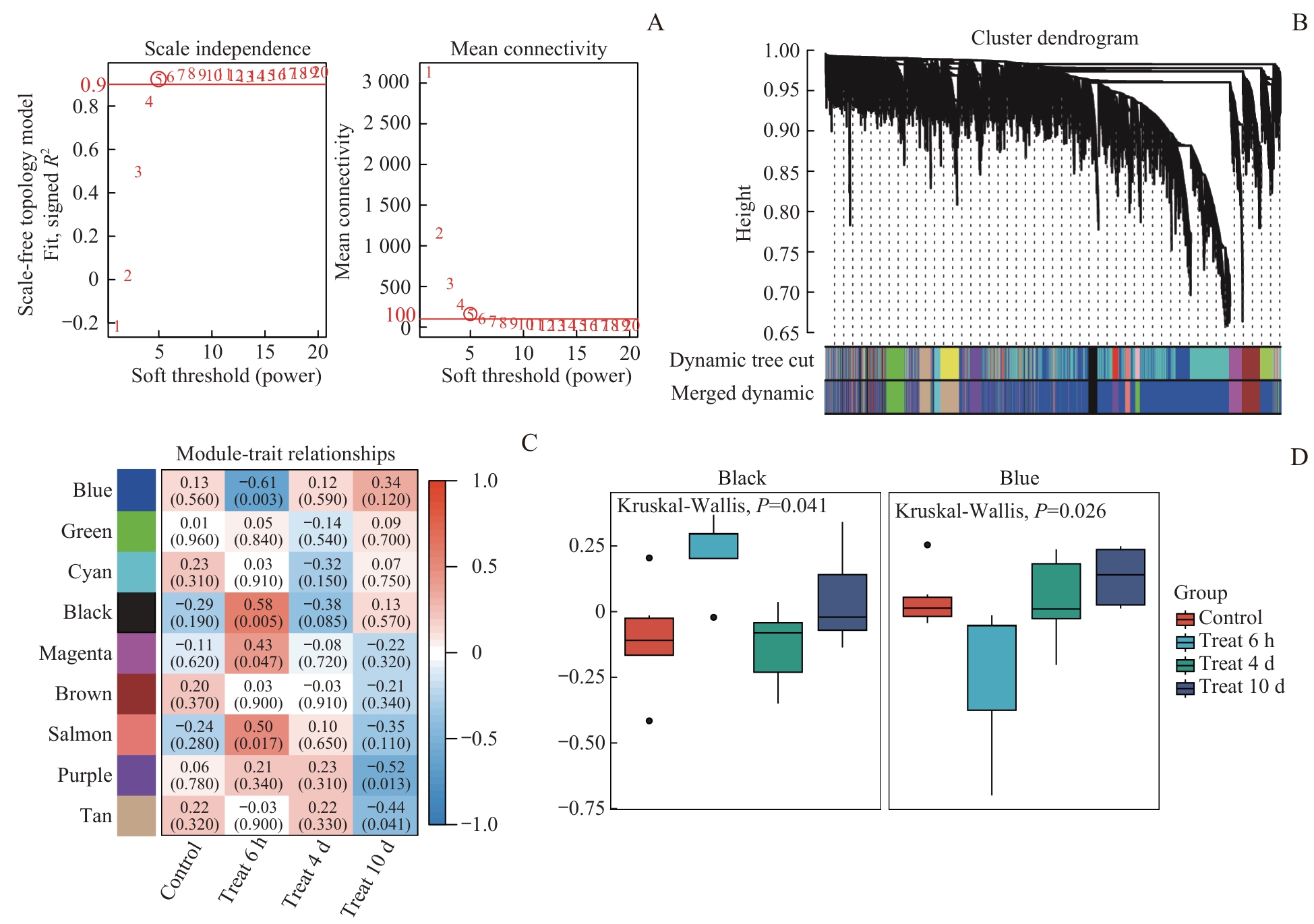
图3 WGCNA筛选吗啡耐受关键基因模块Note: A. Scale-free fit index vs mean connectivity. B. Co-expression module identification using dynamic tree-cutting algorithm. C. Module-treatment group correlation heatmap (Red: positive; Blue: negative). D. Intergroup differences in gene expression of the blue module (P=0.026) and black module (P=0.041) (Kruskal-Wallis test).
Fig 3 Identification of key morphine tolerance-associated gene modules by WGCNA
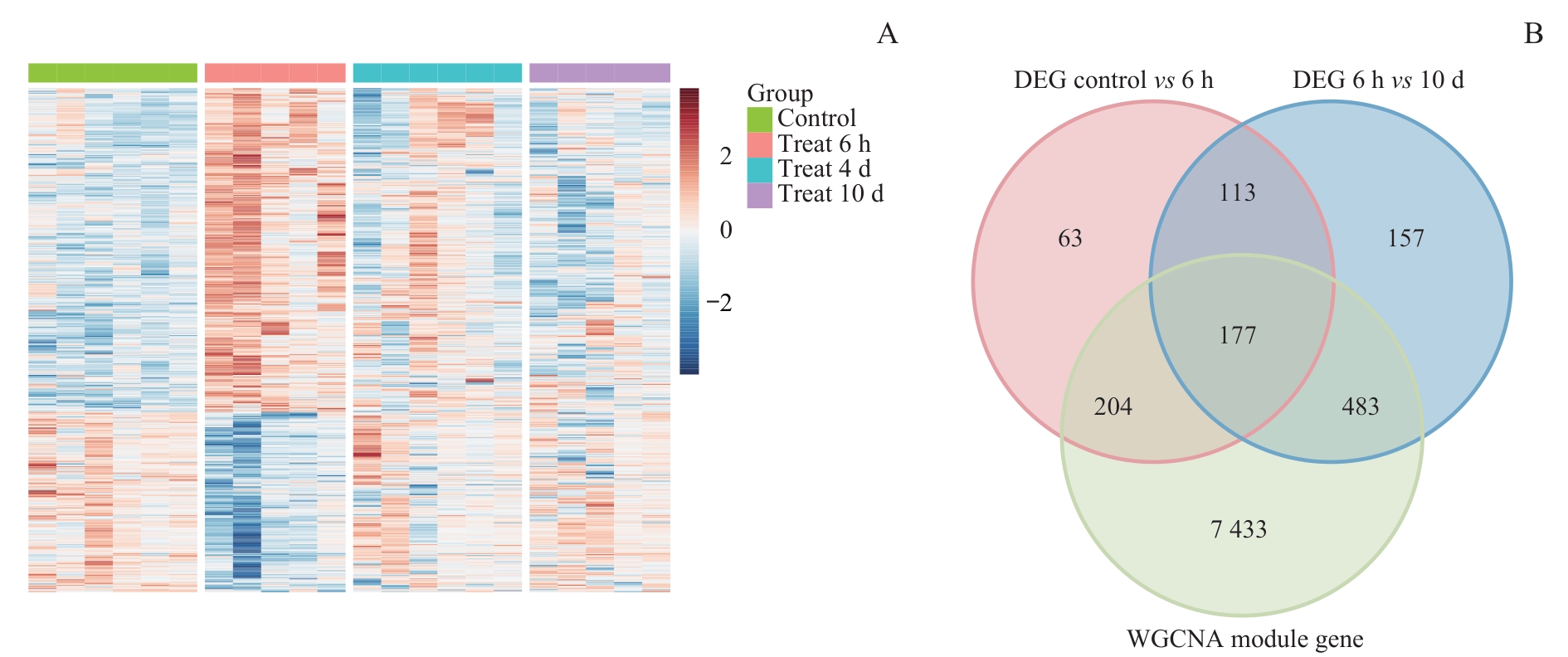
图4 DEGs与WGCNA模块基因的交集分析Note: A. Heatmap of DEGs between morphine treatment groups. Red indicates upregulated genes, and blue indicates downregulated genes. B. Venn diagram intersecting WGCNA module genes with two DEG sets (control vs 6 h, 6 h vs 10 d).
Fig 4 Intersection analysis of morphine tolerance-associated DEGs and WGCNA module genes
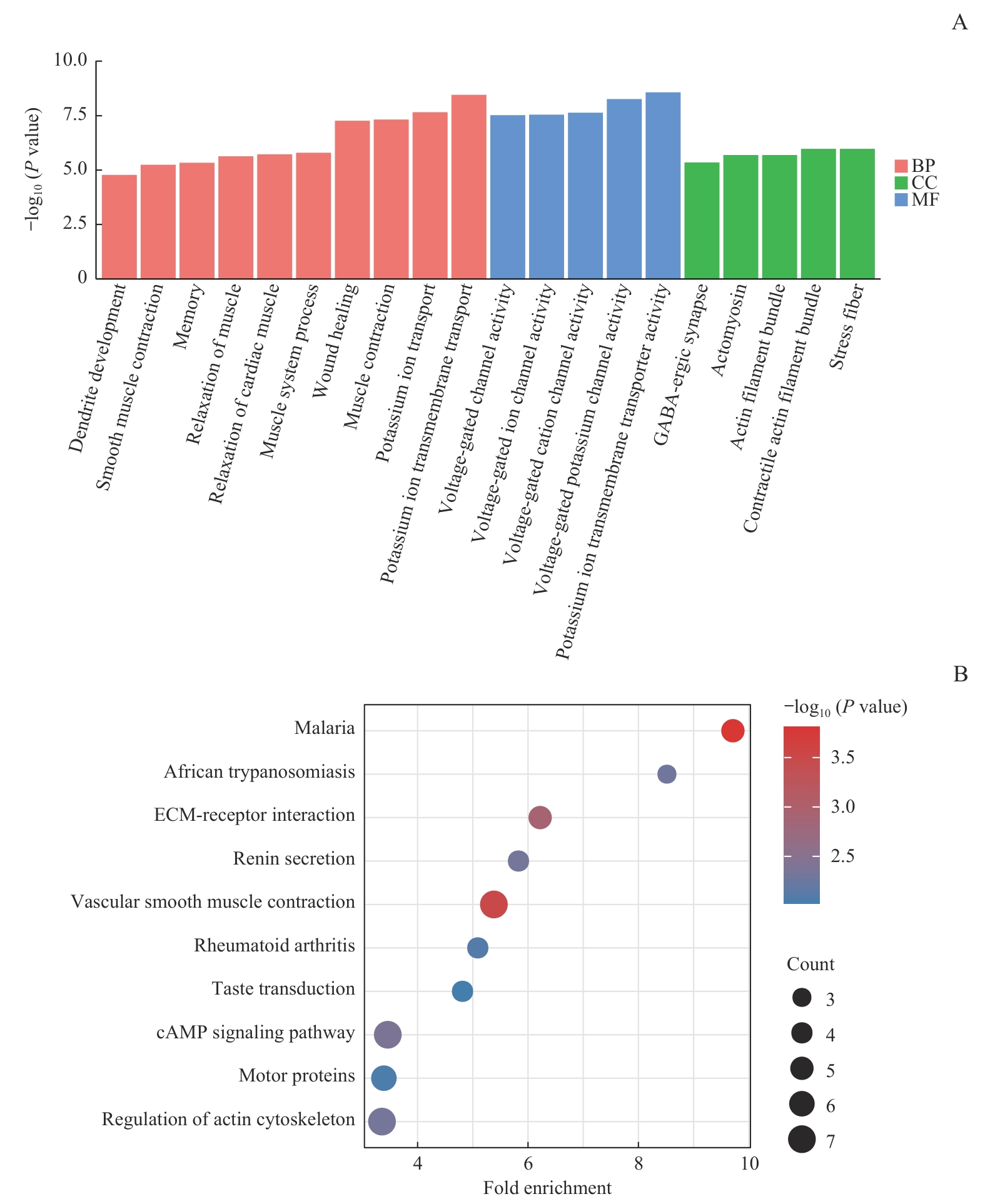
图5 候选基因富集分析结果Note: A. GO enrichment analysis of candidate intersection genes. B. KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of candidate intersection genes. BP—biological process; MF—molecular function; CC—cellular component; ECM—extracellular matrix.
Fig 5 GO and KEGG enrichment analysis of candidate genes
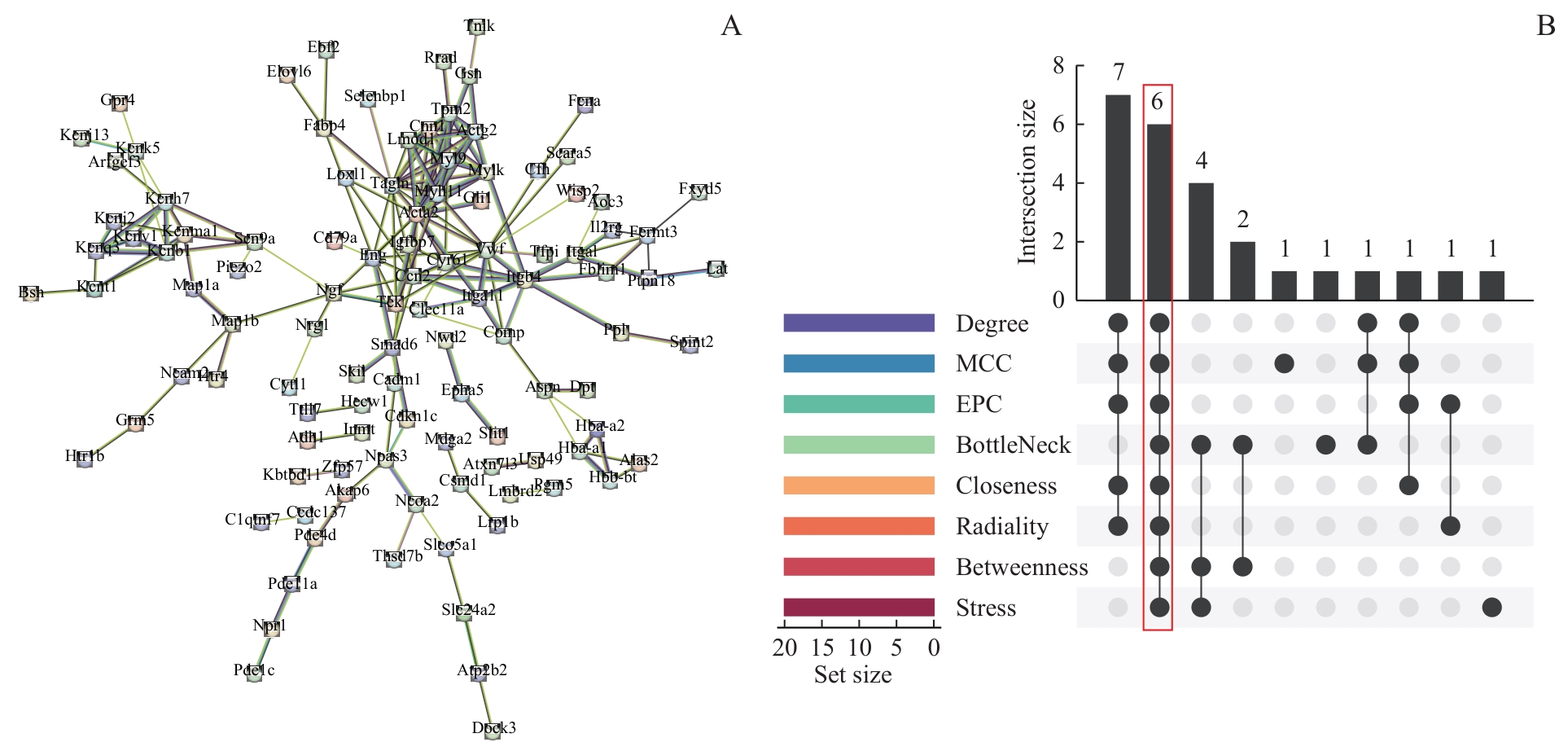
图6 PPI网络和枢纽基因筛选Note: A. PPI network of intersection genes. B. UpSet plot for genes screening using eight cytoHubba algorithms, with red boxes indicating qualified hub genes.
Fig 6 PPI network and screening of hub genes
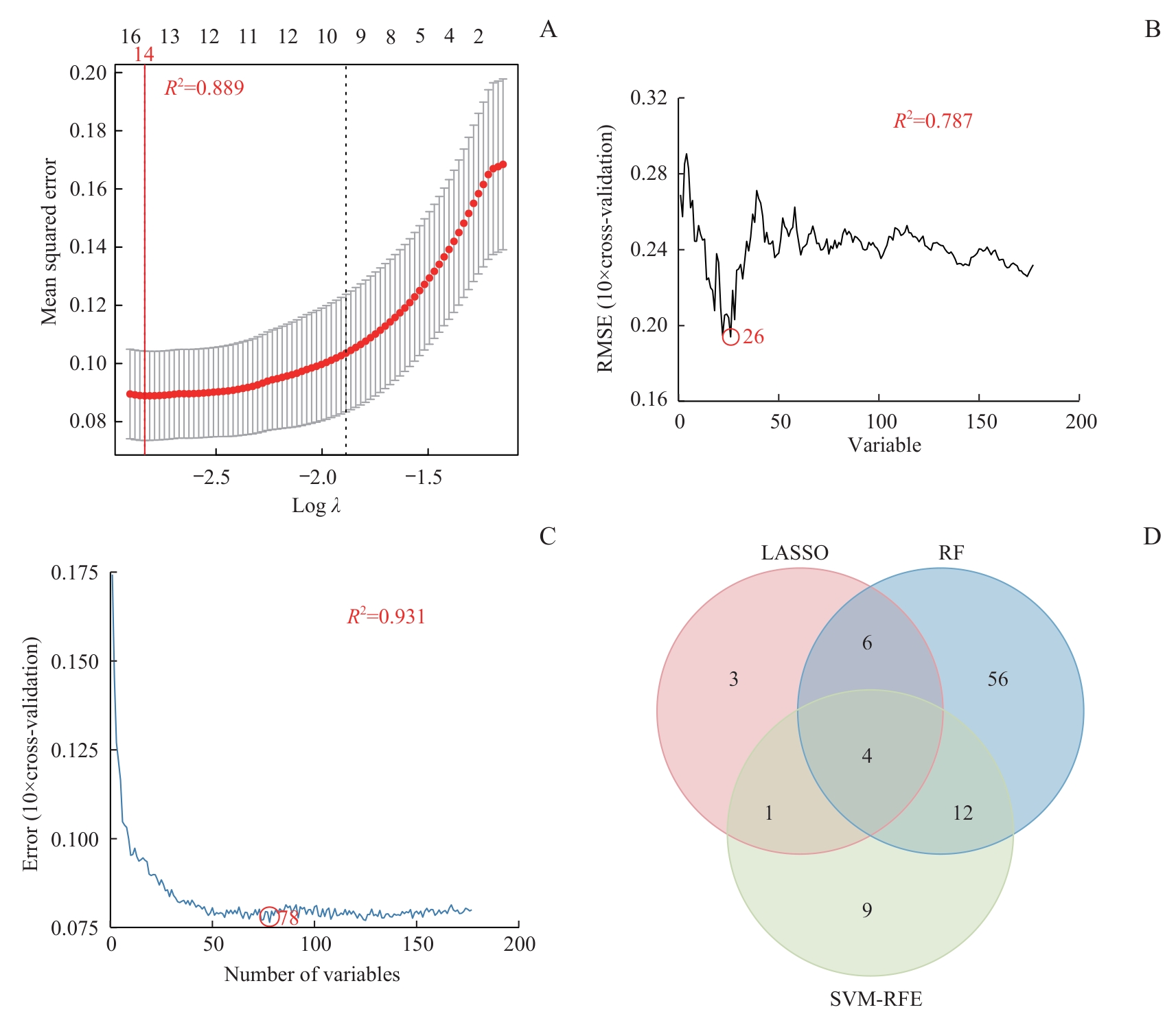
图7 特征基因筛选与整合Note: A. LASSO coefficient profile: the red vertical line indicates the optimal number of genes (n=14) corresponding to the minimum mean squared error (MSE)=0.089, with a model coefficient of determination R²=0.889. B. SVM-RFE model parameter optimization: the lowest root mean squared error (RMSE=0.194) identifies 26 key genes, with a model coefficient of determination R²=0.787. C. RF model parameter optimization: a minimal MSE=0.076 selects 78 candidate genes, with a model coefficient of determination R²=0.931. D. Venn diagram intersecting signature genes from the three algorithms.
Fig 7 Screening and integration of signature genes
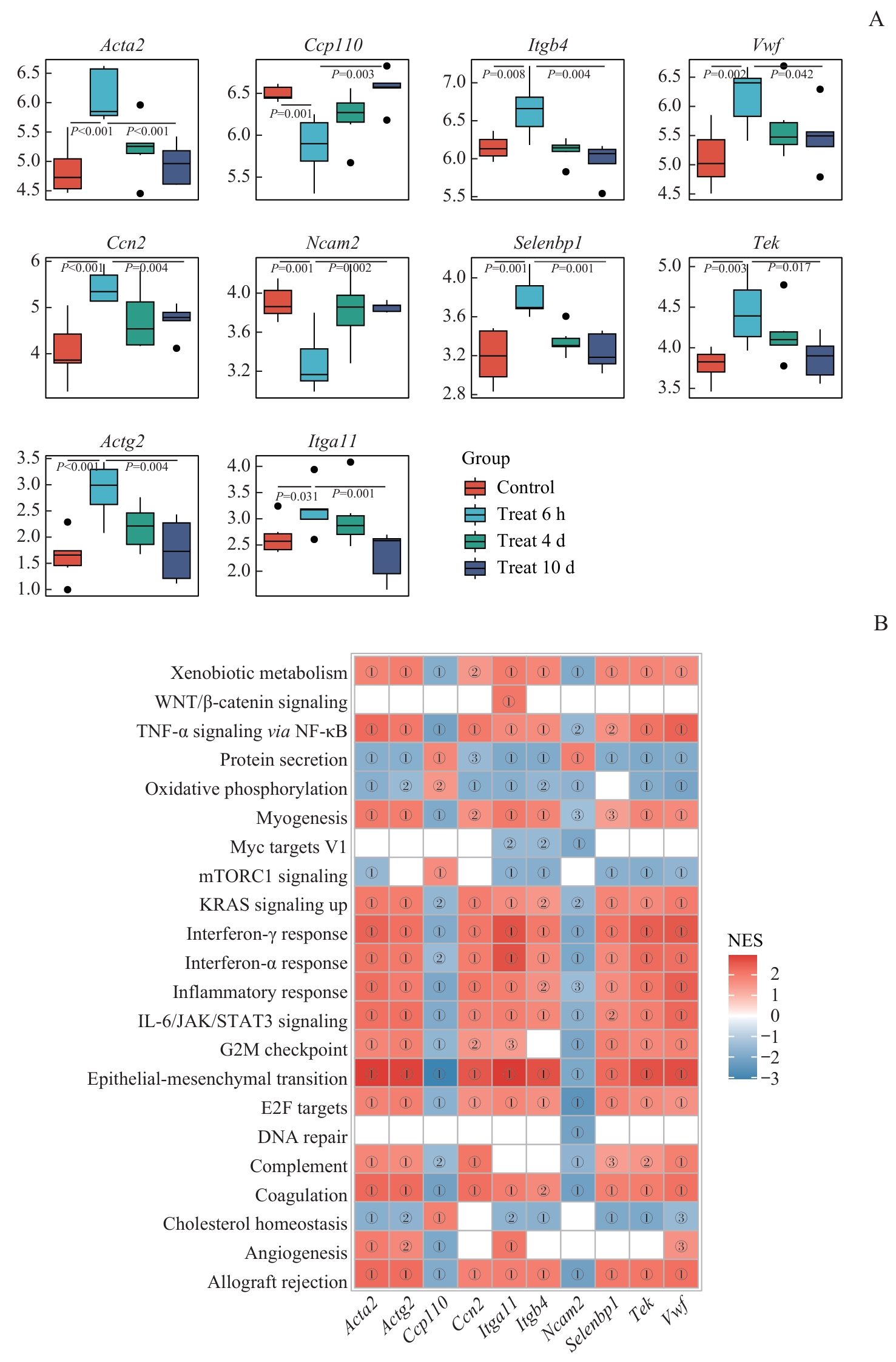
图8 枢纽基因与特征基因的表达差异及GSEA富集关联分析Note: A. Box plots showing expression differences of hub and signature genes across treatment groups (comparisons: 6 h vs control or 10 d groups). Significant P values are indicated directly on the plots. B. Heatmap of GSEA enrichment correlations between hallmark gene sets and hub/signature genes: color intensity represents normalized enrichment score (NES). ①P<0.001, ②P<0.01, ③P<0.05.
Fig 8 Intergroup expression differences of hub and signature genes and their GSEA enrichment associations
| [1] | RUEDA-RUZAFA L, CRUZ F, CARDONA D, et al. Opioid system influences gut-brain axis: dysbiosis and related alterations[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2020, 159: 104928. |
| [2] | TAYLOR J L, SAMET J H. Opioid use disorder[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2022, 175(1): ITC1-ITC16. |
| [3] | CHOE K, ZINN E, LU K, et al. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on chronic pain and opioid use in marginalized populations: a scoping review[J]. Front Public Health, 2023, 11: 1046683. |
| [4] | LEMOS DUARTE M, DEVI L A. Post-translational modifications of opioid receptors[J]. Trends Neurosci, 2020, 43(6): 417-432. |
| [5] | LI L, CHEN J, LI Y Q. The downregulation of opioid receptors and neuropathic pain[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(6): 5981. |
| [6] | OCHANDARENA N E, NIEHAUS J K, TASSOU A, et al. Cell-type specific molecular architecture for mu opioid receptor function in pain and addiction circuits[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2023, 238: 109597. |
| [7] | DUNN A D, ROBINSON S A, NWOKAFOR C, et al. Molecular and long-term behavioral consequences of neonatal opioid exposure and withdrawal in mice[J]. Front Behav Neurosci, 2023, 17: 1202099. |
| [8] | RUIVO J, TAVARES I, POZZA D H. Molecular targets in bone cancer pain: a systematic review of inflammatory cytokines[J]. J Mol Med (Berl), 2024, 102(9): 1063-1088. |
| [9] | BI K, LEI Y, KONG D, et al. Progress in the study of intestinal microbiota involved in morphine tolerance[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(6): e27187. |
| [10] | BERTA T, STRONG J A, ZHANG J M, et al. Targeting dorsal root ganglia and primary sensory neurons for the treatment of chronic pain: an update[J]. Expert Opin Ther Targets, 2023, 27(8): 665-678. |
| [11] | QUIRION B, BEAULIEU C, CÔTÉ L, et al. Distribution of delta and mu opioid receptor mRNA in rodent dorsal root ganglia neurons[J]. Eur J Neurosci, 2022, 56(3): 4031-4044. |
| [12] | RUIZ-CANTERO M C, CORTÉS-MONTERO E, JAIN A, et al. The sigma-1 receptor curtails endogenous opioid analgesia during sensitization of TRPV1 nociceptors[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2023, 180(8): 1148-1167. |
| [13] | FÜRST S, ZÁDORI Z S, ZÁDOR F, et al. On the role of peripheral sensory and gut mu opioid receptors: peripheral analgesia and tolerance[J]. Molecules, 2020, 25(11): 2473. |
| [14] | WANG B, JIANG B W, LI G W, et al. Somatosensory neurons express specific sets of lincRNAs, and lincRNA CLAP promotes itch sensation in mice[J]. EMBO Rep, 2023, 24(2): e54313. |
| [15] | WANG K K, WANG S S, CHEN Y, et al. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of somatosensory neurons uncovers temporal development of neuropathic pain[J]. Cell Res, 2021, 31(8): 904-918. |
| [16] | KUPARI J, USOSKIN D, PARISIEN M, et al. Single cell transcriptomics of primate sensory neurons identifies cell types associated with chronic pain[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 1510. |
| [17] | KONG X J, SUN H R, WEI K M, et al. WGCNA combined with machine learning algorithms for analyzing key genes and immune cell infiltration in heart failure due to ischemic cardiomyopathy[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2023, 10: 1058834. |
| [18] | CHEN Y M, LIU F, SHI S N, et al. The integrated transcriptome bioinformatics analysis of energy metabolism-related profiles for dorsal root ganglion of neuropathic pain[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2025, 62(4): 4149-4171. |
| [19] | RIVAT C, SEBAIHI S, VAN STEENWINCKEL J, et al. Src family kinases involved in CXCL12-induced loss of acute morphine analgesia[J]. Brain Behav Immun, 2014, 38: 38-52. |
| [20] | STRANG J, VOLKOW N D, DEGENHARDT L, et al. Opioid use disorder[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2020, 6(1): 3. |
| [21] | SAKLOTH F, POLIZU C, BERTHERAT F, et al. Regulators of G protein signaling in analgesia and addiction[J]. Mol Pharmacol, 2020, 98(6): 739-750. |
| [22] | MASUHO I, BALAJI S, MUNTEAN B S, et al. A global map of G protein signaling regulation by RGS proteins[J]. Cell, 2020, 183(2): 503-521.e19. |
| [23] | HOU X R, WENG Y Q, GUO Q L, et al. Transcriptomic analysis of long noncoding RNAs and mRNAs expression profiles in the spinal cord of bone cancer pain rats[J]. Mol Brain, 2020, 13(1): 47. |
| [24] | FALCONNIER C, CAPARROS-ROISSARD A, DECRAENE C, et al. Functional genomic mechanisms of opioid action and opioid use disorder: a systematic review of animal models and human studies[J]. Mol Psychiatry, 2023, 28(11): 4568-4584. |
| [25] | COLVIN L A, BULL F, HALES T G. Perioperative opioid analgesia-when is enough too much? A review of opioid-induced tolerance and hyperalgesia[J]. Lancet, 2019, 393(10180): 1558-1568. |
| [26] | GAMBLE M C, WILLIAMS B R, SINGH N, et al. Mu-opioid receptor and receptor tyrosine kinase crosstalk: implications in mechanisms of opioid tolerance, reduced analgesia to neuropathic pain, dependence, and reward[J]. Front Syst Neurosci, 2022, 16: 1059089. |
| [27] | MARTUCCI K T. Neuroimaging of opioid effects in humans across conditions of acute administration, chronic pain therapy, and opioid use disorder[J]. Trends Neurosci, 2024, 47(6): 418-431. |
| [28] | GARCÍA-DOMÍNGUEZ M. Enkephalins and pain modulation: mechanisms of action and therapeutic perspectives[J]. Biomolecules, 2024, 14(8): 926. |
| [29] | NGUYEN D, NGUYEN H, ONG H, et al. Ensemble learning using traditional machine learning and deep neural network for diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease[J]. IBRO Neurosci Rep, 2022, 13: 255-263. |
| [30] | DE ANGELI K, GAO S, BLANCHARD A, et al. Using ensembles and distillation to optimize the deployment of deep learning models for the classification of electronic cancer pathology reports[J]. JAMIA Open, 2022, 5(3): ooac075. |
| [31] | TAKEFUJI Y. Beyond XGBoost and SHAP: unveiling true feature importance[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2025, 488: 137382. |
| [32] | ZHANG W Y, CHEN Z H, AN X X, et al. Analysis and validation of diagnostic biomarkers and immune cell infiltration characteristics in pediatric sepsis by integrating bioinformatics and machine learning[J]. World J Pediatr, 2023, 19(11): 1094-1103. |
| [33] | COBOS E J, NICKERSON C A, GAO F Y, et al. Mechanistic differences in neuropathic pain modalities revealed by correlating behavior with global expression profiling[J]. Cell Rep, 2018, 22(5): 1301-1312. |
| [34] | XIE S W, NASLAVSKY N, CAPLAN S. Emerging insights into CP110 removal during early steps of ciliogenesis[J]. J Cell Sci, 2024, 137(4): jcs261579. |
| [35] | SONG T, YANG Y F, ZHOU P, et al. ENKD1 promotes CP110 removal through competing with CEP97 to initiate ciliogenesis[J]. EMBO Rep, 2022, 23(5): e54090. |
| [36] | NISHIMURA Y, KASAHARA K, SHIROMIZU T, et al. Primary cilia as signaling hubs in health and disease[J]. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2018, 6(1): 1801138. |
| [37] | WACHTEN D, MICK D U. Signal transduction in primary cilia: analyzing and manipulating GPCR and second messenger signaling[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2021, 224: 107836. |
| [38] | HILL S A, FU M, GARCIA A D R. Sonic hedgehog signaling in astrocytes[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2021, 78(4): 1393-1403. |
| [39] | MA R, KUTCHY N A, WANG Z B, et al. Extracellular vesicle-mediated delivery of anti-miR-106b inhibits morphine-induced primary ciliogenesis in the brain[J]. Mol Ther, 2023, 31(5): 1332-1345. |
| [40] | MA R, KUTCHY N A, HU G K. Astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicle-mediated activation of primary ciliary signaling contributes to the development of morphine tolerance[J]. Biol Psychiatry, 2021, 90(8): 575-585. |
| [41] | MELROSE J, HAYES A J, BIX G. The CNS/PNS extracellular matrix provides instructive guidance cues to neural cells and neuroregulatory proteins in neural development and repair[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(11): 5583. |
| [42] | IBÁÑEZ C F, PARATCHA G, LEDDA F. RET-independent signaling by GDNF ligands and GFRα receptors[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 2020, 382(1): 71-82. |
| [43] | PARCERISAS A, ORTEGA-GASCÓ A, PUJADAS L, et al. The hidden side of NCAM family: NCAM2, a key cytoskeleton organization molecule regulating multiple neural functions[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(18): 10021. |
| [44] | RAWAL P, ZHAO L Q. Sialometabolism in brain health and Alzheimer's disease[J]. Front Neurosci, 2021, 15: 648617. |
| [45] | SUZUKI M, NARITA M, NARITA M, et al. Chronic morphine treatment increases the expression of the neural cell adhesion molecule in the dorsal horn of the mouse spinal cord[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2006, 399(3): 202-205. |
| [46] | EL MAAROUF A, KOLESNIKOV Y, PASTERNAK G, et al. Removal of polysialylated neural cell adhesion molecule increases morphine analgesia and interferes with tolerance in mice[J]. Brain Res, 2011, 1404: 55-62. |
| [47] | RYMUT H E, RUND L A, SOUTHEY B R, et al. Prefrontal cortex response to prenatal insult and postnatal opioid exposure[J]. Genes (Basel), 2022, 13(8): 1371. |
| [48] | SLACK R J, MACDONALD S J F, ROPER J A, et al. Emerging therapeutic opportunities for integrin inhibitors[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2022, 21(1): 60-78. |
| [49] | CIECHANOWSKA A, ROJEWSKA E, PIOTROWSKA A, et al. New insights into the analgesic properties of the XCL1/XCR1 and XCL1/ITGA9 axes modulation under neuropathic pain conditions-evidence from animal studies[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 1058204. |
| [50] | PARK J, LEE C, KIM Y T. Effects of natural product-derived compounds on inflammatory pain via regulation of microglial activation[J]. Pharmaceuticals (Basel), 2023, 16(7): 941. |
| [51] | LI H Y, WATKINS L R, WANG X H. Microglia in neuroimmunopharmacology and drug addiction[J]. Mol Psychiatry, 2024, 29(6): 1912-1924. |
| [52] | PAHAN P, XIE J Y. Microglial inflammation modulates opioid analgesic tolerance[J]. J Neurosci Res, 2023, 101(9): 1383-1392. |
| [53] | JALODIA R, ABU Y F, OPPENHEIMER M R, et al. Opioid use, gut dysbiosis, inflammation, and the nervous system[J]. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol, 2022, 17(1/2): 76-93. |
| [1] | 黄昕, 刘家辉, 叶敬文, 钱文莉, 许万星, 王琳. 基于机器学习的小细胞肺癌代谢分子诊断模型的建立和临床应用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(8): 1009-1016. |
| [2] | 霍晓燕, 罗小梅, 叶贤涛, 孙昱, 余永国, 梁黎黎, 范燕洁. MMAA基因非编码区变异叠加单亲二体所致甲基丙二酸血症的多组学分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(6): 800-806. |
| [3] | 李林颖, 蔡晓东, 童冉, 杨晨, 王志明, 贺潇宇, 马子越, 张丰, 李令杰, 周君梅. 人胚胎干细胞向神经前体细胞分化的转录组与染色质可及性变化分析研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(4): 387-403. |
| [4] | 梁乐斌, 陈慧芳, 赖淑静, 顾靓, 苏冰. 基于空间ATAC-seq技术的Apcmin/+小鼠结肠肿瘤表观特征分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2025, 45(10): 1261-1270. |
| [5] | 吴其蓁, 刘启明, 柴烨子, 陶政宇, 王依楠, 郭欣宁, 姜萌, 卜军. 机器学习预测乳腺癌新辅助治疗后炎症代谢状态改变的模型评价[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(9): 1169-1181. |
| [6] | 许万星, 王琳, 郭巧梅, 王薛庆, 娄加陶. 多模态肺结节诊断模型的临床验证及应用价值探索[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 44(8): 1030-1036. |
| [7] | 刘思雨, 张磊. 七氟烷抑制新生小鼠前额叶皮质神经祖细胞向神经元分化发育[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(9): 1115-1130. |
| [8] | 马奔, 赵成, 束翌俊, 董平. CT影像组学在胃肠道间质瘤中的应用进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2023, 43(7): 923-930. |
| [9] | 李欣, 范青. 机器学习在抑郁症患者面部特征研究中的应用进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(1): 124-129. |
| [10] | 王建茹, 彭广操, 朱明军. 基于GEO数据库和生物信息学分析筛选小鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤相关的潜在枢纽基因[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022, 42(1): 51-62. |
| [11] | 徐莹, 褚以忞, 杨大明, 李吉, 张海芹, 彭海霞. 基于差异表达基因组合构建高度微卫星不稳定结直肠癌转移预测模型[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(9): 1197-1206. |
| [12] | 刘音, 杨涛, 谢裕赛, 王玉柱. 基于GEO数据库筛选狼疮性肾炎的关键基因和信号通路[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(6): 749-755. |
| [13] | 耿瑞杰, 姚琳, 黄欣欣, 禹顺英, 苑成梅, 洪武, 吕钦谕, 王庆中, 易正辉, 方贻儒. 基于加权基因共表达网络分析识别抑郁症的差异表达基因模块[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(6): 724-731. |
| [14] | 李玲玲, 李倩, 李明玉, 刘峥, 沈倩诚. 成人与儿童急性髓系白血病患者肿瘤免疫相关的差异表达基因分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(5): 579-587. |
| [15] | 杨鹿笛, 王高明, 胡仁豪, 蒋小华, 崔然. 生物信息学方法筛选胰腺癌进展相关的核心基因[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41(5): 571-578. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||